Submitted:
08 August 2023
Posted:
08 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
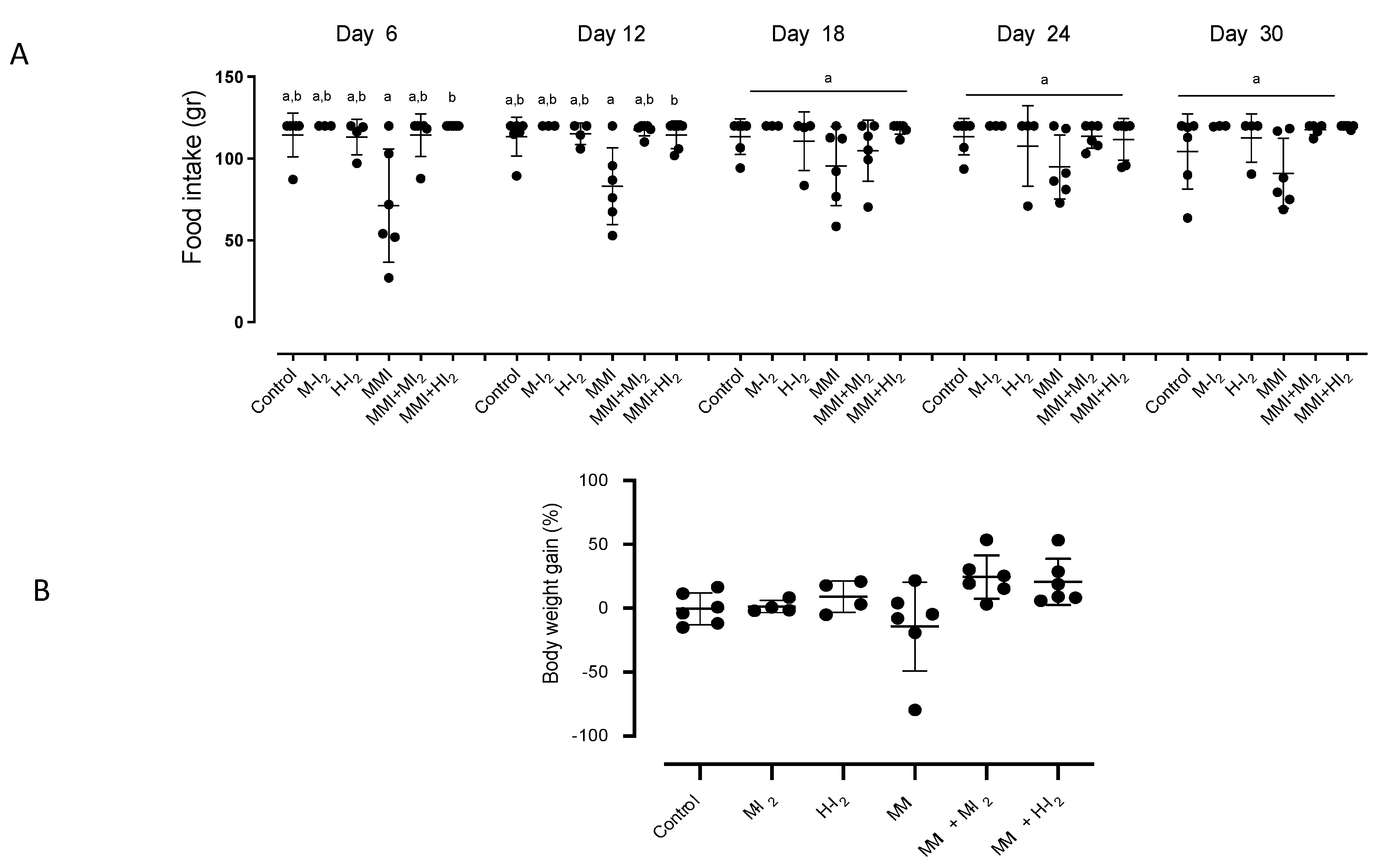
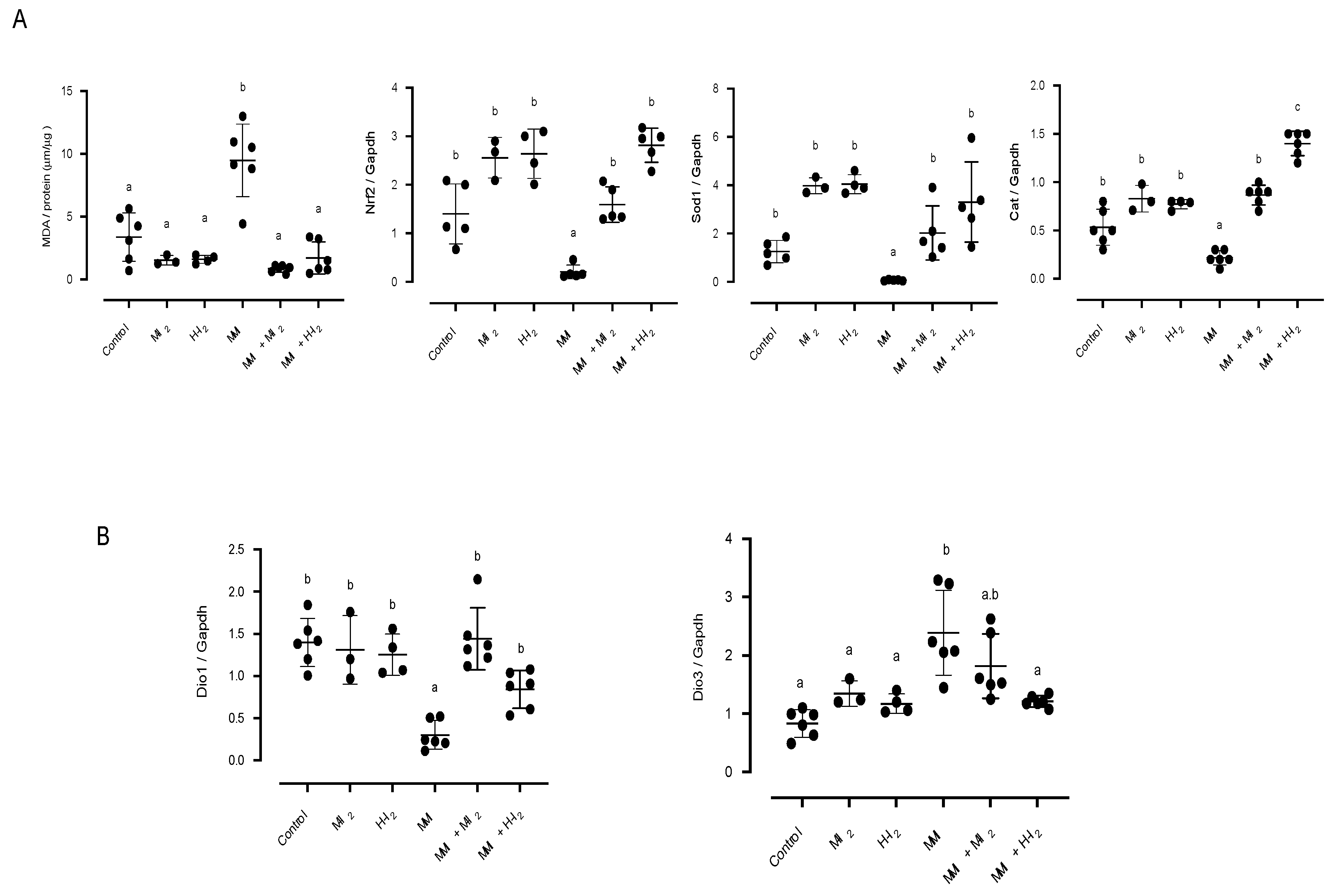
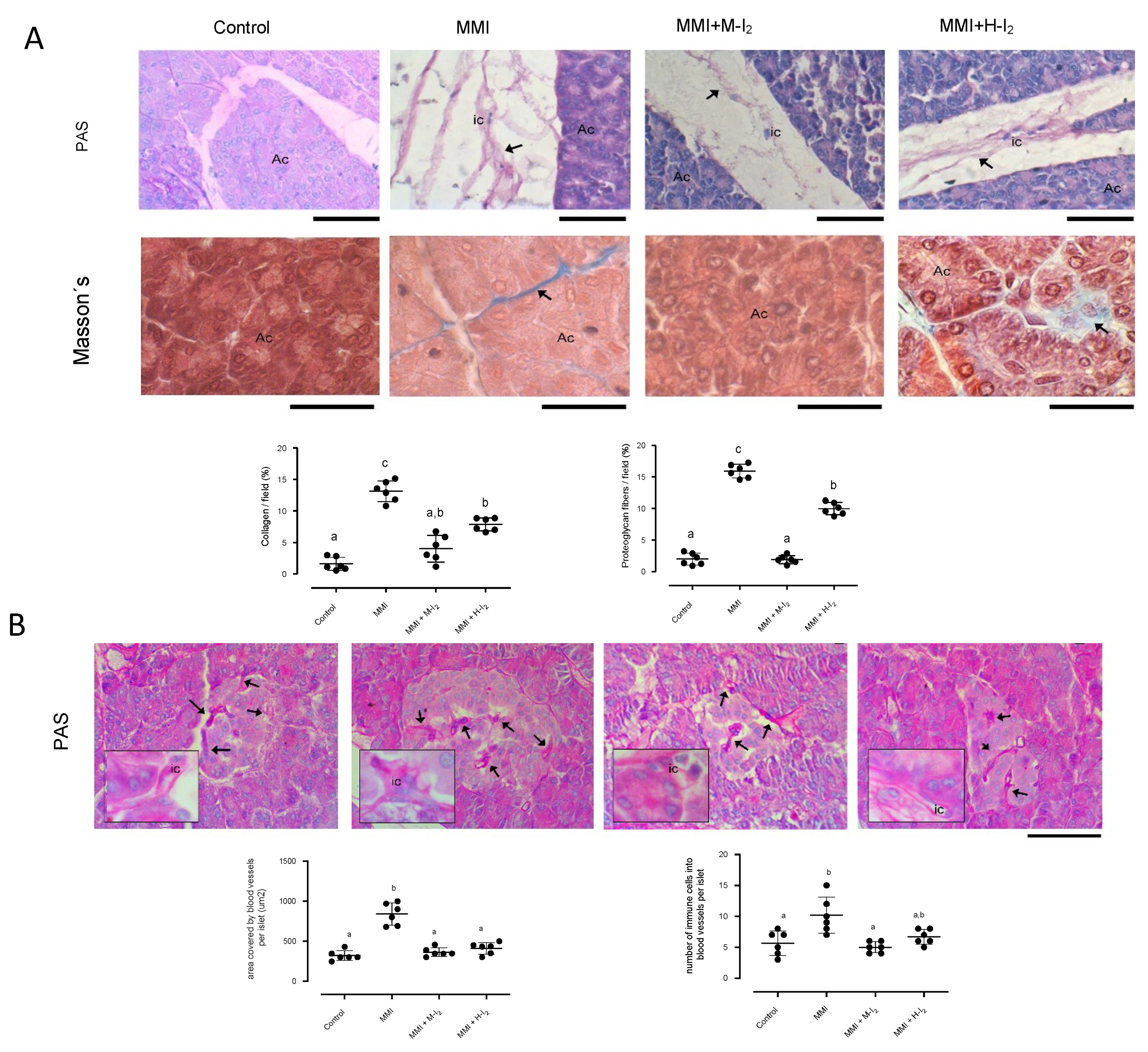
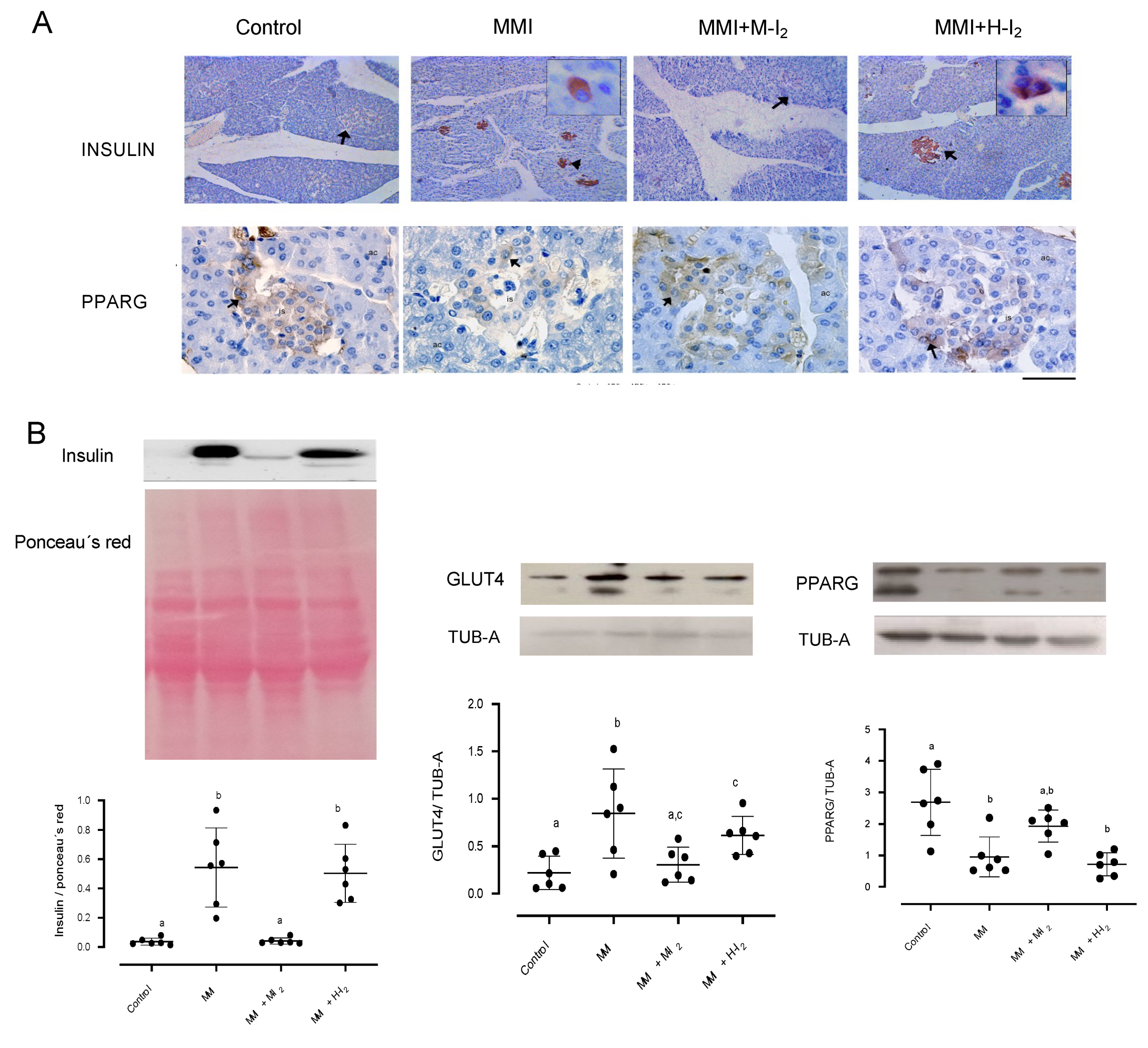
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Animals
Thyroid hormones and metabolic and inflammatory variables
Expression of deiodinases and antioxidant enzymes
Protein extraction and western blotting
Immunohistochemistry
Acinar and islet morphology
Lipids and peroxidation in the pancreas
Statistical analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Xie, Z.; Shen, Y., Xia, S.F. The roles of thyroid and thyroid hormone in pancreas: Physiology and pathology. Int J Endocrinol 2018, 2018, 2861034. [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.S.; Wilson, J.R.; Bernet, V.J. Links between thyroid disorders and glucose homeostasis Diabetes Metab J 2022, 46, 239-256. [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Mazzucato, C.; Zavacki, A.M.; Marinelarena, A.; Hollister-Lock, J.; El Khattabi, I.; Marsili, A.; Weir, G.C.; Sharma, A.; Larsen, P.R.; Bonner-Weir, S. Thyroid hormone promotes postnatal rat pancreatic β-cell development and glucose-responsive insulin secretion through MAFA. Diabetes 2013, 62,1569-80. [CrossRef]
- Ledda-Columbano, G.; Perra, A.; Pibiri, M.; Molotzu, F.; Columbano, A. Induction of pancreatic acinar cell proliferation by thyroid hormone. J Endocrinol 2005, 185, 393-399. [CrossRef]
- Chaker, L.; Ligthart, S.; Korevaa, T.I.; Hofma, A.; Franco, O.H.; Peeters, R.P.; Dehghan, A. Thyroid function and risk of type 2 diabetes: A population-based prospective cohort study. BMC Med 2016, 14, 150-159. [CrossRef]
- Shimizuguchi, R.; Kamisawa, T.; Endo, T.; Kikuyama, M.; Kuruma. S.; Chiba, K.; Tabata, T.; Koizumi, S. Hypothyroidism in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2018, 9, 16-21. [CrossRef]
- Godini, A.; Ghasemi, A.; Zahedias, S. The possible mechanism of the impaired insulin secretion in hypothyroid rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131198. [CrossRef]
- Safayee, S.; Karbalaei, N.; Noorafshan, A.; Nadimi, E. Induction of oxidative stress, suppression of glucose-induced insulin release, ATP production, glucokinase activity, and histomorphometric changes in pancreatic islets of hypothyroid rat. Eur J Pharmacol 2016, 791, 147-156. [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Jeddi, S.; Zadeh-Vakili, A.; Farrokhfall, K.; Rouhollah, F.; Zarkesh, M.; Ghanbari, M.; Ghasemi, A. Transient congenital hypothyroidism alters gene expression of glucose transporters and impairs glucose sensing apparatus in young and aged offspring rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017, 43, 2338-2352. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Castelán, J.; Zepeda-Pérez, D.; Rojas-Juárez, R.; Aceves, C.; Castelán, F.; Cuevas-Romero, E. Effects of hypothyroidism on the female pancreas involve the regulation of estrogen receptors. Steroids. 2022a, 181, 108996. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Castelán, J.; Nicolás, L.; Morimoto, S.; Cuevas, E. The Langherhans islet cells of female rabbits are differentially affected by hypothyroidism depending on the islet size. Endocrine, 2015a, 48, 811-817. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Castelán, J.; Martínez-Gómez, M.; Castelán, F.; Cuevas, E. Hypothyroidism affects vascularization and promotes immune cells infiltration into pancreatic islets of female rabbits. Int J Endocrinol 2015b, 2015, 17806. [CrossRef]
- Venturi, S. Environmental Iodine Deficiency: A Challenge to the Evolution of Terrestrial Life? Thyroid 2000, 10, 727-729. [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, Y.; Delgado, G.; Carabez, A.; Anguiano, B.; Aceves, C, Iodine and doxorubicin, a good combination for mammary cancer treatment: Antineoplastic adjuvancy, chemoresistance inhibition, and cardioprotection. Mol Cancer 2013, 12, 45-49. [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, B.Y.M.; Frusic-Zlotkina, M.; Soroka, Y.; Ben-Sassond, S.; Bianco-Peled, H.; Kohen, R. A novel role of topical iodine in skin: Activation of the Nrf2 pathway. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2017, 104, 238–248. [CrossRef]
- Aceves, C.; Mendieta, I., Anguiano, B.; Delgado-Gonzalez, E. Molecular iodine has extrathyroidal effects as an antioxidant, differentiator, and immunomodulator. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 1228-1243. [CrossRef]
- Hartoft-Nielsen, M.L.; Rasmussen, A.K.; Bock, T.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Kaas, A.; Buschard, K. Iodine and tri-iodo-thyronine reduce the incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in the autoimmune prone BB rats. Autoimmunity. 2009, 42, 131-138. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Castelán, J.; Delgado-González, E.; Varela-Floriano, V.; Anguiano, B.; Aceves, C. Molecular iodine supplement prevents streptomycin-induced pancreatitis in mice Nutrients 2022b, 14, 715-727. [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.C, Molina, J.; Gadea, Y.; Fachado, A.; Murillo, M.; Simovic, G.; Pileggi, C.; Hernández, A.; Edlund, H.; Bianco, A.C. The thyroid hormone-inactivating type III deiodinase is expressed in mouse and human beta-cells and its targeted inactivation impairs insulin secretion. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3717-3727. [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Helguera, O.; Delgado, G.; Anguiano, B.; Aceves, C. Uptake and antiproliferative effect of molecular iodine in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Endocr Related Cancer 2006, 13, 1147-1158. [CrossRef]
- Reed-Tsur, M.D.; De la Vieja, A.; Ginter, C.S.; Carrasco, N. Molecular characterization of v59e NIS, a Na+/I- symporter mutant that causes congenital I- transport defect Endocrinology 2006, 149, 3077–3084. [CrossRef]
- Moller, H.J. Soluble CD163. Scandinavian J Clin Invest 2012, 72 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Etzerodt, A.; Berg, R.M.; Plovsing, R.R.; Andersen, M.N.; Bebien, M.; Habbeddine, M.; Lawrence, T.; Möller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K. Soluble ectodomain CD163 and extracellular vesicle associated CD163 are two differently regulated forms of ‘soluble CD163’ in plasma. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 40286. [CrossRef]
- Bahr, I.; Bazwinsky-Wutschke, I.; Wolgast, S.; Hofmann, K.; Streck, S.; Mühlbauer, E.; Wedekind, D.; Peschke, E. GLUT4 in the endocrine pancreas-indicating an impact in pancreatic islet cell physiology? Horm Metab Res 2012, 44, 442-50. [CrossRef]
- Herter-Aeberli, I.; Cherkaoui, M.; El Ansari, N.; Rohner, R.; Stinca, S.; Chabaa, L.; von Eckardstein, A.; Aboussad, A.; Zimmermann, M.B. Iodine supplementation decreases hypercholesterolemia in iodine-deficient, overweight women: A randomized controlled trial. J Nutr. 2015, 145, 2067-2075. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.J.; Ye, Y.; Sun, F.J.; Tian, E.J.; Chen, Z.P. The impact of dietary iodine intake on lipid metabolism in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 2011, 142, 581-588. [CrossRef]
- Nava-Villalba, M.; Nunez-Anita, R.E.; Bontempo, A.; Aceves, C. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is crucial for antitumoral effects of 6-iodolactone. Mol Cancer 2015, 14, 168-171. [CrossRef]
- Leahy, J.L. Thiazolidinediones in prediabetes and early type 2 diabetes: What can be learned about that disease’s pathogenesis. Curr Diab Rep 2009, 9 215–220. [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.S.; Ahn, B.Y.; Jung, H.S.; Lee, H.M.; Park, K.S. Mechanism for antioxidative effects of thiazolidinediones in pancreatic b-cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2011, 301, E912-E921. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Gurlo, T.; Haataja, L.; Hsueh, W.A.; Butler, P.C. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-g by rosiglitazone protects human islet cells against human islet amyloid polypeptide toxicity by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005, 90 6678–6686. [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.Y., Dambaeva, S.; Kwak-Kim, J.; Gilman-Sachs, A.; Beaman, K.D. A role for iodine and thyroglobulin in modulating the function of human immune cells. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 1573-1578. [CrossRef]
- Valleé, A.; Lecarpentier, Y.; Guillevin, R.; Vallée, J.N. Interactions between TGF-β1, canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway and PPARγ in radiation-induced fibrosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 90579-90604. [CrossRef]
- Zang, G.; Sandberg, M.; Carlsson, P.O.; Welsh, N.; Jansson, L.; Barbu, L. Activated pancreatic stellate cells can impair pancreatic islet function in mice. Ups J Med Sci 2015, 120, 169-80. [CrossRef]
- Tsang, S.W.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.; Mu, H.; Bian, Z.X. Anti-fibrotic effect of tRNAs-resveratrol in pancreatic stellate cells. Biomed Pharmacother 2015, 71, 91-97. [CrossRef]
- Masamune, A.; Suzuki, N.; Kikuta, K.; Satoh, K., Shimosegawa, T. Curcumin blocks activation of pancreatic stellate cells. J Cell Biochem. 2006, 97, 1080-93. [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xiao, H.T.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.J.; Tsang, S.W. Resveratrol ameliorates the severity of fibrogenesis in mice with experimental chronic pancreatitis. Mol Nutr Food Res 2018, 62, e1700561. [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, R.; Zuellig, R.A.; Kugelmeier, P.; Baenninger, P.B.; Moritz, W.; Perren, A.; Clavien, P.A.; Weber, M.; Spinas, G.A. Superiority of small islets in human islet transplantation. Diabetes 2007, 56, 694-603. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cohrs, C.M.; Stertmann, J.; Bozsak, R.; Speier, S. Human beta cell mass and function in diabetes: Recent advances in knowledge and technologies to understand disease pathogenesis. Mol Metab 2017, 6, 943-57. [CrossRef]
- Arunagiri, A.; Haataja, L.; Pottekat, A.; Pamenan, F.; Kim, S.; Zeltser, L.M.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Tsai, B.; Itkin-Ansari, P.; Kaufman, R.J.; Liu, M.; Arvan, P. Proinsulin misfolding is an early event in the progression to type 2 diabetes. eLife 2019, 8, e44532. [CrossRef]
- Weir, G.C.; Bonner-Weir, B. Islet β cell mass in diabetes and how it relates to function, birth, and death. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013,1281, 92-105. [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, H.; Gu, X.; Enge, M.; Dai,X.; Wang, Y.; Damond, N.; Downie, C.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Xing. Y.; Chera, S.; Thorel, F.; Quake, S.; Oberholzer, J.; MacDonald, P.E.; Herrera, P.L.; Kim, S.K. Converting adult pancreatic α cells into β cells by targeting both Dnmt1 and Arx. Cell Metab 2017, 25, 622-634. [CrossRef]
- Bontempo, A.; Ugalde-Villanueva, B.; Delgado-González, E.; Rodríguez, A.L.; Aceves, C. Molecular iodine impairs chemoresistance mechanisms, enhances Doxorubicin retention and induces down regulation of CD44+/CD24+ and E-Cad+/Vim+ subpopulations in MCF-7 cells resistant to low doses of Doxorubicin. Oncology Reports 2017, 38, 2867-2876. [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Sarraf, P.; Ozcan, U.; Okada, T.; Chung-Hsin, H. Targeted elimination of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in β cells leads to abnormalities in islet mass without compromising glucose homeostasis. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23, 7222-229. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.R.; Alonso, L.C. Lipotoxicity in the pancreatic beta cell: Not just survival and function, but proliferation as well? Curr Diab Rep 2014, 14, 492-496. [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, I.; Miyata, N.; Yoshimura, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Tachikawa, N. Methimazole-induced acute pancreatitis: A case report. Clin J Gastroenterol 2019, 12, 239–242. [CrossRef]
- Mendieta, I.; Nuñez-Anita, R.E.; Nava-Villalba, M.; Zambrano-Estrada, X.; Delgado-González, E.; Anguiano, B.; Aceves, C. Molecular iodine exerts antineoplastic effects by diminishing proliferation and invasive potential and activating the immune response in mammary cancer xenografts. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 261-68. [CrossRef]
| Variable | Control | M-I2 | H-I2 | MMI | MMI+ M-I2 | MMI + H-I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3 (ng/dL) | 79.6 + 4.1a | 75.2 + 7.6 a | 74.5 + 4.8 a | 60.9 + 2.3b | 73.0 + 3.9a | 75.8 + 5.3ab |
| T4 (ug/dL) | 2.7 + 0.5a | 2.4 +0.4a | 2.5 + 0.2 a | 1.4 + 0.2b | 2.5 + 0.3a | 2.3 + 0.5a |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 113.2 + 5.1a | 122 +32a | 119 + 23.6a | 138.2 + 4.5a | 113.0 + 5.9a | 114.3 + 1.7a |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 74.3 + 0.8a | 67.6 + 7.2 a | 70.4 + 12.7 a | 105.4 + 5.5b | 63.5 + 7.0a | 75.9 + 2.7a |
| Triacylglycerol (mg/dL) | 72.5 + 4.9a | 70.8 + 16.2 a | 50.9 + 8.7 a | 94.5 + 3.1c | 36.8 + 2.6b | 29.3+ 8.2b |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 12.4 + 1.5a | 11.7 + 1.7 a | 13.2 + 3.9 a | 35.2 + 3.6b | 10.5 + 1.9a | 7.8 + 0.5a |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 46.3 + 3.9a | 42.1+ 7.5 a | 34.3 + 5.9 a | 44.9 + 4.1a | 58.9 + 2.0b | 55.8 + 2.9b |
| VLDL-C (mg/dL) | 14.5 + 1.1a | 14.2 + 3.2 a | 10.2 + 1.7 a | 13.8 + 1.7a | 10.5 + 1.2a | 8.2 + 1.0a |
| sCD163 | 0.04 + 0.01a | 0.04 +0.01 | 0.05 +0.01 | 0.40 + 0.08b | 0.07 + 0.01a | 0.14 + 0.03a |
| Morphometric variable | Control | M-I2 | H-I2 | MMI | MMI + M-I2 | MMI + H-I2 | Statistics |
| Cross-sectional area (CSA) of islets (µm2) | 6218 ± 715a | 7756 ± 130a | 7495 ± 233a | 5752 ± 860a | 6922 ± 878a | 7173 ± 1182a | K=3.5; p=0.62 |
| % Mean of small islets <4000 µm2 | 44.9 ± 6.6a | 6.8 ± 0.5b | 14.4 ± 2.2ab | 52.7 ± 1.8a | 25.6 ± 5.5ab | 35.4 ± 10.1ab | K=19.2; p=0.001 |
| % Mean of medium islets 4000-7000 µm2 | 22.5 ± 3.3a | 17.6 ± 3.0a | 21.8 ± 5.4a | 21.4 ± 1.2a | 36.5 ± 4.5a | 22.8 ± 5.0a | K=8.0; p=0.15 |
| % Mean of large islets >7000 µm2 | 32.6 ± 6.9ab | 75.5 ± 2.7a | 63.9 ± 5.6ab | 25.9 ± 2.9b | 37.9 ± 6.3ab | 41.8 ± 9.9ab | K=14.5; p=0.01 |
| Mean CSA (µm2) for small islets | 2478 ± 221ab | 2350 ± 74ab | 3011 ± 126a | 1971 ± 131b | 2645 ± 272ab | 2328± 118ab | K=12.1; p=0.03 |
| Mean CSA (µm2) for medium islets | 5524 ± 257a | 5624 ± 86a | 5445 ± 138a | 5437 ± 88a | 5579 ± 147a | 5503 ± 271a | K=1.5; p=0.90 |
| Mean CSA (µm2) for large islets | 11046 ± 827a | 14696 ± 349a | 14029 ± 657a | 16603 ± 2194a | 9977 ± 1226a | 11909 ± 586a | K=13.6; p=0.01 |
| Mean number of cells in small islets | 24.3 ± 1.7a | 19.2 ± 3.3ab | 22.6 ± 1.5ab | 16.6 ± 0.9b | 21.4 ± 2.5ab | 17.1 ± 1.3ab | K=16.1; p=0.01* |
| Mean number of cells in medium islets | 45.4 ± 3.7a | 33.2 ± 1.0a | 36.9 ± 3.5a | 45.2 ± 5.3a | 43.4 ± 2.4a | 40.8 ± 4.7a | K=6.0; p=0.29 |
| Mean number of cells in large islets | 103.1 ± 5.3a | 75.6 ± 13.8a | 93.9 ± 10.5a | 84.9 ± 5.1a | 83.8 ± 9.6a | 75.7 ± 8.2a | K=7.3; p=0.19 |
| Gene | Reference | Primer sequence | bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | XM_008258785.3 | FW: 5´- TTCCTCTGCTGCCATTAGTCAGTC-3´ RV: 5´-GCTCTTCCATTTCCGAGTCACTG-3´ |
239 |
| Cat | XM_002709045.4 | FW: 5´-TCCGGGATCTTTTTAACGCCAATTG-3´ RV: 5´-TCGAGCACGGTAGGGACAGTTCAC-3´ |
362 |
| Sod1 | NM_001082627.2 | FW: 5´-GACGCATAACAGGACTGACCG-3´ RV: 5´- AACACATCAGCCACACCATTG-3´ |
196 |
| Dio1 | NM_001099958.1 | FW: 5´-GCCAGAAGACCGGGATAGC-3´ RV: 5´-GGTGCTGAAGAAGGTGGGAAT-3´ |
71 |
| Dio3 | XM_008248683.3 | FW: 5´-CGATGACCCGCCCATCT-3´ RV: 5´-CGCCTGCTTGAAGAAATCCA-3´ |
103 |
| Gapdh | XM_051836117.7 | FW: 5´-GACAACTTTGGCATCGTGGA-3´ RV: 5´-ATGCAGGGATGATGTTCTGG-3´ |
133 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





