Submitted:
03 August 2023
Posted:
04 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
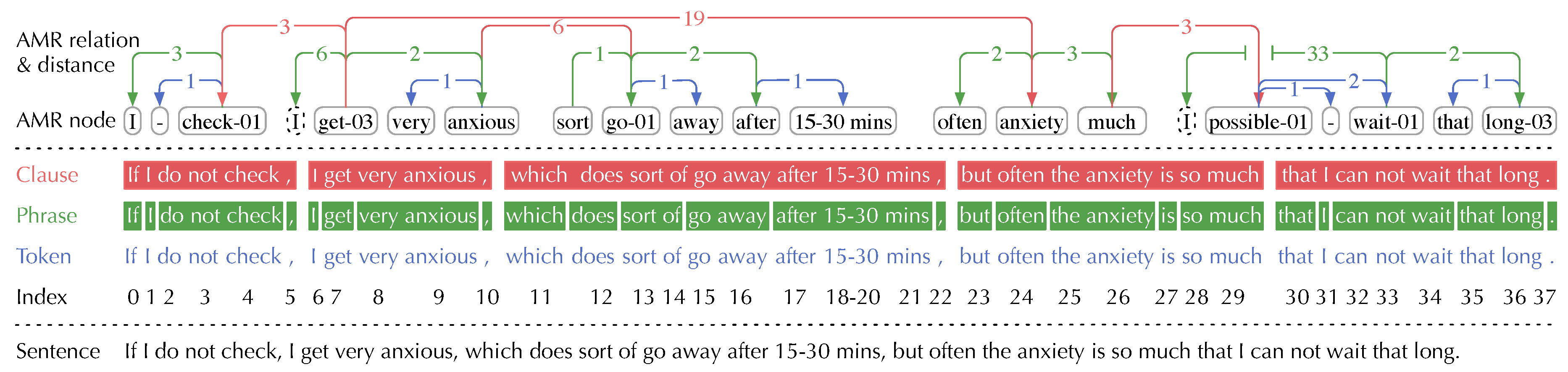
- Dependency distances of inter-clause relations are typically much longer than those of inter-phrase and inter-token relations, leading to the most LDD cases. E.g., the AMR relation, , occurring in the clause “I get very anxious” and its relative clause “which does sort of go away ...”, has a dependency distance of 6 (subtracting the 9th token “anxious” from the 15th token “go”).
- Reentrant AMR nodes abstracted from pronouns also bring the long distant AMR relations. E.g., the AMR relation, , has a dependency distance of 33 (subtracting the 1st token “I” from the 34th token “wait”).
2. Related Work
2.1. Long-Distance Dependencies
2.2. AMR Parsing
- Graph-based: Directly predict nodes and edges in either two-stage procedures [28,29,30] or incremental one-stage [14,31] procedures. The SOTA graph-based model, AMR-gs [14], enhances the incremental graph construction with an AMR graph↔sequence (AMR-gs) iterative inference mechanism in one-stage procedures.
- Seq2seq-based: Model the task as transduction of the sentence into a linearization of the AMR graph [15,17,18,19,20,32,33,34,35]. SPRING [15] is a popular seq2seq-based codebase that employs transfer learning by exploiting pretrained encoder-decoder model, BART [16], to generate a linearized graph incrementally with a single auto-regressive pass of a seq2seq decoder. The subsequent models, ANCES [17], HCL [18], ATP [19], and HGAN [20] all follow the architecture of SPRING, where HGAN integrates SDP and SRL features with heterogeneous graph neural networks and achieves the best performances in the settings of removing extra silver training data, graph re-categorization, and ensemble methods.
- Transition-based: Predict a sequence of actions that generate the graph while processing tokens left-to-right through the sentence [36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. The SOTA transition-based model, StructBART [42], explores the integration of general pre-trained sequence-to-sequence language models and a structure-aware transition-based approach.
- Grammar-based: Peng et al. [43] introduce a synchronous hyperedge replacement grammar solution. Pust et al. [44] regard the task as a machine translation problem, while Artzi et al. [45] adapt combinatory categorical grammar. Groschwitz et al. [46] and Lindemann et al. [47] view AMR graphs as the structural AM algebra.
2.3. Hierarchical Clause Annotation
- Coordination: is an equal relation shared by clauses with the same syntactic status, including And, Or, and But relations
- Subordination: occur in a matrix and a subordinate clause, including Subjective, Objective, Predicative, Appositive, Relative, and nine sublevel Adverbial relations.
3. Model
3.1. HCA-based Self-Attention
3.1.1. Token Visibility Matrix
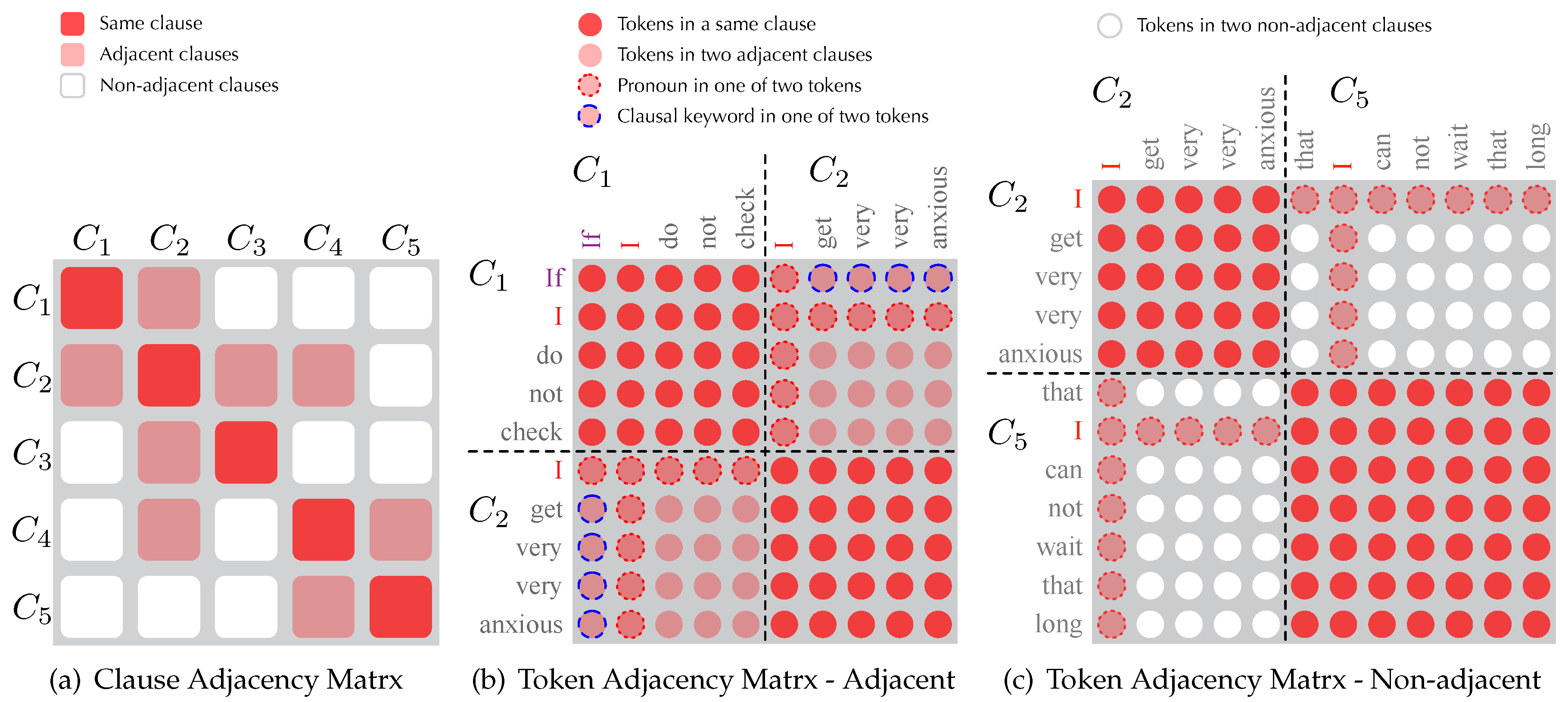
- Full Visibility: tokens in the same clause are fully visible mutually
- Patial Visibility: tokens from two adjacent clauses and are sharing partial visibility
- None Visibility: tokens from non-adjacent clauses and are invisible to each other
- Global Visibility: tokens with a pronoun POS (e.g., “I” in ) are globally visible for linguistic phenomena of co-reference
- Additional Visibility: tokens that are clausal keywords (i.e., coordinators, subordinators, and antecedents) share additional visibilities with the tokens in adjacent clauses (e.g., “if” in to tokens in )
3.1.2. Masked-Self-Attention
3.1.3. Clause-Relation-Binded Attention Head
3.2. HCA-Based Curriculum Learning
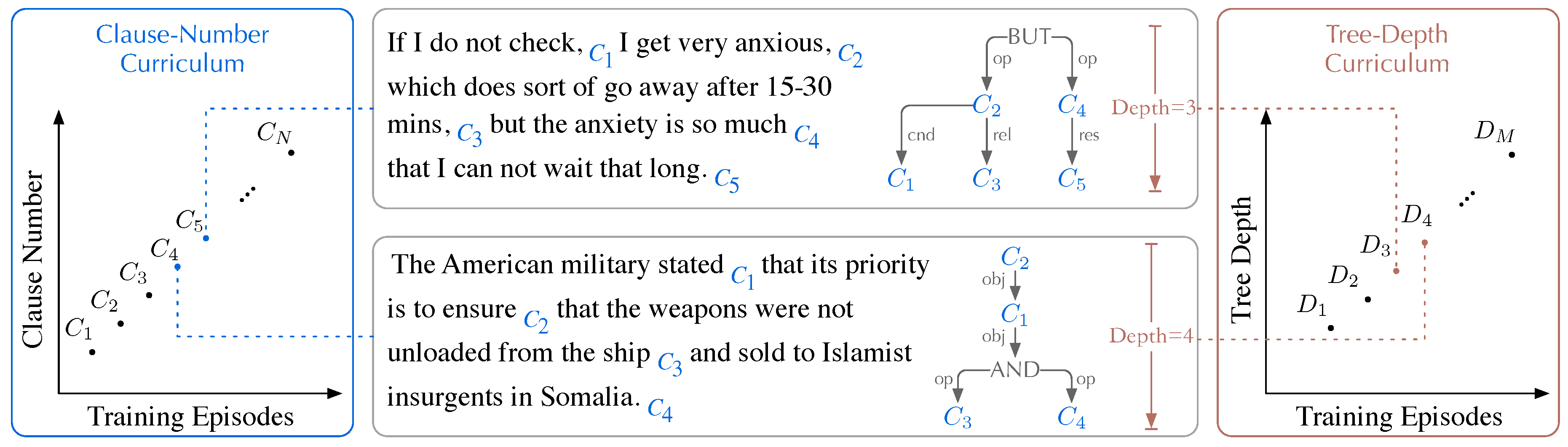
3.2.1. Clause-Number Curriculum
3.2.2. Tree-Depth Curriculum
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. In-Distribution Datasets
- AMR 2.0: includes 39,260 sentence-AMR pairs in which source sentences are collected for the DARPA BOLT AND DEFT programs, transcripts and English translations of Mandarin Chinese broadcast news programming from China Central TV, Wall Street Journal text, translated Xinhua news texts, various newswire data from NIST OpenMT evaluations and weblog data used in the DARPA GALE program.
- AMR 3.0: is a superset of AMR 2.0 and enriches the data instances to 59,255. New source data added to AMR 3.0 includes sentences from Aesop’s Fables, parallel text and the situation frame data set developed by LDC for the DARPA LORELEI program, and lead sentences from Wikipedia articles about named entities.
4.1.2. Out-of-Distribution Datasets
4.1.3. Hierarchical Clause Annotations
4.2. Baseline and Compared Models
- AMR-gs (2020) [14], a graph-based parser that enhances incremental graph construction with an AMR graph↔sequence (AMR-gs) iterative inference mechanism in one-stage procedures.
- APT (2021) [41], a transition-based parser that employs an action-pointer Transformer (APT) to decouple source tokens from node representations and address alignments.
- StructBART (2021) [42], a transition-based parser that integrates the pre-trained language model, BART, for structured fine-tuning.
- SPRING (2021) [15], a fine-tuned BART model that predicts a linearized AMR graph.
- HCL (2022) [18], a hierarchical curriculum learning (HCL) framework that helps the seq2seq model adapts to the AMR hierarchy.
- ANCES (2022) [17], a seq2seq-based parser that adds the important ancestor (ANCES) information into the Transformer decoder.
- HGAN (2022) [20], a seq2seq-based parser that applies a heterogeneous graph attention network (HGAN) to argument word representations with syntactic dependencies and semantic role labelings of input sentences. It is also the current SOTA parser in the settings of removing graph re-categorization, extra silver training data, and ensemble methods.
4.3. Hyper-Parameters
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
- Unlab. does not consider any edge labels and only considers the graph structure.
- Reent. is a typical structure feature for the AMR graph. Without reentrant edges, the AMR graph is reduced to a tree.
- SRL denotes the core-semantic relation of the AMR, which determines the core structure of the AMR.
4.5. Experimental Environments
4.6. Experimental Results
4.6.1. Results in ID datasets
- Equipped with our HCA-SA and HCA-CL approaches, the baseline model SPRING achieves 0.7 Smatch F1 score improvements on both AMR 2.0 and AMR 3.0. The improvements are significant with and , respectively.
- In AMR 2.0, our HCA-based model outperforms all compared models except ANCES and the HGAN version that introduces both DP and SRL features.
- In AMR 3.0, consisting of more sentences with HCA trees, the performance gap between our HCA-based parser and the SOTA (HGAN with DP and SRL) is only 0.2 Smatch F1 scores.
- Our HCA-based model outperforms the baseline model in nearly all fine-grained metrics, especially in structure-dependent metrics with 1.1, 1.8, and 3.9 F1 scores improvements in Unlab., Reent., and SRL, respectively.
- In the , , and metrics, our HCA-based model achieves the best performances against all compared models.
4.6.2. Results in OOD Datasets
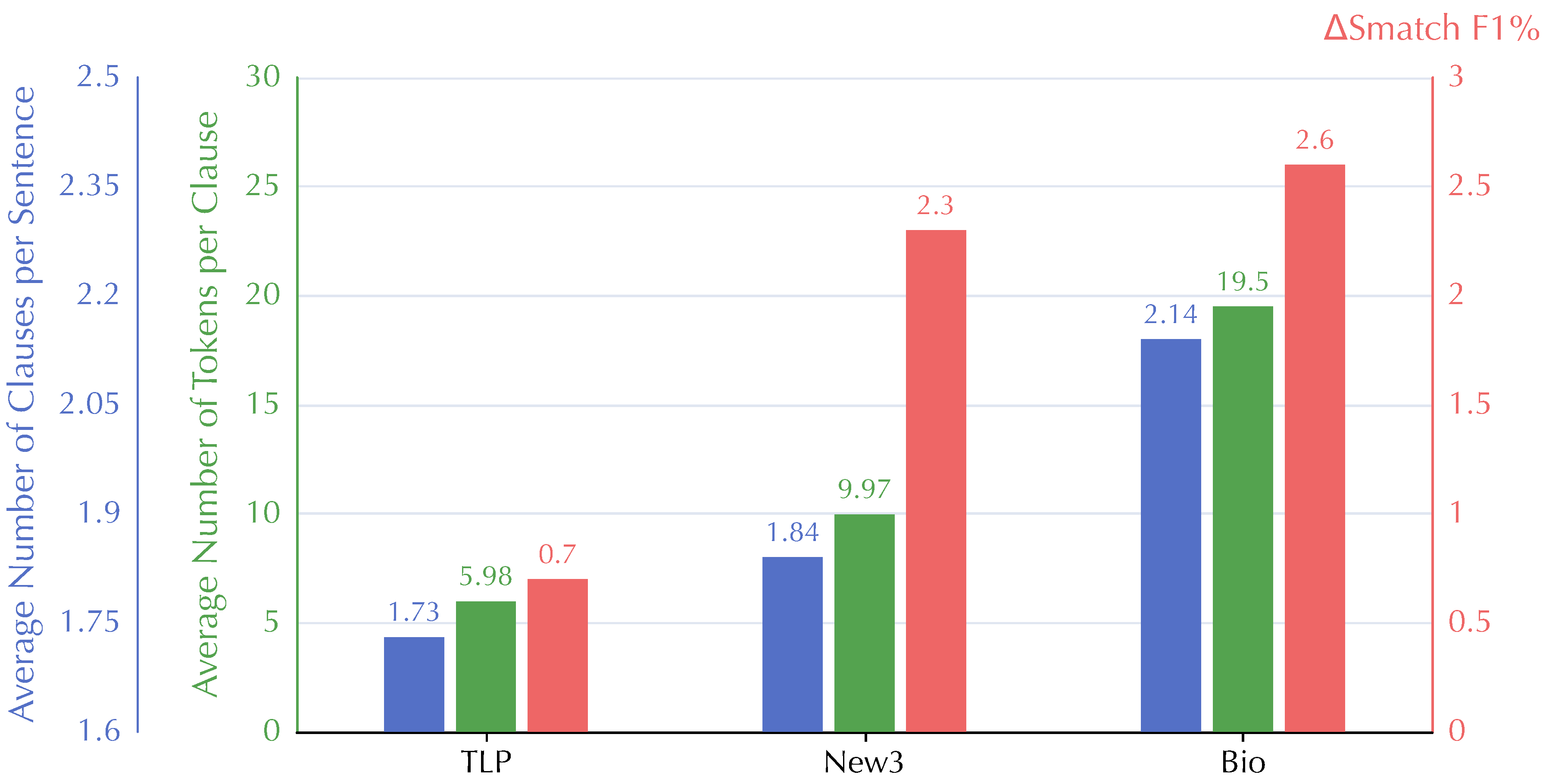
- Our HCA-based model outperforms the baseline model SPRING with 2.5, 0.7, and 3.1 Smatch F1 score improvements in New3, TLP, and Bio test sets, respectively.
- In the New3 and Bio datasets that contain long sentences of newswire and biomedical texts and have more HCA trees, our HCA-based model outperforms all compared models.
- In the TLP dataset that contains many simple sentences of a children’s story and fewer HCA trees, our HCA-based does not perform as well as HCL and HGAN.
5. Discussion
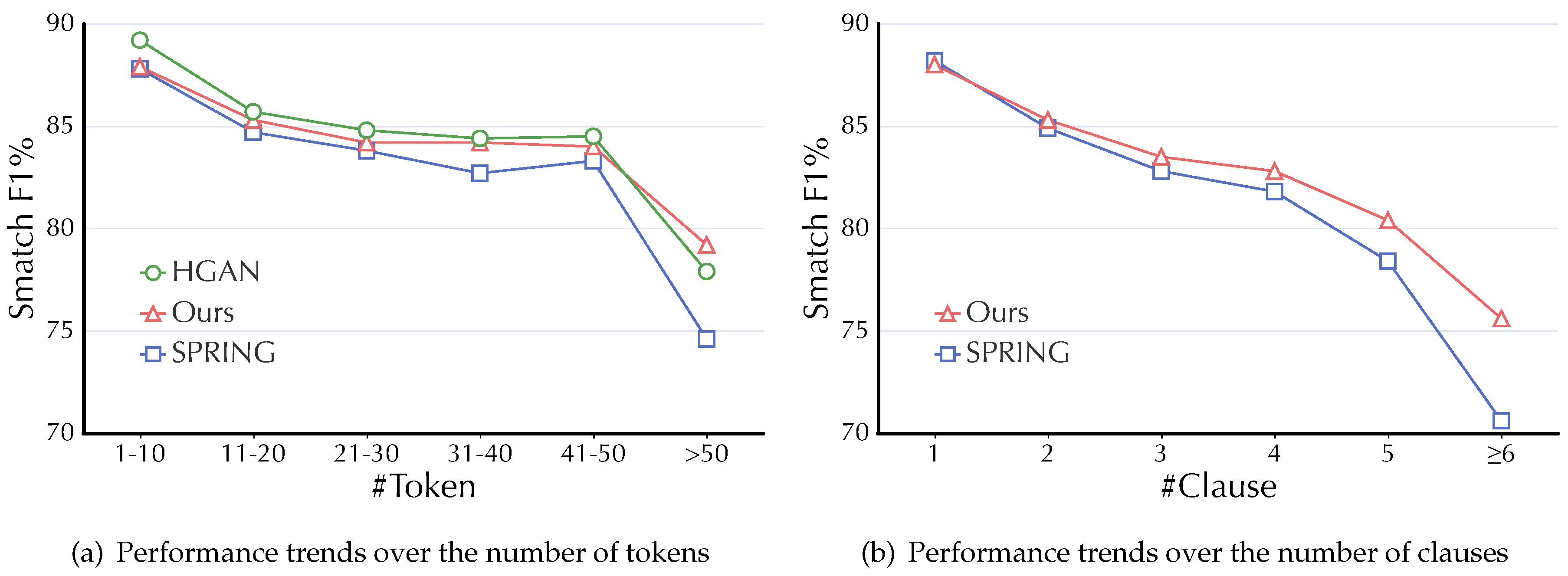
5.1. Effects on Long-Distance Dependencies in ID datasets
- When the number of tokens (denoted as #Token for simplicity ) >20 in a sentence, the performance boosts of our HCA-based model against the baseline SPRING gradually become significant.
- For the case #Token>50 that indicates sentences with many clauses and inter-clause relations, our HCA-based model outperforms both SPRING and HGAN.
- When compared on performances trends over #Clause, the performance lead of our HCA-based model against SPRING becomes much more evident as #Clause increases.
5.2. Effects on Long-Distance Dependencies in OOD datasets
- shows the number of complex sentences with more than one clauses
- depicts the latent dependency distance between two tokens from different clauses
5.3. Ablation Study
- In HCA-SA, the clause-relation-binded attention setting (demoted as “ClauRel”) contributes most in the SRL metric due to the mappings between inter-clause relations (e.g., Subjective and Objective) and SRL-type AMR relations (e.g., :ARG0 and :ARG1).
- In HCA-SA, the masked-self-attention mechanism (demoted as “VisMask”) achieves significant improvements in the Reent. metric by increasing the visibility of pronoun tokens to all tokens.
- In HCA-CL, the Tree-Depth curriculum (demoted as “TD”) has no effects on the parsing performances. We conjecture that sentences with much deeper clausal structures are rare, and the number of split buckets for the depth of clausal trees is not big enough to distinguish the training sentences.
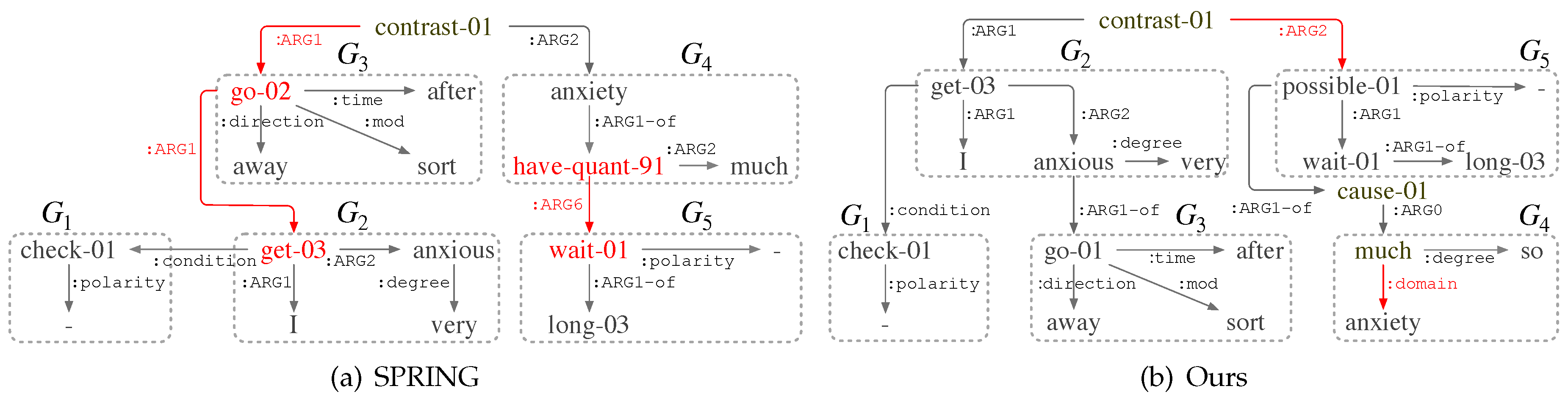
5.4. Case Study
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Abstract Meaning Representation |
| CL | Curriculum Learning |
| HCA | Hierarchical Clause Annotation |
| ID | In-Distribution |
| IGNN | Implicit Graph Neural Network |
| LDD | Long-Distance Dependency |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| OOD | Out-of-Distribution |
| POS | Part-of-Speech |
| RST | Rhetorical Structure Theory |
| SA | Self Attention |
| SDP | Semantic Dependency |
| SRL | Semantic Role Labeling |
| SOTA | State-of-the-Art |
References
- Li, Z.; Cai, J.; He, S.; Zhao, H. Seq2seq Dependency Parsing. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA, 2018; pp. 3203–3214. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Song, Y.; Xia, F.; Zhang, T. Improving Constituency Parsing with Span Attention. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2020; pp. 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lee, K.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep Semantic Role Labeling: What Works and What’s Next. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Vancouver, Canada, 2017; pp. 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Müller, M.; Rios, A.; Sennrich, R. Why Self-Attention? A Targeted Evaluation of Neural Machine Translation Architectures. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 4263–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Ye, Y.; Feng, Y.; Lai, Y.; Yan, R.; Zhao, D. Modeling discourse cohesion for discourse parsing via memory network. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J. Discourse-Aware Neural Extractive Text Summarization. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2020; pp. 5021–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hihi, S.; Bengio, Y. Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Networks for Long-Term Dependencies. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. MIT Press; 1995. Vol. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural computation 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, G.; Ross, R.; Kelleher, J. Attentive Language Models. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Eighth International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers); Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing: Taipei, Taiwan, 2017; pp. 441–450. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.u.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates, Inc; 2017. Vol. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, F.; Chang, H.; Zhu, W.; Sojoudi, S.; El Ghaoui, L. Implicit Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates, Inc; 2020. Vol. 33. pp. 11984–11995. [Google Scholar]
- Banarescu, L.; Bonial, C.; Cai, S.; Georgescu, M.; Griffitt, K.; Hermjakob, U.; Knight, K.; Koehn, P.; Palmer, M.; Schneider, N. Abstract Meaning Representation for Sembanking. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 7th Linguistic Annotation Workshop and Interoperability with Discourse; Association for Computational Linguistics: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2013; pp. 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Gildea, D.; Satta, G. AMR Parsing With Cache Transition Systems. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Lam, W. AMR Parsing via Graph-Sequence Iterative Inference. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2020; pp. 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, M.; Blloshmi, R.; Navigli, R. One SPRING to rule them both: Symmetric AMR semantic parsing and generation without a complex pipeline. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, Vol.35; pp. 12564–12573.
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2020; pp. 7871–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Gildea, D. Sequence-to-sequence AMR Parsing with Ancestor Information. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Dublin, Ireland, 2022; pp. 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Liu, T.; Dai, D.; Cao, Y.; Chang, B.; Sui, Z. Hierarchical Curriculum Learning for AMR Parsing. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Dublin, Ireland, 2022; pp. 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, P.; Xu, R.; Liu, T.; Sui, Z.; Chang, B. ATP: AMRize Then Parse! Enhancing AMR Parsing with PseudoAMRs. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2022; Association for Computational Linguistics: Seattle, United States, 2022; pp. 2482–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sataer, Y.; Shi, C.; Gao, M.; Fan, Y.; Li, B.; Gao, Z. Integrating Syntactic and Semantic Knowledge in AMR Parsing with Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023 - 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP); 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.; McCarthy, M. Cambridge grammar of English: a comprehensive guide; spoken and written English grammar and usage; Cambridge University Press, 2006.
- Liu, Y.; Ryskin, R.; Futrell, R.; Gibson, E. A verb-frame frequency account of constraints on long-distance dependencies in English. Cognition 2022, 222, 104902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, W.C.; Thompson, S.A. Rhetorical structure theory: Toward a functional theory of text organization. Text-interdisciplinary Journal for the Study of Discourse 1988, 8, 243–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, B.; Sataer, Y.; Gao, M.; Shi, C.; Cao, S.; Gao, Z. Hierarchical Clause Annotation: Building a Clause-Level Corpus for Semantic Parsing with Complex Sentences. Preprints.org 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockett, C.F. A formal statement of morphemic analysis. Studies in Linguistics 1952, 10, J39. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalunkar, A.; Kelleher, J.D. Understanding Recurrent Neural Architectures by Analyzing and Synthesizing Long Distance Dependencies in Benchmark Sequential Datasets, 2020. arXiv:cs.LG/1810.02966].
- Szubert, I.; Damonte, M.; Cohen, S.B.; Steedman, M. The Role of Reentrancies in Abstract Meaning Representation Parsing. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2020; pp. 2198–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigan, J.; Thomson, S.; Carbonell, J.; Dyer, C.; Smith, N.A. A Discriminative Graph-Based Parser for the Abstract Meaning Representation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Baltimore, Maryland, 2014; pp. 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Titov, I. AMR Parsing as Graph Prediction with Latent Alignment. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Duh, K.; Van Durme, B. Broad-Coverage Semantic Parsing as Transduction. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP); Association for Computational Linguistics: Hong Kong, China, 2019; pp. 3786–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Duh, K.; Van Durme, B. AMR Parsing as Sequence-to-Graph Transduction. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Florence, Italy, 2019; pp. 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstas, I.; Iyer, S.; Yatskar, M.; Choi, Y.; Zettlemoyer, L. Neural AMR: Sequence-to-Sequence Models for Parsing and Generation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Vancouver, Canada, 2017; pp. 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Song, L.; Gildea, D.; Satta, G. Sequence-to-sequence Models for Cache Transition Systems. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Li, S. Modeling Source Syntax and Semantics for Neural AMR Parsing. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-19. International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization, 2019; pp. 4975–4981. [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, G. Improving AMR Parsing with Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP); Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2020; pp. 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xue, N.; Pradhan, S. A Transition-based Algorithm for AMR Parsing. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2015 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies; Association for Computational Linguistics: Denver, Colorado, 2015; pp. 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, M.; Al-Onaizan, Y. AMR Parsing using Stack-LSTMs. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017; pp. 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilares, D.; Gómez-Rodríguez, C. Transition-based Parsing with Lighter Feed-Forward Networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Universal Dependencies (UDW 2018); Association for Computational Linguistics: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, T.; Shah, A.; Wan, H.; Florian, R.; Roukos, S.; Ballesteros, M. Rewarding Smatch: Transition-Based AMR Parsing with Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Florence, Italy, 2019; pp. 4586–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez Astudillo, R.; Ballesteros, M.; Naseem, T.; Blodgett, A.; Florian, R. Transition-based Parsing with Stack-Transformers. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2020; pp. 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Naseem, T.; Fernandez Astudillo, R.; Florian, R. AMR Parsing with Action-Pointer Transformer. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2021; pp. 5585–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Naseem, T.; Fernandez Astudillo, R.; Lee, Y.S.; Florian, R.; Roukos, S. Structure-aware Fine-tuning of Sequence-to-sequence Transformers for Transition-based AMR Parsing. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online and Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 2021; pp. 6279–6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Song, L.; Gildea, D. A Synchronous Hyperedge Replacement Grammar based approach for AMR parsing. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Nineteenth Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning; Association for Computational Linguistics: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pust, M.; Hermjakob, U.; Knight, K.; Marcu, D.; May, J. Parsing English into Abstract Meaning Representation Using Syntax-Based Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Lisbon, Portugal, 2015; pp. 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artzi, Y.; Lee, K.; Zettlemoyer, L. Broad-coverage CCG Semantic Parsing with AMR. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Lisbon, Portugal, 2015; pp. 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groschwitz, J.; Lindemann, M.; Fowlie, M.; Johnson, M.; Koller, A. AMR dependency parsing with a typed semantic algebra. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, M.; Groschwitz, J.; Koller, A. Compositional Semantic Parsing across Graphbanks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Florence, Italy, 2019; pp. 4576–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessler, L.; Behzad, S.; Liu, Y.J.; Peng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zeldes, A. DisCoDisCo at the DISRPT2021 Shared Task: A System for Discourse Segmentation, Classification, and Connective Detection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2nd Shared Task on Discourse Relation Parsing and Treebanking (DISRPT 2021); Association for Computational Linguistics: Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 2021; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Hirao, T.; Kamigaito, H.; Okumura, M.; Nagata, M. A Simple and Strong Baseline for End-to-End Neural RST-style Discourse Parsing. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2022; Association for Computational Linguistics: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2022; pp. 6725–6737. [Google Scholar]
- Child, R.; Gray, S.; Radford, A.; Sutskever, I. Generating long sequences with sparse transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.10509, 2019. arXiv:1904.10509.
- Liu, W.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ju, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, P. K-bert: Enabling language representation with knowledge graph. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, Vol.34; pp. 2901–2908.
- Bengio, Y.; Louradour, J.; Collobert, R.; Weston, J. Curriculum Learning. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2009. ICML ’09. pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.; Priyadarshi, J. SemEval-2017 Task 9: Abstract Meaning Representation Parsing and Generation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017); Association for Computational Linguistics: Vancouver, Canada, 2017; pp. 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Knight, K. Smatch: an Evaluation Metric for Semantic Feature Structures. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2013; pp. 748–752. [Google Scholar]
- Damonte, M.; Cohen, S.B.; Satta, G. An Incremental Parser for Abstract Meaning Representation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Volume 1, Long Papers; Association for Computational Linguistics: Valencia, Spain; 2017; pp. 536–546. [Google Scholar]
- Riezler, S.; Maxwell, J.T. On Some Pitfalls in Automatic Evaluation and Significance Testing for MT. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization; Association for Computational Linguistics: Ann Arbor, Michigan, 2005; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | |
| 2 | The AMR relation distances between a main clause and a relative/appositive clause are decided by the modified noun phrase in the former and the verb in the latter. |
| 3 | |
| 4 | Located at AMR 3.0/data/amrs/split/test/amr-release-3.0-amrs-test-lorelei.txt |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | We only use the original data published in their paper to draw performance trends over the number tokens, without performances in terms of the number of clauses. |
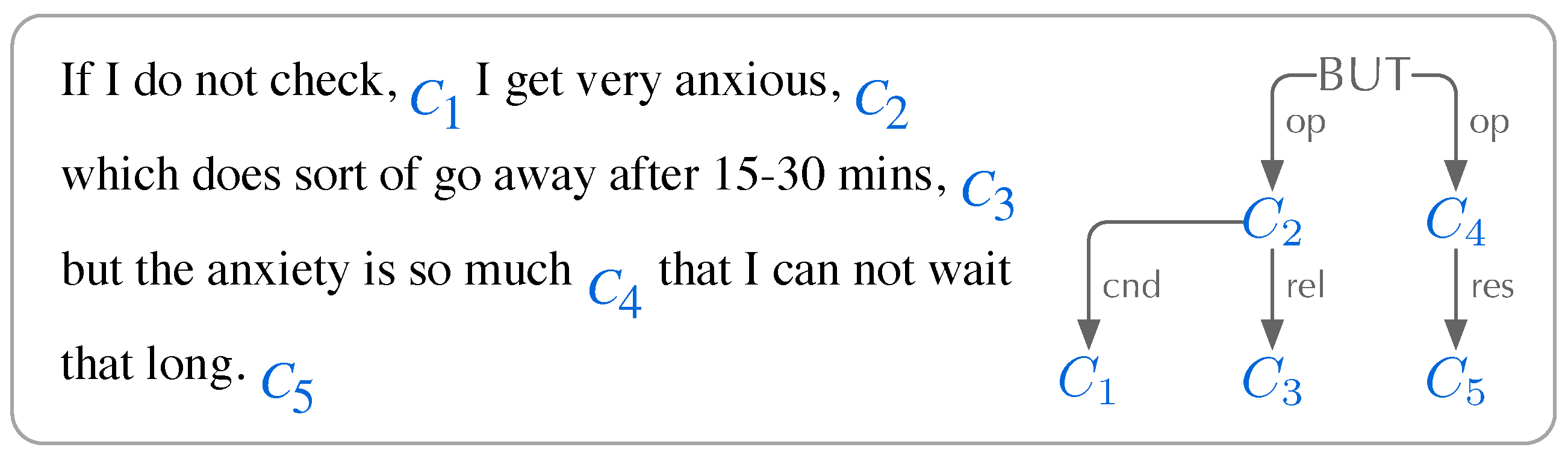
| Dataset | Training | Development | Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #Snt. | #HCA | #Snt. | #HCA | #Snt. | #HCA | ||
| ID | AMR 2.0 | 36,521 | 17,886 | 1,368 | 741 | 1,371 | 753 |
| AMR 3.0 | 55,635 | 36,921 | 1,722 | 1,243 | 1,898 | 1,258 | |
| OOD | New3 | - | - | 527 | 286 | ||
| TLP | - | - | 1,562 | 825 | |||
| Bio | - | - | 500 | 367 | |||
| Layer | Hyper-Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Word Embedding | Bart-large | 1,024 |
| HCA-SA Encoder | layer | 12 |
| head | 16 | |
| 0.5 | ||
| 0.8 | ||
| 1 | ||
| Decoder | layer | 12 |
| head | 16 | |
| HCA-CL Strategy | 500 | |
| 1,500 | ||
| Trainer | optimizer | RAdam |
| weight decay | 4e-3 | |
| loss function | Cross-entropy | |
| learning rate | 5e-5 | |
| batch size | 500 | |
| dropout | 0.25 | |
| maximum epochs | 30 | |
| Prediction | beam size | 5 |
| Environment | Value |
|---|---|
| Hardware | |
| CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) Silver 4216 CPU @ 2.10GHz |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX 2080Ti (11G) |
| Memory | 64 GB |
| Software | |
| Python | 3.8.16 |
| Pytorch | 1.13.0 |
| Anaconda | 4.10.1 |
| CUDA | 11.0 |
| IDE | PyCharm 2022.2.3 |
| Model | Feat. | Smatch | Structure-Dependent | Structure-Independent | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unlab. | Reent. | SRL | NoWSD | Conc. | Wiki. | NER | Neg. | ||||
| AMR 2.0 | AMR-gs (2020) [14] | - | 78.7 | 81.5 | 63.8 | 74.5 | 79.2 | 88.1 | 81.3 | 87.1 | 66.1 |
| APT (2021) [41] | - | 81.7 | 85.5 | 71.1 | 80.8 | 82.3 | 88.7 | 78.8 | 88.5 | 69.7 | |
| StructBART (2021) [42] | - | 84.3 | 87.9 | 74.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HCL (2022) [18] | - | 84.3 | 87.7 | 74.5 | 83.2 | 85.0 | 90.2 | 84.0 | 91.6 | 75.9 | |
| ANCES (2022) [17] | - | 84.8 | 88.1 | 75.1 | 83.4 | 85.3 | 90.5 | 84.1 | 91.8 | 74.0 | |
| HGAN (2022) [20] | DP | 84.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HGAN (2022) [20] | DP,SRL | 84.9 | 87.8 | 73.9 | 83.0 | 85.5 | 90.8 | 84.6 | 91.9 | 74.7 | |
| SPRING (2021) [15] | - | 83.8 | 86.1 | 70.8 | 79.6 | 84.4 | 90.2 | 84.3 | 90.6 | 74.4 | |
| Ours | HCA | 84.5 | 87.0 | 72.5 | 83.5 | 84.5 | 90.7 | 84.4 | 91.2 | 75.2 | |
| AMR 3.0 | AMR-gs (2020) [14] | - | 78.0 | 81.9 | 63.7 | 73.2 | 78.5 | 88.5 | 75.7 | 83.7 | 68.9 |
| APT (2021) [41] | - | 80.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| StructBART (2021) [42] | - | 83.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HCL (2022) [18] | - | 83.7 | 86.9 | 73.9 | 82.4 | 84.2 | 89.5 | 82.6 | 89.0 | 73.0 | |
| ANCES (2022) [17] | - | 83.5 | 86.6 | 74.2 | 82.2 | 84.0 | 89.5 | 81.5 | 88.9 | 72.6 | |
| HGAN (2022) [20] | DP | 83.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HGAN (2022) [20] | DP,SRL | 83.9 | 86.5 | 73.0 | 82.2 | 84.3 | 90.2 | 83.0 | 89.2 | 73.2 | |
| SPRING (2021) [15] | - | 83.0 | 85.4 | 70.4 | 78.9 | 83.5 | 89.8 | 82.7 | 87.2 | 73.0 | |
| Ours | HCA | 83.7 | 86.6 | 72.2 | 82.8 | 83.4 | 90.5 | 82.6 | 88.0 | 73.8 | |
| New3 | TLP | Bio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPRING (2022) [15] | 73.7 | 77.3 | 59.7 |
| HCL (2022) [18] | 75.3 | 78.2 | 61.1 |
| HGAN (2022) [20] | 76.0 | 79.2 | 61.6 |
| Ours | 76.0 | 78.0 | 62.3 |
| Model | Smatch | Unlab. | Reent. | SRL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPRING (2021) [15] | 83.8 | 86.1 | 70.8 | 79.6 | |
| Ours | Full | 84.5 | 87.0 | 72.5 | 83.5 |
| w/o VisMask | 84.1 | 86.5 | 70.9 | 81.2 | |
| w/o ClauRel | 84.4 | 86.8 | 72.4 | 81.5 | |
| w/o CN | 84.2 | 86.7 | 72.4 | 83.4 | |
| w/o TD | 84.5 | 87.0 | 72.5 | 83.4 | |
| w/o CN,TD | 84.2 | 86.7 | 72.4 | 83.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





