Submitted:
04 August 2023
Posted:
07 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Modulation of PI3K signalling pathway in NDDs
2.1. PI3K
2.2. AKT-Protein kinase B (PKB)
2.3. Activation of PI3K/AKT pathway
3. PI3K/AKT pathway in neurodegeneration
4. Neuroprotective role of Avn
4.1. Alzheimer’s disease
4.2. Parkinson’s disease
5. Modulation of other targets by Avns
6. Future perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perrelli, A.; Goitre, L.; Salzano, A.M.; Moglia, A.; Scaloni, A.; Retta, S.F. Biological Activities, Health Benefits, and Therapeutic Properties of Avenanthramides: From Skin Protection to Prevention and Treatment of Cerebrovascular Diseases. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2018, 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strychar, R.; Webster, F.H.; Wood, P.J. World Oat Production, Trade, and Usage. In Oats: Chemistry and Technology; 2011; pp. 77–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, L.A. World Production and Use of Oats. In The Oat Crop Production and Utilization; 1995; pp. 34–61. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; De, S.; Belkheir, A. Avena Sativa (Oat), A Potential Neutraceutical and Therapeutic Agent: An Overview. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2013, 53, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, R.; Gonzalez, T.; Ferruzzi, M.; Jackson, E.; Winderl, D.; Watson, J. Oats—from Farm to Fork. In Advances in food and nutrition research; 2016; Volume 77, pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, A.; Mann, J.; Cummings, J.; Winter, N.; Mete, E.; Te Morenga, L. Carbohydrate Quality and Human Health: A Series of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. The Lancet 2019, 393, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.V.T.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Zurbau, A.; Blanco Mejia, S.; Jovanovski, E.; Au-Yeung, F.; Jenkins, A.L.; Vuksan, V. The Effect of Oat β -Glucan on LDL-Cholesterol, Non-HDL-Cholesterol and ApoB for CVD Risk Reduction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised-Controlled Trials. British Journal of Nutrition 2016, 116, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.; Mann, J.; Cummings, J.; Winter, N.; Mete, E.; Te Morenga, L. Carbohydrate Quality and Human Health: A Series of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. The Lancet 2019, 393, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, K.C.; Galant, R.; Samuel, P.; Tesser, J.; Witchger, M.S.; Ribaya-Mercado, J.D.; Blumberg, J.B.; Geohas, J. Effects of Consuming Foods Containing Oat β-Glucan on Blood Pressure, Carbohydrate Metabolism and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Men and Women with Elevated Blood Pressure. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2007, 61, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripsin, C.M.; Keenan, J.M.; Jacobs, D.R.; Elmer, P.J.; Welch, R.R.; Horn, L. Van; Liu, K.; Turnbull, W.H.; Thye, F.W.; Kestin, M.; et al. Oat Products and Lipid Lowering: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA 1992, 267, 3317–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Chu, Y. Whole Grain Oats, More than Just a Fiber: Role of Unique Phytochemicals. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2017, 61, 1600715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; De, S.; Belkheir, A. Avena Sativa (Oat), A Potential Neutraceutical and Therapeutic Agent: An Overview. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2013, 53, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Murakami, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Kitagishi, Y. Roles of PI3K/AKT/GSK3 Pathway Involved in Psychiatric Illnesses. Diseases 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, K.H.; Golec, D.P.; Thomsen, J.H.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Okkenhaug, K. PI3K in T Cell Adhesion and Trafficking. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilanges, B.; Posor, Y.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. PI3K Isoforms in Cell Signalling and Vesicle Trafficking. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2019, 20, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, H.Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.W.; Luo, H.Y.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, L.C. PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway: A Target of Natural Products in the Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2021, 12, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hsu, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Peng, W. Editorial: Regulation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway: A Feasible Approach for Natural Neuroprotective Agents to Treat Various Neuron Injury-Related Diseases. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Peng, S.; Song, Z.; Bai, F.; Li, X.; Fang, J. Oat Polyphenol Avenanthramide-2c Confers Protection from Oxidative Stress by Regulating the Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway in PC12 Cells. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2021, 706, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.-I.; Bae, H.-B.; Jeong, S. Avenanthramide C Prevents Neuronal Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt/GSK3β Signaling Pathway Following Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Brain Sciences 2020, 10, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, V.S.; Samidurai, M.; Park, H.J.; Wang, M.; Park, R.Y.; Yu, S.Y.; Kang, H.K.; Hong, S.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, Y.Y.; et al. Avenanthramide-C Restores Impaired Plasticity and Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice. Molecular Neurobiology 2020, 57, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-Y.; Wang, M.; Son, Y.; Yang, E.-J.; Kang, M.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Jo, J. Oat Extract Avenanthramide-C Reverses Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation Decline in Tg2576 Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.M.; Hahn, M.J.; Emmons, C.L. Oat Avenanthramides Exhibit Antioxidant Activities in Vitro. Food Chemistry 2002, 79, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helnæs, A.; Kyrø, C.; Andersen, I.; Lacoppidan, S.; Overvad, K.; Christensen, J.; Tjønneland, A.; Olsen, A. Intake of Whole Grains Is Associated with Lower Risk of Myocardial Infarction: The Danish Diet, Cancer and Health Cohort. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2016, 103, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Chu, Y. Whole Grain Oats, More than Just a Fiber: Role of Unique Phytochemicals. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2017, 61, 1600715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.N.; Dilnashin, H.; Birla, H.; Singh, S. Sen; Zahra, W.; Rathore, A.S.; Singh, B.K.; Singh, S.P. The Role of PI3K/Akt and ERK in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurotoxicity Research 2019, 35, 775–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, S.; Kiger, A.A. Classes of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases at a Glance. Journal of Cell Science 2014, 127, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taksande, B.G.; Gawande, D.Y.; Chopde, C.T.; Umekar, M.J.; Kotagale, N.R. Agmatine Ameliorates Adjuvant Induced Arthritis and Inflammatory Cachexia in Rats. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2017, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, M.; Feng, J.; Hemmings, B.A. Structure, Regulation and Function of PKB/AKT—A Major Therapeutic Target. In Proceedings of the Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Proteins and Proteomics; 2004; Volume 1697, pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.W.; Luo, H.Y.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, L.C. PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway: A Target of Natural Products in the Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2021, 12, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Kitagishi, Y.; Nakanishi, A.; Murai, T. Implications of PI3K/AKT/PTEN Signaling on Superoxide Dismutases Expression and in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Diseases 2018, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuksayan, H.H.; Akgun, S.S. Pl3K/Akt/NF-ΚB Signalling Pathway on NSCLC Invasion. Medicinal chemistry 2016, 06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsnelson, A.; De Strooper, B.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Neurodegeneration: From Cellular Concepts to Clinical Applications. Science Translational Medicine 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peplow, P.V.; Martinez, B.; Gennarelli, T.A. Prevalence, Needs, Strategies, and Risk Factors for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neuromethods 2022, 173, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, P. Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease. Annals of Neurology 2003, 53, S26–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Johnson, J.A. Oxidative Damage and the Nrf2-ARE Pathway in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 2014, 1842, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.K. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegeneration: Cause or Consequence? Nature Medicine 2004, 10, S18–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, M.; Ozben, T. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in Alzheimers Disease. Current Alzheimer Research 2004, 1, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Mimura, J.; Yamamoto, M. Discovery of the Negative Regulator of Nrf2, Keap1: A Historical Overview. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2010, 13, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. Toward Clinical Application of the Keap1–Nrf2 Pathway. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 2013, 34, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Tanji, K.; Wakabayashi, K.; Matsuura, S.; Itoh, K. Role of the Keap1/Nrf2 Pathway in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pathology International 2015, 65, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Johnson, J.A. Oxidative Damage and the Nrf2-ARE Pathway in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 2014, 1842, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhry, S.; Zhang, Y.; McMahon, M.; Sutherland, C.; Cuadrado, A.; Hayes, J.D. Nrf2 Is Controlled by Two Distinct β-TrCP Recognition Motifs in Its Neh6 Domain, One of Which Can Be Modulated by GSK-3 Activity. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3765–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Chowdhry, S.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Sutherland, C. Dual Regulation of Transcription Factor Nrf2 by Keap1 and by the Combined Actions of β-TrCP and GSK-3. Biochemical Society Transactions 2015, 43, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Sternberg, P.; Cai, J. Essential Roles of the PI3 Kinase/Akt Pathway in Regulating Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Functions in the RPE. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2008, 49, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armagan, G.; Sevgili, E.; Gürkan, F.T.; Köse, F.A.; Bilgiç, T.; Dagcı, T.; Saso, L. Regulation of the Nrf2 Pathway by Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in MPP+-Induced Cell Damage. Molecules 2019, 24, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotolongo, K.; Ghiso, J.; Rostagno, A. Nrf2 Activation through the PI3K/GSK-3 Axis Protects Neuronal Cells from Aβ-Mediated Oxidative and Metabolic Damage. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy 2020, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, Actions, and Diseases. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kashyap, M.P.; Tripathi, V.K.; Singh, S.; Garg, G.; Rizvi, S.I. Neuroprotection Through Rapamycin-Induced Activation of Autophagy and PI3K/Akt1/MTOR/CREB Signaling Against Amyloid-β-Induced Oxidative Stress, Synaptic/Neurotransmission Dysfunction, and Neurodegeneration in Adult Rats. Molecular Neurobiology 2017, 54, 5815–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. GSK3β in Ethanol Neurotoxicity. Molecular Neurobiology 2009, 40, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Belle, J.E.; Orozco, N.M.; Paucar, A.A.; Saxe, J.P.; Mottahedeh, J.; Pyle, A.D.; Wu, H.; Kornblum, H.I. Proliferative Neural Stem Cells Have High Endogenous ROS Levels That Regulate Self-Renewal and Neurogenesis in a PI3K/Akt-Dependant Manner. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Kim, M.O. Melatonin Ameliorates Amyloid Beta-Induced Memory Deficits, Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Neurodegeneration via PI3/Akt/GSk3β Pathway in the Mouse Hippocampus. Journal of Pineal Research 2015, 59, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagishi, Y.; Nakanishi, A.; Ogura, Y.; Matsuda, S. Dietary Regulation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy 2014, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Yoon, G.H.; Shah, S.A.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, M.O. Osmotin Attenuates Amyloid Beta-Induced Memory Impairment, Tau Phosphorylation and Neurodegeneration in the Mouse Hippocampus. Scientific Reports 2015, 5, 11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Kim, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Amin, F.U.; Khan, M.; Ikram, M.; Kim, M.O. Natural Dietary Supplementation of Anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways Mitigate Oxidative Stress, Neurodegeneration, and Memory Impairment in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecular Neurobiology 2018, 55, 6076–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogdu, Ö.; Nathanson, D.; Sjöholm, Å.; Nyström, T.; Zhang, Q. Exendin-4 Stimulates Proliferation of Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells through ENOS-, PKA- and PI3K/Akt-Dependent Pathways and Requires GLP-1 Receptor. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2010, 325, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Palacios, A.; Ostolga-Chavarría, M.; Zazueta, C.; Königsberg, M. Nrf2: Molecular and Epigenetic Regulation during Aging. Ageing Research Reviews 2018, 47, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-C.; Vargas, M.R.; Pani, A.K.; Smeyne, R.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Kan, Y.W.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2-Mediated Neuroprotection in the MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease: Critical Role for the Astrocyte. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2009, 106, 2933–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, M. Nrf2 as a Potential Target for Parkinson’s Disease Therapy. Journal of Molecular Medicine 2021, 99, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidlin, C.J.; Dodson, M.B.; Madhavan, L.; Zhang, D.D. Redox Regulation by NRF2 in Aging and Disease. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2019, 134, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Xia, X.-J.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yang, Q.-S. Lentiviral Vector-Mediated SHC3 Silencing Exacerbates Oxidative Stress Injury in Nigral Dopamine Neurons by Regulating the PI3K-AKT-FoxO Signaling Pathway in Rats with Parkinson’s Disease. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2018, 49, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Mo, S.-J.; Feng, Q.-Q.; Zhan, M.-L.; OuYang, L.-S.; Chen, J.-C.; Ma, Y.-X.; Wu, J.-J.; Lei, W.-L. EPO-Dependent Activation of PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a Signalling Mediates Neuroprotection in In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 2014, 53, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanda, M.M. A Theoretical Study of the Antioxidant Properties of Phenolic Acid Amides Investigated through the Radical-Scavenging and Metal Chelation Mechanisms. European Food Research and Technology 2015, 241, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.C.; Sirisoma, N.S.; Kuppusamy, P.; Zweier, J.L.; Woster, P.M.; Casero, R.A. The Natural Polyamine Spermine Functions Directly as a Free Radical Scavenger. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1998, 95, 11140–11145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-Antioxidant Activity Relationships of Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palop, J.J.; Mucke, L. Amyloid-β–Induced Neuronal Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Synapses toward Neural Networks. Nature Neuroscience 2010, 13, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, Md.S.; Kabir, Md.T.; Tewari, D.; Mamun, A. Al; Mathew, B.; Aleya, L.; Barreto, G.E.; Bin-Jumah, M.N.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Ashraf, G.M. Revisiting the Role of Brain and Peripheral Aβ in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2020, 416, 116974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festa, G.; Mallamace, F.; Sancesario, G.M.; Corsaro, C.; Mallamace, D.; Fazio, E.; Arcidiacono, L.; Garcia Sakai, V.; Senesi, R.; Preziosi, E.; et al. Aggregation States of Aβ1–40, Aβ1–42 and Aβp3–42 Amyloid Beta Peptides: A SANS Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, A.; Uddin, M.; Mathew, B.; Ashraf, G. Toxic Tau: Structural Origins of Tau Aggregation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neural Regeneration Research 2020, 15, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yerke, A.; Wise, M.L.; Johnson, J.; Chu, Y.; Sang, S. Oat Avenanthramides Induce Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression via Nrf2-Mediated Signaling in HK-2 Cells. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2015, 59, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maso, M.J.; Nepomuceno, G.M.; St. Peter, M.A.; Gitre, H.H.; Martin, K.S.; Shaw, J.T. Synthesis of (±)-Bisavenanthramide B-6 by an Anionic Anhydride Mannich Reaction. Organic Letters 2016, 18, 1740–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Wang, M.; Son, Y.; Yang, E.; Kang, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Jo, J. Oat Extract Avenanthramide-C Reverses Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation Decline in Tg2576 Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Whitcomb, D.J.; Olsen, K.M.; Kerrigan, T.L.; Lo, S.-C.; Bru-Mercier, G.; Dickinson, B.; Scullion, S.; Sheng, M.; Collingridge, G.; et al. Aβ1–42 Inhibition of LTP Is Mediated by a Signaling Pathway Involving Caspase-3, Akt1 and GSK-3β. Nature Neuroscience 2011, 14, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens-Martín, M.; Jurado, J.; Hernández, F.; Ávila, J. GSK-3β, a Pivotal Kinase in Alzheimer Disease. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 2014, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Wang, M.; Son, Y.; Yang, E.; Kang, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Jo, J. Oat Extract Avenanthramide-C Reverses Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation Decline in Tg2576 Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz Vazquez, M.G.; Montiel Condado, D.; Gonzalez Hernandez, B.; Gonzalez-Horta, A. Avenanthramide-C Prevents Amyloid Formation of Bovine Serum Albumin. Biophysical Chemistry 2020, 263, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirdefeldt, K.; Adami, H.-O.; Cole, P.; Trichopoulos, D.; Mandel, J.; Wirdefeldt, K.; Adami, H.-O.; Trichopoulos, Á.D.; Cole, P.; Mandel, J. Epidemiology and Etiology of Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of the Evidence. Eur J Epidemiol 2011, 26, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; De Vos, R.A.I.; Jansen Steur, E.N.H.; Braak, E. Staging of Brain Pathology Related to Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Filamentous Inclusions of Lewy Bodies from Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Kordower, J.H. Age-Associated Increases of α-Synuclein in Monkeys and Humans Are Associated with Nigrostriatal Dopamine Depletion: Is This the Target for Parkinson’s Disease? Neurobiology of Disease 2007, 25, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.-K.; Nodet, G.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jensen, M.R.; Bernado, P.; Fernandez, C.O.; Becker, S.; Blackledge, M.; Zweckstetter, M. Structural Characterization of α-Synuclein in an Aggregation Prone State. Protein Science 2009, 18, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraganore, D.M.; Andrade, M. de; Elbaz, A.; Farrer, M.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Krüger, R.; Rocca, W.A.; Schneider, N.K.; Lesnick, T.G.; Lincoln, S.J.; et al. Collaborative Analysis of α-Synuclein Gene Promoter Variability and Parkinson Disease. JAMA 2006, 296, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier-Harlin, M.C.; Kachergus, J.; Roumier, C.; Mouroux, V.; Douay, X.; Lincoln, S.; Levecque, C.; Larvor, L.; Andrieux, J.; Hulihan, M.; et al. α-Synuclein Locus Duplication as a Cause of Familial Parkinson’s Disease. The Lancet 2004, 364, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, A.B.; Farrer, M.; Johnson, J.; Singleton, A.; Hague, S.; Kachergus, J.; Hulihan, M.; Peuralinna, T.; Dutra, A.N.R.; Lincoln, S.; et al. [Alpha]-Synuclein Locus Triplication Causes Parkinson’s Disease. Science 2003, 302, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Kordower, J.H. Age-Associated Increases of α-Synuclein in Monkeys and Humans Are Associated with Nigrostriatal Dopamine Depletion: Is This the Target for Parkinson’s Disease? Neurobiology of Disease 2007, 25, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.-K.; Nodet, G.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jensen, M.R.; Bernado, P.; Fernandez, C.O.; Becker, S.; Blackledge, M.; Zweckstetter, M. Structural Characterization of α-Synuclein in an Aggregation Prone State. Protein Science 2009, 18, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cores, Á.; Abril, S.; Michalska, P.; Duarte, P.; Olives, A.I.; Martín, M.A.; Villacampa, M.; León, R.; Carlos Menéndez, J. Bisavenathramide Analogues as Nrf2 Inductors and Neuroprotectors in in Vitro Models of Oxidative Stress and Hyperphosphorylation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, N.; Xiong, J.; Jia, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, L.; Luo, Z.; et al. The Role of Autophagy in Parkinson’s Disease: Rotenone-Based Modeling. Behavioral and Brain Functions 2013, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi Naini, S.M.; Soussi-Yanicostas, N. Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Oxidative Stress, a Critical Vicious Circle in Neurodegenerative Tauopathies? Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2015, 2015, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Peng, S.; Song, Z.; Bai, F.; Li, X.; Fang, J. Oat Polyphenol Avenanthramide-2c Confers Protection from Oxidative Stress by Regulating the Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway in PC12 Cells. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2021, 706, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, V.S.; Samidurai, M.; Park, H.J.; Wang, M.; Park, R.Y.; Yu, S.Y.; Kang, H.K.; Hong, S.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, Y.Y.; et al. Avenanthramide-C Restores Impaired Plasticity and Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice. Molecular Neurobiology 2020, 57, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz Vazquez, M.G.; Montiel Condado, D.; Gonzalez Hernandez, B.; Gonzalez-Horta, A. Avenanthramide-C Prevents Amyloid Formation of Bovine Serum Albumin. Biophysical Chemistry 2020, 263, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cores, Á.; Abril, S.; Michalska, P.; Duarte, P.; Olives, A.I.; Martín, M.A.; Villacampa, M.; León, R.; Carlos Menéndez, J. Bisavenathramide Analogues as Nrf2 Inductors and Neuroprotectors in in Vitro Models of Oxidative Stress and Hyperphosphorylation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Peng, S.; Song, Z.; Bai, F.; Li, X.; Fang, J. Oat Polyphenol Avenanthramide-2c Confers Protection from Oxidative Stress by Regulating the Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway in PC12 Cells. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2021, 706, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ma, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, T. Avenanthramide-C Activates Nrf2/ARE Pathway and Inhibiting Ferroptosis Pathway to Improve Cognitive Dysfunction in Aging Rats. Neurochemical Research 2023, 48, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, K.M.A.; El-Amir, Y.O. Protective Effects of Thymoquinone and Avenanthramides on Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Induced Toxicity in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Pathology - Research and Practice 2017, 213, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, K.M.A.; El-Amir, Y.O. Protective Effects of Thymoquinone and Avenanthramides on Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Induced Toxicity in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Pathology - Research and Practice 2017, 213, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosseron, F.; Krauthausen, M.; Kummer, M.; Heneka, M.T. Body Fluid Cytokine Levels in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Comparative Overview. Molecular Neurobiology 2014, 50, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swardfager, W.; Lanctôt, K.; Rothenburg, L.; Wong, A.; Cappell, J.; Herrmann, N. A Meta-Analysis of Cytokines in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biological Psychiatry 2010, 68, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magaki, S.; Mueller, C.; Dickson, C.; Kirsch, W. Increased Production of Inflammatory Cytokines in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Experimental Gerontology 2007, 42, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.F.; Wise, M.L.; Gulvady, A.A.; Chang, T.; Kendra, D.F.; Jan-Willem Van Klinken, B.; Shi, Y.; O’Shea, M. In Vitro Antioxidant Capacity and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Seven Common Oats. Food Chemistry 2013, 139, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amir, Y.O.; Omar, W.; Khabrani, A.Y.; Jahfali, A.E.; Alhakami, S.M.; Dobab, N.M. Protective Effect of Avenanthramides against Cisplatin Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Journal of advanced veterinary and animal research 2019, 6, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, R.; Nigam, A.; Grote, D.; Liebel, F.; Southall, M.D. Avenanthramides, Polyphenols from Oats, Exhibit Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Itch Activity. Archives of Dermatological Research 2008, 300, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Shin, W.S.; Yeo, D.; Lim, W.; Zhang, T.; Ji, L.L. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Avenanthramides via NF-ΚB Pathways in C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2018, 117, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, R.; Nigam, A.; Grote, D.; Liebel, F.; Southall, M.D. Avenanthramides, Polyphenols from Oats, Exhibit Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Itch Activity. Archives of Dermatological Research 2008, 300, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taqui, R.; Debnath, M.; Ahmed, S.; Ghosh, A. Advances on Plant Extracts and Phytocompounds with Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition Activity for Possible Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ou, B.; Wise, M.L.; Chu, Y. In Vitro Total Antioxidant Capacity and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Three Common Oat-Derived Avenanthramides. Food Chemistry 2014, 160, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cores, Á.; Abril, S.; Michalska, P.; Duarte, P.; Olives, A.I.; Martín, M.A.; Villacampa, M.; León, R.; Carlos Menéndez, J. Bisavenathramide Analogues as Nrf2 Inductors and Neuroprotectors in in Vitro Models of Oxidative Stress and Hyperphosphorylation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
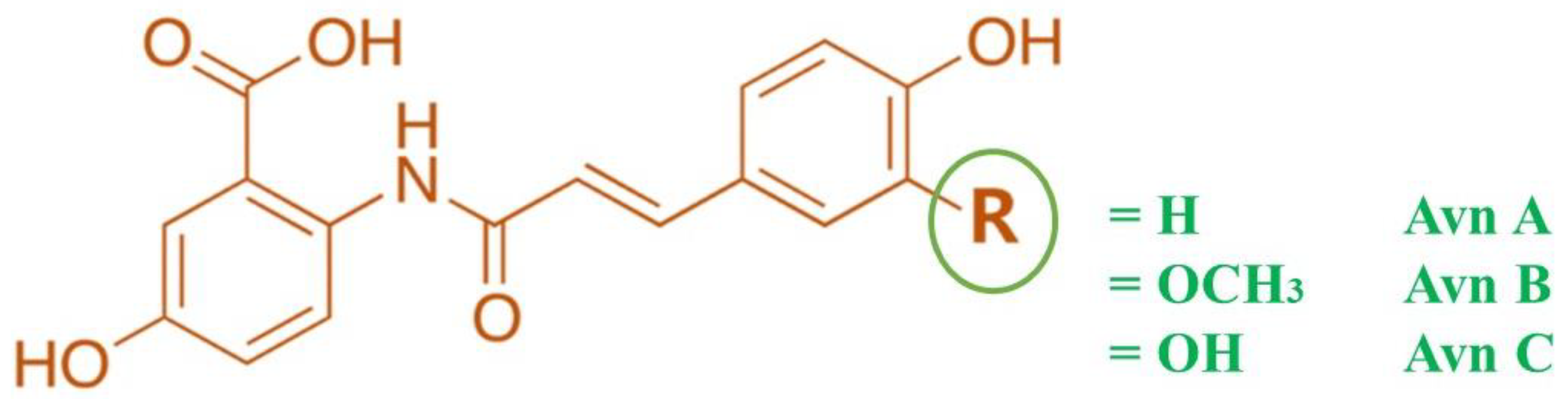
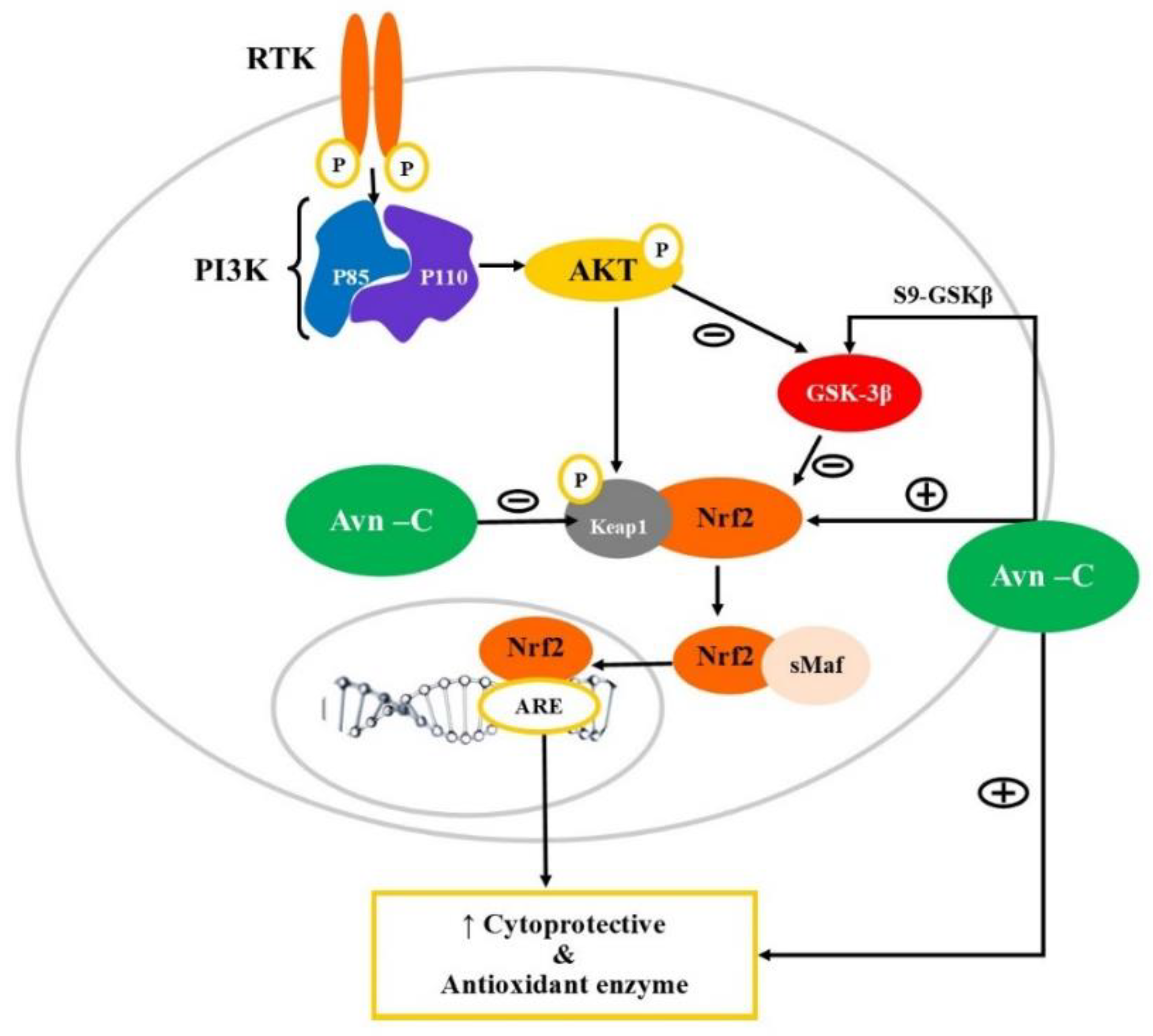
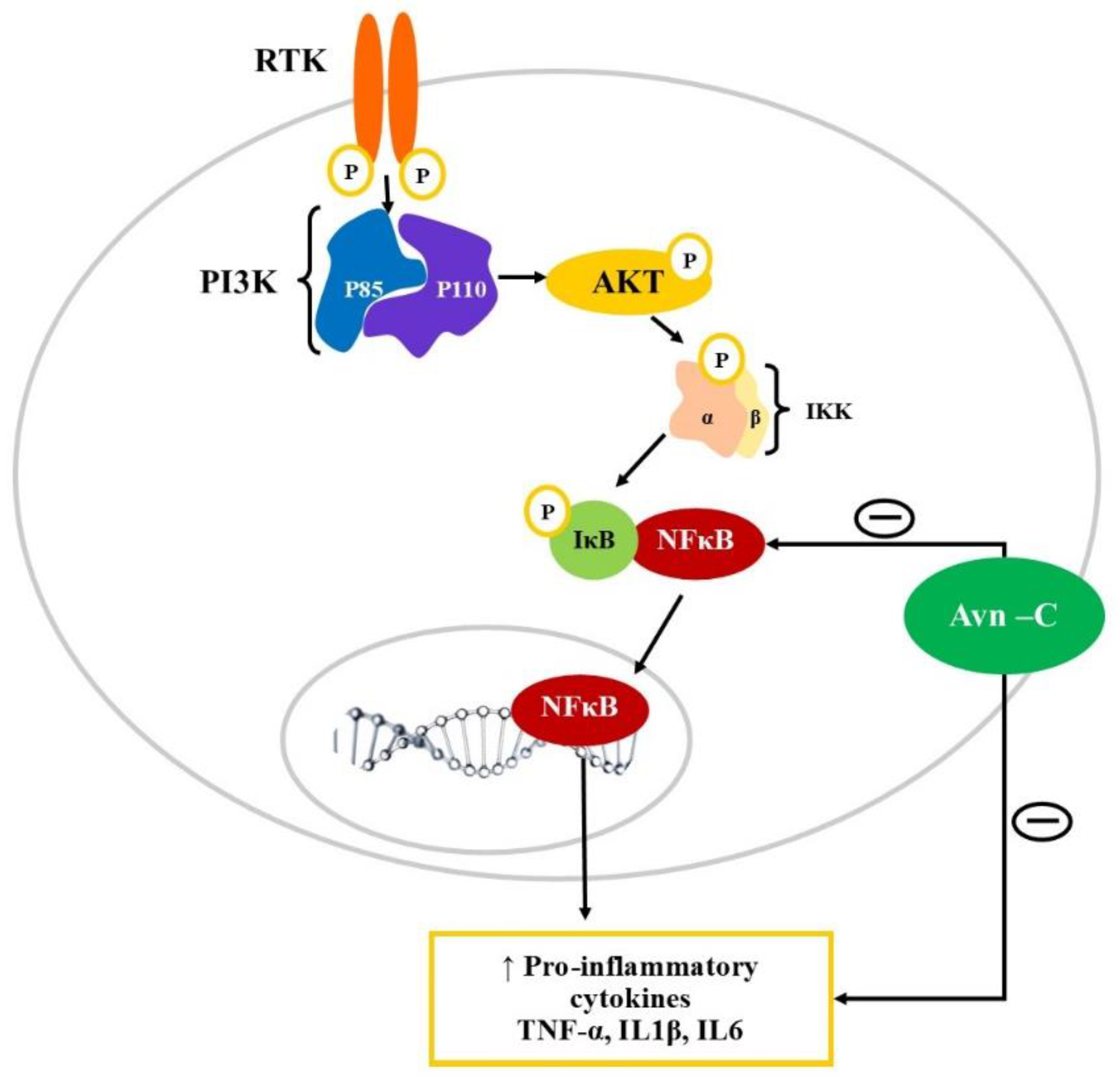
| Sr. No. | Study design | Mechanism | Methodology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electrophysiological study on Hippocampal LTP in Tg2576 male mice | Alteration in p-GSK-3β-S9 levels and reduction in Caspase 3 | Avn-C extracted from germinated oats using column chromatography | [74] |
| 2 | Evaluation of neuro-pathologies and behavioural impairments associated with AD | Modulates p-GSK-3β- S9 Reduced caspase 3 and neuroinflammation Binds to α1A adrenergic receptors to stimulate phospho-AMPK levels |
For electrophysiological studies the hippocampal slices of WT, Tg2576 and 5XFAD mice were treated with Aβ42 oligomers in the presence of Avn-C (10, 25, and 50 μM) | [90] |
| Tg2576 and 5XFAD mice were administered with Avn-C (2, 4, and 6 mg/kg. p.o.) for evaluation of long-term potentiation | ||||
| 3 | Effect on protein aggregation using spectroscopy techniques | Inhibition of BSA oligomerization showing anti-amyloid effect | Protein aggregation in bovine serum albumin was initiated by incubating the protein monomer at an elevated temperature and the aggregation kinetics was monitored by incubating with Avn-C (100, 250 and 500 μM) and was analysed using ThT-fluorescence assay. |
[91] |
| 4 | Evaluation of Bisavenanthramide analogues Nrf2 inductors and neuroprotectors in in-vitro models | Nrf2-ARE dependent protein expression | The antioxidant activity was measured using DPPH scavenging assay, FRAP Method and AChE inhibition assay was performed. Neuroprotection potential against tau hyperphosphorylation was evaluated using SH-SY5Y cell line | [92] |
| 5 | Evaluation of cytoprotective activity against oxidative stress-induced PC12 cell injuries | Activating Nrf2-ARE pathway | Rat PC12 were used to study antioxidant effect of Avns. The antioxidant and cytoprotective activity of Avn-2c, Avn-2f and Avn-2p was measured in-vitro using the ABTS•+ and DPPH scavenging assay, MTT, LDH release assay. | [93] |
| 6 | Cognitive dysfunction induced by repeated propofol anaesthesia in aging rats | Activating Nrf2/ARE pathway | Aging rat model was established by continuous 200 mg/kg propofol anaesthesia | [94] |
| 7 | Protective effect on titanium dioxide nanoparticles induced neurotoxicity in SD rats | Decreases oxidative stress and TNF-α Increases the total antioxidant and GSH levels |
TiO2 NPs (150 mg/kg b.w.) was administered orally for six weeks and Avn was administered daily at a dose of 20 mg/kg by gastric tube. | [95] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





