Submitted:
29 July 2023
Posted:
01 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The nature of virus infections
2.1. Viruses and microbiota
2.2. Species-specificity and adaptation of viruses
2.3. Microbiota, infectious disease, and immune-mediated diseases
3. Pathophysiology of viral infections
3.1. Immune reactions to viral infection
3.2. Common immunopathogenesis of infectious diseases through the PHS hypothesis
| Etiological substances (or events) | Corresponding immune effectors |
| Pathogenic proteins (BCR-associated) | B cells: antibodies against pathogenic proteins |
| Pathogenic peptides (TCR-associated) | T cells: peptides or cytokines against pathogenic peptides |
| Pathogenic small peptides, monoamines, their metabolites (especially in CNS) | Immune proteins such as PrP gene products and other amyloid proteins, mast cell-associated immune responses |
| Non-protein materials such as LPS, RNAs, DNAs, chemicals, biochemicals | TLR-associated immune responses, natural antibodies, other immune systems such as complements and other proteins |
| Large complex substances; viruses, bacteria, parasite, apoptotic & necrotic bodies, and transformed cells | Phagocytes (neutrophils and macrophages), eosinophils (in case of large parasites), and natural killer cells |
| A protein deficiency or malfunctioning protein in organ tissues or within a cell | Production of alternative proteins in genetic diseases and cancers |
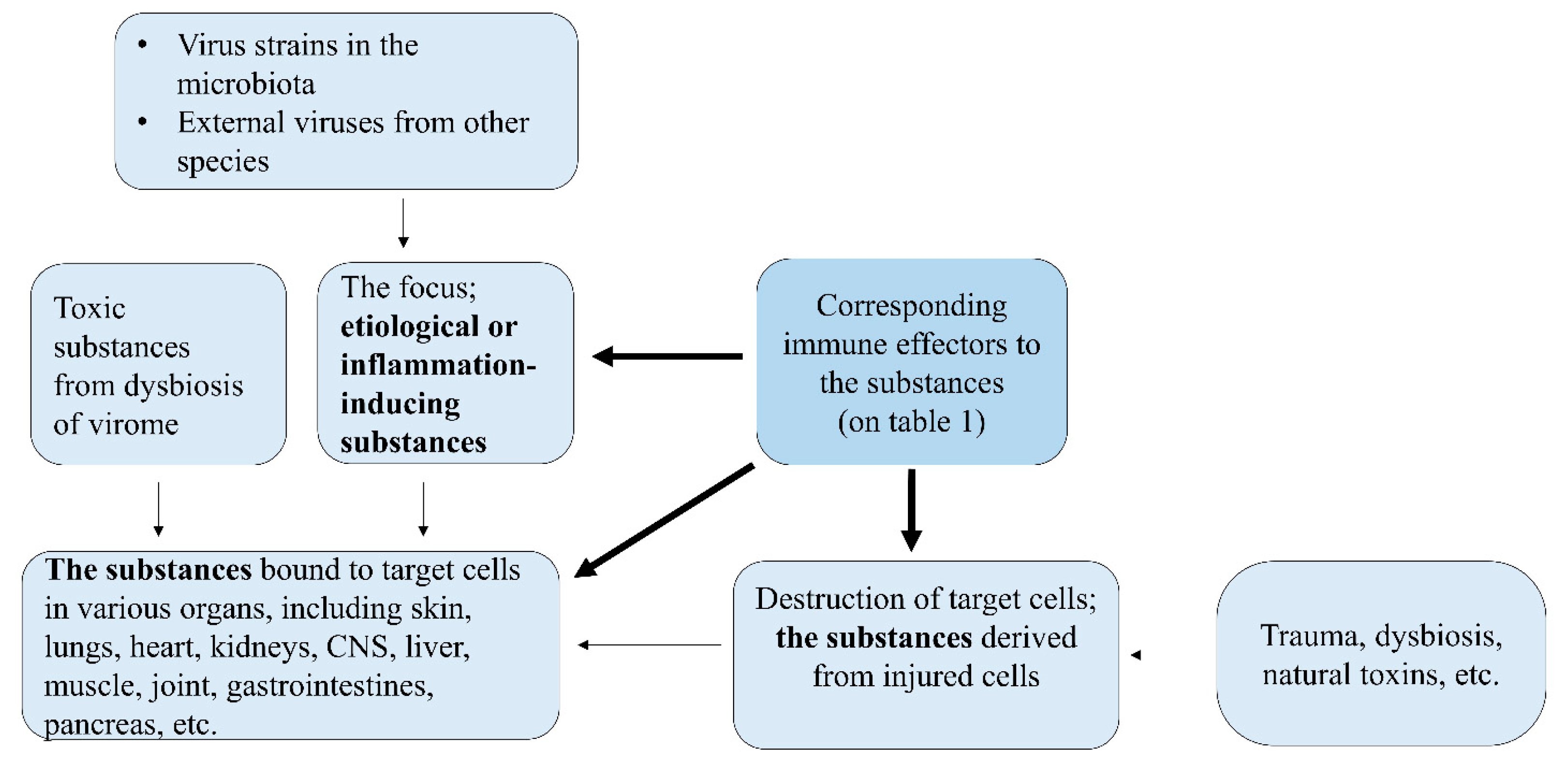
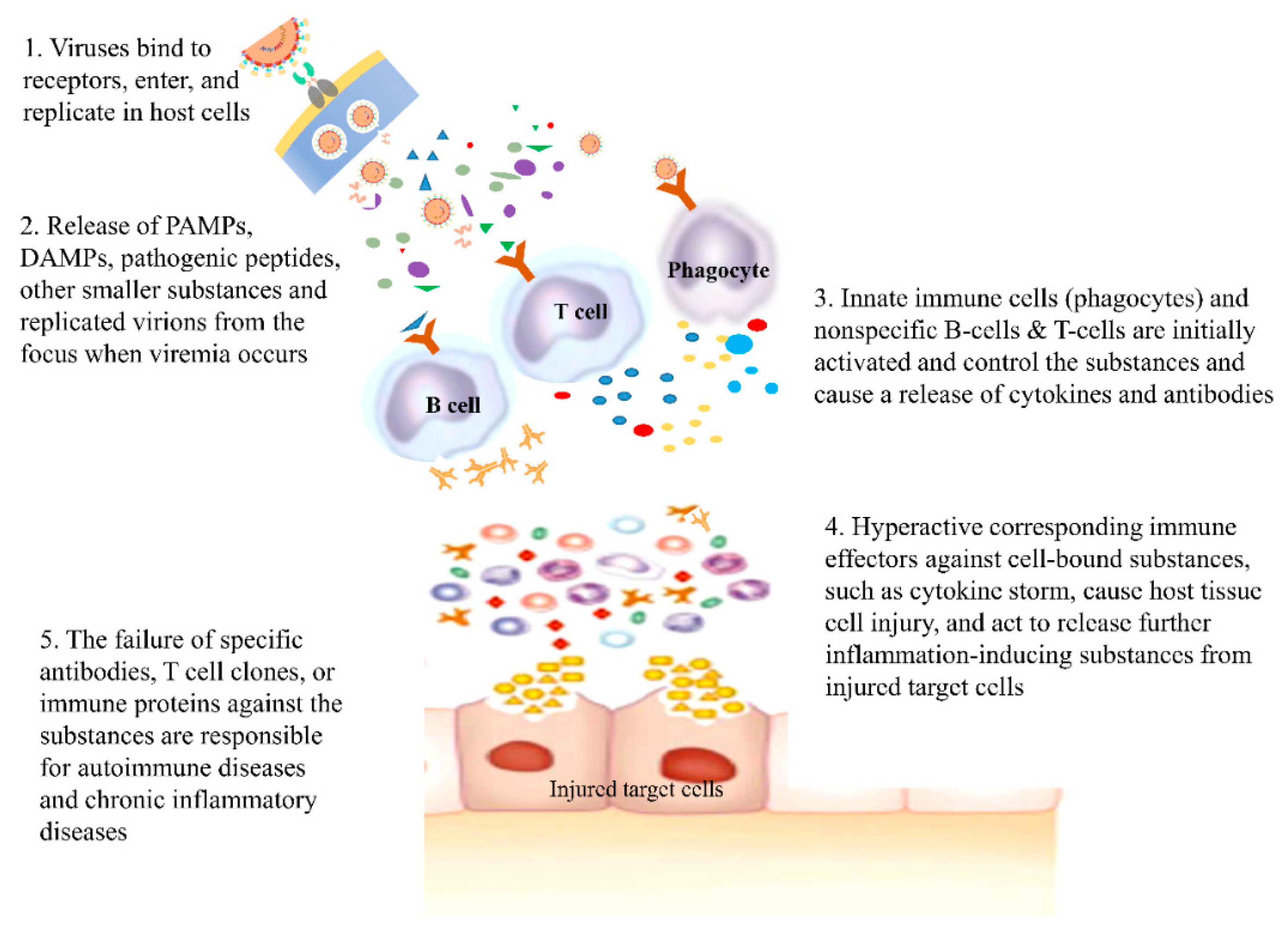
3.3. Clinical aspects of viral infections
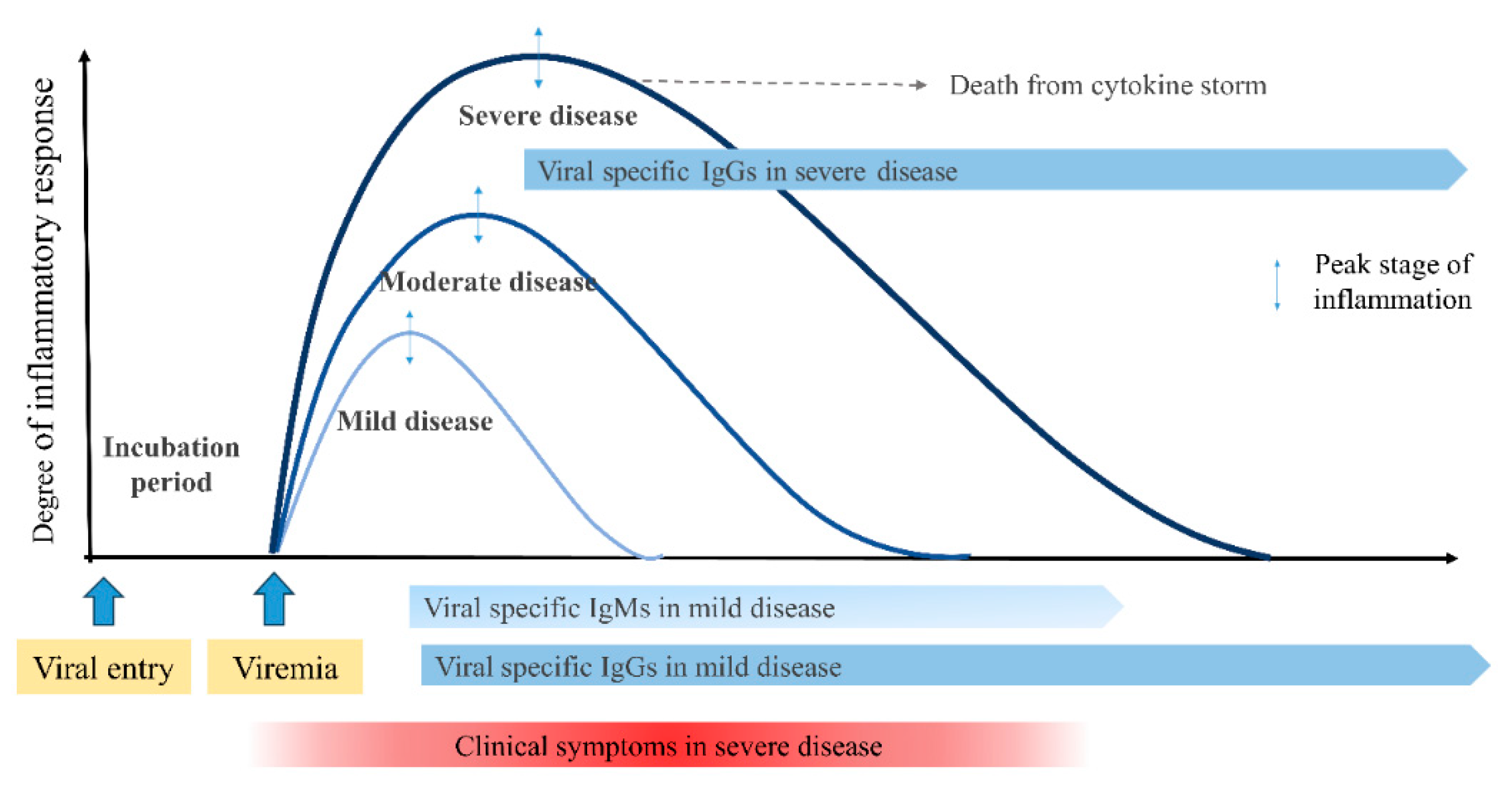
4. Unresolved issues and the PHS hypothesis
4.1. Pathologic findings
4.2. Protein homeostasis (proteostasis), proteasome, and lymphopenia in viral infections
4.3. Antibodies in viral infections
4.4. Unresolved issues in the diagnosis of infectious disease
4.5. Unresolved issues in vaccines
4.6. Viruses and cancers
5. Treatment of virus infections
5.1. Antimicrobials
5.2. Immune modulators
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.-Y.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H. Hyperactive immune cells (T cells) may be responsible for acute lung injury in influenza virus infections: A need for early immune-modulators for severe cases. Med Hypotheses 2011, 76, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y. Pneumonia, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, and Early Immune-Modulator Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H. Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 and early immunomodulators. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y. The solution on enigmas in COVID-19: the protein-homeostasis-system hypothesis. J. Korean Med Assoc. 2020, 63, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H. Kawasaki Disease: Laboratory Findings and an Immunopathogenesis on the Premise of a "Protein Homeostasis System". Yonsei Med J. 2012, 53, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y. A Common Immunopathogenesis Mechanism for Infectious Diseases: The Protein-Homeostasis-System Hypothesis. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 47, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y. A unified pathogenesis for kidney diseases, including genetic diseases and cancers, by the protein-homeostasis-system hypothesis. Kidney Res. Clin. Pr. 2017, 36, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, K.-Y. Etiological and pathophysiological enigmas of severe coronavirus disease 2019, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, and Kawasaki disease. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2022, 65, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y. Common immunopathogenesis of central nervous system diseases: the protein-homeostasis-system hypothesis. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.A.; Rohwer, F. Viral metagenomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Starokadomskyy, P. Are viruses alive? The replicator paradigm sheds decisive light on an old but misguided question. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. Part C: Stud. Hist. Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 59, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaran, N. On the historical significance of Beijerinck and his contagium vivum fluidum for modern virology. Hist. Philos. Life Sci. 2018, 40, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbart, M.; Rohwer, F. Here a virus, there a virus, everywhere the same virus? Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virus Taxonomy: 2021 Release". talk.ictvonline.org. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- Chauhan, R.P.; Gordon, M.L. An overview of influenza A virus genes, protein functions, and replication cycle highlighting important updates. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, S.; Lagaye, S. The remarkable history of the hepatitis C virus. Microbes Infect. 2019, 21, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, G. AIDS pathogenesis: a tale of two monkeys. J. Med Primatol. 2008, 37 (Suppl. 2), 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, D.R.; Immanuel, A.; Srikanth, S.; Kadhirvel, S. Trends and strategies to combat viral infections: A review on FDA approved antiviral drugs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, S.; Khan, F.S.; Rehman, M.I.M.U.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Rasool, G.; Khan, A.H.; Saleem, I.; Shamim, S.; Malik, A. A review: Mechanism of action of antiviral drugs. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 20587384211002621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moelling, K.; Broecker, F. Viroids and the Origin of Life. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1282, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- de Vries, R.D.; Mesman, A.W.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Duprex, W.P.; de Swart, R.L. The pathogenesis of measles. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.-L.; McGinley, J.P.; Drysdale, S.B.; Pollard, A.J. Epidemiology and Immune Pathogenesis of Viral Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bösmüller, H.; Matter, M.; Fend, F.; Tzankov, A. The pulmonary pathology of COVID-19. Virchows Arch. 2021, 478, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorey, T.M.; Ziegler, C.G.K.; Heimberg, G.; Normand, R.; Yang, Y.; Segerstolpe, Å.; Abbondanza, D.; Fleming, S.J.; Subramanian, A.; Montoro, D.T.; et al. COVID-19 tissue atlases reveal SARS-CoV-2 pathology and cellular targets. Nature 2021, 595, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Mohamed, M.S.; Moulin, T.C.; Schiöth, H.B. Neurological manifestations of COVID-19: A comprehensive literature review and discussion of mechanisms. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 358, 577658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.A. Human endogenous retroviruses: friend or foe? APMIS 2016, 124, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.; Dsouza, J.M.; Mathew, J.L. Comparison of microbiota in the upper versus lower respiratory tract in children during health and respiratory disease: protocol for a systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgin, H.W. The Virome in Mammalian Physiology and Disease. Cell 2014, 157, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, N.A.; Hameed, S.A.; Agyei, E.K.; Jacob, J.C.; Oyebanji, V.O.; Jabea, C.E. Crosstalk between the Intestinal Virome and Other Components of the Microbiota, and Its Effect on Intestinal Mucosal Response and Diseases. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 7883945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citti, C.; Blanchard, A. Mycoplasmas and their host: emerging and re-emerging minimal pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzatpour, S.; Portocarrero, A.d.C.M.; Cardelle-Cobas, A.; Lamas, A.; López-Santamarina, A.; Miranda, J.M.; Aguilar, H.C. The Human Gut Virome and Its Relationship with Nontransmissible Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, A.; Biazzo, M.; Gardini, S.; Muda, A.O.; Perno, C.F.; Dallapiccola, B.; Putignani, L. Cross-correlation of virome–bacteriome–host–metabolome to study respiratory health. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 30, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Scarpellini, E.; Colica, C.; Boccuto, L.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Aiello, V.; Romano, B.; De Lorenzo, A.; Izzo, A.A.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Obesity: A Role for Probiotics. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmink, B.A.; Khan, M.A.W.; Hermann, A.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Wargo, J.A. The microbiome, cancer, and cancer therapy. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaiss, C.A.; Zmora, N.; Levy, M.; Elinav, E. The microbiome and innate immunity. Nature 2016, 535, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’donnell, M.P.; Fox, B.W.; Chao, P.-H.; Schroeder, F.C.; Sengupta, P. A neurotransmitter produced by gut bacteria modulates host sensory behaviour. Nature 2020, 583, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.-L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkenhagen, L.K.; Salman, M.D.; Ma, M.-J.; Gray, G.C. Animal influenza virus infections in humans: A commentary. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 88, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A. An Analysis of 38 Pregnant Women With COVID-19, Their Newborn Infants, and Maternal-Fetal Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Maternal Coronavirus Infections and Pregnancy Outcomes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasko, D.A.; Webster, D.R.; Sahl, J.W.; Bashir, A.; Boisen, N.; Scheutz, F.; Paxinos, E.E.; Sebra, R.; Chin, C.-S.; Iliopoulos, D.; et al. Origins of theE. coliStrain Causing an Outbreak of Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome in Germany. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Burgner, D.; Lee, H.-S.; Hong, J.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, B.-C. The changing epidemiology of pediatric aseptic meningitis in Daejeon, Korea from 1987 to 2003. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.-H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Kim, C.-H.; Sim, D. Changing hepatitis A epidemiology and the need for vaccination in Korea. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 22, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shabasy, R.M.; Nayel, M.A.; Taher, M.M.; Abdelmonem, R.; Shoueir, K.R.; Kenawy, E.R. Three waves changes, new variant strains, and vaccination effect against COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 204, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y. New Insights for Febrile Urinary Tract Infection (Acute Pyelonephritis) in Children. Child. Kidney Dis. 2016, 20, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yun, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, E.H. Antimicrobial therapy of macrolide-resistantMycoplasma pneumoniaepneumonia in children. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 2018, 16, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kil, H.-R.; Yu, J.-W.; Lee, S.-C.; Rhim, J.-W.; Lee, K.-Y. Changes in clinical and laboratory features of Kawasaki disease noted over time in Daejeon, Korea. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2017, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuem, S.-W.; Hur, S.-M.; Youn, Y.-S.; Rhim, J.-W.; Suh, J.-S.; Lee, K.-Y. Changes in Acute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis: An Observation Study at a Single Korean Hospital Over Two Decades. Child. Kidney Dis. 2015, 19, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Lee, Y.-T.; Kang, H.-M.; Suh, J.-S.; Lee, K.-Y. Changes in clinical features in Henoch-Schönlein purpura during three decades: an observational study at a single hospital in Korea. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Hamada, H.; Arvonen, M. Editorial: Infection-Related Immune-Mediated Diseases and Microbiota. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gensollen, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Blumberg, R.S. How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes the immune system. Science 2016, 352, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Kennedy, E.; Holtz, L.R. Gut virome in early life: origins and implications. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 55, 101233–101233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallani, M.; Young, D.; Scott, J.; Norin, E.; Amarri, S.; Adam, R.; Aguilera, M.; Khanna, S.; Gil, A.; Edwards, C.A.A.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota of 6-week-old Infants Across Europe: Geographic Influence Beyond Delivery Mode, Breast-feeding, and Antibiotics. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyrer, C.; Baral, S.D.; van Griensven, F.; Goodreau, S.M.; Chariyalertsak, S.; Wirtz, A.L.; Brookmeyer, R. Global epidemiology of HIV infection in men who have sex with men. Lancet 2012, 380, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemaitelly, H.; Chaabna, K.; Abu-Raddad, L.J. The Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Virus in the Fertile Crescent: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0135281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumura, J.; Yashiro, M.; Okamoto, N.; Shabana, K.; Umebayashi, H.; Iwata, N.; Okura, Y.; Kubota, T.; Shimizu, M.; Tomiita, M.; et al. Clinical features and characteristics of uveitis associated with juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Japan: first report of the pediatric rheumatology association of Japan (PRAJ). Rheumatol. 2019, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, H.M.; Han, J.-W.; Lee, K.-Y. A Presumed Etiology of Kawasaki Disease Based on Epidemiological Comparison With Infectious or Immune-Mediated Diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouayad, A. Multifaceted roles of Fcγ receptors in COVID-19 and vaccine responses. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 3040–3059. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern Recognition Receptors and Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katze, M.G.; He, Y.; Gale, M., Jr. Viruses and interferon: a fight for supremacy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Al-Hussaniy, H.A.; Al-Harcan, N.A.H.; Alexiou, A.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) and Covid-19: A new frontiers for therapeutic modality. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 104, 108516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, B.G.; Calado, R.T. Hyper-inflammation and complement in COVID-19. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98 (Suppl. 4), S74–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Quintin, J.; van der Meer, J.W. Trained Immunity: A Memory for Innate Host Defense. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamon, M.A.; Quintin, J. Innate immune memory in mammals. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tso, F.Y.; Lidenge, S.J.; Poppe, L.K.; Peña, P.B.; Privatt, S.R.; Bennett, S.J.; Ngowi, J.R.; Mwaiselage, J.; Belshan, M.; Siedlik, J.A.; et al. Presence of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) against SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 plasma. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, e0247640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, G. The Mechanism behind Influenza Virus Cytokine Storm. Viruses 2021, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkström, N.K.; Strunz, B.; Ljunggren, H.-G. Natural killer cells in antiviral immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzali, B.; Noris, M.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Kemper, C. The state of complement in COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potere, N.; Del Buono, M.G.; Caricchio, R.; Cremer, P.C.; Vecchié, A.; Porreca, E.; Gasperina, D.D.; Dentali, F.; Abbate, A.; Bonaventura, A. Interleukin-1 and the NLRP3 inflammasome in COVID-19: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications. EBioMedicine 2022, 85, 104299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, E.; Díaz-García, E.; García-Tovar, S.; Zamarrón, E.; Mangas, A.; Galera, R.; López-Collazo, E.; García-Rio, F.; Cubillos-Zapata, C. Upregulated Proteasome Subunits in COVID-19 Patients: A Link with Hypoxemia, Lymphopenia and Inflammation. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.A.; Colley, L.; Agbaedeng, T.A.; Ellison-Hughes, G.M.; Ross, M.D. Vascular Manifestations of COVID-19 – Thromboembolism and Microvascular Dysfunction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 598400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodpoor, A.; Sanaie, S.; Roudbari, F.; Sabzevari, T.; Sohrabifar, N.; Kazeminasab, S. Understanding the role of telomere attrition and epigenetic signatures in COVID-19 severity. Gene 2022, 811, 146069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.S.; Laloraya, M. A cytokine super cyclone in COVID-19 patients with risk factors: the therapeutic potential of BCG immunization. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 54, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimdal, I.; Moe, N.; Krokstad, S.; Christensen, A.; Skanke, L.H.; Nordbø, S.A.; Døllner, H. Human Coronavirus in Hospitalized Children With Respiratory Tract Infections: A 9-Year Population-Based Study From Norway. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robb, M.L.; Eller, L.A.; Kibuuka, H.; Rono, K.; Maganga, L.; Nitayaphan, S.; Kroon, E.; Sawe, F.K.; Sinei, S.; Sriplienchan, S.; et al. Prospective Study of Acute HIV-1 Infection in Adults in East Africa and Thailand. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2120–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indolfi, G.; Easterbrook, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Siberry, G.; Chang, M.-H.; Thorne, C.; Bulterys, M.; Chan, P.-L.; El-Sayed, M.H.; Giaquinto, C.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection in children and adolescents. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indolfi, G.; Easterbrook, P.; Dusheiko, G.; El-Sayed, M.H.; Jonas, M.M.; Thorne, C.; Bulterys, M.; Siberry, G.; Walsh, N.; Chang, M.-H.; et al. Hepatitis C virus infection in children and adolescents. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H. The epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection in Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, M.J.; Stumpf, P.S.; MacArthur, B.D. Theory of cell fate. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2020, 12, e1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyapina, I.; Ivanov, V.; Fesenko, I. Peptidome: Chaos or Inevitability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, S.; Yang, C.; Castro, L.M.; Tashima, A.K.; Ferro, E.S.; Moir, R.D.; Willis, I.M.; Fricker, L.D. Analysis of the Yeast Peptidome and Comparison with the Human Peptidome. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0163312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraj, G.G.; Hipp, M.S.; Hartl, F.U. Functional Modules of the Proteostasis Network. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2020, 12, a033951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommen, F.; Bilican, S.; Vilchez, D. Protein clearance strategies for disease intervention. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 141–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zhong, M.B.; Toro, C.A.; Zhang, L.; Cai, D. Endo-lysosomal pathway and ubiquitin-proteasome system dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 703, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, A.V.; Karpov, V.L. Proteasomes and Several Aspects of Their Heterogeneity Relevant to Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbrugge, S.E.; Scheper, R.J.; Lems, W.F.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Jansen, G. Proteasome inhibitors as experimental therapeutics of autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, N.; Talnir, R.; Lavid, O.; Rubinstein, U.; Niven, M.; First, Y.; I Tsivion, A.J.; Schachter, Y. Transient lymphopenia and neutropenia: pediatric influenza A/H1N1 infection in a primary hospital in Israel. Isr. Med Assoc. J. : IMAJ.
- Yan, S.; Wu, G. Is lymphopenia different between SARS and COVID-19 patients? FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Kobune, F.; Sato, T.A.; Kohama, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Abe, T.; Takayama, N.; Tsuchiya, T.; Tashiro, M. Extensive lymphopenia due to apoptosis of uninfected lymphocytes in acute measles patients. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Hong, J.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Burgner, D.; Lee, B.-C. Role of prednisolone treatment in severeMycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2006, 41, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, C.W.; Tapper, M.L. Opportunistic Infection Complicating Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. Clinical features of 25 cases. Medicine 1984, 63, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.W.; Tan, T.-C. Atypical presentation of Good syndrome: acute hepatitis from hepatitis B virus reactivation. Asia Pac. Allergy 2020, 10, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumpey, T.M.; Lu, X.; Morken, T.; Zaki, S.R.; Katz, J.M. Depletion of Lymphocytes and Diminished Cytokine Production in Mice Infected with a Highly Virulent Influenza A (H5N1) Virus Isolated from Humans. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6105–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douek, D.C.; Picker, L.J.; Koup, R.A. T Cell Dynamics in HIV-1 Infection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 265–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisco, A.; Ortega-Villa, A.M.; Mystakelis, H.; Anderson, M.V.; Mateja, A.; Laidlaw, E.; Manion, M.; Roby, G.; Higgins, J.; Kuriakose, S.; et al. Reappraisal of Idiopathic CD4 Lymphocytopenia at 30 Years. New Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1680–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, J.-S. Immunoglobulin G has a role for systemic protein modulation in vivo: A new concept of protein homeostasis. Med Hypotheses 2006, 67, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-W.; Oh, J.-H.; Rhim, J.-W.; Lee, K.-Y. Correlation between elevated platelet count and immunoglobulin levels in the early convalescent stage of Kawasaki disease. Medicine 2017, 96, e7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, H.; Pillat, M.M.; Tárnok, A. Dengue Fever,COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2), andAntibody-DependentEnhancement (ADE): A Perspective. Cytom. Part A 2020, 97, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.-H.; Müller, M.A.; Seok, H.; Park, G.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, S.Y.; Ha, Y.E.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, J.-M.; et al. Serologic responses of 42 MERS-coronavirus-infected patients according to the disease severity. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 89, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilla, M.; Wheeler, B.J.; Keetch, C.; Mitchell, G.; McBreen, J.; Wells, A.; Shurin, M.R.; Peck-Palmer, O.; Wheeler, S.E. Variable Performance in 6 Commercial SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assays May Affect Convalescent Plasma and Seroprevalence Screening. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 155, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-Y.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, J.-C. Difference of clinical features in childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. BMC Pediatr. 2010, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bien, C.I. Autoimmune encephalitis in children and adolescents. Neurol. Res. Pr. 2020, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucher, E.; Sucher, R.; Gradistanac, T.; Brandacher, G.; Schneeberger, S.; Berg, T. Autoimmune Hepatitis—Immunologically Triggered Liver Pathogenesis—Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 9437043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Buitrago-Garcia, D.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano-Achig, P.; Del Campo, R.; Ciapponi, A.; Sued, O.; Martinez-García, L.; Rutjes, A.W.; Low, N.; et al. False-negative results of initial RT-PCR assays for COVID-19: A systematic review. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0242958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winichakoon, P.; Chaiwarith, R.; Liwsrisakun, C.; Salee, P.; Goonna, A.; Limsukon, A.; Kaewpoowat, Q. Negative Nasopharyngeal and Oropharyngeal Swabs Do Not Rule Out COVID-19. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00297–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoraro, V.; Negro, A.; Pirotti, T.; Trenti, T. Estimate false-negative RT-PCR rates for SARS-CoV-2. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-C.; Youn, Y.-S.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, K.-Y. Early Serologic Diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia: An Observational Study on Changes in Titers of Specific-IgM Antibodies and Cold Agglutinins. Medicine 2016, 95, e3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.E.; Kang, H.M.; Yang, E.A.; Han, H.Y.; Han, S.B.; Rhim, J.W.; Lee, K.-Y. Early Confirmation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection by Two Short-Term Serologic IgM Examination. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, V.; Denizer, G.; Friedland, L.R.; Krishnan, J.; Shapiro, M. Understanding modern-day vaccines: what you need to know. Ann. Med. 2018, 50, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Hur, J.-K.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, B.-C. The changing epidemiology of hospitalized pediatric patients in three measles outbreaks. J. Infect. 2007, 54, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.-U.; Kim, E.-K.; Youn, Y.-S.; Rhim, J.-W.; Lee, K.-Y. Outbreaks of mumps: an observational study over two decades in a single hospital in Korea. Korean J. Pediatr. 2014, 57, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, R.; Leung, P.H.M. Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections: Pathogenesis and Vaccine Development. Pathogens 2021, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, K.M.; Graham, B.S. Zika Virus Vaccine Development. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216 (Suppl. 10), S957–S963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Souza, S.; Lau, K.C.; Coffin, C.S.; Patel, T.R. Molecular mechanisms of viral hepatitis induced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5759–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Fera, A.N.; Warburton, A.; Coursey, T.L.; Khurana, S.; McBride, A.A. Persistent Human Papillomavirus Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safai, B.; Sarngadharan, M. G.; Koziner, B.; Godbold, J.; Myskowski, P. L.; Cunningham-Rundles, S.; et al. Spectrum of Kaposi's sarcoma in the epidemic of AIDS. Cancer Res. 1985, 45(9 Suppl), 4646s-4648s. 2: PMID, 2990. [Google Scholar]
- Rossiello, F.; Jurk, D.; Passos, J.F.; di Fagagna, F.D. Telomere dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases. Nature 2022, 24, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Eun, C.S. Inflammatory bowel disease in Korea: epidemiology and pathophysiology. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.R.; Rosa, I.; Claro, I. Early-onset colorectal cancer: A review of current knowledge. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 1289–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, T.; Doshi, P. Multisystem failure: the story of anti-influenza drugs. BMJ 2014, 348, g2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Lee, K.-Y.; Youn, Y.-S.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, J.-C. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of childhood pandemic 2009 H1N1 virus infection: an observational cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vidal, C.; Carratalà, J. Early and Late Treatment Failure in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 30, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, R.; Torres, A.; Zalacaín, R.; Aspa, J.; Villasclaras, J.J.M.; Borderías, L.; Moya, J.M.B.; Ruiz-Manzano, J.; de Castro, F.R.; Blanquer, J.; et al. Risk factors of treatment failure in community acquired pneumonia: implications for disease outcome. Thorax 2004, 59, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, K.B.; Kim, H.J. Management of antiviral drug resistance in chronic hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11641–11649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endalamaw, A.; Mekonnen, M.; Geremew, D.; Yehualashet, F.A.; Tesera, H.; Habtewold, T.D. HIV/AIDS treatment failure and associated factors in Ethiopia: meta-analysis. BMC Public Heal. 2020, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-Y. Mycoplasma pneumoniaepneumonia in children. Korean J. Pediatr. 2012, 55, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ma, S. The cytokine storm and factors determining the sequence and severity of organ dysfunction in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 26, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, J.; Lunsford, L.D.; Li, T.; Tang, R.; He, J.; Xu, P.; Faramand, A.; Xu, J.; et al. Association of Corticosteroid Treatment With Outcomes in Adult Patients With Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, R.S.; O’garra, A.; Sher, A.; Wack, A. Host-directed immunotherapy of viral and bacterial infections: past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The RECOVERY Collaborative Group. ; Horby, P.; Lim, W. S.; Emberson, J. R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J. L.; Linsell, L.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group; Sterne, J. A.C.; Murthy, S.; Diaz, J.V.; Slutsky, A.S.; Villar, J.; Angus, D.C.; Annane, D.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Berwanger, O.; et al. Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis. JAMA 2020, 324, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, J.G.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mehra, M.R.; Lavie, C.J.; Rizk, Y.; Forthal, D.N. Pharmaco-Immunomodulatory Therapy in COVID-19. Drugs 2020, 80, 1267–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H. Early preemptive immunomodulators (corticosteroids) for severe pneumonia patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, H.-R.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Rhim, J.-W.; Youn, Y.-S.; Kang, J.-H. Early corticosteroid treatment for severe pneumonia caused by 2009 H1N1 influenza virus. Crit. Care 2011, 15, 413–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.-A.; Kang, H.-M.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, K.-Y. Early Corticosteroid Therapy for Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia Irrespective of Used Antibiotics in Children. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, P. .; de la Fuente Briongos, E.; Alonso, E.C.; Pérez-Calle, J.L.; Rodríguez, C.F. Hepatitis B and immunosuppressive therapies for chronic inflammatory diseases: When and how to apply prophylaxis, with a special focus on corticosteroid therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewald, H.; Raatz, H.; Boscacci, R.; Furrer, H.; Bucher, H.C.; Briel, M. Adjunctive corticosteroids for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients with HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD006150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.; Zhang, H.-Y.; You, J.-P.; Zhang, X.-Q. Severe acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B during pegylated interferon treatment and early intervention with corticosteroid. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, L.; Perelson, A.S. Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection With Interferon and Small Molecule Direct Antivirals: Viral Kinetics and Modeling. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 30, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivioli, G.; Terrier, B.; Vaglio, A. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: understanding the disease and its management. Rheumatology 2020, 59 (Suppl. 3), iii84–iii94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Lee, K.-Y.; Rhim, J.-W.; Youn, Y.-S.; Oh, J.-H.; Han, J.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; Burgner, D. Assessment of intravenous immunoglobulin non-responders in Kawasaki disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 2011, 96, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.-M.; Kang, H.-M.; Lee, S.-C.; Yu, J.-W.; Kil, H.-R.; Rhim, J.-W.; Han, J.-W.; Lee, K.-Y. Clinical implications in laboratory parameter values in acute Kawasaki disease for early diagnosis and proper treatment. Korean J. Pediatr. 2018, 61, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.Y.; Park, K.C.; Yang, E.-A.; Lee, K.-Y. Macrolide-Resistant and Macrolide-Sensitive Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children Treated Using Early Corticosteroids. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





