1. Introduction
Bio-composites are composite materials using reinforcements such as wood fibers. The development of these materials based on natural fibers has many advantages due to their biodegradability and interesting mechanical properties. [1-5].
Natural fibers can be obtained from natural sources like animals, plants, and minerals [6;7]. Vegetal fibers are classified according to their physiological properties. Bast Fibers are obtained from flax, hemp, kenaf, jute, etc., leaf fibers from sisal, curauá, palm, etc., seed fibers from cotton, soya, kapok, etc., fruit fibers (coir, luffa, etc.), grass fibers from bamboo, baggase etc. and wood fibers such as hardwood and softwood (teak wood, birch, etc...) [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. Fibers are chosen depending on their properties such as mechanical chemical and physical. It is also important to mention that the availability of a local fiber with interesting properties could be a determining factor for fiber choice. Yellow birch fibers have been chosen for our studies because of its abundance in Quebec, being an alternative for the process of residuals remaining from the wood exploitation.[
6]
Wood plastic composites demand is projected to increase considerably between 2016 and 2024 [6;13]. Many sectors (e.g., construction, sporting equipment, automotive parts) are using this material but their development, for example from short fibers, is limited because of insufficient understanding and knowledge of their mechanical behavior and impact to environmental factors [6;14 –17].
Three types of fungal wood rot are known: white, brown, and soft rot.[
18] The damages to trees and wood can be separated into damage to felled, the living tree, and stored wood and in exterior use, and to indoor use wood.[
19] Brown rot fungi are prevalent to attack on structural wood products in North America. The wood attacked by brown rot fungi becomes brown and it is degraded by the non-enzymatic and enzymatic systems. Cellulolytic enzymes are used in the degradation process by brown rot fungi, but lignin degrading enzymes are not involved. Durmaz, S. et Al 2016 in his work observed that when exposed to fungi, wood mass loss increase occurred due to the degradation of wood carbohydrates; he also observed that the intensity of lignin bands increased proportionally to exposure time, and this is characteristic of brown-rot fungus; Lignin content remains constant.[
20] White rot fungi decay patterns have different forms. White rotted wood has a bleached appearance, leaving the wood a spongy mass; it could also appear as a selective decay. White rot fungi have the cellulolytic and lignin degrading enzymes and therefore have the potential to degrade completely wood structure under adequate environmental conditions. Soft rot fungi attack lower lignin content wood and create cavities in wood cell wall. There isn’t much knowledge of soft rot degradative enzyme systems, but their degradative mechanisms are reviewed along with the degradative enzymatic and non-enzymatic systems existing in the brown and white rot fungi.[
21]
WPC are known to be more durable structural material than untreated wood because the plastic matrix encloses the wood and diminishes moisture uptake. However, extended WPC exposure will eventually result in fungal growth. [
22] In WPC, plastics are by and large resistant to fungal attack; although, a major problem with these materials is that wood in the composite is still susceptible to biological degradation. Many industrialists avoid this risk by fabricating products for interior uses with little or no water presence, and then minimizing the risk of fungal attack.[
23] A usage of WPC materials in external condition may affect its performance.
Therefore, understanding the impact of microorganism exposure, and particularly white and brown rots caused respectfully by Trametes versicolor and Gloephyllum trabeum, on the mechanical properties of bio-composites reinforced with yellow birch fibers is necessary to foresee its possible applications. To achieve this goal, biocomposites samples were made, and exposed to fungus; tensile and Izod impact test were realized, and the results obtained compared to properties of samples not exposed to fungus.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungus
Two strains of fungi were used:
Trametes versicolor (ATCC 12679), a white rot fungus, and
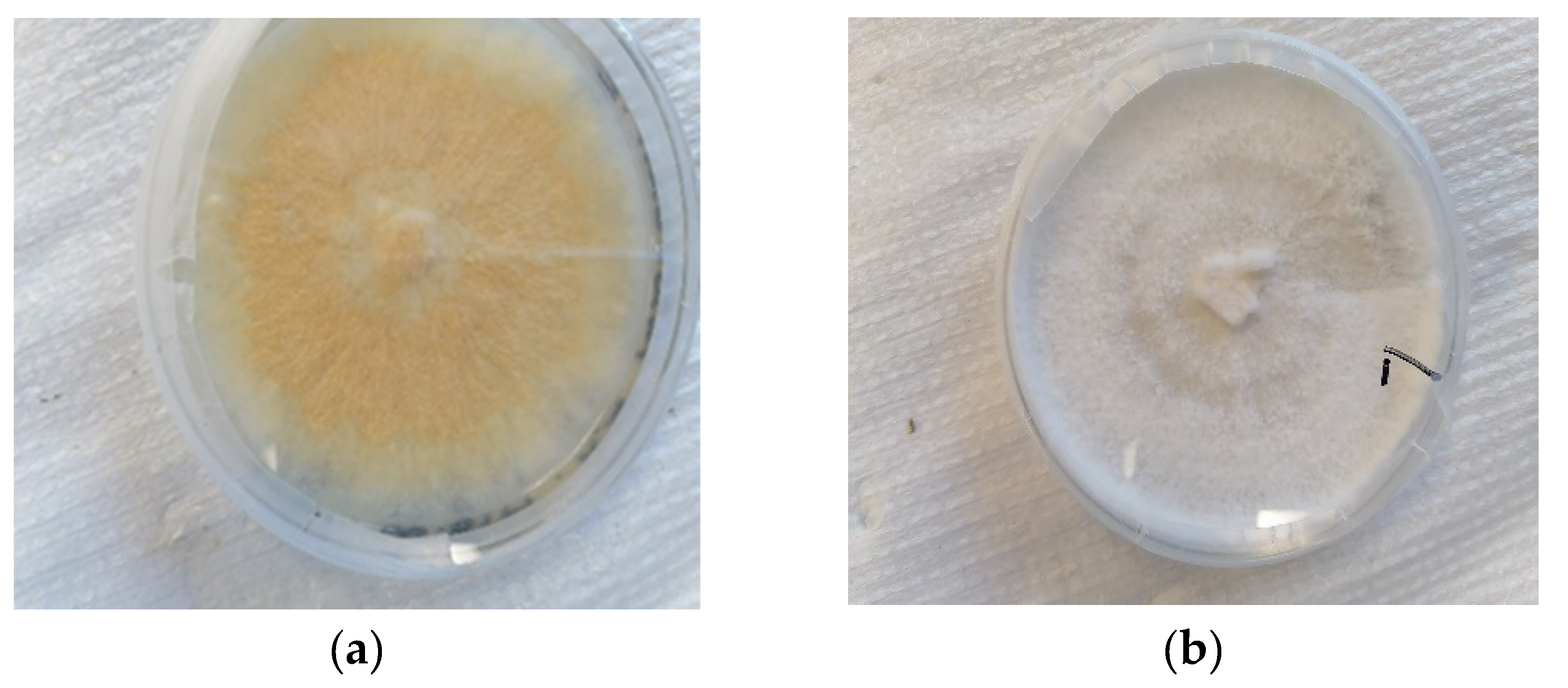
Gloephyllum trabeum (ATCC 11539), a brown rot fungus; Both strains were provided by SEREX in Rimouski (Quebec, Canada). They were cultivated in potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture media and incubated at 25°C with a 70% Relative Humidity for approximately 7 to 10 days (until complete colonization) prior the exposition. (
Figure 1.)
2.2. Birch fiber treatment with Zinc Oxide (ZnO)
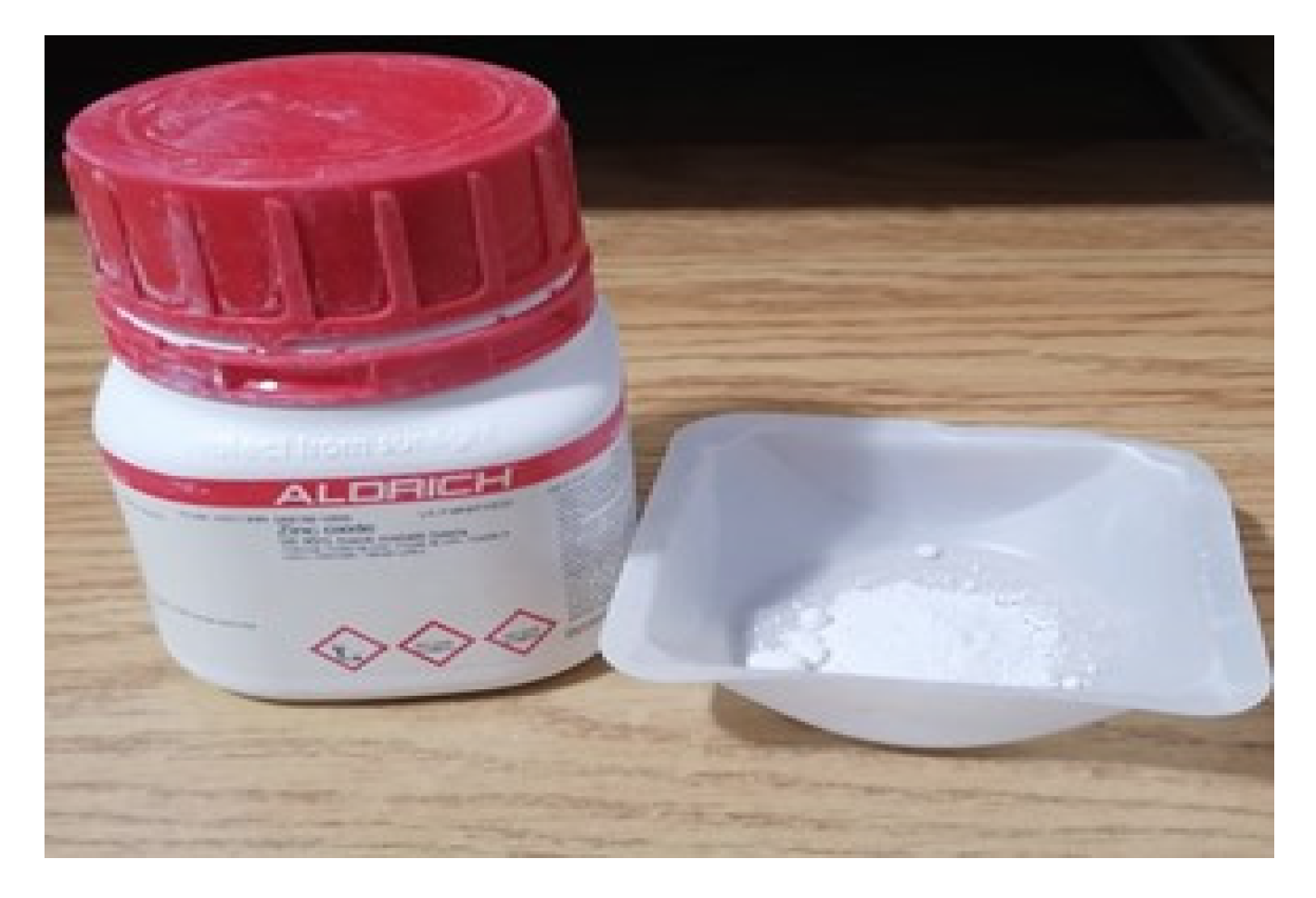
The Zinc oxide ZnO as shown in
Figure 2 was produced by SIGMA Aldrich. It was a 99.99% trace metals basis, with 81.39 g/mol molar weight. It is a white to yellow powder. It was dissolved NaOH solution. The adequate solution was a molar. Solution was obtained by manual stirring when adding the ZnO powder and after heated at 80
oC for approximately 2 minutes until complete dissolution. The fibers were then immersed once until totally wet or absorbed all the solution (
Figure 3). The treated fibers were dried in stove at 60
oC for 5 days.
2.3. Preparation of Bio-composite Samples
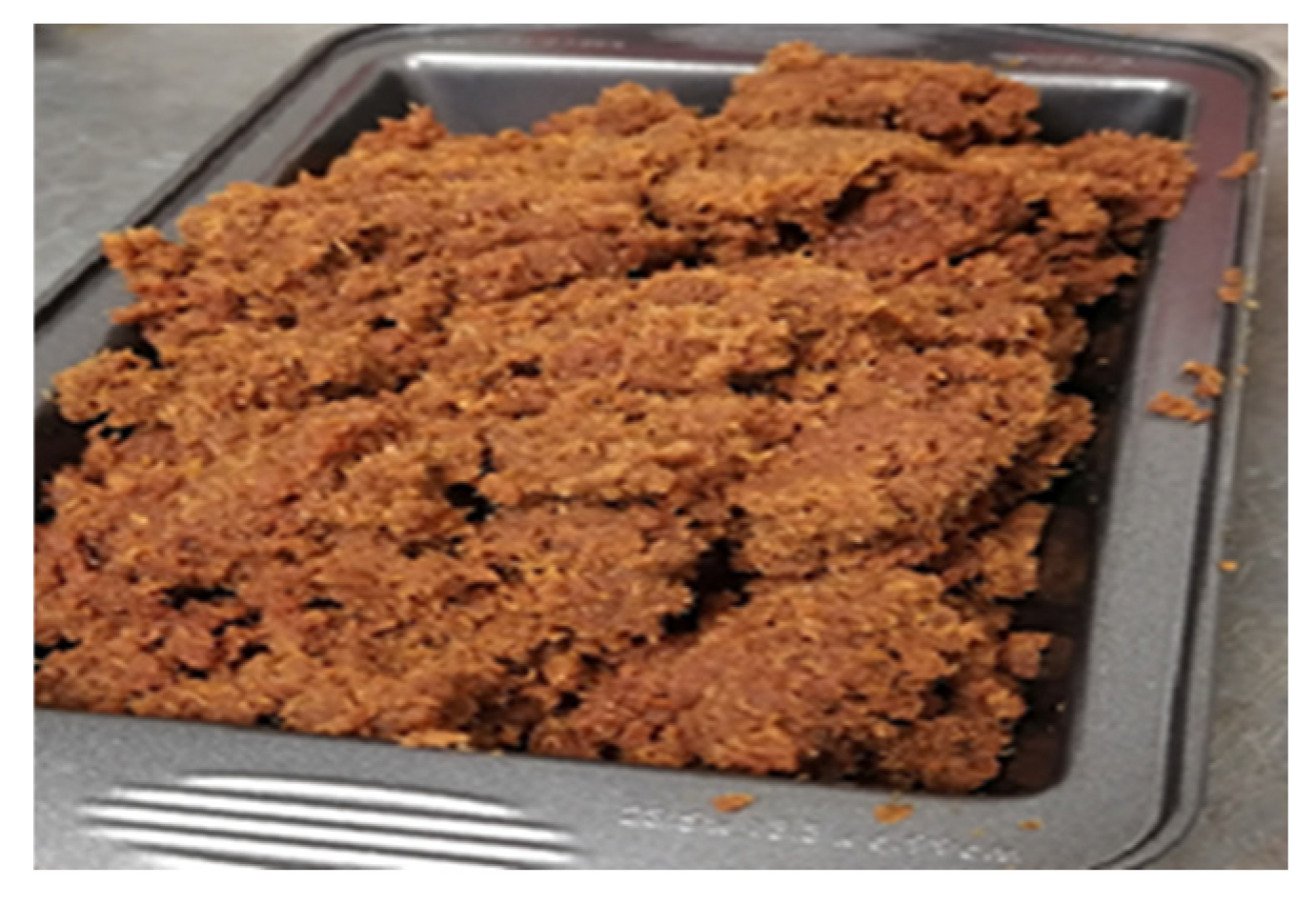
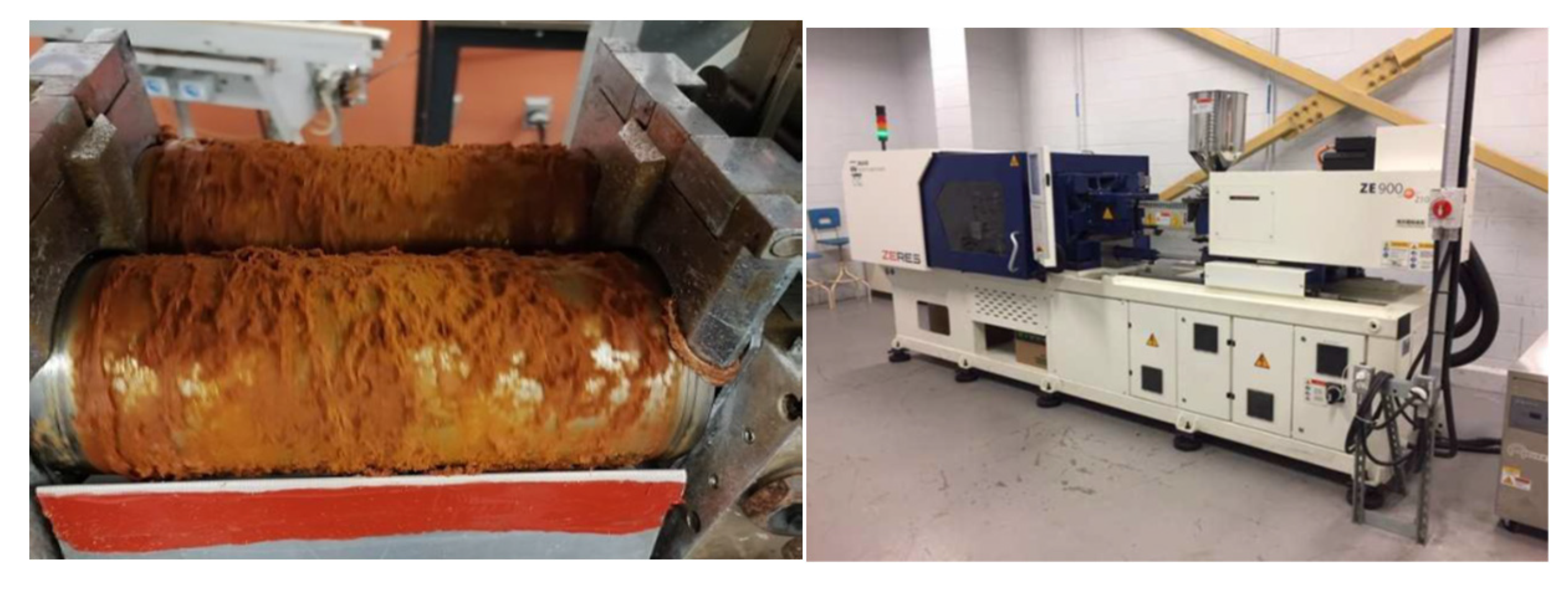
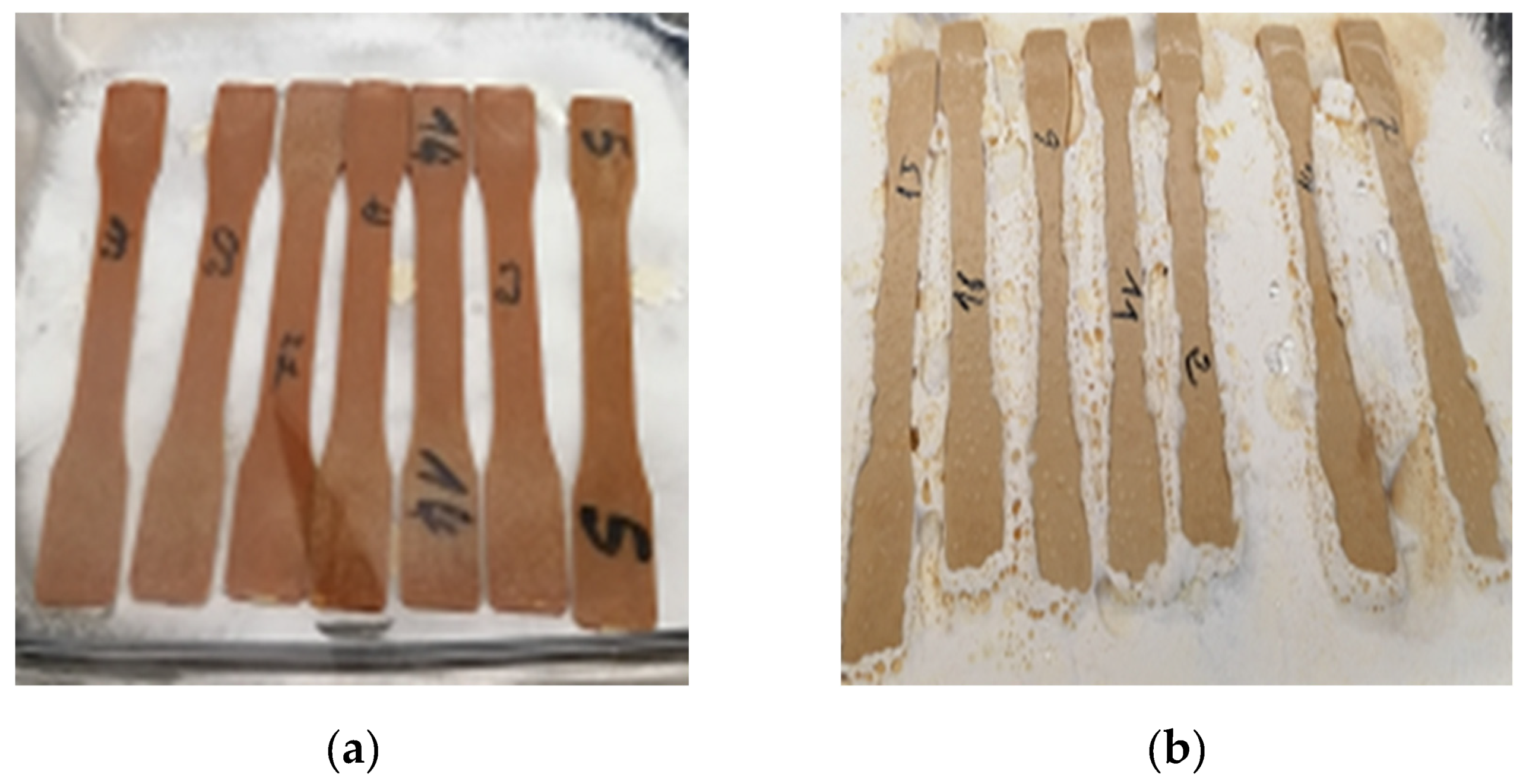
The bio-composite samples were made by mixing the components in a Thermotron mixer (C.W. Brabender; model T-303). HDPE (High Density Polyethylene) was melted on the rollers at 170 ℃ together with Maleic Anhydride Grafted Polyethylene MAPE (3% of mix weight). The remaining HDPE and the fibers were added and blended at 60 rpm and for 7 min. The mix was removed from the roller and re-mixed for 3 min five times to obtain a uniform composite sheet which was further granulated, and injection molded into the test samples. (
Figure 4) Two bio-composite formulations made of HDPE reinforced with 20 and 30 (w/w) % fibers were processed by ZHAFIR Plastics Machinery (100-ton Zerus 900 press).
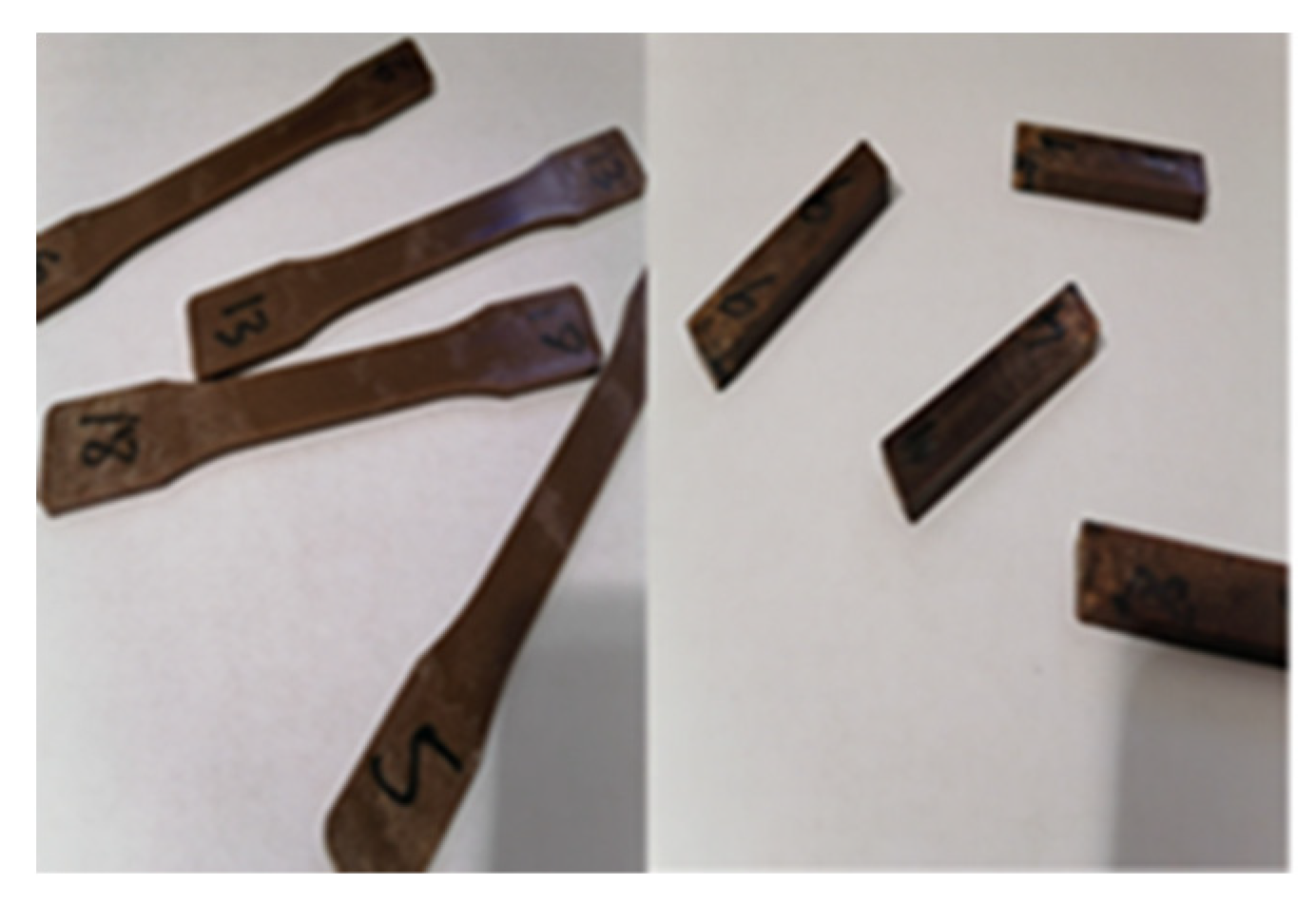
Figure 5 shows an aspect of the tensile and the Izod impact test specimen which specifications follow the ASTM D256 - 10e1 and ISO 527–1 standard. Five samples’ replicates for each material were tested (ZnO treated and non-treated samples). (
Figure 6)
2.4. Culture media
An Agar-Potato dextrose mixture was used as the culture medium for both the white and brown fungi strains. After its preparation, it was sterilized in an autoclave for 45-60 minutes at 121℃ followed by a resting period of 30 minutes under pressure. It was further used to fill the petri dishes and the other containers through the laminar flow cabinet of the CIPP laboratory which was previously disinfected using 70% ethanol and UV lamps. An inoculation of the medium by the two fungi strains was performed after its cooling.
2.5. Exposure tests
The inoculated culture media were fully colonized by the fungi strains for approximately 7 days as attested by a visual inspection done every 2 days before the samples were directly placed on it. This process which was carried out according to the level 2 biosafety standards, lasted 30 days to avoid working with aged strains. A septuplet of each bio-composite formulation was exposed to each fungi strain. After the incubation period, the samples were characterized by tensile and impact tests.
2.6. Impact tests of exposed samples
The impact tests were conducted at the mechanical engineering laboratory of UQTR based on an application of the ASTM D256 - 10e1 standard on the appropriate samples, using an impact pendulum instrument (Instron CEAST 9050) with a 0.5 J hammer. With the pendulum, the resilience, ductile and/or brittle fracture of the investigated material can be determined. According to ASTM D256 - 10e1 standard, the breaking energy of the tested material must be between 10 and 90 % of the hammer’s capacity used for the Izod impact tests [
6,
24].
2.8. Microscope observation
Samples were observed with electronic microscope. It was precisely with the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) (Hitachi) of the electronic microscopy laboratory of I2E3 at University of Quebec in Trois-Rivières (UQTR).
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of brown and white growth on bio-composite samples
Table 1 gives an evaluation of fungal growth on the Zinc oxide treated bio-composites made of HDPE and yellow birch fibers. It is expressed in terms of the proportion of the bio-composite surface occupied by the fungi growth, following a given nomenclature.
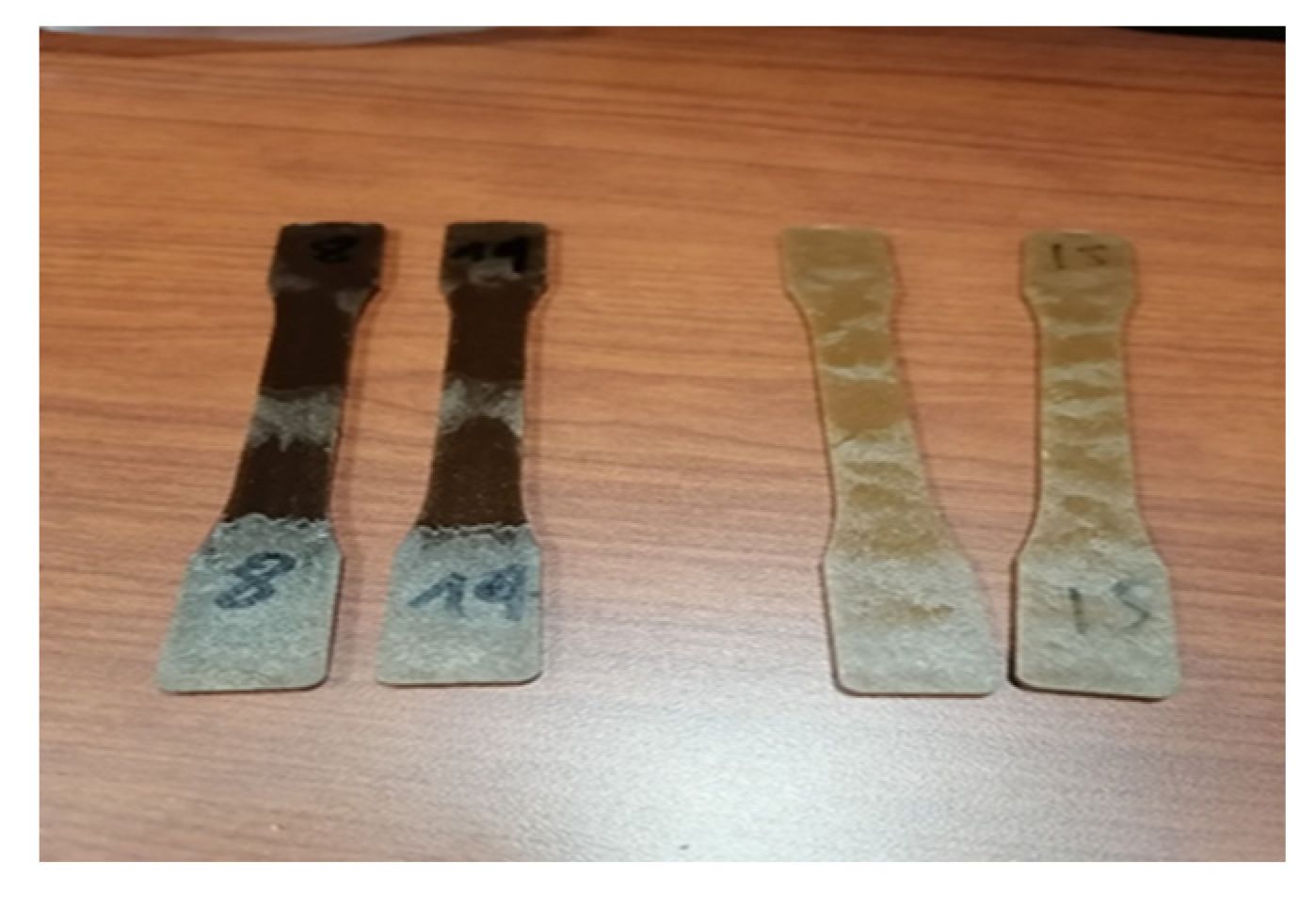
These results suggest that the fungi colonization of the bio-composite surface was nonexistent independently of both fungi strain considered and proportion of birch fibers proportion. The main surface of the bio-composites was not covered at all by the fungi rot in all the cases.
Samples exposed to
G. trabeum and
T. versicolor generally showed the same appearance. No trace of colonization was observed, apparently the hyphae could not propagate; Samples seem to present a lighter color. (
Figure 7).
3.2. Impacts tests results.
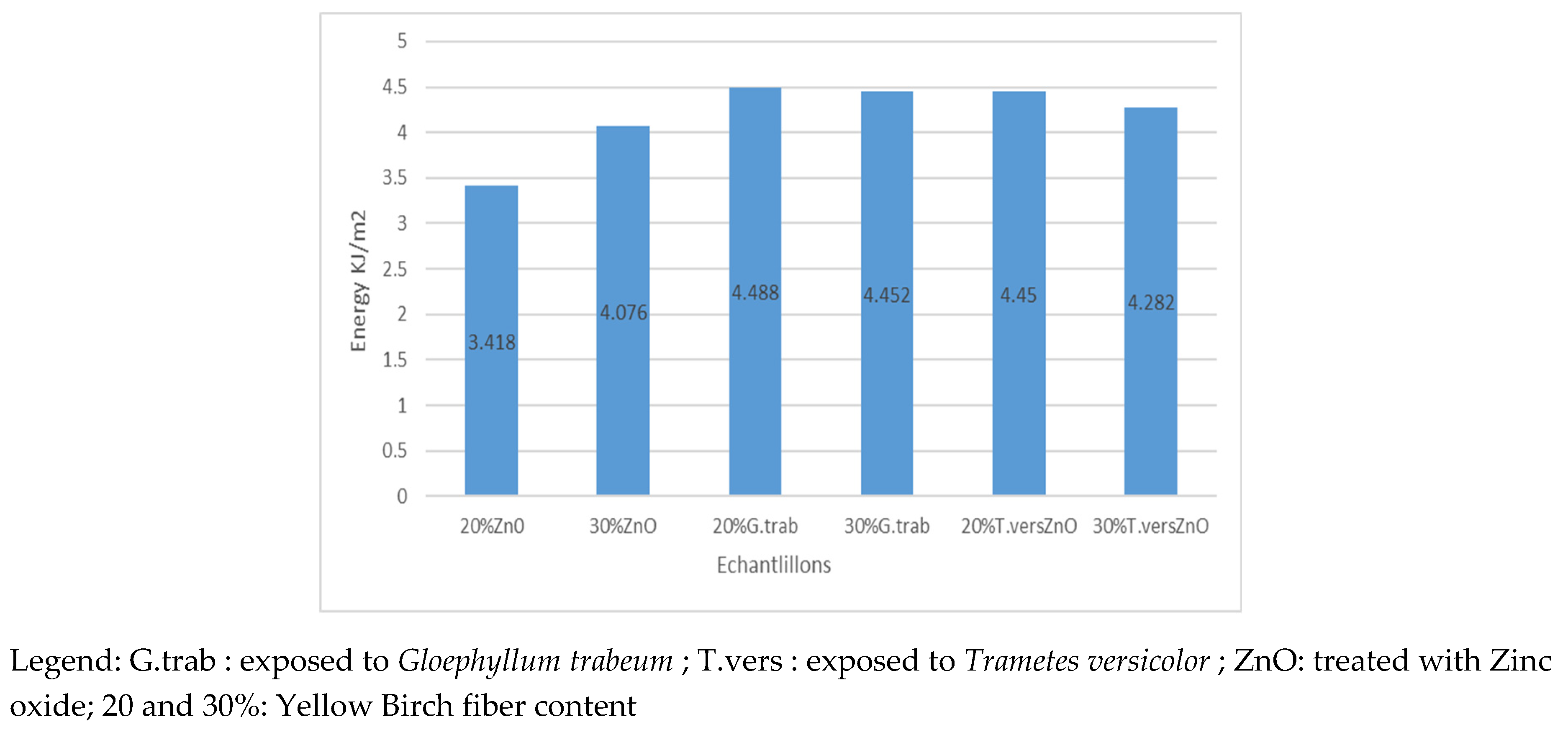
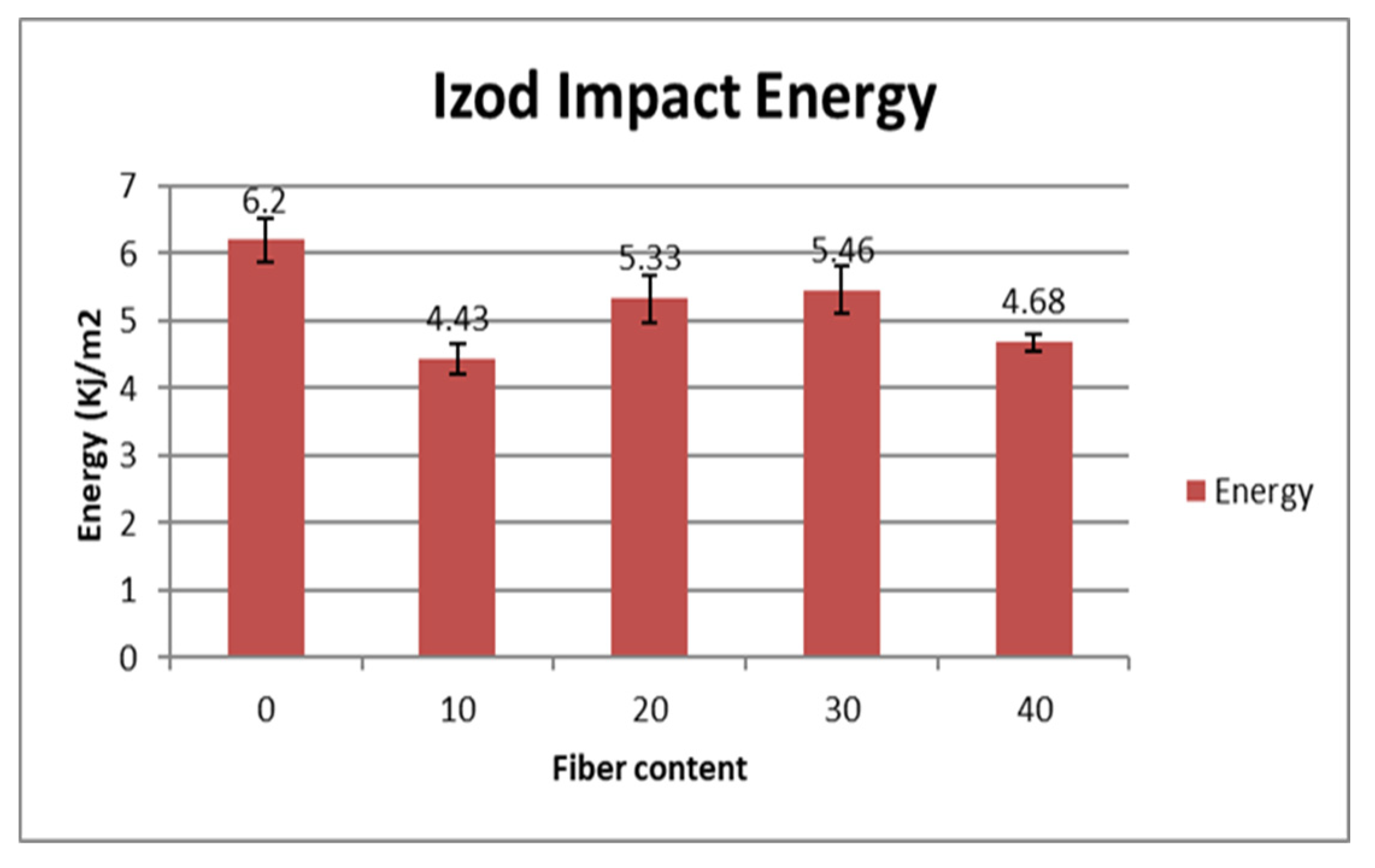
The results are shown on
Figure 8. Results on
Figure 9 correspond to Koffi et Al 2021 works. All samples tested were fabricated with the same method and using the same parameters in both studies.
Legend: G.trab : exposed to Gloephyllum trabeum ; T.vers : exposed to Trametes versicolor ; ZnO: treated with Zinc oxide; 20 and 30%: Yellow Birch fiber content
Treated samples and not exposed to rot had a value of 3.418 KJ/m
2 and 4.076 KJ/m
2 respectively when loaded with 20 and 30% fibers. Non treated and non-exposed samples impact energies were 5,33 et 5,46 KJ/m
2 (
Figure 9). The impact energies were 4.488 and 4.45 KJ/m
2 for the 20% fiber samples ZnO -treated and exposed to
G. trabeum and
T. versicolor. The impact energies of the samples loaded with 30% ZnO-treated fibers and exposed to
G. trabeum and
T. versicolor were 4.452 and 4.282 KJ/m
2 respectively, while they were 5.676 and 6.538 KJ/m
2 [
6] when the samples were not treated with ZnO; impact energy decreases of 21.6% and 34.6%. The decrease is due to the alkaline treatment. In our previous works when WPC samples were exposed to
T. versicolor, an increase in adhesion between fibers and polymeric matrix was noted resulting in an increased impact energy; Schirp et Al 2006 observed similar activity when samples were exposed to the same rot.
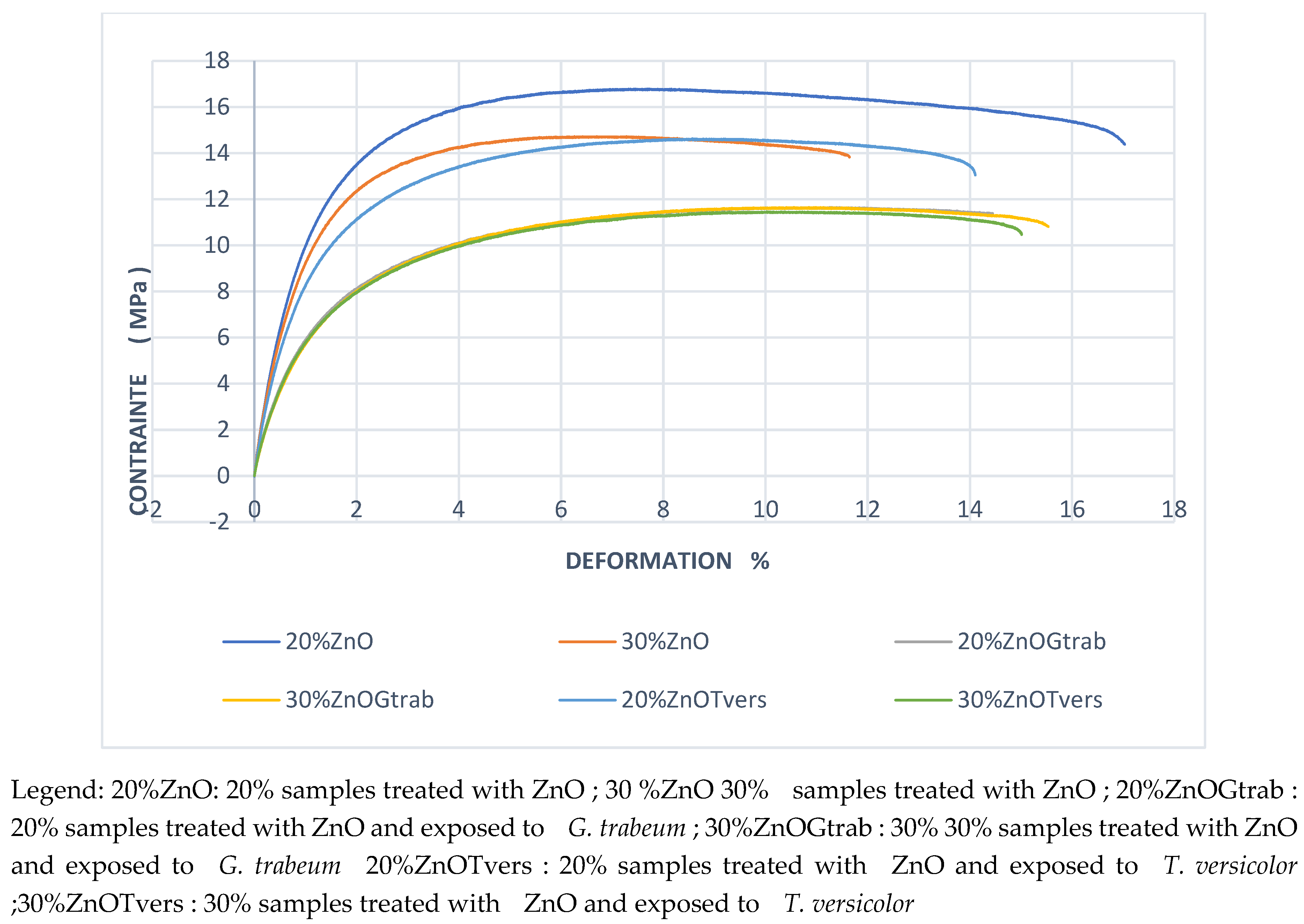
3.3. Tensile test results
Young’s modulus and Strain have been determined (
Figure 10)
Legend: 20%ZnO: 20% samples treated with ZnO ; 30 %ZnO 30% samples treated with ZnO ; 20%ZnOGtrab : 20% samples treated with ZnO and exposed to G. trabeum ; 30%ZnOGtrab : 30% 30% samples treated with ZnO and exposed to G. trabeum 20%ZnOTvers : 20% samples treated with ZnO and exposed to T. versicolor ;30%ZnOTvers : 30% samples treated with ZnO and exposed to T. versicolor
The samples loaded with 20% birch fiber not treated with ZnO and not exposed to decay had a Young's modulus (E) of 2.67 ± 0.13 GPa, while the 20% treated with ZnO and not exposed to rot had a Young's modulus of 1.42 ± 0.05 Gpa which shows a decrease of 53% when samples are treated with ZnO. When treated with ZnO and exposed to T. versicolor the samples loaded with 20% fibers had a Young's modulus of 1.18 ± 0.026 GPa while the samples not treated with ZnO and exposed to the same decay had a young’s modulus of 2.30 ± 0.02 Gpa which represent a decrease of 51 % when treated with ZnO. Samples loaded with 30% fiber treated with ZnO and exposed to T. versicolor had a Young's modulus of 0.79 ± 0.02 GPa while samples with 30% unexposed and untreated with ZnO had a modulus of 3.37 ± 0.16 Gpa; meaning a decreased of 76% is observed when samples were treated and exposed. Young's modulus was 3.22 ± 0.06 GPa for 30% loaded samples not treated with ZnO and exposed to T. versicolor; samples treated with ZnO and exposed to the same decay therefore suffered a decrease in Young's modulus of approximately 75% compared to samples not treated with ZnO. Results were similar when samples were exposed to the brown rot fungi. The samples loaded with 20% fibers not treated with ZnO and exposed to rot had a Young's modulus of 2.36 ± 0.04 GPa while those treated and exposed to rot had a Young's modulus of 1.17 ± 0.07 GPa; there is a decrease of 49.57%. The samples loaded with 30% fibers not treated with ZnO and exposed to G. trabeum had a Young's modulus of 3.42 ± 0.07 GPa while those treated with ZnO and exposed to the same rot had a Young's modulus of 0.86 ± 0.01 GPa, a decrease of 74.85%. This is consequence of alkaline fiber treatment; in this process fibers swell issuing changes in structure, dimension, morphology, and then mechanical performance as mentioned in ASTM-D 1965. As the alkaline treatment eliminates celluloses, pectin and lignin which are the principal natural fiber components, fiber’s tensile strength may decrease [27-29]. A trend of decreasing mechanical properties is observed with increased concentration of NaOH which is likely in our case.
3.4. Electron microscope results
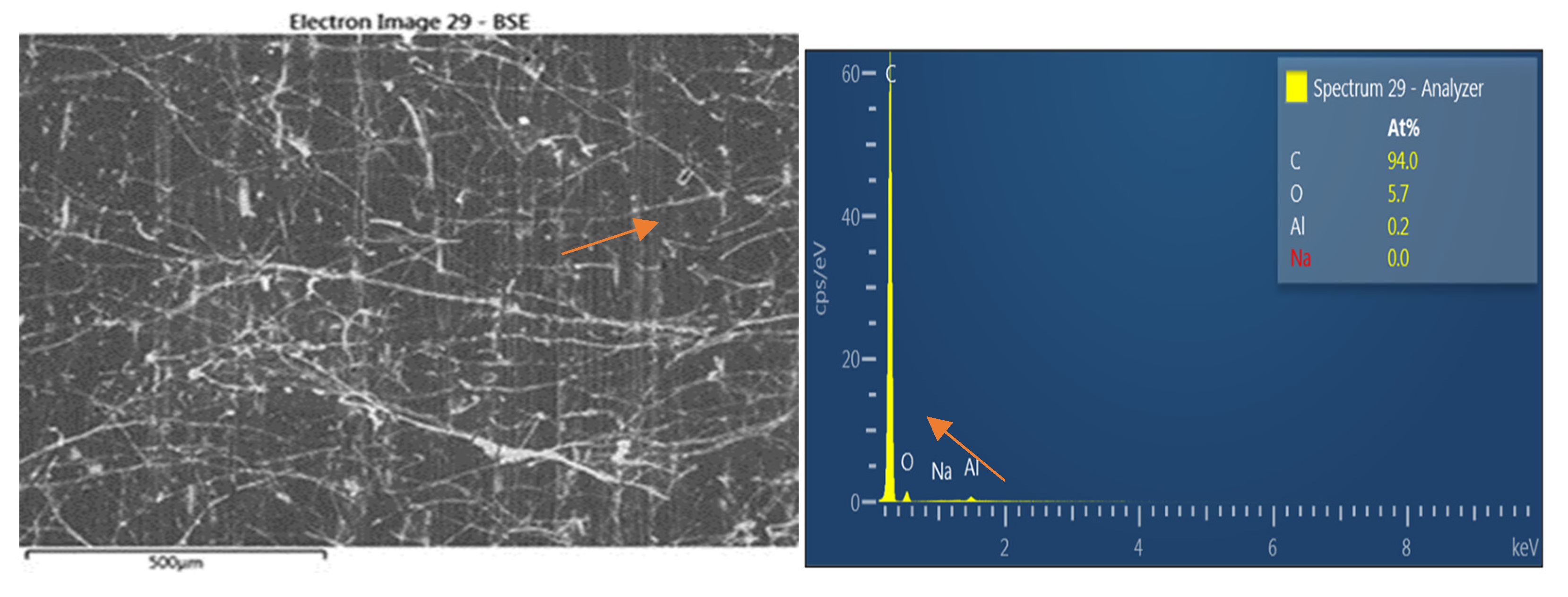
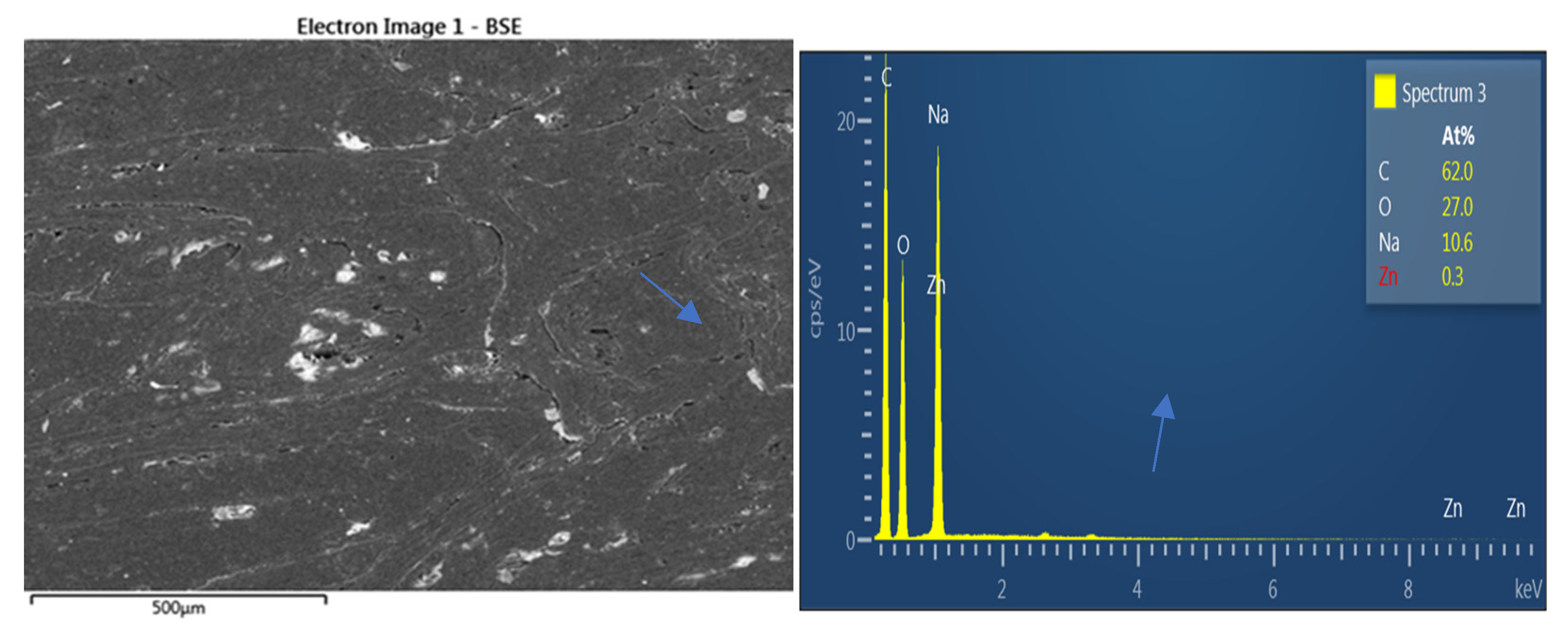
There is mycelium presence on sample surface. (
Figure 12) On ZnO- treated samples exposed to rot, they weren’t no mycelium presence. (
Figure 13)
Figure 12 shows non-treated samples surface with mycelium growth, orange arrows indicate hyphae. Zinc oxide has avoided the effect of rot, during the exposure of the samples; no trace of mycelium was found on any sample. At the same time Zinc presence was evidenced. (
Figure 13) The blue arrows on
Figure 13 indicate Zn presence on sample; EDX analysis corroborates Zn and Na presence even if its concentrations are low when compared to Carbon and oxygen concentrations. The surface image of the sample shows Zn presence at 0.3 % despite the encapsulation of wood fiber with HDPE; low fiber content and limited immersion time of fibers in NaOH- ZnO solution. The mechanical properties of zinc oxide treated WPCs were lower than untreated. Alkaline treatment when NaOH concentration is lower than 5% promotes an increase of interfacial strength between polymeric matrix and lignocellulosic reinforcement (GHASEMI, E. and Farsi, M., 2010) which also improves mechanical properties of WPC. Valášek, Petr, et al 2021 also confirmed that the excessive and long-term action of alkaline treatment of NaOH solution causes deterioration in the mechanical properties of individual fibers. In our work NaOH used as solvent provoked deterioration of treated fibers causing a decrease in mechanical properties.
4. Conclusions
In this work, ZnO anti-fungal properties have been evidenced. Its application protects against fungal rot when Yellow Birch Fiber /HDPE composites were exposed to Trametes versicolor and Gloephyllum trabeum white and brown rots fungi respectively. Fibers were treated with a NaOH- ZnO solution. NaOH treatment affected fibers provoking a decrease in mechanical properties. In the literature review, ZnO has many characteristics such as antifungal. It was chosen due to its availability on the market and is the most used in many works. The samples loaded with 20% birch fiber and ZnO not- treated not exposed to decay had a Young's modulus (E) of 2.67 ± 0.13 GPa, while 20% samples ZnO- treated not exposed had a Young's modulus of 1.42 ± 0.05 GPa representing 53% decrease. It would be recommended to use nano-zinc oxide to avoid a decrease in mechanical properties.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, D.K and F.E.; methodology, S.B and K.A; validation, K.D, F.E. and S.B.; formal analysis, K.A; investigation, K.A.; resources, K.D and S.B.; writing—original draft preparation, K.A.; writing—review and editing, K.A.; visualization, K.D and F.E; supervision, D.K; project administration, D.K; funding acquisition, D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was done with the technical and financial, and logistic support of the Institut d’Innovations en Ecomatériaux Écoproduits et Ecoénergies (I2E3) of the Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières (UQTR), QC., Canada. The authors acknowledge the support of SEREX college transfer center (CCTT) in the processing of forest products affiliated with Cégep de Rimouski.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Scida D, Assarar M, Ayad R, Poilâne C. Effet de l'humidité sur le comportement mécanique des composites à fibres de lin. In17èmes Journées Nationales sur les Composites (JNC17) 2011 Jun 15 (p. 186).
- Laurent A, ´´ Étude de l’élaboration de matériaux composites PVC/bois à partir de déchets de menuiserie : formulation, ca-ractérisation, durabilité et recyclabilité´´ Thèse Doctorale, Toulouse ,2007.
- Tazi, Mostafa. "Valorisation des sciures de bois dans des composites thermoplastiques (HDPE-BOIS): élaboration, caractérisa-tion et modélisation en soufflage libre." PhD diss., Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, 2015.
- Gaudin, Solène. "Étude de la durabilité photochimique de composites bois-polymères biodégradables." PhD diss., Université Blaise Pascal-Clermont-Ferrand II, 2008.
- M.R. Sanjay, P. Madhu, Mohammad Jawaid, P. Senthamaraikannan, S. Senthil, S. Pradeep, Characterization and properties of natural fiber polymer composites: a comprehensive review, J. Clean. Prod. 172 (2018) pp.566–581.
- Koffi, Agbelenko, Demagna Koffi, and Lotfi Toubal. "Mechanical properties and drop-weight impact performance of injec-tion-molded HDPE/birch fiber composites." Polymer Testing 93 (2021): 106956.
- Vinod, M.R. Sanjay, Suchart Siengchin, Jyotishkumar Parameswaranpillai, Renewable and sustainable biobased materials: an assessment on biofibers, biofilms, biopolymers and biocomposites, J. Clean. Prod. 258 (2020) 120978.
- M.R. Sanjay, P. Madhu, Mohammad Jawaid, P. Senthamaraikannan, S. Senthil, S. Pradeep; Characterization and properties of natural fiber polymer composites: a comprehensive review, J. Clean. Prod. 172 (2018) pp.566–581.
- Y.G. Thyavihalli Girijappa, S. Mavinkere Rangappa, J. Parameswaranpillai, S. Siengchin, Natural fibers as sustainable and renewable resource for development of eco-friendly composites: a comprehensive review, Front. Mater. 6 (2019) 226,
. [CrossRef]
- P. Madhu, M.R. Sanjay, Mohammad Jawaid, Suchart Siengchin, Anish Khan, Catalin Iulian Pruncu, A new study on effect of various chemical treatments on Agave Americana fiber for composite reinforcement: physico-chemical, thermal, mechanical and morphological properties, Polym. Test. 85 (2020) 106437.
- Manimaran, P., S. P. Saravanan, M. R. Sanjay, Suchart Siengchin, Mohammad Jawaid, and Anish Khan. "Characterization of new cellulosic fiber: Dracaena reflexa as a reinforcement for polymer composite structures." Journal of Materials Research and Technology 8, no. 2 (2019): pp.1952-1963.
- Alshammari, Basheer A., Majed D. Alotaibi, Othman Y. Alothman, M. R. Sanjay, Lau Kia Kian, Zeyad Almutairi, and Mo-hammad Jawaid. "A new study on characterization and properties of natural fibers obtained from olive tree (Olea europaea L.) residues." Journal of Polymers and the Environment 27 (2019): pp.2334-2340.
- Size, Mechanical Ventilators Market. "Share & trends analysis report." By Product (Intumescent Coatings, Cementitious Ma-terials), By Application (Construction, Warehousing), And Segment Forecasts 2027 (2020).
- Shubhra, Quazi TH, AKM Moshiul Alam, and M. Adul Quaiyyum. "Mechanical properties of polypropylene composites: A review." Journal of thermoplastic composite materials 26.3 (2013): pp.362-391.
- F. Mijiyawa, D. Koffi, B.V. Kokta, F. Erchiqui, Formulation and tensile characterization of wood–plastic composites Polypro-pylene reinforced by birch and aspen fibers for gear applications, J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 28 (12) (2014) pp.1675–1692.
- M. Mejri, L. Toubal, J.C. Cuillière, V. François, Hygrothermal aging effects on mechanical and fatigue behaviors of a short-natural-fiber-reinforced composite, Int. J. Fatig. 108 (2018) pp.96–108.
- L. Toubal, J.C. Cuillière, K. Bensalem, V. Francois, P.B. Gning, Hygrothermal effect on moisture kinetics and mechanical properties of hemp/polypropylene composite: experimental and numerical studies, Polym. Compos. 37 (8) (2016) pp.2342–2352.
- Schmidt, Olaf. "Wood rot." Wood and Tree Fungi: Biology, Damage, Protection, and Use (2006): pp.135-159.
- Schmidt, Olaf. "Habitat of Wood Fungi." Wood and Tree Fungi: Biology, Damage, Protection, and Use (2006): pp.161-236.
- Durmaz S, Özgenç Ö, Boyacı İH, Yıldız ÜC, Erişir E. Examination of the chemical changes in spruce wood degraded by brown-rot fungi using FT-IR and FT-Raman spectroscopy. Vibrational Spectroscopy. 2016 Jul 1; 85:202-7.
- Goodell, Barry, Yuhui Qian, and Jody Jellison. "Fungal decay of wood: soft rot—brown rot—white rot." 2008.
- Fabiyi JS, McDonald AG, Morrell JJ, Freitag C. Effects of wood species on durability and chemical changes of fungal decayed wood plastic composites. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. 2011 May 1;42(5):501-10.
- Catto AL, Montagna LS, Almeida SH, Silveira RM, Santana RM. Wood plastic composites weathering: Effects of compatibil-ization on biodegradation in soil and fungal decay. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation. 2016 Apr 1; 109:11-22.
- ISO 527-1, Plastics -Determination of Tensile Properties - Part 1: General Principles, 2012.
- Valášek, Petr, et al. "Influence of alkali treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of coir and abaca fibers." Materials 14.10 (2021): 2636.
- Schirp A, Ibach RE, Pendleton DE, Wolcott MP. Biological degradation of wood-plastic composites (WPC) and strategies for improving the resistance of WPC against biological decay. InACS symposium series 2008 Apr 2 (Vol. 982, pp. 480-507).
- Koohestani, B. A. B. A. K., et al. "Comparison of different natural fiber treatments: a literature review." International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 16.1 (2019): pp.629-642.
- Anand, P., and V. Anbumalar. "Investigation on thermal behavior of alkali and benzoyl treated hemp fiber reinforced cellulose filled epoxy hybrid green composites." Cellul Chem Technol 51, no. 1-2 (2017): pp.91-101.
- Gurunathan T, Mohanty S, Nayak SK. A review of the recent developments in biocomposites based on natural fibres and their application perspectives. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. 2015 Oct 1;77: pp.1-25.
- GHASEMI, ESMAEIL, and Mohammad Farsi. "Interfacial behaviour of wood plastic composite: effect of chemical treatment on wood fibres." (2010): 811-818.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).