Submitted:
28 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
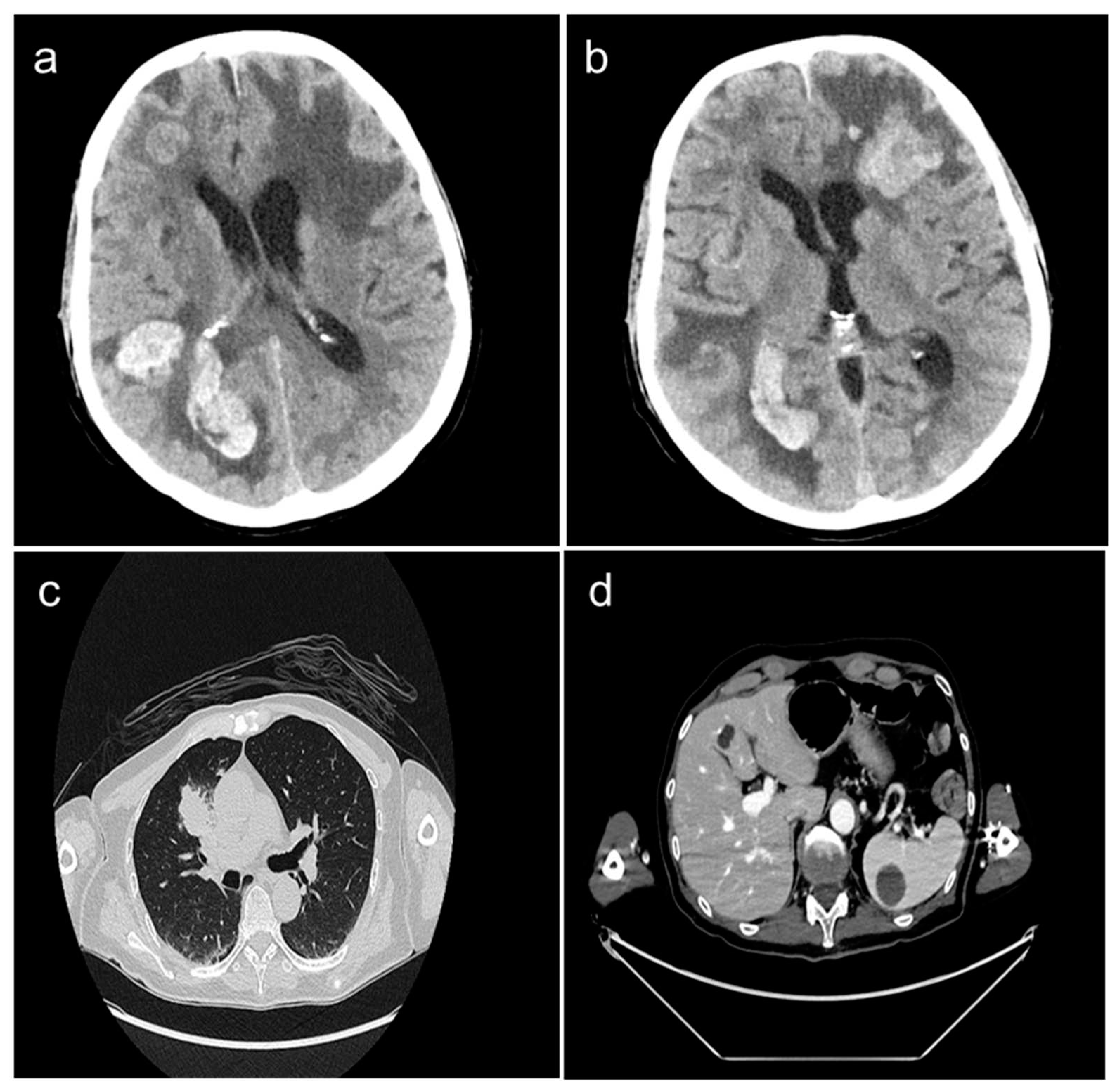
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ricotti, A.; Sciannameo, V.; Balzi, W.; Roncadori, A.; Canavese, P.; Avitabile, A.; Massa, I.; Berchialla, P. Incidence and Prevalence Analysis of Non-Small-Cell and Small-Cell Lung Cancer Using Administrative Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2021, 18, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, N.; Santana-Davila, R.; Molina, J.R. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.G.; Di Noia, V.; D’argento, E.; Vita, E.; Damiano, P.; Cannella, A.; Ribelli, M.; Pilotto, S.; Milella, M.; Tortora, G.; et al. Oncogene-Addicted Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Treatment Opportunities and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2020, 12, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, R.J.; Rubinstein, L.V. Randomized trial of lobectomy versus limited resection for T1 N0 non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1995, 60, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billmeier, S.E.; Ayanian, J.Z.; Zaslavsky, A.M.; Nerenz, D.R.; Jaklitsch, M.T.; Rogers, S.O. Predictors and Outcomes of Limited Resection for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Med. (Russian Journal) 2011, 103, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.M.; Shaikh, T.; Hallman, M. Therapeutic management options for stage III non-small cell lung cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilligan, D.; Nicolson, M.; Smith, I.; Groen, H.; Dalesio, O.; Goldstraw, P.; Hatton, M.; Hopwood, P.; Manegold, C.; Schramel, F.; et al. Preoperative chemotherapy in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer: results of the MRC LU22/NVALT 2/EORTC 08012 multicentre randomised trial and update of systematic review. Lancet 2007, 369, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, E.; Rosell, R.; Maestre, J.A.; Rodríguez-Paniagua, J.M.; Morán, T.; Astudillo, J.; Alonso, G.; Borro, J.M.; González-Larriba, J.L.; Torres, A.; et al. Preoperative Chemotherapy Plus Surgery Versus Surgery Plus Adjuvant Chemotherapy Versus Surgery Alone in Early-Stage Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3138–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignon, J.-P.; Tribodet, H.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Shepherd, F.A.; Stephens, R.J.; Dunant, A.; Torri, V.; Rosell, R.; Seymour, L.; et al. Lung Adjuvant Cisplatin Evaluation: A Pooled Analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3552–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; de Marinis, F.; Dediu, M.; Thomas, M.; Pujol, J.-L.; Bidoli, P.; Molinier, O.; Sahoo, T.P.; Laack, E.; Reck, M.; et al. Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care after induction therapy with pemetrexed plus cisplatin for advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (PARAMOUNT): a double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Li, B.T.; Dy, G.K.; Price, T.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Wolf, J.; Italiano, A.; Schuler, M.; Borghaei, H.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Sotorasib for Lung Cancers with KRAS p.G12C Mutation. New Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Riely, G.J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Heist, R.S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pacheco, J.M.; Johnson, M.L.; Sabari, J.K.; Leventakos, K.; Yau, E.; et al. Adagrasib in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring a KRASG12C Mutation. New Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or Chemotherapy for Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yamamoto, N.; Obyrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III Study of Afatinib or Cisplatin Plus Pemetrexed in Patients With Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma With EGFR Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Lee, M.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Improvement in Overall Survival in a Randomized Study That Compared Dacomitinib With Gefitinib in Patients With Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR-Activating Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Tsuboi, M.; He, J.; John, T.; Grohe, C.; Majem, M.; Goldman, J.W.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Kato, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Resected EGFR-Mutated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.-W.; Nakagawa, K.; Seto, T.; Crinó, L.; Ahn, M.-J.; De Pas, T.; Besse, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Blackhall, F.; et al. Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in AdvancedALK-Positive Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.-J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK -rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Hochmair, M.J.; Li, J.Y.-C.; Chang, G.-C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Brigatinib versus Crizotinib in ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Poddubskaya, E.; Mok, T.; Reck, M.; Wakelee, H.; Chiappori, A.A.; Lee, D.H.; Breder, V.; et al. Ensartinib vs Crizotinib for Patients With Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase−Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Mazieres, J.; Besse, B.; Helland, Å.; Giannone, V.; D’Amelio, A.M., Jr.; Zhang, P.; Mookerjee, B.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously untreated BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: an open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.-Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.; Tan, D.S.; Hida, T.; de Jonge, M.; Orlov, S.V.; et al. Capmatinib inMETExon 14–Mutated orMET-Amplified Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Felip, E.; Veillon, R.; Sakai, H.; Cortot, A.B.; Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Viteri, S.; Senellart, H.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; et al. Tepotinib in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Bang, Y.-J.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.J.; Salgia, R.; Riely, G.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Shapiro, G.I.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Crizotinib in ROS1-Rearranged Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Siena, S.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Barlesi, F.; Krebs, M.G.; Shaw, A.T.; de Braud, F.; Rolfo, C.; Ahn, M.-J.; Wolf, J.; et al. Entrectinib in ROS1 fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 21, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Curigliano, G.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, D.H.; Besse, B.; Baik, C.S.; Doebele, R.C.; A Cassier, P.; Lopes, G.; Tan, D.S.W.; et al. Pralsetinib for RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARROW): a multi-cohort, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.; Loong, H.H.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazières, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Saltos, A.N.; Felip, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Siena, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Farago, A.F.; Blakely, C.M.; Seto, T.; Cho, B.C.; Tosi, D.; et al. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; Dubois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion–Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.; Kilickap, S.; Gümüş, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Gogishvili, M.; Turk, H.M.; Cicin, I.; Bentsion, D.; Gladkov, O.; et al. Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: a multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Cobo, M.; Schenker, M.; Zurawski, B.; Menezes, J.; Richardet, E.; Bennouna, J.; Felip, E.; Juan-Vidal, O.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 9LA): an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.-W.; Felip, E.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.-Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.-J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, L.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; De Angelis, F.; Domine, M.; Clingan, P.; Hochmair, M.J.; Powell, S.F.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2078–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Luft, A.; Vicente, D.; Tafreshi, A.; Gümüş, M.; Mazières, J.; Hermes, B.; Çay Şenler, F.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy for Squamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; de Marinis, F.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.; Geater, S.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of PD-L1–Selected Patients with NSCLC. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; De Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, M.; Paz-Ares, L.; Marreaud, S.; Dafni, U.; Oselin, K.; Havel, L.; Esteban, E.; Isla, D.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Faehling, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy for completely resected stage IB–IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091): an interim analysis of a randomised, triple-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, E.; Altorki, N.; Zhou, C.; Csőszi, T.; Vynnychenko, I.; Goloborodko, O.; Luft, A.; Akopov, A.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Kenmotsu, H.; et al. IMpower010 Investigators. Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in resected stage IB–IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower010): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 1344–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, P.M.; Spicer, J.; Lu, S.; Provencio, M.; Mitsudomi, T.; Awad, M.M.; Felip, E.; Broderick, S.R.; Brahmer, J.R.; Swanson, S.J.; et al. Neoadjuvant Nivolumab plus Chemotherapy in Resectable Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1973–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Senan, S.; Paul, M.A.; Mehran, R.J.; Louie, A.V.; Balter, P.; Groen, H.J.M.; E McRae, S.E.; Widder, J.; Feng, L.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanic, S.; Paulus, R.; Timmerman, R.D.; Michalski, J.M.; Barriger, R.B.; Bezjak, A.; Videtic, G.M.; Bradley, J. No Clinically Significant Changes in Pulmonary Function Following Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Early- Stage Peripheral Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: An Analysis of RTOG 0236. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 88, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, C.; Guckenberger, M.; Gaspar, L.E.; Rusthoven, C.G.; De Ruysscher, D.; Sahgal, A.; Nguyen, T.; Grosu, A.L.; Mehta, M.P. Management of patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer and adverse prognostic features: multi-national radiation treatment recommendations are heterogeneous. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, K.; Cao, D. Optimal dose-fractionation schedule of palliative radiotherapy for patients with bone metastases: a protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabel, A.; Debus, J. Treatment of brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): radiotherapy. Lung Cancer 2004, 45, S247–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary Report on the Graded Prognostic Assessment: An Accurate and Facile Diagnosis-Specific Tool to Estimate Survival for Patients With Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas-Korczynska, B.; Rucinska, M. WBRT for brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: for whom and when?—Contemporary point of view. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 3246–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Lee, E.Q.; Wen, P.Y. Epidemiology of Brain Metastases. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 14, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebben, J.D.; You, M. Brain metastasis in lung cancer: Building a molecular and systems-level understanding to improve outcomes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 78, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancoule, C.; Vallard, A.; Guy, J.-B.; Espenel, S.; Diao, P.; Chargari, C.; Magné, N. Brain metastases from non-small cell lung carcinoma: Changing concepts for improving patients’ outcome. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2017, 116, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.G.; Ball, D.L. Treatment of Brain Metastases in Lung Cancer: Strategies to Avoid/Reduce Late Complications of Whole Brain Radiation Therapy. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2013, 14, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.W.; Scott, C.B.; Sperduto, P.W.; Flanders, A.E.; Gaspar, L.E.; Schell, M.C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Demas, W.; Ryu, J.; Bahary, J.-P.; et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, W.; Qi, C.; Zhou, L.; Wen, F.; Qu, Y.; Yu, H. Optimizing Whole Brain Radiotherapy Treatment and Dose for Patients With Brain Metastases From Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 726613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsa, A.; Jang, J.K.; Baxi, S.; Chen, C.; Akinniranye, O.; Hall, O.; Larkin, J.; Motala, A.; Hempel, S. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: A Systematic Review. Pr. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 11, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, L.E.; Mehta, M.P.; Patchell, R.A.; Burri, S.H.; Robinson, P.D.; Morris, R.E.; Ammirati, M.; Andrews, D.W.; Asher, A.L.; Cobbs, C.S.; et al. The role of whole brain radiation therapy in the management of newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J. Neuro-Oncology 2009, 96, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, H.; Shirato, H.; Tago, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Toyoda, T.; Hatano, K.; Kenjyo, M.; Oya, N.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery Plus Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy vs Stereotactic Radiosurgery Alone for Treatment of Brain Metastases: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikhirhisthit, K.; Setakornnukul, J.; Thephamongkhol, K. Added survival benefit of whole brain radiotherapy in brain metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: Development and external validation of an individual prediction model. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 911835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rades, D.; Hansen, H.C.; Schild, S.E.; Janssen, S. A New Diagnosis-Specific Survival Score for Patients to be Irradiated for Brain Metastases from Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung 2019, 197, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Dunst, J.; Schild, S.E. A New Scoring System to Predicting the Survival of Patients Treated with Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases. Strahlenther. und Onkol. 2008, 184, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, C.; Gastino, A.; Cerrato, M.; Badellino, S.; Ricardi, U.; Levis, M. Modern Radiation Therapy for the Management of Brain Metastases From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 772789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, C.; Grosshans, D.; Duman, J.; Brown, P.; Li, J. Radiation-induced cognitive toxicity: pathophysiology and interventions to reduce toxicity in adults. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 20, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Khan, O.H.; Asher, A.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Gondi, V. Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases: Evolution or Revolution? J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, D.D.; Sperduto, P.W. Neuropsychological effects of cranial radiation: current knowledge and future directions. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1995, 31, 983–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussain, C.; Ricard, D.; Fike, J.R.; Mazeron, J.-J.; Psimaras, D.; Delattre, J.-Y. CNS complications of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Lancet 2009, 374, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bompaire, F.; Lahutte, M.; Buffat, S.; Soussain, C.; Ardisson, A.E.; Terziev, R.; Sallansonnet-Froment, M.; De Greslan, T.; Edmond, S.; Saad, M.; et al. New insights in radiation-induced leukoencephalopathy: a prospective cross-sectional study. Support. Care Cancer 2018, 26, 4217–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G.; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of Radiosurgery Alone vs Radiosurgery With Whole Brain Radiation Therapy on Cognitive Function in Patients With 1 to 3 Brain Metastases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Fu, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liang, Y.; An, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Y. The Effect of Hippocampal Avoidance Whole Brain Radiotherapy on the Preservation of Long-Term Neurocognitive Function in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients With Brain Metastasis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211034268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, W.O.; Verma, S.; Patel, K.P.; Davies, M.A.; Barkoh, B.A.; Galbincea, J.M.; Yao, H.; Lazar, A.J.; Aldape, K.D.; Medeiros, L.J.; et al. Frequency and Spectrum of BRAF Mutations in a Retrospective, Single-Institution Study of 1112 Cases of Melanoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 15, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.V.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Gogas, H.; Levchenko, E.; de Braud, F.; Larkin, J.; Garbe, C.; Jouary, T.; Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.-J.; et al. Dabrafenib and trametinib versus dabrafenib and placebo for Val600 BRAF-mutant melanoma: a multicentre, double-blind, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, R.; Brase, J.C.; Garrett, J.; Campbell, C.D.; Gasal, E.; Squires, M.; Gusenleitner, D.; Santinami, M.; Atkinson, V.; Mandalà, M.; et al. Adjuvant dabrafenib plus trametinib versus placebo in patients with resected, BRAFV600-mutant, stage III melanoma (COMBI-AD): exploratory biomarker analyses from a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, A.R.; Chablani, P.; Siedow, M.R.; Miller, E.D.; Walston, S.; Kendra, K.L.; Wuthrick, E.; Williams, T.M. BRAF mutation correlates with worse local–regional control following radiation therapy in patients with stage III melanoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Menzies, A.M.; Nagrial, A.M.; Haydu, L.E.; Hamilton, A.L.; Mann, G.J.; Hughes, T.M.; Thompson, J.F.; Scolyer, R.A.; Kefford, R.F. Prognostic and Clinicopathologic Associations of Oncogenic BRAF in Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, A.M.; Haydu, L.E.; Visintin, L.; Carlino, M.S.; Howle, J.R.; Thompson, J.F.; Kefford, R.F.; Scolyer, R.A.; Long, G.V. Distinguishing Clinicopathologic Features of Patients with V600E and V600K BRAF-Mutant Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3242–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, E.J.; McKenna, W.G.; Hamilton, A.D.; Sebti, S.M.; Qian, Y.; Wu, J.M.; Muschel, R.J. Inhibiting Ras prenylation increases the radiosensitivity of human tumor cell lines with activating mutations of ras oncogenes. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, T.B.; Cengel, K.A.; Hahn, S.M.; Wu, J.; Fraker, D.L.; McKenna, W.G.; Bernhard, E.J. Pancreatic Cancer Cell Radiation Survival and Prenyltransferase Inhibition: The Role of K-Ras. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 8433–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambade, M.J.; Peters, E.C.; Thomas, N.E.; Kaufmann, W.K.; Kimple, R.J.; Shields, J.M. Melanoma cells show a heterogeneous range of sensitivity to ionizing radiation and are radiosensitized by inhibition of B-RAF with PLX-4032. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 98, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.J.; Barker, C.A.; Carvajal, R.D.; Wolchok, J.D.; Chapman, P.B.; Lacouture, M.E. Cutis Verticis Gyrata in Association With Vemurafenib and Whole-Brain Radiotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, e54–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, C.J.; Grossmann, K.F.; Atkins, M.B.; Suneja, G.; Tarhini, A.A.; Kirkwood, J.M. Avoiding Severe Toxicity From Combined BRAF Inhibitor and Radiation Treatment: Consensus Guidelines from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 95, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, C.J.; Ribas, A.; Grossmann, A.H.; Chen, X.; Narra, K.K.; Akerley, W.; Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Noyes, R.D.; Shrieve, D.C.; Grossmann, K.F. Severe Liver and Skin Toxicity After Radiation and Vemurafenib in Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, e283–e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forschner, A.; Zips, D.; Schraml, C.; Röcken, M.; Iordanou, E.; Leiter, U.; Weide, B.; Garbe, C.; Meier, F. Radiation recall dermatitis and radiation pneumonitis during treatment with vemurafenib. Melanoma Res. 2014, 24, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, T.; Hong, A.; Clements, A.; Forstner, D.; Suchowersky, A.; Guminski, A.; McNeil, C.; Hersey, P.; Fogarty, G.; Kefford, R.; et al. Acute Radiation Skin Toxicity Associated With BRAF Inhibitors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, e17–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conen, K.; Mosna-Firlejczyk, K.; Rochlitz, C.; Wicki, A.; Itin, P.; Arnold, A.W.; Gross, M.; Zimmermann, F.; Zippelius, A. Vemurafenib-Induced Radiation Recall Dermatitis: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Dermatology 2014, 230, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.; Sterzing, F.; Enk, A.H.; Hassel, J.C. Cutis verticis gyrata-like skin toxicity during treatment of melanoma patients with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib after whole-brain radiotherapy is a consequence of the development of multiple follicular cysts and milia. Strahlenther. und Onkol. 2014, 190, 1080–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, M.; Zimmer, L.; Loquai, C.; Weishaupt, C.; Gutzmer, R.; Schuster, B.; Gleisner, S.; Schulze, B.; Goldinger, S.M.; Berking, C.; et al. Radiosensitization by BRAF inhibitor therapy—mechanism and frequency of toxicity in melanoma patients. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuvrel, L.; Ruellan, A.-L.; Thillays, F.; Quereux, G.; Brocard, A.; Saint-Jean, M.; Aumont, M.; Drouet, F.; Dreno, B. Severe radiotherapy-induced extracutaneous toxicity under vemurafenib. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2013, 23, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascierto, P.A.; McArthur, G.A.; Dréno, B.; Atkinson, V.; Liszkay, G.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; Mandalà, M.; Demidov, L.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Thomas, L.; et al. Cobimetinib combined with vemurafenib in advanced BRAFV600-mutant melanoma (coBRIM): updated efficacy results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Ascierto, P.A.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.; Mandala, M.; Liszkay, G.; Garbe, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Krajsova, I.; Gutzmer, R.; et al. Encorafenib plus binimetinib versus vemurafenib or encorafenib in patients with BRAF -mutant melanoma (COLUMBUS): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foppen, M.H.G.; Boogerd, W.; Blank, C.U.; van Thienen, J.V.; Haanen, J.B.; Brandsma, D. Clinical and radiological response of BRAF inhibition and MEK inhibition in patients with brain metastases from BRAF-mutated melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2018, 28, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Mandalà, M.; Ferrucci, P.F.; Guidoboni, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Ferraresi, V.; Arance, A.; Guida, M.; Maiello, E.; Gogas, H.; et al. Sequencing of Ipilimumab Plus Nivolumab and Encorafenib Plus Binimetinib for Untreated BRAF-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma (SECOMBIT): A Randomized, Three-Arm, Open-Label Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.B.; Lee, S.J.; Chmielowski, B.; Tarhini, A.A.; Cohen, G.I.; Truong, T.-G.; Moon, H.H.; Davar, D.; O'Rourke, M.; Stephenson, J.J.; et al. Combination Dabrafenib and Trametinib Versus Combination Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Patients With Advanced BRAF-Mutant Melanoma: The DREAMseq Trial—ECOG-ACRIN EA6134. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, L.; Scott, C.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.; Phillips, T.; Wasserman, T.; McKenna, W.G.; Byhardt, R. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, M.; Switchenko, J.M.; Press, R.H.; Jhaveri, J.; Buchwald, Z.S.; Blumenfeld, P.A.; Marwaha, G.; Diaz, A.; Wang, D.; Abrams, R.A.; et al. Post-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts for overall survival in brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. J. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 139, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, H.; Nakamatsu, K.; Anami, S.; Fukuda, K.; Inada, M.; Tatebe, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Kanamori, S.; Monzen, H.; Nishimura, Y. Neutrophil–to–Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Survival After Whole-brain Radiotherapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Vivo 2019, 33, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Brain metastases | Alone With other brain metastases |
| Primary lesion | Controlled Uncontrolled |
| Primary lesion site | Lung Breast Other |
| Histology | Squamous Adenocarcinoma Large cell Small cell Melanoma NSC Other |
| Prior brain surgery | None Yes |
|
Time interval from diagnosis of primary to brain metastases |
≤ 2 years > 2 years |
|
Headache |
Absent Present |
|
Seizure |
Absent Present |
|
Visual disturbance |
Absent Present |
|
Neurologic function |
None Minor Moderate Major |
|
Midline shift |
No Yes |
|
Mass effect |
No Yes |
|
Location of lesions |
Frontal Temporal Parietal Occipital Basal ganglia/thalamus Cerebellum Brainstem |
|
Sentinel location of lesions |
Frontal Temporal Parietal Occipital Basal ganglia/thalamus Cerebellum Brainstem |
|
Sentinel lesion side |
Left Right Midline |
|
Necrotic center |
No Yes |
|
Number of lesions |
Single Multiple |
|
Tumor response |
Complete Partial Stable Progression |
|
KPS |
30-40 50-60 70-80 90-100 |
|
Area (mm2) |
0-400 401-900 901-1600 > 1601 |
|
Age (years) |
< 40 40-44 45-49 50-54 55-59 60-64 65-69 > 70 |
|
Total dose (cGy) |
2400-3499 3500-4000 4001-5279 5280-6079 6080-6719 6720-9000 |
| Variable | Comparison | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Brain metastases | alone vs with other metastases | < 0.0001 |
| KPS | ≥ 70 vs < 70 | < 0.0001 |
| Age (years) | < 65 vs ≥ 65 | < 0.0001 |
| Prior surgery | no vs yes | 0.005 |
| Histology | squamous vs small cell vs others | < 0.0001 |
| Primary lesion | controlled vs uncontrolled | < 0.0001 |
| Primary site | breast vs lung and others | 0.001 |
| Time interval | < 2 years vs > 2 years | 0.004 |
| Number of lesions | single vs multiple | 0.021 |
| Sentinel lesion side | left and/or right vs midline | 0.038 |
| Sentinel location | frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital and basal ganglia/thalamus vs cerebellum and brainstem | 0.033 |
| Neurologic function | no vs yes | < 0.0001 |
| Headache | no vs yes | 0.003 |
| Total dose (cGy) | ≥ 5200 vs < 5200 | < 0.0001 |
| Tumor response | complete or partial vs stable or progressive | 0.019 |
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | ≤ 62 ≥ 63 |
| Gender | Male Female |
| KPS | < 70 70 > 70 |
| Interval from diagnosis of NSCLC to WBRT | ≤ 1 months ≥ 2 months |
| Pre-WBRT systemic treatment | No Yes |
|
Control of the primary tumor |
No Yes |
|
Number of intracerebral metastases |
1-3 ≥ 4 |
|
Metastasis outside the brain |
No Yes |
| Variable | Factor Score |
|---|---|
|
Age (years) ≤ 62 ≥ 63 |
4 2 |
|
KPS < 70 70 > 70 |
1 3 5 |
|
Pre-WBRT systemic treatment No Yes |
2 4 |
|
Number of intracerebral metastases |
|
| 1-3 ≥ 4 Metastasis outside the brain No Yes |
4 2 5 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





