Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
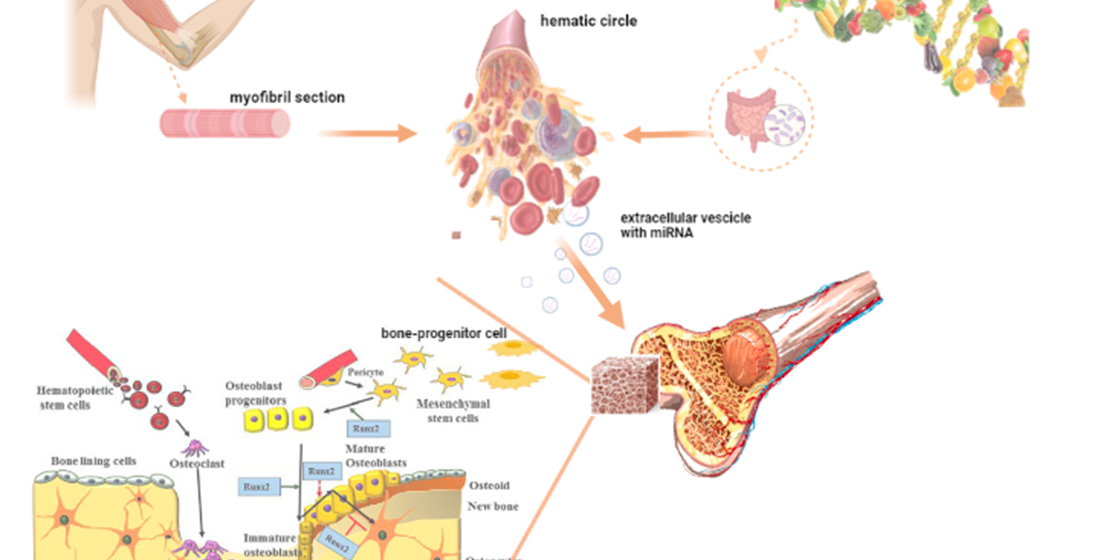
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Exercise and Osteogenic miRNAs Expression
3. Endogenous miRNAs and Bone Metabolism
4. Micronutrients Intake and Osteogenic miRNAs Expression
5. Macronutrients Intake and Osteogenic miRNAs Expression
6. Exogenous miRNA and Bone Metabolism
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledges
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausser, J.; Zavolan, M. Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions--beyond repression of gene expression. Nature reviews. Genetics 2014, 15, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiera, G.; Contrò, V.; Sacco, A.; Macchiarella, A.; Cieszczyk, P.; Proia, P. From epigenetics to anti-doping application: a new tool of detection. Human Movement 2017, 18, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folwarczna, J.; Zych, M.; Burczyk, J.; Trzeciak, H.; Trzeciak, H.I. Effects of natural phenolic acids on the skeletal system of ovariectomized rats. Planta medica 2009, 75, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisse, T.S.; Adams, J.S.; Hewison, M. Vitamin D and microRNAs in bone. Critical reviews in eukaryotic gene expression 2013, 23, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckett, E.L.; Yates, Z.; Veysey, M.; Duesing, K.; Lucock, M. The role of vitamins and minerals in modulating the expression of microRNA. Nutrition research reviews 2014, 27, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, B.; Balagangadharan, K.; Selvamurugan, N. Syringic acid, a phenolic acid, promotes osteoblast differentiation by stimulation of Runx2 expression and targeting of Smad7 by miR-21 in mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of cell communication and signaling 2018, 12, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, R.; Mondal, A.K.; Pundkar, C.; Periyasamy-Thandavan, S.; Mendhe, B.; Hunter, M.; Isales, C.M.; Hill, W.D.; Hamrick, M.W.; Fulzele, S. Modulation of miRNAs by Vitamin C in Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, M.T.; Deiana, M.; Cheri, S.; Dotta, M.; Zamboni, F.; Gabbiani, D.; Schena, F.; Dalle Carbonare, L.; Mottes, M. Physical Exercise Modulates miR-21-5p, miR-129-5p, miR-378-5p, and miR-188-5p Expression in Progenitor Cells Promoting Osteogenesis. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohel, M.M.H. Macronutrient modulation of mRNA and microRNA function in animals: A review. Animal Nutrition 2020, 6, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Ma, W.; Jiao, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y. Ortho-silicic acid enhances osteogenesis of osteoblasts through the upregulation of miR-130b which directly targets PTEN. Life Sciences 2021, 264, 118680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, T.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Dietary microRNA-A Novel Functional Component of Food. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.) 2019, 10, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, D.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Bian, Z.; Liang, X.; Cai, X.; et al. Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA. Cell Research 2012, 22, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimalraj, S.; Arumugam, B.; Miranda, P.J.; Selvamurugan, N. Runx2: Structure, function, and phosphorylation in osteoblast differentiation. International journal of biological macromolecules 2015, 78, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Tewari, N.; Ma, R.; Zhong, L.; Makishima, M.; Liu, Y.; Bhawal, U.K. MicroRNA-21 facilitates osteoblast activity. Biochemistry and biophysics reports 2021, 25, 100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smieszek, A.; Marcinkowska, K.; Pielok, A.; Sikora, M.; Valihrach, L.; Marycz, K. The Role of miR-21 in Osteoblasts-Osteoclasts Coupling In Vitro. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Hassan, M.Q.; Jafferji, M.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Garzon, R.; Croce, C.M.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B. Biological functions of miR-29b contribute to positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation. The Journal of biological chemistry 2009, 284, 15676–15684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Chiang, K.; Zempleni, J.; Cui, J. Computational Characterization of Exogenous MicroRNAs that Can Be Transferred into Human Circulation. PloS one 2015, 10, e0140587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Sainz, E.; Lorente-Cebrián, S.; Aranaz, P.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Martínez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I. Potential Mechanisms Linking Food-Derived MicroRNAs, Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier Functions in the Context of Nutrition and Human Health. Frontiers in nutrition 2021, 8, 586564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Pham, Q.; Davis, C.D.; Yu, L.; Wang, T.T.Y. Delineating effect of corn microRNAs and matrix, ingested as whole food, on gut microbiota in a rodent model. Food science & nutrition 2020, 8, 4066–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Liegro, C.M.; Schiera, G.; Di Liegro, I. Extracellular vesicle-associated RNA as a carrier of epigenetic information. Genes 2017, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Satoh, M.; Pauley, K.M.; Fritzler, M.J.; Reeves, W.H.; Chan, E.K. Detection of the argonaute protein Ago2 and microRNAs in the RNA induced silencing complex (RISC) using a monoclonal antibody. Journal of immunological methods 2006, 317, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, L.D.F.; Oliveira, M.L.d.; Lirani-Galvão, A.P.; Marin-Mio, R.V.; Santos, R.N.d.; Lazaretti-Castro, M. Physical exercise and osteoporosis: effects of different types of exercises on bone and physical function of postmenopausal women. Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia & Metabologia 2014, 58, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.; Baldassano, S.; Cortis, C.; Cooper, J.; Proia, P.J.H.M. Physical activity, nutrition, and bone health. 2018, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Pitari, M.R.; Amodio, N.; Di Martino, M.T.; Conforti, F.; Leone, E.; Botta, C.; Paolino, F.M.; Del Giudice, T.; Iuliano, E.; et al. miR-29b negatively regulates human osteoclastic cell differentiation and function: implications for the treatment of multiple myeloma-related bone disease. Journal of cellular physiology 2013, 228, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, M.; Shen, X.; Xu, J.; Zou, J. The Effect of Exercise on the Prevention of Osteoporosis and Bone Angiogenesis. BioMed research international 2019, 2019, 8171897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.S.; Salmena, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2012, 13, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Regulation of TGF-beta signaling by Smad7. Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica 2009, 41, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, M.T.; Deiana, M.; Cheri, S.; Dotta, M.; Zamboni, F.; Gabbiani, D.; Schena, F.; Dalle Carbonare, L.; Mottes, M. Physical exercise modulates miR-21-5p, miR-129-5p, miR-378-5p, and miR-188-5p expression in progenitor cells promoting osteogenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bruxvoort, K.J.; Zylstra, C.R.; Liu, J.; Cichowski, R.; Faugere, M.C.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Wan, C.; Williams, B.O.; Clemens, T.L. Lifelong accumulation of bone in mice lacking Pten in osteoblasts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2007, 104, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, N.-p.; Granger, L.; Hodes, R.J. Telomere lengthening and telomerase activation during human B cell differentiation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1997, 94, 10827–10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Y.-S.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Human telomerase and its regulation. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews 2002, 66, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle Carbonare, L.; Mottes, M.; Cheri, S.; Deiana, M.; Zamboni, F.; Gabbiani, D.; Schena, F.; Salvagno, G.L.; Lippi, G.; Valenti, M.T. Increased Gene Expression of RUNX2 and SOX9 in Mesenchymal Circulating Progenitors Is Associated with Autophagy during Physical Activity. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2019, 2019, 8426259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Li, C.; Bai, W.D.; Su, L.L.; Liu, J.Q.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.H.; Cai, W.X.; Bai, X.Z.; Jia, Y.H.; et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates hTERT via PTEN in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. PloS one 2014, 9, e97114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Passos, J.F.; Birket, M.J.; Beckmann, T.; Brings, S.; Peters, H.; Birch-Machin, M.A.; von Zglinicki, T.; Saretzki, G. Telomerase does not counteract telomere shortening but protects mitochondrial function under oxidative stress. Journal of cell science 2008, 121, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutteridge, J.M. Biological origin of free radicals, and mechanisms of antioxidant protection. Chemico-biological interactions 1994, 91, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Toxicity of iron and hydrogen peroxide: the Fenton reaction. Toxicology letters 1995, 82, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossbach, M. Small non-coding RNAs as novel therapeutics. Current molecular medicine 2010, 10, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, J.; Huang, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.-M.; Xu, Y.-M.; Huang, L.-F.; Wang, X.-Z. Exosomes: novel biomarkers for clinical diagnosis. The scientific world journal 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic acids research 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Xiao, Z.S. Advances in Runx2 regulation and its isoforms. Medical hypotheses 2007, 68, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.K.F.; Au, P.C.M.; Tan, K.C.; Cheung, C.L. MicroRNA and human bone health. JBMR plus 2019, 3, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrozza, M.J.; Utley, R.T.; Workman, J.L.; Cote, J. The diverse functions of histone acetyltransferase complexes. TRENDS in Genetics 2003, 19, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Fan, G. The role of DNA methylation in the central nervous system and neuropsychiatric disorders. International review of neurobiology 2009, 89, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raisz, L.G. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. The Journal of clinical investigation 2005, 115, 3318–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.; Makela, S.; Treuter, E.; Tujague, M.; Thomsen, J.; Andersson, G.r.; Enmark, E.; Pettersson, K.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiological reviews 2001, 81, 1535–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, E.F.; Pasquinelli, A.E. MicroRNA biogenesis: regulating the regulators. Critical reviews in biochemistry and molecular biology 2013, 48, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, N.F.; Allergens, F.; Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Knutsen, H.K.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; et al. Guidance for establishing and applying tolerable upper intake levels for vitamins and essential minerals. 2022, 20, e200102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liang, J.; Li, M.; Lin, M.; Mai, L.; Huang, X.; Liang, J.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y. Modulation of miRNAs by vitamin C in H2O2-exposed human umbilical vein endothelial cells. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 2020, 46, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolhe, R.; Mondal, A.K.; Pundkar, C.; Periyasamy-Thandavan, S.; Mendhe, B.; Hunter, M.; Isales, C.M.; Hill, W.D.; Hamrick, M.W.; Fulzele, S. Modulation of miRNAs by vitamin C in human bone marrow stromal cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Shoorei, H.; Mohaqiq, M.; Majidpoor, J.; Sayad, A.; Taheri, M. Regulatory role of microRNAs on PTEN signaling. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 133, 110986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, C.; Liang, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, S. MiRNA-155 promotes proliferation by targeting caudal-type homeobox 1 (CDX1) in glioma cells. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2017, 95, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.L.; Yamaguchi, M. Phytocomponent p-hydroxycinnamic acid stimulates bone formation and inhibits bone resorption in rat femoral tissues in vitro. Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2006, 292, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.L.; Yamaguchi, M. Oral administration of phytocomponent p-hydroxycinnamic acid has anabolic effects on bone calcification in femoral tissues of rats in vivo. Journal of health science 2006, 52, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, N.; Wicks, S.M.; Lawal, T.O.; Mahady, G.B. Epigenetic regulation of bone remodeling by natural compounds. Pharmacological research 2019, 147, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Liang, H.L.; Hung, C.H.; Kuo, P.L. Syringetin, a flavonoid derivative in grape and wine, induces human osteoblast differentiation through bone morphogenetic protein-2/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Molecular nutrition & food research 2009, 53, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasulu, C.; Ramgopal, M.; Ramanjaneyulu, G.; Anuradha, C.; Kumar, C.S. Syringic acid (SA)‒a review of its occurrence, biosynthesis, pharmacological and industrial importance. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2018, 108, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, K.; Dong, G.H.; Wang, N.; Zhu, J.F. miR-221-3p and miR-222-3p downregulation promoted osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchyme stem cells through IGF-1/ERK pathway under high glucose condition. Diabetes research and clinical practice 2020, 167, 108121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.; Gong, K.; Yang, H.-S.; Li, Y.-G.; Jiang, T.; Zeng, Z.-M.; Cao, Z.-R.; Pan, X.-M. MiR-449 overexpression inhibits osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via suppressing Sirt1/Fra-1 pathway in high glucose and free fatty acids microenvironment. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2018, 496, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, C.; Tan, J.; Dou, C.; Chen, Y. Modulation of SIRT6 activity acts as an emerging therapeutic implication for pathological disorders in the skeletal system. Genes & Diseases 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Gong, K.; Yang, H.S.; Li, Y.G.; Jiang, T.; Zeng, Z.M.; Cao, Z.R.; Pan, X.M. MiR-449 overexpression inhibits osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via suppressing Sirt1/Fra-1 pathway in high glucose and free fatty acids microenvironment. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2018, 496, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. Role of Neonatal Dietary Ca in Bone Development and Characteristics of Porcine Mesenchymal Stem Cells; North Carolina State University: 2014.
- Ellur, G.; Sukhdeo, S.V.; Khan, M.T.; Sharan, K. Maternal high protein-diet programs impairment of offspring's bone mass through miR-24-1-5p mediated targeting of SMAD5 in osteoblasts. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 2021, 78, 1729–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakis, I.; Alameddine, M.; Scalabrin, M.; van 't Hof, R.J.; Liloglou, T.; Ozanne, S.E.; Goljanek-Whysall, K.; Vasilaki, A. Low protein intake during reproduction compromises the recovery of lactation-induced bone loss in female mouse dams without affecting skeletal muscles. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2020, 34, 11844–11859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proia, P.; Amato, A.; Drid, P.; Korovljev, D.; Vasto, S.; Baldassano, S. The impact of diet and physical activity on bone health in children and adolescents. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2021, 12, 704647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, T.; Manz, F. Estimation of the renal net acid excretion by adults consuming diets containing variable amounts of protein. The American journal of clinical nutrition 1994, 59, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassano, S.; Alioto, A.; Amato, A.; Rossi, C.; Messina, G.; Bruno, M.R.; Stallone, R.; Proia, P. Fighting the Consequences of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Mindfulness, Exercise, and Nutrition Practices to Reduce Eating Disorders and Promote Sustainability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conigrave, A.D.; Brown, E.M.; Rizzoli, R. Dietary protein and bone health: roles of amino acid-sensing receptors in the control of calcium metabolism and bone homeostasis. Annual review of nutrition 2008, 28, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, A.; Ferro, V.A.; Tate, R.J. Determination of the potential bioavailability of plant microRNAs using a simulated human digestion process. Molecular nutrition & food research 2015, 59, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, M.A.; Liang, H.; Li, W.-H. Human polymorphism at microRNAs and microRNA target sites. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2007, 104, 3300–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Pal Bhadra, M.; Girschick, H.J.; Bhadra, U. MicroRNAs–micro in size but macro in function. The FEBS journal 2008, 275, 4929–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, S.R.; Nguyen, C.; Xie, F.; Wood, J.R.; Zempleni, J. MicroRNAs are absorbed in biologically meaningful amounts from nutritionally relevant doses of cow milk and affect gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, HEK-293 kidney cell cultures, and mouse livers. The Journal of nutrition 2014, 144, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, A.; Ferro, V.A.; Tate, R.J. Determination of the potential bioavailability of plant microRNAs using a simulated human digestion process. Molecular nutrition & food research 2015, 59, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Melzig, M.F. The stability of medicinal plant microRNAs in the herb preparation process. Molecules 2018, 23, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askenase, P.W. Exosomes provide unappreciated carrier effects that assist transfers of their miRNAs to targeted cells; I. They are 'The Elephant in the Room'. RNA biology 2021, 18, 2038–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Vashisht, M.; Golla, N.; Shandilya, S.; Onteru, S.K.; Singh, D. Milk miRNAs encapsulated in exosomes are stable to human digestion and permeable to intestinal barrier in vitro. Journal of Functional Foods 2017, 34, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, R.; St. Pierre, J.; Odeh, S.; Surette, M.; Foster, J.A. Microbe and host interaction in gastrointestinal homeostasis. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1623–1640. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, B.C.; Mah, A.T.; Pitman, W.A.; Ding, S.; Lund, P.K.; Sethupathy, P. Functional transcriptomics in diverse intestinal epithelial cell types reveals robust microRNA sensitivity in intestinal stem cells to microbial status. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2017, 292, 2586–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, B.; Shao, Y.; Jing, A.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Z. Assessing the survival of exogenous plant microRNA in mice. Food science & nutrition 2014, 2, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J. Exosome-like nanoparticles from ginger rhizomes inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Molecular pharmaceutics 2019, 16, 2690–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Yan, H.; Han, X.; Weng, L.; Wei, Q.; Sun, X.; Lu, W.; Wei, Q.; Ye, J.; Cai, X. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles alter macrophage polarization to inhibit melanoma growth. Journal for immunotherapy of cancer 2019, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Wang, S.Y.; Kwak, G.; Yang, Y.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, S.H. Exosome-guided phenotypic switch of M1 to M2 macrophages for cutaneous wound healing. Advanced science 2019, 6, 1900513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Mao, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Dou, T.; Wang, Z.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X. Prediction of plant-derived xenomiRs from plant miRNA sequences using random forest and one-dimensional convolutional neural network models. BMC genomics 2018, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




