Submitted:
03 August 2023
Posted:
04 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction of the Notch signaling pathway
2. A brief history of Notch signaling studies in Drosophila
3. Notch signaling in insect embryo development
4. Notch signaling in insect wing development and patterning
5. Notch signaling in insect leg development
6. Notch signaling in insect reproduction
7. Notch signaling in insect stress responses
8. Notch signaling in less studied but more interesting tissues
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, S.J. Notch signalling in context. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2016, 17, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, E.C. Notch signaling: control of cell communication and cell fate. Development 2004, 131, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovall, R.A.; Gebelein, B.; Sprinzak, D.; Kopan, R. The Canonical Notch Signaling Pathway: Structural and Biochemical Insights into Shape, Sugar, and Force. Dev Cell 2017, 41, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, N.; Sharma, V.; Mutsuddi, M.; Mukherjee, A. Notch signaling: Multifaceted role in development and disease. FEBS J 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique, D.; Schweisguth, F. Mechanisms of Notch signaling: a simple logic deployed in time and space. Development 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazave, E.; Lapebie, P.; Richards, G.S.; Brunet, F.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Degnan, B.M.; Borchiellini, C.; Vervoort, M.; Renard, E. Origin and evolution of the Notch signalling pathway: an overview from eukaryotic genomes. BMC Evol Biol 2009, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babonis, L.S.; Martindale, M.Q. Phylogenetic evidence for the modular evolution of metazoan signalling pathways. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachakis, D.; Papageorgiou, L.; Papadaki, A.; Georga, M.; Kossida, S.; Eliopoulos, E. An updated evolutionary study of the Notch family reveals a new ancient origin and novel invariable motifs as potential pharmacological targets. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimento, A.; D'Amico, M.; Pezzi, V.; De Amicis, F. Notch Signaling in Breast Tumor Microenvironment as Mediator of Drug Resistance. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Assoro, A.B.; Leon-Ferre, R.; Braune, E.B.; Lendahl, U. Roles of Notch Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, P.; Lim, J.S.; Sage, J.; Aifantis, I. From fly wings to targeted cancer therapies: a centennial for notch signaling. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Lin, W.; Long, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K.; Chu, Q. Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Fan, L.; Zhao, L.; Su, Y. The interaction of Notch and Wnt signaling pathways in vertebrate regeneration. Cell Regen 2021, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannouli, F. Endocytosis at the Crossroad of Polarity and Signaling Regulation: Learning from Drosophila melanogaster and Beyond. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesel, V.A.; Stan, S.D. Modulation of Notch Signaling Pathway by Bioactive Dietary Agents. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S.; Muskavitch, M.A. Notch: the past, the present, and the future. Curr Top Dev Biol 2010, 92, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, Y.S.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, J.S. Aberrant Notch Signaling Pathway as a Potential Mechanism of Central Precocious Puberty. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y. Biological Significance of NOTCH Signaling Strength. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 652273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprinzak, D.; Blacklow, S.C. Biophysics of Notch Signaling. Annu Rev Biophys 2021, 50, 157–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballhause, T.M.; Jiang, S.; Baranowsky, A.; Brandt, S.; Mertens, P.R.; Frosch, K.H.; Yorgan, T.; Keller, J. Relevance of Notch Signaling for Bone Metabolism and Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, T.H. Sex limited inheritance in Drosophila. Science 1910, 32, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, T.H. The theory of the gene. Am Nat 1917, 51, 513–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.H.; Bridges, C.B. Sex-linked inheritance in Drosophila; Carnegie Institution of Washington: Washington, 1916; pp. 87, 81 p. incl. illus., tables. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, T.H. The Origin of Nine Wing Mutations in Drosophila. Science 1911, 33, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.S. The analysis of a case of continuous variation in Drosophila by a study of its linkage relations. Am Nat 1914, 48, 712–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, O.L. Character Changes Caused by Mutation of an Entire Region of a Chromosome in Drosophila. Genetics 1919, 4, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruharsha, K.G.; Kankel, M.W.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. The Notch signalling system: recent insights into the complexity of a conserved pathway. Nat Rev Genet 2012, 13, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S.; Muskavitch, M.A.; Yedvobnick, B. Molecular cloning of Notch, a locus affecting neurogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1983, 80, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, S.; Lockett, T.J.; Young, M.W. The Notch locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 1983, 34, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, K.A.; Johansen, K.M.; Xu, T.; Artavanistsakonas, S. Nucleotide-Sequence from the Neurogenic Locus Notch Implies a Gene-Product That Shares Homology with Proteins Containing Egf-Like Repeats. Cell 1985, 43, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, S.; Kelley, M.R.; Young, M.W. Sequence of the Notch Locus of Drosophila-Melanogaster - Relationship of the Encoded Protein to Mammalian Clotting and Growth-Factors. Mol Cell Biol 1986, 6, 3094–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, S.J. Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006, 7, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamfirescu, A.M.; Yatsenko, A.S.; Shcherbata, H.R. Notch signaling sculpts the stem cell niche. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 1027222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.L.; Heckscher, E.S. Development of motor circuits: From neuronal stem cells and neuronal diversity to motor circuit assembly. Curr Top Dev Biol 2021, 142, 409–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Su, Y. Regulation of Drosophila Hematopoiesis in Lymph Gland: From a Developmental Signaling Point of View. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Edgar, B.A. Intestinal stem cells in the adult Drosophila midgut. Exp Cell Res 2011, 317, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barad, O.; Hornstein, E.; Barkai, N. Robust selection of sensory organ precursors by the Notch-Delta pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2011, 23, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udolph, G. Notch signaling and the generation of cell diversity in Drosophila neuroblast lineages. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012, 727, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigglesworth, V.B. Local and general factors in the development of "pattern" in Rhodnius prolixus (hemiptera). J Exp Biol 1940, 17, 180–U189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummery-Widmer, J.L.; Yamazaki, M.; Stoeger, T.; Novatchkova, M.; Bhalerao, S.; Chen, D.; Dietzl, G.; Dickson, B.J.; Knoblich, J.A. Genome-wide analysis of Notch signalling in Drosophila by transgenic RNAi. Nature 2009, 458, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saj, A.; Arziman, Z.; Stempfle, D.; van Belle, W.; Sauder, U.; Horn, T.; Durrenberger, M.; Paro, R.; Boutros, M.; Merdes, G. A combined ex vivo and in vivo RNAi screen for notch regulators in Drosophila reveals an extensive notch interaction network. Dev Cell 2010, 18, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Su, Y.; Du, J.; Zhu, A.J. A targeted in vivo RNAi screen reveals deubiquitinases as new regulators of Notch signaling. G3 (Bethesda) 2012, 2, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, D.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J. Use of FLP/FRT System to Screen for Notch Signaling Regulators in the Drosophila Wing. Methods Mol Biol 2022, 2472, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Mo, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Yin, H.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J. A genetic mosaic screen identifies genes modulating Notch signaling in Drosophila. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0203781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Sachan, N.; Mutsuddi, M.; Mukherjee, A. Somatic Clonal Analyses Using FLP/FRT and MARCM System to Understand Notch Signaling Mechanism and Its Regulation. Methods Mol Biol 2022, 2472, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulson, D.F. Chromosomal Deficiencies and the Embryonic Development of Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1937, 23, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulson, D.F. The effects of certain X-chromosome deficiencies on the embryonic development of drosophila melanogaster. J. Exp. Zool. 1940, 83, 271–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, R.; Dietrich, U.; Jimenez, F.; Campos-Ortega, J.A. Mutations of early neurogenesis in Drosophila. Wilehm Roux Arch Dev Biol 1981, 190, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, R.; Jimenez, F.; Dietrich, U.; Campos-Ortega, J.A. On the phenotype and development of mutants of early neurogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Wilehm Roux Arch Dev Biol 1983, 192, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrampour, S.; Thor, S. The Five Faces of Notch Signalling During Drosophila melanogaster Embryonic CNS Development. Adv Exp Med Biol 2020, 1218, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeath, J.B.; Thor, S. Genetic control of Drosophila nerve cord development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2003, 13, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, S.T. Drosophila Embryonic CNS Development: Neurogenesis, Gliogenesis, Cell Fate, and Differentiation. Genetics 2019, 213, 1111–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartenstein, V.; Wodarz, A. Initial neurogenesis in Drosophila. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 2013, 2, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, W.M. Neuroblasts in the Arthropod embryo. J. Morphol. 1891, 4, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, J.W.; Ball, E.E. Patterns of embryonic neurogenesis in a primitive wingless insect, the silverfish, Ctenolepisma longicaudata: comparison with those seen in flying insects. Dev Genes Evol 1998, 208, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.B.; Bastiani, M.J.; Bate, M.; Goodman, C.S. From grasshopper to Drosophila: a common plan for neuronal development. Nature 1984, 310, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate, C.M. Embryogenesis of an insect nervous system. I. A map of the thoracic and abdominal neuroblasts in Locusta migratoria. J Embryol Exp Morphol 1976, 35, 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Biffar, L.; Stollewerk, A. Conservation and evolutionary modifications of neuroblast expression patterns in insects. Dev Biol 2014, 388, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, C.Q.; Goodman, C.S. Early events in insect neurogenesis. II. The role of cell interactions and cell lineage in the determination of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol 1985, 111, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, C.Q.; Goodman, C.S. Early events in insect neurogenesis. I. Development and segmental differences in the pattern of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol 1985, 111, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartenstein, V.; Campos-Ortega, J.A. Early neurogenesis in wild-type Drosophila melanogaster. Wilehm Roux Arch Dev Biol 1984, 193, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwada, J.Y.; Goodman, C.S. Neuronal determination during embryonic development of the grasshopper nervous system. Dev Biol 1985, 110, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, R.; Technau, G.M. Early steps in building the insect brain: neuroblast formation and segmental patterning in the developing brain of different insect species. Arthropod Struct Dev 2003, 32, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, R.; Technau, G.M.; Breidbach, O. Spatial and temporal pattern of neuroblasts, proliferation, and Engrailed expression during early brain development in Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera). Arthropod Struct Dev 2003, 32, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, A.P.; Delgado, M.J.; Lavore, A. Empty-spiracles is maternally expressed and essential for neurodevelopment and early embryo determination in Rhodnius prolixus. Dev Biol 2022, 490, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghert, P.H.; Doe, C.Q.; Goodman, C.S. Cell determination and regulation during development of neuroblasts and neurones in grasshopper embryo. Nature 1984, 307, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, S.; Chen, C.L.; Sproston, C.J.; Kondo, S.; Ramdya, P.; Williams, D.W. Extensive and diverse patterns of cell death sculpt neural networks in insects. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyan, G.; Williams, L. Embryonic development of the insect central complex: insights from lineages in the grasshopper and Drosophila. Arthropod Struct Dev 2011, 40, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stollewerk, A. A flexible genetic toolkit for arthropod neurogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2016, 371, 20150044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mito, T.; Shinmyo, Y.; Kurita, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ohuchi, H.; Noji, S. Ancestral functions of Delta/Notch signaling in the formation of body and leg segments in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Development 2011, 138, 3823–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, F.; Ewen-Campen, B.; Akam, M.; Extavour, C.G. Notch/Delta signalling is not required for segment generation in the basally branching insect Gryllus bimaculatus. Development 2011, 138, 5015–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueyo, J.I.; Lanfear, R.; Couso, J.P. Ancestral Notch-mediated segmentation revealed in the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 16614–16619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kux, K.; Kiparaki, M.; Delidakis, C. The two Tribolium E(spl) genes show evolutionarily conserved expression and function during embryonic neurogenesis. Mech Dev 2013, 130, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlatter, R.; Maier, D. The Enhancer of split and Achaete-Scute complexes of Drosophilids derived from simple ur-complexes preserved in mosquito and honeybee. BMC Evol Biol 2005, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeder, M.L.; Polansky, B.J.; Robson, B.E.; Eastman, D.A. Phylogenetic footprinting analysis in the upstream regulatory regions of the Drosophila enhancer of split genes. Genetics 2007, 177, 1377–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, E.J.; Dearden, P.K. Evolution of a genomic regulatory domain: the role of gene co-option and gene duplication in the Enhancer of split complex. Genome Res 2010, 20, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.H.; Kuehl, J.V.; Wilkinson, G.S. The Enhancer of split complex arose prior to the diversification of schizophoran flies and is strongly conserved between Drosophila and stalk-eyed flies (Diopsidae). BMC Evol Biol 2011, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delidakis, C.; Monastirioti, M.; Magadi, S.S. E(spl): genetic, developmental, and evolutionary aspects of a group of invertebrate Hes proteins with close ties to Notch signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol 2014, 110, 217–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Lv, Z.; Yu, W.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, Z. Cloning and expression characteristics of the notch-associated gene BmE(spl)mgamma from silkworm, Bombyx mori. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2014, 173, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, P.K. Origin and evolution of the enhancer of split complex. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Tanemura, M.; Yoshida, A. Estimation of neuroblast numbers in insect neurogenesis using the lateral inhibition hypothesis of cell differentiation. Development 1990, 110, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.; Peel, A.D.; Akam, M. Arthropod segmentation. Development 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.K.; Oates, A.C. Delta-Notch signalling in segmentation. Arthropod Struct Dev 2017, 46, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.K.; Patel, N.H. Short, long, and beyond: molecular and embryological approaches to insect segmentation. Annu Rev Entomol 2002, 47, 669–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusslein-Volhard, C.; Wieschaus, E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 1980, 287, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesebro, J.E.; Pueyo, J.I.; Couso, J.P. Interplay between a Wnt-dependent organiser and the Notch segmentation clock regulates posterior development in Periplaneta americana. Biol Open 2013, 2, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menne, T.V.; Klambt, C. The formation of commissures in the Drosophila CNS depends on the midline cells and on the Notch gene. Development 1994, 120, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadigan, K.M.; Nusse, R. wingless signaling in the Drosophila eye and embryonic epidermis. Development 1996, 122, 2801–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; McKelvey, B.H.; van der Heide, S.; Dearden, P.K. Notch signaling does not regulate segmentation in the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Dev Genes Evol 2010, 220, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auman, T.; Vreede, B.M.I.; Weiss, A.; Hester, S.D.; Williams, T.A.; Nagy, L.M.; Chipman, A.D. Dynamics of growth zone patterning in the milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus. Development 2017, 144, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auman, T.; Chipman, A.D. Growth zone segmentation in the milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus sheds light on the evolution of insect segmentation. BMC Evol Biol 2018, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahi, R.; Chipman, A.D. Blastoderm segmentation in Oncopeltus fasciatus and the evolution of insect segmentation mechanisms. Proc Biol Sci 2016, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, M.; Marques-Souza, H.; Bayer, T.; Tautz, D. The role of the segmentation gene hairy in Tribolium. Dev Genes Evol 2008, 218, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panin, V.M.; Papayannopoulos, V.; Wilson, R.; Irvine, K.D. Fringe modulates Notch-ligand interactions. Nature 1997, 387, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, D.J.; Panin, V.M.; Johnston, S.H.; Chen, J.; Shao, L.; Wilson, R.; Wang, Y.; Stanley, P.; Irvine, K.D.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; et al. Fringe is a glycosyltransferase that modifies Notch. Nature 2000, 406, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrard, Y.A.; Lun, Y.; Aulehla, A.; Gan, L.; Johnson, R.L. lunatic fringe is an essential mediator of somite segmentation and patterning. Nature 1998, 394, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gridley, T. Defects in somite formation in lunatic fringe-deficient mice. Nature 1998, 394, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, P.; Akam, M. A role for Fringe in segment morphogenesis but not segment formation in the grasshopper, Schistocerca gregaria. Dev Genes Evol 2000, 210, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Functional analyses in the silkworm, Bombyx mori, support a role for Notch signaling in appendage development but not the groucho-dependent pair-rule process. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 2012, 318, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Bmdelta phenotype implies involvement of Notch signaling in body segmentation and appendage development of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Arthropod Struct Dev 2013, 42, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoyasu, Y. What crustaceans can tell us about the evolution of insect wings and other morphologically novel structures. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2021, 69, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, J.; Rosova, K.; Krzeminska, E.; Krzeminski, W.; Nel, A.; Engel, M.S. Abdominal serial homologues of wings in Paleozoic insects. Curr Biol 2022, 32, 3414–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohde, T.; Mito, T.; Niimi, T. A hemimetabolous wing development suggests the wing origin from lateral tergum of a wingless ancestor. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, S.S. Wing vein patterning in Drosophila and the analysis of intercellular signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2007, 23, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, B.K.; Irvine, K.D. The wing imaginal disc. Genetics 2022, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Benjumea, F.J.; Cohen, S.M. Serrate signals through Notch to establish a Wingless-dependent organizer at the dorsal/ventral compartment boundary of the Drosophila wing. Development 1995, 121, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Celis, J.F.; Garcia-Bellido, A.; Bray, S.J. Activation and function of Notch at the dorsal-ventral boundary of the wing imaginal disc. Development 1996, 122, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, D.; Feger, G.; Younger-Shepherd, S.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Delta is a ventral to dorsal signal complementary to Serrate, another Notch ligand, in Drosophila wing formation. Genes Dev 1996, 10, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.D.; Wieschaus, E. fringe, a Boundary-specific signaling molecule, mediates interactions between dorsal and ventral cells during Drosophila wing development. Cell 1994, 79, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Irvine, K.D.; Carroll, S.B. Cell recognition, signal induction, and symmetrical gene activation at the dorsal-ventral boundary of the developing Drosophila wing. Cell 1995, 82, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, R.J.; Gu, Y.; Hukriede, N.A. Serrate-mediated activation of Notch is specifically blocked by the product of the gene fringe in the dorsal compartment of the Drosophila wing imaginal disc. Development 1997, 124, 2973–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.; Arias, A.M. Interactions among Delta, Serrate and Fringe modulate Notch activity during Drosophila wing development. Development 1998, 125, 2951–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckner, K.; Perez, L.; Clausen, H.; Cohen, S. Glycosyltransferase activity of Fringe modulates Notch-Delta interactions. Nature 2000, 406, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, S.; Freeman, M. The notch signalling regulator fringe acts in the Golgi apparatus and requires the glycosyltransferase signature motif DXD. Curr Biol 2000, 10, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Charng, W.L.; Rana, N.A.; Kakuda, S.; Jaiswal, M.; Bayat, V.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, K.; Sandoval, H.; David, G.; et al. A mutation in EGF repeat-8 of Notch discriminates between Serrate/Jagged and Delta family ligands. Science 2012, 338, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Harvey, B.M.; Lopez, M.F.; Ito, A.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Glycosylation of Specific Notch EGF Repeats by O-Fut1 and Fringe Regulates Notch Signaling in Drosophila. Cell Rep 2019, 29, 2054–2066 e2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Benjumea, F.J.; Cohen, S.M. Interaction between dorsal and ventral cells in the imaginal disc directs wing development in Drosophila. Cell 1993, 75, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Celis, J.F.; Bray, S. Feed-back mechanisms affecting Notch activation at the dorsoventral boundary in the Drosophila wing. Development 1997, 124, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.J.; Gu, Y.; Li, W.X.; Fleming, R.J. Multiple signaling pathways and a selector protein sequentially regulate Drosophila wing development. Development 2004, 131, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBon, L.; Lee, T.V.; Sprinzak, D.; Jafar-Nejad, H.; Elowitz, M.B. Fringe proteins modulate Notch-ligand cis and trans interactions to specify signaling states. Elife 2014, 3, e02950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couso, J.P.; Knust, E.; Martinez Arias, A. Serrate and wingless cooperate to induce vestigial gene expression and wing formation in Drosophila. Curr Biol 1995, 5, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulifson, E.J.; Blair, S.S. Notch regulates wingless expression and is not required for reception of the paracrine wingless signal during wing margin neurogenesis in Drosophila. Development 1995, 121, 2813–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Sebring, A.; Esch, J.J.; Kraus, M.E.; Vorwerk, K.; Magee, J.; Carroll, S.B. Integration of positional signals and regulation of wing formation and identity by Drosophila vestigial gene. Nature 1996, 382, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, C.J.; Cohen, S.M. A hierarchy of cross-regulation involving Notch, wingless, vestigial and cut organizes the dorsal/ventral axis of the Drosophila wing. Development 1996, 122, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulifson, E.J.; Micchelli, C.A.; Axelrod, J.D.; Perrimon, N.; Blair, S.S. wingless refines its own expression domain on the Drosophila wing margin. Nature 1996, 384, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micchelli, C.A.; Rulifson, E.J.; Blair, S.S. The function and regulation of cut expression on the wing margin of Drosophila: Notch, Wingless and a dominant negative role for Delta and Serrate. Development 1997, 124, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, M.J.; Eastman, D.S.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. Cell proliferation control by Notch signaling in Drosophila development. Development 1998, 125, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.; Arias, A.M. The vestigial gene product provides a molecular context for the interpretation of signals during the development of the wing in Drosophila. Development 1999, 126, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldez, A.J.; Cohen, S.M. Wingless and Notch signaling provide cell survival cues and control cell proliferation during wing development. Development 2003, 130, 6533–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafel, N.; Milan, M. Notch signalling coordinates tissue growth and wing fate specification in Drosophila. Development 2008, 135, 3995–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Bryant, J.; Jevitt, A.; Calvin, G.; Deng, W.M. The Ecdysone and Notch Pathways Synergistically Regulate Cut at the Dorsal-Ventral Boundary in Drosophila Wing Discs. J Genet Genomics 2016, 43, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturtevant, M.A.; Bier, E. Analysis of the genetic hierarchy guiding wing vein development in Drosophila. Development 1995, 121, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, S.S.; Jacobsen, T.L.; Muskavitch, M.A. Feedback regulation is central to Delta-Notch signalling required for Drosophila wing vein morphogenesis. Development 1997, 124, 3283–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Celis, J.F.; Bray, S.; Garcia-Bellido, A. Notch signalling regulates veinlet expression and establishes boundaries between veins and interveins in the Drosophila wing. Development 1997, 124, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Celis, J.F. Pattern formation in the Drosophila wing: The development of the veins. Bioessays 2003, 25, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozatier, M.; Glise, B.; Khemici, V.; Vincent, A. Vein-positioning in the Drosophila wing in response to Hh; new roles of Notch signaling. Mech Dev 2003, 120, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Dambly-Chaudiere, C.; Ghysen, A. The emergence of sense organs in the wing disc of Drosophila. Development 1991, 111, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troost, T.; Binshtok, U.; Sprinzak, D.; Klein, T. Cis-inhibition suppresses basal Notch signaling during sensory organ precursor selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2214535120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweisguth, F. Asymmetric cell division in the Drosophila bristle lineage: from the polarization of sensory organ precursor cells to Notch-mediated binary fate decision. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 2015, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J. The ATPase TER94 regulates Notch signaling during Drosophila wing development. Biol Open 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J. The Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme UbcD1 is Required for Notch Signaling Activation During Drosophila Wing Development. Front Genet 2021, 12, 770853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, X.; Shen, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. The mitochondrial ribosomal protein mRpL4 regulates Notch signaling. EMBO Rep 2023, 24, e55764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Breugel, F.M. The action of the Notch locus in Drosophila hydei. Genetica 1971, 42, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Breugel, F.M.; Vermet-Rozeboom, E.; Gloor, H. Phenocopies in Drosophila hydei induced by actinomycin D and fluorouracil with special reference to Notch mutants. Wilehm Roux Arch Dev Biol 1975, 178, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breugel, F.M.; van den Broek, H.C.; Grond, C.; den Hertog, F. Bristle patterns, clones and cell competition along the anterior margin of Notch wings of Drosophila hydei. Wilehm Roux Arch Dev Biol 1981, 190, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Breugel, F.M.; Langhout, B.V. The NOTCH Locus of DROSOPHILA HYDEI: Alleles, Phenotypes and Functional Organization. Genetics 1983, 103, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubenko, I.S.; Subbota, R.P.; Kozereretskaia, I.A.; Vagin Iu, V. [The Delta locus in Drosophila virilis: alleles, wing phenotypes and genetic interactions]. Tsitol Genet 1998, 32, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gubenko, I.S.; Zelentsova, E.S.; Kozeretskaia, I.A.; Bagin Iu, V. [Genetic characteristics of the wing mutation Odd(22) and its interaction with alleles of the Delta locus in Drosophila virilis]. Genetika 2000, 36, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Rybtsova, N.N.; Zelentsova, E.S.; Lezin, G.T.; Evgen’ev, M.B.; Korochkin, L.I. Comparison of the structure and embryonic expression of Delta in Drosophila virilis and D. melanogaster. Molecular Biology 2000, 34, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubenko, I.S.; Subbota, R.P.; Zelentsova, E.S. Notch122, mutation of Abruptex-type Notch locus in Drosophila virilis: Peculiarities of genetic interactions. Cytol Genet 2010, 44, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyoshi, T. Some new mutants and linkage groups of the house fly. J Econ Entomol 1960, 53, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, C.A. , Wagoner, D. E. Some New Mutants of House Flies and Their Linkage Groups and Map positions. J Econ Entomol 1970, 63, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiroyoshi, T. Some new mutants and revised linkage maps of the housefly, Musca domestica L. Japan J Genetics 1977, 52, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Warren, W.C.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Bopp, D.; Clark, A.G.; Giers, S.D.; Hediger, M.; Jones, A.K.; Kasai, S.; Leichter, C.A.; et al. Genome of the house fly, Musca domestica L., a global vector of diseases with adaptations to a septic environment. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, S.D.; Kohlbrenner, T.; Ippolito, D.; Meccariello, A.; Burger, A.; Mosimann, C.; Saccone, G.; Bopp, D. CRISPR-Cas9 targeted disruption of the yellow ortholog in the housefly identifies the brown body locus. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G. , Whitten, M., Konovalov, C., Arnold, J., Maffi, G.. Autosomal genetic maps of the Australian Sheep Blowfly, Lucilia cuprina dorsalis R.-D. (Diptera: Calliphoridae), and possible correlations with the linkage maps of Musca domestica L. and Drosophila melanogaster (Mg.). Genet Res 1981, 37, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.G.; Weller, G.L.; Bedo, D.G. Homozygous-viable pericentric inversions for genetic control of Lucilia Cuprina. Theor Appl Genet 1991, 82, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, G.L.; Foster, G.G. Genetic maps of the sheep blowfly Lucilia cuprina: linkage-group correlations with other dipteran genera. Genome 1993, 36, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.G.; Game, A.Y.; Chen, Z.; Williams, T.J.; Goodall, S.; Yen, J.L.; McKenzie, J.A.; Batterham, P. Scalloped wings is the Lucilia cuprina Notch homologue and a candidate for the modifier of fitness and asymmetry of diazinon resistance. Genetics 1996, 143, 1321–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Newsome, T.; McKenzie, J.A.; Batterham, P. Molecular characterization of the Notch homologue from the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 1998, 28, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Hojyo, T. Developmental profiles of wing imaginal discs of flugellos(fl), a wingless mutant of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev Genes Evol 1997, 207, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojyo, T.; Fujiwara, H. Reciprocal transplantation of wing discs between a wing deficient mutant (fl) and wild type of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev Growth Differ 1997, 39, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, T.; Fujiwara, H. Expression of ecdysteroid-regulated genes is reduced specifically in the wing discs of the wing-deficient mutant (fl) of Bombyx mori. Dev Genes Evol 2000, 210, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.M.; Fujiwara, H. Identification and characterization of genes abnormally expressed in wing-deficient mutant (flugellos) of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2002, 32, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Matsunaga, T.M.; Futahashi, R.; Kojima, T.; Mita, K.; Banno, Y.; Fujiwara, H. Positional cloning of a Bombyx wingless locus flugellos (fl) reveals a crucial role for fringe that is specific for wing morphogenesis. Genetics 2008, 179, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kango-Singh, M.; Singh, A.; Gopinathan, K.P. The wings of Bombyx mori develop from larval discs exhibiting an early differentiated state: a preliminary report. J Biosci 2001, 26, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Ge, X.; Li, Z.; Zeng, B.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Shang, P.; James, A.A.; Huang, Y.; Tan, A. MiR-2 family targets awd and fng to regulate wing morphogenesis in Bombyx mori. RNA Biol 2015, 12, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Abe, H.; Katsuma, S.; Shimada, T. Identification and characterization of the fusion transcript, composed of the apterous homolog and a putative protein phosphatase gene, generated by 1.5-Mb interstitial deletion in the vestigial (Vg) mutant of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2011, 41, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.B.; Gates, J.; Keys, D.N.; Paddock, S.W.; Panganiban, G.E.; Selegue, J.E.; Williams, J.A. Pattern formation and eyespot determination in butterfly wings. Science 1994, 265, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.D.; Serfas, M.S. Butterfly wing pattern evolution is associated with changes in a Notch/Distal-less temporal pattern formation process. Curr Biol 2004, 14, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.D.; Chen, P.H.; Frederik Nijhout, H. Cryptic variation in butterfly eyespot development: the importance of sample size in gene expression studies. Evol Dev 2007, 9, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenko, S.V.; Marialva, M.S.; Beldade, P. Involvement of the conserved Hox gene Antennapedia in the development and evolution of a novel trait. Evodevo 2011, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, L.T.; Saenko, S.V.; Keller, R.A.; Jeronimo, M.A.; Brakefield, P.M.; Descimon, H.; Wahlberg, N.; Beldade, P. Evolutionary history of the recruitment of conserved developmental genes in association to the formation and diversification of a novel trait. BMC Evol Biol 2012, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.C.; Tong, X.L.; Gall, L.F.; Piel, W.H.; Monteiro, A. A single origin for nymphalid butterfly eyespots followed by widespread loss of associated gene expression. PLoS Genet 2012, 8, e1002893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.C.; Ramos, D.; Prudic, K.L.; Monteiro, A. Temporal gene expression variation associated with eyespot size plasticity in Bicyclus anynana. PLoS One 2013, 8, e65830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connahs, H.; Rhen, T.; Simmons, R.B. Transcriptome analysis of the painted lady butterfly, Vanessa cardui during wing color pattern development. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, J.L.Q.; Murugesan, S.N.; Wheat, C.W.; Monteiro, A. The genetic basis of wing spots in Pieris canidia butterflies. BMC Genomics 2023, 24, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.D. Evidence for Notch-mediated lateral inhibition in organizing butterfly wing scales. Dev Genes Evol 2004, 214, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, T.; Bergsten, J.; Levkanicova, Z.; Papadopoulou, A.; John, O.S.; Wild, R.; Hammond, P.M.; Ahrens, D.; Balke, M.; Caterino, M.S.; et al. A comprehensive phylogeny of beetles reveals the evolutionary origins of a superradiation. Science 2007, 318, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoyasu, Y.; Arakane, Y.; Kramer, K.J.; Denell, R.E. Repeated co-options of exoskeleton formation during wing-to-elytron evolution in beetles. Curr Biol 2009, 19, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravisankar, P.; Lai, Y.T.; Sambrani, N.; Tomoyasu, Y. Comparative developmental analysis of Drosophila and Tribolium reveals conserved and diverged roles of abrupt in insect wing evolution. Dev Biol 2016, 409, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Ott, U.; Lynch, J.A. Emerging developmental genetic model systems in holometabolous insects. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2016, 39, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingler, M.; Bucher, G. The red flour beetle T. castaneum: elaborate genetic toolkit and unbiased large scale RNAi screening to study insect biology and evolution. Evodevo 2022, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.B.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Y.; Hua, H.X. Notch is an alternative splicing gene in brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 2022, 110, e21894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wei, W.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.; An, C. De novo transcriptome analysis of wing development-related signaling pathways in Locusta migratoria manilensis and Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenee). PLoS One 2014, 9, e106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feindt, W.; Oppenheim, S.J.; DeSalle, R.; Goldstein, P.Z.; Hadrys, H. Transcriptome profiling with focus on potential key genes for wing development and evolution in Megaloprepus caerulatus, the damselfly species with the world's largest wings. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0189898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba, S.; Estella, C. Role of Notch Signaling in Leg Development in Drosophila melanogaster. Adv Exp Med Biol 2020, 1218, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellenbarger, D.L.; Mohler, J.D. Temperature-sensitive periods and autonomy of pleiotropic effects of l(1)Nts1, a conditional notch lethal in Drosophila. Dev Biol 1978, 62, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parody, T.R.; Muskavitch, M.A. The pleiotropic function of Delta during postembryonic development of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1993, 135, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speicher, S.A.; Thomas, U.; Hinz, U.; Knust, E. The Serrate locus of Drosophila and its role in morphogenesis of the wing imaginal discs: control of cell proliferation. Development 1994, 120, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Celis, J.F.; Tyler, D.M.; de Celis, J.; Bray, S.J. Notch signalling mediates segmentation of the Drosophila leg. Development 1998, 125, 4617–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauskolb, C.; Irvine, K.D. Notch-mediated segmentation and growth control of the Drosophila leg. Dev Biol 1999, 210, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, S.A.; Klein, T.; Arias, A.M.; Couso, J.P. Composite signalling from Serrate and Delta establishes leg segments in Drosophila through Notch. Development 1999, 126, 2993–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Agrawal, N.; Banerjee, S.; Sardesai, D.; Dalal, J.S.; Bhojwani, J.; Sinha, P. Spatial regulation of DELTA expression mediates NOTCH signalling for segmentation of Drosophila legs. Mech Dev 2001, 105, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzanne, M. Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in leg joint morphogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2016, 55, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerber, B.; Monge, I.; Mueller, M.; Mitchell, P.J.; Cohen, S.M. The AP-2 transcription factor is required for joint formation and cell survival in Drosophila leg development. Development 2001, 128, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckles, G.R.; Rauskolb, C.; Villano, J.L.; Katz, F.N. Four-jointed interacts with dachs, abelson and enabled and feeds back onto the Notch pathway to affect growth and segmentation in the Drosophila leg. Development 2001, 128, 3533–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Celis Ibeas, J.M.; Bray, S.J. Bowl is required downstream of Notch for elaboration of distal limb patterning. Development 2003, 130, 5943–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, I.; Green, R.B.; Dunaevsky, O.; Lengyel, J.A.; Rauskolb, C. The odd-skipped family of zinc finger genes promotes Drosophila leg segmentation. Dev Biol 2003, 263, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G. Regulation of gene expression in the distal region of the Drosophila leg by the Hox11 homolog, C15. Dev Biol 2005, 278, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanska, E.; Dansereau, D.A.; Svendsen, P.C.; Heslip, T.R.; Brook, W.J. dAP-2 and defective proventriculus regulate Serrate and Delta expression in the tarsus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genome 2007, 50, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, T.; Yorimitsu, T.; Kiritooshi, N.; Matsuzaki, F.; Nakagoshi, H. Notch signaling relieves the joint-suppressive activity of Defective proventriculus in the Drosophila leg. Dev Biol 2007, 312, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, L.; Hatini, V. Essential roles for lines in mediating leg and antennal proximodistal patterning and generating a stable Notch signaling interface at segment borders. Dev Biol 2009, 330, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pueyo, J.I.; Couso, J.P. Tarsal-less peptides control Notch signalling through the Shavenbaby transcription factor. Dev Biol 2011, 355, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capilla, A.; Johnson, R.; Daniels, M.; Benavente, M.; Bray, S.J.; Galindo, M.I. Planar cell polarity controls directional Notch signaling in the Drosophila leg. Development 2012, 139, 2584–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarner, A.; Manjon, C.; Edwards, K.; Steller, H.; Suzanne, M.; Sanchez-Herrero, E. The zinc finger homeodomain-2 gene of Drosophila controls Notch targets and regulates apoptosis in the tarsal segments. Dev Biol 2014, 385, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba, S.; Requena, D.; Jory, A.; Saiz, A.; Estella, C. The evolutionarily conserved transcription factor Sp1 controls appendage growth through Notch signaling. Development 2016, 143, 3623–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Shen, J. T-box transcription factors Dorsocross and optomotor-blind control Drosophila leg patterning in a functionally redundant manner. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2021, 129, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntur, A.R.; Venkatanarayan, A.; Gangula, S.; Lundell, M.J. Zfh-2 facilitates Notch-induced apoptosis in the CNS and appendages of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol 2021, 475, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T. Developmental mechanism of the tarsus in insect legs. Curr Opin Insect Sci 2017, 19, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba, S.; Estella, C. The bHLH-PAS transcription factor dysfusion regulates tarsal joint formation in response to Notch activity during drosophila leg development. PLoS Genet 2014, 10, e1004621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajiri, R.; Misaki, K.; Yonemura, S.; Hayashi, S. Dynamic shape changes of ECM-producing cells drive morphogenesis of ball-and-socket joints in the fly leg. Development 2010, 137, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajiri, R.; Misaki, K.; Yonemura, S.; Hayashi, S. Joint morphology in the insect leg: evolutionary history inferred from Notch loss-of-function phenotypes in Drosophila. Development 2011, 138, 4621–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, D.R.; Smith, F.W.; Jockusch, E.L. Extent With Modification: Leg Patterning in the Beetle Tribolium castaneum and the Evolution of Serial Homologs. G3 (Bethesda) 2012, 2, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemanowski, J.; Richter, T.; Dao, V.A.; Bucher, G. Notch signaling induces cell proliferation in the labrum in a regulatory network different from the thoracic legs. Dev Biol 2015, 408, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Diaz-Benjumea, F.J.; Cohen, S.M. Nubbin encodes a POU-domain protein required for proximal-distal patterning in the Drosophila wing. Development 1995, 121, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, F.J.; Garcia-Bellido, A. Proximo-distal specification in the wing disc of Drosophila by the nubbin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997, 94, 11405–11410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Popadic, A. Analysis of nubbin expression patterns in insects. Evol Dev 2004, 6, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrycaj, S.; Mihajlovic, M.; Mahfooz, N.; Couso, J.P.; Popadic, A. RNAi analysis of nubbin embryonic functions in a hemimetabolous insect, Oncopeltus fasciatus. Evol Dev 2008, 10, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchyn, N.; Chesebro, J.; Hrycaj, S.; Couso, J.P.; Popadic, A. Evolution of nubbin function in hemimetabolous and holometabolous insect appendages. Dev Biol 2011, 357, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yan, S.; Wang, D.; Shen, J. Hedgehog signaling regulates regenerative patterning and growth in Harmonia axyridis leg. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021, 78, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prpic, N.M.; Damen, W.G. Notch-mediated segmentation of the appendages is a molecular phylotypic trait of the arthropods. Dev Biol 2009, 326, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klusza, S.; Deng, W.M. At the crossroads of differentiation and proliferation: precise control of cell-cycle changes by multiple signaling pathways in Drosophila follicle cells. Bioessays 2011, 33, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, S. Drosophila oogenesis: coordinating germ line and soma. Curr Biol 2001, 11, R779–R781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruohola, H.; Bremer, K.A.; Baker, D.; Swedlow, J.R.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Role of neurogenic genes in establishment of follicle cell fate and oocyte polarity during oogenesis in Drosophila. Cell 1991, 66, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, L.B.; Kooh, P.J.; Muskavitch, M.A. Complex function and expression of Delta during Drosophila oogenesis. Genetics 1993, 133, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.K.; Holder, K.; Yost, C.; Giniger, E.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Expression of constitutively active Notch arrests follicle cells at a precursor stage during Drosophila oogenesis and disrupts the anterior-posterior axis of the oocyte. Development 1996, 122, 3639–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.M.; Blochlinger, K. cut interacts with Notch and protein kinase A to regulate egg chamber formation and to maintain germline cyst integrity during Drosophila oogenesis. Development 1997, 124, 3663–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Clyde, D.; Bownes, M. Expression of fringe is down regulated by Gurken/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor signalling and is required for the morphogenesis of ovarian follicle cells. J Cell Sci 2000, 113 Pt 21, 3781–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Schier, H.; St Johnston, D. Delta signaling from the germ line controls the proliferation and differentiation of the somatic follicle cells during Drosophila oogenesis. Genes Dev 2001, 15, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.M.; Althauser, C.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Notch-Delta signaling induces a transition from mitotic cell cycle to endocycle in Drosophila follicle cells. Development 2001, 128, 4737–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammont, M.; Irvine, K.D. fringe and Notch specify polar cell fate during Drosophila oogenesis. Development 2001, 128, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeffer, V.; Althauser, C.; Shcherbata, H.R.; Deng, W.M.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Notch-dependent Fizzy-related/Hec1/Cdh1 expression is required for the mitotic-to-endocycle transition in Drosophila follicle cells. Curr Biol 2004, 14, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shcherbata, H.R.; Althauser, C.; Findley, S.D.; Ruohola-Baker, H. The mitotic-to-endocycle switch in Drosophila follicle cells is executed by Notch-dependent regulation of G1/S, G2/M and M/G1 cell-cycle transitions. Development 2004, 131, 3169–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, J.C.; Montell, D.J. A role for extra macrochaetae downstream of Notch in follicle cell differentiation. Development 2004, 131, 5971–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Deng, W.M. Notch-dependent downregulation of the homeodomain gene cut is required for the mitotic cycle/endocycle switch and cell differentiation in Drosophila follicle cells. Development 2005, 132, 4299–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Deng, W.M. Hindsight mediates the role of notch in suppressing hedgehog signaling and cell proliferation. Dev Cell 2007, 12, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Smith, L.; Armento, A.; Deng, W.M. Regulation of the endocycle/gene amplification switch by Notch and ecdysone signaling. J Cell Biol 2008, 182, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Reyes, A.; St Johnston, D. Role of oocyte position in establishment of anterior-posterior polarity in Drosophila. Science 1994, 266, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, I.L.; Lopez-Schier, H.; St Johnston, D. A Notch/Delta-dependent relay mechanism establishes anterior-posterior polarity in Drosophila. Dev Cell 2003, 5, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assa-Kunik, E.; Torres, I.L.; Schejter, E.D.; Johnston, D.S.; Shilo, B.Z. Drosophila follicle cells are patterned by multiple levels of Notch signaling and antagonism between the Notch and JAK/STAT pathways. Development 2007, 134, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, S.; Lynch, J.A. Symmetry breaking during Drosophila oogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2009, 1, a001891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Gridley, T. Notch Signaling during Oogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res Int 2012, 2012, 648207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Spradling, A.C. A niche maintaining germ line stem cells in the Drosophila ovary. Science 2000, 290, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, E.J.; Shcherbata, H.R.; Reynolds, S.H.; Fischer, K.A.; Hatfield, S.D.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Stem cells signal to the niche through the Notch pathway in the Drosophila ovary. Curr Biol 2006, 16, 2352–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Call, G.B.; Kirilly, D.; Xie, T. Notch signaling controls germline stem cell niche formation in the Drosophila ovary. Development 2007, 134, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Peterson, A.; Kenney, T.; Burrous, H.; Montell, D.J. Quantitative microscopy of the Drosophila ovary shows multiple niche signals specify progenitor cell fate. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, T.; Chen, X.; Alchits, E.; Oh, Y.; Poon, J.; Kouptsova, J.; Laski, F.A.; Godt, D. Specification and spatial arrangement of cells in the germline stem cell niche of the Drosophila ovary depend on the Maf transcription factor Traffic jam. PLoS Genet 2017, 13, e1006790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Wilkin, M.B.; Woodcock, S.A.; Bonfini, A.; Hung, Y.; Mazaleyrat, S.; Baron, M. The Drosophila ZO-1 protein Polychaetoid suppresses Deltex-regulated Notch activity to modulate germline stem cell niche formation. Open Biol 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsenko, A.S.; Shcherbata, H.R. Stereotypical architecture of the stem cell niche is spatiotemporally established by miR-125-dependent coordination of Notch and steroid signaling. Development 2018, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, C.; Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z. Notch signaling governs the expression of glypican Dally to define the stem cell niche. Biol Open 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsenko, A.S.; Shcherbata, H.R. Distant activation of Notch signaling induces stem cell niche assembly. PLoS Genet 2021, 17, e1009489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, G. The expression of Catsup in escort cells affects Drosophila ovarian stem cell niche establishment and germline stem cells self-renewal via Notch signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2023, 641, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.J.; Drummond-Barbosa, D. Insulin levels control female germline stem cell maintenance via the niche in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.J.; Drummond-Barbosa, D. Insulin signals control the competence of the Drosophila female germline stem cell niche to respond to Notch ligands. Dev Biol 2011, 350, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.A.; Wang, W.D.; Chen, C.T.; Tseng, C.Y.; Chen, Y.N.; Hsu, H.J. FOXO/Fringe is necessary for maintenance of the germline stem cell niche in response to insulin insufficiency. Dev Biol 2013, 382, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.Y.; Kao, S.H.; Wan, C.L.; Cho, Y.; Tung, S.Y.; Hsu, H.J. Notch signaling mediates the age-associated decrease in adhesion of germline stem cells to the niche. PLoS Genet 2014, 10, e1004888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfini, A.; Wilkin, M.B.; Baron, M. Reversible regulation of stem cell niche size associated with dietary control of Notch signalling. BMC Dev Biol 2015, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhou, S. Post-transcriptional regulation of insect metamorphosis and oogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2020, 77, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belles, X.; Piulachs, M.D. Ecdysone signalling and ovarian development in insects: from stem cells to ovarian follicle formation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015, 1849, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irles, P.; Piulachs, M.D. Unlike in Drosophila Meroistic Ovaries, hippo represses notch in Blattella germanica Panoistic ovaries, triggering the mitosis-endocycle switch in the follicular cells. PLoS One 2014, 9, e113850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, N.; Piulachs, M.D. Crosstalk of EGFR signalling with Notch and Hippo pathways to regulate cell specification, migration and proliferation in cockroach panoistic ovaries. Biol Cell 2015, 107, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irles, P.; Elshaer, N.; Piulachs, M.D. The Notch pathway regulates both the proliferation and differentiation of follicular cells in the panoistic ovary of Blattella germanica. Open Biol 2016, 6, 150197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Chelemen, F.; Pagone, V.; Elshaer, N.; Irles, P.; Piulachs, M.D. Eyes absent in the cockroach panoistic ovaries regulates proliferation and differentiation through ecdysone signalling. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2020, 123, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumer, D.; Strohlein, N.M.; Schoppmeier, M. Opposing effects of Notch-signaling in maintaining the proliferative state of follicle cells in the telotrophic ovary of the beetle Tribolium. Front Zool 2012, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuscher, M.; Strohlein, N.; Birkenbach, M.; Schultheis, D.; Schoppmeier, M. TC003132 is essential for the follicle stem cell lineage in telotrophic Tribolium oogenesis. Front Zool 2017, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, S. Clustered miR-2, miR-13a, miR-13b and miR-71 coordinately target Notch gene to regulate oogenesis of the migratory locust Locusta migratoria. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2019, 106, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, S. Regulatory Mechanisms of Vitellogenesis in Insects. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 593613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, E.J.; Hyink, O.; Dearden, P.K. Notch signalling mediates reproductive constraint in the adult worker honeybee. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, E.J.; Leask, M.P.; Dearden, P.K. Genome Architecture Facilitates Phenotypic Plasticity in the Honeybee (Apis mellifera). Mol Biol Evol 2020, 37, 1964–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Abbott, H.; Dearden, P.K. The evolution of oocyte patterning in insects: multiple cell-signaling pathways are active during honeybee oogenesis and are likely to play a role in axis patterning. Evol Dev 2011, 13, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, C.; Chen, C.; Lu, Q.; Shi, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, H. Integration of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA reveals novel insights into oviposition regulation in honey bees. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhang, Z.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.J. Comparative Proteomic Profiling Reveals Molecular Characteristics Associated with Oogenesis and Oocyte Maturation during Ovarian Development of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowanski, S.; Walkowiak-Nowicka, K.; Winkiel, M.; Marciniak, P.; Urbanski, A.; Pacholska-Bogalska, J. Insulin-Like Peptides and Cross-Talk With Other Factors in the Regulation of Insect Metabolism. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 701203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smykal, V.; Raikhel, A.S. Nutritional Control of Insect Reproduction. Curr Opin Insect Sci 2015, 11, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouandin, P.; Ghiglione, C.; Noselli, S. Starvation induces FoxO-dependent mitotic-to-endocycle switch pausing during Drosophila oogenesis. Development 2014, 141, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foronda, D.; Weng, R.; Verma, P.; Chen, Y.W.; Cohen, S.M. Coordination of insulin and Notch pathway activities by microRNA miR-305 mediates adaptive homeostasis in the intestinal stem cells of the Drosophila gut. Genes Dev 2014, 28, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradhya, R.; Zmojdzian, M.; Da Ponte, J.P.; Jagla, K. Muscle niche-driven Insulin-Notch-Myc cascade reactivates dormant Adult Muscle Precursors in Drosophila. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutriaux, A.; Godart, A.; Brachet, A.; Silber, J. The insulin receptor is required for the development of the Drosophila peripheral nervous system. PLoS One 2013, 8, e71857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obniski, R.; Sieber, M.; Spradling, A.C. Dietary Lipids Modulate Notch Signaling and Influence Adult Intestinal Development and Metabolism in Drosophila. Dev Cell 2018, 47, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, L.; Carrillo-Tripp, J.; Bonning, B.C.; Cook, D.; Toth, A.L.; Dolezal, A.G. Transcriptomic responses to diet quality and viral infection in Apis mellifera. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Long, Q.; Fan, X.X.; Ye, Y.P.; Zhang, K.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhao, H.D.; Yao, Y.T.; Fu, Z.M.; Chen, D.F.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Characterization of piRNAs during the Developmental Process of European Honey-Bee Larval Guts. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, W.; Guo, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Gao, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, T.; Chen, D.; et al. Expression Profile, Regulatory Network, and Putative Role of microRNAs in the Developmental Process of Asian Honey Bee Larval Guts. Insects 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Yao, C.; Cheng, J.; Kao, S.T.; Tsai, F.J.; Liu, H.P. Molecular pathways related to the longevity promotion and cognitive improvement of Cistanche tubulosa in Drosophila. Phytomedicine 2017, 26, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskalev, A.; Shaposhnikov, M.; Zemskaya, N.; Belyi, A.; Dobrovolskaya, E.; Patova, A.; Guvatova, Z.; Lukyanova, E.; Snezhkina, A.; Kudryavtseva, A. Transcriptome analysis reveals mechanisms of geroprotective effects of fucoxanthin in Drosophila. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beghelli, D.; Zallocco, L.; Barbalace, M.C.; Paglia, S.; Strocchi, S.; Cirilli, I.; Marzano, V.; Putignani, L.; Lupidi, G.; Hrelia, S.; et al. Pterostilbene Promotes Mean Lifespan in Both Male and Female Drosophila Melanogaster Modulating Different Proteins in the Two Sexes. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 1744408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, O.; Holmes, A.C.; Kafai, N.M.; Adams, L.J.; Diamond, M.S. Entry receptors - the gateway to alphavirus infection. J Clin Invest 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudiganti, U.; Hernandez, R.; Brown, D.T. Insect response to alphavirus infection--establishment of alphavirus persistence in insect cells involves inhibition of viral polyprotein cleavage. Virus Res 2010, 150, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xing, D.; Su, D.; Wang, D.; Gao, H.; Lan, C.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Li, C. Transcriptome Analysis of Responses to Dengue Virus 2 Infection in Aedes albopictus (Skuse) C6/36 Cells. Viruses 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrato-Salas, J.; Izquierdo-Sanchez, J.; Arguello, M.; Conde, R.; Alvarado-Delgado, A.; Lanz-Mendoza, H. Aedes aegypti antiviral adaptive response against DENV-2. Dev Comp Immunol 2018, 84, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrato-Salas, J.; Hernandez-Martinez, S.; Martinez-Barnetche, J.; Conde, R.; Alvarado-Delgado, A.; Zumaya-Estrada, F.; Lanz-Mendoza, H. De Novo DNA Synthesis in Aedes aegypti Midgut Cells as a Complementary Strategy to Limit Dengue Viral Replication. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Kang, S.; Smartt, C.T. Profiling Transcripts of Vector Competence between Two Different Aedes aegypti Populations in Florida. Viruses 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taracena, M.L.; Bottino-Rojas, V.; Talyuli, O.A.C.; Walter-Nuno, A.B.; Oliveira, J.H.M.; Anglero-Rodriguez, Y.I.; Wells, M.B.; Dimopoulos, G.; Oliveira, P.L.; Paiva-Silva, G.O. Regulation of midgut cell proliferation impacts Aedes aegypti susceptibility to dengue virus. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2018, 12, e0006498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Garduno, J.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Hernandez-Martinez, S.; Martinez-Barnetche, J.; Alvarado-Delgado, A.; Izquierdo, J.; Herrera-Ortiz, A.; Moreno-Garcia, M.; Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Valverde, V.; et al. Plasmodium berghei induced priming in Anopheles albimanus independently of bacterial co-infection. Dev Comp Immunol 2015, 52, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya-Maldonado, K.; Cardoso-Jaime, V.; Hernandez-Martinez, S.; Recio-Totoro, B.; Bello-Garcia, D.; Hernandez-Hernandez, F.C.; Lanz-Mendoza, H. Plasmodium exposure alters midgut epithelial cell dynamics during the immune memory in Anopheles albimanus. Dev Comp Immunol 2022, 133, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.L.; Yerbanga, R.S.; Lefevre, T.; Ouedraogo, J.B.; Corces, V.G.; Gomez-Diaz, E. Chromatin changes in Anopheles gambiae induced by Plasmodium falciparum infection. Epigenetics Chromatin 2019, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Ren, F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lu, Q.; Swevers, L.; Sun, J. Correlation in Expression between LTR Retrotransposons and Potential Host Cis-Targets during Infection of Antherea pernyi with ApNPV Baculovirus. Viruses 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Liang, X.Y.; Guo, J.; Shi, X.K.; Merzendorfer, H.; Zhu, K.Y.; Zhang, J.Z. V-ATPase subunit a is required for survival and midgut development of Locusta migratoria. Insect Mol Biol 2022, 31, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Lucas, K.J.; Saha, T.T.; Ha, J.; Ling, L.; Kokoza, V.A.; Roy, S.; Raikhel, A.S. MicroRNA-275 targets sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ adenosine triphosphatase (SERCA) to control key functions in the mosquito gut. PLoS Genet 2017, 13, e1006943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlstein, B.; Spradling, A. The adult Drosophila posterior midgut is maintained by pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2006, 439, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micchelli, C.A.; Perrimon, N. Evidence that stem cells reside in the adult Drosophila midgut epithelium. Nature 2006, 439, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlstein, B.; Spradling, A. Multipotent Drosophila intestinal stem cells specify daughter cell fates by differential notch signaling. Science 2007, 315, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Patel, P.H.; Kohlmaier, A.; Grenley, M.O.; McEwen, D.G.; Edgar, B.A. Cytokine/Jak/Stat signaling mediates regeneration and homeostasis in the Drosophila midgut. Cell 2009, 137, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, D.; Bost, A.; Driver, I.; Ohlstein, B. A transient niche regulates the specification of Drosophila intestinal stem cells. Science 2010, 327, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvic, B.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Meister, M.; Royet, J. Notch signaling controls lineage specification during Drosophila larval hematopoiesis. Curr Biol 2002, 12, 1923–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebestky, T.; Jung, S.H.; Banerjee, U. A Serrate-expressing signaling center controls Drosophila hematopoiesis. Genes Dev 2003, 17, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzemien, J.; Dubois, L.; Makki, R.; Meister, M.; Vincent, A.; Crozatier, M. Control of blood cell homeostasis in Drosophila larvae by the posterior signalling centre. Nature 2007, 446, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, C.; Ramroop, J.; Otazo, M.; Huang, L.H.; Saleque, S.; Govind, S. An unexpected link between notch signaling and ROS in restricting the differentiation of hematopoietic progenitors in Drosophila. Genetics 2014, 197, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.H.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, B.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, J.; Kim-Ha, J.; Kim, Y.J. Requirement of Split ends for epigenetic regulation of Notch signal-dependent genes during infection-induced hemocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2009, 29, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, F.J.; Holt, H.L.; Grozinger, C.M. Effects of immunostimulation on social behavior, chemical communication and genome-wide gene expression in honey bee workers (Apis mellifera). BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Abd El Halim, H.M. Re-thinking adaptive immunity in the beetles: Evolutionary and functional trajectories of lncRNAs. Genomics 2020, 112, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, A.; McGillivray, S.M.; Cruz-Moreno, B.; van Sorge, N.M.; Nizet, V.; Bier, E. Anthrax toxins cooperatively inhibit endocytic recycling by the Rab11/Sec15 exocyst. Nature 2010, 467, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, A.; Cruz-Moreno, B.; Aguilar, B.; van Sorge, N.M.; Kuang, J.; Kurkciyan, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hang, S.; Pineton de Chambrun, G.P.; McCole, D.F.; et al. Cholera toxin disrupts barrier function by inhibiting exocyst-mediated trafficking of host proteins to intestinal cell junctions. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harsh, S.; Fu, Y.; Kenney, E.; Han, Z.; Eleftherianos, I. Zika virus non-structural protein NS4A restricts eye growth in Drosophila through regulation of JAK/STAT signaling. Dis Model Mech 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattia, J.R.; Kuraishi, T.; Dimitrov, M.; Chang, I.; Lemaitre, B.; Fraering, P.C. Mercury is a direct and potent gamma-secretase inhibitor affecting Notch processing and development in Drosophila. FASEB J 2011, 25, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, C.; Rand, M.D. Methylmercury induces activation of Notch signaling. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, M.D.; Bland, C.E.; Bond, J. Methylmercury activates enhancer-of-split and bearded complex genes independent of the notch receptor. Toxicol Sci 2008, 104, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, G.L.; Delwig, A.; Rand, M.D. The effects of methylmercury on Notch signaling during embryonic neural development in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicol In Vitro 2012, 26, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, G.L.; Rand, M.D. The Notch target E(spl)mdelta is a muscle-specific gene involved in methylmercury toxicity in motor neuron development. Neurotoxicol Teratol 2014, 43, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yin, H.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Ji, C.D.; Jiang, Q.H.; Du, J.; Yin, M.Z.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J.Z. Combination of a nanocarrier delivery system with genetic manipulation further improves pesticide efficiency: a case study with chlorfenapyr. Environ Sci-Nano 2022, 9, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalev, A.; Shaposhnikov, M.; Snezhkina, A.; Kogan, V.; Plyusnina, E.; Peregudova, D.; Melnikova, N.; Uroshlev, L.; Mylnikov, S.; Dmitriev, A.; et al. Mining gene expression data for pollutants (dioxin, toluene, formaldehyde) and low dose of gamma-irradiation. PLoS One 2014, 9, e86051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhong, G. Natural harmine negatively regulates the developmental signaling network of Drosophila melanogaster (Drosophilidae: Diptera) in vivo. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2020, 190, 110134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farder-Gomes, C.F.; Fernandes, K.M.; Bernardes, R.C.; Bastos, D.S.S.; Oliveira, L.L.; Martins, G.F.; Serrao, J.E. Harmful effects of fipronil exposure on the behavior and brain of the stingless bee Partamona helleri Friese (Hymenoptera: Meliponini). Sci Total Environ 2021, 794, 148678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farder-Gomes, C.F.; Santos, A.A.; Fernandes, K.M.; Bernardes, R.C.; Martins, G.F.; Serrao, J.E. Fipronil exposure compromises respiration and damages the Malpighian tubules of the stingless bee Partamona helleri Friese (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2022, 29, 88101–88108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Jia, Z.Q.; Peng, Y.C.; Sheng, C.W.; Tang, T.; Xu, L.; Han, Z.J.; Zhao, C.Q. Toxicity and sublethal effects of fluralaner on Spodoptera litura Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pestic Biochem Physiol 2018, 152, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojima, Y.; Bono, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Iwabuchi, K.; Sato, R.; Arai, K.; Tabunoki, H. Superoxide dismutase down-regulation and the oxidative stress is required to initiate pupation in Bombyx mori. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 14693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.F.; Greenlee, K.J.; Verberk, W. Functional Hypoxia in Insects: Definition, Assessment, and Consequences for Physiology, Ecology, and Evolution. Annu Rev Entomol 2018, 63, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xue, J.; Lai, J.C.; Schork, N.J.; White, K.P.; Haddad, G.G. Mechanisms underlying hypoxia tolerance in Drosophila melanogaster: hairy as a metabolic switch. PLoS Genet 2008, 4, e1000221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Udpa, N.; Gersten, M.; Visk, D.W.; Bashir, A.; Xue, J.; Frazer, K.A.; Posakony, J.W.; Subramaniam, S.; Bafna, V.; et al. Experimental selection of hypoxia-tolerant Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, P.; Zhou, D.; Zarndt, R.; Haddad, G.G. Identification of genes underlying hypoxia tolerance in Drosophila by a P-element screen. G3 (Bethesda) 2012, 2, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, R.; Udpa, N.; Halperin, E.; Bafna, V. Learning natural selection from the site frequency spectrum. Genetics 2013, 195, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Stobdan, T.; Visk, D.; Xue, J.; Haddad, G.G. Genetic interactions regulate hypoxia tolerance conferred by activating Notch in excitatory amino acid transporter 1-positive glial cells in Drosophila melanogaster. G3 (Bethesda) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Linz, D.M.; Parker, E.S.; Schwab, D.B.; Casasa, S.; Macagno, A.L.M.; Moczek, A.P. Developmental bias in horned dung beetles and its contributions to innovation, adaptation, and resilience. Evol Dev 2020, 22, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Linz, D.M.; Moczek, A.P. Beetle horns evolved from wing serial homologs. Science 2019, 366, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijimoto, T.; Costello, J.; Tang, Z.; Moczek, A.P.; Andrews, J. EST and microarray analysis of horn development in Onthophagus beetles. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Kijimoto, T.; Snell-Rood, E.; Tae, H.; Yang, Y.; Moczek, A.P.; Andrews, J. Gene discovery in the horned beetle Onthophagus taurus. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, J.R.; Macagno, A.L.M.; Moczek, A.P.; Rohner, P.T.; Hu, Y. Notch signaling patterns head horn shape in the bull-headed dung beetle Onthophagus taurus. Dev Genes Evol 2020, 230, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, H.; Matsuda, K.; Niimi, T.; Kondo, S.; Gotoh, H. Genetical control of 2D pattern and depth of the primordial furrow that prefigures 3D shape of the rhinoceros beetle horn. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 18687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Moczek, A.P. Wing serial homologues and the diversification of insect outgrowths: insights from the pupae of scarab beetles. Proc Biol Sci 2021, 288, 20202828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Schmitt-Engel, C.; Schwirz, J.; Stroehlein, N.; Richter, T.; Majumdar, U.; Bucher, G. A morphological novelty evolved by co-option of a reduced gene regulatory network and gene recruitment in a beetle. Proc Biol Sci 2018, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.M.; Hu, Y.; Moczek, A.P. The origins of novelty from within the confines of homology: the developmental evolution of the digging tibia of dung beetles. Proc Biol Sci 2019, 286, 20182427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgar, M.A.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wittwer, B.; Thi Pham, H.; Johnson, T.L.; Freelance, C.B.; Coquilleau, M. Insect Antennal Morphology: The Evolution of Diverse Solutions to Odorant Perception. Yale J Biol Med 2018, 91, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, K.L.; Ranade, S.S.; Curtiss, J.; Mlodzik, M.; Pignoni, F. Coordinating proliferation and tissue specification to promote regional identity in the Drosophila head. Dev Cell 2003, 5, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, H.Y.; Sun, Y.H. Notch-dependent epithelial fold determines boundary formation between developmental fields in the Drosophila antenna. PLoS Genet 2017, 13, e1006898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Palliyil, S.; Ran, C.; Kumar, J.P. Drosophila Pax6 promotes development of the entire eye-antennal disc, thereby ensuring proper adult head formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, 5846–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, D.R.; Kikuchi, M.; Jockusch, E.L. Genetic patterning in the adult capitate antenna of the beetle Tribolium castaneum. Dev Biol 2009, 327, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Kojima, T.; Fujiwara, H. Dramatic changes in patterning gene expression during metamorphosis are associated with the formation of a feather-like antenna by the silk moth, Bombyx mori. Dev Biol 2011, 357, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Kojima, T. The pivotal role of aristaless in development and evolution of diverse antennal morphologies in moths and butterflies. BMC Evol Biol 2018, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.W.; Angelini, D.R.; Gaudio, M.S.; Jockusch, E.L. Metamorphic labral axis patterning in the beetle Tribolium castaneum requires multiple upstream, but few downstream, genes in the appendage patterning network. Evol Dev 2014, 16, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Qiao, L.; Luo, J.; Ding, X.; Wu, S. The evolution and genetics of lepidopteran egg and caterpillar coloration. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2021, 69, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futahashi, R.; Fujiwara, H. Juvenile hormone regulates butterfly larval pattern switches. Science 2008, 319, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Seki, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Fujiwara, H. Prepatterning of Papilio xuthus caterpillar camouflage is controlled by three homeobox genes: clawless, abdominal-A, and Abdominal-B. Sci Adv 2019, 5, eaav7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Yoda, S.; Liu, L.; Kojima, T.; Fujiwara, H. Notch and Delta Control the Switch and Formation of Camouflage Patterns in Caterpillars. iScience 2020, 23, 101315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.H. The ancestry of segmentation. Dev Cell 2003, 5, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truman, J.W. The Evolution of Insect Metamorphosis. Curr Biol 2019, 29, R1252–R1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysore, K.; Sun, L.; Hapairai, L.K.; Wang, C.W.; Roethele, J.B.; Igiede, J.; Scheel, M.P.; Scheel, N.D.; Li, P.; Wei, N.; et al. A Broad-Based Mosquito Yeast Interfering RNA Pesticide Targeting Rbfox1 Represses Notch Signaling and Kills Both Larvae and Adult Mosquitoes. Pathogens 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.N.M.; Choo, A.; Baxter, S.W. Lessons from Drosophila: Engineering Genetic Sexing Strains with Temperature-Sensitive Lethality for Sterile Insect Technique Applications. Insects 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, O.S.; Chen, C.H.; Marshall, J.M.; Huang, H.; Antoshechkin, I.; Hay, B.A. Novel synthetic Medea selfish genetic elements drive population replacement in Drosophila; a theoretical exploration of Medea-dependent population suppression. ACS Synth Biol 2014, 3, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
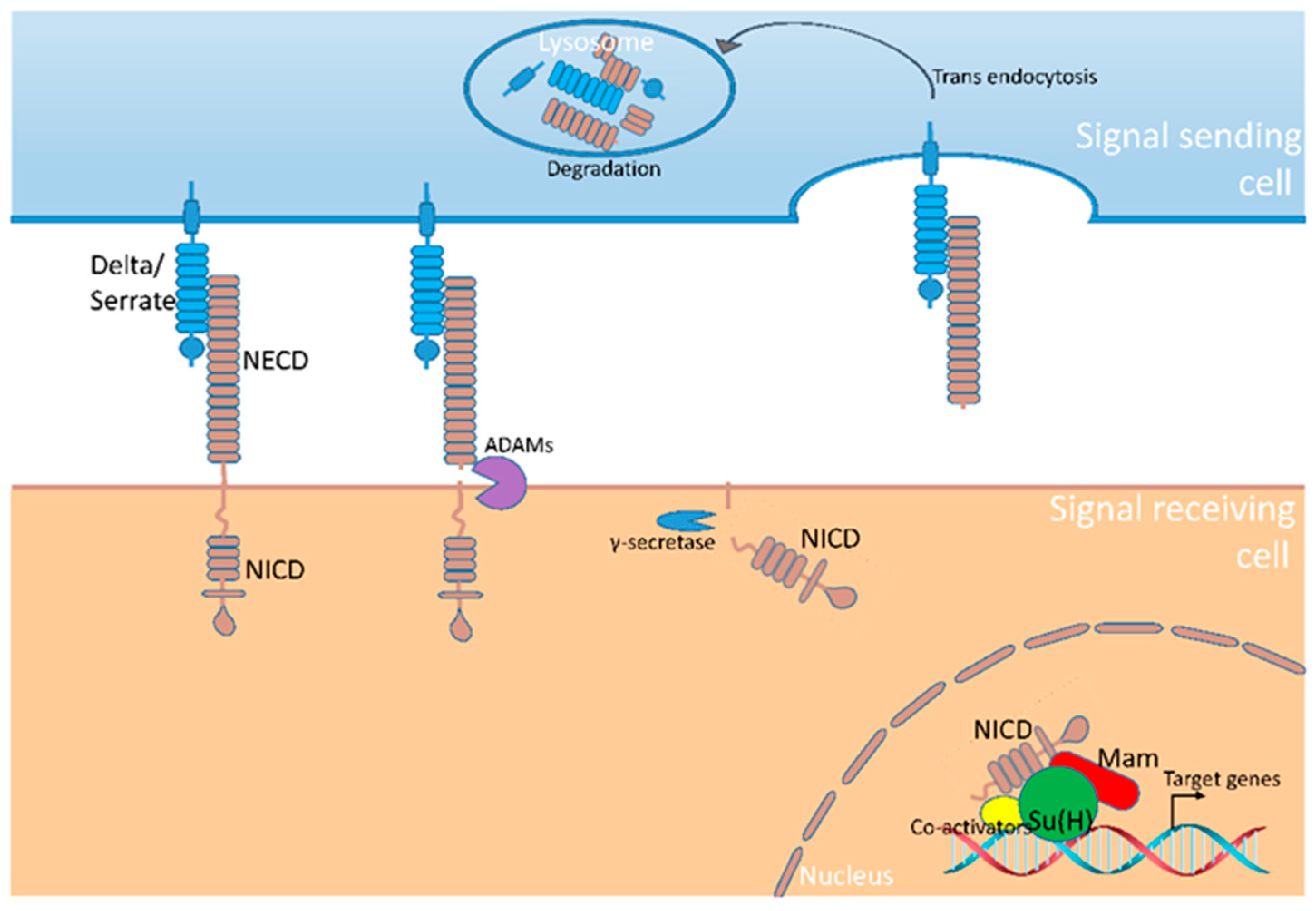

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




