1. Introduction
Hydrogen is seen as a critical component of greening Europe’s energy market to be the first carbon-neutral by 2050 worldwide [
1,
2]. In the context of building a hydrogen economy by gradual transformation of energy industry by using ecological, so-called "green hydrogen" as an energy carrier, the challenge aimed at the safety and reliability of hydrogen production, storage and distribution is becoming upmost crucial [
3,
4,
5,
6]. From the viewpoint of the use of suitable metallic materials for constructing of any equipment exposed to hydrogen, it is necessary to consider eventual possibility for the occurrence of a material degradation phenomenon called hydrogen embrittlement (HE) or hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC). This type of degradation refers to environmental embrittlement of metallic materials by the action of atomic hydrogen having the ability to diffuse into the microstructure of the metals from surrounding environment even at room temperature [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Although intensive research on hydrogen embrittlement has been carried out for several decades, it cannot be concluded that there exists single universal mechanism to explain the action of hydrogen in microstructures of various materials. Nevertheless, it is well-known that a key role in terms of the interaction of diffusible hydrogen with the microstructure having a decisive effect on the material susceptibility to HE, is played by so-called "hydrogen traps" formed by various microstructural or substructural objects capable of attracting and trapping free atomic hydrogen. These traps are various defects of the metal crystal lattice (e.g. dislocations, vacancies, substitution atoms, precipitates, inclusions, etc.) showing the existence of internal stresses in their surroundings [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. Thus there are significant differences in the HE resistance among different classes of metallic materials taking into account not only their varying chemical compositions but also their various processing and service conditions influencing their crystallographic structures and phase composition characteristics.
In our previously published works [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24], we have investigated the effects of various conditions of heat treatment, long-term isothermal expositions and electrolytic hydrogen charging of welded joints of advanced creep-resistant steels on their mechanical and brittle-fracture properties. In these complex material systems, certain small improvements in their HE resistance were observed after laboratory high-temperature ageing experiments which could be explained by internal stress relieving as well as by additional precipitation of fine carbide particles leading to irreversible hydrogen trapping at the carbide/matrix interfaces [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. However, at the same time, gradual development of thermal embrittlement was clearly observed due to precipitate coarsening of several secondary phases (e.g. special alloy carbides and intermetallic phases) with increasing duration of thermal exposure. The results of our recent study [
25] about HE behavior of plastically pre-strained and cathodically hydrogen charged AISI 316H austenitic stainless steel have shown that this material subjected to room-temperature static tensile testing in its solution-annealed (precipitation-free) material condition showed rather small susceptibility to HE and its tendency for HE with increasing the plastic pre-straining was only slightly increasing. It has been concluded that the observed degradation of deformation properties of plastically pre-strained and hydrogen-charged materials was predominantly caused not by HE but by gradual plasticity exhaustion due to excessive, strain-induced generation and multiplication of slip dislocations causing deformation hardening.
The present work is aimed at continuation of our former study which was focused on characterization of HE behavior of solution-annealed and variously pre-strained AISI 316H steel in room-temperature static tensile testing conditions. The currently performed investigation is about the effects of cathodic hydrogen charging on the mechanical response of the same AISI 316H material in dynamic loading conditions employing the Charpy impact bending tests and dry linear sliding tribological tests at room temperature. The obtained results of mechanical and tribological tests are discussed in terms of possible correlations among microstructural features, fracture surface characteristics, and acting tribological mechanisms.
2. Experimental Material and Methods
The input experimental material was a seamless tube (38 mm outer diameter, 6 mm wall thickness) of 1050°C solution annealed and water-quenched AISI 316H stainless steel. With respect to its high elemental alloying (in wt.%), including 0.05 C, 0.51 Si, 1.77 Mn, 16.76 Cr, 2.05 Mo, 11.13 Ni and rest Fe, this material can be regarded as non-equiatomic medium-entropy alloy as also reported in [
26]. The response of the investigated material to dynamic mechanical loading in the initial non-hydrogenated state (i.e. without hydrogen charging) and then also in hydrogenated state (i.e. after electrochemical hydrogen charging at room temperature in a solution of 1 M HCl with 0.05M N
2H
6SO
4 at a current density of 20 mA/cm
2 for 24 hours) was evaluated from the Charpy impact bending tests and dry linear sliding tribological tests at room temperature. The used electrolytic hydrogenation procedure was selected based on our former studies [
23,
24] which indicated unchanging course of deformation properties of hydrogenated steel specimens after exceeding 24 hours of hydrogen charging time, giving the rise for the assumption of their full hydrogen saturation. The electrolytic hydrogen charging of individual specimens of investigated material was performed by using potentiostat/galvanostat model 173 (Princeton Applied Research, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA).
The concentration of the absorbed hydrogen within electrochemically hydrogenated specimen was calculated on the base of the method of hydrogen electrochemical oxidation (HEO) which has been principally defined and described in [
27] and commonly used by many other authors, e.g. [
28,
29,
30]. HEO was conducted out from solution containing 1mol.dm
-3 NaOH and 8 g.dm
-3 of thiourea as a hydrogen recombination poison to avoid H
2 gas evolution, using modular potentiostat/galvanostat Autolab Vionic (Metrohm, Utrecht, Netherlands) in conventional three electrode cells under laboratory temperature. Hydrogenated specimen with surface area 6.7 cm
2 was used as a working electrode and saturated Ag/AgCl and platinum electrode (1×1 cm
2) as a reference and counter electrode, respectively. The applied potential E = -0.9 V was maintained for 1000 s to ensure complete hydrogen oxidation.
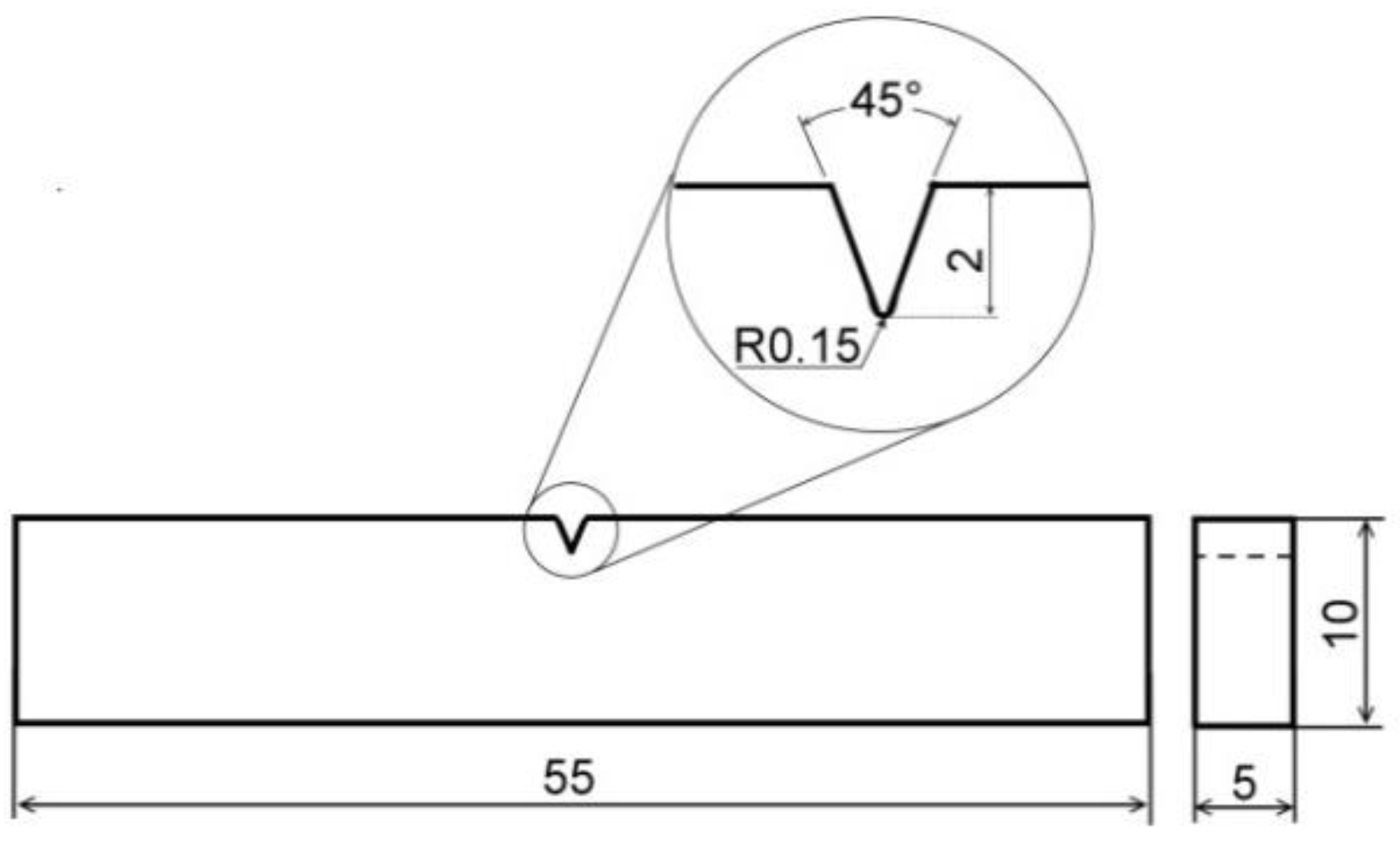
The electrochemically hydrogenated specimens for mechanical and tribological tests were shortly stored in liquid nitrogen immediately after the hydrogen charging. Then, one by one, the specimens were gradually warmed up on still air to room temperature and consecutively subjected to individual testing procedures. A schematic view of employed sub-sized Charpy V-notch (CVN) impact bending test specimen is shown in
Figure 1.
Conventional Charpy pendulum impact tester PSW 30 (VEB Werkstoffprüfmaschinen Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany) with a 300 J impact energy pendulum hammer was employed to determine the CVN impact toughness in conformity with standard ISO 148-1:2016 [
31]. Three individual tests were performed for each material condition. The HE resistance of studied material was determined by calculation of HE index from the results of performed Charpy impact bending tests of non-hydrogenated and hydrogen-charged test specimens. The hydrogen embrittlement index (HEI) was calculated as a relative change in average CVN impact toughness values between the non-hydrogenated and hydrogen-charged test specimens according to the following formula:
The subscripts “0” and “H” refer to the non-hydrogenated and hydrogen-charged material states, respectively. The dehydrogenated Charpy impact bending test specimens obtained by long-term room-temperature holding (25°C/30 days) of originally hydrogenated specimens in dry air environment were also examined. The tribological tests were carried out on metallographically polished surfaces of the same flat prismatic samples as used for the CVN impact toughness tests. These tests were performed in the mode of dry linear sliding at room temperature using SiC ball (5 mm diameter) counterpiece, 10 N loading force, 10 cm/s sliding speed, and 250 m sliding distance. The tribological testing apparatus was universal tribometer BRUKER UMT 3 (Bruker Nano GmbH, Berlin, Germany). The tribological tests were carried out in conformity with standard ASTM G133-05(2016) [
32]. Preliminary microstructural observations were performed by using light optical microscope (LOM) OLYMPUS GX71 (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Detailed microstructural and fractographic analyses including crystallographic orientation measurements and phase mapping analyses were carried out using the scanning electron microscope (SEM) JEOL JSM-7000F (Jeol Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) linked with electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) detector Nordlys-I (HKL technology A/S, Hobro, Denmark). The EBSD analyses were performed on a drawing direction plane (405 μm by 315 μm in size) of prepared metallographic cross-sections and the obtained data were processed by using software CHANNEL-5, HKL (Service pack 7). Detailed morphological observations of tribological tracks including semi-quantitative chemical micro-analyses in selected locations were performed using SEM TESCAN Vega-3 LMU (TESCAN Brno, s.r.o., Brno, Czech Republic) and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectrometer BRUKER XFlash Detector 410-M (Bruker Nano GmbH, Berlin, Germany). Topographical measurements of tribological profiles and specific wear rate determination were performed by using confocal microscope PLu neox 3D Optical Profiler (SENSOFAR, Barcelona, Spain) employing standard evaluation procedure described for instance in [
33].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of solution-annealed material
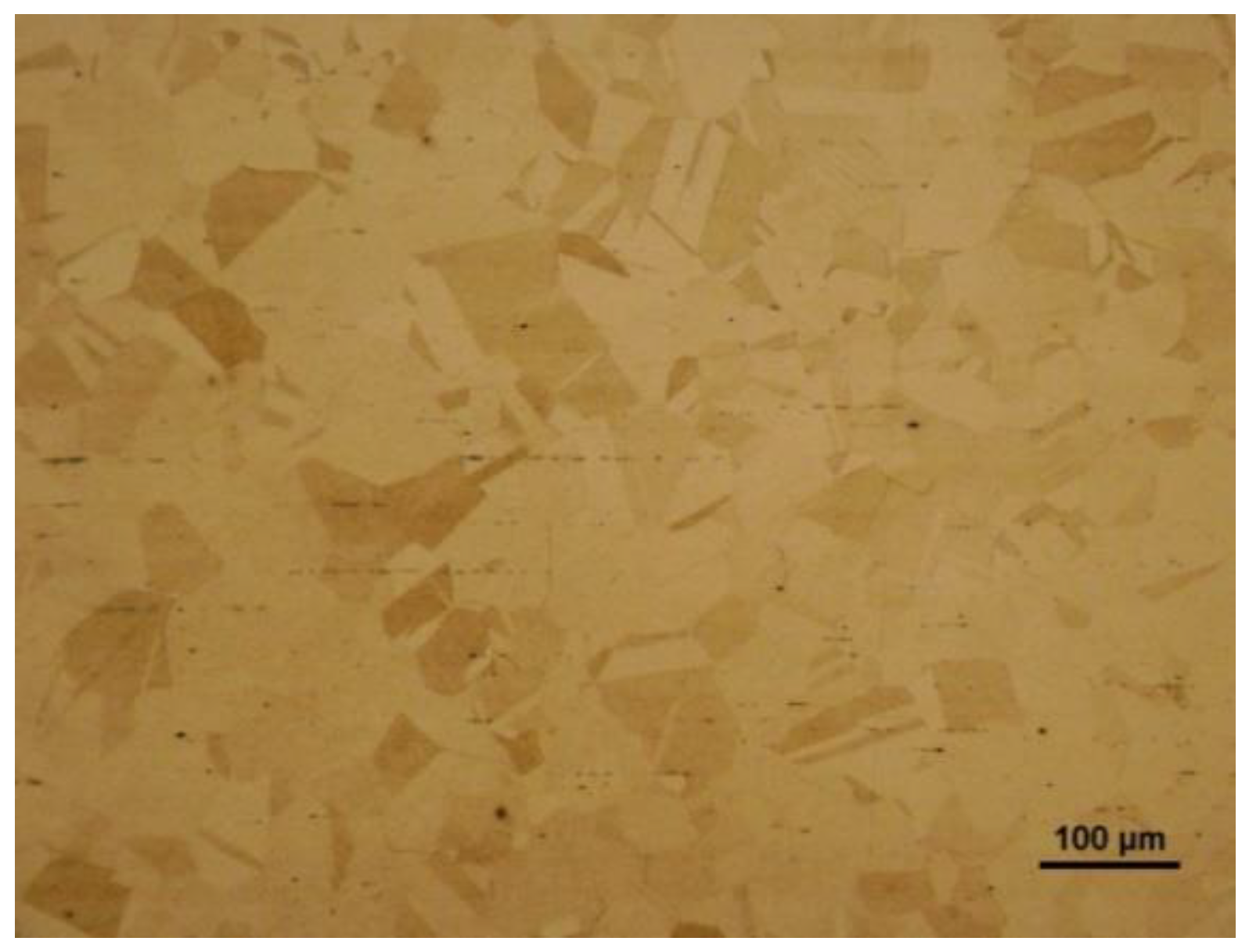
A typical light-optical microstructure of solution-annealed AISI 316H steel is depicted in
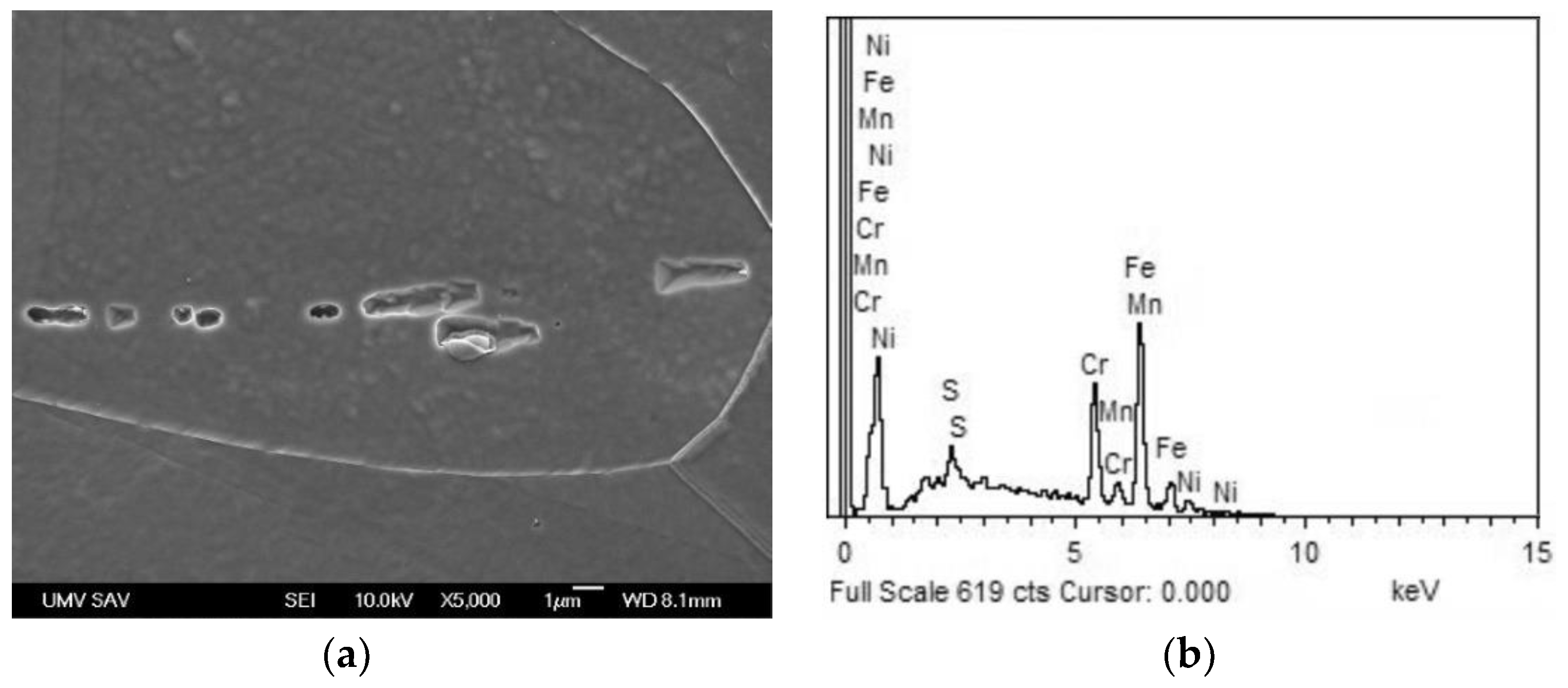
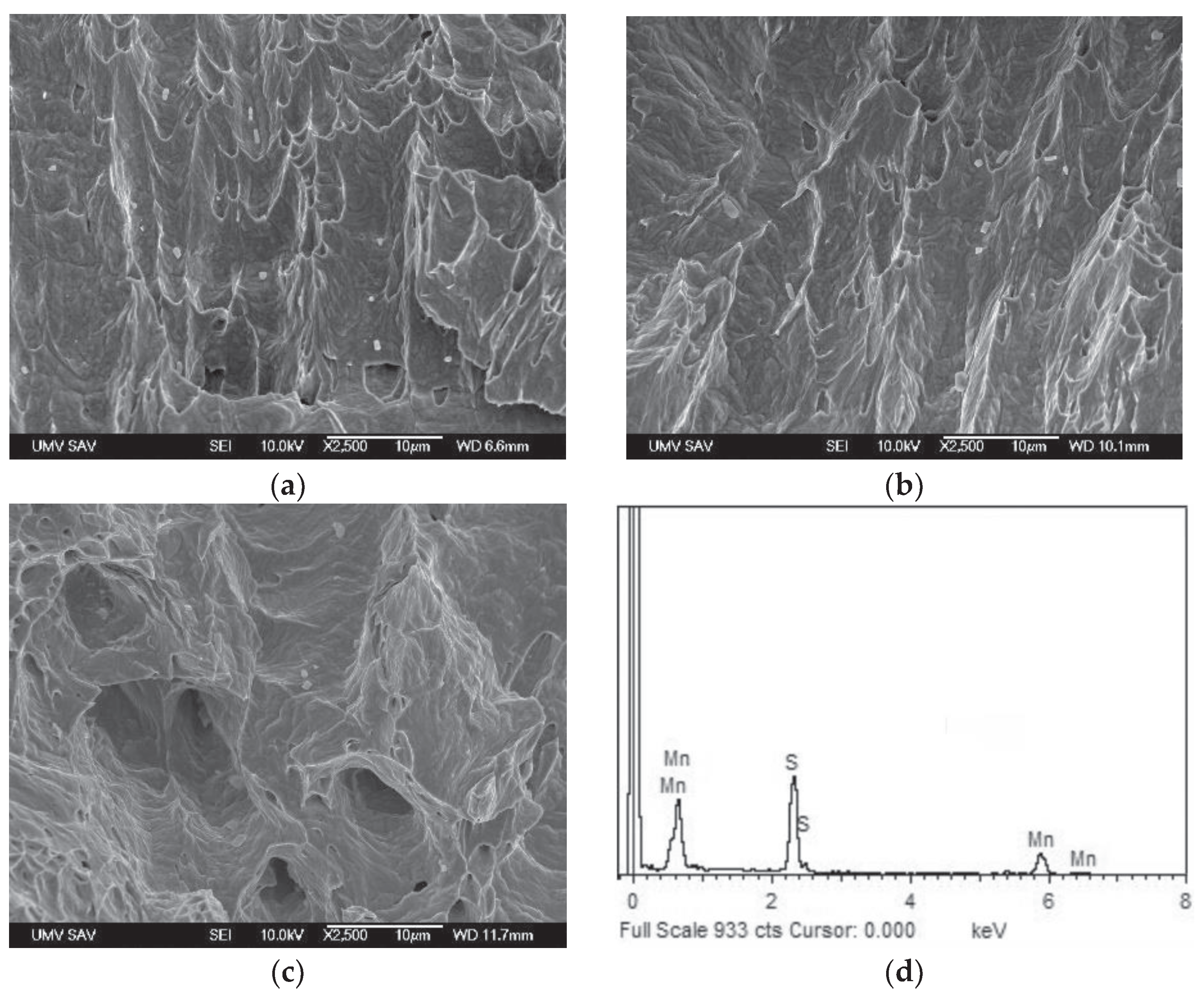
Figure 2 showing polygonal grain structure with presence of annealing twins and longitudinal inclusions in form of dark-appearing chain-like structures. The qualitative chemical micro-analysis of these inclusions was carried out by the combination of SEM and EDX measurement which indicated them to be likely the MnS particles (
Figure 3). The more focused EDX analyses of anticipated MnS inclusions were also carried out on the fracture surfaces of broken CVN test specimens (see further in
Section 3.3).
The results of detailed microstructural analyses of the as-received AISI 316H material were already presented in our previous study [
25]. As also shown here in
Figure 2, it has been concluded that the initial material exhibits polygonal grains with abundant occurrence of annealing twin boundaries. By means of both X-ray diffraction and EBSD phase mapping, the matrix microstructure was found to be a single-phase austenitic structure with face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal lattice [
25]. Minor occurrence of MnS inclusions was not detectable by the used techniques. Random distribution of crystallographic planes did not indicate any pronounced crystallographic texture [
25].
3.2. Determination of Absorbed Hydrogen
As already stated, the concentration of the absorbed hydrogen in CVN impact toughness test specimen was determined immediately after the process of cathodic hydrogen charging by the method of hydrogen electrochemical oxidation (HEO). The calculation of hydrogen amount was done according to formula:
Where QH is the charge value passed through the sample during anodic polarization, in our case at E = -0.9 V, z is the number of electrons take in reaction, F is the Faraday constant and ν is the effective volume of the sample. In our case, we assumed that hydrogen penetrates to a depth of 1 mm, which represents the effective volume 0.67 cm
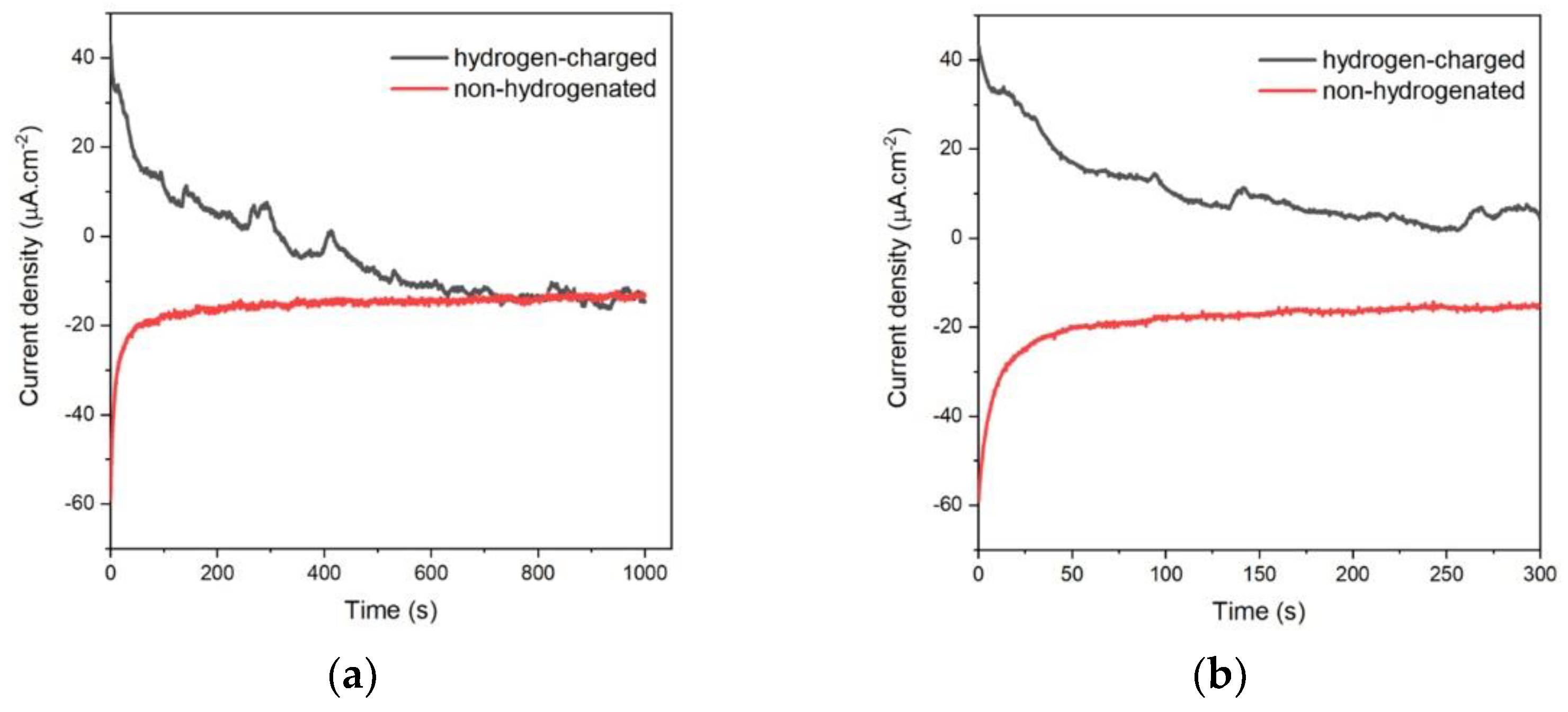
-3. As can be seen from
Figure 4a, during the polarization of hydrogen-charged working electrode at E = - 0.9 V the current drops after first 100 s to value close to the zero, which means that thy hydrogen oxidation reaction is very fast and after 300 s the passivation process occurs. On the other hand, the blank experiment was done with the same sample without hydrogen charging. It is clearly visible from the red curve, that in the case of the same polarization conditions, only the passivation of the sample surface occurs. Finally, the passed charge was calculated by integration of I-t (
Figure 4b) curve in range of 0 – 300 s and the charge value is found as QH = 3.63×10
-3 C.cm
-2. Based on Faraday’s law it corresponds to CH = 3.756 × 10-7 mol.cm
-3. Usually, the hydrogen concentration at saturation in steel is stated in wppm. Thus after employing corresponding calculation procedures detailed in e.g. [
34,
35,
36], the hydrogen concentration reaches a value of 0.47 wppm.
3.3. Effect of Hydrogen Charging on CVN impact toughness
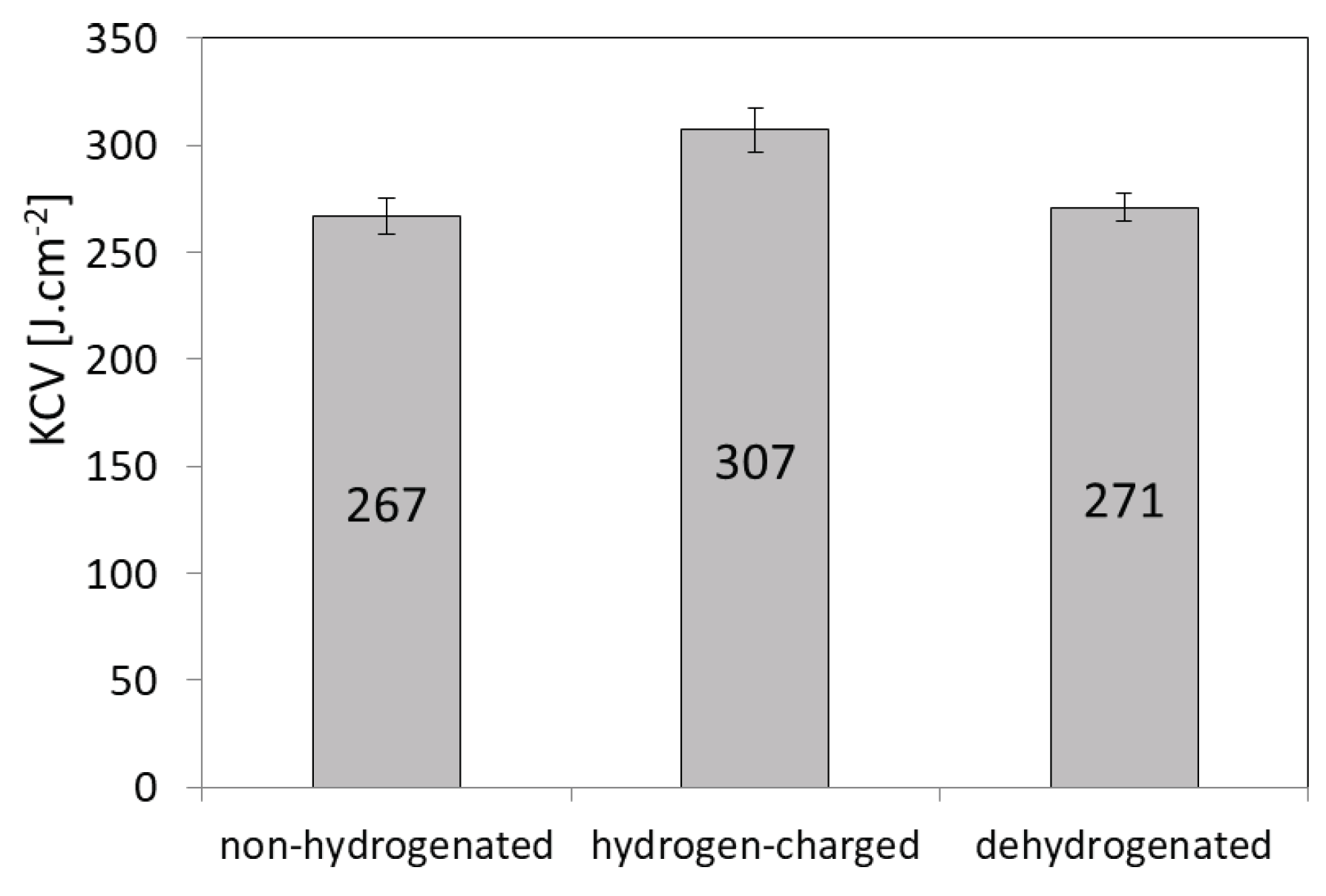
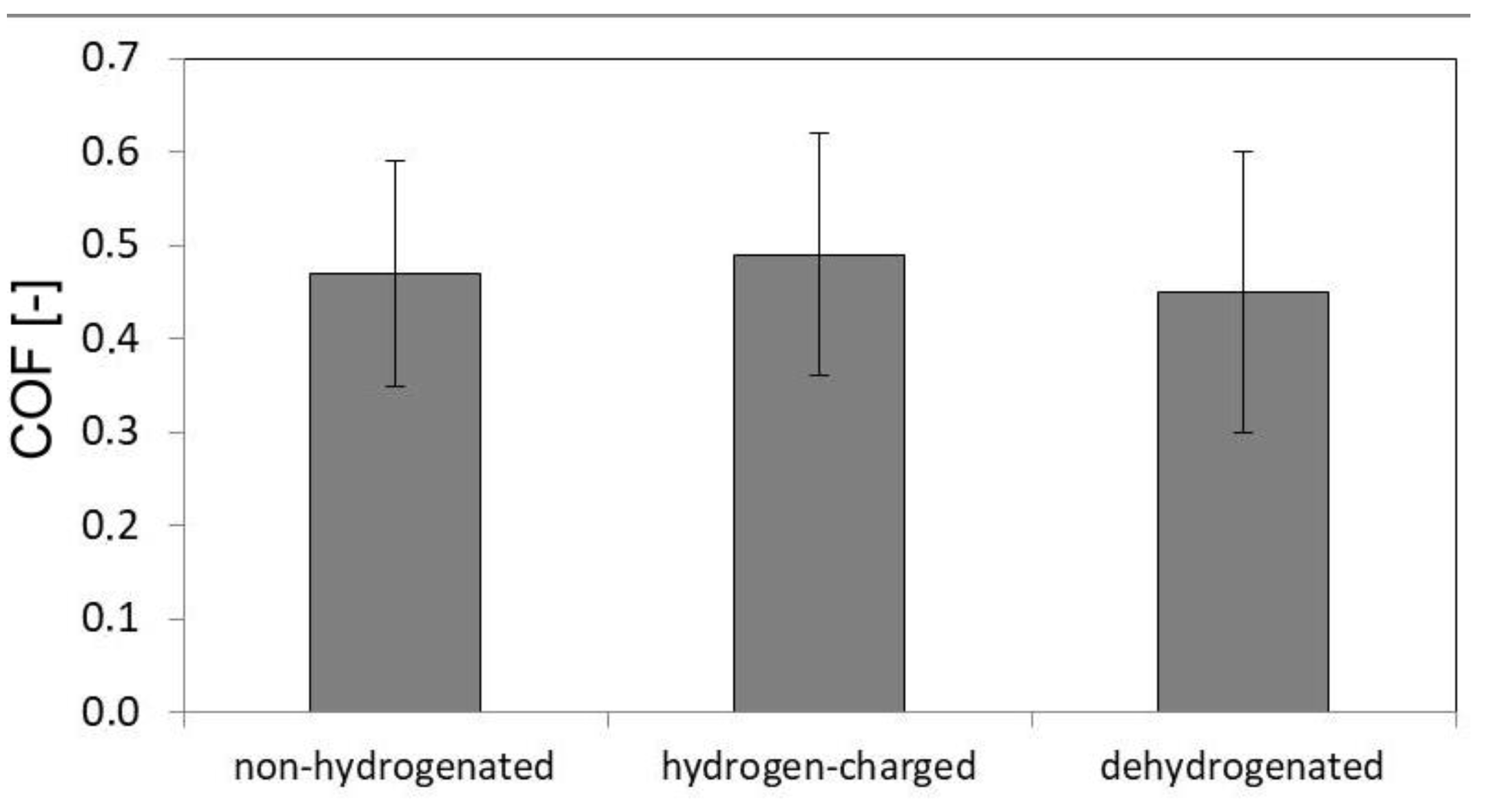
Figure 5 shows average CVN impact toughness values in non-hydrogenated, hydrogen-charged, and dehydrogenated material conditions. It can be seen that the effect of hydrogen charging on CVN impact toughness value was rather small.
The comparison of individual fracture surfaces corresponding to individual material conditions did not reveal any significant differences in fracture micro-mechanisms among individual test specimens (see
Figure 6).
However, as visible in
Figure 5, it is interesting to note that the hydrogen-charged CVN test specimens clearly exhibited a small increase of CVN impact toughness value compared to the non-hydrogenated test specimens. The actual occurrence of slight toughening effect due to hydrogen charging has been additionally verified by the results of performed CVN impact toughness tests on the dehydrogenated test specimens. The obtained results clearly indicated reversibility in dynamic mechanical behavior due to performed dehydrogenation, i.e., the possibility for the original property restoration thanks to hydrogen desorption (see
Figure 5). This double-check for the results of dynamic mechanical tests of CVN test specimens without hydrogen, i.e. the both non-hydrogenated and dehydrogenated ones, strongly supports the observed findings about the occurrence of dynamic hydrogen-toughening effect in hydrogen-charged AISI 316H material. Thus the calculated hydrogen embrittlement index for the currently studied material was resulting in a negative value, i.e., HEI
CVN = -14.98 %. The negative value of the calculated hydrogen embrittlement index may not be so surprising, since in several other studies about the effect of hydrogen charging on mechanical behavior of FCC structured alloys, similar findings have already been reported about some enhancement of deformation properties by hydrogenation [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46]. However, it should be noted that such behavior related to the enhancement of deformation properties by hydrogen charging, has been typically observed in the high-alloyed metallic systems including mainly the high entropy alloys with FCC crystal structure [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43]. From the viewpoint of acting toughening mechanism, it has been generally accepted that the hydrogen-enhanced twinning-induced plasticity including hydrogen facilitated deformation nano-twinning seemed to be the most likely mechanism of hydrogen-induced ductilization [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46]. Murakami et al. [
45] studied fatigue behavior of 304 and 316L stainless steels and revealed their drastically improved fatigue crack growth resistance upon hydrogen charging. This behavior has been ascribed to the interplay between two competitive roles of hydrogen, namely the dislocation pinning and enhancement of dislocation mobility [
45]. In present investigation the occurrence of deformation twinning has been clearly observed in both the non-hydrogenated and hydrogen-charged test specimens after performed CVN impact toughness bending tests (see
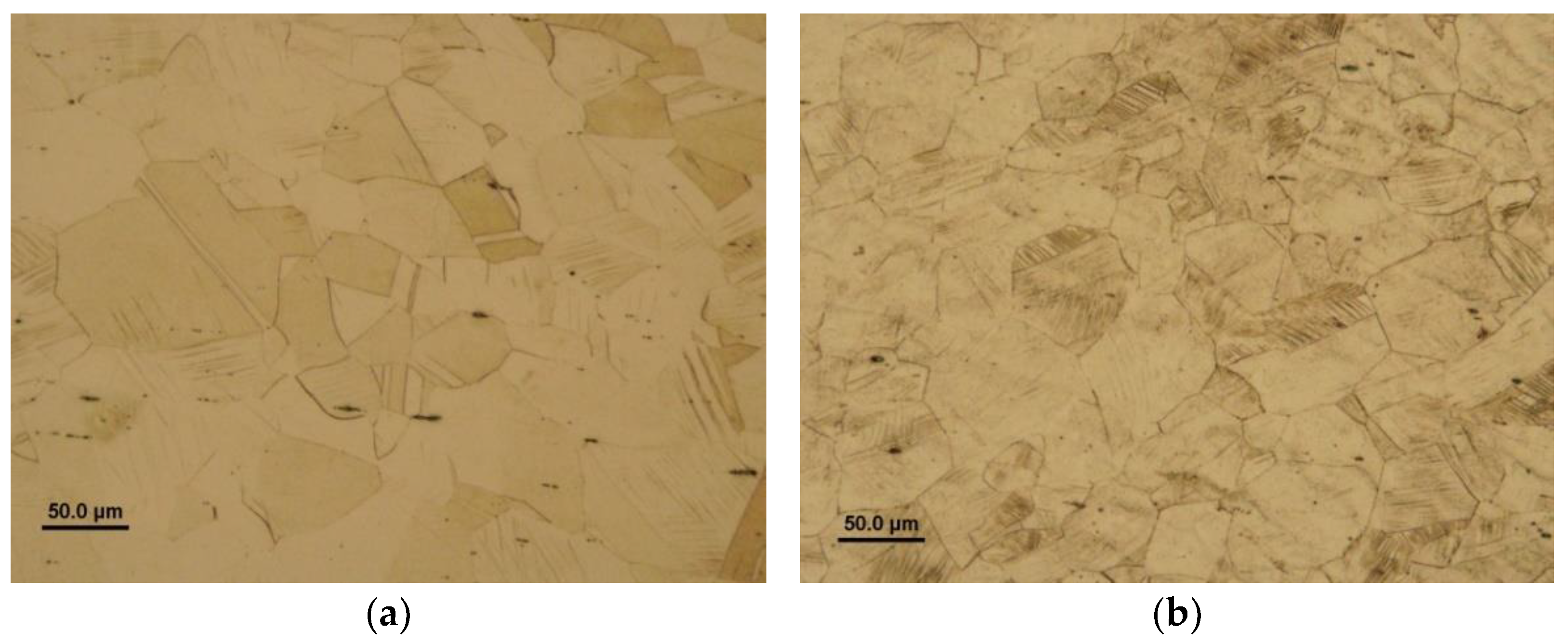
Figure 7). Besides clear occurrence of deformation twinning and intensive slip bands' formation, some random indication of sub-grains has also been observed in the hydrogen-charged material (
Figure 7b) which might be considered the additional toughening effect. On the contrary, no sub-grains were observed in the non-hydrogenated material (
Figure 7a). The toughening effects of microstructural grain refinement are generally well-known and frequently reported in numerous literature sources, e.g. in [
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54] for various classes of structural metallic materials. However, in the case of current investigation it is supposed that the hydrogen-charging might cause just the sub-grain visualization instead of their formation by induced hydrogen. For example, in the study [
55] the origin of sub-grain formation in an austenitic stainless steel was related to the specific mode of its solidification. Thus it is believed that the observed differences in mechanical behavior of currently studied material are mainly attributed to the higher proportion of deformation twinning mechanism in hydrogen-charged material compared to the non-hydrogenated material (
Figure 7) which fairly agrees also with findings of [
56].
In
Figure 8,
Figure 9 and
Figure 10 the results of more focused EBSD crystallographic and phase mapping analyses from the microstructural areas just beneath the fracture locations of the specimens after CVN impact bending tests are visualized. With respect to the relatively small observed difference in measured CVN impact toughness properties between the non-hydrogenated and hydrogen-charged test specimens of studied material, no significant microstructural differences are to be expected between the non-hydrogenated and hydrogen-charged test specimens.
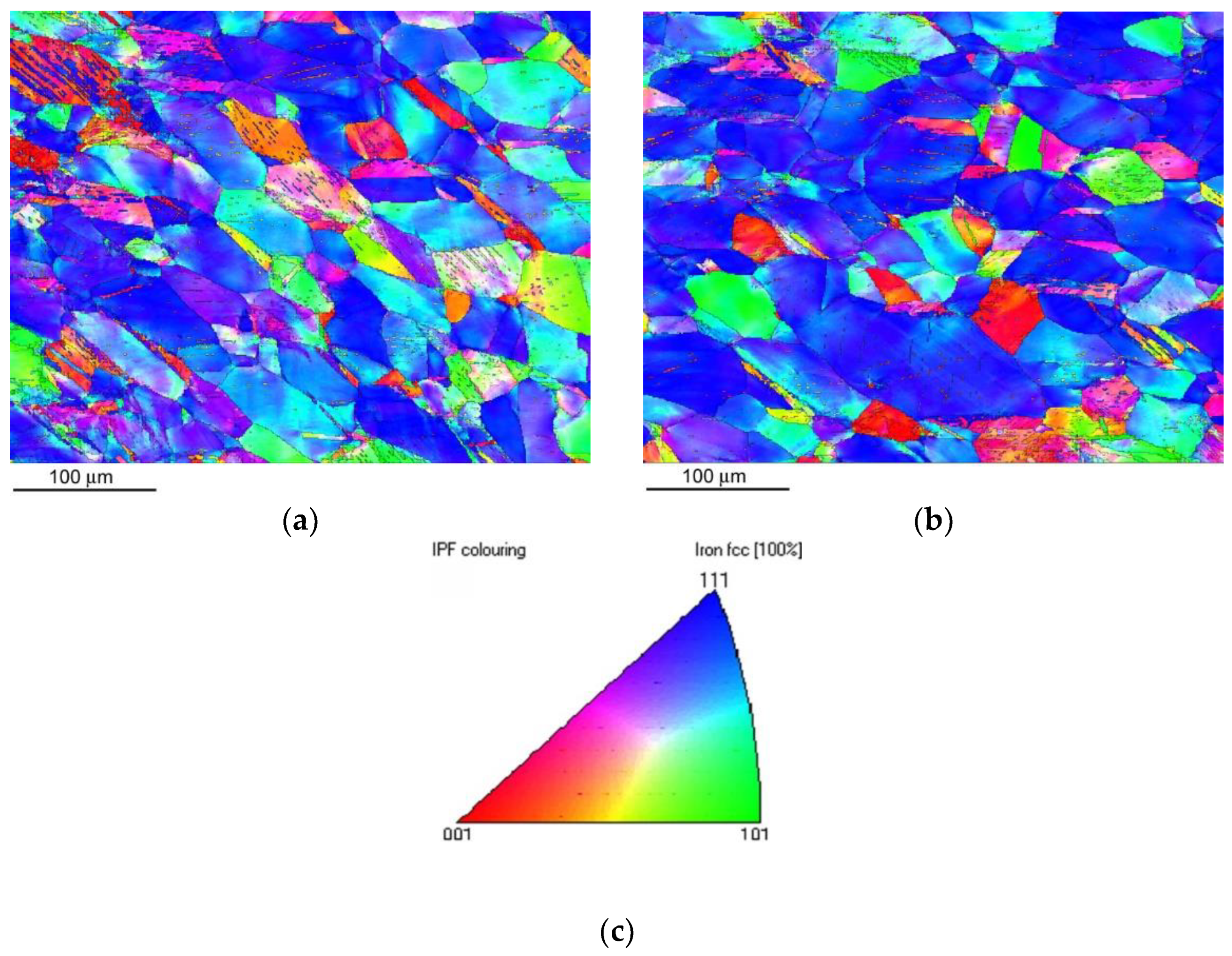
Figure 8 shows crystallographic microstructure visualization by an inverse pole figure (IPF) imaging after CVN impact bending test for the non-hydrogenated (
Figure 8a) and hydrogen-charged (
Figure 8b) CVN test specimen.
Figure 8 indicates highly deformed grain microstructures with a major occurrence of near {111} crystallographic planes besides distinct locations exhibiting higher occurrence of deformation twins which are considered to enhance the material toughening by the effect of twinning-induced plasticity. Due to the very high impact speed of dynamic material testing during the CVN impact bending tests to be about 5.6 m/s, the considerations of the newly formed deformation twins to act like hydrogen diffusion paths can be in this specific case neglected.
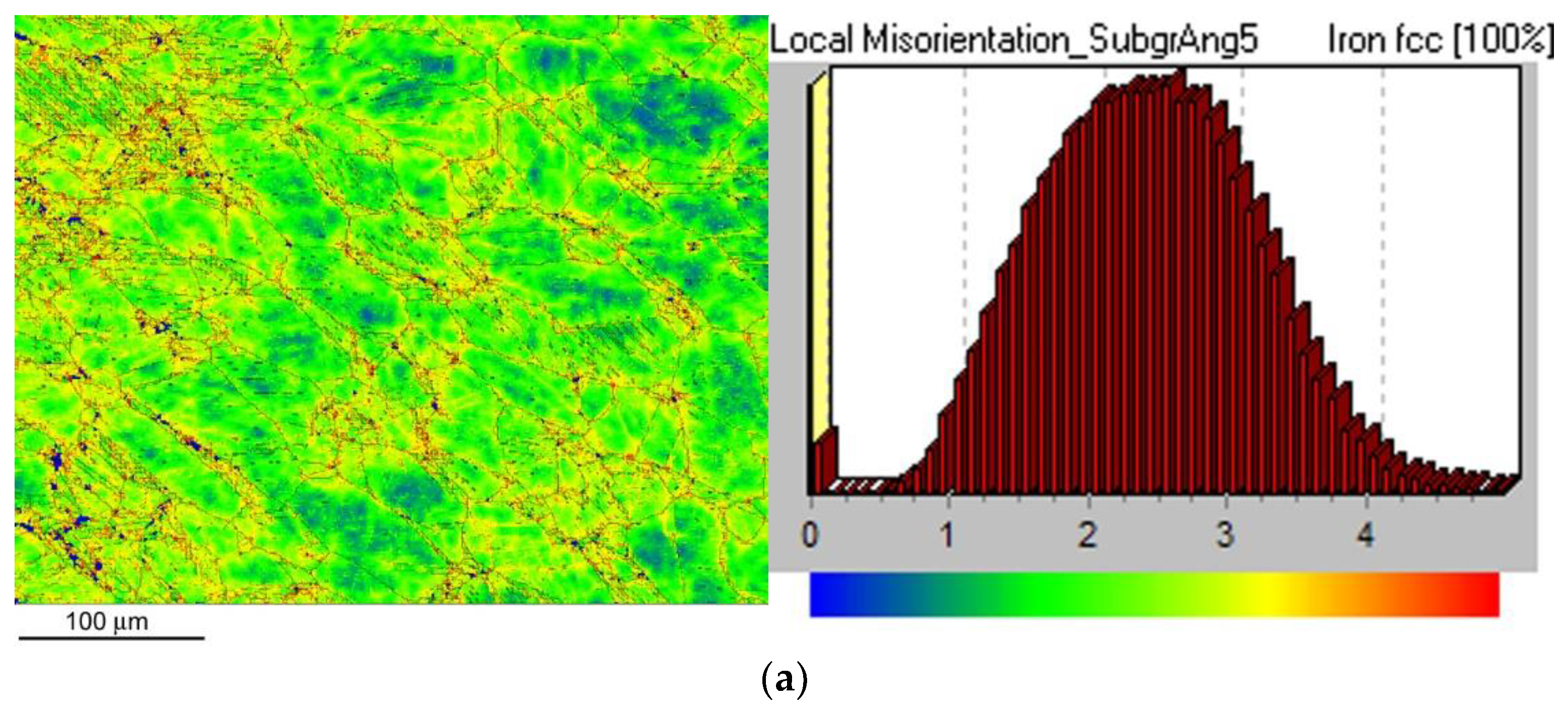
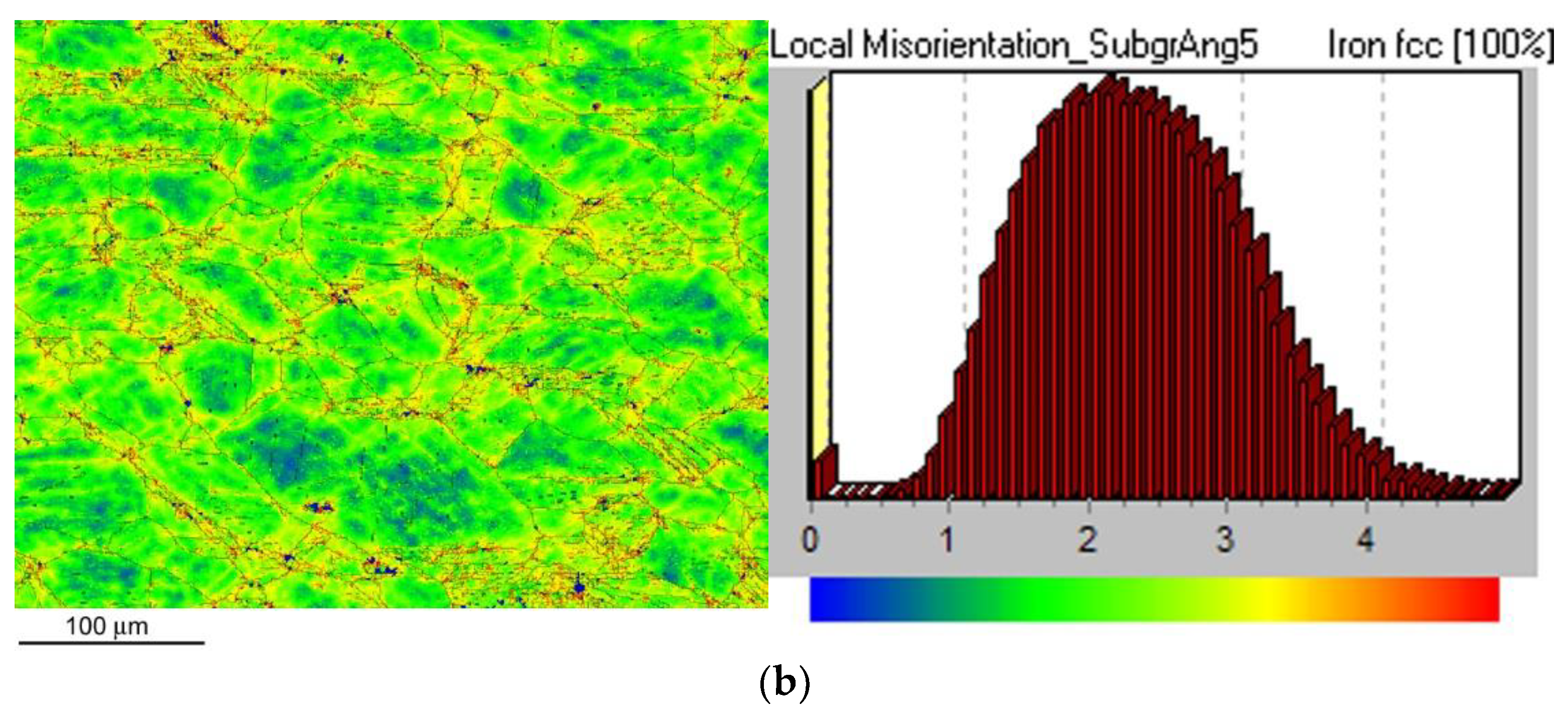
Figure 9 shows local misorientation map (LMM) after CVN impact bending test for the non-hydrogenated (
Figure 9a) and hydrogen-charged (
Figure 9b) CVN test specimen. As expected, by comparison of LMMs of non-hydrogenated and hydrogen-charged test specimens after the CVN impact bending tests, no significant differences in local misorientations were observed between the individual specimens (
Figure 9). In other words, the areas with locally increased misorientations (yellow and red areas) indicating locally increased mechanical strains show very similar characteristics for both material conditions which fairly correlates with measured CVN impact toughness properties (
Figure 5).
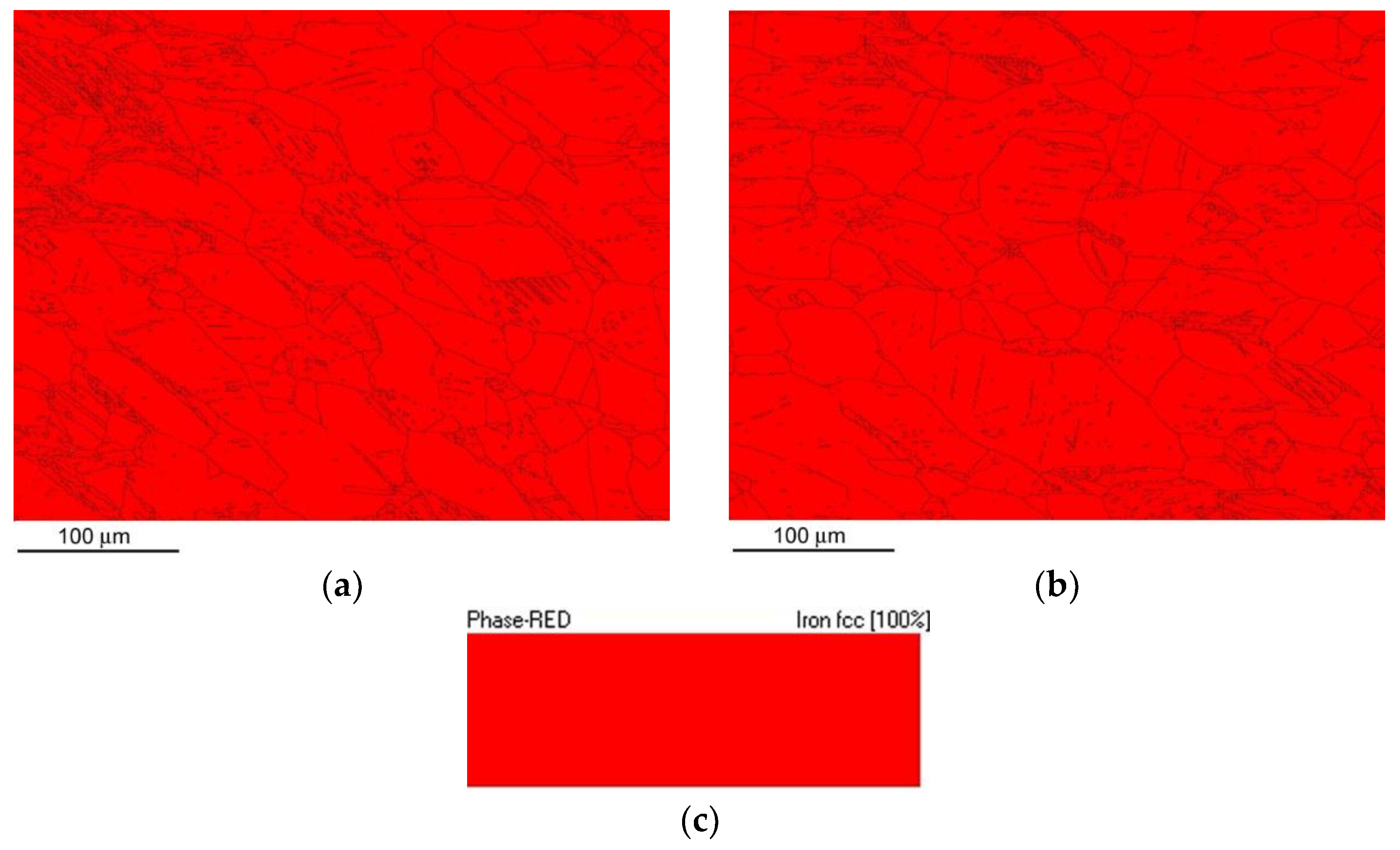
Figure 10 shows the phase mapping EBSD images for the non-hydrogenated (
Figure 10a) and hydrogen-charged (
Figure 10b) AISI 316H material microstructure after performing the CVN impact bending tests. The recorded phase maps (
Figure 10) indicated pure FCC austenitic crystal structure of the CVN impact bending tested specimens in both the non-hydrogenated and hydrogen-charged material conditions. This observation has shown that neither the impact straining nor the electrolytic hydrogenation resulted in any phase changes in studied AISI 316H material states at room temperature.
Thus the microstructural and supplemental EBSD analyses additionally supported conclusions regarding the observed dynamic mechanical behavior of solution-annealed AISI 316H steel, i.e., obviously insignificant effect of applied hydrogen charging on the resulting CVN impact toughness which clearly indicated very good resistance of studied material against hydrogen-related degradation in currently performed hydrogenation experiments.
3.4. Effect of Hydrogen Charging on Tribological Behavior
Figure 11 shows average values of coefficient of friction (COF) of studied AISI 316H material for individual material conditions with respect to the hydrogen charging application.
The results in
Figure 11 indicate that studied material in all material conditions exhibits similar average COF values. The non-hydrogenated material shows slightly lower average COF value (0.47) than the hydrogen-charged material (0.49). The higher average COF value of hydrogen-charged AISI 316H material might be ascribed to slight local overheating of its tribological surface due to decreased thermal conductivity by the presence of hydrogen. Indeed, it has been reported that for pure metals and alloys, the thermal conductivity is reduced because the insertion of hydrogen atoms hinders the thermal conduction of free electrons [
57]. Such behavior was also confirmed by Luo et al. [
58] in their first-principles study dealing with the effect of interstitial hydrogen on the mechanical and thermal properties of tungsten. Thus, it is assumed that the increasing COF values in currently hydrogenated AISI 316H steel is likely attributed to the fact that the hydrogen absorbed within surface layers decreases the material thermal conductivity leading to local superheating and consequently the change of tribological behavior from pure abrasive wear (
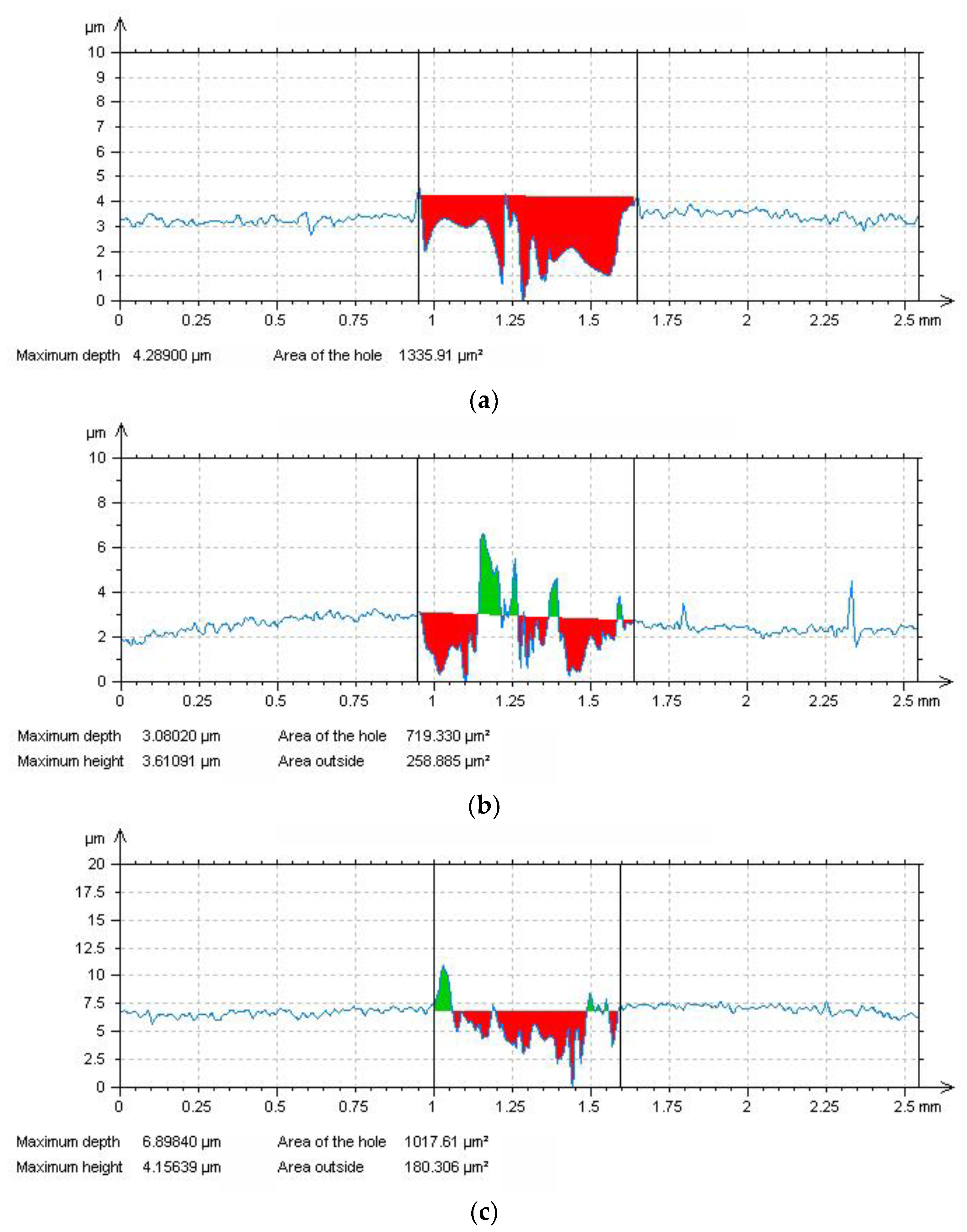
Figure 12a) to the complex abrasive/adhesive wear mechanism (
Figure 12b). For the sake of completeness, the dehydrogenated material was also tribologically tested (
Figure 11) and it was found out that its measured average COF value decreased (0.45), compared to the COF values of the non-hydrogenated (0.47) and hydrogen-charged materials (0.49). The observed decrease in COF value of the dehydrogenated material is likely ascribed to the clear suppression of adhesive wear component which has been clearly observed on corresponding tribological track (
Figure 12c). This behavior might be related to the mitigation of hydrogen-related decrease of thermal conductivity in superficial layers after the dehydrogenation of studied material as well as additional surface oxidation serving as solid lubricating agent during tribological testing [
59].
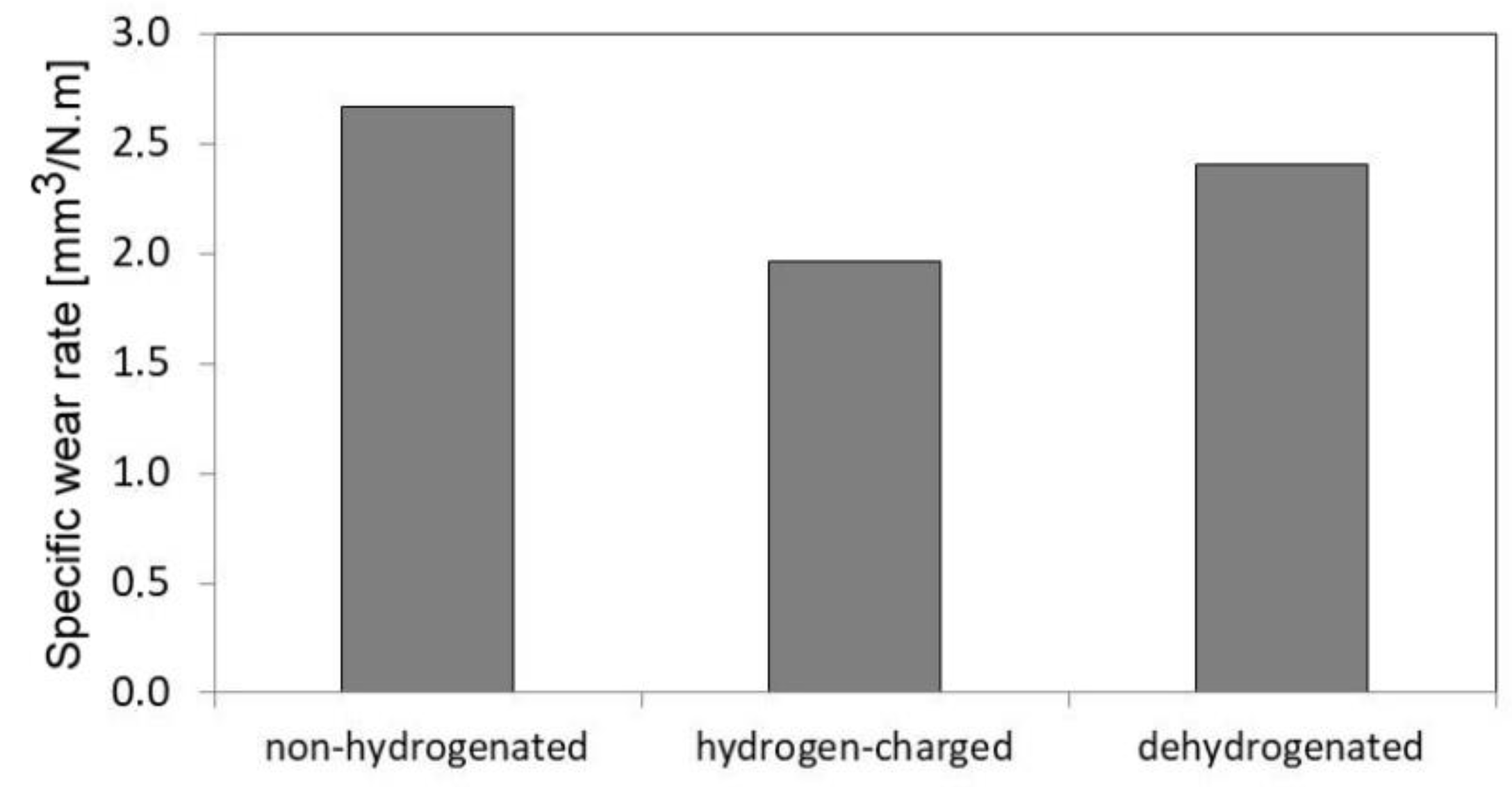
Figure 13 shows average values of specific wear rates of studied AISI 316H material for individual material conditions with respect to the hydrogen charging application.
The highest wear rate shows the non-hydrogenated material (
Figure 13) which exhibits pure abrasive wear mechanism (
Figure 12a). In contrast, both the hydrogen-charged and dehydrogenated materials exhibit much lower wear rates compared with the non-hydrogenated material (
Figure 13) which is probably caused by their complex abrasive/adhesive wear mechanism (
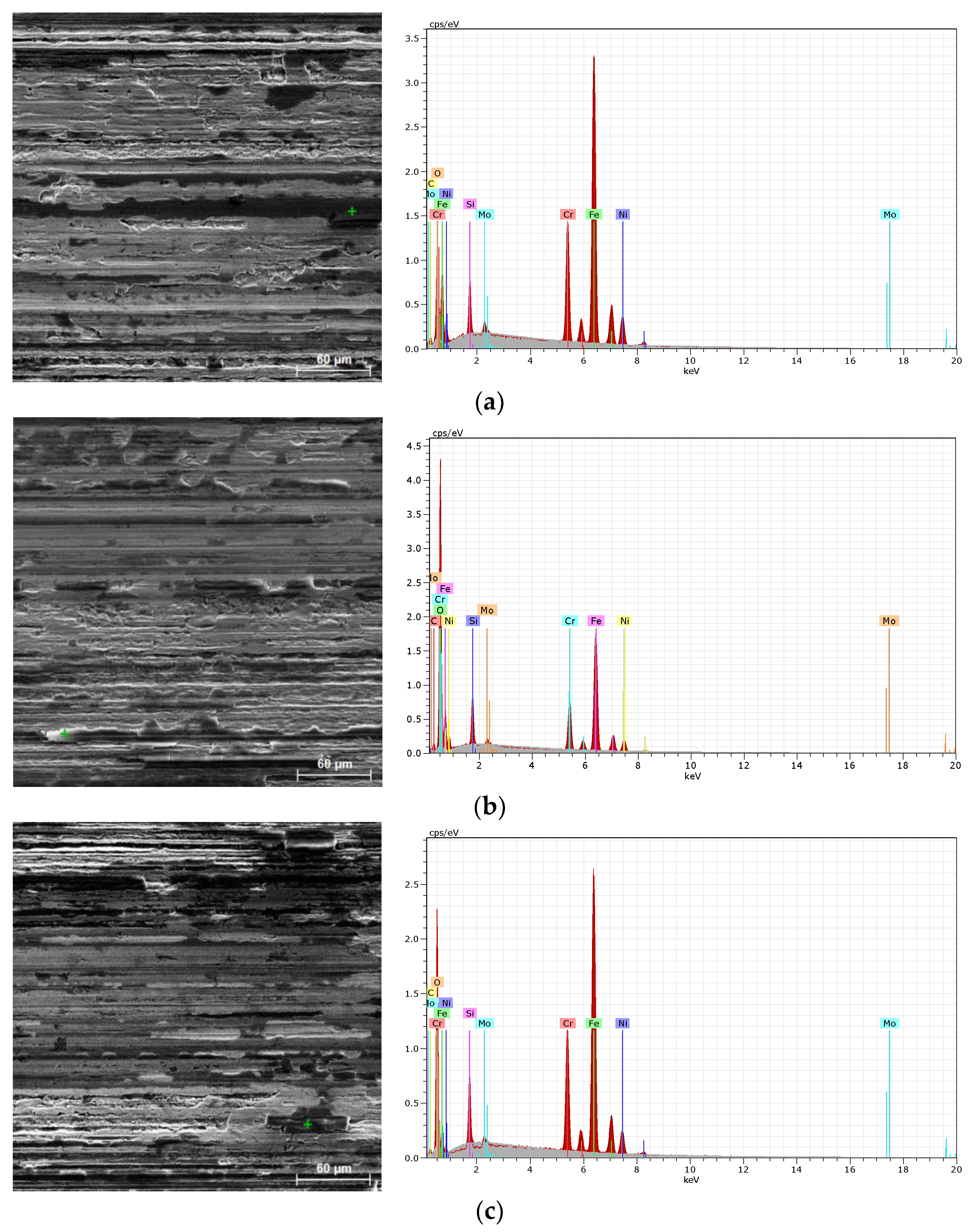
Figure 12b,c). The morphological characteristics of individual tribological tracks are shown on the SEM images in
Figure 14.
From
Figure 14 it can be concluded that all investigated material states exhibited morphologically similar tribological behavior, characterized by plastic deformation and tribo-oxidation reaction of the steel substrate with regular occurrence of SiC debris of tribological ball counter-piece coming out of the tribological track surface. On the whole it can be stated that the results of tribological tests supported the rest findings of present investigation pointing out that the hydrogen-charging of fully-recrystallized AISI 316H steel led to small effects on investigated properties studied under dynamic loading conditions, thus indicating very good resistance of studied material against hydrogen-related degradation in currently applied electrolytic hydrogenation conditions.
4. Summary and Conclusions
Room-temperature mechanical and tribological testing procedures in correlation with microstructural analyses were employed to characterize the applied hydrogen charging effects on AISI 316H grade material. Thus the following conclusions can be summarized:
The EBSD crystallographic phase analyses indicated that the applied electrochemical hydrogen charging and subsequent dynamic loading tests did not result in any phase transformations of studied austenitic steel at room temperature.
The used electrochemical hydrogen charging of investigated material resulted in slight increase of both the CVN impact toughness and COF frictional coefficient. At the same time, the specific wear rate of electrochemically hydrogenated material exhibited a slight decrease compared to the non-hydrogenated material.
The observed slight improvement in CVN impact toughness of electrochemically hydrogenated AISI 316H steel is mainly related to the hydrogen-enhanced twinning-induced plasticity mechanism. However, owing to rather small changes of CVN impact toughness due to hydrogen charging, the hydrogenation effects on microstructural and fractographic characteristics were rather negligible in comparison with the non-hydrogenated material.
The COF increase of hydrogenated material can be ascribed to local overheating of tribological surface due to decreased thermal conductivity by the presence of hydrogen. This conclusion can be supported by the observed transition of acting wear mechanism from pure abrasive wear for the non-hydrogenated material to the more complex abrasion/adhesion wear mechanism for the hydrogen-charged material. The changes of specific wear rates for individual material states also correlate well with observed changes in acting wear mechanisms.
The both CVN impact toughness tests and dry linear sliding tests performed on the dehydrogenated materials indicated their reversible behavior leading to the nearly original properties restoration. On the whole, it can be concluded that the observed hydrogen-induced changes of individual properties determined under dynamic loading conditions, indicated high resistance of studied solution-annealed AISI 316H steel against material degradation in currently performed electrolytic hydrogen-charging experiments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F.; methodology, L.Č., V.P. I.P. and O.P.; formal analysis, L.F.; investigation, L.F., L.Č., O.P. V.P., I.P., K.K., R.D.; data curation, L.Č., O.P., V.P. and I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, L.F. and L.Č.; writing—review and editing, L.F. and L.Č.; visualization, L.Č., O.P. and I.P.; supervision, L.F.; project administration, L.F.; funding acquisition, L.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education, Science, Research and Sport of the Slovak Republic and the Slovak Academy of Sciences, project VEGA 2/0072/22. The research was also supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency under the Contract No. APVV-20-0229.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors cordially wish to thank RNDr. Magdaléna Strečková, PhD. (IMR SAS, Košice, Slovakia) for the possibility of using modular potentiostat/galvanostat Autolab Vionic (Metrohm, Utrecht, Netherlands) and helpful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Simon, F. EU Commission unveils ‘European Green Deal’: The key points. Available online: https://www.euractiv.com/section/energy-environment/news/eu-commission-unveils-european-green-deal-the-key-points/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Kušnírová, K.; Varcholová, D.; Molčanová, Z.; Ballóková, B.; Möllmer, J.; Jasminská, N.; Lazár, M.; Brestovič, T.; Podobová, M.; Džunda, R.; Motýľ, R.; Saksl, K. Multicomponent metal alloys tested for hydrogen storage. In Proceedings of the Conference Proceedings: 31st International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials, Metal 2022, Brno, Czech Republik, 18-19 May 2022; pp. 339–344, ISBN 978-171386230-7. Code 184827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, F.; Van Nuffel, L.; Smit, T.; Yearwood, J.; Černý, O.; Michalski, J.; Altmann, M. Opportunities for Hydrogen Energy Technologies considering the National Energy & Climate Plans. Trinomics B.V. Final Report. FCH 2 JU, 2020. https://trinomics.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Final-Report-Hydrogen-in-NECPs.pdf.
- Akhtar, M.S.; Khan, H.; Liu, J.J.; Na, J. Green hydrogen and sustainable development – A social LCA perspective highlighting social hotspots and geopolitical implications of the future hydrogen economy. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 395, 136438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashie-Lewis, B.C.; Nnabuife, S.G. Hydrogen Production, Distribution, Storage and Power Conversion in a Hydrogen Economy - A Technology Review. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances 2021, 8, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, F.; Anda, M.; Shafiullah, G.M. Hydrogen production for energy: An overview. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3847–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.H. On some remarkable changes produced in iron and steel by the action of hydrogen and acids. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1875, 23, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhy, G.K.; Komizo, Y. I, Diffusible Hydrogen in Steel Weldments-A Status Review. Transactions of JWRI 2013, 42, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.K.; Vishwakarma, M. Hydrogen embrittlement in different materials: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 21603–21616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depover, T.; Verbeken, K. The detrimental effect of hydrogen at dislocations on the hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of Fe-C-X alloys: An experimental proof of the HELP mechanism. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 3050–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Venezuela, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Q.; Atrens, A. Hydrogen trapping in some advanced high strength steels. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.J.; Kim, N.M.; Jo, J.W.; Lee, C.S. Effect of tempering duration on hydrogen embrittlement of vanadium-added tempered martensitic steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 19670–19681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, Y.; Shobu, T.; Hisamori, N.; Suzuki, H.; Takai, K.; Hirai, K. Delayed Fracture Using CSRT and Hydrogen Trapping Characteristics of V-bearing High-strength Steel. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, D.P.; Verbeken, K.; Duprez, L.; Verhaege, M. Evaluation of hydrogen trapping in high strength steels by thermal desorption spectroscopy. Mater. Sci Eng. A 2012, 551, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadžipašić, A.B.; Malina, J.; Malina, M. The influence of microstructure on hydrogen diffusion and embrittlement of fine-grained high strength dual-phase steels. Kov. Mater. 2021, 59, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Xie, C. Phase-Field Insights into Hydrogen Trapping by Secondary Phases in Alloys. Materials 2023, 16, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshtaghi, M.; Safyari, M.; Mori, G. Combined thermal desorption spectroscopy, hydrogen visualization, HRTEM and EBSD investigation of a Ni–Fe–Cr alloy: The role of hydrogen trapping behavior in hydrogen-assisted fracture. Mater. Sci Eng. A 2022, 848, 143428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toribio, J.; Lorenzo, M.; Aguado, L. Innovative Design of Residual Stress and Strain Distributions for Analyzing the Hydrogen Embrittlement Phenomenon in Metallic Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 9063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čiripová, L.; Falat, L.; Homolová, V.; Džupon, M.; Džunda, R.; Dlouhý, I. The Effect of Electrolytic Hydrogenation on Mechanical Properties of T92 Steel Weldments under Different PWHT Conditions. Materials 2020, 13, 3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ševc, P.; Falat, L.; Čiripová, L.; Džupon, M.; Vojtko, M. The Effects of Electrochemical Hydrogen Charging on Room-Temperature Tensile Properties of T92/TP316H Dissimilar Weldments in Quenched-and-Tempered and Thermally-Aged Conditions. Metals 2019, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Čiripová, L.; Homolová, V.; Kroupa, A. The influence of isothermal ageing and subsequent hydrogen charging at room temperature on local mechanical properties and fracture characteristics of martensitic-bainitic weldments for power engineering. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 2017, 53, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Čiripová, L.; Homolová, V.; Futáš, P.; Ševc, P. Hydrogen pre-charging effects on the notch tensile properties and fracture behaviour of heat-affected zones of thermally aged welds between T24 and T92 creep-resistant steels. Kov. Mater. 2016, 54, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, J.; Falat, L. The influence of thermal exposure and hydrogen charging on the notch tensile properties and fracture behaviour of dissimilar T91/TP316H weldments. High Temp. Mater. Proc. 2014, 33, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, J.; Falat, L.; Ševc, P. The influence of hydrogen charging on the notch tensile properties and fracture behaviour of dissimilar weld joints of advanced Cr–Mo–V and Cr–Ni–Mo creep-resistant steels. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2011, 18, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Čiripová, L.; Petryshynets, I.; Milkovič, O.; Džupon, M.; Kovaľ, K. Hydrogen Embrittlement Behavior of Plastically Pre-Strained and Cathodically Hydrogen-Charged 316H Grade Austenitic Stainless Steel. Crystals 2022, 12, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, D.; Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, X.; Li, B. Design of non-equiatomic medium-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Weng, Y. Study on hydrogen absorption of pipeline steel under cathodic charging. Corrosion Science 2006, 48, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdirik, B.; Baert, K.; Depover, T.; Vereecken, J.; Verbeken, K.; Terryn, H.; De Graeve, I. Development of an Electrochemical Procedure for Monitoring Hydrogen Sorption/Desorption in Steel. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2017, 164, C747–C757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelle, J.; Gilgert, J.; Dmytrakh, I.; Pluvinage, G. Sensitivity of pipelines with steel API X52 to hydrogen embrittlement. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 7630–7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelle, J.; Gilgert, J.; Pluvinage, G. A fatigue initiation parameter for gas pipe steel submitted to hydrogen absorption. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 148-1:2016 Metallic materials—Charpy Pendulum Impact Test—Part 1: Test Method. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/63802.html (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- ASTM G133-05(2016) Standard Test Method for Linearly Reciprocating Ball-on-Flat Sliding Wear. Available online: https://www.astm.org/g0133-05r16.html (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Medved', D.; Ivor, M.; Kovalčíková, A.; Múdra, E.; Csanádi, T.; Sedlák, R.; Ünsal, H.; Tatarko, P.; Tatarková, M.; Šajgalík, P.; Dusza, J. Wear behavior of (Mo–Nb–Ta–V–W)C high-entropy carbide. Int. Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology 2023, 20, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T. Calculation of the Amount of Hydrogen Absorbed by Steel During the Mechanical Plating Operation. MacDermid Industrial Solutions 4/2/2015. Available online: https://anochrome.com/wp-content/uploads/Embrittlement-in-Mech.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Lovicu, G.; Bottazzi, M.; D’aiuto, F.; De Sanctis, M.; Dimatteo, A.; Santus, C.; Valentini, R. Hydrogen embrittlement of automotive advanced high-strength steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 4075–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Kim, G.-I.; Ko, S.-J.; Yoo, J.-S.; Jung, Y.-S.; Yoo, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-G. Comparison of Hydrogen Embrittlement Susceptibility of Different Types of Advanced High-Strength Steels. Materials 2022, 15, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Li, Z.; Raabe, D. Hydrogen enhances strength and ductility of an equiatomic high-entropy alloy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Li, X.; Song, X.; Gu, T.; Zhang, Y. Hydrogen Embrittlement of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy Compared with 304 and IN718 Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Luo, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, X. Immunity of Al0.25CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy to hydrogen embrittlement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 821, 141590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Novelli, M.; Arita, M.; Bae, J.W.; Kim, H.S.; Grosdidier, T.; Edalati, K. Gradient-structured high-entropy alloy with improved combination of strength and hydrogen embrittlement resistance. Corros. Sci. 2022, 200, 110253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dai, L.H. Strong resistance to hydrogen embrittlement of high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Won, J.W.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, K.R.; Na, Y.S.; Lee, C.S. Ultrahigh-strength CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy wire rod with excellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 732, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, W.J.; Seok, M.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Han, H.N.; Suh, J.Y.; Ramamurty, U.; Jang, J.i. Influence of pre-strain on the gaseous hydrogen embrittlement resistance of a high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 718, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Sun, Y.H.; Tu, J.F.; Yen, H.W. Hydrogen-induced ductilization in a novel austenitic lightweight TWIP steel. Scripta Materialia 2022, 213, 114629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Kanezaki, T.; Mine, Y. Hydrogen Effect against Hydrogen Embrittlement. Metall Mater Trans A 2010, 41, 2548–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Oura, R.; Mine, Y.; Takashima, K. Micro-mechanical characterisation of hydrogen embrittlement in nano-twinned metastable austenitic stainless steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 27950–27957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xie, Z.; Misra, R.D.K.; Shang, C. The Effects of Prior Austenite Grain Refinement on Strength and Toughness of High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Dong, L.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Shang, C. The Significance of Coherent Transformation on Grain Refinement and Consequent Enhancement in Toughness. Materials 2020, 13, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kang, M.S.; Park, G.-W.; Choi, E.Y.; Kim, H.-C.; Moon, H.-S.; Jeon, J.B.; Kim, H.; Kwon, S.-H.; Kim, B.J. The Effects of Recrystallization on Strength and Impact Toughness of Cold-Worked High-Mn Austenitic Steels. Metals 2019, 9, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Hotta, M.; Kaneko, K.; Kondoh, K. Enhanced impact toughness of magnesium alloy by grain refinement. Scripta Materialia 2009, 61, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, T.; Thomas Paul, V.; Saroja, S.; Moitra, A.; Sasikala, G.; Vijayalakshmi, M. Grain refinement to improve impact toughness in 9Cr–1Mo steel through a double austenitization treatment. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 419, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, Z.H.; Shang, X.; Chen, S.G.; Zhang, L.J.; Peng, X. Enhancement of the strength-toughness balance in a quenched laser-additively-manufactured low alloy mild steel: Effect of grain refinement and nanotwin bundle formation. Materials Science & Engineering A 2023, 862, 144488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Wu, X.; Yuan, F. Superior fracture toughness with high yield strength in a high-Mn steel induced by heterogeneous grain structure. Materials & Design 2023, 225, 111473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrovskaia, V.E.; Efremenko, V.G.; Zurnadzhy, V.I.; Zotov, D.S.; Sagirov, R.I.; Chabak, Y.G.; Brykov, M.N.; Efremenko, B.V. Effect of Chemical Composition and Normalization Parameters on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Microalloyed Sheet Steel for Structural Purposes. In Advances in Materials Science Research; Wythers, M.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: NY, USA, 2022; Volume 55, ISBN 979-8-88697-213-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, R.; Biermann, H.; Volkova, O.; Mola, J. On the origin of subgrain boundaries during conventional solidification of austenitic stainless steels. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2018, 373, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Nishida, H.; Takakuwa, O.; Tsuzaki, K. Hydrogen-enhanced deformation twinning in Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic steel characterized by in-situ EBSD observation. Materials Today Communications 2023, 34, 105433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Measurement and the improvement of effective thermal conductivity for a metal hydride bed – a review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Jiang, D.; Liu, S.; Ouyang, C. Effect of Interstitial Hydrogen on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Tungsten: A First-Principles Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, D.; Singh, D.; Kumar Sharma, S. Thermal Characteristics and Tribological Performances of Solid Lubricants: A Mini Review. In: Advances in Rheology of Materials, Editor: Ashim Dutta and Hafiz Muhamad Ali, IntechOpen, 2023. https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/86047.
- Roy, A.; Patel, P.; Sharifi, N.; Chromik, R.R.; Stoyanov, P.; Moreau, C. Binary and ternary lubricious oxides for high temperature tribological applications: A review. Results in Surfaces and Interfaces 2023, 11, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Schematic Charpy V-notch (CVN) impact bending test specimen. All dimensions are in mm.
Figure 1.
Schematic Charpy V-notch (CVN) impact bending test specimen. All dimensions are in mm.
Figure 2.
Ligh-optical micrograph of AISI 316H steel in solution-annealed material condition showing polygonal grain structure with abundant occurrence of parallel annealing twin boundaries and dark-appearing longitudinal traces of presumable MnS inclusions.
Figure 2.
Ligh-optical micrograph of AISI 316H steel in solution-annealed material condition showing polygonal grain structure with abundant occurrence of parallel annealing twin boundaries and dark-appearing longitudinal traces of presumable MnS inclusions.
Figure 3.
Higher-magnification scanning-electron micrograph of over-etched AISI 316H steel in solution-annealed material condition with typical morphology of polygonal grain boundaries and longitudinal chain-like traces of former MnS inclusions (a); typical EDX spectrum of mixed MnS trace/matrix local chemical micro-analysis (b).
Figure 3.
Higher-magnification scanning-electron micrograph of over-etched AISI 316H steel in solution-annealed material condition with typical morphology of polygonal grain boundaries and longitudinal chain-like traces of former MnS inclusions (a); typical EDX spectrum of mixed MnS trace/matrix local chemical micro-analysis (b).
Figure 4.
Potentiostatic hydrogen discharging at E = -0.9 V for 1000 s for hydrogen-charged (black line) and non-hydrogenated (red line) sample (a) and zoom of the part of I-t curve in a range of 0 – 300 s (b).
Figure 4.
Potentiostatic hydrogen discharging at E = -0.9 V for 1000 s for hydrogen-charged (black line) and non-hydrogenated (red line) sample (a) and zoom of the part of I-t curve in a range of 0 – 300 s (b).
Figure 5.
CVN impact toughness values of solution-annealed AISI 316H steel for individual test conditions with respect to hydrogen charging.
Figure 5.
CVN impact toughness values of solution-annealed AISI 316H steel for individual test conditions with respect to hydrogen charging.
Figure 6.
Scanning electron microscopic fractographs of broken CVN impact toughness test specimens of solution-annealed AISI 316H steel for individual test conditions: non-hydrogenated (a); hydrogen-charged (b); and dehydrogenated (c). Typical EDX spectrum of MnS inclusions abundantly occurring on the visualized fracture surfaces (d).
Figure 6.
Scanning electron microscopic fractographs of broken CVN impact toughness test specimens of solution-annealed AISI 316H steel for individual test conditions: non-hydrogenated (a); hydrogen-charged (b); and dehydrogenated (c). Typical EDX spectrum of MnS inclusions abundantly occurring on the visualized fracture surfaces (d).
Figure 7.
Ligh-optical micrographs of AISI 316H steel microstructure after CVN impact toughness test performed in: non-hydrogenated condition (a) and hydrogen-charged condition (b).
Figure 7.
Ligh-optical micrographs of AISI 316H steel microstructure after CVN impact toughness test performed in: non-hydrogenated condition (a) and hydrogen-charged condition (b).
Figure 8.
EBSD crystallographic microstructure visualization of AISI 316H steel by Z-direction inverse pole figure (IPF) imaging of sub-fracture surface area of CVN impact bending test specimen in non-hydrogenated (a) and hydrogen-charged (b) material state. The legend (c) is the corresponding IPF color key.
Figure 8.
EBSD crystallographic microstructure visualization of AISI 316H steel by Z-direction inverse pole figure (IPF) imaging of sub-fracture surface area of CVN impact bending test specimen in non-hydrogenated (a) and hydrogen-charged (b) material state. The legend (c) is the corresponding IPF color key.
Figure 9.
EBSD local misorientation mapping (LMM) microstructure visualization of AISI 316H steel in sub-fracture surface area of CVN impact bending test specimen in non-hydrogenated (a) and hydrogen-charged (b) material state. The corresponding legends (right portions) depict misorientation angle distributions.
Figure 9.
EBSD local misorientation mapping (LMM) microstructure visualization of AISI 316H steel in sub-fracture surface area of CVN impact bending test specimen in non-hydrogenated (a) and hydrogen-charged (b) material state. The corresponding legends (right portions) depict misorientation angle distributions.
Figure 10.
EBSD phase mapping microstructure visualization of AISI 316H steel in sub-fracture surface area of CVN impact bending test specimen in non-hydrogenated (a) and hydrogen-charged (b) material state. The legend (c) is the phase map color key.
Figure 10.
EBSD phase mapping microstructure visualization of AISI 316H steel in sub-fracture surface area of CVN impact bending test specimen in non-hydrogenated (a) and hydrogen-charged (b) material state. The legend (c) is the phase map color key.
Figure 11.
Average coefficients of friction of AISI 316H steel determined for its non-hydrogenated, hydrogen-charged, and dehydrogenated material states.
Figure 11.
Average coefficients of friction of AISI 316H steel determined for its non-hydrogenated, hydrogen-charged, and dehydrogenated material states.
Figure 12.
Characteristic tribological track profiles of studied AISI 316H material: non-hydrogenated material (a), hydrogen-charged material (b), dehydrogenated material (c).
Figure 12.
Characteristic tribological track profiles of studied AISI 316H material: non-hydrogenated material (a), hydrogen-charged material (b), dehydrogenated material (c).
Figure 13.
Average specific wear rates of studied 316H material determined for its non-hydrogenated, hydrogen-charged, and dehydrogenated material states.
Figure 13.
Average specific wear rates of studied 316H material determined for its non-hydrogenated, hydrogen-charged, and dehydrogenated material states.
Figure 14.
SEM morphological characterizations of tribological tracks including the EDX spectra of performed chemical micro-analyses of selected (marked by green cross) locations: non-hydrogenated material (a), hydrogen-charged material (b), dehydrogenated material (c).
Figure 14.
SEM morphological characterizations of tribological tracks including the EDX spectra of performed chemical micro-analyses of selected (marked by green cross) locations: non-hydrogenated material (a), hydrogen-charged material (b), dehydrogenated material (c).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).