Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
03 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility criteria
2.2. Search strategies
2.3. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Synthesis of the results
| Author, Date, Country | Sample & Method | Aim of study | Study findings | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iurova et al (2022) Russia (10) | CC Total (n=41) HGSC (n=28): Stage I-II (n=5) Stage III-IV (n=23) HC (n=13) Pre-operative plasma samples HPLC-QTOF-MS |
D | Decreased plasma concentration of Plasmanyl-LPC(O-16:0), Plasmenyl-PE(P-18:0/18:2,18:0/20:3,18:0/20:4, 18:1/22:6), Plasmenyl-PC(P-16:1/18:0), LPC(14:0,17:0,18:2), PS(37:5), SM(d20:0/18:4) and CerNS(d18:1/24:0) in patients with early OC. | Lipid profiling by HPLC-MS can improve identification of early-stage OC and thus increase the efficiency of treatment |
| Salminen et al (2021) Germany, Finland (11) | CC Total (n=711) Turku (Finland): Malignant (n=197) Benign (n=114) Charite 1 (Germany): Malignant (n=51) Charite 2 (Germany): Malignant (n=104) Charite 3 (Germany): Malignant (n=147) Benign (n=98) Pre-treatment serum samples LC-QTRAP |
P | A two-lipid signature, based on the ratio of the ceramide Cer(d18:1/18:0) and the phosphatidylcholine PC-O(38:4) identified especially poor-outcome patients at the time of diagnosis, before any oncological treatment |
The two-lipid signature was able to identify EOC patients with an especially poor prognosis at the time of diagnosis, showing promise for the detection of disease relapse. |
| Wang et al (2021) China (12) | CC Total (n=340) Discovery set (n=153) EOC (n=62): Early (n=25)/Advanced (n=37) BOT (n=41) HC (n=50) Validation set (n=187): EOC (n=47) BOT (n=29) HC (n=39) Else (n=72) Serum samples UPLC-QTOF-MS |
D | Compared to HC, levels of FAs, LPCs and LPEs were significantly increased, while PCs, PC-Os, PE-Os, SMs and PIs were decreased in BOT and EOC. All of SFAs, MUFAs and PUFAs in BOT and EOC presented a considerable increase simultaneously. PC-O 36:2 (FA18:2), PC-O 38:3 (FA20:3), PC-O 38:4 (FA20:4), PE (16:0p 18:1) and PE (18:0p 22:5) presented lower levels in EEOC vs AEOC. Levels of TGs were remarkably decreased in BOT, compared with HC. Levels of Cers and FAs increased, and levels of PCs, PC-Os and PE-Os decreased in EOC, compared with HC. Cers, DGs, PCs, PEs, and TGs presented high level in EOC, while PC-Os and PE-Os presented low level in EOC, compared to BOT. Cer(d18:1/16:0), PC-O(36:2), PE(16:0p_18:1), OAHFA(18:2_24:6) were selected as the combinational diagnostic marker. |
This study provided evidence for the mechanistic understanding of OC at the level of lipid metabolism. The defined potential combinational marker would be helpful for aiding EOC diagnosis, especially for early stage EOC. |
| Buas et al (2021) USA (13) | CC Total (n=218) 1st cohort (FH) (n=100) OC (n=50) BOT (n=50) 2nd cohort (RP) (n=118) OC (n=60) BOT (n=58) Pre-operative Plasma samples Ascites samples (n=15) Direct infusion MS |
D | In both cohorts, reductions in TAG, PC, CE species, DAG, PE, LPC, LPE and SM species were observed in patients vs controls, while CER(18:0) was elevated. Differentially abundant lipid species in Early stage (I/II): TAG, DAG, PC, PE Late stage (III/IV): TAG, CE, PC, PE, LPC, LPE, SM, CER. PE, LPC, LPE exhibited significant reductions in cases vs controls. In stage-stratified analyses, certain significant class-level differences were detected only in late-stage (LPC, LPE, SM), only in early-stage (DAG, TAG) or in both subgroups (PC, PE). Results suggest that combining CA125 with specific individual lipid metabolites, such as DAG(16:1/18:1), may provide a substantial boost to specificity at 90% sensitivity, relative to CA125 alone, in separating early-stage ovarian malignancies from benign adnexal masses. Certain metabolites may exhibit changes in circulation years before an OC diagnosis: PCs (34:2, 38:3), PEs (36:3, 38:5), TAGs (46:0, 52:4/5, 54:4/5/6/7, 56:4/5/7/8), and SM 22:1 |
Potential translational utility of specific circulating lipid metabolites to aid in the clinical diagnosis and triage of women with adnexal mass. |
| Niemi et al (2018) Germany, Finland (14) | CC Total (n=604) Malignant (n=290): Charite (n=62) Finland (n=76) Charite discovery (n=152) Borderline (n=25): Charite (n=18) Finland (n=7) Benign (n=289): Charite (n=109) Finland (n=82) Charite discovery (n=98) Pre-operative serum/plasma samples Non-targeted & Targeted lipidomics UPLC-QTRAP |
D | Patients showed a consistent decrease in the concentration of most of phospholipids (PCs, LPCs, PIs), cholesteryl esters, glucosyl/galactosyl Cers, and sphingomyelins. Cers with 18:0, 20:0 and 24:1 FAs were increased, while 24:0 FA-containing Cers were decreased. TAGs with shorter FA side chains were decreased, whereas those with longer FA side chains were increased. Twenty-one of 23 lipids analyzed were decreased in all histological subtypes, and only Cer(d18:1/18:0) and TAG (18:1/18:1/20:4) were increased. It appears that borderline tumors do not cause as much of a change to the lipidome as malignant tumors. Lipids improved diagnostic value of CA125 for the detection of stage I/II |
Changes in lipid metabolism due to OC occur in early-stage disease but intensify with increasing stage. Understanding lipid metabolism in OC may lead to new therapeutic and diagnostic alternatives |
| Braicu et al (2017) Germany (15) | CC Total (n=245) Pre-operative serum samples: HGSC (n=147) Controls (n=98) Pre-operative tissue samples: HGSC (n=140) LC-QTOF-MS |
D, P | OC patients exhibit decreased serum levels of PCs, PEs, PIs, CEs, DAGs, SMs, cerebrosides (Glc/GalCers), LacCers, Gb3s, S1Ps. Cers, with 16:0, 18:0, 20:0 and 24:1 FAs were increased, while those containing 23:0 and 24:0 FAs were decreased. TAGs with short FA side chain were decreased, while long chain TAGs were the same or increased compared to controls. The predictive value of diagnosis was improved by the combination of CA125 with PEO-36:1. Lipids belonging to the CE, SM, LPC, PC, PC O and PE O lipid classes were decreased in all OC patients and progressed to lower levels especially in patients where the whole macroscopic tumor could not be removed during the surgery. Ceramides elevated in cancer patients continued to increase during disease progression. Cer(d18:1/16:0) showed significant hazard ratio both in overall and progression-free survival analyses. |
Alterations in lipid metabolism in OC could contribute to diagnosis and prognosis of the disease |
| Xie et al (2017) China (16) | Prospective study Median follow-up (37,5months) Total (n=98) Dead in 3 years (n=46) Survived after 3 years (n=52) Pretreatment plasma samples UPLC-QTOF-MS |
Pr | Poor survival with the increase of Kynurenine, Acetylcarnitine and PC(42:11) and with the decrease of LPE(22:0/0:0). The 4 potential predictive biomarkers were significantly altered in short-term mortality compared to long-term survival patients (P<0.05). PC (42:11) and LPE(22:0/0:0) were significantly altered in short-term mortality and medium survival. Patients with long-term survival showed increased plasma relative intensity of LPE (20:0/0:0) and decreased relative intensity of PC(42:11) | Plasma metabolites could be utilized to predict the overall survival and discriminate the short-term mortality and long-term survival for EOC patients |
| Li et al (2017) China (17) | Prospective study Total (n=70) EOC recurrent (n=39): ER (n=12) LR (n=27) Non recurrent (n=31): Pre-operative plasma samples UPLC-QTOF-MS |
Pr | Most of the identified lipids in EOC recurrent patients were decreased compared with the non-recurrent ones, except up-regulated PC(31:2) and PE-P(42:4). LysoPG(20:5), as a potential biomarker, could provide an AUC value of 0.736, significantly increasing the predictive power of clinical characteristics from AUC value 0.739 to 0.875. Decreased LysoPG(20:5) level was identified as the most important prognostic feature. LysoPCs were down-regulated in recurrent EOC patients compared with the non- recurrent patients. A series of PCs were down-regulated in EOC recurrent patients. Cer(d18:1/23:0), SM(d18:1/14:0), SM(d18:2/14:0) were decreased in EOC recurrent patients. PIs levels were lower in patients with recurrent EOC than in those without recurrent EOC. Decreased levels of TGs: a specific metabolic feature for early relapse. |
Plasma lipidomics study could be used for predicting EOC recurrences, as well as early and late recurrent cases. The lipid biomarker research improves the predictive power of clinical predictors, and the identified biomarkers are of great prognostic and therapeutic potential |
| Buas et al (2016) USA (18) | CC Total (n=100) Serous OC (n=50) Serous BOT (n=50) Plasma samples at the time of surgery Non-targeted & Targeted lipidomics LC-QTOF-MS |
Discr | Glycerolipids and glycerophospholipids, were found to be decreased in abundance in cases relative to controls |
Alterations in circulating plasma lipid metabolites are associated with the presence of malignant ovarian carcinoma versus benign ovarian tumor. |
| Ke et al (2016) China (19) | CC Total (n=105) Primary EOC (n=35) The same Post-operative EOC (n=35) Relapsed EOC (n=35) Controls (n=35) Plasma samples UPLC-QTOF-MS |
P,Pr | Compared with controls, significantly lower concentrations of tetracosahexaenoic acid, 2-octenoic acid, 12,13-DiHODE and 19,20-DiHDPA were observed in primary EOC. Post-operative EOC patients had increased fatty acids and decreased LPCs. Significantly increased levels of LPCs, LPEs and fatty acids were seen in EOC recurrent patients. |
There are delineated metabolic changes in response to advanced EOC, surgery and recurrence, and identified biomarkers that could facilitate both understanding and monitoring of EOC development and progression |
| Y.Zhang et al (2016) China (20) | CC Total (n=65) OC (n=27) BOT (n=27) HC (n=11) Plasma samples UPLC-QTOF-MS |
D | LPCs were up-regulated and PCs and TGs were down-regulated in OC patients compared to Benign and Healthy controls. (Potential biomarkers: 16:0 LPC, 18:1 LPC, 20:3 LPC, 20:4 LPC, 22:6 LPC, 16:0/18:1 PC, 16:0/18:2 PC, 18:0/18:2 PC, 18:0/20:5 PC, 18:2/18:2 PC, 18:2/18:2/16:0 TG) |
MS-based lipidomics is a powerful method in discovering new potential clinical biomarkers for diseases. |
| Hou et al (2016) China (21) | CCTotal (n=215) EOC (n=139) BOT (n=38) UF (n=38) Pre-operative plasma samples UPLC-QTOF-MS |
D,Pr | All the GPs were decreased in EOC patients vs controls, except PC(33:5) and PC(34:3). SPs were remarkably increased in EOC patients, except SM(d18:2/14:0). Two types of glycerolipids showed the opposite trend in EOC patients: MG were significantly increased, whereas DG were significantly decreased in EOC patients vs BOT/UF. All the PCs and pPEs were negatively associated with pathological stage, except PC(33:5), and SMs and Cers were positively associated with pathological stages, except SM(d18:2/14:0). MG was positively associated, whereas DG was negatively associated with pathological staging. PC(P-38:4), PC(35:5), PC(34:3), SM(d18:1/17:0) and SM(d18:0/16:1) together with CA125 improved the diagnostic and predictive accuracy of CA125. |
Plasma lipid profiles analyzed by UPLC- QTOF/MS could be used to discriminate EOC from controls. Promising lipid metabolites together with CA125 improved the diagnostic and predictive performance and accuracy of EOC. |
| Gaul et al (2015) USA (22) | CC Total (n=95) EOC (I/II) (n=46) HC (n=49) Serum samples Non-targeted & targeted lipidomics UPLC-HRMS |
D | 16 metabolites were found to have optimal accuracy in distinguishing between early-stage EOC and controls when used in a linear support vector machine model, most of which were lipids and fatty acids, including lysophospholipids: LPE and LPI |
The results provide the foundation of clinically significant diagnostic tests and evidence for the importance of alterations in lipid and fatty acid metabolism in the onset and progression of the disease. |
| Zhang et al (2015) China (23) | Prospective study Total (n=38) EOC (III/IV) (n=38): With recurrence (n=26) Without recurrence (n=12) Pre-treatment plasma samples UPLC-QTOF-MS |
P/Pr | Metabolites identified as potential metabolic biomarkers of EOC recurrence: L-tryptophan(AUC=0.80), LysoPC(14:0)(AUC=0.77) and LysoPE(18:2)(AUC=0.82) decreased in EOC patients with recurrence, whereas kynurenine(AUC=0.79) and bilirubin(AUC=0.76) increased. Patients with and without recurrent EOC could be distinguished using this panel of metabolites (AUC = 0.91). |
Remarkably, combining of these five biomarkers provided an AUC value of 0.91, which suggests strong potential for predicting EOC recurrence. |
| T. Zhang et al (2012) China (24) | CC Total (n=170) Training samples: EOC (n=50): BOT (n=50) External validation samples: EOC (n=30) BOT (n=40) Pre-operative plasma samples UPLC-QTOF-MS |
Discr | The plasma L-Tryptophan, LysoPC(18:3), LysoPC(14:0), and 2-Piperidinone concentrations were lower among EOC patients than those among BOT patients, either in the training set or in the external validation set |
UPLC-QTOF/MS based metabolomic platform possessed a favorable value in discriminating malignant from benign ovarian tumors. |
| Author, Date, Country | Sample & Method | Aim of study | Study findings | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hishinuma et al (2021) Japan (25) | CC Total (n=160) EOC (n=80) HC (n=80) Plasma samplesUHPLC-MS/MS |
D, Pr | Decreased concentrations of LPCs and PCs and increased concentrations of TGs were observed in EOC patients compared to HCs | Plasma metabolome analysis is useful not only for the diagnosis of EOC, but also for predicting prognosis. |
| Yagi et al (2020) USA (26) | CC Total (n=62) OC (n=20) BOT (n=20) HC (n=22) Plasma samples HPLC-MS |
D | LPE (22:6)/LPE (o-16:0) has the best sensitivity in distinguishing between control and benign, SM (d18:1/24:1)/SM (d18:1/22:0) has the best sensitivity between control and cancer, and PE (16:0/18:1)/PE (o-18:0/18:2) has the best specificity in distinguishing between benign and cancer. |
Potential of plasma phospholipids as a novel marker of OC with great sensitivity and specificity by utilizing the unique characteristics of phospholipids to further enhance the diagnostic power. |
| Zeleznik et al (2020) USA (27) | Nested CC Total (n=504) Mean follow-up (n=12,3years) Cases (n=252) Serous/PD tumors (n=176) Endometrioid/CC (n=34) Rapidly fatal tumors (n=86) Controls (n=252) Pre-diagnosis plasma samples LC-MS/MS |
A | The top three metabolites associated with risk were pseudouridine, C18:0 sphingomyelin (SM) and 4-acetamidobutanoate. Differential association by acyl carbon number and double bond content of TAGs with risk of OC overall was observed. Specifically, TAGs with higher number of acyl carbon atoms and double bonds were associated with increased risk, while TAGs with lower number of acyl carbon atoms and double bonds were associated with decreased risk. Fifty-three lipid-related metabolites (26TAGs, 7PCs, 6LPEs, 3PEs, 3LPC, 4DAGs, 2LPSs, and 2PSs) showed differences by tumor aggressiveness. |
This study suggests that TAGs may be important as a novel risk biomarker for OC, particularly for rapidly fatal tumors, with associations differing by structural features. |
| Plewa et al (2019) Poland (28) | CC Total (n=76) OC (n=26) BOT (n=25) HC (n=25) Serum samplesHPLC-TQ/MS |
D | Decreased serum levels of LPC a C16:1, PC aa C32:2, PC aa C34:4 and PC aa C 36:6 in OC patients compared to BOT and HCs | There is dominant role of lipid alterations in OC. |
| Kozar et al (2018) Slovenia (29) | CC Total (n=57) EOC (n=15) BOT (n=21) HC (n=21) Pre-treatment serum samplesHPLC-TQ/MS |
D | Five most significant markers were Cer 34:1;2 (C16), Cer 40:1;2 (C22), Cer 42:1;2 (C24), SM 36:0;2 and SM 36:1;2 (C18 and C18:1). Important increase in levels of C16-Ceramide, long chain Ceramides C22/C24 and in C18 and C18:1 Sphingomyelin levels in EOC vs Controls were observed |
Long chain ceramides and sphingomyelins may serve as a novel biomarker for EOC detection and may also offer insight into the role of sphingolipid metabolism in cell proliferation. |
| Knapp et al (2017) Poland (30) | CC Total (n=155) AOC (n=74) HC (n=81) Pre-operative Plasma samples LC-MS/MS Post-surgery Tissue samples UHPLC/MS/MS |
Pr | Significant increase (higher risk of OC) in C16-Cer (>311.88 ng/100 μl), C18:1-Cer (>4.75 ng/100 μl) and C18-Cer (>100.76 ng/100 μl) was noticed in plasma of AOC patients vs controls. Increase in C16-Cer, C18:1-Cer, C18-Cer, C24:1-Cer, C24-Cer and S1P was noticed in ovarian tissue of AOC women compared to controls. |
Some sphingolipids can be used as potential biomarkers of advanced ovarian cancer and they can play an important role in the pathogenesis of this disease. |
| Shan et al (2012) USA (31) | CC Total (n=423) EOC (n=211): Stage I/II (n=78) Stage III/IV (n=133) BOT (n=212) Pre-operative serum samplesLC-ESI-MS/MS |
D | The additional measurement of LPA, PPE, LPC (14:0, 12:0) supplements results of CA125 measurement and improves diagnostic accuracy. Measurement of phospholipids improved the identification of early-stage cases from 65% (based on CA125) to 82%, and for mucinous cases from 44% to 88%. |
Measurement of specific biologically active phospholipids improves diagnostic sensitivity and accuracy among women with suspected ovarian cancer |
| Study ID | Study Type | Pre-Intervention | At-Intervention | Post-Intervention | Total Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confounding Bias | Selection Bias | Classification Bias | Deviation Bias | Missing Data Bias | Measurement of outcome Bias | Selective reporting Bias | Overall risk of bias judgement | ||
| Iurova et al (2022) Russia (10) | CC | S | M | L | L | L | L | L | S |
| Salminen et al (2021) Germany, Finland (11) | CC | M | M | L | L | L | M | L | M |
| Wang et al (2021) China (12) | CC | S | L | L | L | L | L | L | S |
| Buas et al (2021) USA (13) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Niemi et al (2018) Germany, Finland (14) | CC | M | M | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Braicu et al (2017) Germany (15) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Xie et al (2017) China (16) | PS | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Li et al (2017) China (17) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Buas et al (2016) USA (18) | CC | M | M | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Ke et al (2016) China (19) | CC | M | M | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Y. Zhang et al (2015) China (20) | CC | S | M | L | L | L | M | L | S |
| Hou et al (2015) China (21) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | M | L | M |
| Gaul et al (2015) USA (22) | CC | S | M | L | L | L | M | L | S |
| H. Zhang et al (2014) China (23) | PS | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| T. Zhang et al (2012) China (24) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | M | L | M |
| Study ID | Study Type | Pre-Intervention | At-Intervention | Post-Intervention | Total Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confounding Bias | Selection Bias | Classification Bias | Deviation Bias | Missing Data Bias | Measurement of outcome Bias | Selective reporting Bias | Overall risk of bias judgement | ||
| Hishinuma et al (2021) Japan (25) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Yagi et al (2020) USA (26) | CC | S | L | L | L | L | S | L | S |
| Zeleznik et al (2020) USA (27) | CC | M | M | M | L | L | L | L | M |
| Plewa et al (2019) Poland (28) | CC | M | L | L | L | M | L | L | M |
| Kozar et al (2018) Slovenia (29) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | M | M | M |
| Knapp et al (2018) Poland (30) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | L | L | M |
| Shan et al (2012) USA (31) | CC | M | L | L | L | L | M | L | M |
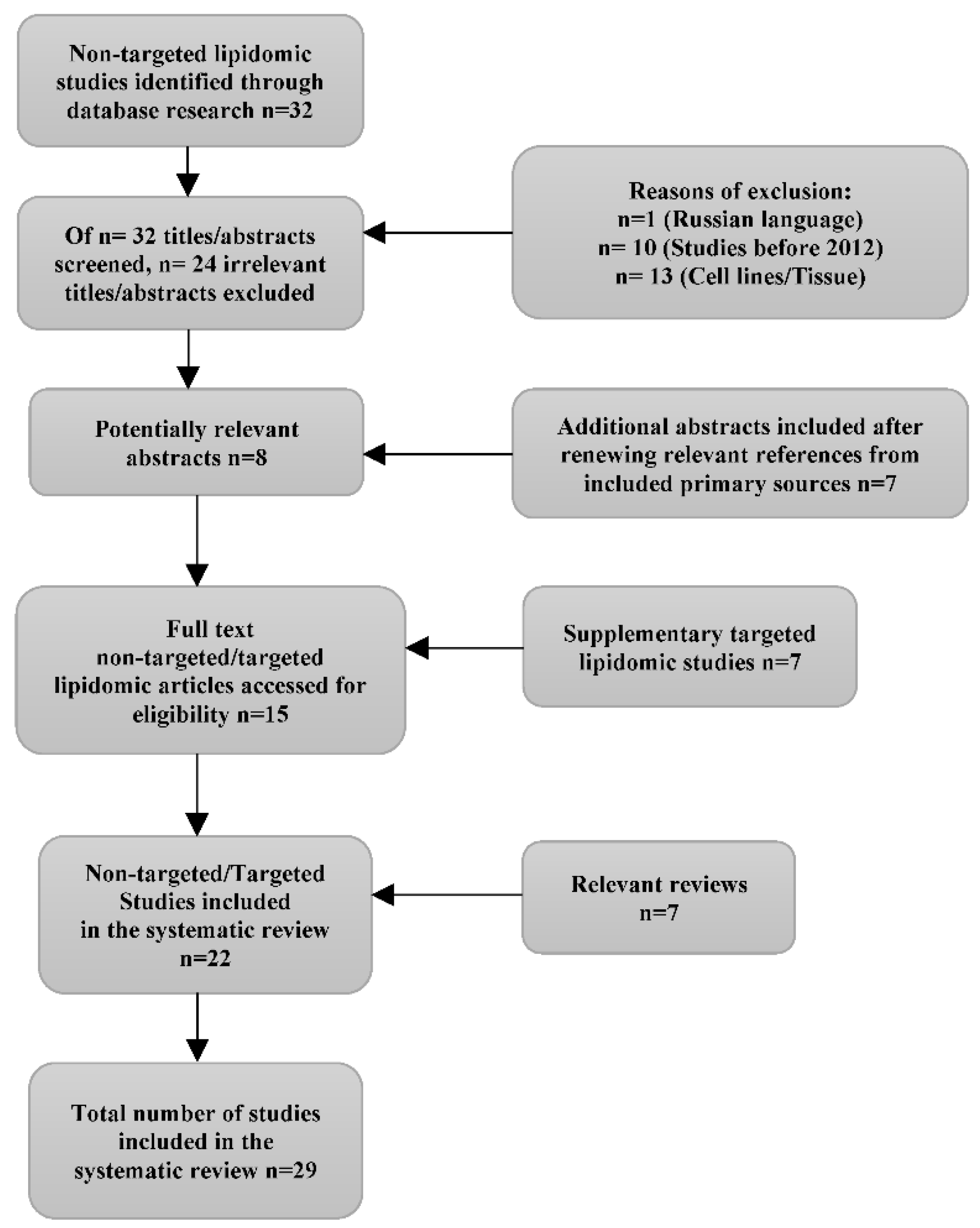
3. Results
3.1. Study selection and characteristics
3.2. Risk of Bias in studies
3.3. Results of syntheses
3.3.1. Diagnosis
3.3.2. Prognosis
3.3.3. Prediction
3.3.4. Discrimination between OC and BOT
| Non-targeted Study | Up-regulated lipids | Down-regulated lipids |
|---|---|---|
| Iurova et al (2022) | Plasmanyl-LPC(O-16:0), Plasmenyl-PE(P-18:0/18:2,18:0/20:3,18:0/20:4,18:1/22:6), Plasmenyl-PC(P-16:1/18:0), LPC (14:0,17:0,18:2), PS(37:5), SM(d20:0/18:4) and CerNS(d18:1/24:0) in patients vs controls |
|
| Salminen et al (2021) | Cer(d18:1/18:0) | PC-O(38:4) |
| Wang et al (2021) | FFAs, LPCs and LPEs in EOC/BOT vs controls. Cers in EOC vs controls |
PCs, PC-Os, PE-Os, SMs and PIs in EOC/BOT vs controls |
| Buas et al (2021) | CER(18:0) in patients vs controls | TAG, PC, CE species, DAG, PE, LPC, LPE and SM species in patients vs controls |
| Niemi et al (2018) | Cers with 18:0, 20:0 and 24:1 FAs, TAGs with longer FA side chains |
Phospholipids (PCs, LPCs, PIs), cholesteryl esters, glucosyl/galactosyl Cers, and sphingomyelins, 24:0 FA-containing Cers, TAGs with shorter FA side chains |
| Braicu et al (2017) | Cers, with 16:0, 18:0, 20:0 and 24:1 FAs. Long chain TAGs. |
PCs, PEs, PIs, CEs, DAGs, SMs, cerebrosides(Glc/GalCers), LacCers, Gb3s, S1Ps. CERs containing 23:0 and 24:0 FAs. TAGs with short FA side chain. |
| Li et al (2017) | PC(31:2) and PE-P(42:4) in EOC recurrent patients | LysoPCs, PCs, PIs in recurrent EOC patients compared with the non-recurrent patients. LysoPG(20:5), Cer(d18:1/23:0), SM(d18:1/14:0), SM(d18:2/14:0), TGs in EOC recurrent |
| Xie et al (2017) | Plasma relative intensity of LPE (20:0/0:0) in patients with long-term survival | Relative intensity of PC(42:11) in patients with long-term survival |
| Buas et al (2016) | Glycerolipids and glycerophospholipids in cases versus controls | |
| Ke et al (2016) | Fatty acids in Post-operative EOC patients. LPCs, LPEs and fatty acids in EOC recurrent patients. |
LPCs, Tetracosahexaenoic acid, 2-octenoic acid, 12,13-DiHODE and 19,20-DiHDPA of primary EOC patients compared to controls. |
| Y.Zhang et al (2016) | LPCs in patients compared to BOT and controls | PCs and TGs in patients compared to BOT and controls |
| Hou et al (2016) | All the GPs in EOC patients vs controls, except PC(33:5) and PC(34:3). MG and SPs in EOC patients, except SM(d18:2/14:0) |
DG in EOC patients vs BOT/UF |
| Gaul et al (2015) | LPE and LPI in OC patients vs controls | |
| H. Zhang et al (2015) | LysoPC(14:0) and LysoPE(18:2) decreased in EOC patients with recurrence compared to non-recurrent | |
| T. Zhang et al (2012) | LysoPC(18:3), LysoPC(14:0) levels were lower in EOC patients compared to BOT patients |
| Targeted Study | Up-regulated lipids | Down-regulated lipids |
|---|---|---|
| Hishinuma et al (2021) | TGs in EOC vs HCs | LPCs and PCs in EOC vs HCs |
| Yagi et al (2020) | ||
| Zeleznik et al (2020) | ||
| Plewa et al (2019) |
LysoPC a C16:1, PC aa C32:2, PC aa C34:4 and PC aa C 36:6 | |
| Kozar et al (2018) | C16-Ceramide, long chain Ceramides C22/C24 and C18 and C18:1 Sphingomyelin levels in EOC vs Controls |
|
| Knapp et al (2017) | C16-Cer, C18:1-Cer and C18-Cer in AOC patients compared to controls | |
| Shan et al (2012) | PPE, LPC (14:0, 12:0) in OC patients compared to controls |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Ovarian Cancer Coalition Atlas, 2020, available at worldovariancancercoalition.org. [accessed cited 2023 Feb 3].
- NCCN (National Comprehensive Cancer Network), NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology, Ovarian Cancer Including Fallopian Tube Cancer and Primary Peritoneal Cancer, Version 1.2022, available at www.nccn.org/patients. [accessed cited 2022 Jan 5].
- Ferrarow S, Braga F, Lanzoni M, Boracchi P, Biganzoli EM, Panteghini M. Serum human epididymis protein 4 vs carbohydrate antigen 125 for ovarian cancer diagnosis: A systematic review. J Clin Pathol, 2013, 66, 273–81. [CrossRef]
- Perrotti F, Rosa C, Cicalini I, Sacchetta P, Del Boccio P, Genovesi D, et al. Advances in lipidomics for cancer biomarkers discovery. Vol. 17, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2016, 17. [CrossRef]
- Wenk M. The Emerging Field of Lipidomics. Nature, 2005, 4, 594-610. [CrossRef]
- Yan F, Zhao H, Zeng Y. Lipidomics: a promising cancer biomarker. Clin Transl Med., 2018, 7. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed-Salim Y, Galazis N, Bracewell-Milnes T, Phelps DL, Jones BP, Chan M, et al. The application of metabolomics in ovarian cancer management: A systematic review. Int J Gynecol Cancer., 2021, 31, 647–55. [CrossRef]
- Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021, 372.
- Sterne JAC, Hernan MA, Reeves BC, Savovic J, Berkman ND et al Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I): detailed guidance, 2016, available from: http://www.riskofbias.info [accessed cited 2023 Mar 15].
- Iurova M V., Chagovets V V., Pavlovich S V., Starodubtseva NL, Khabas GN, Chingin KS, et al. Lipid Alterations in Early-Stage High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Front Mol Biosci., 2022, 9. [CrossRef]
- Salminen L, Braicu EI, Lääperi M, Jylhä A, Oksa S, Hietanen S, et al. A novel two-lipid signature is a strong and independent prognostic factor in ovarian cancer. Cancers, 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Wang Y, Chen C, Ren F, Cao R, Wang Y, et al. Serum lipid profiling analysis and potential marker discovery for ovarian cancer based on liquid chromatography–Mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal., 2021, 199.
- Buas MF, Drescher CW, Urban N, Li CI, Bettcher L, Hait NC, et al. Quantitative global lipidomics analysis of patients with ovarian cancer versus benign adnexal mass. Sci Rep., 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Niemi RJ, Braicu EI, Kulbe H, Koistinen KM, Sehouli J, Puistola U, et al. Ovarian tumours of different histologic type and clinical stage induce similar changes in lipid metabolism. Br J Cancer., 2018, 119, 847–54. [CrossRef]
- Braicu EI, Darb-Esfahani S, Schmitt WD, Koistinen KM, Heiskanen L, Pöhö P, et al. High-grade ovarian serous carcinoma patients exhibit profound alterations in lipid metabolism Oncotarget, 2017, 8, 102912-22.
- Xie H, Hou Y, Cheng J, Openkova MS, Xia B, Wang W, et al. Metabolic profiling and novel plasma biomarkers for predicting survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncotarget, 2017, 8, 32134-46. [CrossRef]
- Li j, Xie H, Li A, Cheng J, Yang K, Wang J, et al. Distinct plasma lipids profiles of recurrent ovarian cancer by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Oncotarget, 2017, 8, 46834–45.
- Buas MF, Gu H, Djukovic D, Zhu J, Drescher CW, Urban N, et al. Identification of novel candidate plasma metabolite biomarkers for distinguishing serous ovarian carcinoma and benign serous ovarian tumors. Gynecol Oncol., 2016, 140, 138–44. [CrossRef]
- Ke C, Li A, Hou Y, Sun M, Yang K, Cheng J, et al. Metabolic phenotyping for monitoring ovarian cancer patients. Sci Rep., 2016, 6. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Liu Y, Li L, Wei J, Xiong S, Zhao Z. High resolution mass spectrometry coupled with multivariate data analysis revealing plasma lipidomic alteration in ovarian cancer in Asian women. Talanta, 2016, 150, 88–96. [CrossRef]
- Hou Y, Li J, Xie H, Sun F, Yang K, Wang J, et al. Differential plasma lipids profiling and lipid signatures as biomarkers in the early diagnosis of ovarian carcinoma using UPLC-MS. Metabolomics, 2016, 12, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Gaul DA, Mezencev R, Long TQ, Jones CM, Benigno BB, Gray A, et al. Highly-accurate metabolomic detection of early-stage ovarian cancer. Sci Rep., 2015, 5. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Ge T, Cui X, Hou Y, Ke C, Yang M, et al. Prediction of advanced ovarian cancer recurrence by plasma metabolic profiling. Mol Biosyst., 2015, 11, 516–21. [CrossRef]
- Zhang T, Wu X, Yin M, Fan L, Zhang H, Zhao F, et al. Discrimination between malignant and benign ovarian tumors by plasma metabolomic profiling using ultra performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Clinica Chimica Acta, 2012, 413, 861–8. [CrossRef]
- Hishinuma E, Shimada M, Matsukawa N, Saigusa D, Li B, Kudo K, et al. Wide-targeted metabolome analysis identifies potential biomarkers for prognosis prediction of epithelial ovarian cancer. Toxins, 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Yagi T, Kuschner CE, Shoaib M, Choudhary RC, Becker LB, Lee AT, et al. Relative ratios enhance the diagnostic power of phospholipids in distinguishing benign and cancerous ovarian masses. Cancers, 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Zeleznik OA, Heather Eliassen A, Kraft P, Poole EM, Rosner BA, Jeanfavre S, et al. A prospective analysis of circulating plasma metabolites associated with ovarian cancer risk. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1357–67.
- Plewa S, Horała A, Dereziński P, Nowak-Markwitz E, Matysiak J, Kokot ZJ. Wide spectrum targeted metabolomics identifies potential ovarian cancer biomarkers. Life Sci., 2019, 222, 235–44. [CrossRef]
- Kozar N, Kruusmaa K, Bitenc M, Argamasilla R, Adsuar A, Goswami N, et al. Metabolomic profiling suggests long chain ceramides and sphingomyelins as a possible diagnostic biomarker of epithelial ovarian cancer. Clinica Chimica Acta., 2018 481, 108–14. [CrossRef]
- Knapp P, Bodnar L, Błachnio-Zabielska A, Świderska M, Chabowski A. Plasma and ovarian tissue sphingolipids profiling in patients with advanced ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol., 2017, 147, 139–44. [CrossRef]
- Shan L, Chen YA, Davis L, Han G, Zhu W, Molina AD, et al. Measurement of Phospholipids May Improve Diagnostic Accuracy in Ovarian Cancer. PLoS One., 2012, 7. [CrossRef]
- Korthauer K, Kimes PK, Duvallet C, Reyes A, Subramanian A, Teng M, et al. A practical guide to methods controlling false discoveries in computational biology. Genome Biol., 2019, 20. [CrossRef]
- Considine EC, Thomas G, Boulesteix AL, Khashan AS, Kenny LC. Critical review of reporting of the data analysis step in metabolomics. Metabolomics, 2018,14. [CrossRef]
- Pitman MR, Oehler MK, Pitson SM. Sphingolipids as multifaceted mediators in ovarian cancer. Cellular Signalling, 2021,81. [CrossRef]
- Kreitzburg KM, van Waardenburg RCAM, Yoon KJ. Sphingolipid metabolism and drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2018, 1, 181–97. [CrossRef]
- Turkoglu O, Zeb A, Graham S, Szyperski T, Szender JB, Odunsi K, et al. Metabolomics of biomarker discovery in ovarian cancer: a systematic review of the current literature. Metabolomics, 2016, 12. [CrossRef]
- Pyragius CE, Fuller M, Ricciardelli C, Oehler MK. Aberrant lipid metabolism: An emerging diagnostic and therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2013, 14, 7742–56. [CrossRef]
- Meleh M, Požlep B, Mlakar A, Meden-Vrtovec H, Zupančič-Kralj L. Determination of serum lysophosphatidic acid as a potential biomarker for ovarian cancer. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007, 858, 287–91. [CrossRef]
- Yagi T, Shoaib M, Kuschner C, Nishikimi M, Becker LB, Lee AT, et al. Challenges and inconsistencies in using lysophosphatidic acid as a biomarker for ovarian cancer. Cancers, 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





