Submitted:
24 July 2023
Posted:
03 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics in the Use of Animals
2.2. Animals
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Gastroscopy
2.5. Hematological Evaluation
2.6. Coagulation Evaluation
2.7. Biochemical Evaluation
2.8. Statistical methods
3. Results
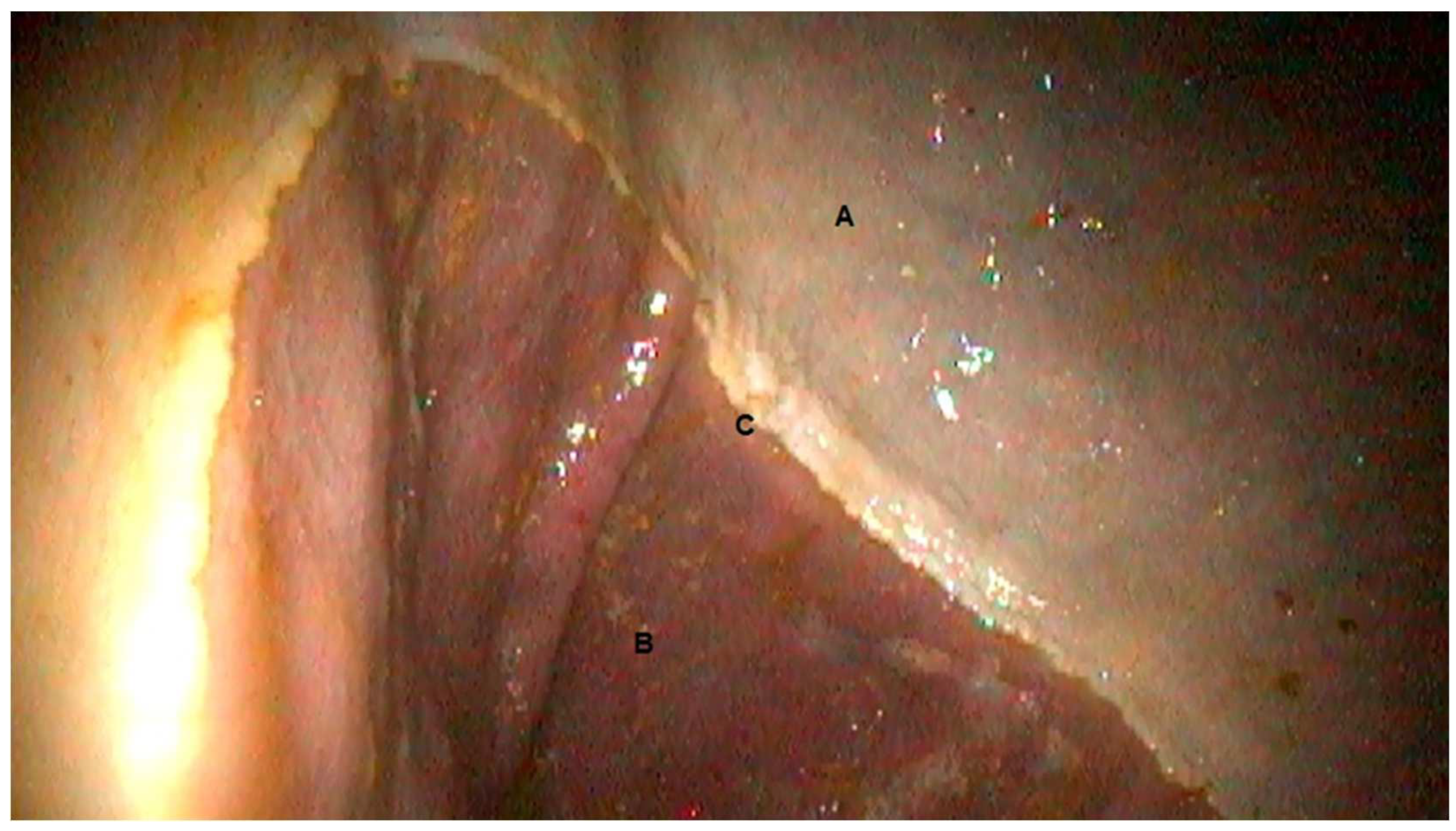
3.1. Gastroscopic Evaluation
3.2. Complete blood count (CBC)
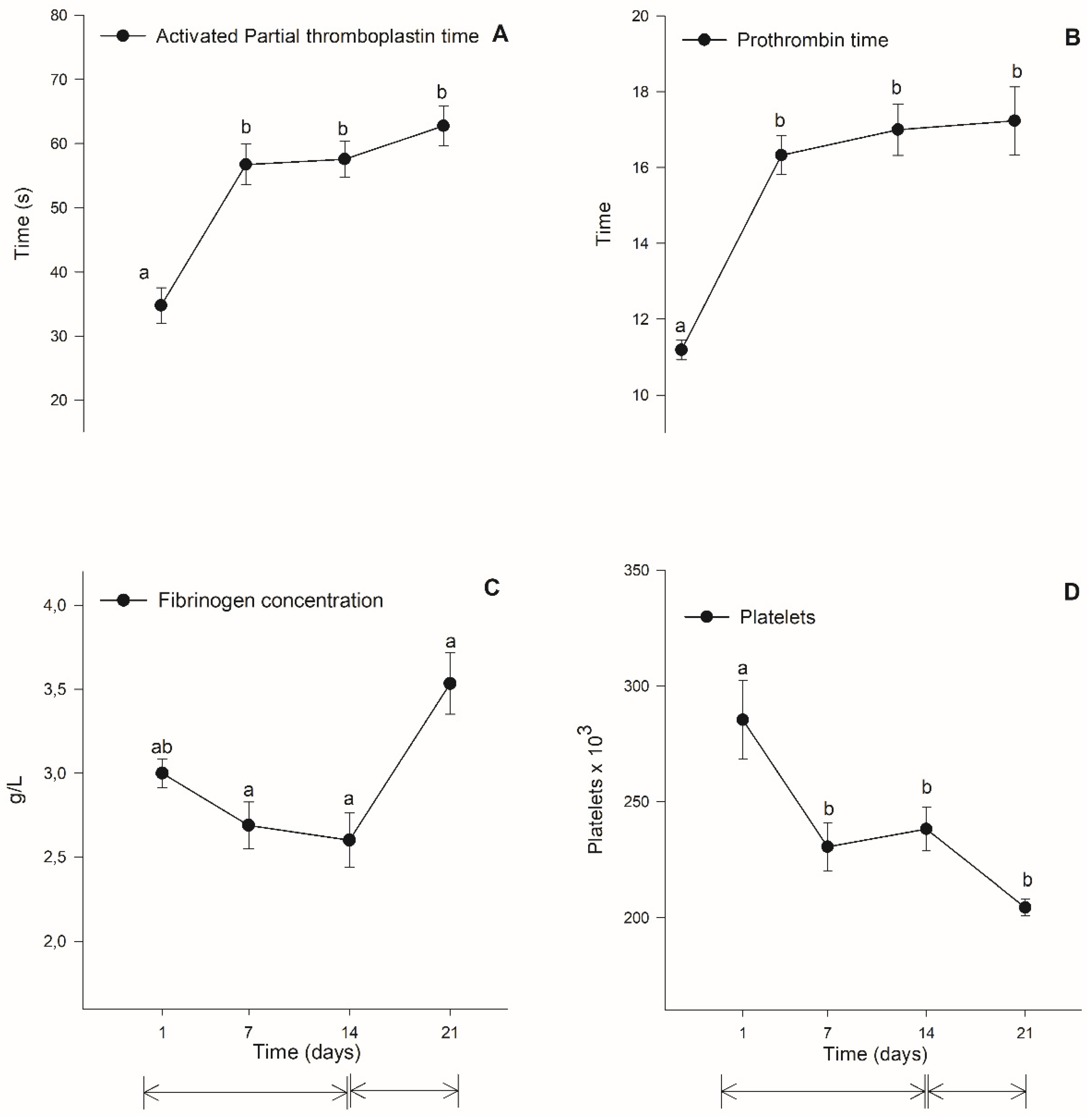
3.3. Coagulation Evaulation
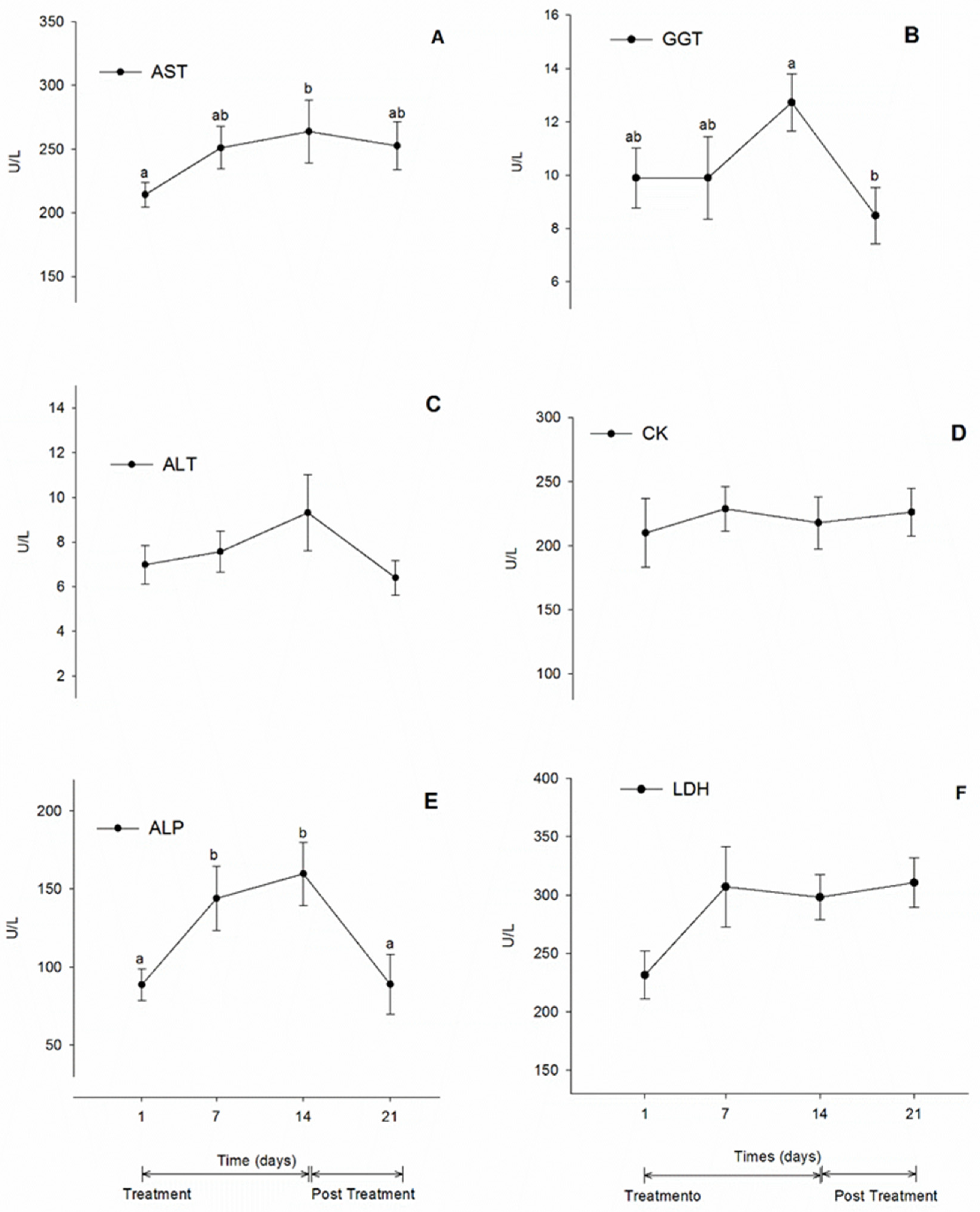
3.4. Biochemistry Values
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godoy, P.A. Uso de antiinflamatorios no esteroidales en equinos. Monografías de Medicina Veterinaria 2010, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Menzies-Gow, N. Colic: Medical Treatment and Management in Horses. Vet. Times 2016, 46, 19–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lees, P.; Landoni, M.F.; Giraudel, J.; Toutain, P.L. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in veterinary species. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 27, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotz, F.; Schiele, T.M.; Klauss, V.; Sohn, H.Y. Selective COX-2 Inhibitors and Risk of Myocardial Infarction. J. Vasc. Res. 2005, 42, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brater, D.C.; Harris, C.; Redfern, J.S.; Gertz, B.J. Renal effects of COX-2-Selective Inhibitors. Am. J. Nephrol. 2001, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.P. The Clinical Pharmacology of Cyclooxygenase-2-Selective and Dual Inhibitors. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2006, 36, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvaternick, V.; Pollmeier, M.; Fischer, J.; Hanson, P.D. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of orally administered firocoxib, a novel second-generation coxib, in horses. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 30, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.L.; Xie, W.; Chipman, J.G.; Evett, G.E. Multiple cyclooxygenases: Cloning of an inducible form. In: Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, Lipoxins and PAF. Nova York: Plenum Press, 1991. p.67-78.
- Bertolini, A.; Ottani, A.; Sandrini, M. Selective COX-2 Inhibitors and Dual Acting Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Critical Remarks. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, G.A. Coxibs and Cardiovascular Disease. N Engl J Med. 2004, 351, 1709–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, M.L.; Giguère, S.; Pozor, M.A.; Burden, C.A.; Berghaus, L.J.; Berghaus, R.D.; Varner, J.C.; Hayna, J.T.; Benson, S.M.; Randell, S.A.; et al. Evidence for Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Firocoxib Administered to Mares with Experimentally Induced Placentitis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2021, 86, e13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.E.; Andersen, D.R.; Zhang, D.; Brideau, C.; Black, W.C.; Hanson, P.D.; Hickey, G.J. In vitro effects and in vivo efficacy of a novel cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in dogs with experimentally induced synovitis. Am. J. Vet. Res., 2004, 65, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, C.; Giorgi, M. Synopsis of the Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Applications, and Safety of Firocoxib in Horses. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2023, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnell, J.R.; Frisbie, D.D. Use of Firocoxib for the Treatment of Equine Osteoarthritis. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2014, 5, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F.D.A. (Food and Drug Administration). Freedom of Information Summary: Equioxx Injection - Firocoxib. US Food and Drug Administration, Rockville (MD), 2010.
- Cook, V.; Meyer, C.; Campbell, N.; Blikslager, A. Effect of Firocoxib or Flunixin Meglumine on Recovery of Ischemia-Injured Equine Jejunum. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.E.; Wilder, B.O.; Young, K.M.; Blikslager, A.T. Effects of Flunixin Meglumine or Etodolac Treatment on Mucosal Recovery of Equine Jejunum after Ischemia. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 65, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.E.; Blikslager, A.T. Effects of Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors Flunixin and Deracoxib on Permeability of Ischaemic-Injured Equine Jejunum. Equine Vet. J. 2005, 3791), 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, D.; Jones, S.L.; Blikslager, A.T. Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibitors and the Intestine. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonam, D.; Vinay, C.S.; Gautam, P. Cyclo-oxygenase-2 Expression and Prostaglandin E2 Production in Experimental Chronic Gastric Ulcer Healing. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2005, 519, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Fidalgo, S.; Martín-Lacave, I.; Illanes, M.; Motilva, V. Angiogenesis, Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Gastric Ulcer Healing. Effect of a Selective COX-2 Inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 555, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcallister, C.G.; Andrews, F.M.; Deegan, E.; Ruoff, W.; Olovson, S.G. A Scoring System for Gastric Ulcers in the Horse. Equine Vet. J. 1997, 29, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jericó, M.; Andrade, S.F. Antiinflamatórios. In Andrade, S.F. Manual de Terapêutica Veterinária, 3rd ed.; Roca: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008; pp. 115–140. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, P.; Burgess, H.; Wood, D. Hemostasis. In Kaneko, J.J.; Harvey, J.W., Ed.; Bruss, M.L. Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals. 6th ed. Academic Press; San Diego, 2008; pp. 379–412. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, D.J.; Coles, E.H.; Rich, L.J. Medicina de laboratório veterinário: interpretação e diagnóstico, 3rd ed.; Roca: São Paulo, Brazil, 1995; 308p. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, J.J. Carbohydrate Metabolism and its diseases. In: Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals. 6º Ed. San Diego: Academic Press, 2008. p. 45-80.
- Navab, F.; Steingrub, J. Stress ulcer: is routine prophylaxis necessary? Am. J. Gastroenterol., 1995, 90, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mozaffari, A.A.; Derakhshanfar, A.; Alinejad, A.; Morovati, M.A. A Comparative Study on the Adverse Effects of Flunixin, Ketoprofen, and Phenylbutazone in Miniature Donkeys: Haematological, Biochemical, and Pathological Findings. N Z Vet J. 2010, 58, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecoindre, O.; Pepin-Richard, C. Tolerance of Firocoxib in Dogs with Osteoarthritis during 90 Days. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 34, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, C.M.; Sakate, M.; Camplesi, A.C.; Vailati, M.C.F.; Moraes, L.F.; Takahira, R.K. Avaliações Hematológicas e Bioquímicas do Uso de Diclofenaco de Sódio, Meloxicam e Firocoxibe em Ratos. Braz J Vet Res Anim Sci. 2010, 47, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaterka, S. Lesões Induzidas por AINEs no Sistema Digestório. Rev Bras Med. 2000, 57, 882–900. [Google Scholar]
- F.D.A. (Food and Drug Administration). Celecoxib side effect: Leukopenia, 2011.
- Marini-Filho, R. Alterações hematológicas, hemostáticas e bioquímicas de cães tratados com anti-inflamatórios não esteroidais. Master's thesis, Universidade do Oeste Paulista, Presidente Prudente, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, F.L.; Soeiro, A.M.; Fernandes, J.L.; Serrano-Junior, C.V. Eventos Cardiovasculares: Um Efeito de Classe dos Inibidores de COX-2. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2005, 85, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.; Hall, J.C. Tratado de Fisiologia Médica, 9th ed.; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pozzobon, R. Avaliação Farmacocinética, Hematológica e Espermática de Pôneis Tratados com Meloxicam. Ph.D. thesis, Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, Santa Maria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, R.C. Short-term Administration of Flunixin Meglumine or Firocoxib Does Not Alter Viscoelastic Coagulation Profiles in Healthy Horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2022, 260, 1963–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, B.R.; Mcfarland, J.G.; Wu, G.G.; Visentin, G.P.; Aster, R.H. Antibodies in Sulfonamide-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia Recognize Calcium-Dependent Epitopes on the Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Complex. Blood. 1994, 84, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aster, H. Drug-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia: An Overview of Pathogenesis. Semin. Hematol. 1999, suppl. 1, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.A.F.; Dearo, A.C.O.; Biondo, A.W.; Godin, L.F.P.; Iamaguti, P.; Thomassian, A.; Kohayagawa, A. Exame do Fluido Peritoneal e Hemograma de Eqüinos Submetidos à Laparotomia e Infusão Intraperitoneal de Carboximetilcelulose. Cienc. Rural. 1999, 29, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.M. Manual Merk de veterinária: um manual de diagnóstico, tratamento, prevenção e controle de doenças para o veterinário, 6th ed.; Rocca: São Paulo, Brazil, 1991; 1803p. [Google Scholar]
- Trent, A.M. The peritoneum and peritoneal cavity. Kobluk, C.N. Ames, T.R., Geor, R.J., Eds.; In The Horse Diseases & Clinical Management; Saunders: Philadelphia, 1995; pp. 373–404. [Google Scholar]
- Boelsterli, U.A. Mechanisms of NSAID-Induced Hepatotoxicity: Focus on Nimesulide. Drug Saf. 2002, 25, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steagall, P.V.M.; et al. Evaluation of the adverse effects of oral firocoxib in healthy dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 30, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satué, K; Miguel-Pastor, L. ; Chicharro, D.; Gardón, J.C. Hepatic enzyme profile in horses. Anim. 2022, 12, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Neto, A.R.; et al. Alterations in muscular enzymes of horses competing long-distance endurance rides under tropical climate. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec. 2008, 60, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiness, E.; Rasmussen, F.; Svedsen, O.; Nielsen, P. A comparative study of serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) activity in rabbits, pigs, and humans after intramuscular injection of local damaging drugs. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1978, 42, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galan, M.V.; Gordon, S.C.; Silverman, A.L. Celecoxib-induced cholestatic hepatitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachimuthu, S.; Volfizon, L.; Gopal, L. Acute hepatocellular and cholestatic injury in a patient taking celecoxib. Postgrad. Med. J. 2001, 77, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, R.L. Exames laboratoriais de avaliação hepática nos equinos: perfil bioquímico sanguíneo. Rev. Bras. Med. Equina. 2012, 40(Supl. 1), 48–66. [Google Scholar]
- Koene, M.; Goupil, X.; Kampmann, C.; Hanson, P.D.; Denton, D.; Pollmeier, M.G. Field trial validation of the efficacy and acceptability of firocoxib, a highly selective COX-2 inhibitor, in a group of 96 lame horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2010, 30, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivett, L.; Taintor, J.; Wright, J. Evaluation of the safety of a combination of oral administration of phenylbutazone and firocoxib in horses. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 37, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, M.Y.; Bertone, A.L.; Hendrickson, D.; Hughes, F.; Macallister, C.; McClure, S.; Reiniemeyer, C.; Rossier, Y.; Sifferman, R.; Vrins, A.A.; et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of paste formulations of firocoxib and phenylbutazone in horses with naturally occurring osteoarthritis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 232, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divers, T.J. COX inhibitors: Making the best choice for the laminitis case. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2008, 28, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Moments of evaluation (days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D7 | D14 | D21 | |
| Red blood cells (millions/mm3) | 7.45±1.14 | 7.78±1.140 | 7.78±1.06 | 7.51±1.09 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.38±1.28a | 12.02±1.30b | 12.61±1.17b | 12.67±1.03ab |
| Hematocrit (%) | 36.54±5.53 | 37,36±4.29 | 37,39±3.94 | 37.61±4.75 |
| Leukocites (mm3) | 8.39±11.40a | 7.70±1.35ab | 7.28±1.18 | 8.27±1.30a |
| Segmented Neutrofils (%) | 56.44±5.39 | 59.11±3.18 | 58.0±4.72a | 60.56±4.33 |
| Neutrofils Band(%) | 1.78±0.83 | 1.89±0.93 | 2.0±0.71 | 1.67±0.87 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 36.22±5.61 | 33.0±3.5 | 33.67±5.77 | 32.67±3.04 |
| Monocytes (%) | 3.11±1.54 | 2.67±1.15 | 3.78±1.39 | 2.89±1.17 |
| Eosinophils (%) | 2.44±1.42 | 3.78±0.97 | 2.11±1.62 | 2.22±0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





