Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
03 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Phase 1
3.2. Phase 2
3.3. Phase 3
3.4. Model key points from parts 1, 2, and 3 of the findings
3.4.1. HIV-TB coinfection
3.4.2. Smoking
3.4.3. Gene mutation and regions of mutations
3.4.4. Heteroresistance
3.4.5. Type of lineage
3.4.6. Treatment outcomes
3.5. Main Findings from the Original Investigations (Phases 1, 2, and 3)
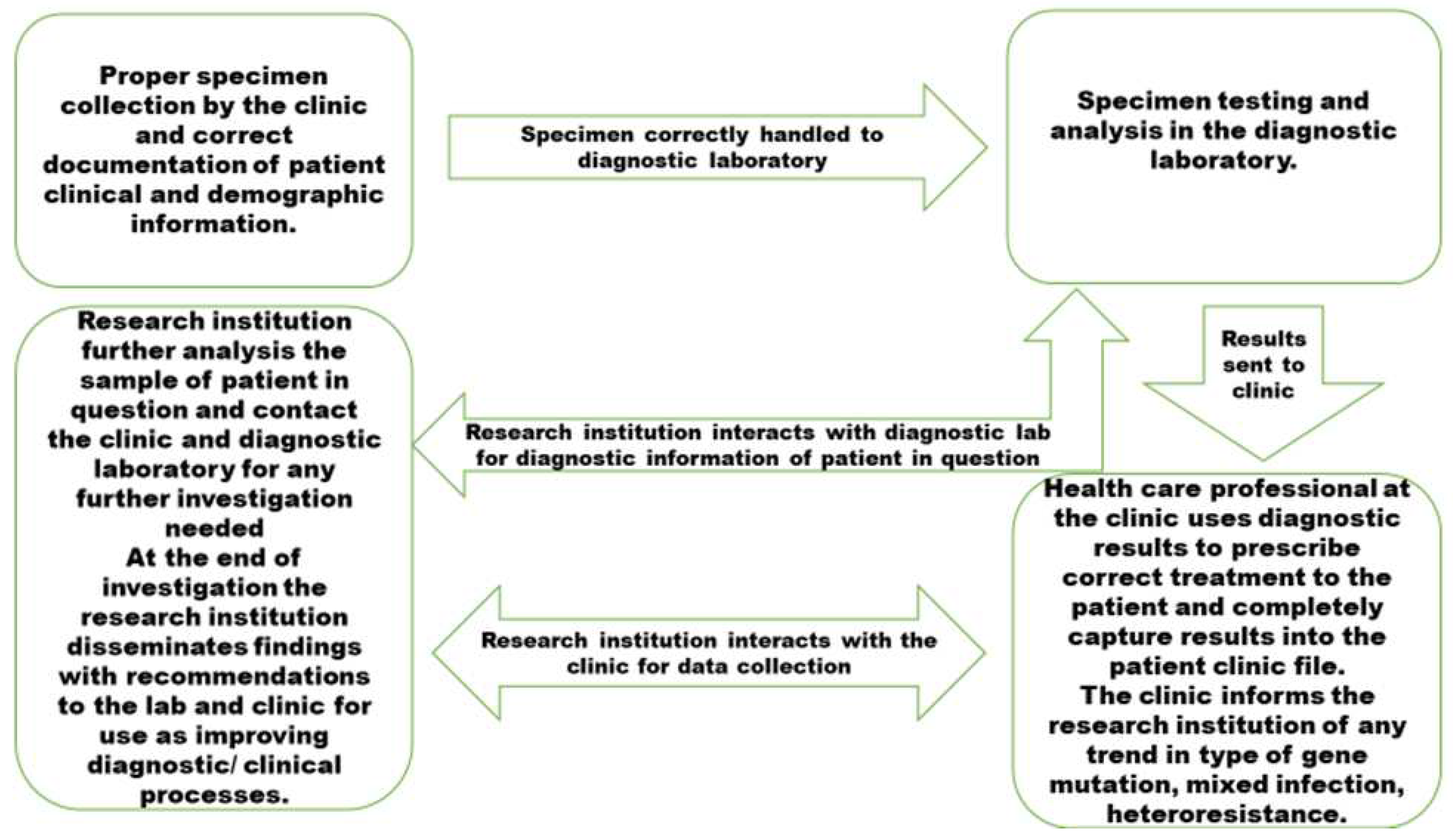
4. Discussion
5. Definition of operational concepts
6. Study Limitation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Notoatmodjo, S. ; Promosi Kesehatan dan Ilmu Perilaku; Rineka Cipta: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bam, T.S.; Aditama, T.Y.; Chiang, C. Y.; Rubaeah, R.; Suhaemi, A. Smoking cessation and smoke-free environments for tuberculosis patients in Indonesia A cohort study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera Rahardjo, S.S.; Murti, B. Health Belief Model and Precede Proceed on the Risk Factors of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Surakarta, Central Java. J. Epidemiol. Public Health 2017, 2, 241–254. [Google Scholar]
- Louwagie, G.M.; Ayo-Yusuf, O.A. Tobacco use patterns in tuberculosis patients with high rates of human immunodeficiency virus co-infection in South Africa. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, H.; Mahajan, S.; Lal, M.; Toor AK, Deepti, S. S.; Chawla, N. Prevalence of tobacco consumption and smoking and its effect on outcome among microbiologically confirmed new pulmonary tuberculosis patients on daily regimen of DOTS in Amritsar city. J Family Med Prim Care 2022, 11, 2150–2154. [Google Scholar]
- Kant, S.; Maurya, A.K.; Kushwaha, R.A.S.; Nag, V.L. Multi Drug-resistant tuberculosis; an i6trogenic problem. Biosciences Trends 2010, 4, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Santha, T.; Garg, R.; Frieden, T.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Subramani, R.; Gopi, P.; Selvakumar, N.; Ganapathy, S.; Charles, N.; Rajamma, J. Risk Factors associated with default, failure, and death among tuberculosis patients treated in a DOTS program in Tiruvallur District, South India, 2000. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2002, 6, 780–788. [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne, M.; Rocher, I.; Steensma, C.; Brassard, P. The impact of smoking on adherence to treatment for latent tuberculosis infection. BMC Public Health. 2006, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujaili, J.A.; Sulaiman, S.A.S.; Awaisu, A.; Muttalif, A.R.; Blebil, A.Q. Outcomes of tuberculosis treatment: a retrospective cohort analysis of smoking versus non-smoking patients in Penang, Malaysia. J Public Health. 2011, 19, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Sulaiman, S.A.S.; Hassali, M.A.; Khan, K.U.; Ming, L.C.; Mateen, O.; Ullah, M.O. ; 2020. Effect of smoking on treatment outcome among tuberculosis patients in Malaysia; a multicenter study. BMC Public Health, 20, pp.1-8.
- Hazbon, M.H. Population genetics study of isoniazid resistance mutations and evolution of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2006, 50, 2640–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipin, M.Y.; Stepanshina, V.N.; Shemyakin, I.G.; Shinnick, T.M. Association of specific mutations in katG, rpoB, rpsL, and rrs genes with spoligotypes of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in Russia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2010, 10, 43.
- Tola, H.H.; Shojaeizadeh, D.; Tol, A.; Garmaroudi, G.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Kebede, A.; Ejeta, L.T.; Kassa, D.; Klinkenberg, E. Psychological and educational intervention to improve Tuberculosis treatment adherence in Ethiopia based on health belief model: A cluster randomized control trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimy, M.; Araban, M.; Zareban, I.; Taher, M.; Abedi, A. Determinants of adherence to self-care behavior among women with type 2 diabetes: an explanation based on health belief model. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2016, 30, 368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baird, S.T.; Bogart, L.M.; Delahanty, D.L. Health-related correlates of perceived discrimination in HIV care. AIDS Patient Care and STDs 2004, 18, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, B.; Alebel, A.; Gebrie, A.; Zegeye, A.; Tesema, C.; Kassie, B. The twin epidemics: Prevalence of TB/HIV co-infection and its associated factors in Ethiopia; A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13, e0203986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Narendran, G. HIV and tuberculosis in India. Journal of Biosciences. 2008, 33, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagneux, S. Impact of bacterial genetics on the transmission of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog 2006, 2, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameeruddin, N. U.; Luke Elizabeth, H. Impact of isoniazid resistance on the virulence of global and south Indian clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2014, 94, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, H. Relationship between the isoniazid-resistant mutation katGS315T and the prevalence of MDR-/XDR-TB in Osaka, Japan. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2008, 12, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Oni, T.; Bangani, H.P. Smoking, BCG and employment and the risk of tuberculosis infection in HIV-infected persons in South Africa. PloS One. 2012, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedegaard, U.; Hallas, J.; Kjeldsen, L.J. Multifaceted Intervention Including Motivational Interviewing to Support Medication Adherence after Stroke/Transient Ischemic Attack: A Randomized Trial. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Extra 2014, 4, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Mokaddas, E.; Al-Mutairi, N.; Eldeen, H.S.; Mohammadi, S. Discordance across Phenotypic and Molecular Methods for Drug Susceptibility Testing of Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates in a Low TB Incidence Country. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolani, et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12, 9, http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2334/12/9.
- Richardson, E.T.; Lin, S.Y.G.; Pinsky, B.A.; Desmond, E.; Banaei, N. First documentation of isoniazid reversion in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2009, 13, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Doorn, H.R.; de Haas, P.E.W.; Kremer, K.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; Borgdorff, M.W.; van Soolingen, D. Public health impact of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains with a mutation at amino acid position 315 of katG: a decade of experience in The Netherlands. Clin Microbiol Infect 2006, 12, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangase, Z.; Tsoka-Gwegweni, J. M.; Okem, A. Smoking prevalence among inpatients with drug-resistant tuberculosis in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Tobacco-Induced Diseases. 2018, 16, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Mokaddas, E. Current status and future trends in the diagnosis and treatment of drug-susceptible and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. J. Infect. Public Health 2014, 7, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradana, A.R.; Purnami, C.T.; Mawarni, A. Literature review: data quality assessment methods of tuberculosis recording and reporting electronically. Int J Health Educ Soc. 2020, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kementerian Kesehatan, Republik Indonesia. Information Tuberculosis; Ministry of Health: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018; Available online: https://pusdatin.kemkes.go.id/article/view/18101500001/infodatin-tuberkulosis-2018.html (accessed on 27 July 2023).
- Holmes, E.A.F.; Hughes, D.A.; Morrison, V.L. Predicting adherence to medications using health psychology theories: A systematic review of 20 years of empirical research. Value Health 2014, 17, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global tuberculosis report. WHO/HTM/TB/2017.23, Geneva, 2017.
- Karmakar, M.; Trauer, J.M.; Ascher, D.B.; Denholm, J.T. Hyper transmission of Beijing lineage Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2019, 79, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, H.; Ratabane, J.; Erasmus, L.; Gardee, Y.; Omar, S.; Dreyer, A.; Ismail, F.; Bhyat, Z.; Lebaka, T.; van der Meulen, M.; et al. Distribution and Clonality of drug-resistant tuberculosis in South Africa. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguga-Phasha, N.T.; Munyai, N.S.; Mashinya, F.; Makgatho, M.E.; Mbajiorgu, E.F. Genetic diversity and distribution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genotypes in Limpopo, South Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 764. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Mathema, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, X.; Li, D.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Xu, B. Comparison of the sociodemographic and clinical features of pulmonary TB patients infected with sub-lineages within the W-Beijing and non-Beijing Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis, 2016, 97, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.I.; Nicoloff, H.; Hjort, K. Mechanisms and clinical relevance of bacterial heteroresistance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2019, 17, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Xia, H.; Bao, X.; Zhao, B.; He, P.; Zhao, Y. Highly Sensitive Detection of Isoniazid Heteroresistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis by Droplet Digital PCR. Infection and Drug Resistance. 2022, 1, 6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Magula, N.P. Treatment outcomes of Gene Xpert positive tuberculosis patients in KwaMashu Community Health Centre, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: A retrospective review. S. Afr. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 36, a217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report. Available online, 2019: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10 665/329368/9789241565714. (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Raviglione, M.; Uplekar, M. WHO’s new Stop TB strategy. Lancet 2006, 367, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.S.; Arcoverde, M.A.M.; Andrade RLP, Zilly A, Villa TCS, Silva-Sobrinho RA. Information system on tuberculosis: data completeness spatial analysis in the state of Paraná, Brazil. Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2021, 55, e20200538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amere, G.A.; Nayak, P.; Salindri, A.D.; Venkat Narayan, K.M.; Magee, M.J. Contribution of smoking to tuberculosis incidence and mortality in high tuberculosis burden countries. Am J Epidemiol 2018, 187, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, L.M.; Hosu, M.C.; Oostvogels, S.; Dippenaar, A.; Warren, R.M.; Sineke, N.; Vasaikar, S.; Apalata, T. The Detection of Mutations and Genotyping of Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Strains Isolated from Patients in the Rural Eastern Cape Province. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2023, 15, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, L.M.; Hosu, M.C.; Vasaikar, S.; Dippenaar, A.; Oostvogels, S.; Warren, R.M.; Apalata, T. Spatial Distribution of Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infections in Rural Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Pathogens 2023, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faye, L.M.; Hosu, M.C.; Iruedo, J.; Vasaikar, S.; Nokoyo, K.A.; Tsuro, U.; Apalata, T. Treatment Outcomes and Associated Factors among Tuberculosis Patients from Selected Rural Eastern Cape Hospitals: An Ambidirectional Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics South Africa. Poverty Trends in South Africa: An examination of absolute poverty between 2006 and 2011. Report No. 03-10-06 Statistics South Africa. 2014. [Updated 17, cited July 2023]. http://www.statssa.gov.za/publications/Report-03-10-06/Report-03-10-062015.pdf. 20 August.
- Department of Health (South Africa). Multi-drug resistant tuberculosis: A policy framework on decentralized and deinstitutionalized management for South Africa. 2015. p. 3–11. [Updated 2023, cited 23]. https://www.inpracticeafrica.com/~/media/Guidelines/SA_NDOH_MDR_TB.pdf. 20 July.
- National Department of Health (South Africa). Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Policy Guidelines. 2011. p. 4–7–12, 54, 81, 122. [updated 2013; cited 23]. https://www.health-e.org.za/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/MDR-TB-Clinical-Guidelines-Updated-Jan-2013.pdf. 20 July.
- Loveday, M.; Wallengren, K.; Brust, J.; Roberts, J.; Voce, A. ; Margot B, et al. Community-based care vs. centralized hospitalization for MDR-TB patients, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2015;19(2):163–71. Epub 2015/01/13. [CrossRef]
- Graham, I.D.; Kothari, A.; McCutcheon, C.; Alvarez, G.; Banner, D.; Botti, M. Moving knowledge into action for more effective practice, programmes and policy: protocol for a research program on integrated knowledge translation. Implement Sci. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlatu, N.; Oladimeji, K.E.; Apalata, T. Voices from the Patients: A Qualitative Study of the Integration of Tuberculosis, Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Primary Healthcare Services in O.R. Tambo District, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2023, 15, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
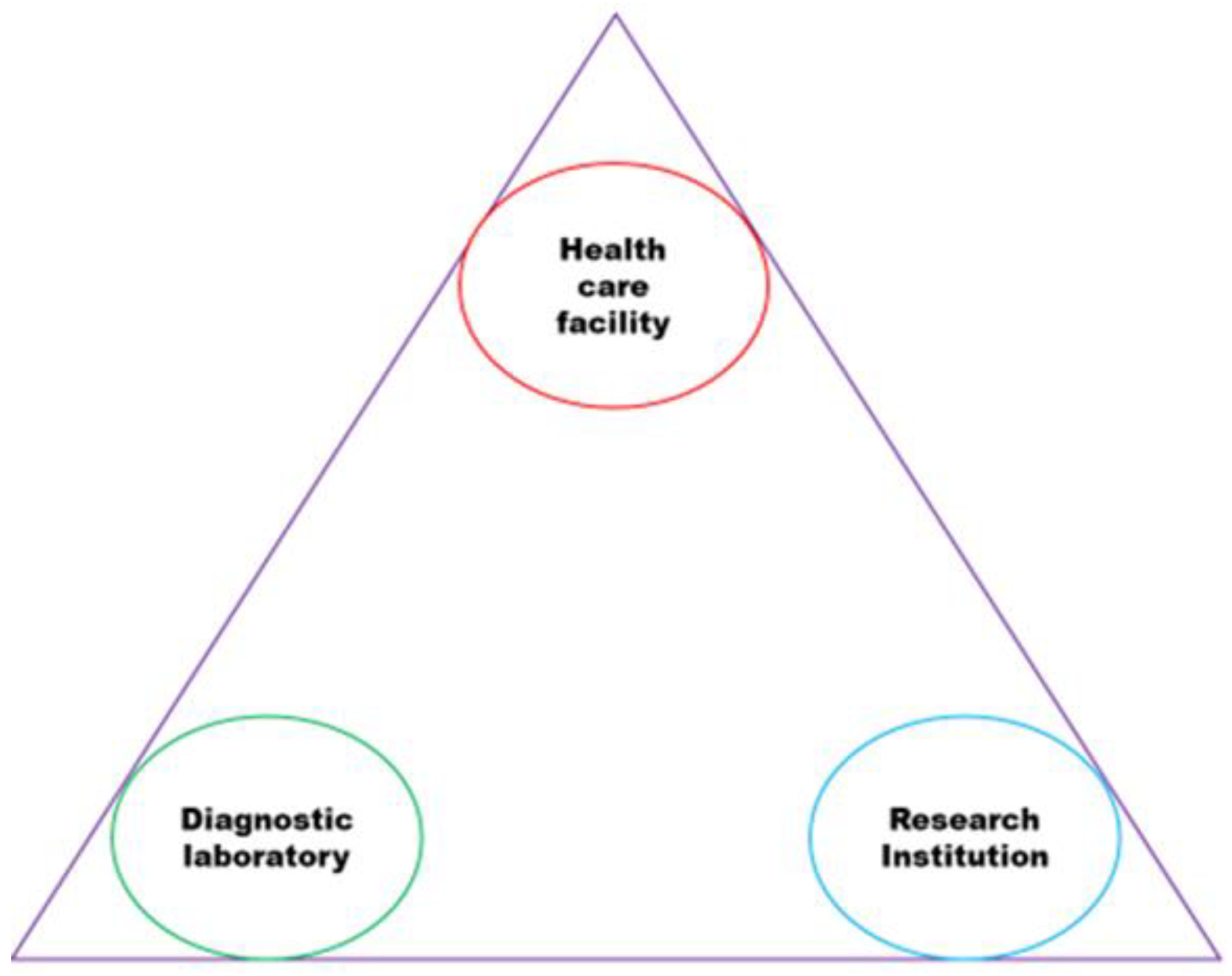
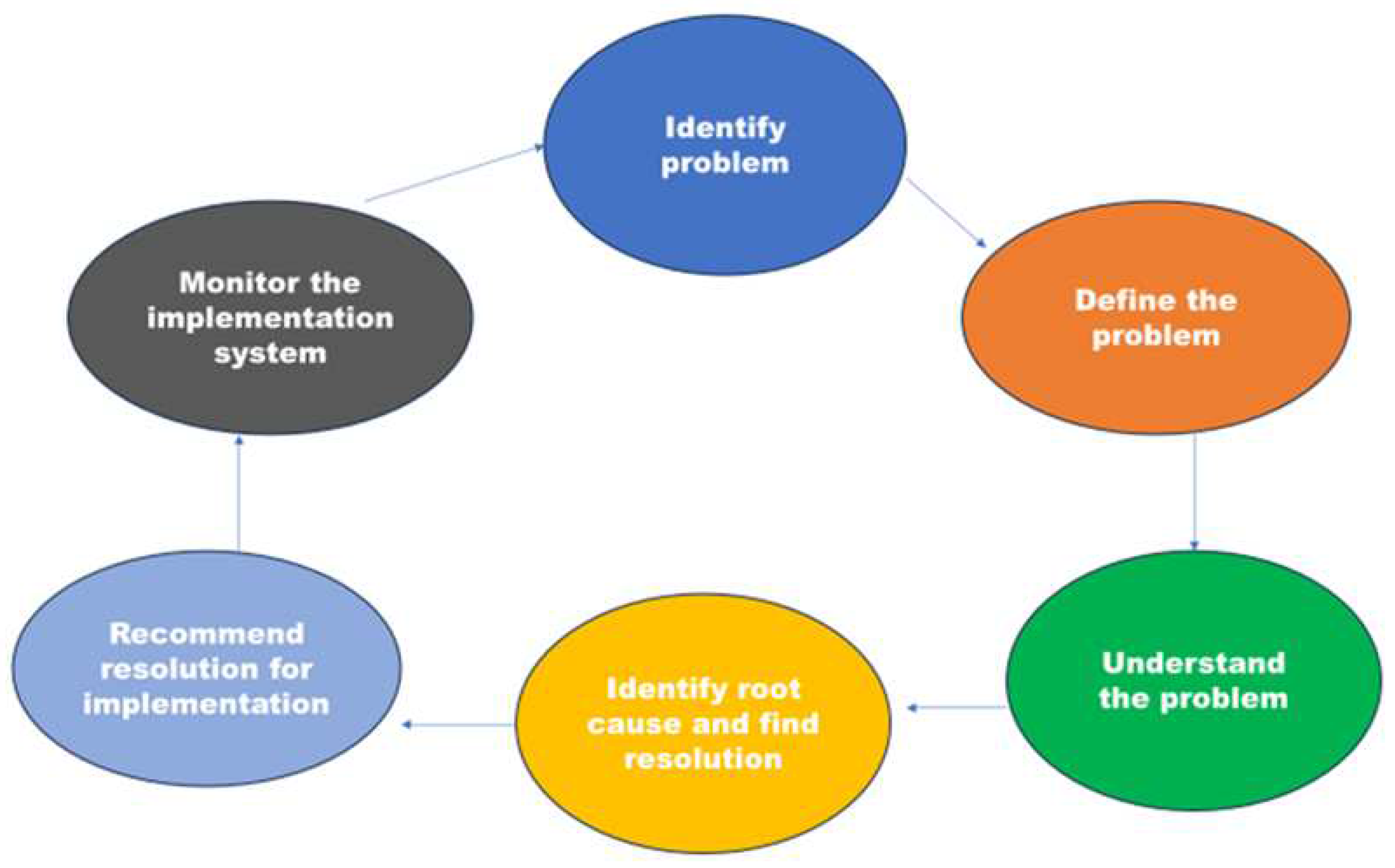
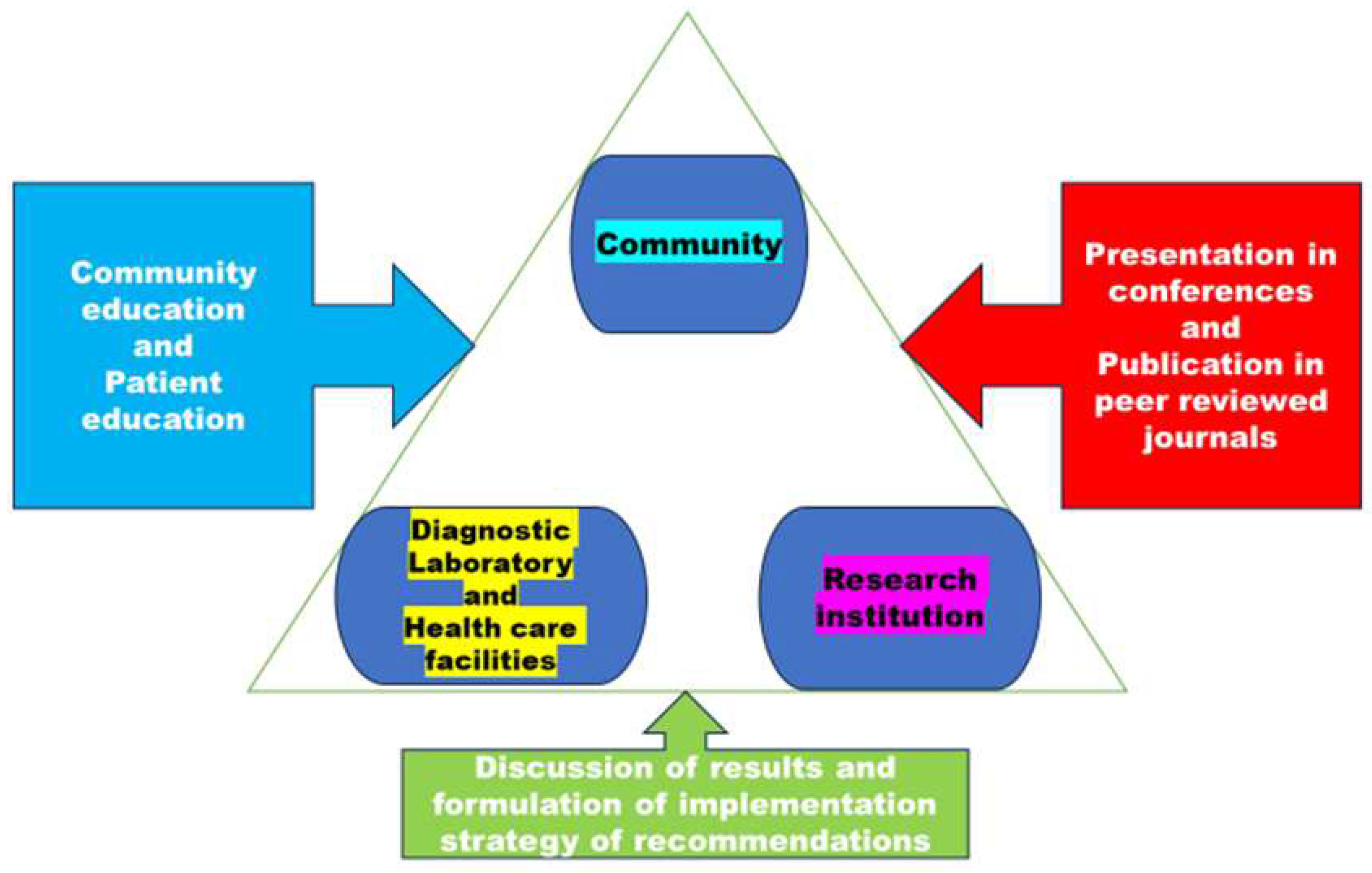
| Technical approach | Justification |
|---|---|
|
For trend analysis and root course analysis, the significant gene mutation and regions should be documented and shared with TB research institutions. According to Ameeruddin and Luke [19], Ano et al. [20], and Gagneux et al. [18], the katG-S315T mutation has a low-fitness cost, spreads to Beijing strains and other strains, and is more likely to be clustered. Treatment failure is correlated with katG mutations [24] |
|
To stop the spread of these strains, it's crucial to identify critical gene alterations and heterogeneity hot spots. In patients from various geographic backgrounds who had drug-resistant M. tuberculosis infections, the prevalence of particular mutations of rpoB, katG, and inhA differed significantly [23]. It may be necessary to develop a diagnostic test specific to each country due to the significant variations in the types of mutations observed. To enhance the management of TB, it is essential to conduct further research on the drug resistance mechanisms of M. tuberculosis prevalent in rural Eastern Cape regions, to facilitate rapid assessment of drug resistance. |
|
To conduct trend analysis and root cause analysis, it is essential to document and engage in discussions with research institutions that specialize in TB. This involves analyzing the prevalence of significant gene mutations and the heterogeneity of strains. |
|
Knowing the type of prevalent DR-TB is crucial for keeping track of M. tuberculosis transmission and hot spots. The heterogeneity of strains and their relationship with major gene mutations to improve control measures and identify which affect treatment outcomes that are successful and unsuccessful should be tracked. |
| Technical approach | Justification |
|
Which demographic and clinical category contributes to poor treatment outcomes? This knowledge will assist in designing informed interventions and targeting the patient category that contributes the most to poor treatment outcomes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





