1. Introduction
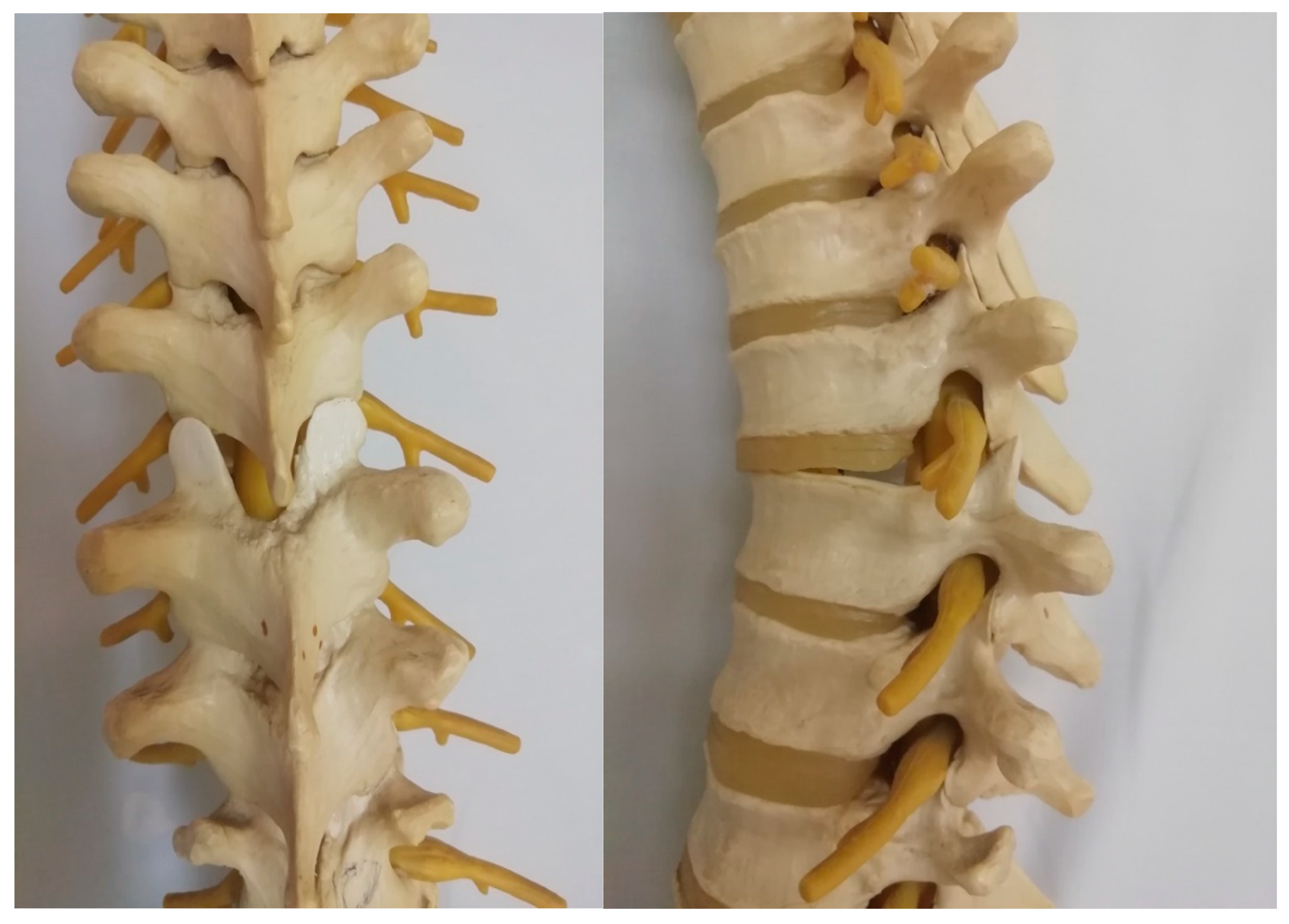
Spinal injuries constitute about 3% of all injury cases and most of them affect the thoracolumbar transition levels (Th11-L2). Thoracolumbar fracture-dislocations (AO-type C injuries) are rare injuries that occur due to very high-energy trauma, and the result is transitional and rotational instability of the spinal column, as well as severe neurological impairment (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2) [
1]. Thoracic and thoracolumbar fractures with bilateral dislocation and locking of the facet joint are rare and challenging fracture types for correction and management by surgical treatment (
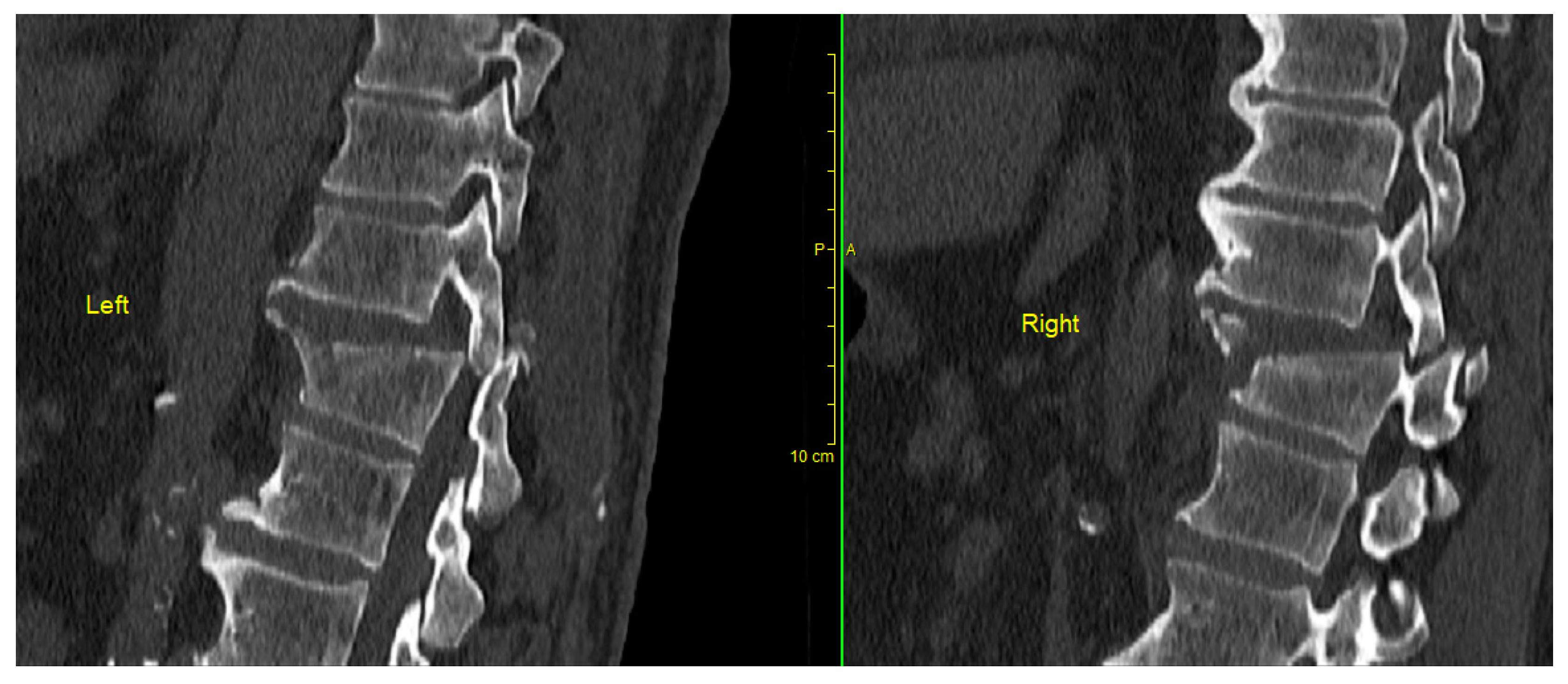
Figure 3). Various reduction techniques have been described, generally in a small series of patients, using a posterior approach with reduction and stabilization based on levering and manipulation using temporary short rods that join transpedicular screws [
2,
3,
4,
5].
The primary goals of the treatment are decompression of the spinal canal, realignment of the vertebral column, and stabilization to prevent further injury. Decompression is mainly performed if there is compression on the spinal cord due to bone fragments, disc material, or hematoma. This involves laminectomy, facetectomy, or discectomy, depending on the nature of the injury [
2]. The reduction of dislocated or locked facets in the thoracic vertebrae is a critical step in the surgical management of this injury. The goal of the reduction is to realign the dislocated vertebrae and unlock the facets. There are several techniques that a surgeon might employ depending on the specifics of the injury and the surgeon's expertise [
3,
5]. In the case of locked facets, unlocking and realignment can be particularly challenging and may require a partial facetectomy. The exact technique used to unlock the facets can vary, but it often involves a combination of gentle distraction and rotation of the involved vertebrae, under direct visualization.
Occasionally, the dislocation may be so rigidly locked that great force is required to achieve reduction (such as in cases with intact intervertebral discs, which provide a lot of resistance to distraction) necessitating staged reduction procedures [
6]. We introduce a novel technique that places less emphasis on the strong traction of the temporary rods placed in the proximal end, thus reducing the risk of screw pull-out and the need to extend the fixation due to the potential loss of purchase of the pedicle screw (
Figure 4).
In any reduction technique, it is critical to be extremely cautious to avoid causing further injury to the spinal cord or the nerves exiting the spine. Once the dislocation is successfully reduced, the vertebrae are typically stabilized with a fusion to maintain the correction and allow for healing. This study aims to report on the technique and the outcomes of this modified novel reduction technique employed in the management of thoracic fracture-dislocations.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted after obtaining approval from the institutional ethical committee. A retrospective review was conducted to identify the patients presenting with thoracic fracture-dislocations (AO type C) and managed by the modified novel reduction technique. The success of the reduction and iatrogenic intraoperative complications such as dural tear and screw pull out were the outcomes analyzed.
Surgical Technique
Under general anesthesia, the patient is placed in the standard prone position on a soft support frame. Using the posterior approach, bilateral pedicular fixation is performed, two levels above the fracture, using the free hand technique with fluoroscopic screw verification.
Before the reduction itself, we create an initial laminotomy window to get a sense of the damage done to the spinal cord, as intact spinous processes and laminae are required for the reduction technique. Definitive laminectomy and wide decompression are performed after reduction. Alternatively, if one has access to extra wide lamina spreaders, a laminectomy can be performed before reduction (skipping one lamina with the spreader), although we believe this to be a more dangerous alternative due to the proximity of the dura below the lamina to be removed.
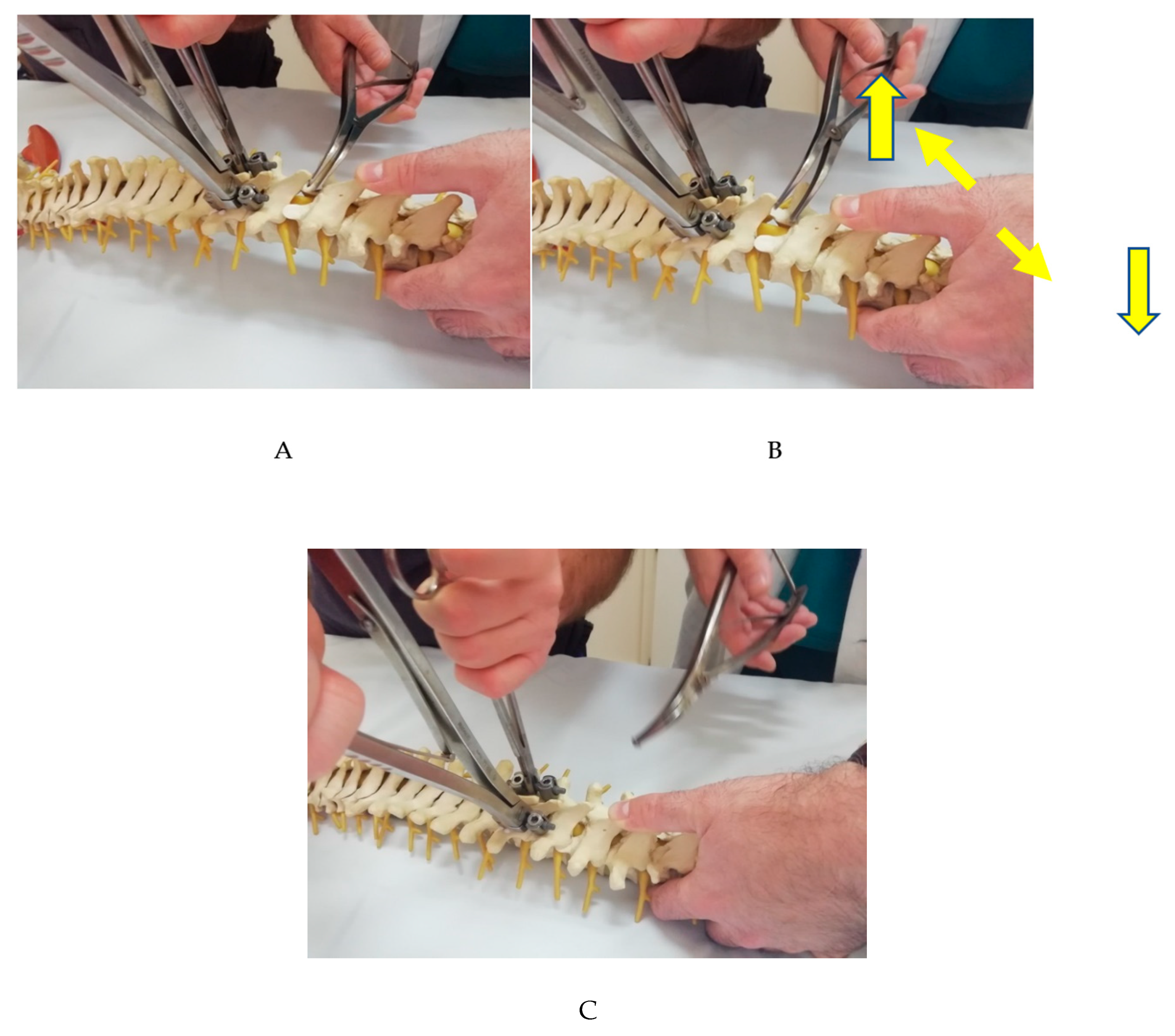
Our technique adds the use of a lamina spreader diagonally placed in the interspinous space of the dislocated level, combined with the temporary rod placement described above. The idea is that the lamina spreader provides two-dimensional correction forces, one blade simultaneously distracting and depressing the distal vertebra and the other simultaneously distracting and elevating the proximal vertebra. It may be necessary to "trim" the tips of the lower-level facet joints to facilitate "unlock" and further reduce the necessary force for the reduction maneuver, particularly in obese patients, where greater reduction forces are anticipated. Manual depression of the distal segment is performed simultaneously. The combination of the three simultaneous techniques reduces the overall force required at each individual component of the combined maneuver, making it overall easier to control and therefore safer (
Figure 5 A-C).
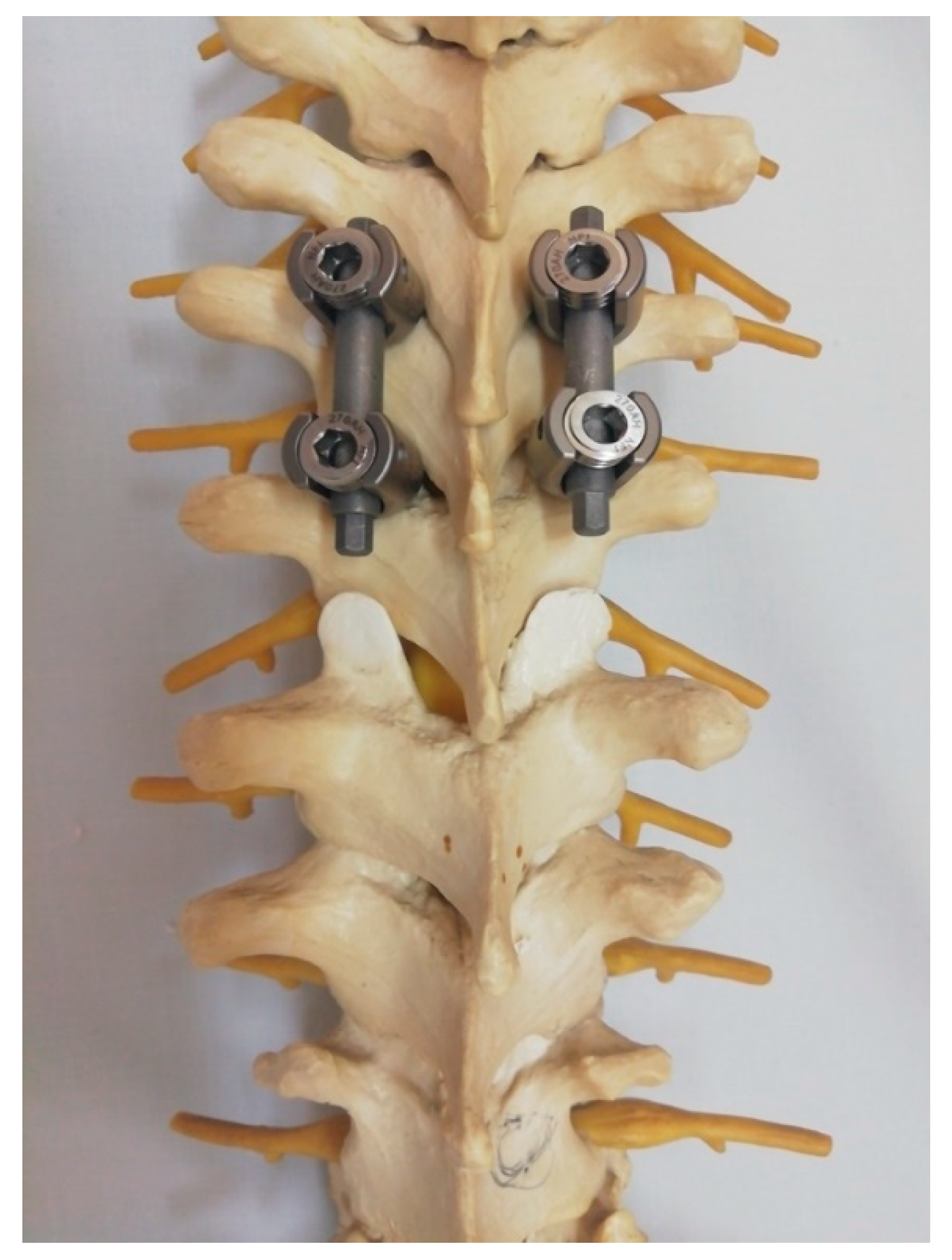
Following a successful reduction, a definitive laminectomy and wide decompression were performed and stabilized with instrumentation two levels above and below the level of injury along with adequate grafting to achieve posterolateral fusion of the index level. We used mean and standard deviation to denote continuous variables.
3. Results
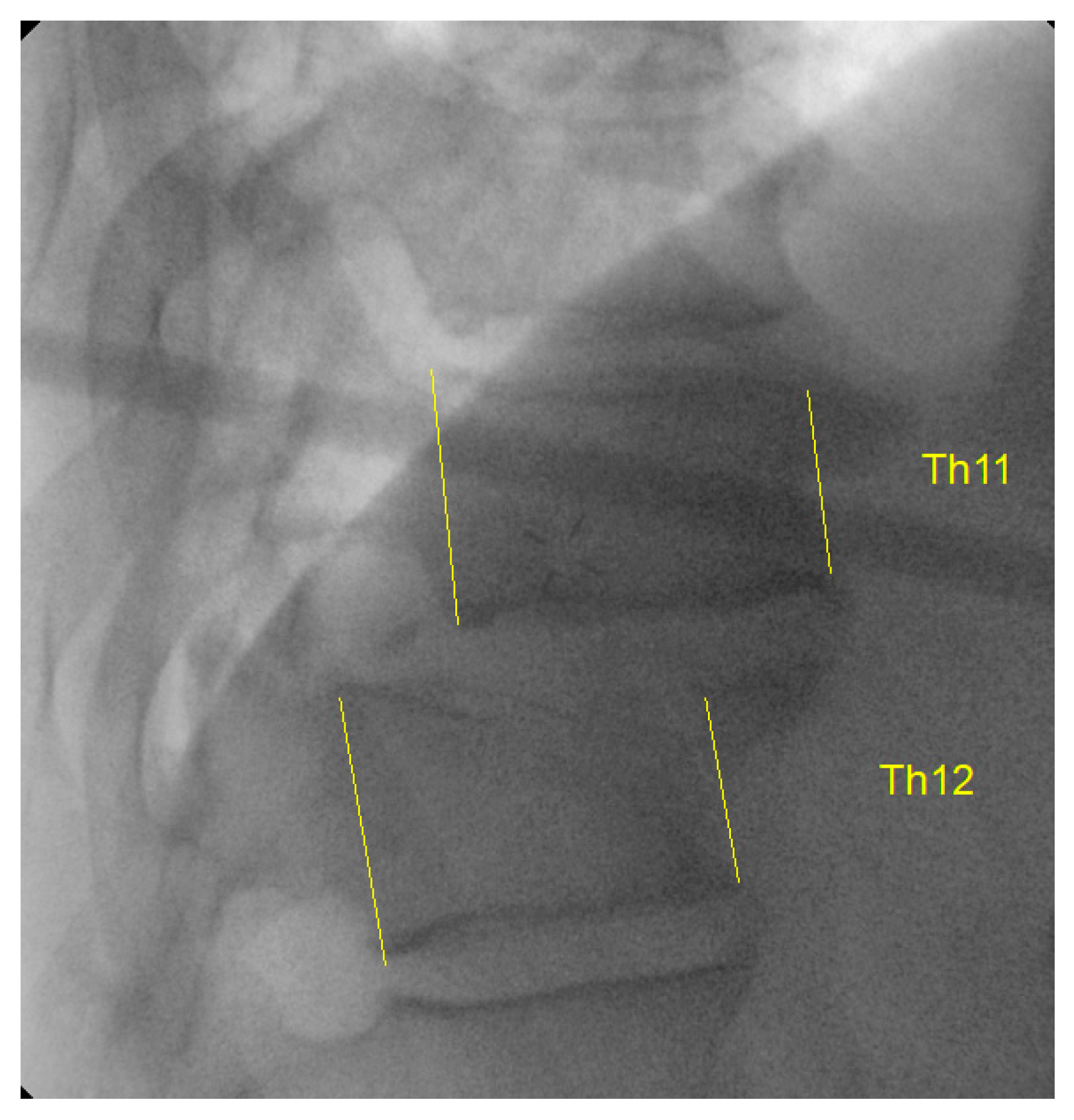
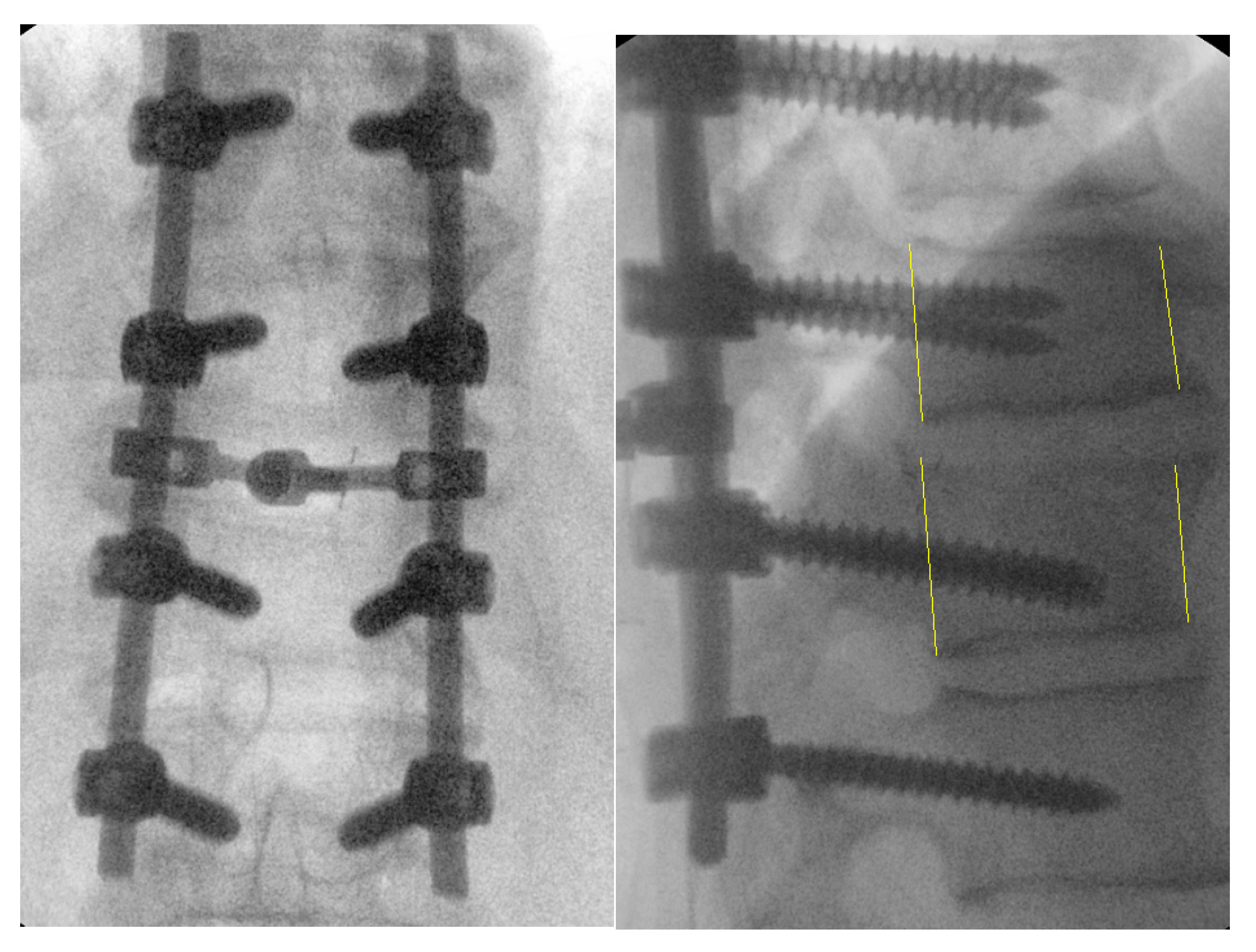
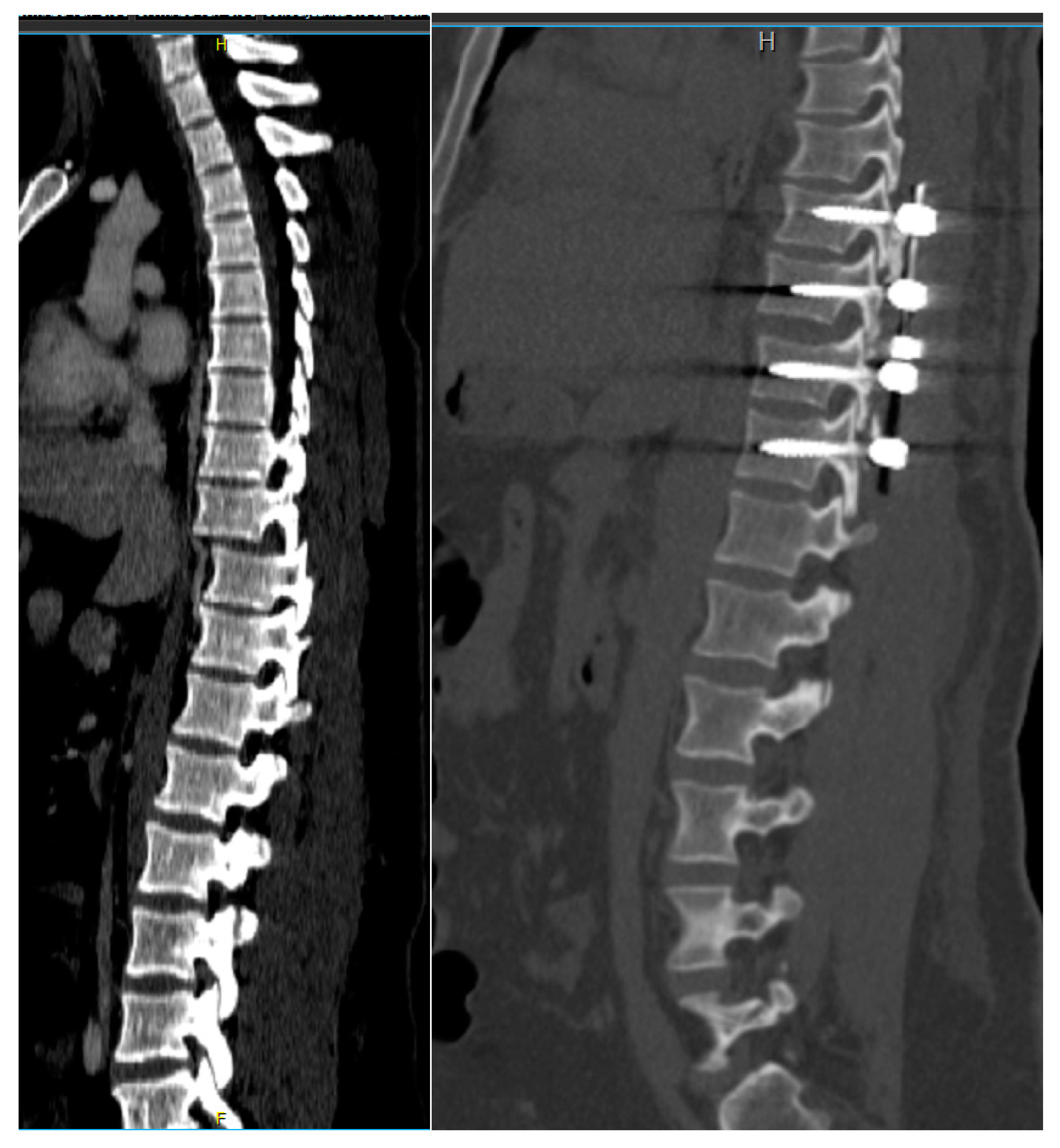
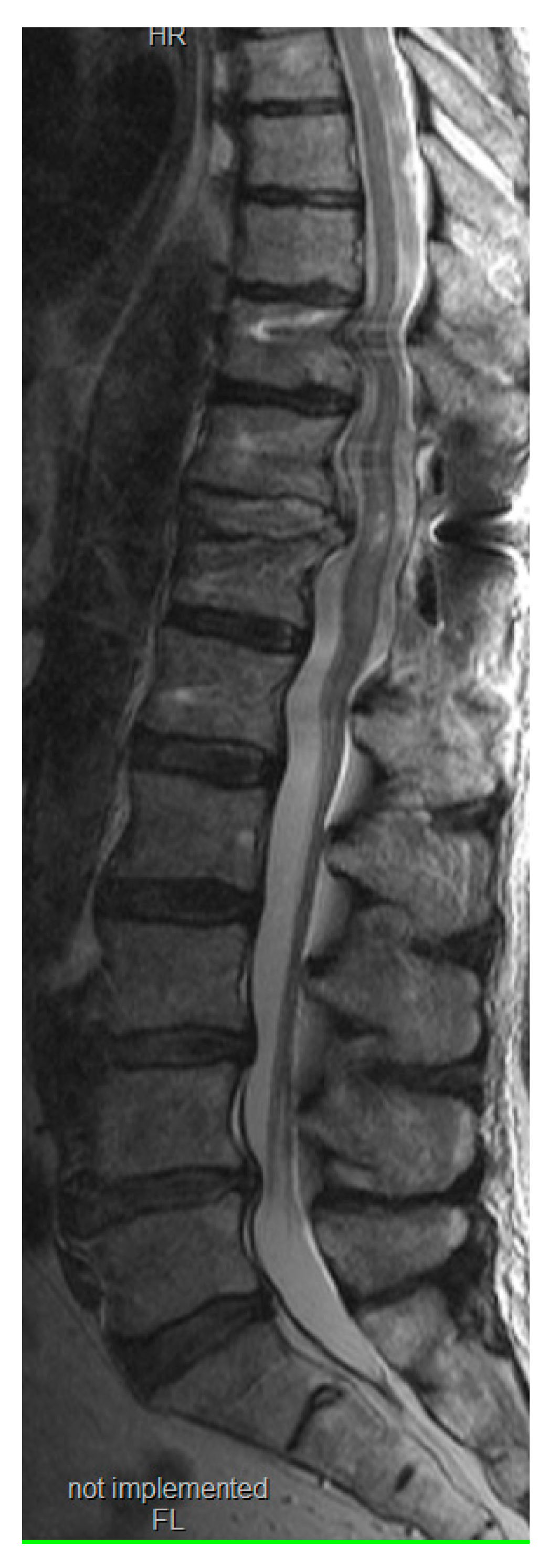
This modified novel reduction technique was performed in 4 cases presenting with thoracic fracture-dislocations with complete paraplegia. The mean age of the patients presented was 32.2 (±7.1) years. All the patients presented in complete paraplegia. All the patients were operated as early as possible with mean time to surgery of 1.5 (±0.5) days. Upon utilization of the above-mentioned technique, we did not experience any technical difficulties in carrying out the reduction, and the post-operative period was uneventful in all the cases without any intraoperative complications such as dural tears or screw failure (
Figure 6,7) [
7]. The reduction was smooth, and we managed to avoid a 'second hit' to the already damaged spinal cord. (
Figure 8) Due to the extreme compression of the spinal cord that occurs with spinal dislocation, patients remained paralyzed on follow-up visits until one year, although they did not experience back pain.
4. Discussion
The thoracolumbar junction acts as a transition zone from a rigid thoracic spine to a more mobile lumbar spine. Injuries to this transitional level are typical due to the relative mismatch in stiffness on either side of the junction. High-energy trauma can affect any level, including dislocating the relatively stiff thoracic spine, and is frequently associated with severe neurologic deficits [
8]. Although some cases of complete thoracic spine fracture-dislocations without neurological injury have been described [
9], as a rule, these types of injuries result in paraplegia as noted in all our cases.
Despite the grim prognosis, we believe that most fracture-dislocations with complete neurologic deficits should be operated on as soon as possible (as soon as the patient arrives and is cleared for surgery) due to the sheer unpredictability of neurological recovery [
10]. The main goals of surgical management include the reduction and stabilization of the unstable spinal segment. In the case of patients presenting with paraplegia, the goal of surgery is towards early mobilization and rehabilitation [
11]. Surgical treatment of these injuries is challenging, and the forces needed to achieve adequate reduction often result in complications such as dural tears, screw failure, or iatrogenic spinal cord injury. Our modified novel reduction maneuver is a simple, reliable, and safe method of reducing rigidly locked thoracic fracture-dislocations. The technique can be reliably used with minimal risk of dural tear utilizing the sufficient “laminotomy window” performed before the reduction. It requires minimal inventory to perform this technique without the need for additional expensive specialized reduction instruments, which may not be readily available at every center.
A similar technique utilizing short horizontal rods connected across the pedicle screws to enable the distraction across the locked facets employing three surgeons to act in synchrony has been documented earlier [
12,
13]. The greatest advantage of our described technique is the emphasis on leverage rather than strength, which allows for more precise maneuvering, which is a crucial element to take into consideration when performing complex reductions caused by high-energy trauma without demanding manpower. Using less brute force and strength while performing the reduction additionally allows for a slower, more deliberate, delicate movement which reduces the risk of adverse surgical events such as accidental slippage, which may have catastrophic consequences [
14].
Some of the key aspects that should be reminded before embarking on the surgical reduction of the locked thoracic facets to maintain the efficacy and safety of the procedure. First, preoperative planning with comprehensive imaging is vital to understand the exact nature and extent of the injury. This helps to plan the reduction strategy and predict potential challenges. If needed, technology with the three-dimensional reconstruction with simulation and virtual navigation can be utilized [
15]. Further, intraoperative use of fluoroscopy or other real-time imaging aids during the procedure allows the surgeon to verify the positioning and progress of the reduction with every step followed. Intraoperative neuromonitoring during the procedure can help detect potential spinal cord or nerve root compromise early [
16]. The facets must be manipulated gently to unlock them. Forceful manipulation may lead to further injury. In some cases, partial facetectomy may be necessary to unlock the facets. A combination of gentle distraction and rotation of the involved vertebrae is often employed to unlock the facets which is made in a controlled manner using the laminar spreader in our technique. If there is spinal cord or nerve root compression due to disc material, bone fragments, or hematoma, a decompression laminectomy, or discectomy might be necessary. Once the facets are unlocked and the vertebrae are realigned, it is important to stabilize the spine using pedicle screw fixation, followed by fusion to maintain the correct alignment and allow healing. In addition to the above measures postoperative neurologic assessment, pain control, and early mobilization are crucial for recovery.
Thoracic vertebrae fractures with facet dislocation are serious injuries that can result in significant complications. These complications can arise from the injury itself, or they can be associated with the surgical interventions used to manage the condition. One of the most serious complications is injury to the spinal cord or nerve roots, which can result in paralysis or sensory changes below the level of the injury. This can occur as a result of the initial trauma, or it can occur intraoperatively during the reduction or stabilization procedures [
17,
18]. Pseudoarthrosis from the fusion construct may result in thoracic malalignment with persistent pain or instability resulting in hardware failure. Further, the patient should be protected from immobility induced deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Despite successful treatment, some patients may still experience chronic pain due to other factors such as depression and anxiety, which may require appropriate intervention and support. Management of these complications often requires a multidisciplinary approach [
19]. Prevention of the avoidable complications is crucial and it includes careful surgical technique, meticulous perioperative care, early mobilization, deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis, and close postoperative follow-up [
20].
Our study has its limitations. The sample size of the cases managed with the proposed reduction technique is not sufficient to generalize the results obtained. However, considering the rarity of the event, and the consistent performance of the technique at its every attempt, the authors recommend this technique for routine surgical usage in thoracic fracture-dislocation reduction scenarios. We did not explore the long-term outcome of the patients managed by this technique. However, the authors believe that the impact of the reduction techniques is mostly evaluated in the immediate postoperative complications associated with the technique itself rather than the long-term outcomes which are influenced by the initial spinal cord trauma [
21].
5. Conclusions
Our modified novel reduction maneuver is a simple, reliable, and safe method of reducing rigidly locked through-disk thoracic fracture-dislocations. The technique can be reliably used with minimal risk of iatrogenic complications due to the reduction maneuver.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.P. and M.J..; methodology, J.P. and M.J.; writing—original draft preparation, J.P., M.J., S.D., S.I.; writing—review and editing, M.J., S.Ć., S.M., A.M., V.B.; visualization, S.I.; supervision, M.J. and V.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects that underwent mentioned surgical procedure.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available for privacy reasons by the patients and must be anonymized before disclosure to third parties.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kumar, S.; Patralekh, M.K.; Boruah, T.; Kareem, S.A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R. Thoracolumbar Fracture Dislocation (AO Type C Injury): A Systematic Review of Surgical Reduction Techniques. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, Y. Treatment of Complete Fracture-Dislocation of Thoracolumbar Spine. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2013, 26, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, A.R.; Albert, T.J. Spine Surgery: Tricks of the Trade; 2nd ed.; Thieme: New York, 2009; ISBN 978-1-58890-519-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.; Agrawal, D.; Gupta, D.; Sinha, S.; Satyarthee, G.D.; Singh, P.K. Traumatic Spondyloptosis: A Series of 20 Patients. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 22, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, D.; Semonche, A.; Tyagi, R. Novel Method for Stepwise Reduction of Traumatic Thoracic Spondyloptosis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygogiannis, K.; Manolakos, K.; Kalampokis, A.; Thivaios, G.C.; Moschos, S. Traumatic Fracture of the Thoracic Spine With Severe Posterolateral Dislocation: A Case Report. Cureus 14, e23830. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Fattah, H.; Rizk, A.H. Complete Fracture-Dislocation of the Lower Lumbar Spine with Spontaneous Neurologic Decompression. Clin. Orthop. 1990, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Gong, Q.; Liu, H.; Rong, X.; Ding, C. Complete Fracture-Dislocation of the Thoracolumbar Spine without Neurological Deficit: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e0050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, P.; Patralekh, M.K.; Srinivasan, R.; Agarwal, A.; Boruah, T. Fracture-Dislocation of the Thoracolumbar Spine without Neurological Deficit: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review. Spinal Cord Ser. Cases 2020, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshamrani, A.M.; Aldawsari, A.M.; Alhassoun, S.A.; Albahkali, A.M.; Alhussain, N.F.; Moqeem, A.L.; Mohammed, R.H.; Hasanain, A.M.; Almutairi, A.M.; Abu Shaheen, H.M.; et al. Complete Lumbar Spine Dislocation With Full Neurological Recovery. Cureus 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimizadeh, A.; Rahimizadeh, A. Management of Traumatic Double-Level Spondyloptosis of the Thoracic Spine with Posterior Spondylectomy: Case Report. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 23, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Manzano, G. Traumatic Dorsal Spondyloptosis of Upper Thoracic Spine: Case Report and Novel Open Reduction Technique. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.A.; Steinmetz, M.P.; Anderson, P.A. Novel Reduction Technique for Thoracolumbar Fracture-Dislocations. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2011, 15, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalva-Iborra, A.; Alcanyis-Alberola, M.; Grao-Castellote, C.; Torralba-Collados, F.; Giner-Pascual, M. Risk Factors in Iatrogenic Spinal Cord Injury. Spinal Cord 2017, 55, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuts, S.; Sardari Nia, P.; Maessen, J.G. Preoperative Planning of Thoracic Surgery with Use of Three-Dimensional Reconstruction, Rapid Prototyping, Simulation and Virtual Navigation. J. Vis. Surg. 2016, 2, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Hyun, S.-J. Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in Spinal Surgery. World J. Clin. Cases WJCC 2015, 3, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.; Abel, T.; Rodgers, R.B. Traumatic Thoracic Spinal Fracture Dislocation with Minimal or No Cord Injury. Report of Four Cases and Review of the Literature. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 96, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Huang, Y.; He, S.; Tang, C.; Peng, M.; Dai, M.; Chen, W. Clinical Characteristics and Treatment of Fracture-Dislocation of Thoracic Spine with or without Minimal Spinal Cord Injury. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2020, 33, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadla, S.; Lebude, B.; Tender, G.C.; Sharan, A.D.; Harrop, J.S.; Hilibrand, A.S.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Ratliff, J.K. Traumatic Spondyloptosis of the Thoracolumbar Spine. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2008, 9, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, T.; Sharan, A.D.; Garg, B. Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) Protocol in Spine Surgery. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2022, 31, 101944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.F.; Thayer, C.; Weinberg, P.E.; Kim, K.S. Acute Injuries of the Upper Thoracic Spine Associated With Paraplegia. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1980, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).