Introduction
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an autosomal recessive monogenic disorder with an estimated annual medical cost over
$1.1 billion in the US[
1,
2,
3,
4]. A point mutation at the sixth position in the β-globin gene substituting glutamic acid with valine results in sickled hemoglobin (HbS)[
4]. Patients homozygous for this mutation are at increased risk for developing multiple organ failure due to vasoocclusion, hemolysis, and sterile inflammation[
4]. Liver abnormalities in SCD are frequent and the disease etiology remains largely unknown[
5,
6,
7]. Elevated levels of liver enzymes (alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP)), hepatic iron-heme-hemoglobin accumulation, inflammation, abnormal coagulation are commonly seen in hospitalised SCD patients[
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. Currently, there are no effective medical therapies available for both the morbidities and the disease management is mostly limited to supportive therapy[
13,
14,
15].
L-glutamine was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for sickle cell disease (SCD) in 2017. L-Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid required for synthesis of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), glutathione and glutamate, and reduced oxidative stress[
16]. Previous studies have shown that l-glutamine administration increases NADH and reduced in RBC adhesion SCD patients[
17,
18,
19]. In a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial, l-glutamine ameliorated episodes of pain crisis in children and adults[
19]. However, L-glutamine treatment was also associated with few limitations such as low toleration (only tolerated in two-thirds of patients) as well as organ complications[
20,
21]. To understand the effect of L-glutamine in SCD related liver dysfunction we evaluated the long-term effect of L-glutamine administration in SCD liver. Here, we show that eight weeks of l-glutamine treatment in SCD mice significantly reduced accumulation of hemoglobin-heme-iron without ameliorating ischemic liver injury and fibrosis in SCD mouse liver. Remarkably, we find that this failure in resolution of hepatobiliary injury post l-glutamine treatment is associated with reduced expression of hepatic Kupffer cells.
Methods
Surgical preparation and quantitative liver intravital imaging (qLIM) : Details of the surgical method are described here[
22,
23]. Intravascular fluorescent dyes included 200 μg of Texas red (TXR) dextran which was used to visualize the blood flow through the liver sinusoids. Microscopy was performed using a Nikon MPE multi-photon excitation microscope at CBI U.Pitt. The percentage of regions with vaso-occlusion (as seen by TXR-Dextran staining) per field of view (FOVs) was quantified from at least 3 different mice /group.
Animals : Townes SCD mice (SS, homozygous for Hba
tm1(HBA)Tow, homozygous for Hbb
tm2(HBG1,HBB*)Tow) and non-sickle control mice (AS, homozygous for Hba
tm1(HBA)Tow, compound heterozygous for Hbb
tm2(HBG1,HBB*)Tow/Hbb
tm3(HBG1,HBB)Tow)[
24] were obtained from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME) and housed in a specific pathogen-free animal facility at the University of Pittsburgh. All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Pittsburgh. Five or more mice were assessed at all given time points.
L-glutamine treatment: 5-6 weeks old SCD mice received l-glutamine treatment via drinking water at a dosage of 10-12 mg/ml[
25].
Heme assay: Heme assay was performed as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Heme assay kit; ABCAM; ab272534). Briefly, liver tissue was homogenized as directed. The homogenates were centrifuged and heme levels were measured for each sample as per the manufacturer’s instructions .
Iron colorimetric assay: Hepatic total iron, Fe2+ and Fe3+ levels were measured using an Iron colorimetric assay, as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Iron Assay Kit, ABCAM, ab83366). Briefly, liver tissue was homogenized in PBS. The homogenates were centrifuged at 6,000g for 10 minutes to remove debris. Iron levels were measured, and concentrations were determined using the calibration curve and mean change in absorbance value for each sample.
Western Blot: Western Blot: Immunoblotting was performed as described elsewhere[
26]. The primary antibodies used in this study are : CLEF4C (R&D Systems, AF2784, 0.025μg/mL), CD45 (CST, 70257S, 19 µg/mL, HbA1 (abcam, AB92492, 0.815 mg/ml), HbA2 (ABclonal, A8427, 1.203µg/mL) Ferritin (abcam, AB75973, 0.07 µg/ml). Membranes were 4 washed five times for 5m each in TBST before being probed with HRP–conjugated secondary antibodies (1:5000 diluted in TBST; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) / IgG conjugates secondary antibodies (1:5000/ 1:30000 diluted in TBST; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 1.5h at room temperature. Membranes were washed three times for 10m each in TBST and visualized using the Enhanced Chemiluminescence System (GE Healthcare)/ Odyssey Clx li-cor system.
Immunohistochemistry .Tissue samples were frozen in OCT compound (Sakura, 4583) on dry ice and stored at - 80°C. Cryopreserved samples were cut into 5 µm sections, washed in PBS, and then fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde for 30 minutes. Following washing, slides were washed with PBS and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 20 minutes at room temperature. Samples were washed three times with PBS and then blocked with 2% goat serum in 0.1% Tween-20 in PBS (PBST) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Antibodies were diluted in 2% goat serum/PBST and incubated at 4°C overnight. Primary and secondary antibodies used are: Primary antibodies: F4/80 (CST, 70076S, 0.435 μg/ml), CLEF4C (R&D Systems, AF2784, 0.025μg/mL) and (abcam, AB75973, 0.07 µg/ml). Secondary antibodies used are anti-Mouse/Rabbit Cy3/Cy5. Images were taken on a Nikon A1 spectral confocal microscope.
Statistical Analysis: All comparisons between two groups were deemed statistically significant by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test if p<0.05. (*) denotes p<0.05.
Serum biochemistry: Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were measured in serum samples taken before sacrifice. Serum biochemistry was measured by automated testing in the Clinical Chemistry Division, University of Pittsburgh school of medicine.
mRNA isolation and real time polymerase chain reaction: mRNA was isolated and purified from livers of SCD mice at baseline and post l-glutamine treatment (n=4-5/group). mRNA was isolated using Trizol (Invitrogen). RT-PCR was performed as described elsewhere[
27]. 18S and GAPDH were used to normalize the m-RNA expression data. Sequences of primers are as follows:
CD45: F-GAACATGCTGCCAATGGTCT R-TGTCCCACATGACTCCTTTCC;
F4/80: F- GCCCAGGAGTGGAATGTCAA R- CAGACACTCATCAACATCTGCG;
IL1β: F- CCATGGCACATTCTGTTCAAA R- GCCCATCAGAGGCAAGGA;
CLEC4F: F- GGAAAGTCATTCCAGACCCA R- AAGACGCCATTTAACCCACA;
TGFβ: F- GTGTGGAGCAACATGTGGAACTCTA R- TTGGTTCAGCCACTGCCGTA;
α-SMA: F- GTTCAGTGGTGCCTCTGTCA R- ACTGGGACGACAGGAAAAG;
Col1A1: F- TAAGGGTACCGATGGAGAAC R- CTCCCTGAGCTCCAGCTTCT;
Col3A1: F- TCCCCTGGAATCTGTGAATC R- TGAGTCGAATTGGGGAGAAT;
HBA1: F- ACTCTTCTGGTCCCCACAGACTCAG R- GGGCAGAGCCGTGGCTCAGGTCGAA;
ACS14: F- CGTTTGGCTCATGTGCTGGAAC R- AGTCCAGGGATACGTTCACAC;
PTGS2: F- GGGAGTCTGGAACATTGTGAA R- GTGCACATTGTAAGTAGGTGGACT;
GAPDH: F-GACAGTCAGCCGCATCTTCT R- TTAAAAGCAGCCCTGGTGAC;
18S: FCGGCTACCACATCCAAGGAA R- GCTGGAATTACCGCGGCT.
Results and discussions
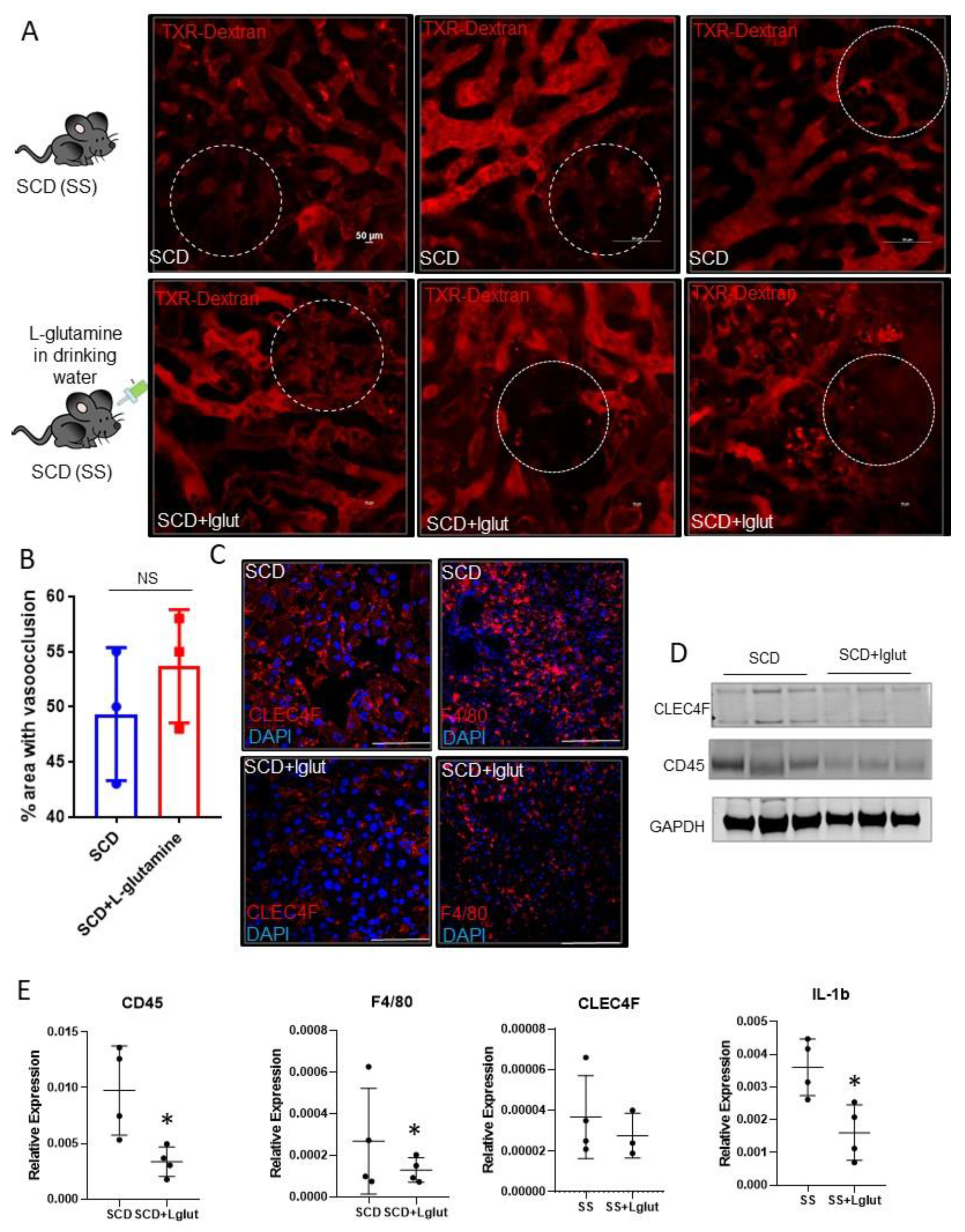
Sinusoidal vasoocclusion is a common phenotype associated with SCD[
4]. Previously, we have shown that SCD (SS) mice manifest sinusoidal ischemia and hepatobiliary injury under baseline conditions[
7]. Here, we administered l-glutamine for upto eight weeks in SCD mice to study its effect on the hepatic blood flow. Identical to our previous findings, quantitative liver intravital imaging (qLIM) revealed sinusoidal ischemia in several regions of the liver
in SCD mice
at baseline
(Figure 1A; upper panel; supplemental movies: 1, 2, 3). As shown in
Figure 1A, these ischemic areas were evident as black voids in qLIM images due to the absence of TXR-dextran (red), suggestive of blood flow stasis. Interestingly, the blood flow stasis (red) did not show significant amelioration within the sinusoids of l-glutamine treated SCD mice (n=3;
Figure 1A (lower panel), supplemental movies: 4, 5, 6). Further quantification confirmed that sinusoidal ischemia was comparable in the livers of l-glutamine treated SCD mice (
Figure 1B) and SCD mice at baseline. Vasoocclusion is associated with increased vascular cell adhesion and sterile inflammation[
7,
28]. Previously we have shown the activation of inflammatory cells including hepatic Kupffer cells in SCD liver at baseline[
7,
29] . We next examined the Kupffer cell population post l-glutamine treatment. SCD mice showed enhanced expression of hepatic Kupffer cell markers CLEC4F and F4/80 staining which were reduced in l-glutamine treated SCD liver (
Figure 1C). Western blot analysis showed reduced expression of CLEC4F and CD45 protein in l-glutamine treated SCD mice liver (
Figure 1D). Moreover, gene expression analysis of liver mRNA from the l-glutamine treated SCD mice compared with SCD mice at baseline showed significant reduction in the expression of inflammatory cell markers (including F4/80, Clec4F, CD45 and cytokines (IL1β) (
Figure 1E) post l-glutamine treatment suggestive of reduced activation of inflammatory cells in the SCD mice liver post l-glutamine treatment.
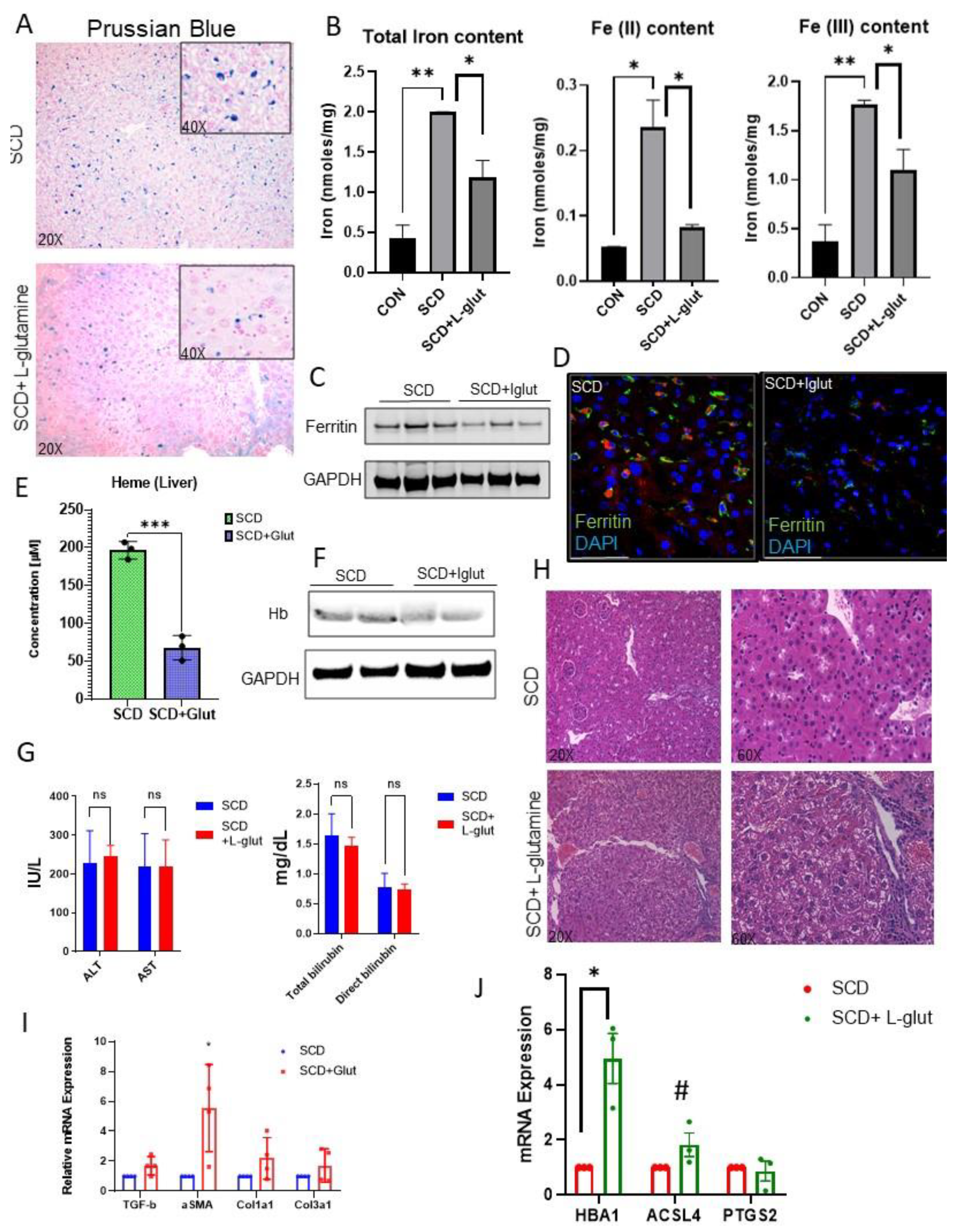
Activation of Kupffer cells is closely associated with hepatic iron-heme- hemoglobin recycling[
30,
31,
32]. As we see reduced expression of hepatic macrophages in l-glutamine treated SCD liver, we hypothesized that l-glutamine treatment might regulate hemoglobin-heme-iron accumulation in SCD liver. Prussian blue staining revealed hepatic iron accumulation is SCD liver (
Figure 2A), which was mildly reduced in l-glutamine treated SCD liver. We next determined the hepatic iron level by performing an iron colorimetric assay. As shown in
Figure 2B, l-glutamine administration resulted in reduction of total iron , Fe
+2 and Fe
+3 in SCD mice liver. When examined, we found reduced expression of ferritin, the surrogate marker for iron accumulation, in l-glutamine treated SCD mice liver by western blot (
Figure 2C) and immunofluorescence (
Figure 2D) analysis. Similarly, we found significant reduction in hepatic heme (
Figure 2E) and hemoglobin (
Figure 2F) level as seen by ELISA and western blot analysis respectively in l-glutamine treated SCD mice compared to SCD mice with no treatment. Interestingly, serum markers of liver injury (ALT and AST) did not show any improvement post l-glutamine treatment compared to their baseline values in SCD mouse (
Figure 2G). In addition, we found sinusoidal congestion and ballooning of cells by H&E staining (
Figure 2H) post l-glutamine treatment in SCD liver. qRT-PCR analysis confirmed significant upregulation of fibrosis markers (including TGFβ, αSMA, Col1A1, Col3a1) in l-glutamine treated SCD mice (
Figure 2I) as compared to untreated SCD mice. As we see unaltered vasocclusion and liver fibrosis in l-glutamine treated SCD mice , we hypothesized that the ongoing liver fibrosis seen in l-glutamine treated SCD mice is caused by impaired clearance of hepatic hemoglobin-heme-iron due to Kupffer cell depletion[
32,
33,
34]. Remarkably, when analyzed, we found significant increase in some of the liver fibrosis and cell death associated markers (such as HBA1, ACSL4 and PTGS2) in l-glutamine treated SCD mice liver as compared untreated SCD mice (
Figure 2J). Taken together, these data suggest that long term l-glutamine treatment can reduce hepatic heme-hemoglobin-iron level but has no effect on vasoocclusion associated acute ischemic injury and liver fibrosis in SCD. Moreover, long term l-glutamine treatment depletes hepatic Kupffer cells leading to fibrosis and hepatic cell death.
Our current study is the first to highlight the long-term effects of l-glutamine in SCD mice liver. Interestingly, despite a considerable decrease in hepatic heme-hemoglobin-iron accumulation, chronic liver injury did not ameliorate post l-glutamine treatment. We hypothesize that this could be due to the following reasons. Firstly, the injury was already established in SCD mice prior to l-glutamine treatment. Thus, the reduced expression of hepatic Kupffer cells l-glutamine contributed to impaired clearance of Hb-Heme-iron in the liver, leading to tissue damage. Secondly, the persistent injury and fibrosis seen in SCD mice post l-glutamine treatment could be solely due to ongoing vasoocclusive crisis. Thirdly, increased hepatic cell death following l-glutamine treatment can also result in persistent liver fibrosis in SCD mice.
Organ damage in SCD is caused by both hemolysis and vasoocclusion[
4]. In this study we found that l-glutamine can potentially be useful to reduce hemolysis but does not have any beneficial effect in attenuating hepatic vasoocclusion. Emerging evidence emphasizes the significance of a combinatorial approach in addressing the multifaceted pathophysiology associated with SCD[
35]. Our research suggests that one such combinatorial strategy could involve adding l-glutamine and inhibiting p-selectin simultaneously. Previously we have shown that blocking p-selectin can significantly ameliorate vasoocclusion without affecting hemolysis[
29]. Therefore, future studies should investigate the simultaneous effect of l-glutamine administration and p-selectin inhibition in attenuating SCD associated vasoocclusion and hemolysis.
A major limitation of our study is the use of l-glutamine in SCD mice to model the effects of l-glutamine therapy in SCD patients. Thus, species specific differences can’t be ruled out. Also, in our current study the l-glutamine was administered for up to eight weeks via drinking water. L-glutamine therapy in SCD patients may not result in the same extent of liver pathophysiology as what was caused by the continuous administration in mice. Notwithstanding these limitations, our current findings highlight the need to investigate the long-term effects of l-glutamine therapy on vasoocclusion, Kupffer cell expression, hepatic cell death and liver fibrosis in SCD patients.