1. Introduction
One of the services people consume most on the Internet is social networks. The popularity of these sites derives from the advances in the information technology area, which provide users the practicality and simplicity to use these digital media, allowing them to access these services from anywhere with an Internet connection through an electronic device. Nowadays, social networks have become an excellent medium for sharing information, reaching places humanity could hardly have imagined. In these interaction spaces [
1], users are the main actors, who involuntarily participate in the generation of data, this happens from the moment they post any comment about an event that attracts their attention.
The amount of information that circulates on social networks minute by minute is enormous because the data is generated and published not only by member users but also by public and private institutions, government entities, and even electronic devices such as sensors and actuators [
2], which integrate intelligent systems as processes within the Internet of Things (IoT) technology [
3].
With events such as COVID-19, people were forced to work remotely, which caused many individuals to enter into digital interaction to do different activities such as homework, reports, meetings, and other activities on the Internet. Traditional communications changed to digital platforms such as social networks, and being the most used services, they became a broader panorama to carry out attacks on different users and institutions, facts that have been worrisome and recurring to be victims of these threats within these platforms. Furthermore, just as social networks have captured the attention of many people, in the same way, these services have attracted various malicious users whose purpose is to compromise the assets of other members through different cyberattacks, which represent a threat within these communities [
4].
The practicality, security controls, and mechanisms implemented on current web platforms [
5] to face different types of cyberattack demonstrate that threats grow along with advances and technological developments. These facts have concerned many researchers, institutions, and companies, in such a way that it has prompted the tasks of developing different works, mechanisms, and software tools as a countermeasure against different threats from malicious users or groups who have contemplated to use social networks as an attack vector to compromise the assets of the victim.
Therefore, this paper presents a novel approach based on a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture to detect and classify four different cyberattacks such as malware, phishing, spam, and even one whose purpose is to deceive the user into spreading malicious messages to other users, which in this work is defined as a bot attack. An essential feature of this task involves utilizing Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques such as filtering, Part-Of-Speech (POS) tagging, lemmatization, tokenization, and stop-word removal. These techniques extract specific text attributes from each message to represent and create the subsequent inputs to the Deep Learning (DL) architecture.
In addition to the vector that represents the content of the message, two vectors complement the information utilized for the detection and classification activities. The first vector comprises the features of the plaintext structure with a size equal to 16, which is the total number of extracted values that describe how the user typed the message.
The second vector is created based on the properties of each URL mentioned in the message. Even if a URL is not present in the content, a vector with specific attributes is utilized to indicate the absence of a URL. In general, the characteristics extracted from each URL integrate this vector with a total of 25 properties that define its size. It is essential to highlight that the analysis is applied to textual content and not to multimedia such as images, audio, video, or other formats.
One remarkable feature of this work is that it detects the previously mentioned four types of cyberattacks using just this proposed approach without needing to employ different models for each type of threat, allowing users to expand the detection landscape of these threats in social network messages, and even if the message does not have a URL. This CNN architecture was tested on real data, demonstrating its results in two stages. The first detects the existence of any of the four cyberattacks within the message, obtaining an accuracy value of 0.91. On the other hand, after detecting a message as a cyberattack, the next stage is to classify it into one of the four types of cyberattack, achieving an accuracy score of 0.82.
This paper is organized as follows. First, a review of the literature about related works is presented in
Section 2. The methodology for analyzing messages is described in
Section 3. The cyberattack detection model is explained in
Section 4.
Section 5 shows relevant numerical results, evaluations, and a discussion of results. Finally,
Section 6 presents conclusions.
2. Related Works
The diversity of topics within social networks has allowed considering the content of messages as an information source. Research and studies about different topics analyze the posted messages on these sites, such as the acceptance and trends of a product in the market [
6,
7], the study of preferences and reactions to a new law [
8,
9], movements in the stock market [
10,
11], among other topics, which demonstrate that users perform a function similar to observers of social events or preference indicators and all this information is helpful for further analysis.
Similarly, the information from these sites is analyzed to identify malicious content within the messages shared among users on social networks to prevent diverse forms of cyberattacks from affecting the assets of users or institutions through this route as an attack vector [
12], such as Kunwar et al. [
13] mentioned that social networks have become a new attack vector, and various malicious users are looking for opportunities to take advantage of them. Meanwhile, Saidi et al. [
14] have exposed the importance of analyzing the communities and information in social networks, concluding that modeling and semantic analysis can extract information from these sites to provide a profound vision of the operations of clandestine groups of cybernetic terrorists.
It is important to remark that the activities of analyzing the information contained in social network messages for the detection of cyberattacks cannot compare its performance with software tools and mechanisms used in the area of cybersecurity, such as antivirus, firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), among others security software, but due to the popularity of social networks, cybercriminals have found these sites as a way of accessing the assets of the victims and avoid the before security controls, turning these services into spaces for the propagation of cyberattacks.
On the other hand, Lippmann et al. [
15] contributed to the creation of an automated process for extracting cybersecurity discussions from online forums, arguing that this would reduce the amount of time an analyst needs to remove irrelevant content to their investigation in this area. Similarly, information sources such as blogs and discussion forums are analyzed to find malicious content in shared messages. In this sense, Grishman et al. [
16] proposed a method to identify messages containing information or distribution characteristics of malware applications to determine the users that spread threats in Deep/Dark web forums and blogs through a Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) architecture and an analysis of connections among users using graphs.
Therefore, the following works focus on detecting the existence of some variant of cyberattack in messages from social networks. Unlike traditional security controls, these works do not contain, mitigate, or eliminate threats. However, these report findings to the user to evaluate the actions to commit.
Liao et al. [
17] presented iACE, a framework to extract Indicators of Compromise (IoC) from unstructured texts. The IoC [
18] concept describes a malicious activity or artifact relevant to a cybersecurity incident by analyzing its behavior patterns to be identified. Liao et al. proposed using NLP NER/ER techniques to gather information from public sources such as blogs, articles, and other publicly accessible written media and create a series of tokens and terms that allow defining unique characteristics of different cyberattacks.
A work to detect Phishing was done by Liew et al. [
19], which developed a real-time security alert mechanism using a classification model derived from a supervised machine learning technique of Random Forest (RF), identifying 11 classification features that yielded a 94.75% accuracy value after analyzing 200 phishing URLs collected from Twitter and PhishTank to determine the effectiveness of their model.
Erkal et al. [
20] proposed an alert system to detect cybersecurity threats such as spam and malware spreading on Twitter messages utilizing a Naive Bayes classifier and a vectorization based on the weights of the TF/IDF terms (Term Frequency/Inverse Document Frequency), achieving a success rate of 70.03% in detecting phishing and spam contents.
Ashour et al. [
21] evaluated the performance of their classifier based on n-grams for spam detection on Twitter messages, and they obtained better results than those performed with TF/IDF techniques, achieving an F1 value of 0.794, according to their reported results.
Wu et al. [
22] proposed a model based on deep learning techniques to address spam detection, where the syntax of each tweet was learned through WordVector technique for pre-processing and converting them into high-dimension vectors, achieving an F-measure up to 0.942.
Meanwhile, Feng et al. [
23] proposed a framework based on DL for spam detection, which sets up a detection system at the mobile terminal and the server. This model utilizes the Word2vec tool to convert words to vectors, achieving an accuracy value of 0.9136 in the classification model on the server side.
Madisetty et al. [
24] presented a method that combines five CNN models and one feature-based model through a neural network for spam detection at the tweet level, where each CNN was trained with word embeddings of different dimensions and the feature-based model utilized three types of features, named as user-based, content-based, and n-gram features, achieving an F-measure of 0.894.
Chen et al. [
25] proposed an analysis to detect low-quality content in real-time from tweet messages, which involves valueless content of different types from the perspective of user, which include spam and phishing content. The method requires direct and indirect tweet features, also a word-level analysis to capture the content characteristics of the tweet text. The results of their research show that this method achieved an F1 score of 0.8379 through a random forest classifier.
Djaballah et al. [
26] presented an approach to detect phishing on Twitter messages that combines a verification method in a database or “Blacklist” with a classification model based on URL and a web page content analysis, achieving an accuracy that exceeds 95% with the Random Forest classifier.
The previous works have analyzed messages from social networks through different models to detect from one to three specific cyberattacks. Nevertheless, this work proposes using a detection model that combines NLP tools and a CNN architecture to detect on social network messages four types of cyberattacks: phishing, spam, malware, and bot cyberattacks, which involve deceiving users into spreading malicious content. Furthermore, this approach analyzes the messages even if there is no URL in the content. Similarly, when the message has more than one URL, this model examines each one to detect the possible existence of more than one cyberattack in a single message.
One advantage of this proposed work is that it does not require consideration of specific characteristics from social networks, such as the number of followers, likes, people the user follows, and other details that different social networks may share, but others lack them to analyze the content message.
Therefore, this work can be used to examine the content of diverse blogs, discussion forums, and social networks as sources of information for cyberattack detection tasks. After detecting a message with characteristics of any of the four cyberattacks, this model classifies it into the type of cyberattack to which the malicious content belongs. The following section presents the proposed methodology of this work that outlines the phases for analyzing each message.
3. Methodology of Social Network Messages Analysis
This work aims to detect four types of cyberattacks: spam, phishing, malware distribution, and bot activity (which refers to the spreading of harmful messages among users, whether or not the attacker interacts with the victim). Therefore, the problem is defined as follows: given a message m, consider four subsets of a set C – for spam, for phishing, for malware, and for bot. The task is to detect whether m belongs to the C set. If m is in C, classify m to which subset of C belongs.
In order to address this problem, this work presents the following methodology, which involves analyzing text content from diverse social networks, discussion forums, and blogs to detect and classify the content according to the previous problem. This methodology utilizes tools and techniques from NLP and a DL model based on CNN to detect and classify each message. Therefore, it just considers text and does not include multimedia elements like images, videos, animations, or audio. Moreover, the importance of creating a model capable of detecting a more significant number of threats and being utilized regardless of the data source is a factor considered as an opportunity for extending the landscape of cyberattack detection activities on this kind of content.
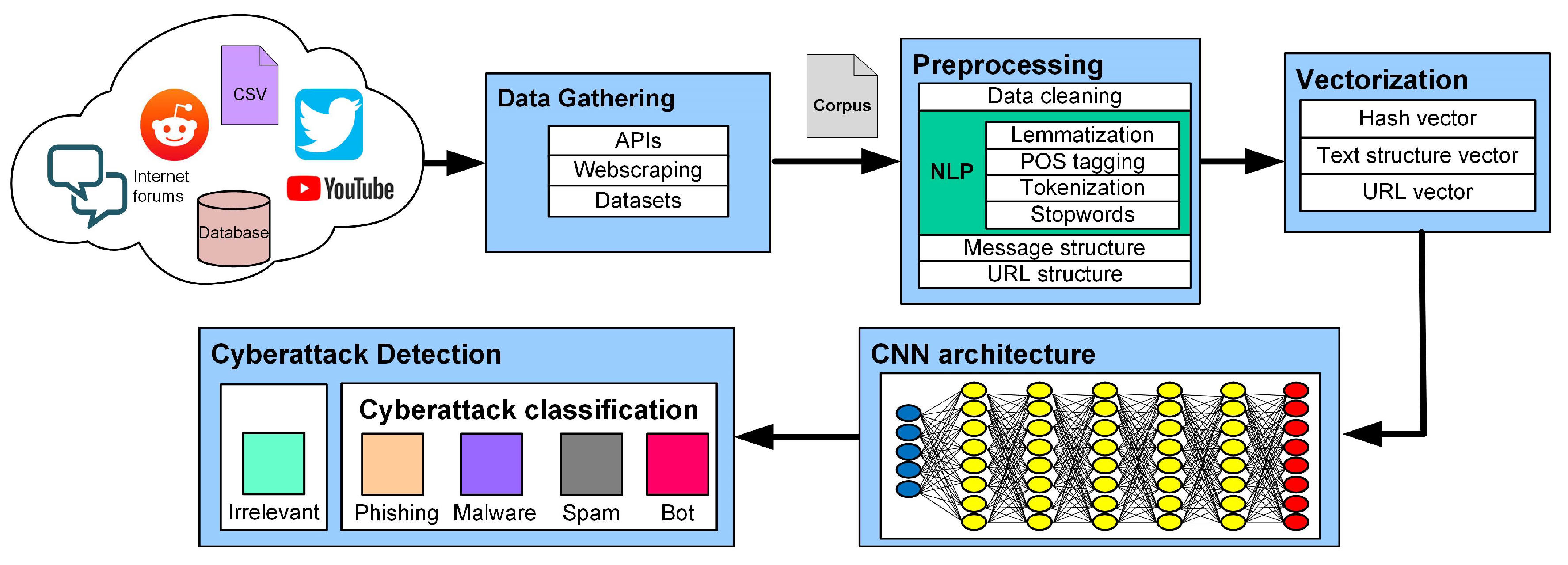
Figure 1 illustrates the proposed pipeline for cyberattack detection on social network messages, depicting the stages from a gathered message to the results of detection and classification tasks from the CNN model.
3.1. Data Gathering
The gathered information integrates the dataset utilized for the training and testing activities of the CNN model, making this data the corpus for the model. The messages obtained through the following mechanisms and resources served as inputs for the NLP stage of this methodology.
3.1.1. API
This service allowed the execution of activities to request samples of publications through functionalities according to each social network, such as searching by keywords, specific accounts, retrieval of messages by ID, publication dates, and other properties. For example, to collect tweets and retweets from Twitter, an endpoint connection from their API was used to download available public messages.
3.1.2. Scraping
Websites such as blogs and discussion forums are based on browsing through the HTTP protocol. In order to extract messages from these interaction spaces, this work utilized web-scraping and crawling techniques to simulate recursive browsing through different websites.
3.1.3. Datasets
In order to complement the corpus of this work, a subset of messages of different Datasets was used from works such as Lampu [
27], Behzadan [
31], and Chen [
25], in which content refers to messages labeled as spam, phishing, and spam, respectively.
3.2. Preprocessing
After gathering the messages into a corpus, the next step is preprocessing, which involves using NLP techniques to create three arrays. These arrays represent the properties of each message, such as the grammar, lexical, and semantics through tokens, the structural composition of the message, and the representation of features based on the URL structure.
3.2.1. Corpus
This corpus comprises two values for each message: the raw text content and the label that categorizes the message into one of the subsets related to the initial problem. In addition, this corpus includes a selection of messages labeled as “irrelevant” due to their non-malicious content, according to the data sources used for this work. Hence, there are five labels in this corpus: malware, phishing, spam, bot, and irrelevant.
3.2.2. Data Cleaning
This activity removes unnecessary characters from the text without altering the main idea of the message. In order to filter each message, different tasks were performed, such as eliminating unrecognized characters, replacing repetitive line breaks and blank spaces with just one, and removing emoticons and emojis by using regular expression rules.
3.2.3. Lemmatization
The lemmatization procedure reduces morphological variants of a word to their roots or lexemes. Thus, the number of words that appear in this corpus is reduced, which makes it possible to diminish the diversity of needed words to represent the content of a message.
3.2.4. POS Tagging
The purpose of the Part-Of-Speech (POS) tags in this work is to accurately define the intended lemma based on the context and grammar of a message rather than assuming a generic lemma transformation of a word. By applying POS tagging analysis to change words correctly into lemmas, the number of words in this corpus is reduced compared to considering the text of a message in its raw form.
3.2.5. Tokenization
Tokenization involves breaking down the text of each message from this corpus at the word level to produce an array of individual elements called tokens.
3.2.6. Stopwords
Stopwords play a crucial role in the text by serving as the connecting point for syntax and grammar. However, they do not have meaning when written alone. Thus, to represent the main idea of each message with a reduced number of tokens, stopwords in each token array were removed.
3.2.7. Message Structure
The text structure of a message shows how the content was posted and shared on social networks. In this sense, the use of features based on the structure of the text derives from the following hypothesis: extracting morphological properties from the structure of the text of a message could reveal those characteristics that harmful content may share with written messages from malicious users. Through experimental analysis of diverse characteristics from messages of this corpus,
Table 1 shows 16 properties that delivered the most satisfactory results during the subsequent stages of this work.
3.2.8. URL Structure
URLs in a message sometimes may not show the true website domain to the user because of URL shortening services, causing users to be redirected to a different website than expected when clicking the URL. By implementing software tools to reveal the final website of shortened URLs, this stage analyzed the authentic domain and extracted characteristics from the resulting URL.
Table 2 shows 27 characteristics used to represent the properties of a URL present in a message, which delivered the most satisfactory results during the subsequent stages of this work.
Furthermore, if a message does not contain a URL, the structure uses specific values called “URL_ZERO” to indicate the absence of a URL in the message. Sometimes, messages may have more than one URL. In such cases, each URL is analyzed separately, resulting in a structure for every URL included in the message.
3.3. Vectorization
This step involves encoding the arrays containing tokens, text structure, and URL structure into numeric values, which will be the input, as vectors, to the CNN architecture. The procedures to obtain these vectors are explained below.
3.3.1. Hashing Vector
Each word in the dictionary of this corpus is assigned a unique integer hash using the hashing model. The hash acts as an identifier for each token in the array, resulting in a vector of integers representing the initial token array. In addition to the token array, two characteristics from the URL structure are appended as tokens, such as “Domain suffix” and “Registrant,” that complement the content with information referring to each URL that appears. Likewise, if the message does not have a URL, the tokens “no_domain” and “no_suffix” are appended from URL_ZERO values.
Finally, the size of vectors using this model does not depend on the number of words in the vocabulary as other models do, such as the bag-of-words model. Therefore, the vector size was determined based on the length of the message with the maximum number of tokens after the content analysis from the training dataset, resulting in 93 elements, the same number that defines the size of these output vectors.
3.3.2. Text Structure
This vector represents the structural and typographic characteristics of the raw text from a message. The vector consists of the extracted values, shown in
Table 1, from the message structure array. Thus, the size of this vector is equal to the number of extracted features, with a total of 16 values.
3.3.3. URL Structure
This vector is created for each URL present in the message. The extracted values from the URL structure array, shown in
Table 2, integrate this vector. Likewise, if the message does not have a URL, this vector is created with predefined values, defined as “URL_ZERO” values, that symbolize the lack of a URL in the message.
Although the quantity of elements of the URL structure is 27, this vector utilizes 25 because two of them, “Domain suffix” and “Registrant” values, are utilized as tokens for the hashing vector process. Therefore, this final number of elements represents the size of the resulting URL vector.
3.4. Deep Learning Model
Such as Kim [
28] mentions, a CNN model can utilize documents as a matrix of words, similar to how it handles pixels for image recognition and computer vision tasks. For this reason and according to works from this literature review that employ this model, this part presents a CNN architecture that utilizes the three resulting vectors from the before stages to detect and classify the cyberattacks defined in the initial problem.
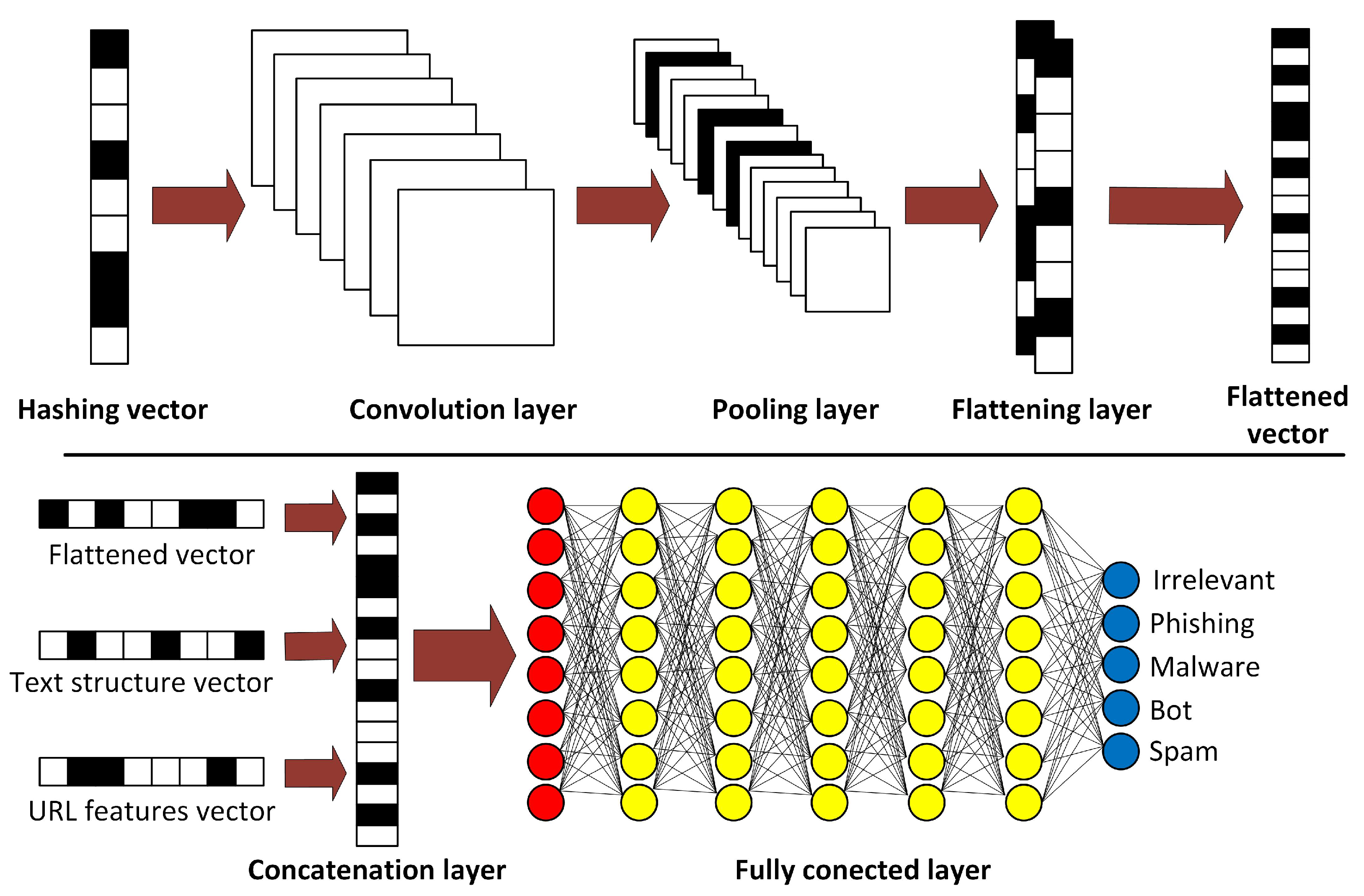
After the flattening layer, an additional layer is added to the architecture. This layer concatenates the resulting convolutional vector with “text” and “URL” structure vectors before continuing with the fully connected layers. The details of each stage in this CNN architecture are shown below.
3.4.1. Convolution Layer
The initial layer of this architecture is convolution, which extracts the features from the hash tokens to preserve the relationship between each value. This layer utilized a RELU activation function to break the linearity and increase non-linearity during this process.
3.4.2. Dropout Layer
This layer utilizes a down-sampling operation [
29] to make this model susceptible to variation, absence, and distortion.
3.4.3. Pooling Layer
The pooling operation involves sliding a two-dimensional filter to summarise the features within a region covered by a filter and reduce the number of parameters to learn during the computation performed in the DL model.
3.4.4. Flattening Layer
This layer sets the pooling output into a one-dimension matrix.
3.4.5. Concatenation Layer
This layer concatenates the resulting flattened vector with the text and URL structure vectors to create an input vector for the fully connected layers.
3.4.6. Fully Connected Layers
These layers utilize the resulting concatenated vector as input. It is integrated by the input, hidden, and output layers, where the output layer utilizes Softmax as an activation function to generate the final results.
4. Cyberattack Detection Model
This section presents details about the amount of utilized data for test and training, the implementation of the developed tools by this research team through an algorithm, and details about this proposed CNN architecture with TensorFlow [
30] framework to detect cyberattacks on social network messages.
4.1. Dataset
The data source of the messages utilized in this work is diverse. A part of these messages comes from sampling in Twitter, through its API, to create a compilation of available messages and extract different types of content and integrate them into a corpus.
Meanwhile, other messages were gathered from websites, such as Reddit blogs and software product announces on Youtube. On the other hand, this work complemented the corpus with specific message collections from websites like Kaggle, such as SMS messages [
27] marked as spam, and tweet subsets from related studies, such as Behzadan et al. [
31] and Chen et al. [
25].
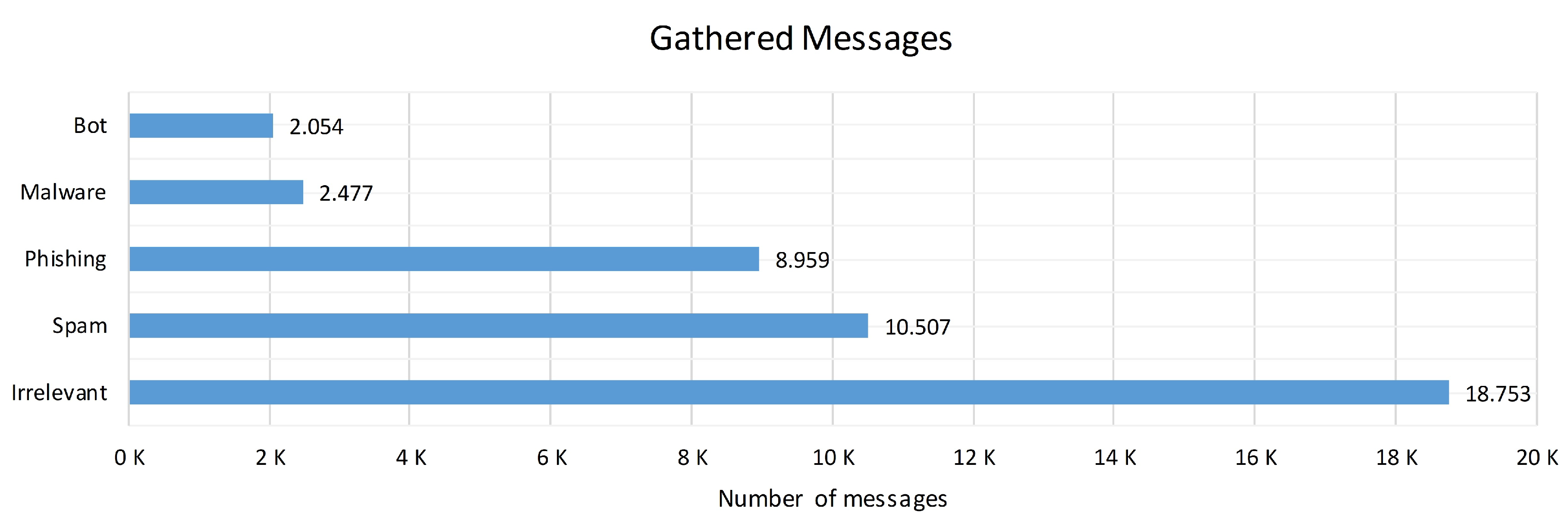
Figure 2 shows the number of messages utilized in this work, with a total of 42,751 posts, where each item has just the raw text and a label that identifies the type of content. In addition, the quality of the messages was reviewed to avoid details such as empty content and repeated messages.
This corpus contains five labels: spam, phishing, malware, bot, and irrelevant for messages that did not fit into those categories of cyberattack. Therefore, these samples are considered a representative portion within a scenario where the information is labeled for testing and training purposes of the CNN architecture.
4.2. Analysis
Once the corpus has the gathered messages, then this is saved in a CSV file for the stages of training and testing of the model. The next step is analyzing each message from the CSV file through all the stages explained previously in this paper. Algorithm 1 shows this novel approach to analyze each message through before methodology, returning a list of 3-tuple objects that contain the tokens, text structure, and URL structure, ready for the next stage, vectorization.
|
Algorithm 1:Message analysis. |
- 1:
functionanalyze_message(message_text) - 2:
STOP_WORDS ← load_stopWords() - 3:
structure_vector ← structure_features(message_text) - 4:
Tokens ← empty list - 5:
text ← clean_data(message_text) - 6:
Sentences ← text_to_sentences(text) - 7:
len(Sentences) - 8:
for to N do
- 9:
sentence ← Sentences[i] - 10:
tagged_tokens ← POS_tags(sentence) - 11:
len(tagged_tokens) - 12:
for to M do
- 13:
append lemmatize(tagged_tokens[j]) to Tokens - 14:
end for
- 15:
end for
- 16:
tokens_message ← empty list - 17:
len(Tokens) - 18:
for to L do
- 19:
if Tokens[k] not in STOP_WORDS then
- 20:
append Tokens[k] to tokens_message - 21:
end if
- 22:
end for
- 23:
Vectors ← empty list - 24:
URLs ← find_URLs(message_text) - 25:
len(URLs) - 26:
if then
- 27:
URLs URL_zero - 28:
end if
- 29:
for to K do
- 30:
URL_features ← extract_URLfeatures(URLs[w]) - 31:
append URL_features.domain_suffix to tokens_message - 32:
append URL_features.registrant to tokens_message - 33:
URL_vector ← URL_features[] - 34:
v ← (tokens_message, structure_vector, URL_vector) - 35:
append v to Vectors - 36:
end for
- 37:
return Vectors - 38:
end function
|
The vectorization process involves taking each element from a 3-tuple list and converting it into a one-dimensional array using the corresponding vectorizing model. The Hashing model creates hashes that replace each token with a hash value in a vector. The size of the vector depends on the maximum number of tokens in the most extended analyzed message of the corpus.
Meanwhile, for the two remaining vectors, the vector’s size representing the structural text is 16 features, and the URL vector is a size of 25 extracted features. After the convolution process, the text and URL structure vectors are combined with the flattened vector to create a final vector. This final vector is then fed into the input layer for the fully connected layer of the CNN architecture.
4.3. CNN Architecture
This approach employs a DL model based on CNN architecture to detect four types of cyberattacks: spam, malware, phishing, and a previously defined bot type. Content that falls outside of these categories is deemed irrelevant.
Figure 3 shows the main components of this CNN architecture.
This architecture used 70% of the data for training and 30% for testing. Thus, the main parameters and features of the architecture after the Convolution process, which delivered the most satisfactory results during these activities, are as follows:
One input layer for the concatenated vector;
Six hidden layers;
Five outputs concerning to each class;
Adam optimizer;
Kullback Leibler divergence as loss function.
Besides the previous features of the architecture, the team defined the most outstanding parameters that showed acceptable behavior through a series of experiments during the training, such as the filter size for the convolution is 8 and a kernel of size 8. Meanwhile, for each layer of the model, the implementation of activation functions from the input up to the output layer was: three Sigmoid, four Relu, and one Softmax.
Once the three vectors (Hashing, text and URL structure) enter into CNN architecture, the final result must arise from any of the five neurons in the last layer. In this part, the result comes from the neuron with the maximum value, whose activation function in this layer is defined by the Softmax function
when
, this result is defined by:
where the input vector
Z consisting of
N real numbers in the last layer, each component must be in the interval (0,1). The values in the
Z vector should add up to 1, and each value represents the probability of each neuron. Finally, the maximum value from this layer represents the outcome of this architecture.
5. Results and Discussion
This section shows, interprets, and discusses the results obtained by this CNN architecture for cyberattack detection and classification activities. The first part shows the results, graphs, tables, and confusion matrices referring outcomes and behavior of this proposed approach. Finally, the discussion part about the obtained results is shown.
5.1. Results
The labeled messages to perform the training and test activities come from the review tasks carried out by the research team and from previously cited information sources.
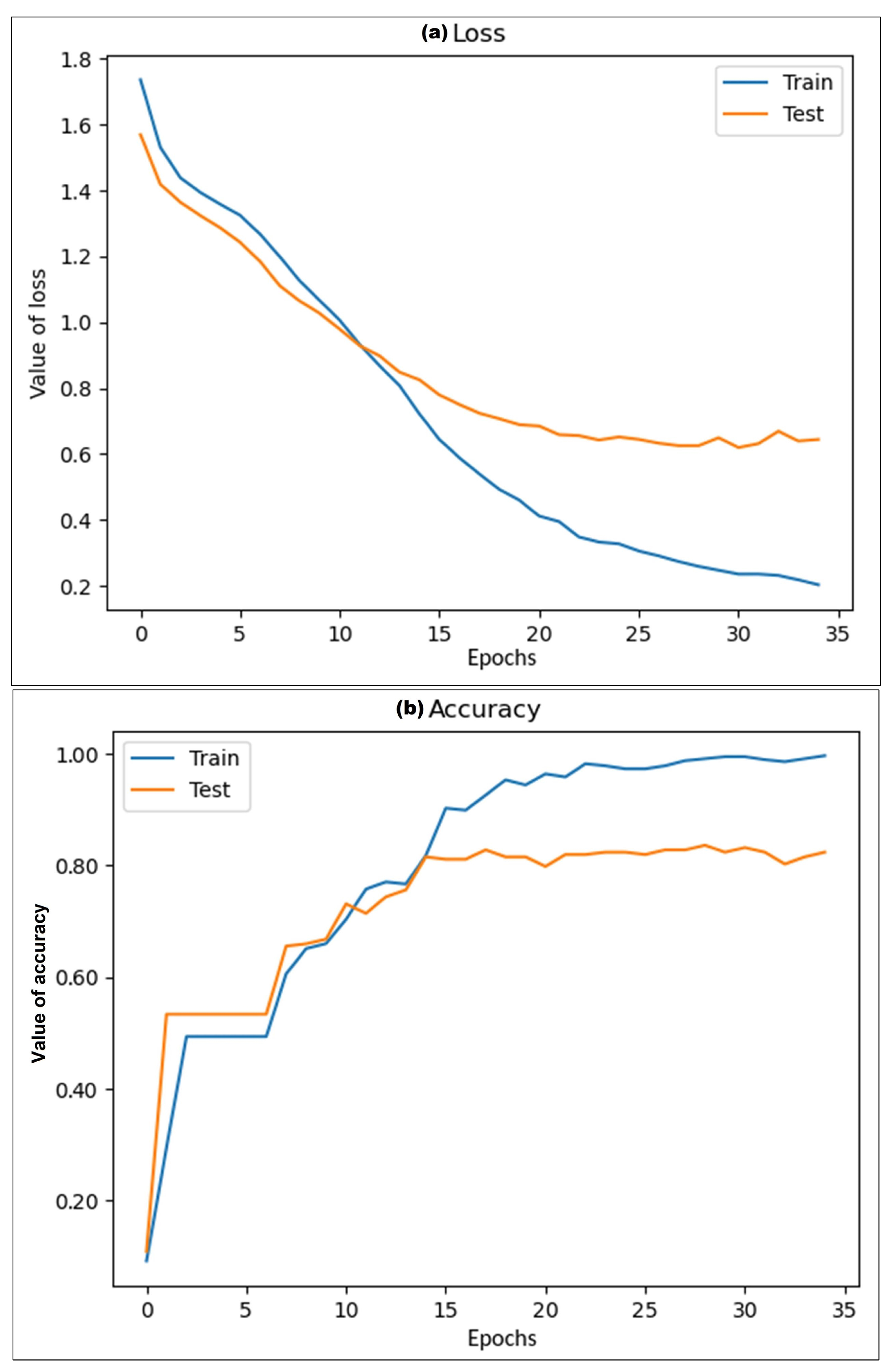
Figure 4 shows the performance of the model using the final settings of the architecture, where the graphs represent the behavior of the loss function and accuracy value during the training and testing process.
As can be seen,
Figure 4a shows that the loss function or cost function tends to decrease in value simultaneously in training and testing, reaching a point where the error value of the model is much lower for the training data than for the test data due to the system adjusts the values during training. Meanwhile, the test data shows the effects on the model with these settings. Furthermore, this graph depicts how the performance of the model does not fall in overfitting when the training process tries to decrease the error value, achieving an error cost of 0.23 on the training data and 0.64 on the test data during the loss function evaluation.
On the other hand,
Figure 4b shows the accuracy value obtained during the optimization of the model. As can be seen, the model reaches a maximum level of 0.96 on training data. Similarly, the behavior of the model on test data grows, achieving an accuracy value of 0.82 on this data, demonstrating that these values remain almost constant during training and testing, presenting only minimal variation, which there is no reason to continue training the model and avoid falling into overfitting.
In order to address the first part of the problem outlined in
Section 3, which involved detecting whether a message contains characteristics of any of the four analyzed cyberattacks or not,
Table 3 shows the accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score values obtained from the model with the test data.
For the second part of the initial problem, this model shows the results of classified messages based on the cyberattack features related to spam, phishing, malware, and bots. In addition, a subset of irrelevant messages was utilized to evaluate the accuracy in situations where false positives occur during the detection task of the model, achieving an accuracy value of 0.82 during this task.
Table 4 shows the precision, recall, F1 score, and accuracy values achieved during the evaluation of this activity.
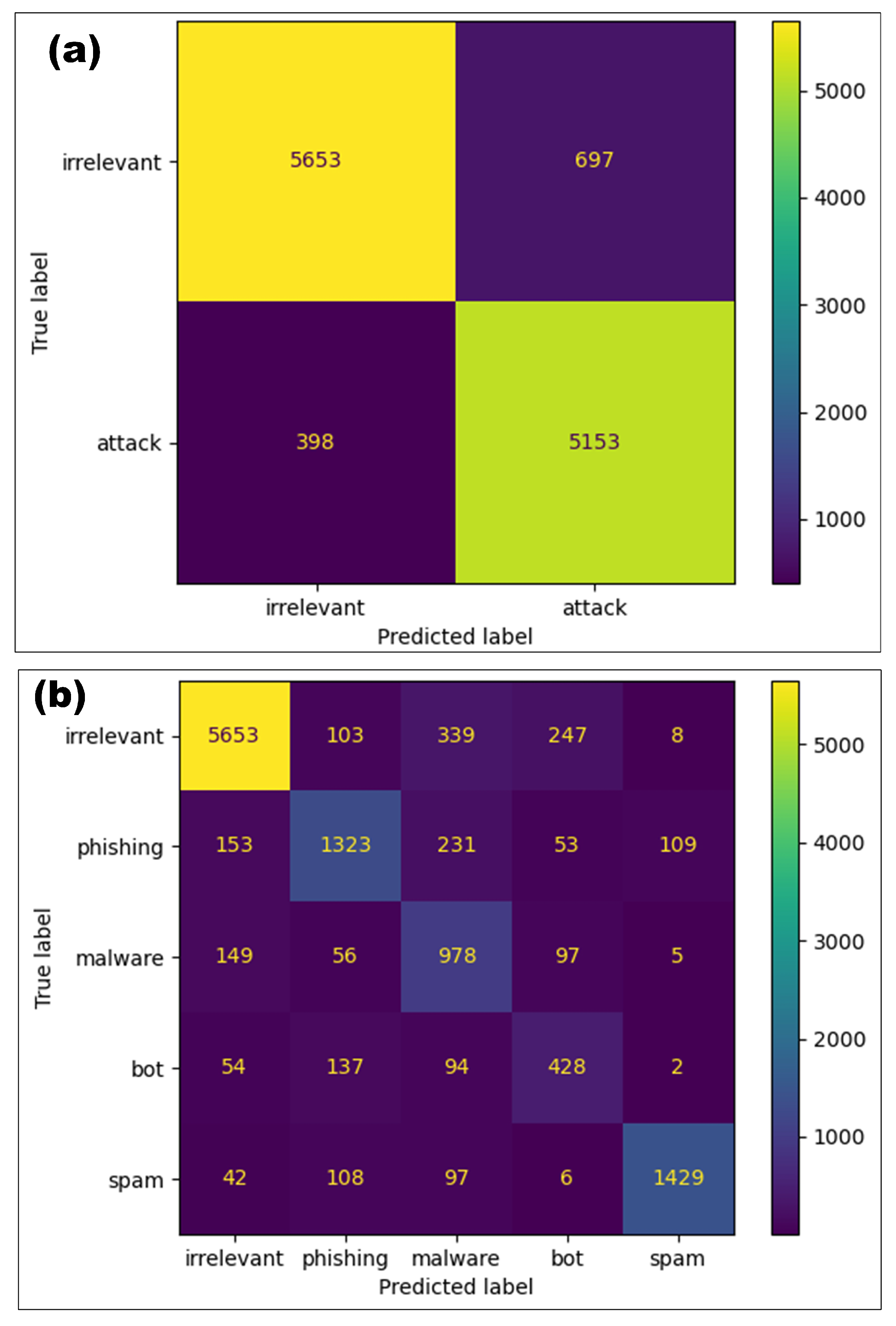
Figure 5 demonstrates the confusion matrices referring to the results of the analyzed messages through this CNN architecture utilizing test data to evaluate the cyberattack detection and classification activities.
Figure 5a shows the number of cyberattacks and irrelevant messages correctly detected, or true positives and negatives. As can be seen, the correct results are much higher than the remaining values in this confusion matrix, validating the cyberattack detection performance with a 0.91 accuracy value.
Meanwhile,
Figure 5b displays the distribution of results when the model performs activities to classify the type of cyberattack to which the detected message belongs, showing how the predicted results appear against labeled messages in the confusion matrix into the five categories. Hence, this CNN architecture shows its capability through the number of true positives and negatives correctly classified against the remaining values of this matrix.
Even though this proposed approach has a lower accuracy value in classification compared to the detection process, it still identifies a considerable number of messages related to any of the four cyberattack subsets from the initial problem. Likewise, if the model misclassifies the content into another category, it can identify a threat as any possible cyberattack rather than irrelevant content.
5.2. Discussion
One of the details of this work is the implementation of NLP tools combined with a learning model, which has proven to be a synergy in cyberattack detection tasks, as demonstrated by the works of Ashour et al. [
21], Wu et al. [
22], and Feng et al. [
23]. Therefore, the results of this work are shown in
Table 5 and compared to results obtained from the literature review presented in
Section 2.
These works are arranged, in descending order, according to the F1 score value. The F1 score is a more effective metric for solving class imbalance issues than the accuracy metric, which is better suited for balanced classes.
In this comparison, Liew et al. [
19] and Djaballah et al. [
26] are the top performers with the highest F1 value. They analyze URLs from social network messages to detect phishing. However, this work performs the tasks of detection regardless of whether there is a URL in the content. Even if multiple URLs appear, it detects any of the four studied cyberattacks, making it possible to explore whether more than one cyberattack may appear in a single message.
Although this work did not obtain the highest F1, its score is promising, with a 0.904 value. One notable aspect of this work is that it detects up to four different variants of cyberattacks. Meanwhile, works like Chen et al. [
25] and Erkal et al. [
20], through their message analysis, found up to 3 different variants but with F1 values less than 0.84 value.
Finally, the analysis of messages based on the content and characteristics of social network accounts has proven to be a complementary resource in detection tasks, such as demonstrated in the works of Madisetty et al. [
24] and Chen et al. [
25], who developed methodologies based on features from specific social networks. On the other hand, this work presented a model that relies solely on the message content, being independent of the data source, allowing its implementation for the detection and classification of cyberattacks on contents from diverse social networks.
6. Conclusions
Nowadays, social networks are being used as attack vectors to distribute malicious content to numerous users. Therefore, this work presented an approach for analyzing social network messages using CNN and NLP tools through a methodology to detect and classify four types of cyberattacks, such as malware, phishing, spam, and a defined version of a bot.
In this work, a collection of labeled messages was utilized as a corpus, where each element was categorized based on its content as either a cyberattack or considered irrelevant if it did not fit into any of the established cyberattack categories. Thus, this corpus is defined as an imbalanced dataset because the number of messages is different for each class, allowing represent the environment where, by itself, the amount of irrelevant messages is superior to those identified as cyberattacks.
Regarding the initial problem, this approach showed promising results in detecting cyberattacks, or elements that belong to the set C, with an accuracy value of 0.91. It also demonstrated a favorable trend in classifying malicious content into one of the four cyberattack categories, or the classification of elements into subsets of C (, , , and ) for the second part of the problem, with an accuracy value of 0.82.
Finally, this model has shown that it can work without relying on specific social networks, third-party services, or blacklists that identify users or addresses reported and updated by a provider service. The analysis is applied just to the textual content of social network messages. Therefore, this work presented an approach that is not dependent on specific characteristics of particular social networks, and it can be implemented to analyze the content from various social media services.
Acknowledgments
The work was done with partial support from the Mexican Government through the grant A1-S-47854 of CONACYT, Mexico, grants 20220852 and 20220859 of the Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Mexico. The authors thank the CONACYT for the computing resources brought to them through the Plataforma de Aprendizaje Profundo para Tecnologías del Lenguaje of the Laboratorio de Supercómputo of the INAOE, Mexico and acknowledge the support of Microsoft through the Microsoft Latin America PhD Award.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CNN |
Convolutional neural network |
| DL |
Deep learning |
| IDF |
Inverse document frequency |
| IDS |
Intrusion detection system |
| IoC |
Indicators of compromise |
| IoT |
Internet of things |
| IPS |
Intrusion prevention system |
| ML |
Machine learning |
| NER |
Named entity recognition |
| NLP |
Natural language processing |
| NN |
Neural network |
| POS |
Part of speech |
| RF |
Ramdom forest |
| RNN |
Recurrent neural network |
| TF |
Term frequency |
| URL |
Uniform Resource Locator |
References
- Subrahmanyam, K.; Reich, S. M.; Waechter, N.; Espinoza, G. Online and offline social networks: Use of social networking sites by emerging adults. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology 2008, 29, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meana-Llorián, D.; González-García, C.; Pelayo, B. C.; Cueva, J. M. BILROST: Handling actuators of the internet of things through tweets on twitter using a domain-specific language. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Anand, A.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, R. K. Internet of Things and Social Media: A review of Literature and Validation from Twitter Analytics. 2020 International Conference on Emerging Smart Computing and Informatics (ESCI) 2020, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Bendovschi, A. Cyber-Attacks – Trends, Patterns and Security Countermeasures. Procedia Economics and Finance 2015, 28, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, V.; Asante, M.; Kofi Nti, I.; Nyarko-Boateng, O. Survey of websites and web application security threats using vulnerability assessment. Journal of Computer Science 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.; Kar, A. K.; Janssen, M.; Ilavarasan P., V. Perceived usefulness, ease of use and user acceptance of blockchain technology for digital transactions–insights from user-generated content on Twitter. Enterprise Information Systems 2019, 13, no–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindado, E.; Barrena, R. Using Twitter to explore consumers’ sentiments and their social representations towards new food trends. British Food Journal 2021, 123, 1060–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukma, E. A.; Hidayanto, A. N.; Pandesenda, A. I.; Yahya, A. N.; Widharto, P.; Rahardja, U. Sentiment Analysis of the New Indonesian Government Policy (Omnibus Law) on Social Media Twitter. 2020 International Conference on Informatics, Multimedia, Cyber and Information System (ICIMCIS) 2020, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Khurniawan, F. S.; Ruldeviyani, Y. Twitter Sentiment Analysis: Case Study on the Revision of the Indonesia’s Corruption Eradication Commission (KPK) Law 2019. 2020 International Conference on Data Science and Its Applications (ICoDSA) 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Y.; Durresi, A.; Alfantoukh, L. Using Twitter trust network for stock market analysis. Knowledge-Based Systems 2018, 145, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. S. Exploring the Initial Impact of COVID-19 Sentiment on US Stock Market Using Big Data. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyac-Torres, J. E.; Sidorov, G.; Anaya-Aguirre, E. Detección de ciberataques a través del análisis de mensajes de redes sociales: revisión del estado del arte. Res. Comput. Sci. 2020, 149, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Kunwar, R. S.; Sharma, P. Social media: A new vector for cyber attack. 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication, & Automation (ICACCA) (Spring) 2016, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Saidi, F.; Trabelsi, Z.; Salah, K.; Ghezala, H. B. Approaches to analyze cyber terrorist communities: Survey and challenges. Computers & Security 2017, 66, 66–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann, R.; Campbell, J.; Weller-Fahy, D.; Mensch, A.; Campbell, W. Finding malicious cyber discussions in social media. Lincoln Laboratory Journal 2016, 22, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Grisham, J.; Samtani, S.; Patton, M.; Chen, H. Identifying mobile malware and key threat actors in online hacker forums for proactive cyber threat intelligence. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics (ISI) 2017, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, X.; Yuan, K.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Xing, L.; Beyah, R. Acing the IOC Game: Toward Automatic Discovery and Analysis of Open-Source Cyber Threat Intelligence. Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security 2016, 755–766. [Google Scholar]
- Iocs, ¿realmente conocemos sus capacidades? Available online:. Available online: https://www.pandasecurity.com/spain/mediacenter/seguridad/iocs-y-sus-capacidades (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Liew, S. W.; Sani, N. F. M.; Abdullah, M. T.; Yaakob, R.; Sharum, M. Y. An Effective Security Alert Mechanism for Real-Time Phishing Tweet Detection on Twitter. Comput. Secur. 2019, 83, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkal, Y.; Sezgin, M.; Gunduz, S. A New Cyber Security Alert System for Twitter. 2015 IEEE 14th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA) 2015, 766–770. [Google Scholar]
- Ashour, M.; Salama, C.; El-Kharashi, M. W. Detecting Spam Tweets using Character N-gram Features. 2018 13th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Systems (ICCES) 2018, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, Y. Twitter Spam Detection Based on Deep Learning. Proceedings of the Australasian Computer Science Week Multiconference 2018, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Fu, Q.; Dong, M.; Guo, D.; Li, Q. Multistage and Elastic Spam Detection in Mobile Social Networks through Deep Learning. IEEE Network 2018, 32, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madisetty, S.; Desarkar, M. S. A Neural Network-Based Ensemble Approach for Spam Detection in Twitter. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems 2018, 5, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yeo, C. K.; Lau, C. T.; Lee, B. S. A study on real-time low-quality content detection on Twitter from the users’ perspective. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaballah, K. A.; Boukhalfa, K.; Ghalem, Z.; Boukerma, O. A new approach for the detection and analysis of phishing in social networks: the case of Twitter. 2020 Seventh International Conference on Social Networks Analysis, Management and Security (SNAMS) 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lampu, B. SMS_ Spam_Ham_Prediction. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/lampubhutia/email-spam-ham-prediction (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Kim, Y. Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification. Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2014, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee, J. Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing, 1st ed.; Machine Learning Mastery, Australia, 2017; 322.
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. 2015.
- Behzadan, V.; Aguirre, C.; Bose, A.; Hsu, W. Corpus and Deep Learning Classifier for Collection of Cyber Threat Indicators in Twitter Stream. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) 2018, 5002–5007. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).