1. Introduction
Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) encompasses various forms of visual, written or audio content that depicts or describes sexual abuse of children. This can include photographs, videos, stories, chats, comments, drawings or any other form of media that portrays or discusses such abusive acts.
1. The production and distribution of CSAM have profound and detrimental impacts on both the victims and society as a whole. The victims of CSAM often endure long-lasting psychological, emotional, and physical harm as a result of the abuse they have experienced [
1]. A high volume of CSAM is generated and shared on a daily basis, not only on surface web platforms like social network sites but also within dark web forums. The sheer volume of this content makes it impractical for human experts to manually investigate, detect, and prevent CSAM effectively [
2]. Indeed, automatically detecting and analysing online CSA text poses significant challenges and can be an exceedingly time-consuming task, due to language complexity, contextual ambiguity, dynamic nature of language and large volume of data. The challenges are particularly pronounced when it comes to CSAM shared in the dark web. The dark web prioritizes privacy and anonymity, making it a breeding ground for illicit activities, including the dissemination of CSAM. In addition, CSAM creators on the dark web employ various techniques to evade detection and conceal their activities. They may resort to using code words, slang, or other forms of obfuscation to camouflage their communication and intentions. This deliberate effort to disguise their actions adds another layer of complexity to the detection and analysis process. Efforts to combat CSAM in the dark web necessitate ongoing research and development of advanced technologies, collaboration between law enforcement agencies and technology experts.
In this context, we propose a CSAM detection intelligence system based on Machine Learning (ML) or Deep Learning (DL) techniques. Our system aims to address the challenges associated with detecting CSAM, particularly in real-time, while ensuring a high level of precision and recall. By accomplishing this, we can significantly improve the protection of children from harmful content online. To achieve an accurate and effective CSAM detection intelligence system, we have created a manually labeled dataset that includes both CSAM and non-CSAM content. This dataset serves as a crucial resource in building and refining the classification model of the system, ensuring it performs at its best to detect CSAM posts and non-CSAM posts in the dark web. Our system holds tremendous potential as it goes beyond merely detecting CSAM and the CSAM creators responsible for creating such content. It can also identify CSAM creators’ behaviors, gather critical forensic evidence, and extract valuable insights. These capabilities will be invaluable to various stakeholders, including child protection agencies, hotlines, educational programs, law enforcement agencies, and policy makers. By delivering comprehensive and actionable information, our model aims to make a substantial contribution to the fight against CSAM, actively working to safeguard children from online harm. Its implementation can play a pivotal role in creating a safer digital environment for our young people.
The remainder of the paper is organised as follows. In
Section 2, we review the related work.
Section 3 outlines how we collected the dark web data and describes our system architecture.
Section 4 presents the ML and DL algorithms, training and testing datasets, evaluation methodology, and experimental results for CSAM detection model of the system. In
Section 5, we focus on quantitative information extraction and discussion about CSAM creators, victims and social media platforms mentioned in CSAM posts. Finally, we conclude and offer some future directions in
Section 6.
2. Related Work
Disturbingly, there is a significant distribution of videos, images, and text depicting or discussing children engaged in sexual activities across the internet. To address this issue, research works [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7] applied deep convolutional neural network models or deep perceptual hashing algorithms with the goal of removing CSAM from social media sites. With the exception of [
3], papers [
4,
5,
6,
7] used datasets from third-parties to train and test their models. However, these papers only considered CSA images and not text. Similar to our work, research works [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12] applied ML and DL models to process CSA text. In [
8], Naive Bayes (NB), Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Random Forest (RF) were applied to detect online abusive and bullying comments on Facebook and Twitter. In [
9], the histogram gradient boosted decision trees were exploited for predatory chat conversation detection. In [
10], Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) were applied for YouTube comments. In [
11], deepWalk model and graph embedding representations were used to detect abuse chat logs in French on the SpaceOrigin game. In [
12], Logistic Regression (LR), XGBoost and Multi Layer Perceptron (MLP) were exploited to detect sexual predatory chats in social networks. To train and test ML/DL models, the papers [
8,
11] created their own datasets and the papers [
9,
10,
12] used datasets of third-parties. However, these papers considered the clear web, not the dark web.
Challenging more than the clear web, the dark web not only contains complex and unclear data, but it is also difficult to access. The papers [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17] processed the dark web data in text format. However, the approaches did not automatically detect CSA text in the dark web by using post contents and artificial intelligence. In [
13], the 450 authorised hidden service sites were manually classified. In [
14], the authors analysed seven popular dark web sites to monitor the sites by using their metadata, e.g. the number of users, site names and common users in sites. In [
15], the authors statistically analysed some simple metadata e.g. victim ages and the number of CSAM reports per year. In [
16], K-Means algorithm was applied to cluster the forum comments into the selected seven labels, i.e. breach, financial, drug, vendor, account, product and other. In [
17], the authors manually analysed transcripts of 53 anonymous suspects in United Kingdom to understand suspects’ interaction behaviors and sexual interests.
3. Method
3.1. Collecting Data on the Dark Web
In order to gain insights into CSAM in the dark web, our N-Light project has established a collaboration with Hotline.ie and Web-IQ. Web-IQ has developed the DarkCloud system
2 specifically designed for the detection, investigation, and monitoring of the hidden areas of the internet. This system efficiently collects and organizes cached pages from dark web forums involved in CSAM sharing. The collected data is then stored in an ATLAS dataset for further analysis and research purposes. Hotline.ie has received the ATLAS dataset from Web-IQ and subsequently transferred it to the N-Light project.
The ATLAS dataset encompasses a vast array of valuable information regarding posts within the dark web. This includes the text content of the posts, timestamps indicating when they were created, the language used in the posts, the names of the forums where the posts originated, the topics discussed within those forums, the online platforms mentioned in the posts, and even details about the nationalities of the victims mentioned in the posts. The information is very useful for various entities such as law enforcement, government agencies, and educational institutions. Specially, N-Light project can apply artificial intelligence algorithms to discover child sexual CSAM creators’ behaviors and preferences.
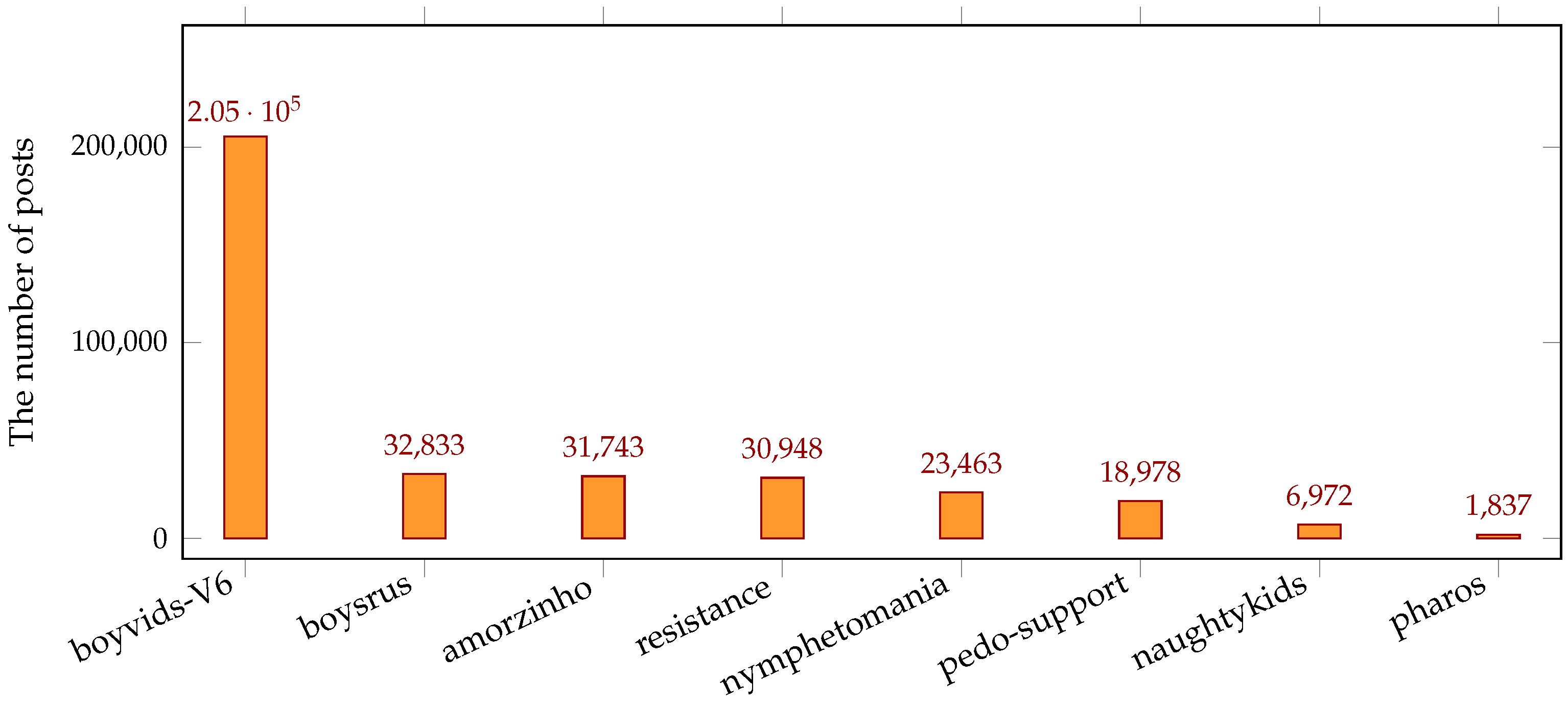
In 2022, the ATLAS dataset comprised a total of 353,218 posts from eight distinct forums, namely
boyvids-V6,
boysrus,
amorzinho,
resistance,
nymphetomania,
pedo-support,
naughtykids, and
pharos. These forums and their corresponding post counts are presented in
Figure 1. Among them,
boyvids-V6 has the most number of posts with 205,444 posts, approximately 58.3% of all posts form the eight forums. The next three forums,
boysrus,
amorzinho and
resistance, have a similar number of posts, each comprising approximately 9% of the total. On the other hand,
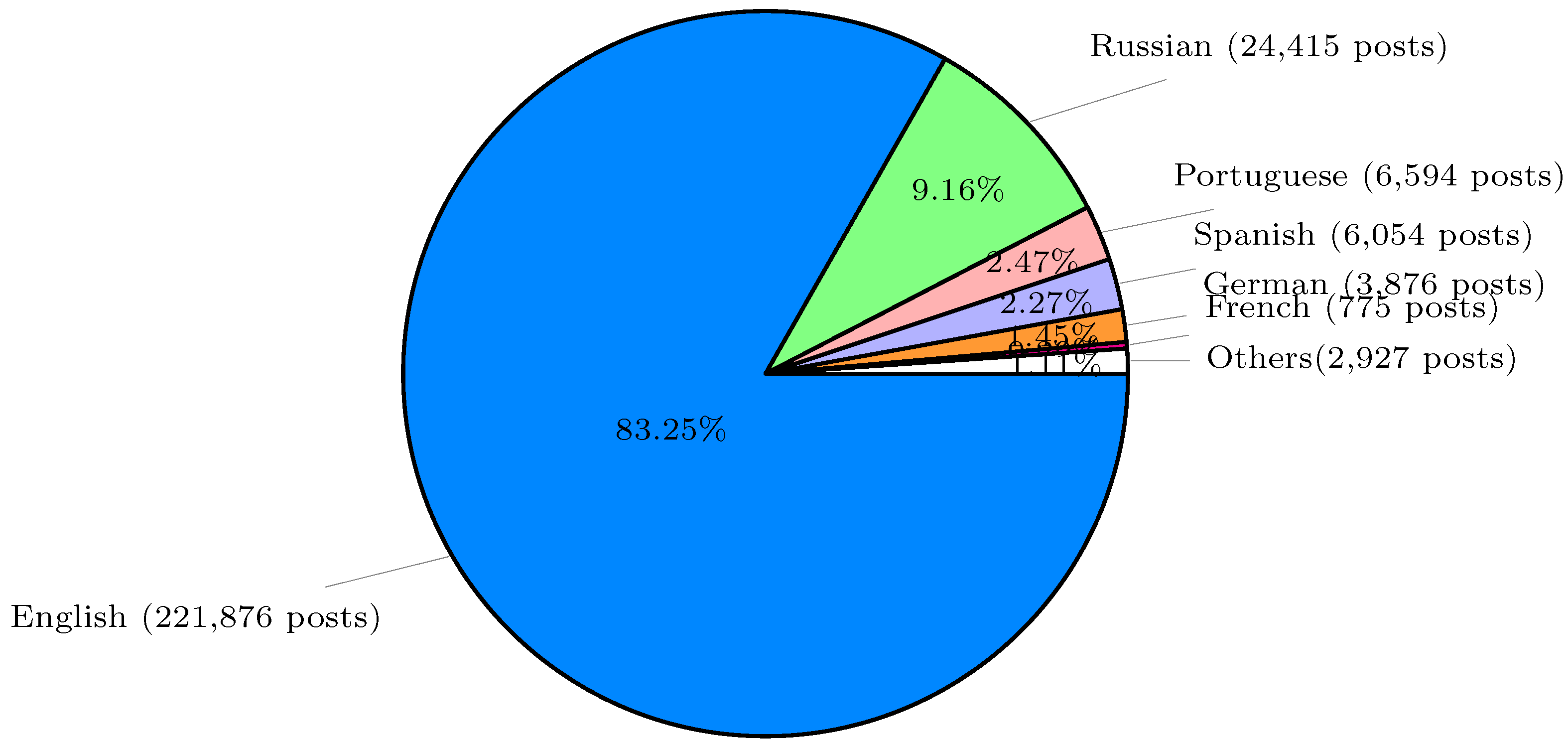
pharos only has 1,837 posts, approximately 0.5%. Out of the total 353,218 posts, Web-IQ successfully identified the languages used in 266,517 posts, covering 118 different languages. Among these detected posts, the distribution of the top 6 languages is as shown in
Figure 2: English, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, German and French. English has the highest number of posts, with 221,876 posts, approximately 83.25% of the identified posts. Russian ranks second, with 24,415 posts, accounting for approximately 9.16%, and French ranks the last, with only 775 posts, approximately 0.29%. In this paper, we solely focus on analyzing the 221,876 English posts (for more details, please refer to
Section 5.1).
Figure 1.
The number of posts of eight forums in 2022.
Figure 1.
The number of posts of eight forums in 2022.
Figure 2.
The number of posts of languages in 2022.
Figure 2.
The number of posts of languages in 2022.
3.2. System Architecture
Supervised learning in ML and DL models is a prevalent method for text classification, as it involves learning patterns from labeled training samples [
18,
19,
20]. Each supervised learning algorithm possesses its own set of strengths and weaknesses. Therefore, to identify a suitable algorithm to classify CSAM post contents, we evaluate the three most popular classical ML algorithms, NB, LR and SVM, alongside the three most popular DL algorithms, CNN, LSTM and BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers). More comprehensive information about these algorithms can be found in
Section 4.1 and
Section 4.2.
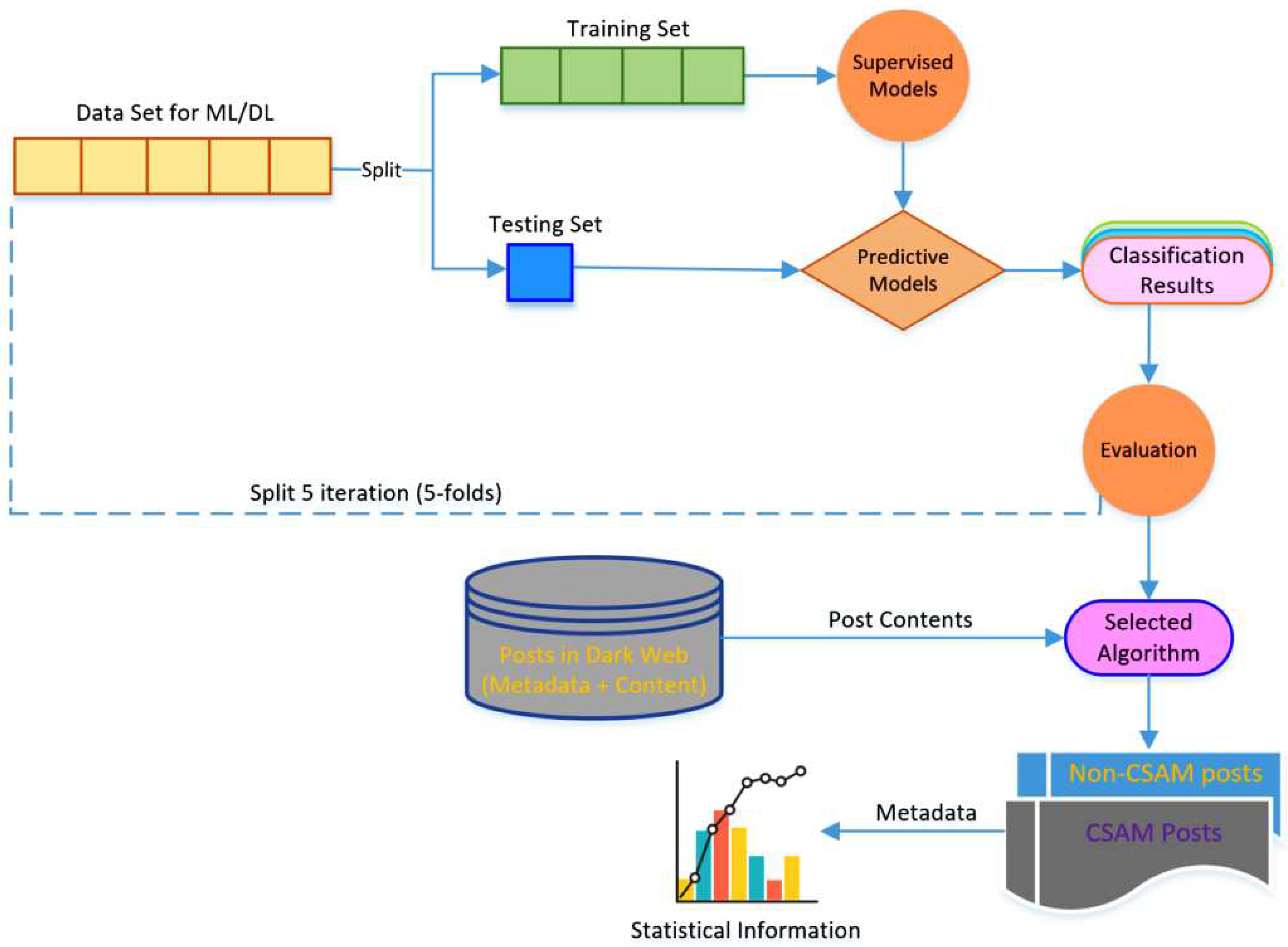
Figure 3 illustrates our system architecture, which is employed to design and implement our novel algorithm for CSAM text classification. Additionally, the system enables the analysis of CSAM posts to discover information related to CSAM creators and victims. In that, the
Supervised Models component implements several ML and DL algorithms, including NB, LR, SVM, CNN, LSM and BERT algorithms. These algorithms tokenize the post texts and convert them into vector representation using TF.IDF
3 in the case of NB, LR and SVM, and embedding layers
4 for CNN, LSTM and BERT.
Figure 3.
The architecture of the CSAM classification system.
Figure 3.
The architecture of the CSAM classification system.
The
Evaluation component serves the purpose of determining the execution times, including training time and prediction time, as well as the classification performance metrics, such as precision, recall, and accuracy, for each combination of algorithms. For more details about the metrics, please refer to
Section 4.4. To mitigate the risk of overfitting, we employ a 5-fold cross-validation approach on our dataset. This involves dividing the dataset into five subsets or folds, where four folds are used for training the algorithm, and the remaining fold is used for testing. This process is repeated until each fold serves as the testing set. The recorded classification measures from five rounds are then averaged to obtain the algorithm’s classification performance measures. Finally, we analyse experimental results on the data set to determine the best algorithm for CSAM text classification on the dark web, and make recommendations based on these findings.
Using our most effective CSAM classifier, posts in the dark web are categorized into two distinct sets: CSAM post set and non-CSAM post set, based on their contents. Along with the content itself, each CSAM post is accompanied by associated metadata, including factors such as (1) nationalities and ages of victims mentioned within the post’s content, (2) the specific forum topic where the post was uploaded under the appropriate topic of the forum, (3) any online platforms referenced within the post’s content, and (4) the unique identifier code of the individual who created the post, referred to as the CSAM creator’s ID. These metadata are then analyzed to uncover and visualize valuable information that can aid in CSAM prevention and investigation efforts.
4. CSAM Detection
4.1. Machine Learning Algorithms
NB is a specific type of probabilistic classifier that operates by applying Bayes’ theorem with certain simplifying assumptions. It finds extensive use in in natural language processing, spam filtering, and other applications where categorizing items into different classes based on probabilistic features is essential. One key assumption of NB is that the features are strongly independent, which allows for simplified computations during classification. We employed the Gaussian Naive Bayes algorithm, implemented by using the library [
21], with the following parameters:
and
. Here,
represents the additive smoothing parameter, and
determines whether to learn the prior probabilities of the classes or not.
Logistic Regression (LR) is a statistical model used to predict the probability of a binary outcome based on one or more independent variables (also called features). It works by transforming the linear combination of independent variables using a logistic function (also known as the Sigmoid function), which maps the linear output to a value between 0 and 1. We used the Logistic Regression implemented in [
22], with parameters:
and
. Where,
refers to a regularization technique that is applied to the model’s coefficients to prevent overfitting. The
term refers to the optimization algorithm used to estimate the optimal coefficients for the model.
The SVM algorithm represents patterns as points in space and effectively separates data points with a clear gap. It constructs a maximum margin separator, which maximizes the distance between the separating hyperplane and the nearest data points of each class. Additionally, SVM can handle non-linearly separable data by employing the "kernel trick." This technique allows SVM to transform the original feature space into a higher-dimensional space, where the data becomes linearly separable. By doing so, SVM can perform non-linear classification with accuracy and efficiency. We utilized the C-support vector classification algorithm, implemented by using the library [
23], with the following parameters:
,
,
and
. Where,
C represents the regularization parameter and
denotes the type of kernel used. The
term refers to the degree of the polynomial kernel function, while the
term represents the kernel coefficient.
4.2. Deep Learning Algorithms
CNN is a type of regularized version of multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) which are usually fully connected networks. CNN utilizes convolutional layers in at least one of their layers. This operation allows the network to efficiently process grid-like data, such as images or sequences data like sentences or documents. We employed the CNN Conv1D layer algorithm, implemented by using the library [
24] with the following parameters:
and
’relu’). The
parameter specifies the embedding layer dimensions.
LSTM is a specialized variant of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), a type of neural network frequently utilized for natural language processing models. RNN is capable of retaining information from sequences of data and employs data patterns and feedback loops to make predictions. However, in regular RNNs, there is a challenge known as the "long-term dependency problem". LSTM was introduced to mitigate the long term dependency problem encountered in traditional RNNs. We used the Bidirectional-LSTM algorithm implemented by using the library [
25], with the following parameters:
,
,
and
’sigmoid’).
BERT is a language model utilizing the transformer encoder architecture to process tokens in text. It follows a two-step process: pre-training and fine-tuning. During pre-training, BERT is trained in an unsupervised manner on a large corpus of general text to create the BERT model. In contrast, during the fine-tuning stage, BERT undergoes supervised training on a specific task, using a relatively small number of labeled data, as the model has already acquired knowledge of general linguistic patterns from pre-training. Fine-tuning allows BERT to adapt its understanding to the targeted task efficiently, making use of the existing knowledge to perform well with limited labeled examples. We deployed BERT algorithm, implemented by using in the library [
26], with the follwing parameters:
(bert_en _uncased_ preprocess_3, bert_en_uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12_4),
(1, activation=’sigmoid’) and
=’adam’. In this configuration, the
represents the BERT model, specifying the preprocessing method, architecture, and other necessary details.
4.3. Training and Testing Datasets for Supervised Algorithms
Our first step is to create a labelled dataset that can be used for training or fine-tuning our classifier. For our study, we obtained the labeled dataset from Web-IQ, a company that supplied us with over 352,000 posts collected from 8 dark web forums in 2022. These posts were written in 118 different languages, and approximately 221,000 of them were in English.
Using a dictionary of 12,628 Sexual Abuse Phrases (SAPs) extracted from the THORN project’s
5 CSAM keyword list and Web-IQ dark web forums
6, we successfully identified approximately 177,000 English posts with no SAP and approximately 44,000 English posts containing at least one SAP. This provides us with a high level grouping of posts, but with refinement required to allow for CSAM posts that does not contain any SAPs, and vice versa.
Figure 4 presents the word clouds of single words and two-word phrases related to sexual abuse, extracted from post contents in dark web forums. The size of each word in the clouds corresponds to its frequency within the forums.
From the group of 177,000 posts with no SAP, experts randomly selected 2,000 non-CSAM posts and 500 CSAM posts. Similarly, from the group of 44,000 posts with at least one SAP, experts randomly selected 2,000 CSAM posts and 100 non-CSAM posts. As a result, our manually labelled dataset comprises 4,600 posts from the dark web, consisting of 2,500 CSAM posts and 2,100 non-CSAM posts.
Figure 4.
Sexual abuse phrases in dark web forums in 2022.
Figure 4.
Sexual abuse phrases in dark web forums in 2022.
4.4. Experiment Setup and Quality Measures
The algorithms were implemented using Python 3.10. For LR, NB, and SVM, we used the scikit-learn library version 1.2.2. For CNN, LSTM, and BERT, we utilized the keras library version 1.1.2, running on top of the tensorflow library version 2.10.0. All experiments were run under Windows 10 (64-bit) on a Dell laptop with an Intel Core i7 CPU (3.00 GHz) and 16 GB memory.
For the purpose of measuring the quality of the predicted classes of posts compared to the correct classes, we apply the most commonly used metrics namely accuracy, precision and recall ([
27,
28]). The metrics are derived from four categories in the confusion matrix: True Positive (TP), False Positive (FP), True Negative (TN) and False Negative (FN) as follows:
TP: Posts in which the algorithm predicted CSAM and the correct class was also CSAM.
FP: Posts in which the algorithm predicted CSAM, but the correct class was non-CSAM.
TN: Posts in which the algorithm predicted non-CSAM and the correct class was non-CSAM.
FN: Posts in which the algorithm predicted non-CSAM, but the correct class was CSAM.
Accuracy (ACC) in binary classification is defined as a ratio between the correctly classified samples to the total number of samples: . The accuracy puts the same emphasis on all these factors. However, when categorising pairs, there is usually a bias: it is much easier to identify true negatives correctly, due to their large number. So, we also look at the the precision and the recall .
4.5. Experiment Results
Using the 5-fold cross-validation methodology, each experimental round includes a training set of 3,680 posts (2,000 CSAM and 1,680 non-CSAM) and a testing set of 920 posts (500 CSAM and 420 non-CSAM).
Table 1 presents the average training time, average prediction time, average precision, average recall and average accuracy of six algorithm combinations as follows:
NB: The training time and prediction time were 0.5 and 0.001 seconds, respectively. The precision was 76.1%, recall was 89%, and accuracy was 78.8%.
LR: The training time and prediction time were 0.5 seconds and 0.4 milliseconds, respectively. The precision archived 91.4%, the recall rate was 85%, and accuracy reached 87.5%.
SVM: The training time and prediction time were recorded as 1.8 and 0.27 seconds, respectively. The algorithm demonstrated a precision of 92.3%, a recall of 84.2%, and an accuracy of 87.6%.
CNN: The training time and prediction time were recorded as 21.47 and 0.223 seconds, respectively. The precision achieved by the algorithm was 88.8%, with a recall rate of 85.4% and an accuracy of 86.2%.
LSTM: The training process took approximately 32.5 seconds, while the prediction time was recorded as 1.01 seconds. The precision achieved by the algorithm was 90.3%, with a recall rate of 85.6% and an accuracy of 87.2%.
BERT: The training process took a significant amount of time, specifically 4,261 seconds (or approximately 1 hour and 11 minutes), while the prediction time was 215.3 seconds (around 3.6 minutes). The precision achieved by BERT was 85.9%, with a recall rate of 83% and an accuracy of 83.4%.
Table 1.
Average execution time and binary classification performance of the NB, LR, SVM, CNN, LSTM and BERT algorithms.
Table 1.
Average execution time and binary classification performance of the NB, LR, SVM, CNN, LSTM and BERT algorithms.
| Results |
Algorithms |
| NB |
LR |
SVM |
CNN |
LSTM |
BERT |
| Training time
|
0.5 |
0.5 |
1.8 |
21.47 |
32.5 |
4,261 |
| Prediction time |
0.001 |
0.0004 |
0.27 |
0.223 |
1.01 |
215.3 |
| # True Positive |
445 |
425 |
421 |
427 |
428 |
415 |
| # False Positive |
140 |
40 |
35 |
54 |
46 |
68 |
| # True Negative |
280 |
380 |
385 |
366 |
374 |
352 |
| # False Negative |
55 |
75 |
79 |
73 |
72 |
85 |
| Precision |
76.1% |
91.4% |
92.3% |
88.8% |
90.3% |
85.9% |
| Recall |
89% |
85% |
84.2% |
85.4% |
85.6% |
83% |
| Accuracy |
78.8% |
87.5% |
87.6% |
86.2% |
87.2% |
83.4% |
The combination of the LR algorithm has the fastest execution time, taking approximately 0.43 microseconds to detect a post (or roughly 0.4 milliseconds to detect 920 posts) based on our laptop’s capabilities. The NB algorithm follows as the second-best performing algorithm, with an average detection time of around 0.1 microseconds. The SVM algorithm comes in third place, taking approximately 0.3 milliseconds to detect a post. The DL algorithms have longer training and prediction times compared to the ML algorithms. These fast prediction times make our ML models well-suited for processing CSA text in real-time on social networks. Additionally, the ML models can run on edge devices with limited computational resources and power supply.
In terms of classification precision, the SVM combination performs the best with 92.3%. Following closely behind are LR and LSTM, ranked as the second and third-best performers with precision rates of 91.4% and 90.3% respectively. On the other hand, in terms of recall rate, the NB combination has the highest recall rate of 89%, followed by LSTM and CNN as the second and third-best performers with 85.6% and 85.4% respectively. When it comes to accuracy, SVM is the best with 87.6% which is slightly higher than LR and LSTM with accuracy rates of 87.5% and 87.2%. Among the listed algorithms, BERT exhibits the lowest recall rate of 83% and also has the second-lowest precision and accuracy rates, with values of 85.9% and 83.4% respectively, surpassing only the NB algorithm. This indicating that BERT is not suitable for binary classification of CSAM posts in the dark web. The DL models have a classification performance lower than the ML models. This could be due to our dataset being small, which is not suitable for DL models that typically require a large amount of data to achieve optimal performance.
NB aims to prioritize maximizing true positives, which proves valuable in the identification and removal of CSAM posts from online platforms. This proactive approach is crucial for protecting potential victims, as it helps prevent harmful content from spreading and reaching vulnerable individuals. On the other hand, SVM focuses on minimizing false positives, enabling the identification of CSAM posts to gather information about potential abusers and victims for investigative purposes. Investigators can use the algorithm’s results with more confidence to target and apprehend offenders, as well as to support efforts to rescue victims and prevent future abuse.
5. Quantitative Information Extraction and Discussion
5.1. Our Dark Web Data
We only analyse quantitative information of English posts for our paper. Therefore, when we refer to CSAM posts, non-CAM posts, or forum posts, we specifically mean English CSAM posts, English non-CSAM posts, or English forum posts. The size of each forum on the dark web can be determined by the number of CSAM posts, forum posts, CSAM creators, victim nationalities described in the CSAM posts, online platforms mentioned in the CSAM posts and forum topics including the CSAM posts. All metrics for the crawled forums are presented in
Table 2. In 2022, the eight forums on the dark web contained 63,008 CSAM posts, equivalent to 28.4% of 221,876 forum posts. These CSAM posts were created by 10,490 CSAM creators. Additionally, these CSAM posts referenced 119 victim nationalities, 110 platforms and 12 topics.
The three forums with the largest number of CSAM posts are boyvids-V6, pedo-support and amorzinho which contain 37,158, 8,458 and 6,338 CSAM posts out of 132,274, 18,617 and 21,588 forum posts, respectively. This corresponds to 28.1%, 45.4% and 29.4% of the percentages of the CSAM posts out of the forum posts of the respective forums. While, the three forums with the moderate number of CSAM posts are resistance, boysrus and naughtykids which contain 5,874, 4,079 and 917 CSAM posts out of 23,695, 18,166 and 5,508 forum posts, respectively. This corresponds to 24.8%, 22.5% and 16.6%, of the percentages of the CSAM posts out of the forum posts of the respective forums. The remaining two forums, pharos and nymphetomania, have the fewest CSAM posts. The pharos forum has 138 CSAM posts out of 1,641 forum posts (equivalent to 8.4%). The nymphetomania forum has 46 CSAM posts out of 387 forum posts (equivalent to 11.9%).
The number of CSAM creators and victim nationalities are 3,675 and 117 for boyvids-V6, 864 and 74 for pedo-support, 2,171 and 62 for amorzinho, 2,174 and 66 for resistance, 1,136 and 79 for boysrus and 451 and 34 for naughtykids, respectively. In term of the number of platforms and topics, there are 100 and 8 for boyvids-V6, 68 and 2 pedo-support, 73 and 10 for amorzinho, 75 and 10 resistance, 60 and 6 for boysrus, and 28 and 9 for naughtykids, respectively. However, the remaining two forums, pharos and nymphetomania, have either a small number of or no available information regarding the number of CSAM creators, victim nationalities, platforms and topics.
Table 2.
Statistical information of some metadata of 221,876 English posts of 8 dark web forums in 2022.
Table 2.
Statistical information of some metadata of 221,876 English posts of 8 dark web forums in 2022.
| Forum |
# CSAM |
# forum |
% CSAM |
# CSAM |
# victim |
# |
# |
| Names |
Posts
|
Posts
|
in Forum
|
Creators
|
Nationalities
|
Platforms
|
Topics
|
| boyvidsV6 |
37,158 |
132,274 |
28.1% |
3,675 |
117 |
100 |
8 |
| pedosupport |
8,458 |
18,617 |
45.4% |
864 |
74 |
68 |
2 |
| amorzinho |
6,338 |
21,588 |
29.4% |
2,171 |
62 |
73 |
10 |
| resistance |
5,874 |
23,695 |
24.8% |
2,174 |
66 |
75 |
10 |
| boysrus |
4,079 |
18,166 |
22.5% |
1,136 |
79 |
60 |
6 |
| naughtykids |
917 |
5,508 |
16.6% |
451 |
34 |
28 |
9 |
| pharos |
138 |
1,641 |
8.4% |
N/A |
6 |
N/A |
1 |
| nymphetomania |
46 |
387 |
11.9% |
19 |
7 |
5 |
1 |
| All |
63,008 |
221,876 |
28.4% |
10,490 |
119 |
110 |
12 |
5.2. CSAM Creator Profiles
Among 10,490 CSAM creators on the dark web in 2022, we have compiled data on the 20 most active CSAM creators. For our analysis, we have selected three informative classifications (
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7) for discussion.
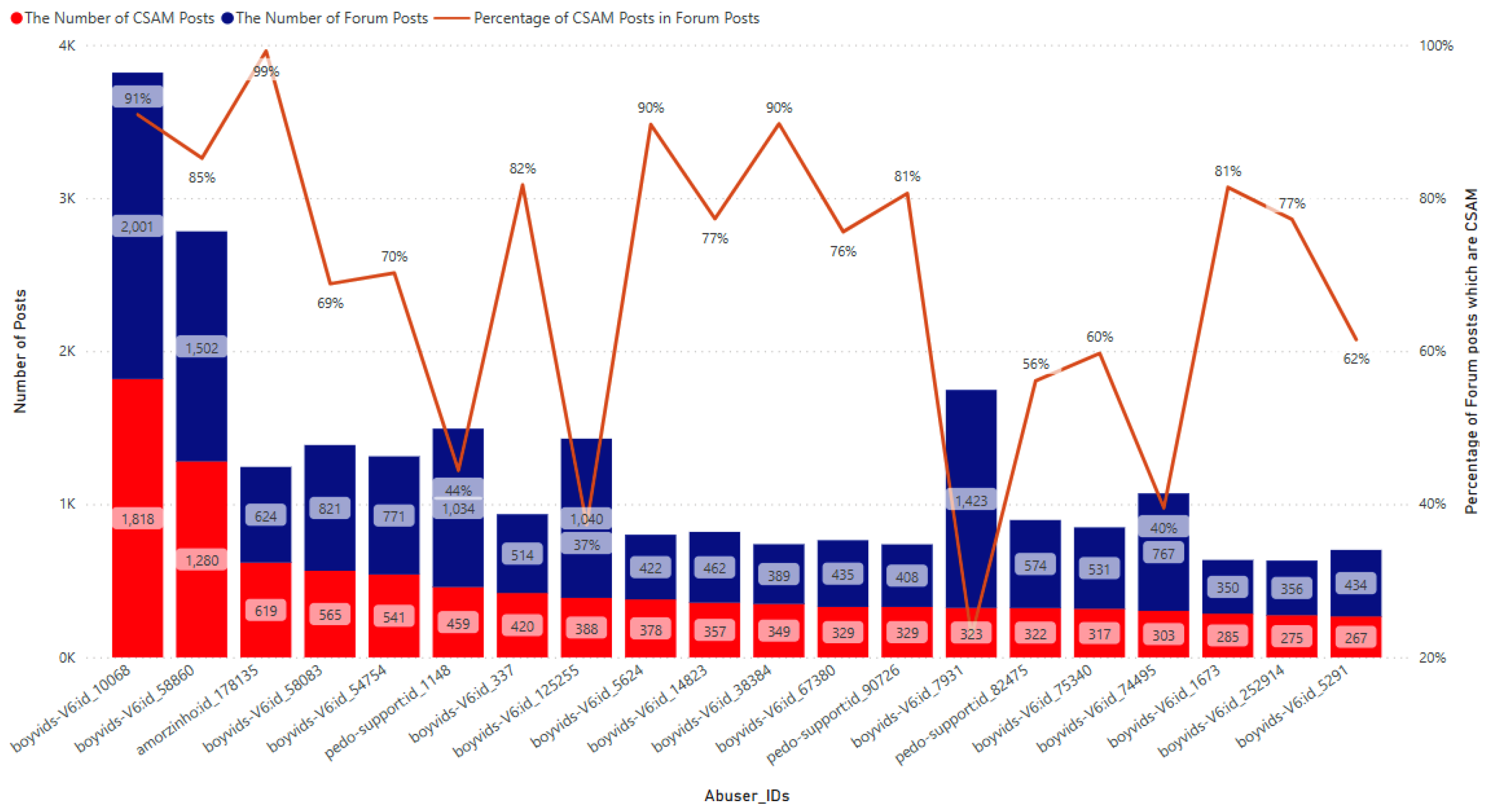
Figure 5 presents the statistics on the number of CSAM posts and forum posts made by the 20 most active CSAM creators, along with the corresponding percentage relationship between the two. This information sheds light on the posting behavior of these individuals and provides insights into their activities. All of the identified CSAM creators belong to the forum group known for having the largest number of CSAM posts, namely
boyvids-V6,
pedo-support and
amorzinho. Specifically, there are 16 CSAM creators associated with
boyvids-V6, 3 CSAM creators associated with
pedo-support, and 1 CSAM creator associated with
amorzinho. The most active CSAM creator is identified as a creator within
boyvids-V6 with
id_10068 who posted 1,818 CSAM posts out of a total of 2,011 forum posts (equivalent to 91%). The identified CSAM creator within
amorzinho is only the 3rd ranking in the number of CSAM posts, but his percentage of CSAM posts out of the total posts is the highest with 99%. While, the CSAM creator with ID
boyvids-V6:id_7931 has the lowest percentage of CSAM posts out of the total posts is lowest, at 23%, and is ranked 14th.
On the dark web, numerous forum topics are available where users can upload their posts under the appropriate topic. There are the 9 topics collected, namely
Chat,
General,
Girl,
Hardcore,
Photo,
Softcore,
Video,
Webcam and
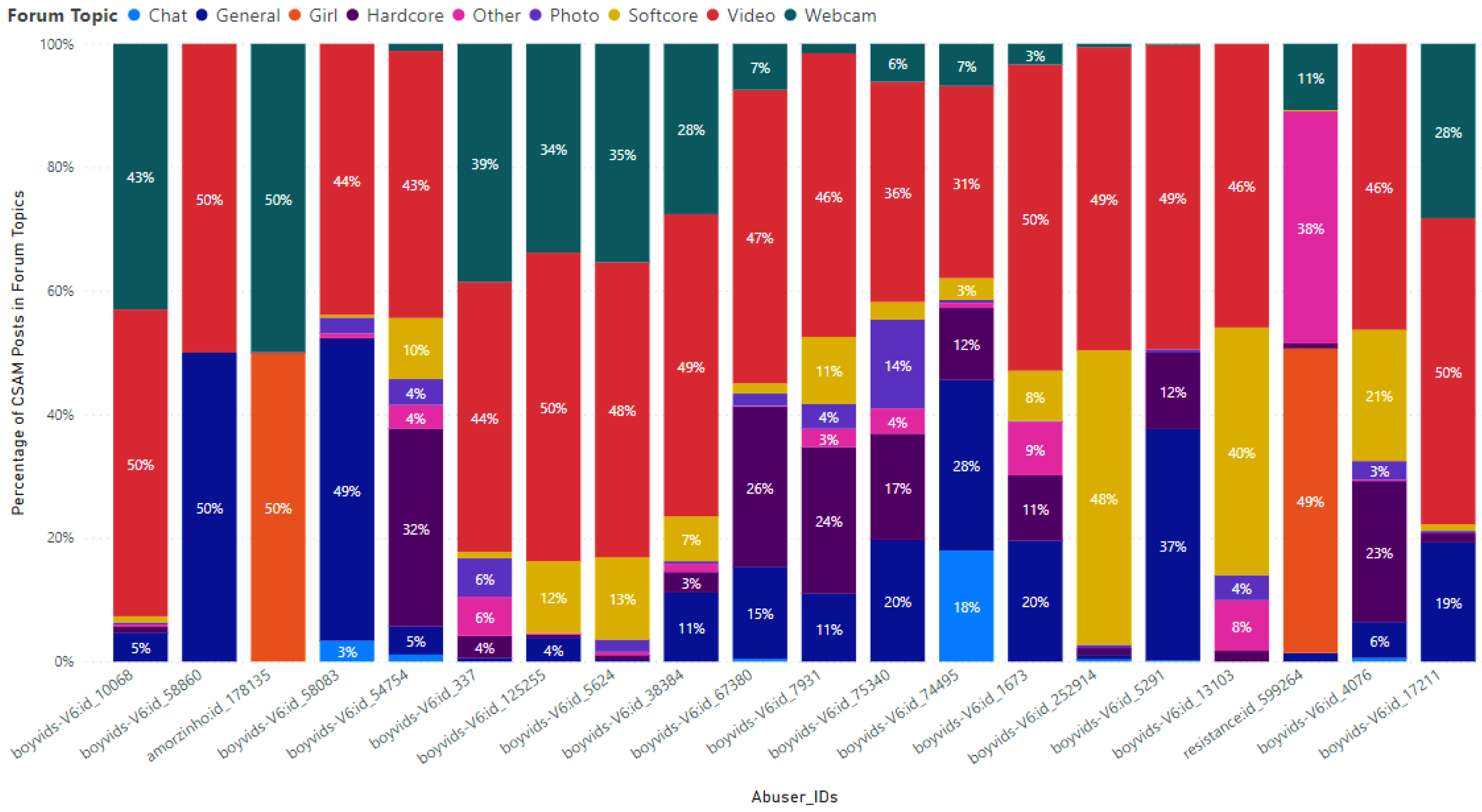
Other. In
Figure 6, the percentages of CSAM posts out of forum topics of the top 20 CSAM creators are presented for each topic. The top-ranked CSAM creator, identified as
boyvids-V6:id_10068, uploaded CSAM posts in a total of 7 topics. Notably, the percentages of CSAM posts out of forum topics in the
Video and
Webcam categories are 50% and 43% respectively. The second ranked CSAM creator,
boyvids-V6:id_58860, and the third ranked CSAM creator,
amorzinho:id_178135, uploaded CSAM posts in only 2 topics. In each of these topics, the percentage of CSAM posts out of forum topics was 50%. Specifically,
boyvids-V6:id_58860 utilized
Video and
General topics, while
amorzinho:id_178135 used
Girl and
Webcam topics. Among the remaining CSAM creators, it was observed that although they used multiple topics, they frequently focused on two specific topics. Among the top 20 CSAM creators, the most common topic for posting CSAM content was Video, followed by Webcam as the second most utilized topic.
Figure 5.
The number of CSAM posts and forum posts by the 20 most active CSAM creators in 2022.
Figure 5.
The number of CSAM posts and forum posts by the 20 most active CSAM creators in 2022.
Figure 6.
Percentages of the CSAM posts in forum topics uploaded by the 20 most active CSAM creators of the topics in 2022.
Figure 6.
Percentages of the CSAM posts in forum topics uploaded by the 20 most active CSAM creators of the topics in 2022.
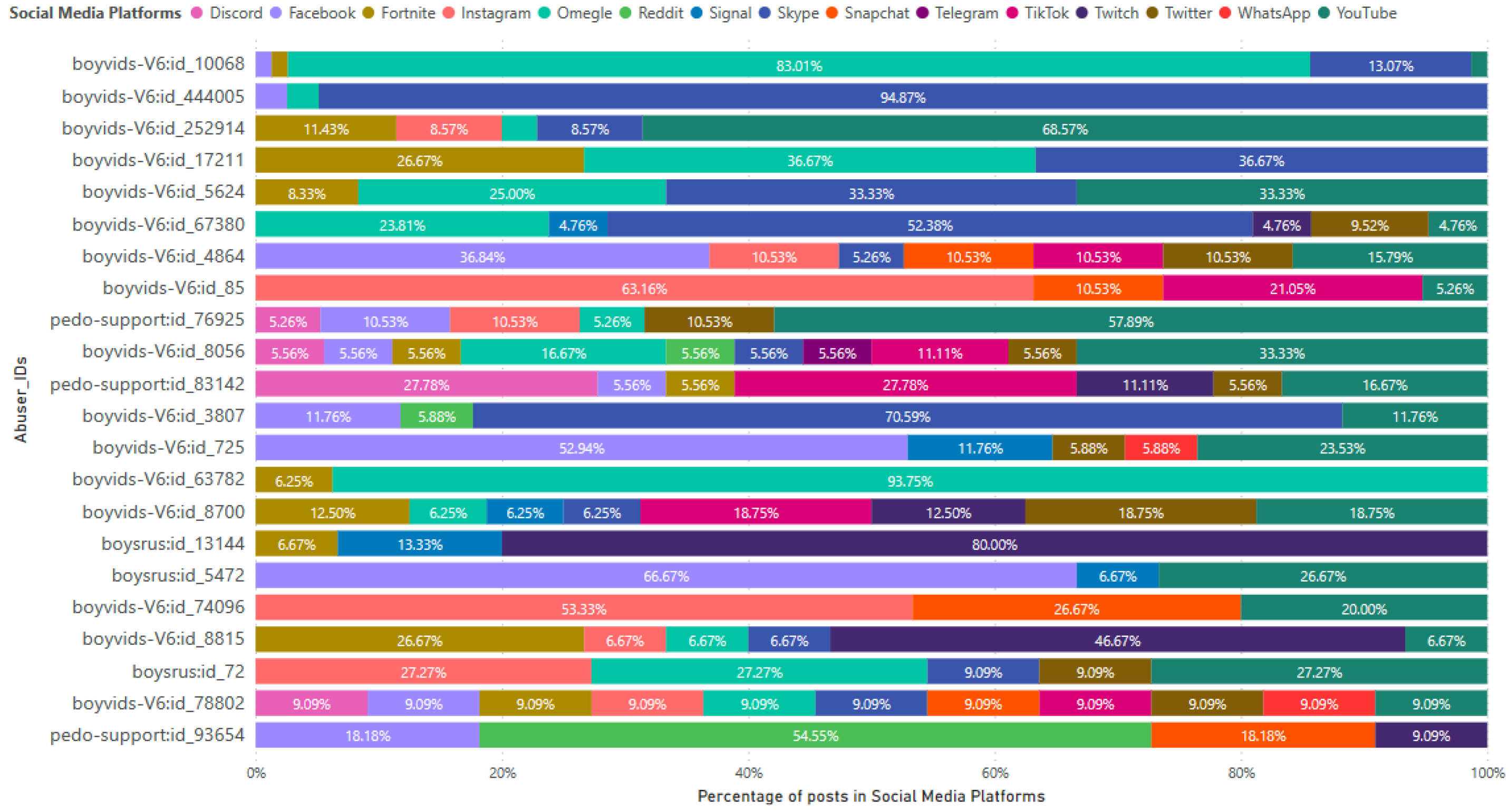
Figure 7.
Percentages of the CSAM posts in social media platforms mentioned by the 22 most active CSAM creators of the platforms in 2022.
Figure 7.
Percentages of the CSAM posts in social media platforms mentioned by the 22 most active CSAM creators of the platforms in 2022.
CSAM creators frequently engage in the creating, uploading and/or sharing of CSAM on various online platforms, with a particular emphasis on social media platforms. These individuals often include links to such platforms within their posts in the dark web.
Figure 7 presents the distribution of CSAM posts mentioning different social media platforms, specifically focusing on the 22 most active CSAM creators of these platforms. The analysis encompasses famous social media platforms, e.g. Facebook, Instagram, Skype, TikTok, Twitter, WhatsApp and YouTube. Certain CSAM creators exhibit a significant concentration of their CSAM posts on a specific social media platform, accounting for over 80% of their total CSAM posts. The top CSAM creator (
boyvids-V6:id_10068) and the 14th ranked CSAM creator (
boyvids-V6:id_63782) allocated 83.01% and 93.75% of their CSAM posts to Omegle, respectively. The second highest CSAM creator, identified as
boyvids-V6:id_444005, attributed 94.87% of their CSAM posts to Skype. On the other hand, some CSAM creators utilized multiple social media platforms to distribute their CSAM posts. For example, CSAM creators identified as
boyvids-V6:id_8056,
boyvids-V6:id_8700 and
boyvids-V6:id_78802, ranked 10th, 15th and 21th respectively, mentioned 10, 8 and 11 social media platforms respectively in their posts.
5.3. Victim Profiles
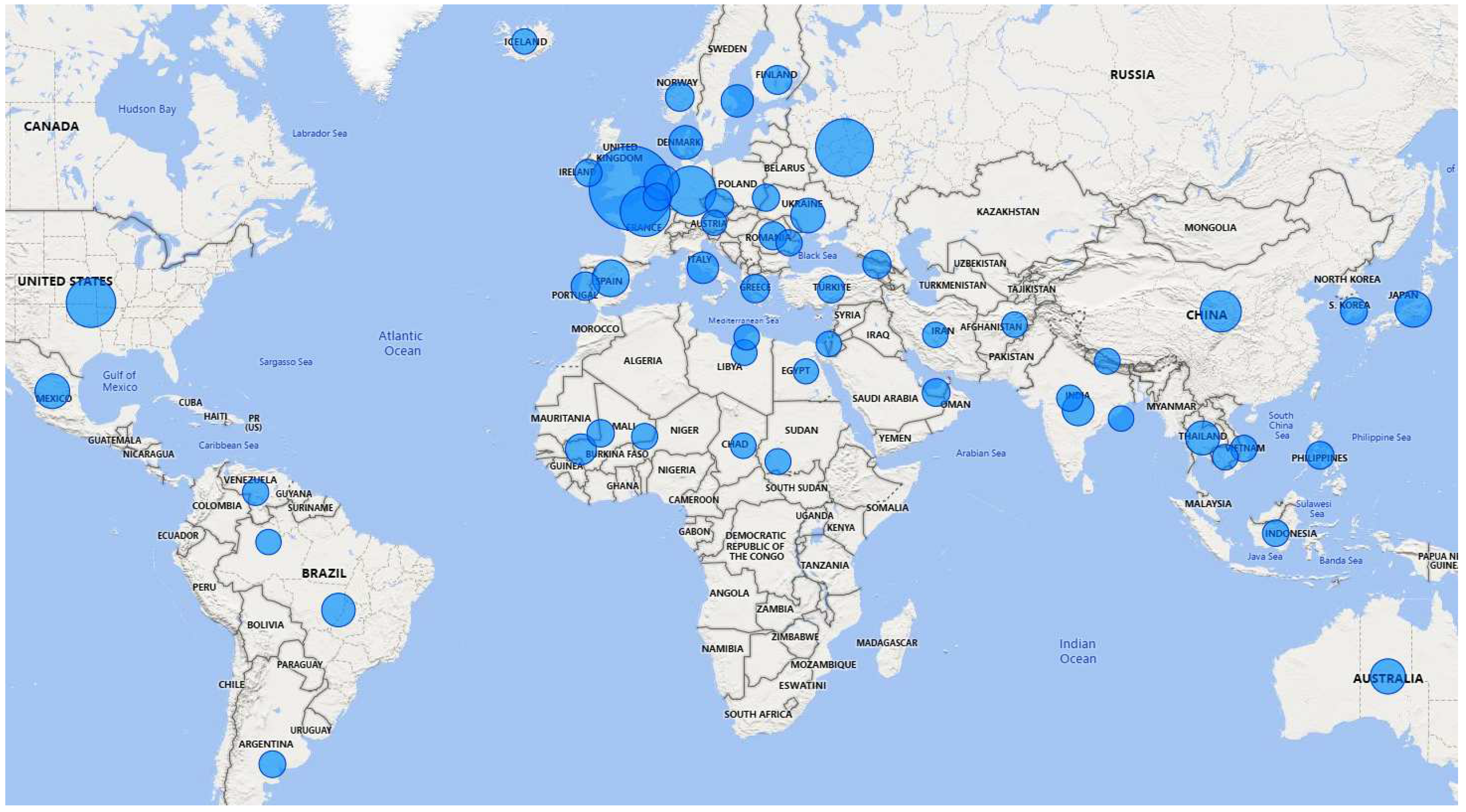
The nationalities of victims are often described in CSAM posts.
Figure 8 depicts a world map illustrating the countries of the victims mentioned in 2022, with the size of the circle indicating the number of CSAM posts associated with that particular country. Thus, countries with larger circle sizes indicate a higher number of CSAM posts that mentions those locations. Based on the visualization, it is evident that the top 5 countries with the highest number of CSAM mentions are Great Britain, Russia, German, France and United States. We can zoom-in view of the visualization that allows for a closer examination of the number of CSAM posts specifically mentioning each country.
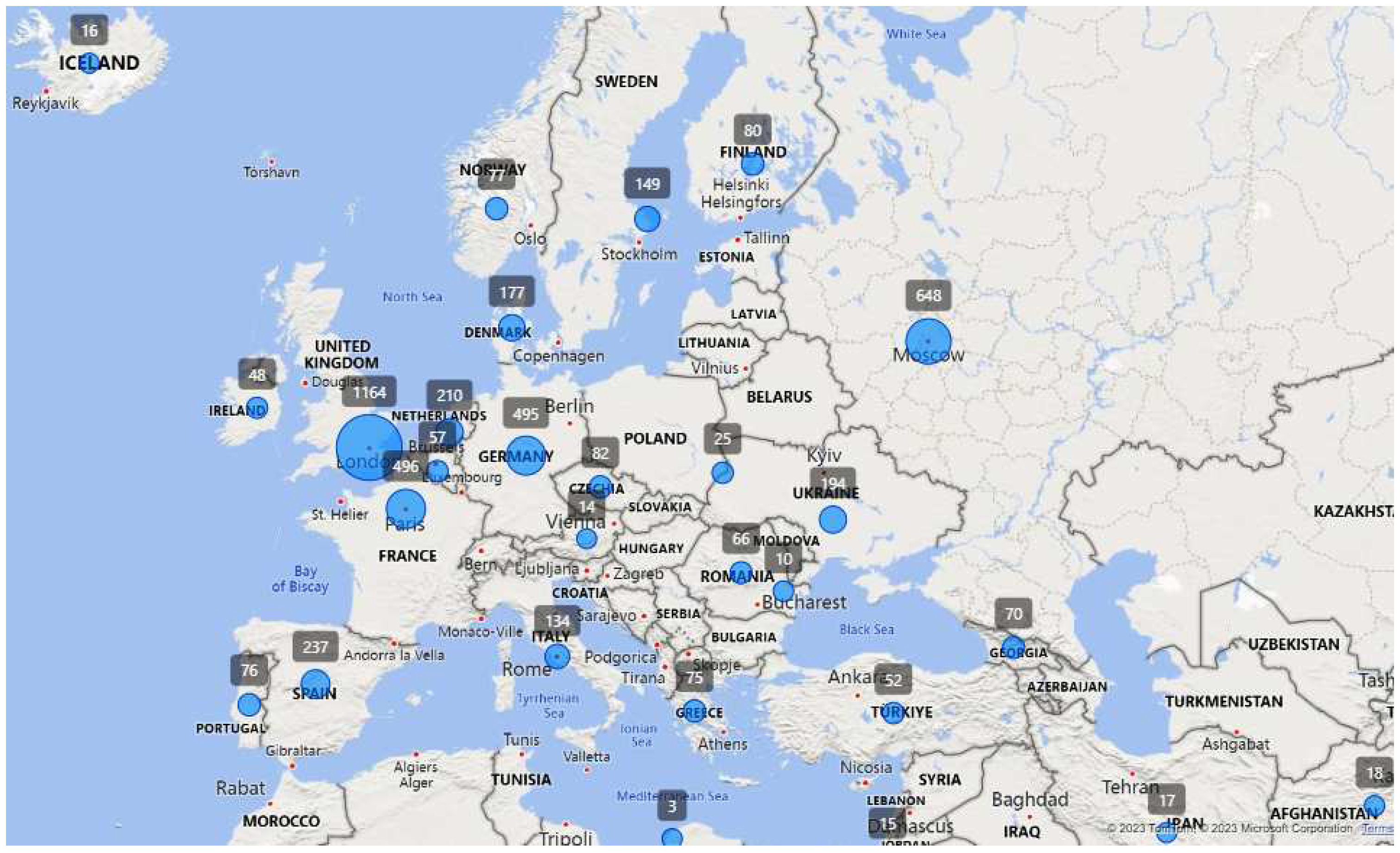
Figure 9 provides valuable insights into the prevalence of CSAM posts referencing these countries within the European context in 2022. Specifically, Great Britain was mentioned in 1,164 CSAM posts, while France, Germany, and Spain were mentioned in 496, 495, and 327 CSAM posts, respectively.
Figure 8.
The number of CSAM posts and victim countries described in CSAM posts in 2022.
Figure 8.
The number of CSAM posts and victim countries described in CSAM posts in 2022.
Figure 9.
The number of CSAM posts and victim countries in Europe described in CSAM posts.
Figure 9.
The number of CSAM posts and victim countries in Europe described in CSAM posts.
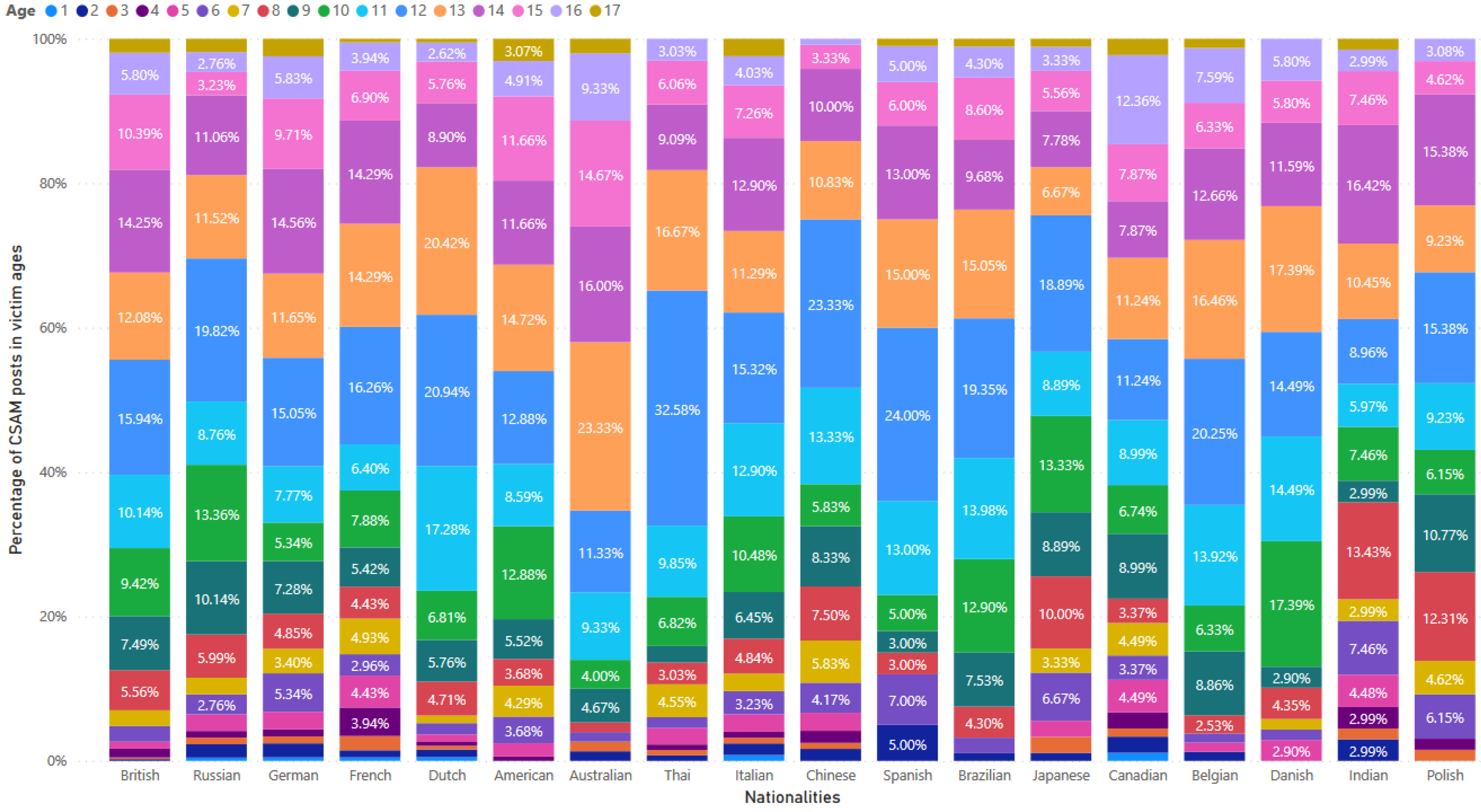
Figure 10 displays distribution of CSAM posts based on the percentages per victim age, ranging from 1 to 17 years old, for the top 18 victim nationalities. Among these nationalities, victims at the age of 12 were most frequently mentioned in 12 out of 18, specifically British, Russian, German, French, Dutch, Thai, Italian, Chinese, Spanish, Brazilian, Japanese and Belgian. The most commonly mentioned ages for Polish victims were 12 and 14 years old. In contract, victims at the age of 13 were most prevalent among American, Australian and Danish. Indian victims were most frequently mentioned at the age of 14, while Canadian victims were most commonly mentioned at 16 years old.
The chord diagram in
Figure 11 presents relationships between the top ten victim nationalities and the top ten social media platforms. Certain nationalities were exclusively mentioned on specific social media platforms. For example, Chinese victims were mentioned only on Twitter and Telegram, while Mexican victims were exclusively mentioned on YouTube and Facebook. Conversely, certain social media platforms were used exclusively for specific nationalities. For instance, TikTok was solely used for Russian and Ukrainian victims. Whereas, Omegle was utilized for British, Australian, Italian, Brazilian, Belgian and German victims.
Figure 10.
Percentages of CSAM posts per victim age in the top 18 victim nationalities described in the posts.
Figure 10.
Percentages of CSAM posts per victim age in the top 18 victim nationalities described in the posts.
Figure 11.
Relationships between the top ten victim nationalities and the top ten social media platforms.
Figure 11.
Relationships between the top ten victim nationalities and the top ten social media platforms.
5.4. Social Media Platform Profiles
In 2022, among the 110 online platforms used by CSAM creators on the dark web, there were 15 notably popular social media platforms. These platforms include Discord, Facebook, Fortnite, Instagram, Omegle, Reddit, Signal, Skype, Snapchat, Telegram, TikTok, Twitch, Twitter, WhatsApp and YouTube. Some selected information associated with these platforms are presented in
Figure 12,
Figure 13 and
Figure 14.
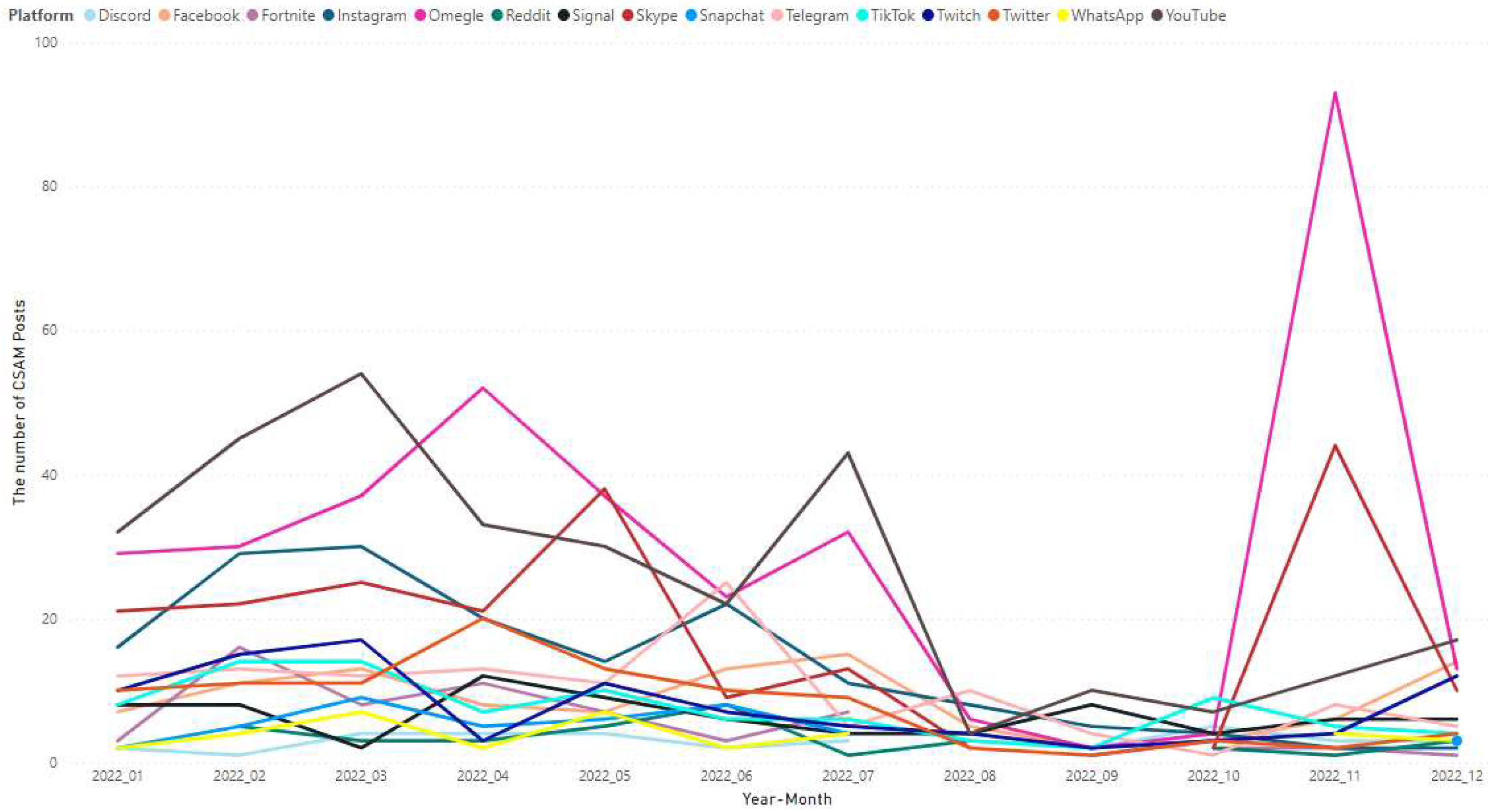
Figure 12 displays the monthly count of CSAM posts per social media platform in 2022. Omegle recorded the highest values in November and April, with 93 and 52 CSAM posts respectively. Conversely, the lowest number of CSAM posts on Omegle was observed in September, with only 2 CSAM posts. Meanwhile, the highest number of CSAM posts on YouTube was recorded in March, with 54 posts, while Skype had its highest number of CSAM posts in November, with 44 posts. From a different perspective, it is worth noting that in September, these platforms had a relatively low number of CSAM posts. Among them, YouTube had the highest value, with only 10 CSAM posts recorded during that month.
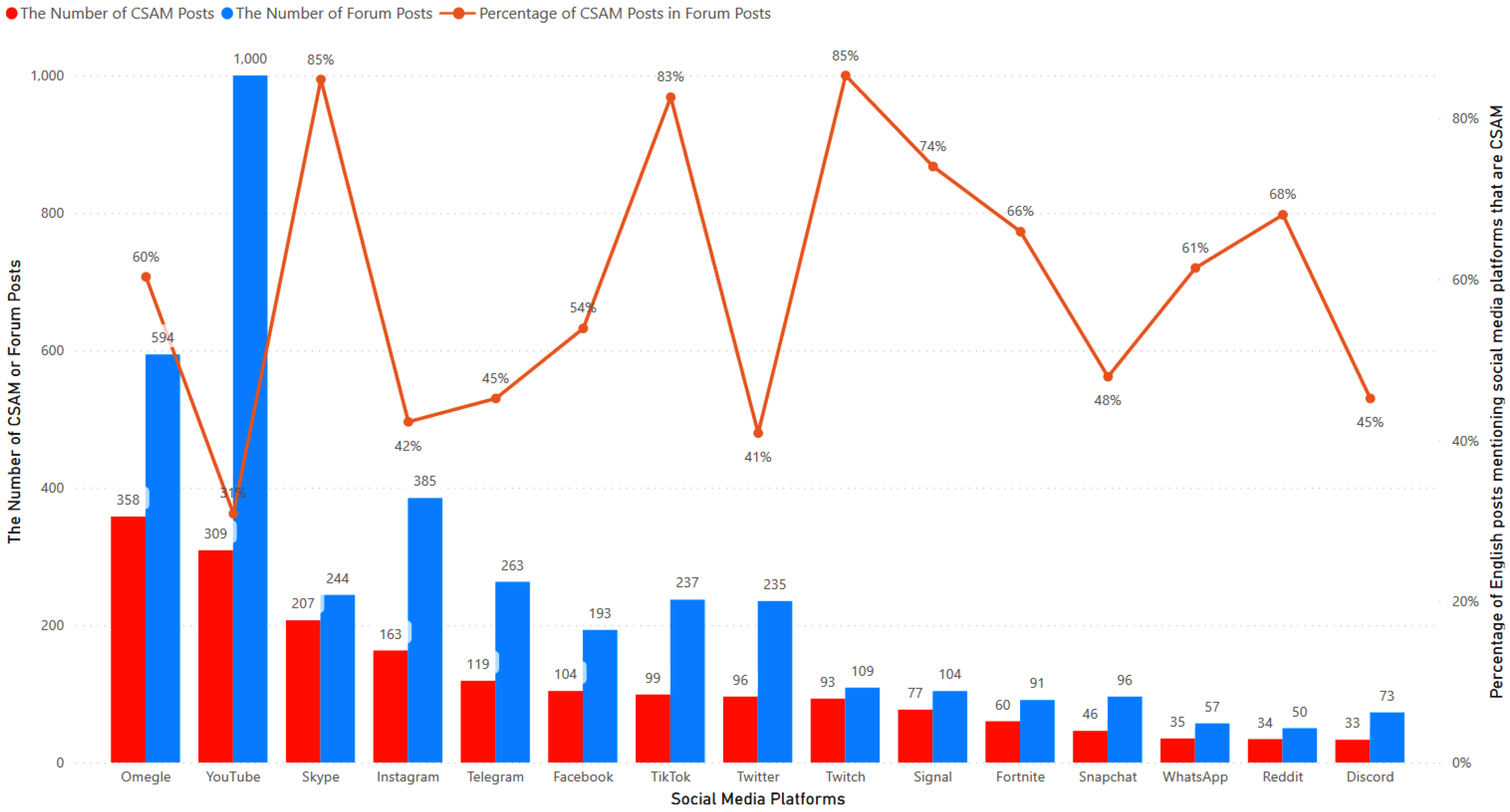
Figure 13 illustrates the number of CSAM posts and forum posts, along with the corresponding percentage, for each platform. The leading social media platform mentioned in CSAM posts is Omegle, with 358 CSAM posts out of 594 forum posts, accounting for approximately 60% of the total. The second and third social media platforms, YouTube and Skype, recorded 309 and 207 CSAM posts, respectively. Some platforms with a high percentage of CSAM posts compared to forum posts include Skype, TikTok, and Twitch, with percentages of 85%, 83% and 85%, respectively. On the other hand, YouTube, Instagram and Twitter has the lowest percentages, with less than 45%.
Figure 12.
The number of CSAM posts per social media platform per month in 2022.
Figure 12.
The number of CSAM posts per social media platform per month in 2022.
Figure 13.
The number of CSAM posts and forum posts, and the percentages between them in the top 15 social media platforms.
Figure 13.
The number of CSAM posts and forum posts, and the percentages between them in the top 15 social media platforms.
Figure 14.
The number of CSAM posts per type of link per social media platform.
Figure 14.
The number of CSAM posts per type of link per social media platform.
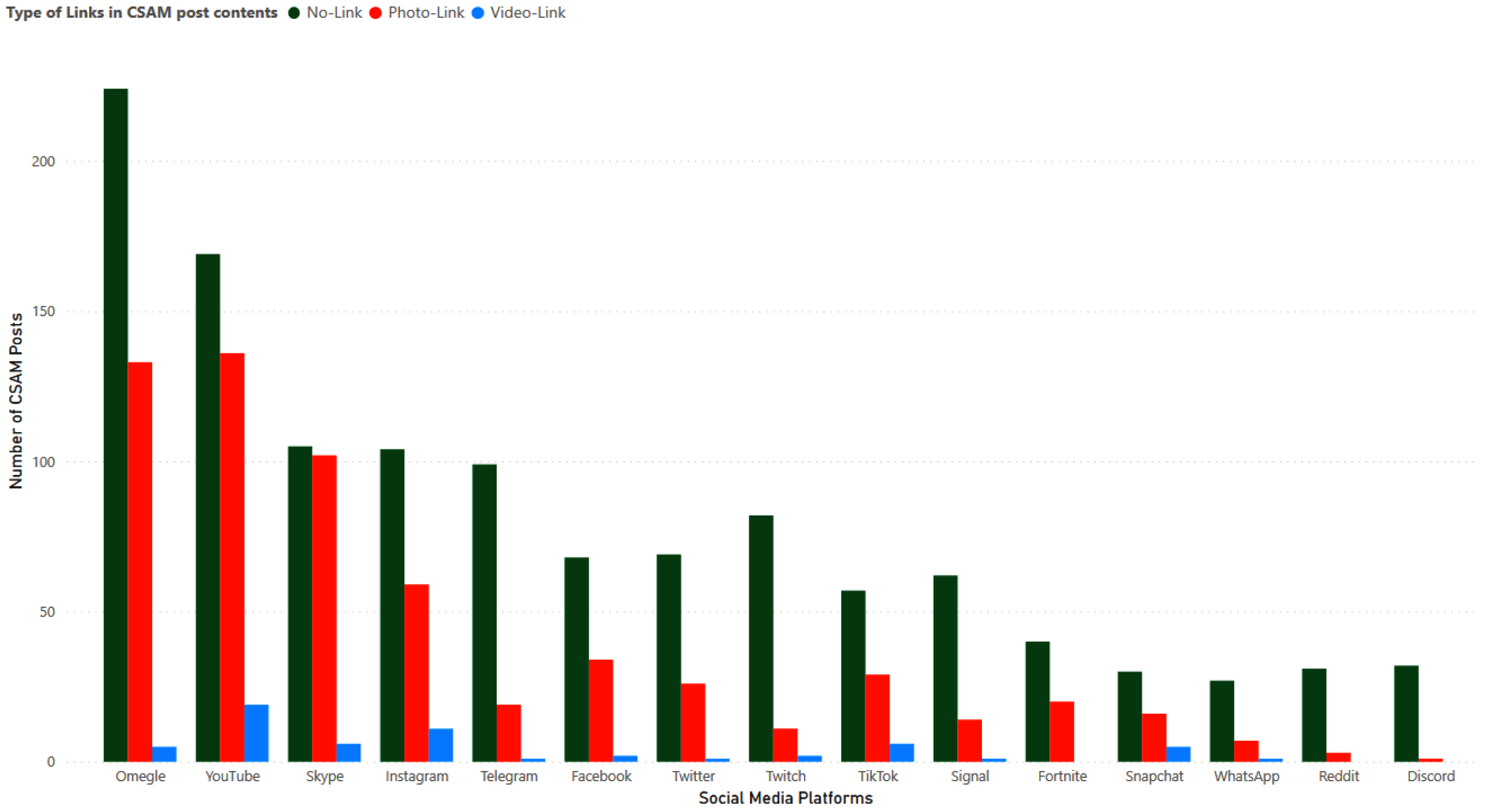
Figure 14 presents the number of CSAM posts categorized as having no link, containing photo links, and containing video links. Omegle had 225 CSAM posts without any links, 133 CSAM posts with photo links, and a mere 5 CSAM posts with video links. YouTube had the highest number of CSAM posts with both photo links and video links, with a total of 136 with photo links and 19 posts with video links, respectively. The number of posts with no link and photo links in Skype is similar, with approximately 100 posts each. Three platforms, namely Fortnite, Reddit, and Discord, did not have any CSAM posts with video links.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
We proposed and implemented a novel algorithm based on machine learning and natural language processing to automatically detect and classify CSAM text post content in the dark web. In the experimental evaluation on the dataset of 4,600 CSAM and non-CSAM posts with 5-fold cross-validation, the combination of NB algorithm performed the best in terms of classification recall with 89%, and it was the second best in execution time with 0.1 microsecond/post. On the other hand, the SVM combination performed the best in terms of classification precision and accuracy with 92.3% and 87.6% respectively, and it was the third-best in execution time with 0.3 milliseconds/post. The choice of NB and SVM depends on the specific goals and requirements of the CSAM classification task. NB aims to maximize the number of true positives, which could be useful in identifying and removing CSAM posts from online platforms to protect potential victims. In contrast, SVM aims to minimize false positives, which could be useful for identifying CSAM posts to extract information about potential predators and victims for investigative purposes.
We also applied and analysed the statistics on CSAM creators, victim nationalities, online platforms, and forum topics in each forums on the dark web in 2022. In particular, we extracted, analyzed and discussed the preferences of CSAM creators regarding children’s age and nationality, online platforms, and forum topics that allows us to gain valuable insights into CSAM creators’ behaviors and motivations. By exploring the intricate relationships between these factors, we supplied a deeper understanding of the patterns and trends associated with CSAM activities on the dark web.
As part of our future work, CSAM detection APIs will be designed and implemented to seamlessly integrate into the websites of hotlines and helplines.This integration will facilitate the direct reporting of CSAM incidents to online platforms, ensuring swift removal of harmful content. These APIs will also enable the creation of visualizations that provide efficient CSAM information for educational and legal agencies. Additionally, we plan to conduct more in-depth investigations into activities of CSAM creators and victims on the dark web. This includes exploring the complex relationships between CSAM creators and victims, identifying potential collaborations among CSAM creators, and assessing the extent of victims’ losses.
Moreover, we will focus on recognizing named entities in CSA text to provide crucial concepts for our ML models [
29]. By enhancing our ML model’s understanding of post contents, we can further improve its efficiency and accuracy in detecting and classifying CSAM content. Overall, our future endeavors aim to strengthen the fight against CSAM on the dark web by developing practical tools and gaining a deeper understanding of the dynamics involved. Through these efforts, we strive to protect vulnerable individuals and contribute to a safer online environment for all.
Acknowledgments
The paper is an extension of the long abstract [
30] and the conference paper [
31]. The paper is also part of the N-Light project which is funded by the Safe Online Initiative of End Violence and the Tech Coalition through the Tech Coalition Safe Online Research Fund (Grant number: 21-EVAC-0008-Technological University Dublin).
References
- Ngo, V.M.; Thorpe, C.; Dang, C.N.; Mckeever, S. Investigation, Detection and Prevention of Online Child Sexual Abuse Materials: A Comprehensive Survey. the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computing and Communication Technologies (RIVF-2022). IEEE, 2022, pp. 707–713. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ermakova, T.; Ververis, V.; Fabian, B. Detecting Child Sexual Abuse Material: A Comprehensive Survey. Forensic Science International: Digital Investigation 2020, 34, 301022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, A.; González-Castro, V.; Alegre, E.; Fidalgo, E. AttM-CNN: Attention and metric learning based CNN for pornography, age and Child Sexual Abuse (CSA) Detection in images. Neurocomputing 2021, 445, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, E.; Westlake, B.G. Detecting child sexual abuse images: traits of child sexual exploitation hosting and displaying websites. Child Abuse & Neglect 2021, 122, 105336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, P.; Avila, S.; Perez, M.; Rocha, A. Leveraging deep neural networks to fight child pornography in the age of social media. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation 2018, 50, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjeira, C.; Macedo, J.; Avila, S.; Santos, J. Seeing without Looking: Analysis Pipeline for Child Sexual Abuse Datasets. the 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (FAccT’22). ACM, 2022, p. 2189–2205. [CrossRef]
- Struppek, L.; Hintersdorf, D.; Neider, D.; Kersting, K. Learning to break deep perceptual hashing: The use case neuralhash. the 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, 2022, pp. 58–69. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Uddin, M.A.; Islam, L.; Akter, A.; Sharmin, S.; Acharjee, U.K. Cyberbullying detection on social networks using machine learning approaches. the 2020 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Computer Science and Data Engineering (CSDE). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Borj, P.R.; Raja, K.; Bours, P. Detecting Sexual Predatory Chats by Perturbed Data and Balanced Ensembles. the 2021 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.; Jiangbin, Z.; Naqvi, I.; AbdelMajeed, M.; Zia, T. Abusive Language Detection from Social Media Comments Using Conventional Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches. Multimedia Systems 2022, 28, 1925–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecillon, N.; Labatut, V.; Dufour, R.; Linares, G. Graph embeddings for abusive language detection. SN Computer Science 2021, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngejane, C.H.; Eloff, J.H.; Sefara, T.J.; Marivate, V.N. Digital forensics supported by machine learning for the detection of online sexual predatory chats. Forensic science international: Digital investigation 2021, 36, 301109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, G.; Savage, N. The Tor dark net. Chatham House 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, M.; Fuchs, M.; Strohmeier, M.; Engel, M.; Liechti, M.; Lenders, V. BlackWidow: Monitoring the Dark Web for Cyber Security Information. the 11th International Conference on Cyber Conflict (CyCon), 2019, Vol. 900, pp. 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Kokolaki, E.; Daskalaki, E.; Psaroudaki, K.; Christodoulaki, M.; Fragopoulou, P. Investigating the dynamics of illegal online activity: The power of reporting, dark web, and related legislation. Computer Law & Security Review 2020, 38, 105440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazah, S.; Huda, S.; Abawajy, J.H.; Hassan, M.M. An Unsupervised Model for Identifying and Characterizing Dark Web Forums. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 112871–112892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhams, J.; Kloess, J.A.; Jose, B.; Hamilton-Giachritsis, C.E. Characteristics and behaviors of anonymous users of dark web platforms suspected of child sexual offenses. Frontiers in Psychology 2021, 12, 623668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.N.T.; Nguyen, L.K.N.; Ngo, V.M. Machine Learning based English Sentiment Analysis. Journal of Science and Technology 2014, 52(4D), 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.J.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (4th Edition); Pearson, 2022.
- Dang, C.; Moreno-García, M.; Prieta, F.; Nguyen, K.; Ngo, V. Sentiment Analysis for Vietnamese – Based Hybrid Deep Learning Models. the 18th International Conference on Hybrid Artificial Intelligence Systems (HAIS 2023). Springer-LNAI, 2023, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Scikit-learn. Multinomial Naive Bayes. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.naive_bayes.MultinomialNB.html#sklearn.naive_bayes.MultinomialNB, 2023. Version 1.2.2, accessed , 2023. 01 April.
- Scikit-learn. Logistic Regression. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression.html, 2023. Version 1.3.0, accessed , 2023. 02 July.
- Scikit-learn. C-Support Vector Classification. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.svm.SVC.html, 2023. Version 1.2.2, accessed , 2023. 01 April.
- Keras-Tensorflow. Convolution Layer with Conv1D Layer. https://keras.io/api/layers/convolution_layers/convolution1d/, 2023. accessed July 02, 2023. 02 July.
- Keras-Tensorflow. Long Short Term Memory. https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/LSTM, 2023. Version 1.1.2, accessed April 01, 2023. 01 April.
- Keras-Tensorflow. Text Classsification with BERT. https://www.tensorflow.org/text/tutorials/classify_text_with_bert, 2023. Version 1.1.2, accessed April 01, 2023. 01 April.
- Ngo, V.M.; Duong, T.V.T.; Nguyen, T.B.T.; Nguyen, P.T.; Conlan, O. An efficient classification algorithm for traditional textile patterns from different cultures based on structures. Journal on Computing and Cultural Heritage (JOCCH) 2021, 14(4), 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, A. Classification Assessment Methods. Applied Computing and Informatics 2021, 17(1), 168–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.M.; Munnelly, G.; Orlandi, F.; Crooks, P.; O’Sullivan, D.; Conlan, O. A Semantic Search Engine for Historical Handwritten Document Images. Linking Theory and Practice of Digital Libraries; Berget, G.; Hall, M.M.; Brenn, D.; Kumpulainen, S., Eds. LNCS, vol. 12866, Springer, 2021, pp. 60–65. [CrossRef]
- Mckeever, S.; Thorpe, C.; Ngo, V.M. Determining Child Sexual Abuse Posts based on Artificial Intelligence. the 2023 International Society for the Prevention of Child Abuse & Neglect Congress (ISPCAN-2023), Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, September 24-27, 2023, 2023, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.M.; Mckeever, S.; Thorpe, C. Identifying Online Child Sexual Texts in Dark Web through Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms. the APWG.EU Technical Summit and Researchers Sync-Up (APWG.EU-Tech 2023). CEUR Workshop Proceedings, 2023, pp. 1–6.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).