1. Introduction
Since the accidental discovery of Teflon in 1938, the material has gained considerable attention in the chemical industries due to its exceptional chemical stability, water-repellency properties, and high surface activity (Ebnesajjad, 2013). The favorable properties of Teflon led to the development of closely related chemicals, namely, perluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Thereafter, PFAS-related products have been widely used in various applications including in textiles, food packaging, fire retardants, and other industrial applications (Brase et al., 2021; Krafft and Riess, 2015; Ruan et al., 2022).
PFAS have become ubiquitous in ecosystems and have been detected in humans (Caron-Beaudoin et al., 2019) as well as in the environment and wildlife (Ahrens et al., 2015; Giesy and Kannan, 2001; Hu et al., 2016). With the advancement of analytical and toxicological methods, various adverse effects of PFAS have been reported. In particular, eight-carbon congeners (C8), perfluoro-octane sulfonic acid (PFOS), and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) are the most widely distributed and bio-accumulated, and have been reported to be toxic. As a result of this probable toxicity, the production of these chemicals has been voluntarily discontinued by their manufacturer, the 3M company. Numerous substitutes for these legacy PFAS have been introduced, including perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA), perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS), perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA), and perfluorohexanesulfonic acid (PFHxS), but these alternatives are also potentially toxic (Roth et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2021).
PFHxS, a six-carbon congener developed as a substitute for PFOS, is widely used in industrial and consumer applications, particularly in the electroplating industry (Ateia et al., 2019), and is highly prevalent in the environment and living organisms. Due to its persistent, bio-accumulative, and toxic properties (Butenhoff et al., 2009; Das et al., 2017; Xie et al., 2020), PFHxS and its salts have been listed in Annex A of the 2021 Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants. Consequently, regulations on the use of PFHxS are being strengthened worldwide. For example, Korea and Japan are considering adding PFHxS to the PFAS survey items for water quality, which already includes PFOS and PFOA.
Studies on the toxico-kinetics of PFAS have shown that the distribution of PFHxS has a high liver-to-plasma ratio after oral and intravenous administration (Huang et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2018). Animal studies have demonstrated that PFHxS promotes hepatic steatosis and exacerbates the hepatic symptoms of non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLD) in obese mice (Das et al., 2017; He et al., 2022). Similarly, an epidemiological study has indicated a positive association between serum PFHxS levels and the NAFLD index in obese people (Jain and Ducatman, 2019), suggesting that PFHxS is potentially toxic to the liver. However, there is a scarcity of human studies specifically examining the effects of PFHxS on the liver, including the potential to cause liver cancer. Liver cancer was the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide in 2020 (Sung et al., 2021). Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common form of liver cancer, accounting for 90% of cases, and is associated with poor prognosis (Singal et al., 2014). Therefore, the identification of environmental factors contributing to the progression of HCC is crucial for developing effective therapeutic and preventative strategies for liver cancer. In this study, we investigated the effects of PFHxS on the proliferation of the human HCC cell lines Hep3B and SK-Hep1.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
K+PFHxS (≥99.9% purity) was obtained from 3 M Company (St. Paul, MN). PFHxS was prepared by dissolving in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Antibodies of Cdk2, Cdk4, Cyclin D1, Cyclin E, PCNA, and GAPDH were purchased from Santa Cruz (Dallas, USA). Anti-rabbit IgG and anti mouse IgG were from GeneTex (Irvine, USA).
2.2. Cell Culture
Human hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCC), Hep3B and SK-Hep1, were obtained from the Korean Cell Line Bank (Seoul, Korea). Cells were cultured in Minimum essential medium (MEM, GIBCO) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Hyclone) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (GIBCO). The cells were maintained in a humidified atmosphere at 37℃ with 5% CO2.
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
Hep3B (8 × 103/well) and SK-Hep1 (6.5 × 103) cells were seeded in 96-well plates and treated with various concentrations of PFHxS for 24 or 48 h. The plates were treated with tetrazolium salt 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) solution at 37℃ for 4 h. Formazan crystals were dissolved with DMSO, and the absorbance was measured at 595 nm as previously described (Lee et al., 2016).
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
Cells seeded into 24 well plates (4 x 104 cells/well) were treated with different concentrations of PFHxS for 12‒14 days to allow colony formation. Colonies consisting of more than 50 cells were stained with 0.5% crystal violet (Junsei Chemical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) in 60% methanol. Images were acquired using the Chemi-Doc XRS imaging system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA), and the numbers of colonies was quantified by measuring the optical density of the extracted crystal violet dye with DMSO at 570 nm.
2.5. Western Blotting
Cells lysates were prepared using lysis buffer containing 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 10 mM NaF, 2 mM MgCl2, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM KCl, 1 mM Na3VO4, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM benzamide, 1 mM PMSF, 10 μg/ml aprotinin, 10 μg/ml leupeptin, 10 μg/ml pepstatin A, and 1% NP40. Equal amount of proteins from each sample were separated by SDS-PAGE gel and were transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane. After blocking with non-fat dry milk, primary antibodies were applied overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with secondary antibodies. Protein bands were detected using chemiluminescence reagents. Band intensities were analyzed using Chemi-Doc XRS imaging system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). The membranes were re-probed with anti-GAPDH antibody, which was used as a loading control for each gel.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using the two sample t-test for two-group comparison or one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple group comparisons. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered significant. Statistical analysis was conducted using GraphPad Prism 4.0 software.
3. Results and Discussion
Exposure to PFAS potentially contributes to the development of NAFLD, which has become the most common cause of chronic liver diseases, including HCC, in recent years (Foulds et al., 2017; Ioannou, 2021). Furthermore, animal and human studies have demonstrated that exposure to PFHxS promotes NAFLD-related symptoms (He et al., 2022; Jain and Ducatman, 2019), raising the possibility that PFHxS may also affect the proliferation of HCC cells.
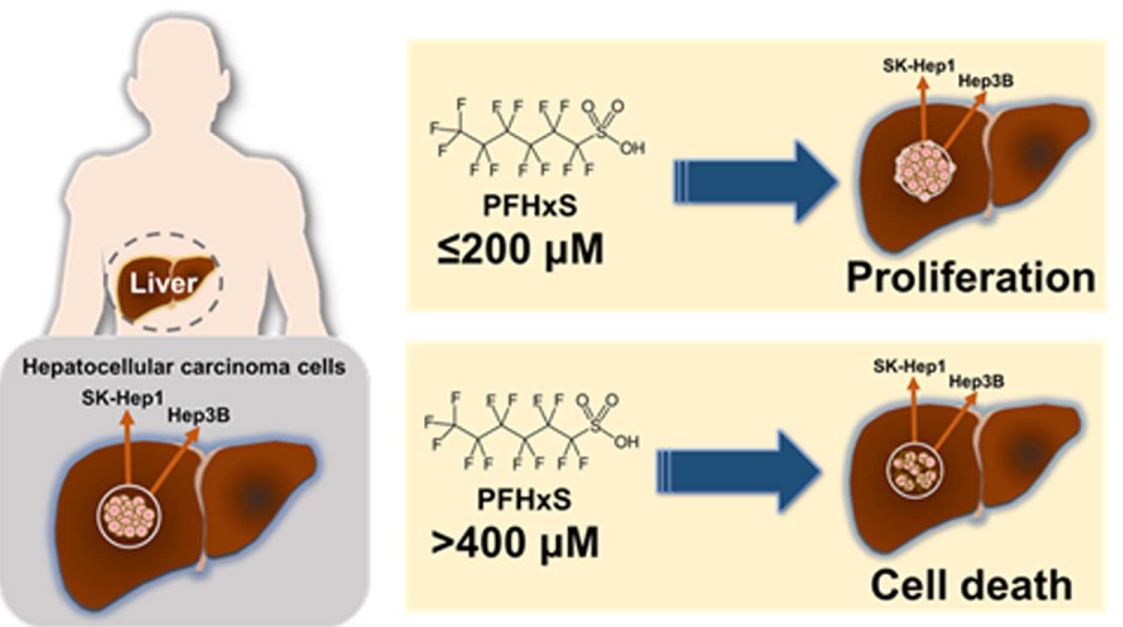
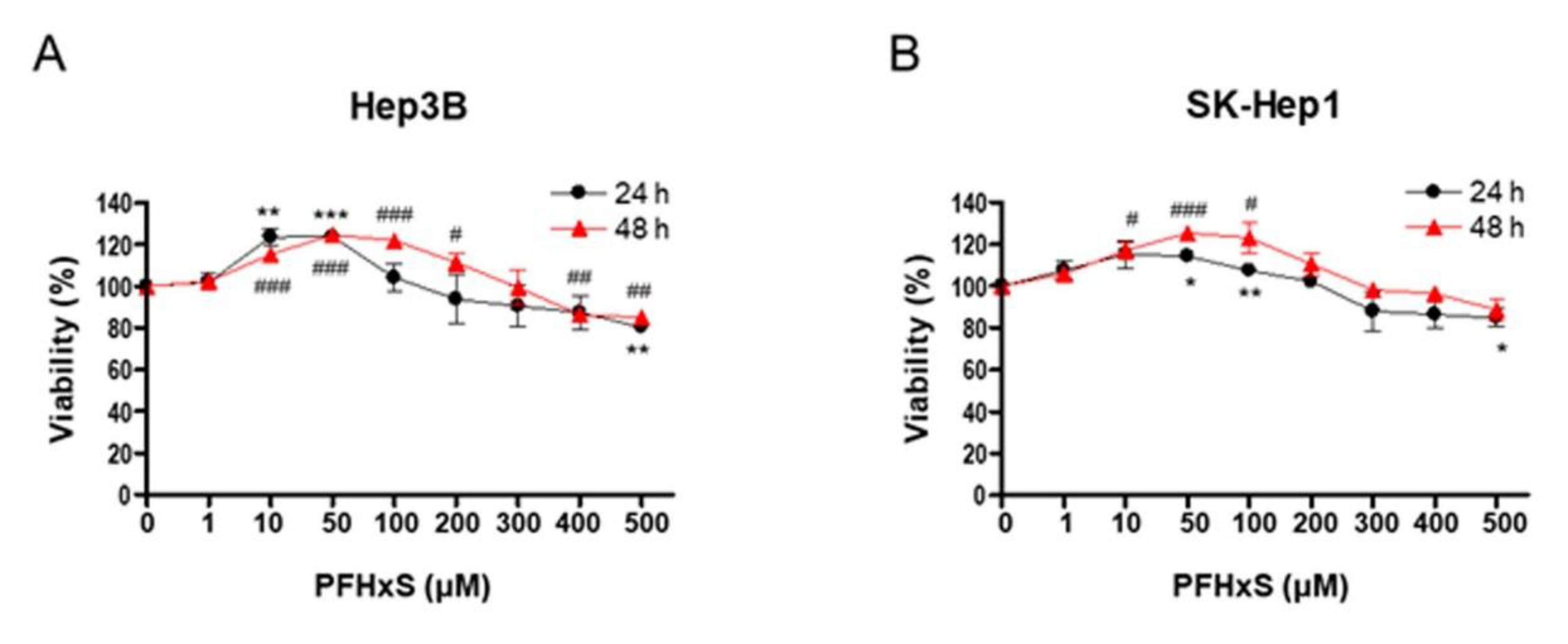
To investigate the effect of PFHxS on the proliferation of HCC cells, we assessed cell viability and colony formation in Hep3B and SK-Hep1 cells treated with different concentrations (0–500 μM) of PFHxS for 24 and 48 h. Treatment with PFHxS for 24 h significantly increased the viability of Hep3B cells at concentrations ≤ 50 μM and significantly increased the viability of SK-Hep1 cells at concentrations ≤ 100 μM. Similarly, treatment with PFHxS for 48 h significantly increased the viability of Hep3B cells at concentrations ≤ 200 μM and significantly increased the viability of SK-Hep1 cells at concentrations ≤ 100 μM. However, cell viability decreased compared with the control group in both cell lines at PFHxS concentrations ≥ 400 μM (
Figure 1).
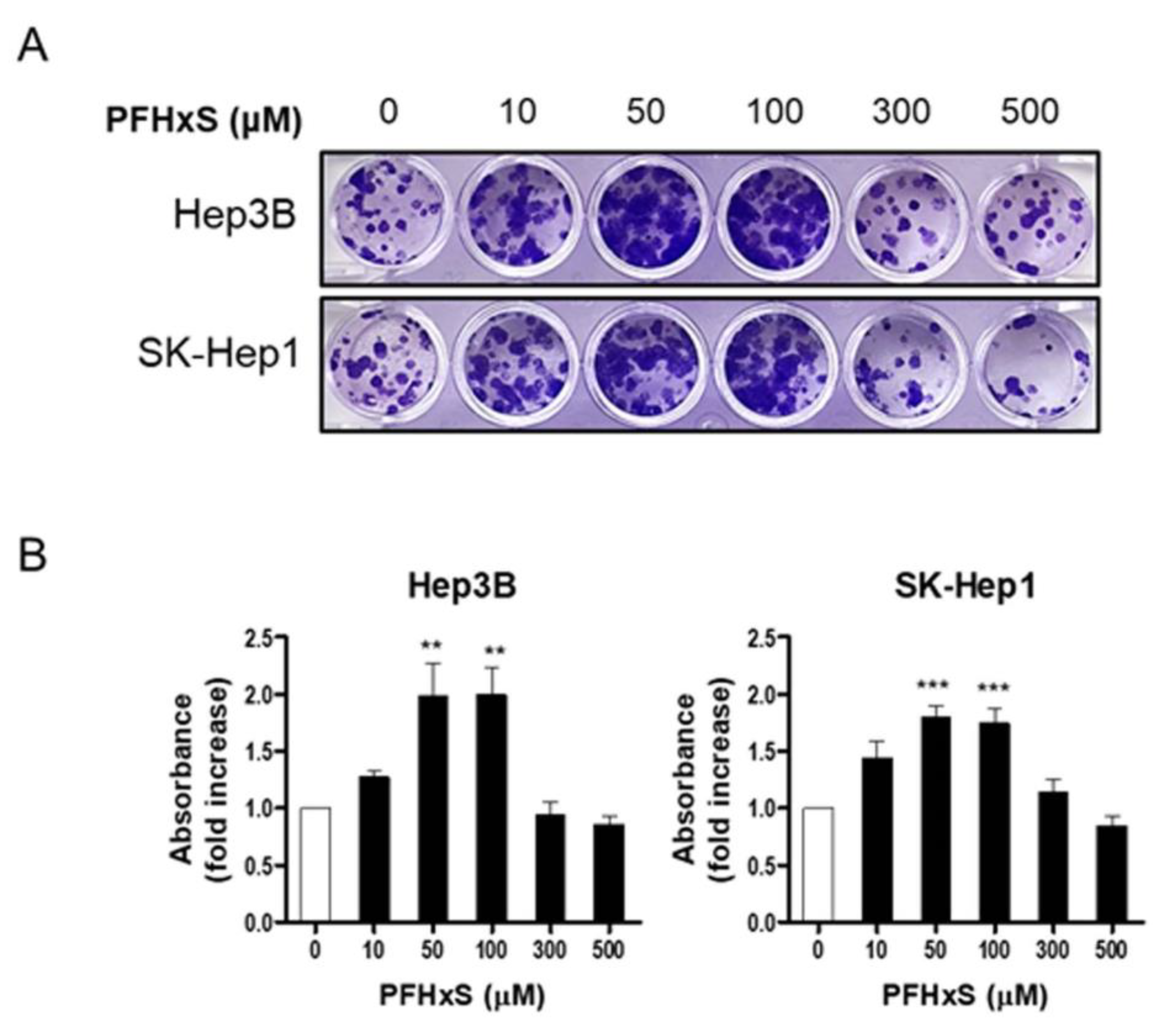
To confirm the stimulatory effect of PFHxS on HCC proliferation, we measured colony formation. Cells were treated with PFHxS at various concentrations for 12–14 days. Consistent with the cell viability results, PFHxS significantly increased colony formation at concentrations ≤ 300 μM in both Hep3B and SK-Hep1 cells, while 500 μM of PFHxS decreased colony formation (
Figure 2). These results indicate that PFHxS enhances HCC proliferation at concentrations below 200 μM but becomes cytotoxic at concentrations above 400 μM.
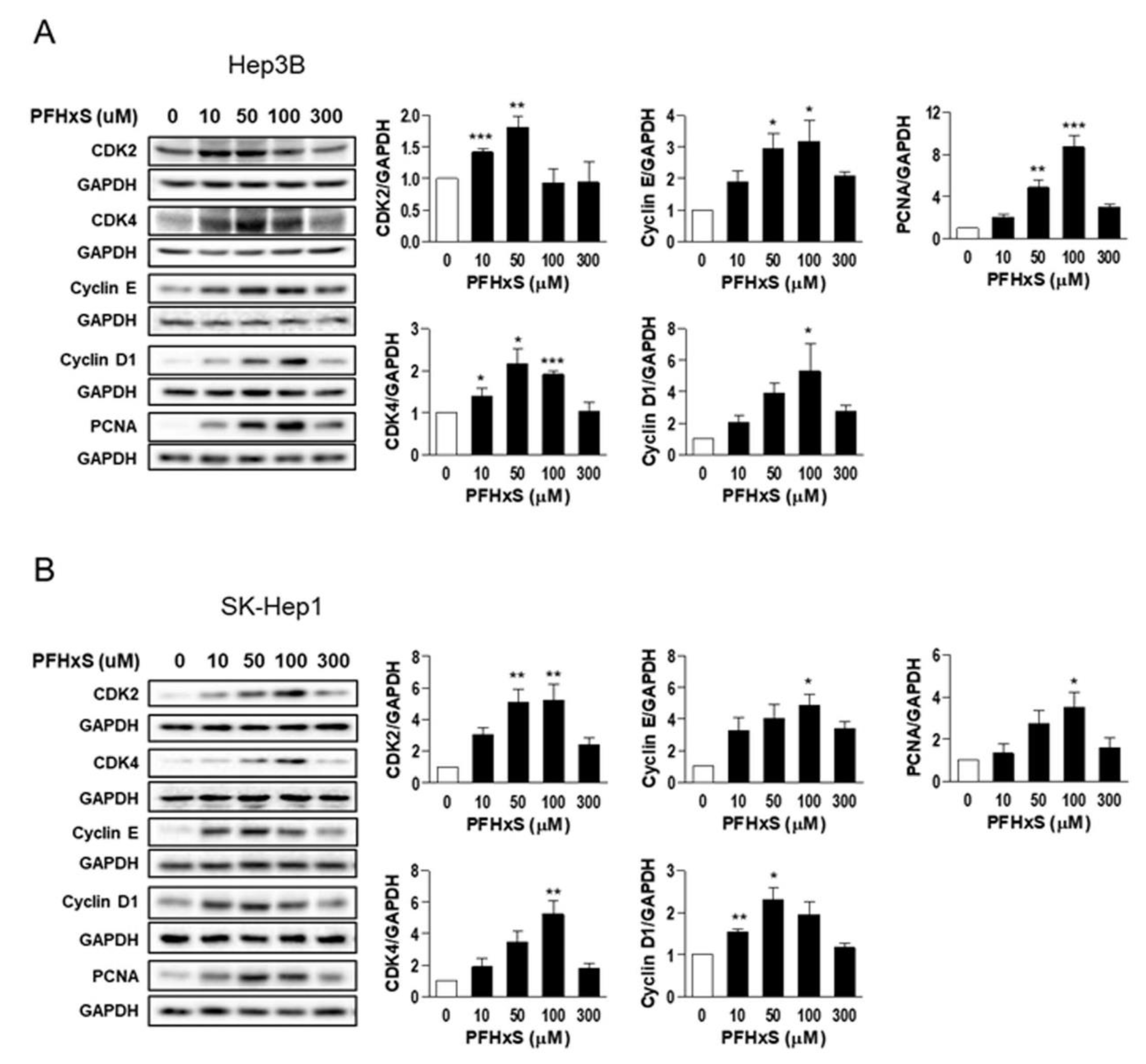
We also examined the effect of PFHxS on the levels of key regulators of the cell cycle, such as cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which drive cell-cycle progression from the resting G
0 phase to growth phases, as well as the effect of PFHxS on proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), a marker of proliferation. Treatment of Hep3B and SK-Hep1 cells with 10–100 μM PFHxS for 48 h significantly increased the levels of cyclin E, cyclin D1, CDK2, CDK4, and PCNA (
Figure 3).
Overall, our findings indicate that at concentrations below 200 μM, PFHxS stimulates HCC cell proliferation by enhancing HCC cell survival and colony formation. Conversely, at concentrations above 400 μM, PFHxS exhibits cytotoxic effects. The PFHxS-mediated increase in HCC cell proliferation was associated with an increase in the level of cell-cycle markers. These observations align with previous studies on the cellular effects of PFOA and PFOS, which showed that the compounds increased cell viability at 100 μM but were cytotoxic at higher concentrations (Behr et al., 2020). Recent epidemiological studies have also reported an association between elevated blood levels of PFOS and an increased risk of non-viral HCC and higher levels of alpha fetoprotein, a hepatic tumor marker (Goodrich et al., 2022; Cao et al., 2022). Although shorter-chain PFAS are generally considered to be less toxic than PFOA or PFOS, previous studies suggest that some shorter-chain replacements have similar or higher toxicity than long-chain PFAS, and the toxic potencies of PFAS cannot be determined by chain length (Gomis et al 2018; Naile et al., 2012).
In addition, multiple PFAS are detected in most environmental and biological samples. Recent studies have shown that PFAS mixtures can have synergistic, additive, or less than additive effects on liver cells, depending on the specific PFAS combination and the cellular targets (Bjork et al., 2021; Ojo et al., 2022; Ojo et al., 2021). Therefore, the potency of PFHxS in promoting HCC proliferation may depend on the exposure mode, such as exposure to PFHxS alone or in a mixture with other PFAS.
Although evidence regarding the initiation and carcinogenesis of liver cancer by PFHxS is lacking, our finding suggests that certain concentrations of PFHxS, a ubiquitous persistent organic pollutant, may exacerbate HCC progression. Considering that PFAS mixtures have been detected in human blood, the high distribution of PFHxS and PFOS in the liver, and the physiochemical similarities between PFOS and PFHxS, it is possible that PFHxS could increase the risk of HCC at concentrations lower than those identified in our study.
Our study provides insight into how a chemical found in the environment might contribute to HCC risk. However, larger-scale studies, including epidemiological and mechanistic investigations, are needed to validate these findings. Additionally, further research should explore how exposure to other individual substitute PFAS compounds, such as PFBS, PFBA, and PFHxA, as well as single or combined exposure to PFHxS and legacy PFAS, affects the development of HCC.
4. Conclusions
Our study suggests that PFHxS, a well-known alternative to PFOS, may contribute to the progression of HCC in humans. PFHxS increased the survival and proliferation of HCC cells at relatively low concentrations (10–200 μM). Conversely, higher concentrations of PFHxS (>400 μM) were cytotoxic.
These findings provide valuable insights into PFHxS kinetics and facilitate the contextualization of human toxicity data, which is crucial for risk assessment of PFAS exposure in humans. In particular, this finding is of great importance in Japan and South Korea, where concerns about the potential toxicity of PFHxS is growing.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
KH Sim: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Visualization. HS Oh: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft preparation. C Lee: Methodology, Visualization. H Eun: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing—original draft preparation, Supervision. YJ Lee: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing—review & Editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. .
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant of Research Institute of Medical Science, Daegu Catholic University (2022).
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ahrens, L.; Norström, K.; Viktor, T.; Cousins, A.P.; Josefsson, S. Stockholm Arlanda Airport as a source of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances to water, sediment and fish. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ateia, M.; Maroli, A.; Tharayil, N.; Karanfil, T. The overlooked short- and ultrashort-chain poly- and perfluorinated substances: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 866–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjork, J.A.; Dawson, D.A.; Krogstad, J.O.; Wallace, K.B. Transcriptional effects of binary combinations of PFAS in FaO cells. Toxicology 2021, 464, 152997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brase, R.A.; Mullin, E.J.; Spink, D.C. Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Analytical Techniques, Environmental Fate, and Health Effects. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butenhoff, J.L.; Chang, S.C.; Ehresman, D.J.; York, R.G. Evaluation of potential reproductive and developmental toxicity of potassium perfluorohexanesulfonate in Sprague Dawley rats. Reprod Toxicol 2009, 27, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron-Beaudoin, É.; Ayotte, P.; Laouan Sidi, E.A.; Gros-Louis McHugh, N.; Lemire, M. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and associations with thyroid parameters in First Nation children and youth from Quebec. Environ Int 2019, 128, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.P.; Wood, C.R.; Lin, M.T.; Starkov, A.A.; Lau, C.; Wallace, K.B.; Corton, J.C.; Abbott, B.D. Perfluoroalkyl acids-induced liver steatosis: Effects on genes controlling lipid homeostasis. Toxicology 2017, 378, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebnesajjad, S. Introduction to Fluoropolymers: Materials, Technology and Applications. PDL Handbook Series. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Foulds, C.E.; Treviño, L.S.; York, B.; Walker, C.L. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2017, 13, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ Sci Technol 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, X.X. Environmental exposure to low-dose perfluorohexanesulfonate promotes obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice fed a high-fat diet. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2022, 29, 49279–49290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.C.; Andrews, D.Q.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bruton, T.A.; Schaider, L.A.; Grandjean, P.; Lohmann, R.; Carignan, C.C.; Blum, A.; Balan, S.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Sunderland, E.M. Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ Sci Technol Lett 2016, 3, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.C.; Dzierlenga, A.L.; Robinson, V.G.; Waidyanatha, S.; DeVito, M.J.; Eifrid, M.A.; Granville, C.A.; Gibbs, S.T.; Blystone, C.R. Toxicokinetics of perfluorobutane sulfonate (PFBS), perfluorohexane-1-sulphonic acid (PFHxS), and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) in male and female Hsd:Sprague Dawley SD rats after intravenous and gavage administration. Toxicol Rep 2019, 6, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N. Epidemiology and risk-stratification of NAFLD-associated HCC. Journal of Hepatology 2021, 75, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.B.; Ducatman, A. Selective Associations of Recent Low Concentrations of Perfluoroalkyl Substances With Liver Function Biomarkers: NHANES 2011 to 2014 Data on US Adults Aged ≥20 Years. J Occup Environ Med 2019, 61, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Shin, H.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.Y. Sex-specific risk assessment of PFHxS using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. Arch Toxicol 2018, 92, 1113–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krafft, M.P.; Riess, J.G. Selected physicochemical aspects of poly- and perfluoroalkylated substances relevant to performance, environment and sustainability-part one. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Yang, J.H. AMP-activated protein kinase is involved in perfluorohexanesulfonate-induced apoptosis of neuronal cells. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, A.F.; Peng, C.; Ng, J.C. Genotoxicity assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances mixtures in human liver cells (HepG2). Toxicology 2022, 482, 153359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, A.F.; Xia, Q.; Peng, C.; Ng, J.C. Evaluation of the individual and combined toxicity of perfluoroalkyl substances to human liver cells using biomarkers of oxidative stress. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, K.; Yang, Z.; Agarwal, M.; Liu, W.; Peng, Z.; Long, Z.; Birbeck, J.; Westrick, J.; Liu, W.; Petriello, M.C. Exposure to a mixture of legacy, alternative, and replacement per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) results in sex-dependent modulation of cholesterol metabolism and liver injury. Environ Int 2021, 157, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, T.; Field, J.; Cousins, I.; Lohmann, R.; Jiang, G. Emerging Contaminants: Fluorinated Alternatives to Existing PFAS. Environ Sci Technol 2022, 56, 6001–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; Pillai, A.; Tiro, J. Early detection, curative treatment, and survival rates for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. PLoS Med 2014, 11, e1001624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Z.; Magand, O.; Thollot, A.; Ebinghaus, R.; Mi, W.; Dommergue, A. Occurrence of legacy and emerging organic contaminants in snow at Dome C in the Antarctic. Sci Total Environ 2020, 741, 140200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.L.; Zheng, C.; Weifeng, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, W. PFAS and their substitutes in groundwater: Occurrence, transformation and remediation. J Hazard Mater 2021, 412, 125159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).