1. Introduction
Sound is an essential component of daily life, serving as a means of communication, entertainment, and environmental perception. The ability to recognize and interpret sound is a fundamental human trait that enables us to navigate our surroundings and recognize emotions. Therefore, the processing and utilization of audio signals are vitally important [
1]. However, individuals with hearing impairments have reduced sensitivity to sound recognition, leading to inconvenience in daily life and an inability to hear warning sounds from vehicles or people. This deficiency can expose them to certain dangers. Consequently, the development of a device capable of classifying various sounds on the road could substantially improve the quality of life for those who are hearing impaired.
Recently, deep learning has been widely applied in voice recognition [
2,
3]. In 2021, Bonaventure et al. proposed the FSER architecture, which converts speech files into spectrograms and inputs them into a two-dimensional convolutional neural network (2D CNN) for identification [
4]. Its accuracy surpasses that of the one-dimensional convolutional neural network (1D CNN), as 2D CNN models can extract finer features from the spectrogram [
5]. Kevin et al. aimed to build a more accurate sound classification model and proposed a two-stream neural network architecture that includes the EfficientNet model [
6]. Lee et al. utilized preoperative and postoperative voice spectrograms as features to predict three-month postoperative vocal recovery [
7]. This model could be widely applied for transfer learning in sound classification. Lu et al. used the morphology of spectrograms as the input pattern to recognize speech using EfficientNet [
8]. Padi et al. employed transfer learning to improve the accuracy of speech emotion recognition through spectrogram augmentation [
5]. Additionally, Allamy and Koerich utilized a 1D CNN to classify music genres based on audio signals [
9].
Ensemble learning is a powerful technique that involves the amalgamation of predictions from multiple classifiers to create a single classifier, resulting in notably enhanced accuracy compared to any individual classifier [
10,
11]. Research has demonstrated that an effective ensemble consists of individual classifiers with similar accuracies, yet with distributed errors across different aspects [
12,
13]. Essentially, ensemble learning encompasses two necessary characteristics: the generation of distinct individual classifiers and their subsequent fusion. Two common strategies for generating individual classifiers include the heterogeneous type, which employs various learning algorithms, and the homogeneous type, which uses the same learning algorithm but requires different settings. Thus, Tan et al. proposed ensemble learning to classify human activities, combining a gated recurrent unit (GRU), a CNN stacked on the GRU, and a deep neural network [
14]. Xie et al. proposed three DNN-based ensemble methods that fused a series of classifiers whose inputs are representations of intermediate layers [
15]. Erdal et al. proposed a voting-based ensemble learning architecture to improve identification results in tuberculosis classification, traditionally using a single CNN model [16 10]. This fusion method used a voting algorithm to determine the output. However, its disadvantage is that it simply votes on the model's output, only considering the number of predicted results and not the probability value of those predictions. Kavitha et al. proposed a weighted average-based ensemble learning architecture to improve the accuracy of cell locations in cut electronic microscope images [
17]. The disadvantage of this method is that when a large error occurs in the same prediction result, the weighted average result would be affected. Manna et al. proposed a fuzzy-based ensemble learning architecture to improve the identification results of cervical cancer based on different CNN models. The output results of CNN models, including InceptionV3, Xception, and DenseNet-169, were ensembled through fuzzy rank-based fusion [
18]. The advantages of fuzzy rank-based fusion include less computing time and memory consumption compared to fully connected layers.
The explosive growth of the Internet of Everything (IoE) has led to a surge in smart devices connecting to the internet, consequently generating a vast amount of data. This increase in data has presented challenges for traditional cloud computing models, including burdensome bandwidth loads, sluggish response speeds, compromised security, and privacy concerns. To address these limitations, innovative edge computing technologies have emerged as a promising solution [
19,
20]. Edge computing offers a more distributed and localized approach to data processing, allowing data to be handled closer to the source of its generation. Hochst et al. proposed an edge artificial intelligence (AI) system to recognize bird species by their audio sounds, utilizing the EfficientNet-B3 architecture based on an NVIDIA Jetson Nano board [
21]. They demonstrated that the EfficientNet model could be efficiently implemented on an edge device. Rahman and Hossain developed an edge IoMT system using deep learning to detect various types of health-related COVID-19 symptoms based on a smartphone [
22]. Nath et al. provided an overview of studies related to stress monitoring with edge computing, highlighting that computations performed at the edge can reduce response time and are less vulnerable to external threats [
23].
Based on the review of the above literature, the goal of this study is to develop a wearable assistant device for the hearing impaired, designed to recognize emergency vehicle sirens on the road using edge computing. An EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model was proposed to classify human vocalizations and emergency vehicle sirens. This model was embedded in an Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense development board. The audio signals, including human vocalizations and emergency vehicle sirens, were obtained from the CREMA-D dataset [
24] and Large Scale Audio dataset of emergency vehicle sirens on the road [
25], respectively. The categorization encompassed seven types of audio sounds: neutral vocalization, anger vocalization, fear vocalization, happy vocalization, normal sound, car horn sound, siren sound, and ambulance siren sound. The spectrogram of the audio signal served as the feature. When one of the car horn, siren, or ambulance siren sounds was detected, the wearable assistant device presented alarms through a vibrator and displayed messages on the OLED panel. The results in edge computing were very close to those classified by offline computing. Moreover, we compared the performance between our proposed method and the iOS method, finding that our method outperformed the results of the iOS method. Thus, the proposed wearable assistant device has the potential to assist the hearing impaired in avoiding traffic accidents.
2. Materials and Methods
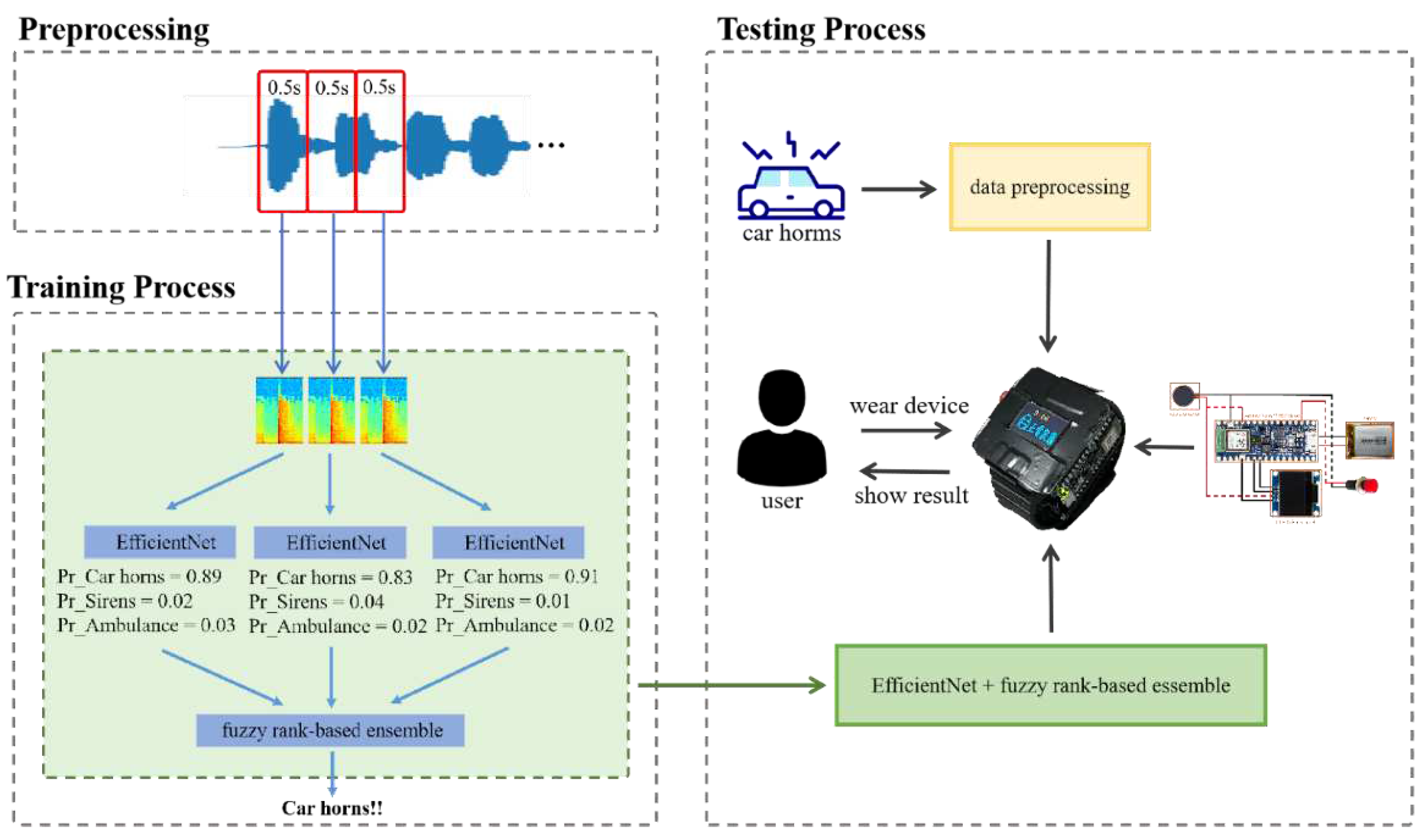
Figure 1 illustrates the architecture of the proposed method, including the data processing, training phase, and testing phase. The EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model is utilized to recognize human vocalizations and emergency vehicle sirens. During the training phase, this model is executed on a personal computer (PC). In contrast, during the testing phase, the proposed model is run on an Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense development board. When the system detects specific sounds, such as car horns, sirens, or ambulance sirens, it alerts the user through the device's vibrator and displays messages on an OLED panel. The audio signal is converted into a spectrogram to serve as the input pattern. Three separate EfficientNets are employed to recognize the siren sound, and their outputs are fused using a fuzzy rank-based model. Once trained, the model is implemented in the wearable device, heightening the user's awareness of vehicle warning sounds. This approach aims to bolster public safety consciousness and minimize the potential for accidents.
2.1. Features
In this study, human vocalizations and emergency vehicle sirens on the road were classified. The human vocalizations, including neutral, anger, fear, and happy vocalizations, were sourced from the CREMA-D dataset, an emotional multimodal actor dataset [
24]. A total of 5,324 audio files were extracted from this dataset, and these files were augmented to create a total of 10,648 files. The emergency vehicle sirens on the road were acquired from the Large Scale Audio dataset [
25]. This dataset contained 3,432 audio files featuring the car horn sound, siren sound, and ambulance siren sound. These files were augmented to a total of 6,864 audio files using the rand augment method [
26]. The files were then divided into 80% for training, 10% for testing, and 10% for validation. The audio signals were segmented into 0.5-second intervals and transformed into spectrograms using the short-time Fourier transform. Each sample was represented by three spectrograms, which served as features for the classification of emergency vehicle sirens. Therefore, for the samples of emotional vocalizations, the numbers of training, testing, and validation samples were 25,555, 3,195, and 3,194, respectively. For the samples of emergency vehicle sirens, the numbers of training, testing, and validation samples were 16,474, 2,058, and 2,060, respectively.
2.2. EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model
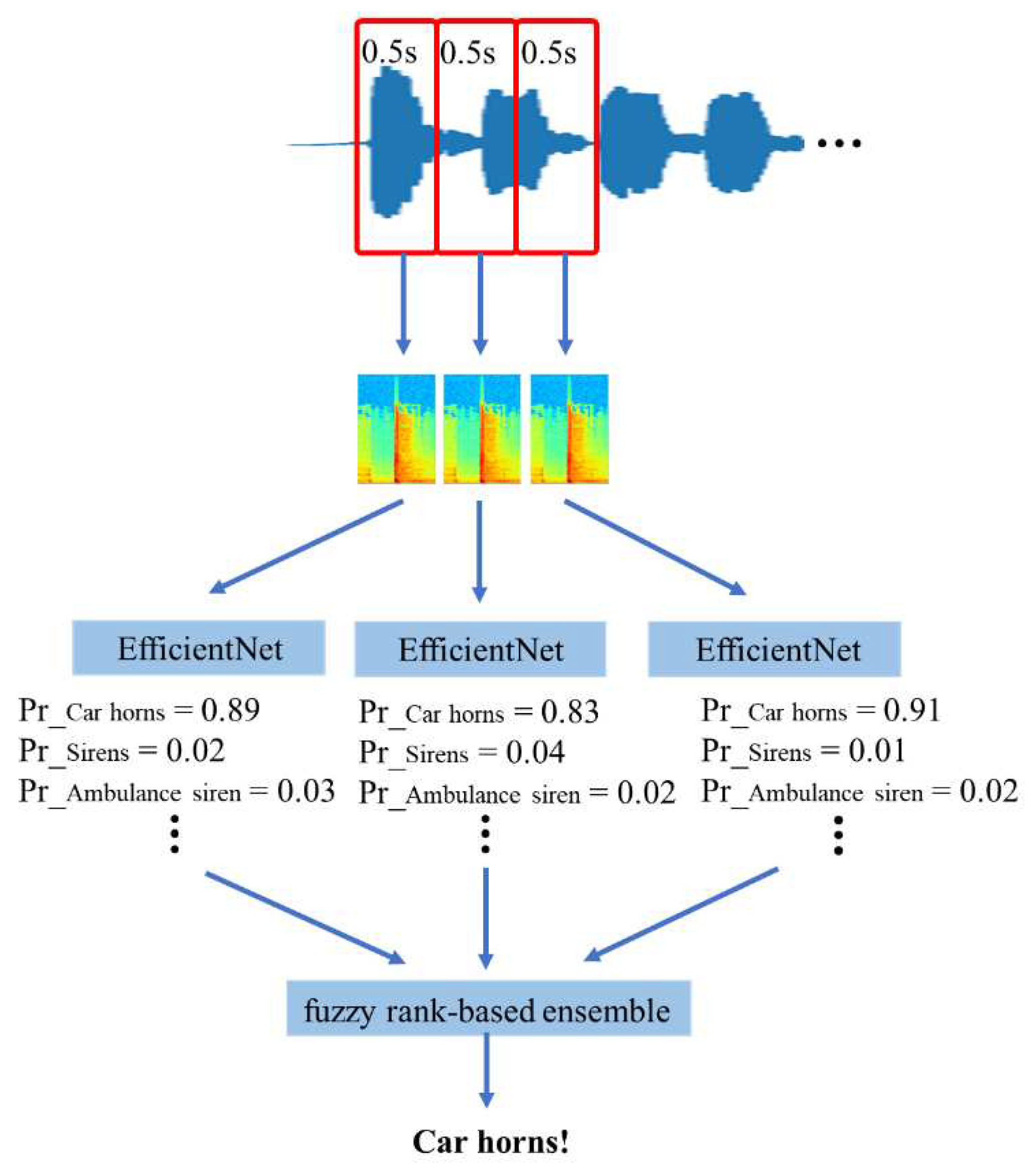
In order to develop the wearable assistant device for improving the road safety of the hearing impaired, this study proposes an EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model to classify the emergency vehicle sires on the road, as show in
Figure 2. One sample contains three spectrograms feeding the three EfficientNet models, respectively. The EfficientNet models will estimate the weight of each category. Then, the fuzzy rank-based model determines the winner of classes.
2.2.1. EfficientNet-based model
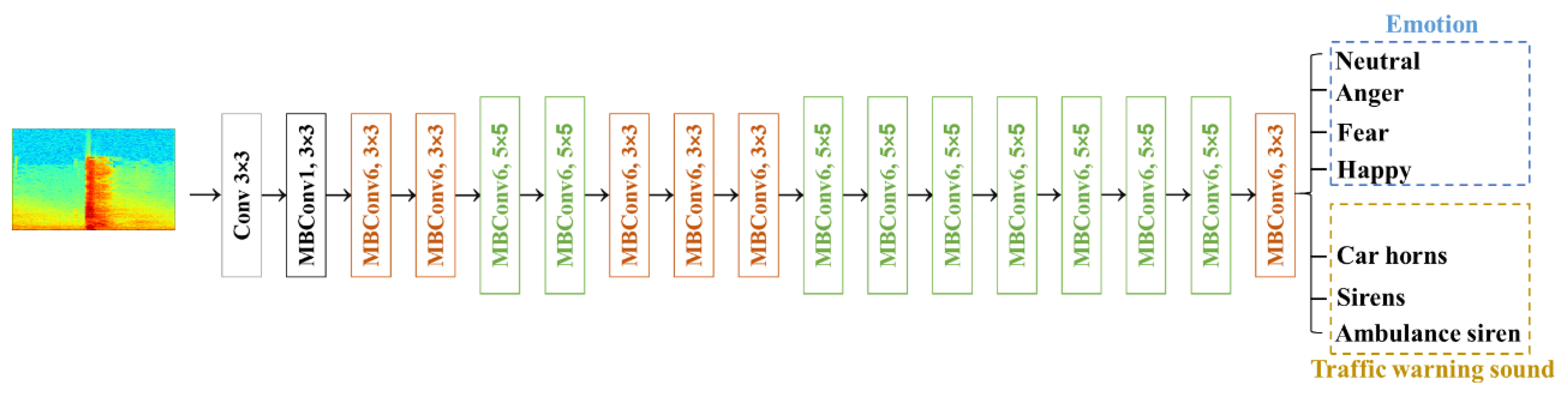
To recognize the human vocalizations and emergency vehicle sires in real time in the edge computing, the EfficientNet model was selected to estimate the weights of all categories. The EfficientNet is a deep learning model that has achieved top performance in image classification tasks and has demonstrated State-of-the-Art (SOTA) performance in the ImageNet image classification challenge [
27]. The EfficientNet builds on the base architectures of ResNet [
28] and MobileNet [
29] and leverages the compound scaling method [xxx] to achieve a balance between model size, computational efficiency, and accuracy. As a result, EfficientNet has become one of the most popular convolutional neural network models in current research. The structure of model is shown in
Figure 3, which has one layer of Conv3
3, one layer of MBConv1, k3×3, six layers of MBConv6, k3×3, nine layers of and MBConv6, k5×5, and one layer of full connection. The number of output layer is 7. The resolution and channel number of each layer are described in
Table 1 Each row describes a stage i with
i layers, with input resolution {
i,
i} and output channels
i. The hyperparameters of EfficientNet model is shows in
Table 2 used for all experiments. The optimizer is the Adam, learning rate is 1×10^-5, batch size is 16, and the number of epoch is 1000. The sum of label smooth cross entropy loss function (
LLSCE) [
30] and focal cross entropy loss function (
LFCE) [
31] is defined as the total loss function (
LT) to validate the performance of EfficientNet model.
where N is the number of samples, M is the number of categories,
is the classifier, x
j is the sample. When x
j belongs to lth class, P
ji = 1-ε, and P
ji = ε/M-1 for the other classes. ε is 0.2.
where p is the probability of target.
where
αi is the weight of loss function, γ is 2.
2.2.2. Fuzzy Rank-based Model
This method combines the outputs of the three-stream EfficientNet-based models using the fuzzy rank-based model. The fuzzy rank-based model takes the results from the three EfficientNets and calculates two fuzzy ranks by applying the exponential function and hyperbolic tangent function transformations.,
R1 and
R2 [
18].
where
Pik is the estimating weight of
th category on
th EfficientNet.
RS is the fused rank score.
The confidence score of a particular category, CS, is the sum of RSsk.
The category with the minimum confidence score is considered as the winner.
2.3. Wearable Device
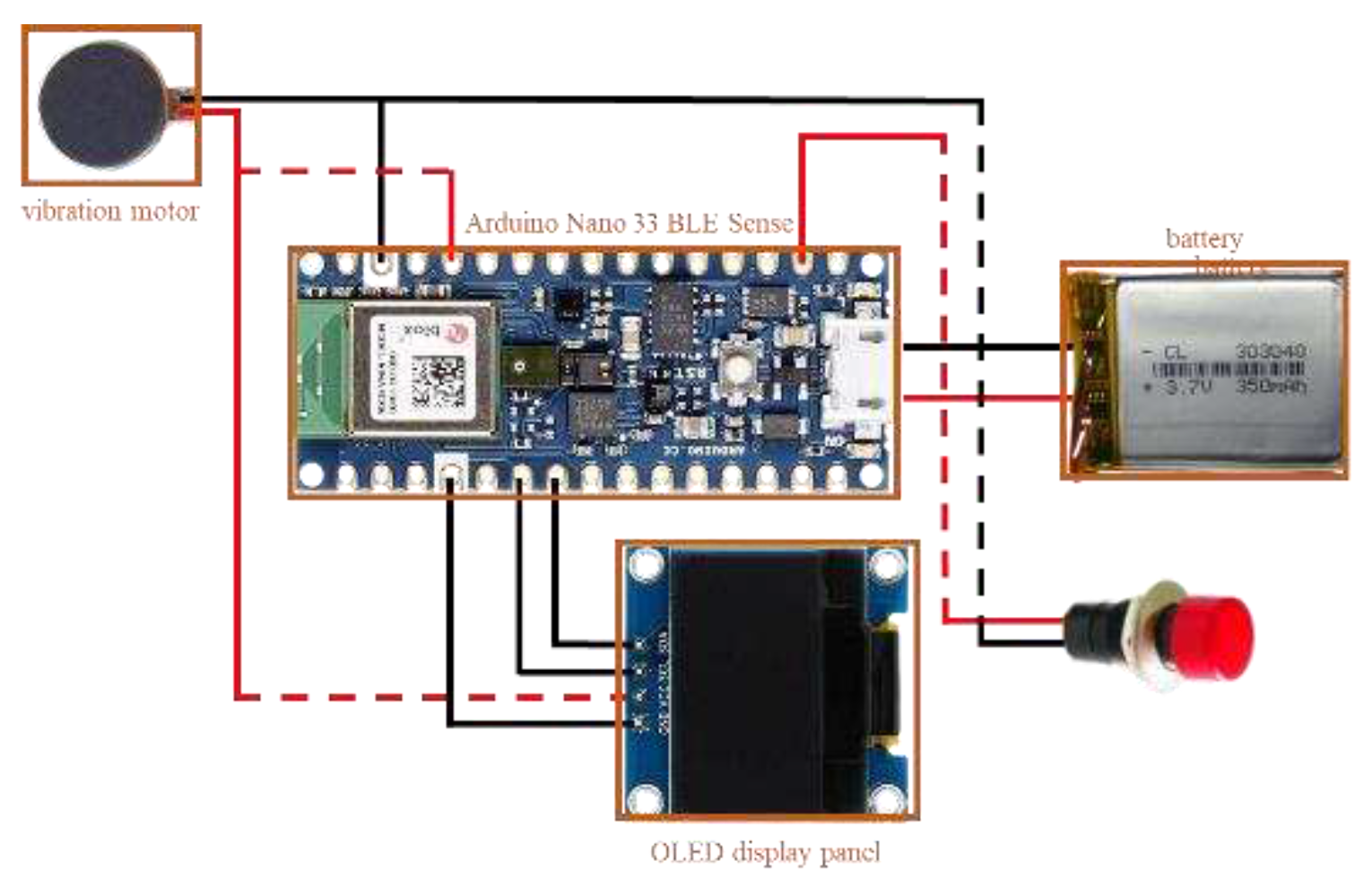
This system operates on the Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense development board [
32], linked to various hardware modules such as an OLED panel, vibrator, GPS positioning module, microphone, and relay module, as depicted in
Figure 4. The relay module governs the power of the OLED panel to conserve energy, while the microphone captures the audio sound. When the wearable assistant device detects a car horn, siren, or ambulance siren, it activates the vibration module and displays a message on the OLED panel
2.4. Performances
The results of the tests are summarized in a confusion matrix, outlined in
Table 3. This matrix illustrates the relationship between the actual and estimated classes in the test set, with each row corresponding to the actual classes and each column representing the estimated classes. According to the proposed method, a sample is classified as a true positive (TP) if the activity is correctly recognized, a false positive (FP) if the activity is incorrectly recognized, a true negative (TN) if the activity classification is correctly rejected, and a false negative (FN) if the activity classification is incorrectly rejected. To evaluate the performance of the proposed model, metrics such as accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and precision are utilized, as described in Equations (9), (10), (11), and (12).
3. Results
The proposed model underwent training, validation, and testing processes on a computer equipped with an 8-core CPU (Intel Xeon W-3223), 64 GB of RAM, a GPU (RTX 3090) with 24 GB of graphics memory, and 10,496 CUDA cores. PyTorch was the framework used for the implementation.
Table 4 presents the confusion matrix for the EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model in offline computing. The results clearly show that the study achieved an accuracy of 97.05%, a precision of 97.79%, a sensitivity of 96.8%, and a specificity of 97.04%.
In order to evaluate the robust of EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model in a noise environment, we collected the road noise and superimposed the spectrogram of road noise to the testing samples. In this experiment, the number of testing samples is same to the number of EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model in the offline computing.
Table 5 shows the confusion matrix of EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model in the offline computing under the noise environment. It is evident that this study achieved an accuracy of 96.84%, precision of 96.17%, sensitivity of 96.13%, and specificity of 96.90%. We found that our proposed model exhibited the high robust. The accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and specificity only drop 0.21%, 1.62%, 0.67%, and 0.14%, respectively.
The iOS system, developed by Apple Inc., is one of the most prevalent mobile operating systems, holding a substantial market share. Thanks to its vast user base, the iOS system has become highly popular. Starting with version 14, iOS has integrated sound recognition functionality, providing options to recognize various sounds such as alarms, car horns, and shouting, among others. To compare our proposed method with the iOS system, we utilized the sound recognition feature in iOS to classify emergency vehicle sirens [
33]. The training, validation, and testing samples were the same as those used in the offline computing experiment with the EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model.
Table 6 displays the confusion matrix for the iOS system in offline computing, showing an accuracy of 70.82%, precision of 76.67%, recall of 76.22%, and specificity of 71.02%. Comparing the results in
Table 4 and
Table 6, our proposed model outperformed the iOS system. The accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and specificity of our model exceeded those of the iOS system by 26.23%, 21.57%, 20.58%, and 26.02%, respectively
In this study, we imbedded the trained EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model to the Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense development board. The testing samples were played by the speaker of PC. This board was recording the sound and recognize the class of this sound. If the sound belongs to the car horn, siren, and ambulance siren, it would start the vibrator and send the message to the OLED. Then, we counted the numbers of all categories. The testing samples were same to the experiment of EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model in the offline computing.
Table 7 shows the confusion matrix of EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model in the edge computing. The performances of edge computing achieved an accuracy of 95.22%, precision of 93.19%, sensitivity of 95.27%, and specificity of 95.09%. According to the results shown in
Table 4 and
Table 7, we find that the performances of edge computing are close to the offline computing. our proposed model exhibited the better performance. The accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and specificity only drop 1.83%, 4.6%, 1.53%, and 1.95%, respectively.
4. Discussion
In the ensemble learning, the voting and weight average methods are the popular methods [
34,
35]. When the prediction class with the maximum voting number, the class is considered as the winner. The disadvantage of the voting method is to ignore the probabilities of truth and false classes. It only focuses on the counting numbers of truth classes. Although the weight average method could make the balance of truth and false classes, this method would determine the wrong winner when the number of false classes is larger than the truth classes. In this study, we proposed the fuzzy rank-based model to determine the winner of classification. The model uses the two nonlinear functions, exponential function and hyperbolic tangent function, to estimate the rank, respectively. The two functions are the antisymmetric functions. Thus, it can inhibit the mistake decision by the false classes with the large amount.
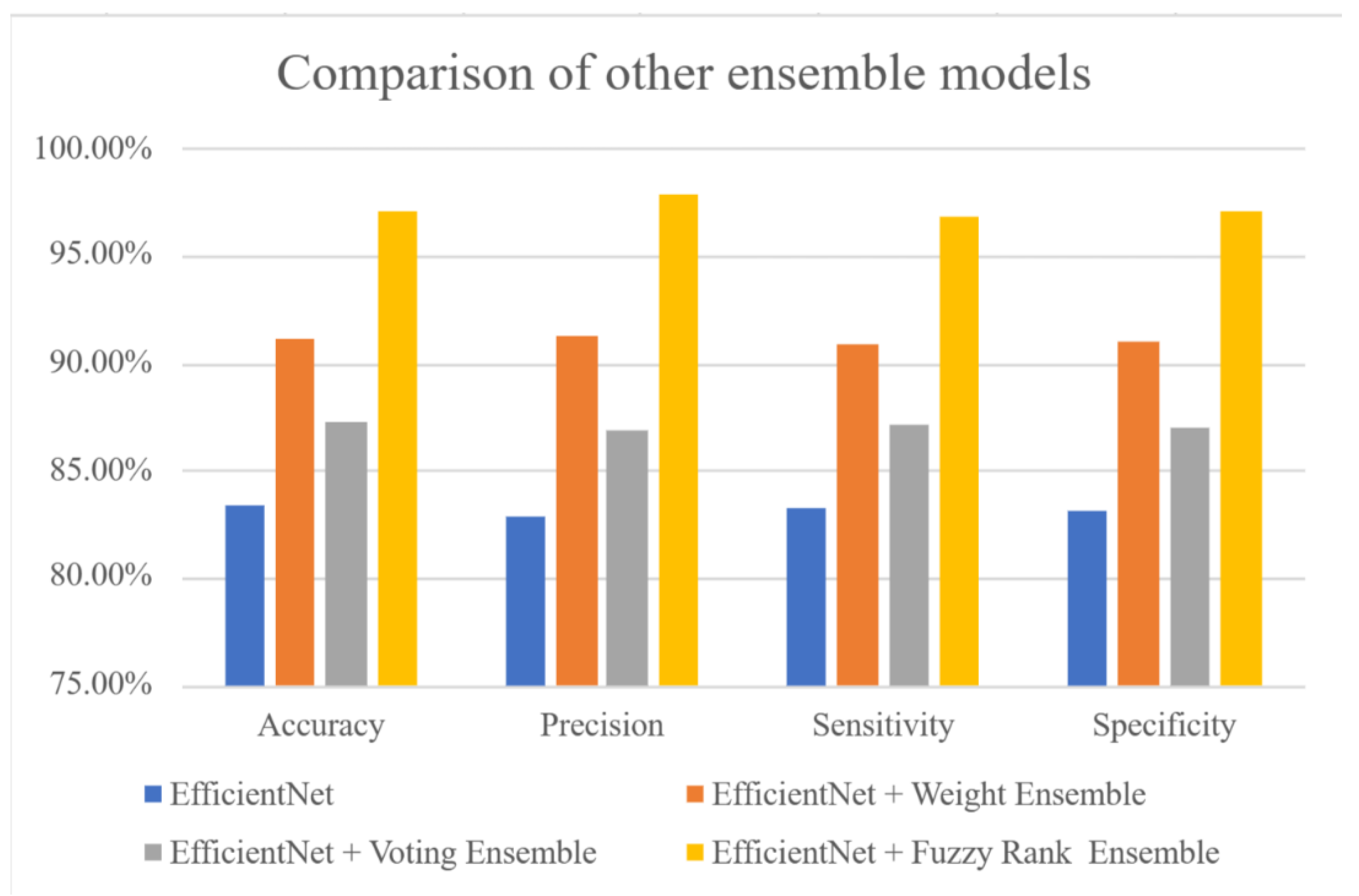
Figure 5 shows the performances of the non-using ensemble (EfficientNet), voting and weight average methods (EfficientNet + voting ensemble and EfficientNet + weight ensemble) and EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble. The results are the accuracies of 83.31%, 87.23%, and 91.25%, the precisions of 82.87%, 86.82%, and 91.73%, the sensitivities of 83.01%, 87.11%, and 90.96%, and the specificities of 83.33%, 86.74%, and 91.17%. The performances of EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model are the best, accuracy of 97.05%, precision of 97.79%, sensitivity of 96.8%, and specificity of 97.04%.
When compared to the iOS system, our method demonstrated significantly higher accuracy, outperforming it by a remarkable margin of 26.23%. This performance advantage can be attributed to the innovative EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model that we meticulously developed for this study. The strength of this model lies not only in recognizing warning sounds in road scenarios but also in identifying emotions within human vocalizations. It is worth noting that emotion recognition is an essential feature not present in the iOS system, making this recognition capability a potential superiority of our method.
Table 8 presents a comparative analysis of our proposed method against other studies that utilized the CREMA-D dataset [
24]. Previous studies [36-39] only classified 4 sounds, while our study classified seven. As shown, the proposed EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model achieved an accuracy of 97.05%, which ranks among the best results reported in the literature. For the Large-scale audio dataset of emergency vehicle sirens on the road [
14], a previous study showed that the best result for the classification of four sounds was an accuracy of 97%. This result was very close to our study. However, we emphasized that our approach classified seven sounds, broadening the scope of sound recognition.
In this study, we used two datasets, CREMA-D dataset and Large Scale Audio dataset to evaluate the performance of the EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model. The number of each category is very different. The samples’ numbers of the neutral vocalization, anger vocalization, fear vocalization, happy vocalization, car horn sound, siren sound, and ambulance siren sound were 7,921, 7,834, 7,621, 8,568, 7,128, 7,484, and 5,979, separately. Moreover, the target output used the one-hot coding. If the model uses general cross entropy loss, the model may have poor training results due to sample imbalance. The label smooth cross entropy loss function and focal loss function could overcome these problem [
30,
31]. Thus, we used the sum of two loss functions to validate the performance of the proposed model to avoid the overfitting and local minimum problems in the training phase.
5. Conclusions
We proposed a wearable assistant device to help the hearing-impaired recognize emergency vehicle sirens on the road. By employing an edge computing method in the Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense development board, we executed the EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model. To evaluate the performance of this model, we used the CREMA-D dataset and Large Scale Audio dataset for training and testing. In offline computing, the accuracy reached 97.05%, while in edge computing, it also achieved 95.22%. These results demonstrate that the EfficientNet-based fuzzy rank-based ensemble model has the potential to be applied in edge computing for other image classifications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-L. C.; Data curation, C.-C. L., J.-W. W., W.-C. C., Y.-H. C., S.-W. C., P.-C. H.; Investigation, C.-L. C.; Methodology, C.-C. L., J.-W. W., W.-C. C., Y.-H. C., S.-W. C., P.-C. H.; Project administration, C.-L. C.; Software, C.-C. L., J.-W. W., W.-C. C., Y.-H. C., S.-W. C., P.-C. H.; Supervision, C.-L. C.; Validation, C.-L. C. and S.-H. L.; Writing—original draft, C.-L. C. and S.-H.L.; Writing—review and editing, X. Z., Y.-L. H., S.-H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan, under grants NSTC 111-2221-E-324-003-MY3.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cornelius, C.; Marois, Z.; Sober, J.; Peterson, R.; Mare, S.; Kotz, D. Vocal resonance as a passive biometric. Computer Science Technical Report 2014, 747–761. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Seong, J.J.; Ozlu, B.; Shim, B.S.; Marakhimov, A.; Lee, S. Biosignal Sensors and Deep Learning-Based Speech Recognition: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, A.B.; Shahin, I.; Attili, I.; Azzeh, M.; Shaalan, K. Speech Recognition Using Deep Neural Networks: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 19143–19165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossou, B.F.P.; Gbenou, Y.K.S. FSER: Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Speech Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2021) Workshops, pp. 3533–3538.
- Padi, S.; Sadjadi, S.O.; Sriram, R.D.; Manocha, D. Improved Speech Emotion Recognition using Transfer Learning and Spectrogram Augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI 2021), QC, Montréal, Canada, 18-22 October 2021; pp. 645–652. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan, K.W.; Hidayat, A.A.; Cenggoro, T.W.; Pardamean, B. Repurposing transfer learning strategy of computer vision for owl sound classification. Procedia Computer Science 2023, 216, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Eom, J.S.; Pak, M.; Jeong, H.S.; Son, H.Y. Predictions for Three-Month Postoperative Vocal Recovery after Thyroid Surgery from Spectrograms with Deep Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y. Speech Recognition using EfficientNet. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Multimedia Systems and Signal Processing (ICMSSP 2020), Chengdu, China, 28-30 May 2020; pp. 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Allamy, S.; Koerich, A.L. 1D CNN Architectures for Music Genre Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI 2021), Orlando, FL, USA, 5-7 December 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Stacked regressions. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H. Stacked generalization. Neural Networks 1992, 5, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, D.W.; Shavlik, J.W. Actively Searching for an Effective Neural Network Ensemble. Connection Science 1996, 8, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, S. Optimal linear combinations of neural networks. Neural Networks 1997, 10, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.H.; Wu, J.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Gochoo, M. Human Activity Recognition Using an Ensemble Learning Algorithm with Smartphone Sensor Data. Electronics 2022, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xu, B.; Chuang, Z. Horizontal and vertical ensemble with deep representation for classification. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1306.2759.
- Tasci, E.; Uluturk, C.; Ugur, A. A voting-based ensemble deep learning method focusing on image augmentation and preprocessing variations for tuberculosis detection. Neural Comput. & Applic. 2021, 33, 15541–15555. [Google Scholar]
- Shaga Devan, K.; Kestler, H.A.; Read, C.; Walther, P. Weighted average ensemble-based semantic segmentation in biological electron microscopy images. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 158, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, A.; Kundu, R.; Kaplun, D.; Sinitca, A.; Sarkar, R. A fuzzy rank-based ensemble of CNN models for classification of cervical cytology. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Liu, Y.; Meng, G.; Sun, Q. An Overview on Edge Computing Research. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 85714–85728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, B.; Wang, N.; Barbhuiya, S.; Kilpatrick, P.; Nikolopoulos, D.S. Challenges and Opportunities in Edge Computing. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Smart Cloud (SmartCloud 2016), New York, NY, USA, 18-20 November 2016; pp. 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Höchst, J.; Bellafkir, H.; Lampe, P.; Vogelbacher, M.; Mühling, M.; Schneider, D.; Lindner, K.; Röcner, S.; Schabo, D.G.; Farwig, N.; Freisleben, B. Bird@ Edge: Bird Species Recognition at the Edge. In International Conference on Networked Systems (NETYS 2022), Networked Systems; pp. 69–86.
- Rahman, M.A.; Hossain, M.S. An Internet-of-Medical-Things-Enabled Edge Computing Framework for Tackling COVID-19. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 15847–15854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, R.K.; Thapliyal, H.; Caban-Holt, A.; Mohanty, S.P. Machine Learning Based Solutions for Real-Time Stress Monitoring. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine 2020, 9, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CREMA-D Dataset. Available online: https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/crema-d (accessed on 2 May 2020).
- Asif, M.; Usaid, M.; Rashid, M.; Rajab, T.; Hussain, S.; Wasi, S. Large-scale audio dataset for emergency vehicle sirens and road noises. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2020) Workshops; pp. 702–703.
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR 2019); 97; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H.; Li, R.X.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, W.; Su, C.H. Classification of Photoplethysmographic Signal Quality with Deep Convolution Neural Networks for Accurate Measurement of Cardiac Stroke Volume. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1704.04861.
- Chen, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhou, P.; Ban, X.; He, D. Improved cross entropy loss for noisy labels in vision leaf disease classification. IET Image Processing 2022, 16, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2017), pp. 2980–2988.
- Kurniawan, A. Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense Board Development. In IoT Projects with Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense; Apress: Berkeley, CA, 2021; pp. 21–74. ISBN 978-1-4842-6457-7. [Google Scholar]
- Classifying Live Audio Input with a Built-in Sound Classifier. Available online: https://developer.apple.com/documentation/soundanalysis/classifying_live_audio_input_with_a_built-in_sound_classifier (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Leon, F.; Floria, S.A.; Bădică, C. Evaluating the Effect of Voting Methods on Ensemble-Based Classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on INnovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications (INISTA 2017), Gdynia, Poland, 3-5 July 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Xie, G.; Xiao, R. Research on Ensemble Learning. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence (AICI 2009), Shanghai, China, 7-8 November 2009; 3; pp. 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Zielonka, M.; Piastowski, A.; Czyżewski, A.; Nadachowski, P.; Operlejn, M.; Kaczor, K. Recognition of Emotions in Speech Using Convolutional Neural Networks on Different Datasets. Electronics 2022, 11, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, A.S.A.; Rao, S. A CNN-LSTM based deep neural networks for facial emotion detection in videos. International Journal Of Advances In Signal And Image Sciences 2021, 7, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, R.; Das, R.; Ng, R.W.; Gopalakrishnan, P.K.; Eerens, L.; Swietojanski, P.; Miksik, O. Multi-Modal Sequence Fusion via Recursive Attention for Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 22nd Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL 2018), Brussels, Belgium, October 2018; pp. 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Jain, S.; Raman, B.; Roy, P.P.; Iwamura, M. End-to-end Triplet Loss based Emotion Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2021), Milan, Italy, 10-15 January 2021; pp. 8766–8773. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).