1. Introduction
Over 60 % of the world’s population performs physical activity for less than 30 minutes per week. Well-known consequences of health-damaging everyday habits are obesity [
1,
2], decreasing performance capability/resilience, and the occurrence of chronic secondary diseases [
3]. This development is also reflected in the candidate selection or day-to-day military duties. However, health and fitness are currently the most discussed topics in society when lifestyle is concerned. Many manufacturers try to implement this new idea of all-day measuring of physiological data on the commercial market in order to show the users their activities so that one can deduce how to improve their nutrition and physical activity, including the sleep-wake rhythm – in short, how to improve one entire behavior (consumer-oriented fitness and health offers) in the future. While some systems may stay on standby until needed (e.g., pacemakers that detect arrhythmia), other data should be recorded permanently so that the user or a surveying person in a remote setting, is informed online, and can change the behavior in real-time [
4]. The digitization of the health sector virtually moves from bottom to top. The consumers set the plan, with the increased health consciousness being the primary reason for this trend. More than 100,000 applications from the health and fitness areas are on the market and can be displayed on a smartphone [
5]. In recent years, the so-called wearables (mainly as a bracelet or integrated into watches) were placed on the market. They can be operated autonomously or connected to a smartphone [
6]. Wearables use simple physiological parameters (movement, heart rate) and convert them into distances covered and calories consumed utilizing specific algorithms. Thus, fitness apps and wearables constitute the interface between leisure time and health offers and are currently the growth engine of the e-health market [
7]. Previously, these opportunities were only available to chronically sick persons and top athletes [
8,
9,
10]. Meanwhile, smartphones are even scheduled for diagnostic purposes, which is critical from a physician's point of view [
11] because it will be possible for amateurs to make examinations, which will not be evidence-based medicine [
12].
In extreme environments where it may be very difficult or even impossible to provide medical assistance in the case of an emergency, telemedical systems that allow remote control of the person(s) are of particular interest. Such a setting may significantly increase health, safety, and performance, not only in the military but also in a civilian setting. Examples are firefighters who must handle extreme heat and the risk of hyperthermia or mountain rescuers who have to work in cold – sometimes extreme cold – environments and face difficult terrain, hypoxia, helicopter noise, and other stressors [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. However, to increase health and safety in such situations, real-time monitoring is needed in contrast to the alarm systems mentioned above [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24].
2. History of Telemedicine
Telemonitoring is not a new issue. Dr. Einthoven already demonstrated this in 1906 when he had electrocardiogram (ECG) data transmitted from a hospital to his laboratory using a telephone line [
25]. For astronautics, the first time in history that the medical data transfer principle was applied on a large scale was situation-related. The Russian space agency (today: Roskosmos) and the US-American space agency (NASA) started medical telemetry programs at the end of the 1950s in order to check the physiological functions of astronauts and to transmit data to Earth [
26]. At that time, television technology was used.
1964, the first interactive T.V. telemedicine project started, permitting medical care using a secure T.V. link between a psychiatric ward in Nebraska and a Norfolk clinic. Due to the enormous expenditure and lack of financial profitability, such projects were terminated at the beginning of the 1970s. Only the emergence of digital communications technology and the strongly criticized medical care of cosmonauts/astronauts led to another increase in research work in the early 1990s. With the development of new mobile communications technologies like infrared, Bluetooth, LTE, and 5G, telemedicine has become a growing market and will presumably remain in the future [
27]. Image digitization and data compression procedures permitted video data transmission via low-bandwidth lines. With the World Wide Web introduced into the Internet by Tim Berners-Lees in 1993, data files stored on different computers could be interconnected [
28]. This enabled second-generation telemedicine to provide medical knowledge in otherwise medically inaccessible regions, i.e., aviation and sea travel and areas like the Arctic or the Antarctic [
29] or Space [
30].
All examinations performed in the laboratory must prove whether the results are valid for daily life circumstances [
31], a problem already emphasized by Nathan Zuntz [
32] at the beginning of the twentieth century. His primary interest was to explore the physiology of animals and humans in stressful situations (physical labor, physical exercise, stays in high-altitude places) in laboratory and field studies [
33,
34] or during high-altitude balloon flights [
35,
36]. He developed mobile measuring systems and even included meteorological conditions in his interpretation. His motto was: "The knowledge of the relations between climate and humans […] provides us with the basis for evaluating human performance capability […] (and) also with the foundation of human activity under extreme climatic conditions" [
37]. After his death, this approach faded into obscurity. In physiological studies conducted, there were instead no significant relationships between heart rates measured in the laboratory and the field [
38], whereas other studies yielded different [
39] or only minor associations [
40]. In a multimodally-conceived comparison between laboratory and field, no significant predictability of the reactions could be found, leading to the far-reaching conclusion of relative independence of field data [
41]. So, it can be assumed that data collected in the laboratory are probably valid for some, but not all, daily life situations, i.e., they can hardly be generalized.
For the reasons mentioned above, it is stated that the advantages of field research, on the one hand, and the questionable external or ecological validity and reliability of test and laboratory findings, on the other hand, have long since been discussed in the literature. However, empirical field studies can only sometimes be found [
42]. This is primarily due to the lack of methodical experience or the need for more suitable equipment. The transferability of examination results from the laboratory to everyday life is considered critical.
For decades, examining humans freely moving during their activities under natural conditions was impossible. Therefore, humans were primarily examined at rest before or after their activities or possibly in their actions, but this needed interruptions. Consequently, active human physiology primarily developed into rest physiology [
43] or the physiology of recovery [
44]. During the transition from rest to activity, the organism's fundamental adaptation processes during the entire training and during the transition from activity to rest could not be recorded under natural conditions [
45]. Moreover, the data’s significance decreases as time passes between stress and measurement. Therefore, a more precise and, thus more significant measurement of physiological framework data must be performed on-site. With all conventional methods, the subjects must be connected to the point of registration through hoses and wires, resulting in a significant number of activities remaining elusive for exact measurement [
46]. Also, measurements where the examiner can't be together with the proband or where the examiner's presence may be perceived as disturbing will have an impact on the data (e.g., the "white coat effect" [
47]).
Moreover, the mental situation impacts the data [
48]. Physical and psychological stress are intertwined; thus, it is not astonishing that permanent stress also results in clinical abnormalities [
49]. This is also true the other way around. These relationships are scientifically edited within the studies' scope on psychophysical connections, show a distinct correlation, and attract attention [
50]. However, laboratory studies are performed in an idealized way, i.e., excluding disturbing influences that exist in the real world [
46]. These studies simulate stress situations, and the influencing environmental factors are systematically standardized or eliminated. Yet, this causes problems when these results are transferred to reality; some examples are listed below:
Examinations of the working and performance capability are performed using conventional, i.e., clinical standards [
51]. The equipment used consists of medical devices and is thus validated but mostly inaccurate for field equipment [
52].
Functional diagnoses are made based on short-time examinations, which have little to do with the proper working environment regarding the temporal aspect [
41].
Physiological stress indices are generated statically. They constitute the mathematic-functional correlation between a few characteristic physiological parameters [
53], which cannot be generally transferred to the natural, dynamic situation [
54].
Studies are mostly conducted with a few persons with limited statistical power. In addition, "idealized persons" are recruited, i.e., mostly young men aged between 20 and 30 years, sporty, with normal weight, etc. However, the results are then extrapolated and transferred to all other persons. But the transfer can neither be applied to all age groups (age physiology) nor both genders (gender physiology).
In the real human environment, numerous additional influences significantly impact performance capability and resilience [
55]. In this context, the combination of temperature, altitude (oxygen pressure), wind, radiation, precipitation, pressure changes, noise disturbances, etc., must be mentioned [
56]. The complexity of these factors is not taken into account in the laboratory.
In the future, more reliable indices will have to include more parameters on the one hand and take into account intra-individual dynamic factors, e.g., sleep deficit, inadequate food intake, beginning or healing infectious diseases, or influences due to the unique environment (family, friends, etc.) [
57]. “Dynamic” in this context primarily means weighting the individual parameters, which may sometimes impact the person in the respective situation, sometimes more or less intensively [
58].
3. Physiological monitoring in the military area
For decades, the American military sector (e.g., U.S. Army Research Institute of Environmental Medicine - USARIEM) has been working on a technology to support soldiers medically in the theater of operations or during training. The Future Force Warrior, formerly called Objective Force Warrior, was part of the Future Combat System project of the United States Army [
59]. It enabled infantry members to participate in the Global Information Grid. It was designed to increase soldiers' survivability, robustness, and networkability on the future battlefield, but it was stopped for political reasons. This program also included the so-called Warfighter Physiological Status Monitor (WPSM) subsystem [
60]. The WPSM had sensors integrated into a suit to monitor each individual soldier's physiological and medical condition (pulse, body temperature, blood pressure, respiration, stress, and posture). If necessary, the WPSM could transfer the corresponding data to the military leaders or the medical personnel when the respective soldier was tired, wounded, or even fatally hit and should calculate a soldier's survival probability during combat [
61]. But this seems to be more an evaluation and an estimation of military combat efficiency, not a caring approach. Work continues on parts of the former program, now called Brigade Combat Team Modernization. The project is subdivided into subareas, including the Early Infantry Brigade Combat Team Capability Package. The field units will be equipped with a Network Integration Kit to permit network-centric warfare. Later, additional elements of the Follow-On Incremental Capabilities are scheduled to supplement the Global Information Grid network; this program was planned to be operational by 2020 [
62]. Due to their orientation towards physical performance optimization, cognitive performance, decision-making, and judgment, deployment health protection, heat and cold stress, high altitude, and pathophysiology, the two latter aspects, in particular, have determined the focal points. During their missions, the Americans particularly focus on heat stress and the significant failure rates that go with it. Due to these data on heat sicknesses or heat death, a parameter measurement has been introduced into the U.S. military, where intensive work has been performed (Thermal and Mountain Medicine, USARIEM).
In Europe, this approach has yet to attract much attention. Within the scope of a European Defence Agency project, it was attempted from 2010 to develop a new kind of biomonitoring and use it for military purposes, all under the slogan "Soldier Modernization Harmonization – Biosensor Information Demonstrator" [
63]. All in all, it must be noted that this concept did not work, particularly concerning data transfer. Within the Bundeswehr, the "Future Infantryman/Infantrywoman" (German abbreviation: IdZ) project [
64] is the German modernization program for the infantry, which is affected in NATO under the slogan "Future Soldier" and serves the purpose of improving the "personal combat equipment of infantry in the Bundeswehr". The manufacturer's overall system responsibility lies with Rheinmetall Defence Electronics residing in Bremen. The current system status (2021) is IdZ-4, which was delivered to the Bundeswehr under the designation "Gladius" (implementation phase 2) in 2013. Although many components for the infantryman/infantrywoman have been incorporated into this system or are available, there is no mature physiological monitoring. However, it is obligatory for the employer and the executive personnel responsible to fully comply with their legally imposed overall care responsibility [
65].
In contrast, telemedicine in the Bundeswehr already began before the year 2000 and is still employed successfully [
66]. It is primarily used for transferring X-ray data and on sea-based units and medical facilities during missions abroad. The main purpose of telemedicine is to evaluate symptoms and abnormalities by a medical specialist located in the home country, who can then help initiate the ensuing therapy or make recommendations. As early as 1997, such a system was established in the Bundeswehr and has been extended until now [
67].
4. Occupational fields of high responsibility in a stressful environment
In aviation, various environmental and aircraft type-related factors impact the human organism, which is not tailored to these conditions from an evolutionary perspective. The said factors must be coped with either behavioral measures or technical solutions. Pilots and flying personnel are significantly affected by stress [
68], especially when the military flight service is concerned [
69]. Considering the job of a pilot acting in extreme flights as the operator of high-performance and agile military aircraft is characterized by high physical stress and mental and neuropsychological strain [
70] within the human-machine system. This can have acute [
71] and chronic [
72] effects, thus also resulting in creeping exhaustion. And the stressors cannot be denied, not only in the real situation but even during training [
73]. Due to the high responsibility in this occupational field, a decline in or loss of operational capability constitutes an increased risk for the persons themselves and others (e.g., passenger transport). In addition to person-specific factors, the respective environmental conditions, which still need to be considered in most of the monitoring performed so far, are essential when evaluating stress situations where the different factors often coincide. There is a high physical [
74], and increasingly psychological, psychophysiological [
75], and cognitive [
76] stress not only in jet aviation but also in modern fixed-wing aircraft used for transport and in helicopters. This trend is additionally enhanced by an ever-increasing use of equipment [
77] (e.g., night vision goggles. Unmanned air vehicle pilots, who primarily have to cope with mental stress, must not be ignored entirely [
78,
79]. Performing regular medical assessments and maintaining the fitness status through appropriate programs [
80] makes it possible to preserve and ensure flight operations, but more is needed from today's point of view.
Therefore, physiological monitoring would be desirable for various reasons. Literature research is only very fruitful from Russian publications [
81]. In the library of the former Institute of Aviation Medicine (Königsbrück, German abbreviation: ILM), however, reports and treatises from the former East German National People's Army (Nationale Volksarmee, German abbreviation: NVA) could be found [
82]. The paper stated: "The progressive development of aviation technology imposes very high requirements on flying personnel's psychological and physical performance capability” [
83]. Thus, the responsibility of aviation medicine increases as well. In order to meet this responsibility, they must know the stress affecting flying personnel during flight and the response reactions triggered by the human organism. Undoubtedly, these factors can be determined most effectively utilizing corresponding examinations performed during flight combat training”. Besides this, data are scarce, focusing on telemetric ECG recordings during flights [
84,
85,
86]. The requirements imposed on the biotelemetric complex, i.e., tele-measuring of biophysical or physiological parameters, during which signal transmission is partly affected using radio or carrier frequency procedures [
87], must include the following characteristics:
No impairment of flight safety and the activities of flying personnel
Small dimensions and low weight
No changes concerning aircraft engineering (except for attachment of the transmitter and the antenna as well as the power supply from the aircraft electrical system for the transmitter)
Low operating and servicing effort
No disturbing influences on airborne equipment and no corresponding disturbances of the biotelemetry device
High stability with regard to flight and environmental factors
Relatively high transmitter power to bridge long distances, with high constancy of the transmission frequency
These aspects are still relevant today and serve as a basis for developing such systems or have already been implemented in the commercial wearables mentioned above. In the concluding remark, the biotelemetry device used is described as valid and operational. The expected assumptions and requirements have been fulfilled so that it has been possible to collect valuable aeromedical data for the purpose of evaluation and can be used as a monitoring system.
5. Current technologies
5.1. Sensors for field use
In everyday clinical life, patients' instrumentation with sensors is a routine procedure [
88,
89]. The sensors used are well-established and function properly, and the measuring points are clearly defined and validated. When using sensors outside a clinic, it is vital that they have a high degree of safety, thus permitting valuable measurements. Sensors used in the field must be non-invasive mandatorily because the "carrier" does not accept any sensor insertion in most cases (compliance). Ideally, the sensors must not strain or disturb the "carrier"; it is best when they either do not feel the sensor at all or quickly forget it after the application [
90]. Any disturbance could negatively affect the person concerned, resulting in additional physical and/or psychological stress (pain, mobility limitations, being permanently reminded of the sensor, etc.). If the sensor is an additional stressor, it adversely affects the measurement results and may negatively influence the interpretation [
91].
Another consequence is that the actual measuring point may no longer be identical to the validated measuring point. It is possible to measure something almost anywhere on the human body, but the result and the interpretation are significantly affected by the measuring point. When it comes to evaluating an ECG, the places where it is derived are clearly defined and cannot be deviated from, particularly in diagnostics. However, they must possibly be changed in the field, and a diagnostic interpretation is questionable or excluded. As far as respiration is concerned, there are limitations when it is intended to measure respiratory gases. Although it is indirectly possible to measure these gases at points on the skin (e.g., peripheral oxygen saturation), it must always be understood that the results of these measurements may differ from the actual values. As described in the introduction, wearables are thus usable to a minimal extent only. In most cases, they can merely show a trend, whereas the actual measurements should subsequently be performed using other, better sensors.
However, this senor version is used sparingly; ingestible sensors have also been developed [
92,
93]. In the course of the corresponding procedure, a sensor as small as possible is ingested and will be excreted again, with the average intestinal transit time amounting to 3 days. Reusing such sensors is not recommended for hygienic reasons, making continuous measuring very expensive. So far, this method has only been possible to record very few parameters. These parameters are basically limited to temperature measurement [
94]; nevertheless, it has been tried to detect heart and lung parameters [
95]. From a physiological point of view, such data must always be treated with caution. Thus, the dynamic measuring of parameters in a moving individual plays a particular part in the evaluation. Additional methods would include implantable sensors, which are primarily used in animals [
96]. Such sensors can technically be applied in humans, but there are significant ethical concerns regarding their application in healthy humans; however, these sensors already have clinical use [
97].
5.2. Smart Textiles
This term describes various characteristics of textiles [98–10]. On the one hand, it comprises clothing pieces worn in sports and is intended to influence an athlete's temperature regulation positively. Thus, a sportswear supplier has developed an innovative, prize-winning new training jacket for soccer players. In this case, dynamic temperature regulation is affected through the athlete's movement, i.e., inserts in the textile open and thus cool in case of activity. In contrast, they close again during rest periods, keeping the athlete warm. Such textiles are called performance textiles, and there is a growing market for innovations like that. However, because of this paper’s subject, the integration of sensors and cables into clothing is the most crucial aspect of this textile type [
102]. The Sensatex
® company offers a smart shirt system. The prototype was manufactured after long-term development and research work at the Georgia Institute of Technology and is called a "wearable motherboard". Following a revision of the design, it is now commercially marketed as a smart shirt. The device concerned comes from the research area of wearable computing.
While the smart shirt is worn, the wearer's vital parameters, e.g., body temperature, pulse rate, respiration, or transpiration degree, are perceived by sensors [
100]. The collected data can be stored in a small box located on the shirt's underside and transmitted later via Bluetooth, WLAN, or a cellular phone modem. The sensors are integrated into a mesh of woven-in electrooptical fibers, comparable with a plug-and-play bus. Due to this fact, any number of sensors can be added with little effort, so there are various application areas for the smart shirt [
101]. It would be conceivable, for example, to use “intelligent” shirts for special weapons and tactics (SWAT) teams or elite troops. Thus, it could be checked at any time whether the vital functions of all persons involved are in the normal range, mainly when a person concerned is no longer able to make an emergency call [
102]. A similar situation exists for fire departments in case of large fires. A smart shirt worn under the overall can permanently measure the temperature or respiratory activity. This means that, in any situation where direct eye contact with the emergency forces is not possible, the use of intelligent clothing is reasonable. This may also fit Astronauts, chronically sick or older persons, or top athletes [
103]. This approach is downright positive, although it is still challenging to implement at present [
104,
105]. For permanent monitoring of data and to keep the noise levels of data at a minimum, it is essential that all sensors have permanent and good contact with the skin. Therefore, the textile should be highly elastic to fit perfectly with the body.
5.3. Electronic Transfer Routes
Mobile systems for professional use need advanced properties for data transfer (distance, obstacles, data volume). This and data safety (personal rights, military service, etc.) are still problematic, even with radio or LAN. The German Aerospace Center (German abbreviation: DLR) has assumed a crucial role in this context [
106] (telemedicine in the Bundeswehr Medical Service for the purpose of operational support [
107]). This technology will be extended further in existing and future projects (tele-neurosurgery, intraoperative tele-tutoring) [
92]. However, this only applies to stationary data transfer, which must be ensured through a mature infrastructure. The primary challenge is the data transfer of several mobiles and located persons in areas with an insufficient structure [
108].
6. Current systems
6.1. Mobile Medical Terminals - Wearables
Commercially available measuring instruments are often limited, but only one parameter can display individual measurements [
109]. This is mostly due to the fact that an increase in parameters would considerably enhance the size of the system, which would thus not be attractive for the wearer any longer (mobility) [
110]. In addition, an increase in the number of sensors makes instrumenting rather comprehensive, negatively affecting user compliance, and is also a disadvantage in extreme environments [
111].
6.1.1. POLAR®
Beginning with the probably best-known solution, the POLAR
® watch [
112], a product offering monitoring via heart rate measurement, is available. Many customers have found this type of monitoring in popular sports i.e., in amateur and semiprofessional areas. In long-distance track races, which are part of popular sports, the heart rate is recorded through a watch, albeit not 1:1, but in an averaged way to compensate for artifacts. This solution also offers GPS/GALILEO for the purpose of position determination. In connection with a smartphone, this can also be used for training on running tracks. In addition, the associated software promises lifestyle interpretation and a comprehensive physiological evaluation. From a scientific point of view, it hardly seems to be possible to make an evaluation and a valid statement based on one parameter. Thus, this monitoring type is obviously not suited for performing precise tracking with high requirements on the data. A heart variance analysis cannot be achieved by averaging the said data. Beat-to-beat data output is almost impossible without disturbances. The recording of this physiological parameter would be desirable, however, because it has been found that there is a measurable synchronization of the heart and breathing rhythms [
113]. But the balance between these two rhythms disappears when an increased release of stress hormones accompanies reactions like stress, anger, or anxiety. In behavior therapy-oriented psychotherapy, the heart rate variability feedback has been used for quite some time in the form of coaching or a complementary medicine method. Studies in the USA show that this can positively influence depression, cardiac diseases, asthma, anxiety disorders, and sleeplessness [
114]. These parameters would thus be an essential factor when employing military personnel.
6.1.2. Vitaport
The Vitaport-4 system reaches a somewhat more professional level [
115]. According to the manufacturer, this portable recorder offers excellent recording quality and optimum convenience for the person to be measured during the EEG or PSG recordings. Due to the parameters, however, the device manufactured and marketed by the Dutch Temec Technologies B.V. company is only suited for some areas requiring soldiers or flying personnel. The software offered makes some evaluations, but the display on a screen is impossible. Therefore, subsequent evaluation can be performed only. However, this is not suited for the area of application described above.
6.1.3. SenseWear
Another device on the market is the SenseWear
® [
116,
117], an existing armband version. The upper arm version is suited for the scientific level, whereas the watch has been produced for the commercial market. The data can be evaluated via Bluetooth or LAN, and the software calculates different results, which are difficult to interpret for an amateur. The following parameters can be recorded: active energy expenditure, energy expenditure at rest, metabolic units, the overall number of steps, duration of physical activity, and sleep duration and activity. The device belongs to the so-called actimeters, which can measure movement data non-invasive. Since the 1980s, actimeters have also been used for evaluating human sleep [
118]. Studies performed in young, healthy test persons comparing actimetry and polysomnography (PSG) concerning sleep data validation showed a conformance of 91–93 % [
119]. This device is relatively inexpensive and comparatively uncomplicated. It is only suited for the parameters and cannot cover other required physiological parameters [
120]. In addition, the (data) transfer through Bluetooth is not done for monitoring over long distances.
6.1.4. Equivital Hidalgo
The Equivital™ Physiological Monitor System [
121], a fieldable system offered by the English Hidalgo company, Cambridge, is on the market. According to the manufacturer, this system is a product that permits the measurement of individual physiological parameters. The company states that the system is used in the scientific area and sports and clinical science on its homepage [
122]. In Pubmed, there are four entries regarding this system and even one military application in Afghanistan [
123]. The software permits a 1:1 display of the data on a (hand-held) screen, even for several persons simultaneously (Military Black Ghost Training System). All sensors are in a breast strap (heart and respiration rate, skin, “core body temperature”, accelerometry with fall alert, skin conductance, and even O
2-saturation – all in one). As far as wearing comfort is concerned, this is a convenient solution, but the measuring point must be questioned critically [
124].
6.1.5. Zephyr
The Zephyr
TM Performance system pursues a similar approach [
125], which is marketed by an American supplier (Medical). The evaluation system resembles that of Equivital
TM. On the homepage, it is possible to have a look at the list of customers and users; they include the space agencies and the military. The USARIEM does not have any publications on this system. In Pubmed, there is also a low number of publications [
126].
6.1.6. Sensor Mobile SM 100
Regarding professional medical devices, the Sensor Mobile SM 100 device was developed by TMS – Telemedizinische Systeme GmbH (current name: Vitasystems GmbH) – and was certified and approved in 2002. It belongs to the tele-ECG devices that can record an ECG and transfer it to a switching and exchange center or directly to a physician. The patient autonomously records one or several ECGs, sends the corresponding data to a receiving center, and waits for feedback. The transmitting device can either be a mobile telephone or a fixed-line telephone that receives and sends the data by infrared or acoustic transmission. During transmission by infrared to the cellular phone, the evaluation center's number is automatically dialed by the mobile telephone [
127]. Such systems can transfer data but not field physiology because there is no appropriate infrastructure.
7. Recent developments: The Mobile Physiological Laboratory
The HealthLab system, which is a core component of the mobPhysioLab
® (KORA Industrial Electronics GmbH, Hambühren, Germany [
128]) and has been under development in Germany for several decades, is a mobile physiological system intended to examine stress situations affecting humans in various working environments. It permits both physiological data collection and the conduct of specific studies on persons in extreme stress situations under the conditions directly prevailing on site.
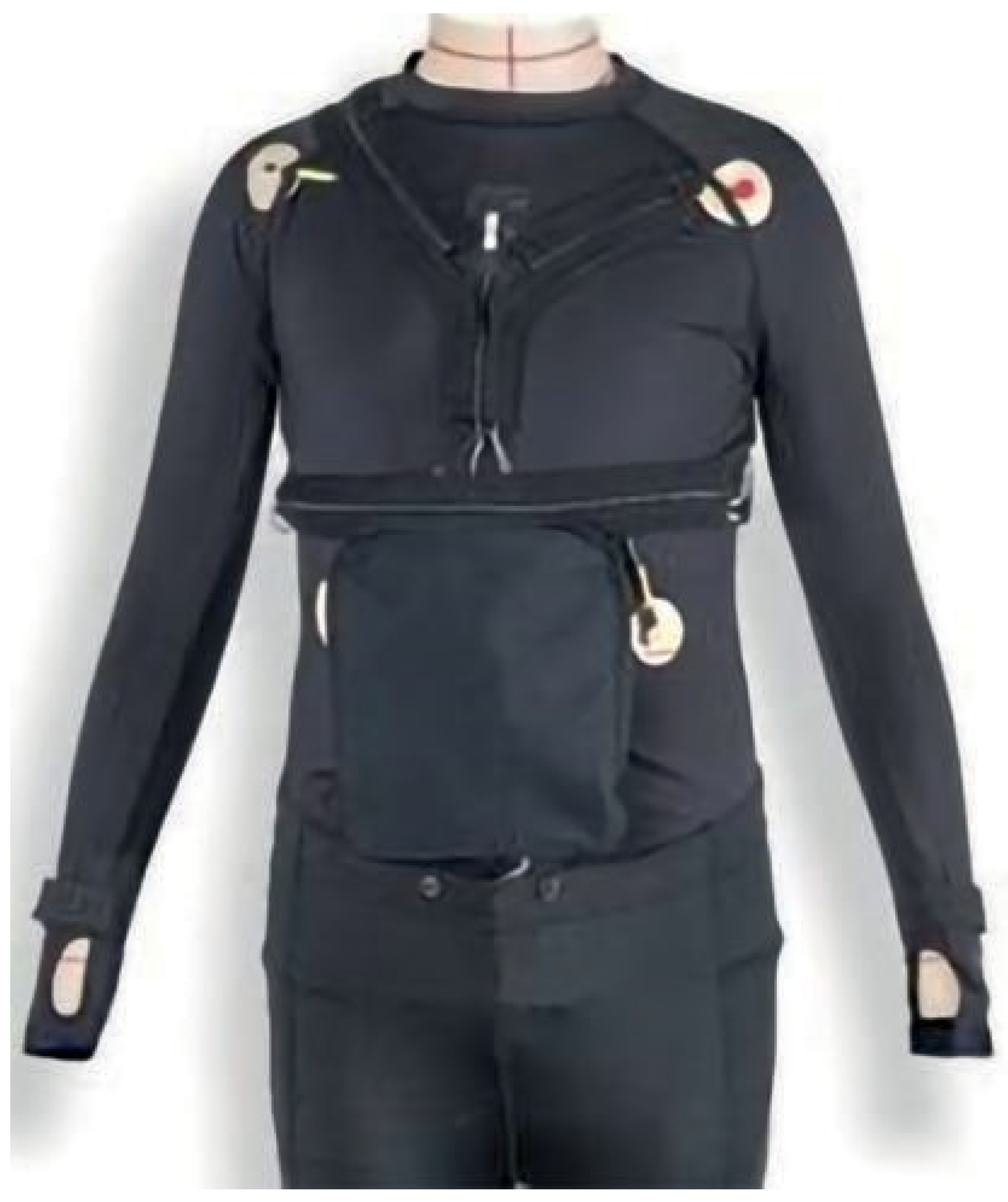
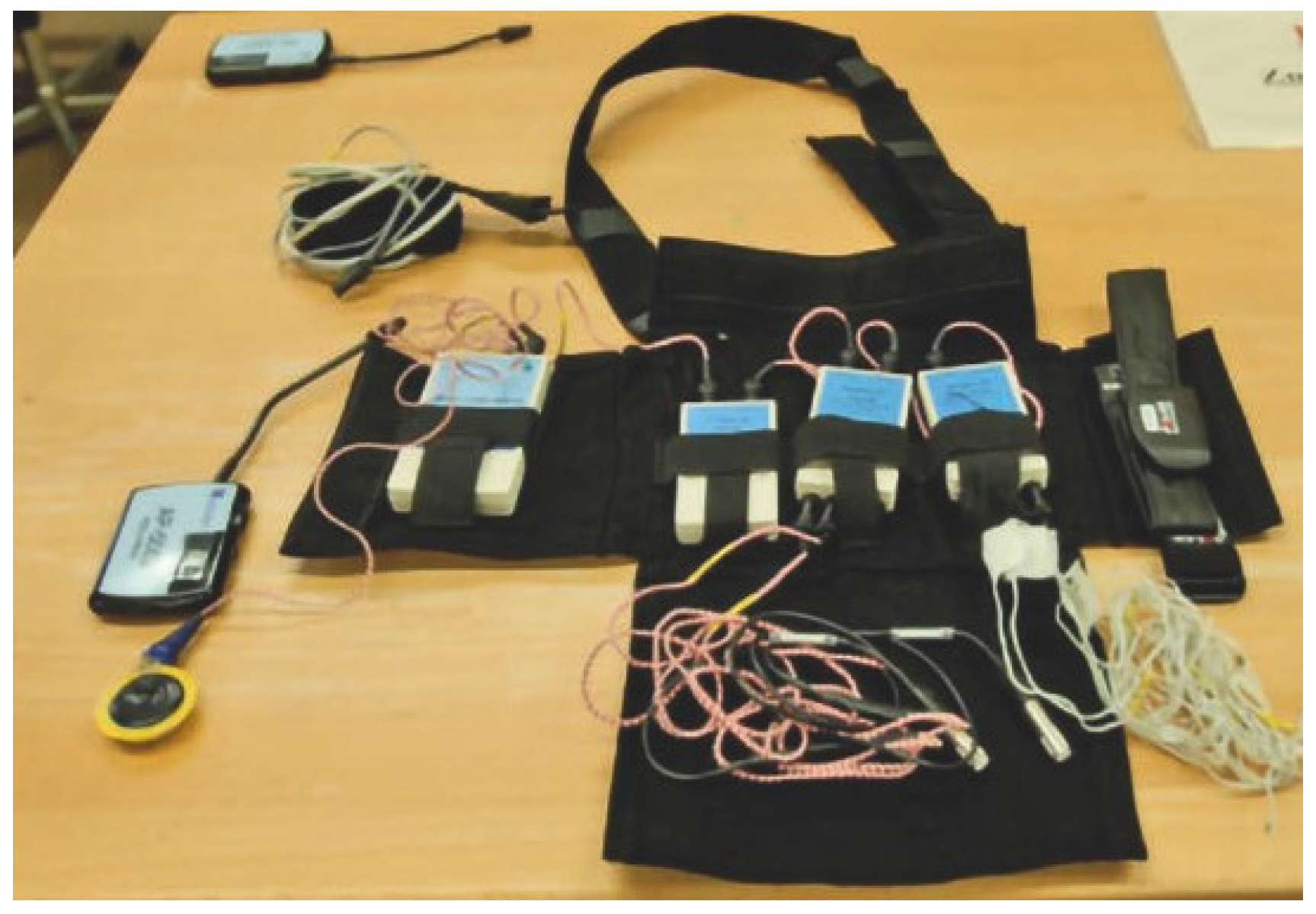
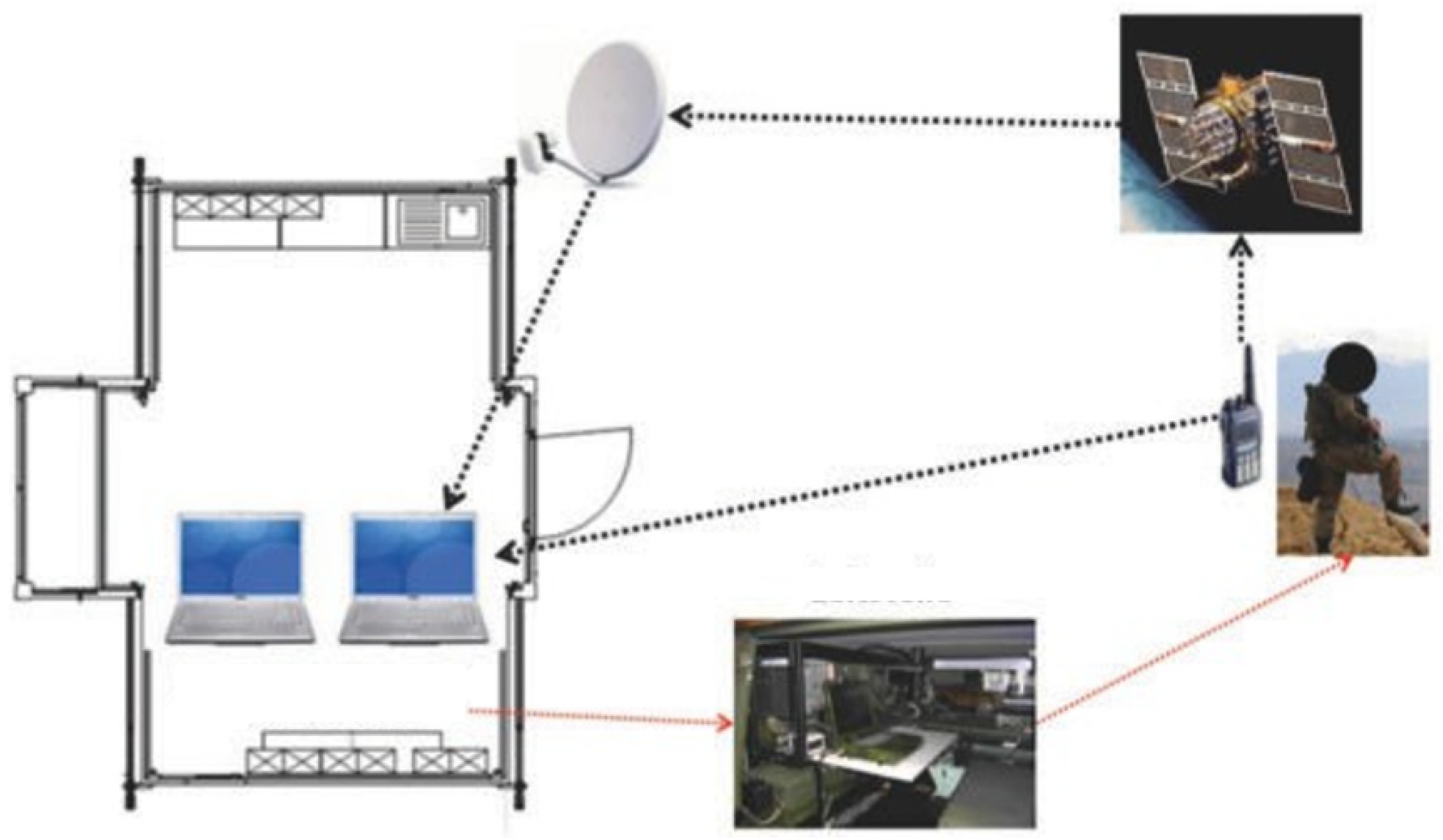
Contrary to conventional procedures, this system permits continuous, non-invasive, and synchronized physiological data measurements through innovative medical technology. It consists of flexible individual components that connect psychophysiological measuring methods with collecting environmental parameters through information technology. This system's current development status integrates and combines physiological measuring procedures in a flexible, mobile, and relatively small device. This device is based on a multiprocessor system combining a network of satellites with a master. The satellite elements have a respective "intelligence" of their own (i.e., a separate BUS). The satellite elements communicate via a bus with the central processing unit. In principle, this first seems to be more complex than developing one single measuring unit with four channels and particularly one processor only, but it has several advantages:
The analog and digital measuring techniques are distributed among several small units and can, for example, be placed in a vest.
The connection of unique measuring methods (e.g., core body temperature, heart rate, fundamental vocal frequency, etc.) is possible due to the development of a corresponding satellite, which can be used directly on the system without any further settings.
The central processing unit automatically recognizes the respective satellites and immediately records the data with the satellite's signal-specific parameters.
With the help of the software and hardware provided, users can also develop satellites and programs of their own.
Moreover, the system can monitor the data online and thus already evaluate them.
The described modularity and the versatile applicability regarding adaptation options and the system's mobility have yet to be commercially available in this form. The freely programmable software applications give the user a great variety of modification options, depending on the respective special applications and requirements. Thus, only the individual wearer's appropriate parameters are recorded, making the system extremely flexible and lighter (
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4).
It has been possible to employ the system in terrestrially extreme environments successfully (i.e., in salt mines at a depth of 1,450 m [occupational medicine], in water applications [therapy], at high altitudes [military] and in the [civilian and military] flying service, even in Space [ESA and NASA, ThermoLab]; IBMP [MARS500, Russia]):
The Double Sensor (Tcore® [
129,
130,
131,
132]) – A Non-Invasive Device to Continuously Monitor Core Temperature in Humans on Earth and Space [
133]
Metabolic and Physiological Changes in the Human Organism during Overwintering in the Antarctic [
134]
Monitoring of Vital Parameters in a Real-World Environment Using a Flexible Modular Telephysiological System [
135]
Oxygen Supply for Parachutists at Operational Altitudes – Laboratory Studies and their Benefits in an Extreme and a Real-World Environment [
136]
Heat Exposure of Jet Pilots during Air Traffic [
137]
Mars500 Project – Circadian Rhythm and Body Core Temperature in Humans during Long-Term Isolation and Confinement [
138]
The Role of Exercise in Synchronizing the Circadian Timing System during 60 Days of Bed Rest [
139]
Core Body Temperature Changes during Long-Duration Space Flights [
140]
Currently, this system is advanced by miniaturization, insertion of sensors into a smart textile, and data transfer via radio; with the focus being on the following requirements:
Provision of emergency functions and algorithms [
141]
Development of built-in-test functions to ensure operation through monitoring of all necessary functions, including power supply
Algorithms regarding the trend statement of vital parameters during missions
Recording of system parameters
Safety functions for the mission duration (reliability)
Unique algorithms for processing large and complex data quantities with low demand for computing power, yielding a valid diagnostic value
Data safety (especially for military use) and person’s privacy
8. Discussion & Conclusions
In the future, it can be expected that this measuring system will have a far-reaching influence on the physiological parameters to be recorded in the field [
142,
143]. The benefit of this development is that the results obtained in the laboratory can be reproduced within the scope of a field trial [
144,
145]. Thus, the simulation can advance, resulting in a more realistic depiction [
146,
147]. The presented solution approach (mobPhysioLab(R) is a significant improvement in collecting field physiological data. However, the authors are aware that there is still a lot of research to be done to fully cover the many application scenarios that achieve the optimal result in each situation.
Author Contributions
AW and H-CG contributed to their own studies in conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, project administration, and funding acquisition. AW writing—original draft preparation, H-CG; writing—review and editing. TK contributed with his own research, review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for this article's authorship and/or publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This work is not a clinical study. Thus, ethical approval is not required. Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in each named and listed their own investigations.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author Statement
The author autonomously prepared this article. It neither reflects the Federal Ministry of Defense (FMoD) opinion, the Bundeswehr, the German Air Force (GAF), or the Centre of Aerospace Medicine.
References
- World Health Organization. The Challenge of Obesity – Quick Statistics. Available online: www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/ noncommunicable-diseases/obesity/data-and-statistics (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- The State of Obesity. Available online: http://stateofobesity.org (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Rohde U, Sievert A, Rüther T, Witzki A, Leyk D. Concept for a Predeployment Assessment of Basic Military Fitness in the German Armed Forces. J Strength Cond Res 20150; 29: S211-5. [CrossRef]
- Kim J, Campbell AS, de #xC1;vila BE, Wang J. Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat Biotechnol 2019; 37: 389-406. [CrossRef]
- Bork U, Weitz J, Penter V. Apps und Mobile Health: Viele Potenziale noch nicht ausgeschöpft [Apps and Mobile Health: Many Potentials Not Yet Exploited]. Dtsch Arztebl 2018; 115: A 62 / B-57 / c-57.
- Majumder S, Mondal T, Deen MJ. Wearable Sensors for Remote Health Monitoring. Sensors (Basel) 2017; 17: 130. [CrossRef]
- E-HEALTH-COM. Available online: www.e-health.com.eu/ (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- 7 Stetter BJ, Buckeridge E, Nigg SR, Sell S, Stein T. Towards a wearable monitoring tool for in-field ice hockey skating performance analysis. Eur J Sport Sci 2019; 19: 893-901.
- Ajana B. Digital health and the biopolitics of the Quantified Self. Digit Health. 2017; 3: 2055207616689509. [CrossRef]
- Allouch SB, van Velsen L. Fit by Bits: An Explorative Study of Sports Physiotherapists' Perception of Quantified Self Technologies. Stud Health Technol Inform 2018; 247: 296-300.
- Heyen NB. From self-tracking to self-expertise: The production of self-related knowledge by doing personal science. Public Underst Sci 2020; 29: 124-138. [CrossRef]
- Baron KG, Abbott S, Jao N, Manalo N, Mullen R. Orthosomnia: Are Some Patients Taking the Quantified Self Too Far? J Clin Sleep Med 2017; 13: 351-354.
- Fehrenbacher K, Apel C, Bertsch D, van der Giet MS, van der Giet S, Grass M, Gschwandtl C, Heussen N, Hundt N, Kühn C, Morrison A, Müller-Ost M, Müller-Tarpet M, Porath S, Risse J, Schmitz S, Schöffl V, Timmermann L, Wernitz K, Küpper T. Temporary threshold shift after noise exposure in hypobaric hypoxia at high altitude - Results of the ADEMED Expedition 2011. Int Arch Occup Environm Health 2021; 84, 1191-1199. [CrossRef]
- Kupper T. [Workload and professional requirements for alpine rescue], Professoral Thesis, Dept. of Aerospace Medicine, RWTH Aachen Technical University, Aachen, 2006.
- Kupper, T. High altitude, hypoxia, and human performance (editorial). Med Sport 2010; 14: 1.
- Kupper T. Occupational Health in Mountain rescue, in: Brugger, H., Zafren, K., Festi, L. (Eds.), Mountain Emergency Medicine. Edra, Milano 2021: pp. 599-608.
- Kupper T, Gieseler U, Schöffl V. Occupational Aspects of Alpine Helicopter Rescue Operations. Recommendation of the UIAA Medical Commission Vol.23. Union Internationale des Associations d'Alpinisme (Medical Commission), Bern / Switzerland, 2015.
- Kupper T, Hillebrandt D, Steffgen J, Schoffl V. Safety in alpine helicopter rescue operations--minimal requirements of alpine skills for rescue personnel. Ann Occup Hyg 2013; 57: 1180-1188. [CrossRef]
- Kubalova J, Hefti U, Basnyat B, Gieseler U, Pullan R, Schoffl V. Work in hypoxic conditions - consensus statement of the Medical Commission of the Union Internationale des Associations d'Alpinisme (UIAA MedCom). Ann Occup Hyg 2011 55, 369-386. [CrossRef]
- Küpper T, Steffgen J, Jansing P. Cold exposure during helicopter rescue operations in the Western Alps. Ann Occup Hyg 2003; 47: 7-16. [CrossRef]
- Küpper T, Milledge JS, Hillebrandt D, Kubalová J, Hefti U, Basnyat B, Gieseler U, Pullan R, Schöffl V. Work in hypoxic conditions--consensus statement of the Medical Commission of the Union Internationale des Associations d'Alpinisme (UIAA MedCom). Ann Occup Hyg 2011; 55: 369-86. [CrossRef]
- Kupper T, Steffgen J, Jansing P. Cold exposure during helicopter rescue operations in the Western Alps. Ann Occup Hyg 2003; 47, 7-16. [CrossRef]
- Kupper T, Steffgen J, Jansing P. Noise exposure during alpine helicopter rescue operations. Ann Occup Hyg 2004; 48: 475-481. [CrossRef]
- Lehmacher EJ, Jansing P, Kupper T. Thermophysiological responses caused by ballistic bullet-proof vests. Ann Occup Hyg 2004; 51: 91-96. [CrossRef]
- Einthoven W. Le Télécardiogramme. Arch Int de Physiol 1906; 4: 132–164.
- Licklider JCR. Man-Computer Symbiosis. IRE Transactions of Human Factors in Electronics 1960; HFE-1: 4–11.
- Seising R. Frühe Visionen der Telemedizin: Technische Möglichkeiten und gesellschaftliche Wirklichkeit [Early Visions of Telemedicine: Technical Possibilities and Social Reality]. INFORMATIK 2003 – Innovative Informatikanwendungen. 33. Jahrestagung der Gesellschaft für Informatik 2003 [Innovative informatics applications. 33rd Annual Conference of the German Informatics Society 2003], Frankfurt a.M.
- Gabriel MR. Guide to the Literature of Electronic Publishing. London: Jai Pr; 1989.
- Alfred-Wegener-Institut. Neumayer Station III. Available online: www.awi.de/en/expedition/stations/neumayer-station-iii.html (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Ivanova T, Sapunova S, Dandolov I et al. 'SVET' Space Greenhouse Onboard Experiment Data Received from 'MIR' Station and Future Prospects. Adv Space Res 1994; 14: 343–346.
- Shephard RJ, Aoyagi Y. Measurement of human energy expenditure, with particular reference to field studies: a historical perspective. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012; 112: 2785-815.
- Gunga HC. Nathan Zuntz. His Life and Work in the Fields of High-Altitude Physiology and Aviation Medicine. American Physiological Society, Elsevier, ISBN 978-1-4614-7575-0, 2009.
- Zuntz N, Lehmann C, Hagemann O. Der Stoffwechsel des Pferdes bei Ruhe und Arbeit [The Metabolism of the Horse at Rest and Work]. Berlin: Parey; 1889.
- Zuntz N, Schumburg W. Studien zu einer Physiologie des Marsches [Studies on the Physiology of Marching]. Berlin: Hirschwald; 1901.
- Zuntz N, Loewy A, Müller F, Caspari W. Höhenklima und Bergwanderungen in ihrer Wirkung auf den Menschen [High Altitude Climate and Mountain Walks in their Effect on Humans]. Berlin: Bong; 1906.
- Zuntz N. Zur Physiologie und Hygiene der Luftfahrt [On the Physiology and Hygiene of Aviation]. Berlin: Springer; 1912.
- Zuntz N. Zur Methodik der Klimaforschung [On the Methodology of Climate Research]. Med Klin 1911; 22: 855–856.
- Johnston DW, Anastasiades P, Wood C. The Relationship between Cardiovascular Responses in the Laboratory and in the Field. Psychophysiology 1990; 27: 34–44. [CrossRef]
- Langewitz W, Rüddel H, Schächinger H et al. Standardized Stress Testing in the Cardiovascular Laboratory: Has It Any Bearing on Ambulatory Blood Pressure Values? J Hypertens Suppl 1989; 7: S41–S48.
- Pollak MH. Heart Rate Reactivity to Laboratory Tasks and Ambulatory Heart Rate in Daily Life. Psychosom Med 1991; 53: 25–35. [CrossRef]
- Fahrenberg J, Heger R, Foerster F et al. Differentielle Psychophysiologie von Befinden, Blutdruck und Herzfrequenz im Labor-Feld-Vergleich [Differential Psychophysiology of Well-Being, Blood Pressure and Heart Rate in laboratory-field comparison]. Zeitschrift für Differentielle und Diagnostische Psychologie [Journal of Differential and Diagnostic Psychology] 1991; 12: 1–25.
- Jain A, Schmidt T, Johnson D et al. Cardiovascular Reactivity in the Laboratory and in the Field: Comparing Different Methods to Assess Reactivity in Real Life. J Psychophysiol 1994; 8: S44.
- Bassan L. Über die Notwendigkeit einer Übereinstimmung zwischen der prinzipiellen und technischen Methodik bei der arbeitsphysiologischen Forschung [On the Necessity of Agreement between the Principle and Technical Methodology in Occupational Physiological Research]. Savremena Medizina 1955; 1: 77–85.
- Rosenblat VV. Verwendung der Radiotelemetrie in der Arbeits- und Sportphysiologie und einige Schlußfolgerungen aus der Arbeit der Sverdlovsker biotelemetrischen Gruppe [Use of Radiotelemetry in Work and Sport Physiology and Some Conclusions from the Work of the Sverdlovsk Biotelemetric Group]. In: Die Radiotelemetrie in der Physiologie und Medizin [Radiotelemetry in Physiology and Medicine]. Sverdlovsk 1963: 14–23.
- Bassan L. Forderungen des Physiologen und Arztes an die Biotelemetrie [Demands of Physiologist and Physician to Biotelemetry]. Z ges Hyg 1966; 12: 755.
- Fahrenberg J, Myrtek M. Ambulantes Monitoring [Ambulatory Monitoring]. In: Rösler F, Hrsg. Enzyklopädie der Psychologie: Bereich Psychophysiologie [Encyclopedia of Psychology: Section Psychophysiology] Band 1. Göttingen: Hogrefe; ISBN 3801705544, 1994.
- Thomas O, Shipman KE, Day K et al. Prevalence and Determinants of White Coat Effect in a Large UK Hypertension Clinic Population. J Hum Hypertens 2016; 30: 386–391. [CrossRef]
- Johnston DW, Anastasiades P. The Relationship between Heart Rate and Mood in Real Life. J Psychosom Res 1990; 34: 21–27. [CrossRef]
- Hocking Schuler JL, O‘Brien WH. Cardiovascular Recovery from Stress and Hypertension Risk Factors: A Meta-Analytic Review. Psychophysiology 1997; 34: 649−659.
- Deter HC, Blecher A. First Results of a Psychophysiological Comparative Study of Patients with Essential Hypertension and Normal Subjects in a Psychoanalytic Interview. 12th World Congress of Psychosomatic Medicine 1993, Bern.
- Sokolov M, Werdegar D, Perloff DB, Cowan RM, Bienenstuhl H. Preliminary Studies Relating Portably Recorded Blood Pressure to Daily Life Events in Patients with Essential Hypertension. In: Koster M, Musaph H, Visser P, eds. Psychosomatics in Essential Hypertension. Basel: Karger; 1970: 164−189.
- Rumo M, Amft O, Tröster G, et al. A Stepwise Validation of a Wearable System for Estimating Energy Expenditure in Field-Based Research. Physiol Meas 2011; 32: 1983−2001. [CrossRef]
- Moran D, Shapiro Y, Epstein Y et al. Validation and Adjustment of the Mathematical Prediction Model for Human Rectal Temperature Responses to Outdoor Environmental Conditions. Ergonomics 1995; 38: 1011−1018. [CrossRef]
- Fahrenberg J, Foerster F, Schneider HJ et al. Predictability of Individual Differences in Activation Processes in a Field Setting Based on Laboratory Measures. Psychophysiology 1986; 23: 323−333. [CrossRef]
- Templer KJ. Blutdruck, Verhalten und Persönlichkeit [Blood Pressure, Behavior and Personality]. Bern: Huber; 1993.
- Shapiro D, Jamner LD, Goldstein IB. Ambulatory Stress Psychophysiology: The Study of "Compensatory and Defensive Counterforces" and Conflict in a Natural Setting. Psychosom Med 1993; 55: 309−323. [CrossRef]
- Kirsch KA, Gunga HC. Extreme Umwelten: Leben und Mobilität in Kälte [Extreme Environments: Life and Mobility in Cold]. Flug u Reisemed 1999; 6: 36−38.
- Olsen CH, Ottesen JT, Smith RC, Olufsen MS. Parameter subset selection techniques for problems in mathematical biology. Biol Cybern. 2019; 113(1-2): 121-138. [CrossRef]
- Pernin, CG, Axelband E, Drezner JA, Dille BB, Gordon IV J, Held B, McMahon KS, Perry WL, Rizzi C, Shah AR, Wilson PA, Sollinger JM, Lessons from the Army's Future Combat Systems Program. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2012.
- U.S. Army. Researchers Test Warfighter Physiological Statuts Monitor. July 26, 2007. Available online: www.army.mil/ article/4157/researchers-test-warfighter-physiological-status-monitor/ (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Hoyt RW, Reifman J, Coster TS et al. Combat Medical Informatics: Present and Future. Proc AMIA Symp 2002: 335−339.
- Cyber Security & Information Systems Information Analysis Center. The DoD Cybersecurity Policy Chart. July 23, 2019. Available online: http://iac.dtic.mil/csiac/ia_policychart.html (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- European Defence Agency. Soldier Modernization Harmonization. 2012-11-22. Available online: www.eda.europa.eu/docs/ default-source/news/biosensors.pdf (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Ley S. Infanterist der Zukunft – Erweitertes System: Die Kampfausstattung auf dem Weg zur Realisierung [Infantryman of the Future - Advanced System: Combat Equipment on the Way to Realization]. Strategie und Technik [Strategy and Technology]. 2010: 18–23.
- Gesetz über die Rechtsstellung der Soldaten (Soldatengesetz - SG) [Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Act)], zuletzt geändert am [last amended on] 20.08.2021.
- Weber T, Wickenhöfer R, Lülsdorf P, et al. Telemedizin in der Bundeswehr [Telemedicine in the Bundeswehr]. Wehrmedizinische Monatsschrift [Monthly journal of military medicine] 2000; 3: 64–69.
- Seidel M. Telemedizin bei der Bundeswehr: Einsatz zwischen Bonn und Koblenz [Telemedicine in the German Armed Forces: Deployment between Bonn and Koblenz]. Dtsch Ärztebl 1997; 94: A-2383/B-2017/ C-1912.
- Thomas G. Stressed out? May 29, 2015. Available online: www. airlineratings.com/news.php?id=502 (accessed on 20th of May 2023).
- Schumm JA, Monson CM, O’Farrell TJ, et al. Couple Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorder and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Pilot Results from U.S. Military Veterans and Their Partners. J Trauma Stress 2015; 28: 247–252. [CrossRef]
- Leino TK, Leppäluoto J, Ruokonen A et al. Neuroendocrine Responses and Psychomotor Test Results in Subjects Participating in Military Pilot Selection. Aviat Space Environ Med 1999; 70: 571–576.
- Herbison CE, Henley D, Marsh J et al. Characterization and Novel Analyses of Acute Stress Response Patterns in a Population-Based Cohort of Young Adults: Influence of Gender, Smoking, and BMI. Stress 2016; 19: 139–150. [CrossRef]
- Tomei F, De Sio S, Tomao E, Anzelmo V, Baccolo TP, Ciarrocca M, Cherubini E, Valentini V, Capozzella A, Rosati MV. Occupational exposure to noise and hypertension in pilots. Int J Environ Health Res 2005; 15: 99-106. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Lin PC, Li SC. Measuring the Ability of Military Aircrews to Adapt to Perceived Stressors when Undergoing Centrifuge Training. J Appl Meas 2014; 15: 200–212.
- Truszczynski O, Wojtkowiak M, Lewkowicz R et al. Reaction Time in Pilots at Sustained Acceleration of +4.5 G(z). Aviat Space Environ Med 2013; 84: 845–849. [CrossRef]
- Simonov PV, Frolov MV, Ivanov EA. Psychophysiological Monitoring of Operator’s Emotional Stress in Aviation and Astronautics. Aviat Space Environ Med 1/980; 51: 46–49.
- Sekiguchi C, Handa Y, Gotoh M et al. Evaluation Method of Mental Workload under Flight Conditions. Aviat Space Environ Med 1978; 49: 920–925.
- Kirsch KA, Vogt-Kirsch C. Die Leistungsgrenzen des Menschen beim Tragen von Atemschutz und Schutzanzug [Human Performance Limits when Wearing Respiratory Protection and Protective Suits]. Arbeitsmedizin Sozialmedizin Präventivmedizin [Occupational Medicine Social Medicine Preventive Medicine] 1985; 20: 173–176.
- Internationale Nachrichtenagentur [International News Agency] Rossiya Segodnya. Pentagon kürzt Drohnenflüge wegen Piloten-Stress [Pentagon Cuts Drone Flights because of Pilot Stress]. 17.06.2015. Available online: http://de.sputniknews.com/militar/ 20150617/302795904.html (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Werner A, Kreutzmann U, Glowka S, Schinkel C. The New Quality of Aviation Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) Prevent Psychological Stress of Military Drone Operators, Clin Med Res Vol. 9, No. 1, 2020, pp. 25-30. [CrossRef]
- Deutsche Luftwaffe. Konzept für Human Performance Enhancement (HPE) im fliegerischen Dienst der Bundeswehr [German Air Force. Concept for Human Performance Enhancement (HPE) in the Flying Service of the Bundeswehr.]. 18. September 2012.
- Litovchenko VV, Malinin ID, Mnatsikan’ian AZ. [Operative Medical Control of the Status of the Pilot in Flight]. Voen Med Zh 1981: 71–73.
- Fritze H, Kollande G, Mocker R. Die Komplexanalyse – eine Methodik zur ergonomischen Untersuchung der fliegerischen Tätigkeit in der Militärluftfahrt [The Complex Analysis - a Methodology for Ergonomic Examination of Flying Activities in Military Aviation [Biotelemetry Device for Aeromedical Examinations]. Zeitschrift für Militärmedizin [Journal of Military Medicine] 1974; 5: 339–343.
- Otto K. Entwicklung einer 1/3-Telemetrieanlage für die drahtlose Übertragung der Herzfrequenz, der Atemfrequenz und der Bewegungsfrequenz von freibeweglichen Probanden. Kurzdokumentation [Development of a 1/3 Telemetry Device for Wireless Transmission of Heart Rate, Respiratory Rate, and Exercise Rate of Free-Moving Subjects. Brief Documentation], TMA 74.1/3, Vertrag Nr.: FE/68- 71/40 434, Berlin, 1971.
- Kessel R, Lang E, Denkl P. [Stress and Electrocardiogram. Telemetric Investigations during a Stunt Flight Program (Telemetric Circulatory Observations in Jet Pilots. In: Graul EH. Current Problems in Aerospace Medicine]. MMW - Münch Med Wochenschr 1976; 118: 1001–1006.
- Pircher, Hardmeier. Telemetrische Kreislaufbeobachtungen bei Jetpiloten [Telemetric Circulatory Observations in Jet Pilots]. In: Graul EH. Aktuelle Probleme der Luft- und Raumfahrtmedizin [Current Problems in Aerospace Medicine]. Gießen: Eli Lilly GmbH; 1967: 73.
- Rice GM, VanBrunt TB, Snider DH et al. Wearable Accelerometers in High Performance Jet Aircraft. Aerosp Med Hum Perform 2016; 87: 102–107. [CrossRef]
- Murray RH, Marko A, Kissen AT, et al. A New, Miniaturized, Multichannel, Personal Radiotelemetry System. J Appl Physiol 1968; 24: 588–592.
- Calton B, Abedini N, Fratkin M. Telemedicine in the Time of Coronavirus. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2020; 60: e12-e14. [CrossRef]
- Contreras CM, Metzger GA, Beane JD, Dedhia PH, Ejaz A, Pawlik TM. Telemedicine: Patient-Provider Clinical Engagement During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020; 24: 1692-1697. [CrossRef]
- Vevere A, Oks A, Katashev A, Terlecka G, Saiva L, Jansons M, Dyachenko N, Seglina P. Smart textile device for shooter's fingers movement monitoring. Technol Health Care 2022; 30: 217-229.
- van Doornen LJ, van Blokland RW. The Relationship between Cardiovascular and Catecholamine Reactions to Laboratory and Real-Life Stress. Psychophysiology 1992; 29: 173–181.
- Ardenne M. Der verschluckbare Intestinalsender – ein Beispiel für den Einsatz moderner Technik in der Medizin [The Swallowable Intestinal Transmitter - an Example of the Use of Modern Technology in Medicine]. Die Technik [The Technology] 1961; 12: 9.
- O’Brien C, Hoyt RW, Buller MJ, et al. Telemetry Pill Measurement of Core Temperature in Humans during Active Heating and Cooling. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998; 30: 468–472. [CrossRef]
- Hoskins S, Sobering T, Andresen D et al. Near-Field Wireless Magnetic Link for an Ingestible Cattle Health Monitoring Pill. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009; 2009: 5401–5404.
- Tolles WE. Short Range Telemetry of Ingested or Implanted Sensors. In: Slater LE. Bio-Telemetry, Pergamon Press; 1963: 330–340.
- Tortora G, Fontana R, Argiolas S, et al. A Dynamic Control Algorithm Based on Physiological Parameters and Wearable Interfaces for Adaptive Ventricular Assist Devices. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2015; 2015: 4954–4957.
- Scheit L, Werner A. „Wearable Sensors“ zur Unterstützung eines medizinischen Monitorings für militärische Zwecke ["Wearable Sensors" to Support Medical Monitoring for Military Purposes]. WMM 2021; 65: 225-235.
- Goncalvas, C.; da Silva, A.F.; Gomes, J.; Simoes, R. Wearable E-Textile Technologies: A Review on Sensors, Actuators and Control Elements. Inventions 2018, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayem, A.S.M.; Haider, J. An Overview on the Development of Natural Renewable Materials for Textile Applications. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Science Direct; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 201983.
- Muhammad Sayem AS, Hon Teay S, Shahariar H, Fink PL, Albarbar A. Review on Smart Electro-Clothing Systems (SeCSs). Sensors (Basel). 2020; 20: 587.
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Towards The Internet of Smart Clothing: A Review on IoT Wearables and Garments for Creating Intelligent Connected E-Textiles. Electronics 2018, 7, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consumer Products Inventory. Sensatex™ SmartShirt System. Available online: www.nanotechproject.org/cpi/products/ sensatextm-smartshirt-system/ (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Alwis LSM, Bremer K, Roth B. Fiber Optic Sensors Embedded in Textile-Reinforced Concrete for Smart Structural Health Monitoring: A Review. Sensors (Basel). 2021; 21: 4948. [CrossRef]
- Georgia Tech Wearable Motherboard™. Available online: www. gtwm.gatech.edu/ (accessed on 20th of May 2023).
- Khundaqji H, Hing W, Furness J, Climstein M. Smart Shirts for Monitoring Physiological Parameters: Scoping Review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020; 8(5): e18092. [CrossRef]
- Weber T, Lindlar M. Im Alltag der Telemedizin: Entwicklung aus der Luft- und Raumfahrtmedizin im weltweiten Einsatz [In everyday telemedicine: development from aerospace medicine in worldwide use]. DLR Nachrichten [DLR News] 2006, 113: 76–79.
- Otto C. Telemedizin im Sanitätsdienst der Bundeswehr: Das Ziel ist ein Telematikverbund [Telemedicine in the Bundeswehr Medical Service: The goal is a Telematics Network]. Dtsch Ärztebl 2003; 100: A 99–102 / B-90 / C-88.
- Padeken D, Weber TP, Wilke D, et al. Telemedizin im Sanitätsdienst der Bundeswehr. Conference: Präsentation vor dem Inspekteur der Bundeswehr [Telemedicine in the Medical Service of the German Armed Forces. Conference: Presentation to the Chief of Staff of the German Armed Forces] DLR, Köln, 20. Januar 1999.
- Spaite DW, Valenzuela TD, Meislin HW. Physician in-field observation of prehospital advanced life support personnel: a statewide evaluation. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1993; 8(4): 299-302. [CrossRef]
- Isakadze N, Martin SS. How useful is the smartwatch ECG? Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2020; 30: 442-448.
- Harst L, Lantzsch H, Scheibe M. Theories Predicting End-User Acceptance of Telemedicine Use: Systematic Review. J Med Internet Res 2019; 21: e13117. [CrossRef]
- Polar H10 – The Gold Standard of Heart Rate Measurement. Available online: https://www.polar.com/en (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Tiller WA, McCraty R, Atkinson M. Cardiac Coherence: A New, Noninvasive Measure of Autonomic Nervous System Order. Altern Ther Health Med 1996; 2: 52–65.
- Achmon J, Granek M, Golomb M, et al. Behavioral Treatment of Essential Hypertension: A Comparison between Cognitive Therapy and Biofeedback of Heart Rate. Psychosom Med 1989; 51: 152–164. [CrossRef]
- Natus – Ambulatory polysomnograph. Available online: https://healthmanagement.org/products/view/ambulatory-polysomnograph-with-eeg-vitaport-4-natus-medical-incorporated?channel=all (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- BodyMedia. SenseWear Manual. Pittsburgh: BodyMedia Inc.; 2007. Available online: https://www.manualslib.com/manual/895732/Bodymedia-Sensewear.html (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- SenseWear Fitness Tracker – Bodymedia. Available online: http://www.fitness-tracker24.com/sensewear/9-bodymedia (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Weeß H-G. Diagnostische Methoden [Diagnostic Methods]. In: Stuck BA, Maurer JT, Schredl M, Weeß H-G. Praxis der Schlafmedizin [Practice of Sleep Medicine]. Heidelberg: Springer 2009; 23–78.
- O’Driscoll DM, Turton AR, Copland JM, et al. Energy Expenditure in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Validation of a Multiple Physiological Sensor for Determination of Sleep and Wake. Sleep Breath 2013; 17: 139–146. [CrossRef]
- Conradt R, Brandenburg U, Ploch T et al. [Actigraphy: Methodological Limits for Evaluation of Sleep Stages and Sleep Structure of Healthy Probands]. Pneumologie [Pneumology] 1997; 51 Suppl 3: 721–724.
- Professional wearable technology that provides physiological data you can trust – Equivital. Available online: https://www.equivital.com/ (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Equivital™. Media Centre. Internet: www.equivital.co.uk/ media-center (accessed on 20th of May 2023).
- Welles AP, Buller MJ, Margolis L et al. Thermal-Work Strain during Marine Rifle Squad Operations in Afghanistan. Mil Med 2013; 178: 1141–1148. [CrossRef]
- Equivital™. EQ02 LifeMonitor. Available online: www.equivital. co.uk/assets/common/SEM_Data_Sheet_General_HI- DA3330-DSG-02.2_.2_.pdf (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- ZephyrTM Performance Systems. Available online: https://www.zephyranywhere.com/ (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Kim JH, Roberge R, Powell JB et al. Measurement Accuracy of Heart Rate and Respiratory Rate during Graded Exercise and Sustained Exercise in the Heat Using the Zephyr BioHarness. Int J Sports Med 2013; 34: 497–501.
- Vitasystems GmbH. Available online: www.vitagroup.ag/de_DE/ Ueber-uns/vitasystems (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- HealthLab / mobPhysioLab®. Available online: https://www.kie-hb.de/en/healthlab-mobphysiolab.html (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- TcoreTM Temperaturemonitoring System. Available online: https://www.draeger.com/de_de/Products/Tcore-Temperature-Monitoring-System (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Kimberger O, Saager L, Egan C, Sanchez IP, Dizili S, Koch J, et al. The accuracy of a disposable noninvasive core thermometer. Can J Anaesth 2013, 60, 1190–1196. [CrossRef]
- Gunga HC, Sandsund M, Reinertsen RE, Sattler F, Koch J. A non-invasive device to continuously determine heat strain in humans. Journal of Thermal Biology 2008; 33, 297–307. [CrossRef]
- Masè M, Werner A, Putzer G, Avancini G, Falla M, Brugger H, Micarelli A, Strapazzon G. Low Ambient Temperature Exposition Impairs the Accuracy of a Non-invasive Heat-Flux Thermometer. Front Physiol. 2022; 13: 830059. [CrossRef]
- Gunga HC, Werner A, Stahn A et al. The Double Sensor – A Non-Invasive Device to Continuously Monitor Core Temperature in Humans on Earth and in Space. J Resp Neurol Physiol 2009; 169 Suppl 1: S63–S68. [CrossRef]
- Tiedemann J. Physiologische Veränderungen des menschlichen Organismus während einer fünfzehnmonatigen Überwinterung in der Antarktis [Physiological Changes in Human Organism during a Fifteen-Month Hibernation in Antarctica]. Doctoral Thesis 2012. Refubium – Repositorium der Freien Universität Berlin [Refubium - Repository of the Free University Berlin].
- Steinach M. Physiologische Langzeitveränderungen bei Überwintern in der Antarktis unter besonderer Berücksichtigung von Aktivitätsparametern [Long-Term Physiological Changes during Hibernation in the Antarctic with Special Consideration of Activity Parameters]. Doctoral Thesis 2013. Institut für Physiologie, Zentrum für Weltraummedizin Berlin, Bibliothek der [Institute of Physiology, Center for Space Medicine Berlin and extreme Environments, Library of the] Charité.
- Michael S. Human Performance von Fallschirmspringern in großen Höhen mit den Sprungverfahren High Altitude High Opening (HaHo) und High Altitude Low Opening (HaLo) in der realen Umgebung im Vergleich zur Ausbildung in der Höhen-Klima-Simulationsanlage (HKS). [Human Performance of Skydivers at High Altitudes using the High Altitude High Opening (HaHo) and High Altitude Low Opening (HaLo) Jumping Procedures in the Real Environment compared to Training in the High-Altitude Climate Simulation Chamber (HAC)]. Doctoral Thesis 2020. Institut für Physiologie, Zentrum für Weltraummedizin und extreme Umwelten, Berlin, [Institute of Physiology, Center for Space Medicine and extreme Environments Berlin, Library of the] Bibliothek der Charité.
- Werner A, Lang V, Brix B et al. Heat Exposure of Jet Pilots during Air Traffic. 82nd Annual Scientific and Human Performance Meeting, AsMA, Anchorage, USA, 2011.
- Werner A. Mars500 Project – Circadian Rhythm and Body Core Temperature in Humans during Long-Term Isolation and Confinement. Flight Surgeon Conference USAF, Ramstein, 2013.
- Stahn A, Mendt S, Steinach M, Opatz O, Werner A, Kunz D, Belavy DL, Felsenberg D, Sattler F, Koch J, Gunga HC. The Role of Exercise in Synchronizing the Circadian Timing System during 60 Days of Bed-Rest Using Rectal Recordings and a New Non-Invasive Heatflux Technology. Proceedings of the 62nd International Astronautical Congress 2011.
- Stahn AC, Werner A, Opatz O, et al. Increased Core Body Temperature in Astronauts during Long-Duration Space Missions. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 16180. [CrossRef]
- Scheuermann C, Binderberger T, von Frankenberg N, Werner A. Digital twin: a machine learning approach to predict individual stress levels in extreme environments. , Sep 2020. Pages 657–664.
- Cesarelli G, Donisi L, Coccia A, Amitrano F, D'Addio G, Ricciardi C. The E-Textile for Biomedical Applications: A Systematic Review of Literature. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021; 11(12): 2263. [CrossRef]
- Dolez PI. Energy Harvesting Materials and Structures for Smart Textile Applications: Recent Progress and Path Forward. Sensors (Basel). 2021; 21: 6297. [CrossRef]
- Alwis LSM, Bremer K, Roth B. Fiber Optic Sensors Embedded in Textile-Reinforced Concrete for Smart Structural Health Monitoring: A Review. Sensors (Basel). 2021; 21: 4948. [CrossRef]
- Stylios GK. Novel Smart Textiles. Materials (Basel). 2020; 13: 950.
- Marsch LA. Digital health data-driven approaches to understand human behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021; 46: 191-196. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh A, Anderson M, Albala S, Casadei B, Franklin BD, Richards M, Taylor D, Tibble H, Mossialos E. Health information technology and digital innovation for national learning health and care systems. Lancet Digit Health. 2021; 3(6): e383-e396. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).