Introduction
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a member of the ESKAPE group of highly resistant pathogens and represents a formidable challenge in healthcare settings (Daikos et al., 2021). Carbapenems remain the mainstay for treating severe and complicated P. aeruginosa infections. Unfortunately, the emergence of carbapenem resistance has become a global concern in the last decade (Toleman et al., 2005; Zavascki et al., 2006), and is commonly associated with mutations in the outer-membrane porin OprD, overexpression of efflux pumps and horizontal acquisition of carbapenemase genes, including both serine- and metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) (Walsh et al., 2005; Quale et al., 2006; Zavascki et al., 2006; Rodríguez-Martínez, Poirel and Nordmann, 2009).
Carbapenemase activity in clinical strains P. aeruginosa due to KPC and certain GES variants (Ambler class A) is less frequently reported similar to the OXA carbapenemases from Ambler class D (Hong et al., 2015). MBLs (Ambler class B) are characterized by their dependency on one or two zinc cations for enzymatic activity (Walsh et al., 2005). Various types of MBLs have been identified in P. aeruginosa, including IMP, VIM, SPM, GIM, NDM, FIM, BIM types (Hong et al., 2015; Souza et al., 2023). Among these, IMP- and VIM-type enzymes are the most abundant and are of particular clinical importance, as they efficiently inactivate most β-lactam antibiotics, with the exception of monobactams (Gupta, 2008; Zhao and Hu, 2010).
Integrons play a crucial role in capturing and disseminating antibiotic resistance genes including MBLs (Walsh et al., 2005) as they are often associated with large transposon structures found on plasmids or chromosomes (Mazel, 2006; Zhao and Hu, 2011). Transposable elements utilize specific transposase-mediated mechanisms for their insertion and excision within the bacterial genome. Composite transposons are flanked by Insertion Sequence (IS) elements. Unit transposons, on the other hand, encode an excision/integration-associated enzyme, recombinase or resolvase, along with accessory genes such as resistance genes, within a single genetic unit. Conjugative transposons, also referred to as integrative conjugative elements (ICEs), carry genes for excision, conjugative transfer, and integration, often accommodating a diverse repertoire of accessory genes, including antibiotic resistance genes (Roberts et al., 2008).
The first identification of IMP-1 metallo-β-lactamase, conferring acquired resistance to carbapenems, was reported in 1988 in a P. aeruginosa strain isolated from Japan (Watanabe et al., 1991). Since then the emergence and spread of blaIMP-carrying P. aeruginosa strains has been reported globally (Wang et al., 2021). The IMP-type enzymes represent a highly heterogeneous group of carbapenemases, frequently found as gene cassettes in class 1 integrons harboring additional resistance determinants (Walsh et al., 2005; Zhao and Hu, 2011).
P. aeruginosa isolates in Bulgaria display a range of carbapenemases, of which VIM-type enzymes are commonly reported (Schneider et al., 2008; Strateva, Setchanova and Peykov, 2021). Co-occurrence of NDM-1 and GES-5 carbapenemases were recently identified (Kostyanev et al., 2020). Detection of OXA-50 carbapenemase has also been documented (Petrova et al., 2019).
In this study, we performed genomic analysis of three clinical P. aeruginosa isolates, revealing to our knowledge the first occurrence of blaIMP in Bulgaria. In addition, one of the isolates carried a novel IMP-type metallo-β-Lactamase variant, referred to as blaIMP-100, located on a multidrug-resistant plasmid and in combination with a chromosomally encoded blaVIM-4.
Materials and methods
Strains
The three strains (Paer3541, Paer3796A, and Paer4782MK) were initially isolated in Sofia, Bulgaria between 2018 and 2022. Paer3541 was obtained from throat swab from hospitalized patient, Paer3796A was derived from urine sample of an individual in outpatient settings, and Paer4782MK was isolated from a blood culture of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. Strains were sent to the National Reference Laboratory, department of Microbiology within the National Center of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases, Sofia, Bulgaria for carbapenem resistance confirmation purposes (
Supplementary Table S1).
Phenotypic and molecular analysis
Strains were cultured on Columbia agar at 35 °C overnight. A single colony of each strain was identified via MALDI Biotyper (Bruker Daltonics GmbH & Co. KG, Bremen, Germany) with MALDI Reference 2022 Library v4.0.0. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST) was performed using MICRONAUT-S Pseudomonas MIC and UMIC® Cefiderocol assay (Bruker Daltonics GmbH & Co. KG, Bremen, Germany). The interpretation of the AST results was in accordance to EUCAST clinical breakpoints v13.0.
Initially, the isolates were analyzed for carbapenemase activity by a modified CarbaNP test (Nordmann, Poirel and Dortet, 2012). In parallel, an in-house carbapenemase genes detection multiplex PCR was performed with the PCR components, conditions and protocols described in detail in
Supplementary Table S1. Primer pairs for each gene were obtained from previously published sources, including
blaSIM,
blaSPM,
blaOXA-48-like,
blaGES and
blaKPC (Poirel, Naas and Nordmann, 2006; Mendes
et al., 2007; Cole
et al., 2009; Gröbner
et al., 2009) along with additional primer pairs for
blaIMP,
blaVIM and
blaNDM (Goudarzi
et al., 2019). High-resolution capillary electrophoresis was used following the PCR (QIAxcel, QIAGEN) with protocol 0M800 (3 kV for 800 s) for precise size estimation.
Antimicrobial resistance gene expression assay of AMR-associated genes mexA, mexC, mexE, mexX, ampC and oprD was performed as previously described (Quale et al., 2006; Wi et al., 2018), and results interpreted according to (Cabot et al., 2011). Biofilm formation was quantified by the crystal violet assay (Shukla and Rao, 2017).
Genomic and plasmid DNA extraction and WGS
Total genomic DNA extraction was performed with PureLink™ Genomic DNA Mini Kit (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.) according to manufacturer’s instructions except that all homogenization steps were carried out by pipetting. Plasmid DNA was acquired using NucleoSpin Plasmid Mini kit for plasmid DNA (Macherey-Nagel) following the “low-copy plasmid” protocol. Short-read NGS sequencing was performed using Illumina DNA Prep kit for sequencing libraries preparation and MiSeq V3 (2 × 300 bp), (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) for strains PA3541 and PA3796A, whereas PA4782 was sequenced on NextSeq 550 with V2.5 (2 x 150 bp) mid output flow cell. The same DNA extract without additional size-selection was used for long-read sequencing on a MinION Mk1C with the Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 (SQK-RBK110.96) and FLO-MIN106D (R9.4.1) (Oxford Nanopore Technologies plc.). The final purification step of the library pool was performed with 0.4x SPRI magnetic particles as recently suggested for removal of DNA fragments <1.5 kb (Alvarez-Arevalo et al., 2022).
Data availability
The complete genomes of the three strains were deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) under project accession PRJEB62425. The genomes were assigned the following accession numbers: Paer4782MK - ERZ18545754, Paer3541 - ERZ18545673, Paer3796A - ERZ18545648. In the case of Paer4782MK, a novel variant of IMP-100, a subclass B1 metallo-beta-lactamase, was detected, validated and submitted to GenBank with accession number NG_203391.1.
Results
Genome quality assessment and features
Аll three genomes achieved a completeness score close to 100%, indicating that the majority of the expected conserved genes were present. A high level of genome integrity without duplications is evidenced by the 99.2 % single-copy genes detected. No fragmented or missing conserved genes were identified. In line with these findings, CheckM revealed relatively low foreign DNA contamination levels ranging from 0.63% to 0.7%. Detailed information on assembly statistics and genome quality assessment are available in
Supplementary Table S5.
Two plasmids p4782-IMP (61.5 Kbp) and p4782_002 (290.8 Kbp) were identified in Paer4782MK. p4782-IMP (OX638703.1) was related to the MOB
F and MPF
T plasmid pMOS94-like family. Notably, this plasmid carried the novel
blaIMP-100 (NG_203391.1) allele, in addition to other genes associated with AMR. The p4782_002 (OX638702.1), was untypable and lacked both resistance and virulence determinants, thus it was excluded from further analysis. The two plasmids detected in Paer3541 were p3541_1 (179.3 Kbp, OX638611.1) and p3541_2 (41.5 Kbp, OX638612.1). Similar to p4782-IMP, plasmid p3541_2 was MOB
F and MPF
T and was found to harbor a single
aac(6’)-29 gene, encoding an aminoglycoside acetyltransferase. The plasmid p3541_1 had unknown MOB and MPF types, similar to p4782_002. For Paer3796A, a single plasmid p3796A (178.5 Kbp, OX638565.1) with unknown MOB and MPF types was identified and did not harbor any resistance or virulence determinants. Additional information regarding plasmid analysis is available in
Supplementary Table S6.
Paer3541 and Paer3796A were assigned to ST621, a clone previously associated with blaIMP carriage (Giani et al., 2018), while Paer4782MK belonged to the international high-risk clone ST233. In-silico serotyping revealed that Paer3541 and Paer3796A were serogroup O4, while Paer4782MK was O11.
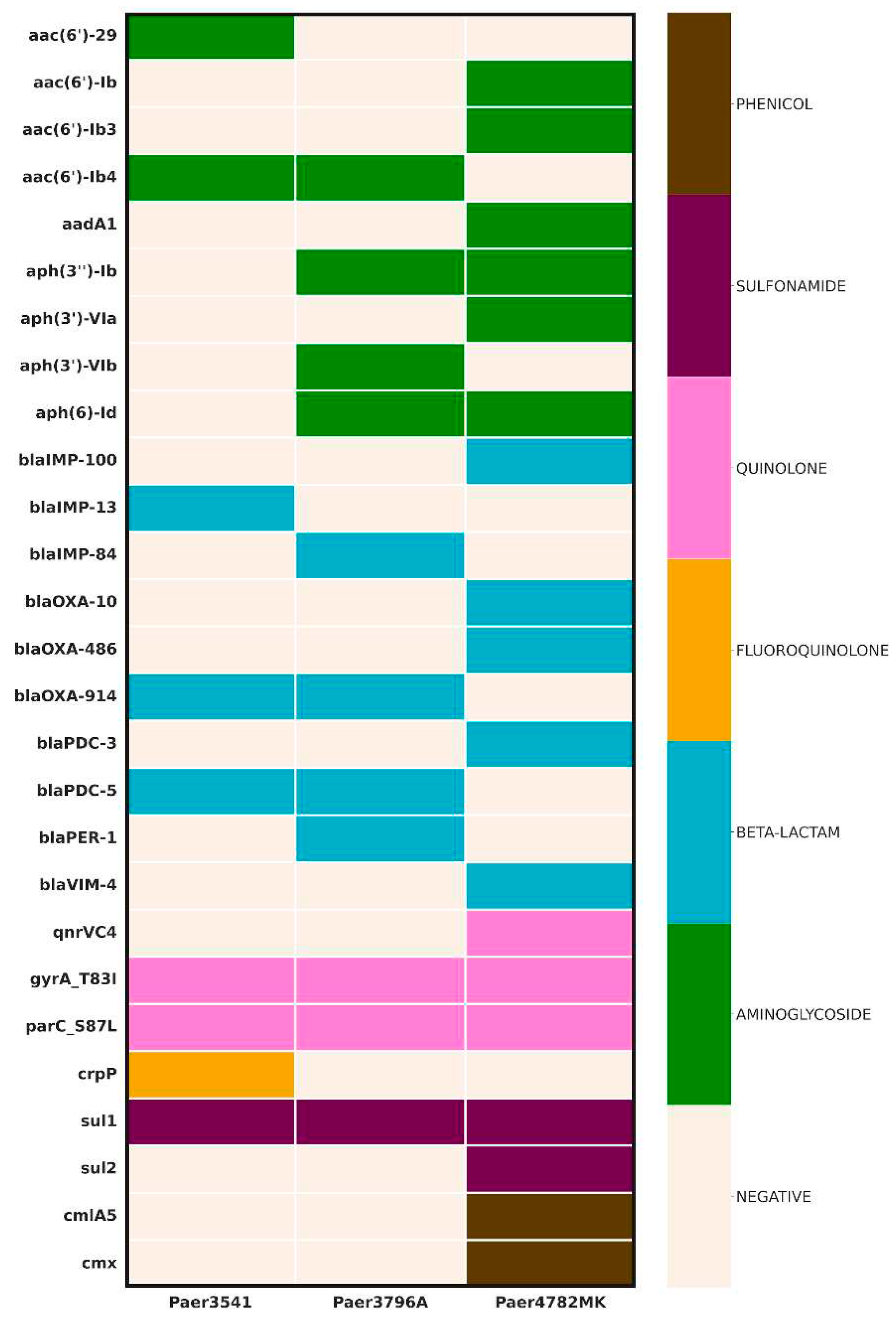
Detection of AMR determinants
The AMR screening uncovered a diverse array of genes (
Figure 1.) All three isolates demonstrated the presence of an IMP carbapenemase, with the unique
blaIMP-100 allele identified in а pMOS94-like plasmid in Paer4782MK. Additionally, strain Paer4782MK also harbored
blaVIM-4. Two other closely related chromosomal
blaIMP variants, IMP-13 and IMP-84, were detected in Paer3541 and Paer3796A respectively. Additional acquired ESBL such as PER-1 and multiple genetic determinants associated with resistance to most non-beta-lactam antimicrobial groups were present as well.
In-silico analysis of the
oprD gene revealed that both Paer3541 and Paer3796A harbour an intact and functional
oprD porin. Despite the identification of a missense mutation (S325F) in the
oprD gene of Paer3796A, the gene appeared intact. Conversely, a truncated
oprD protein was evident in Paer4782MK potentially compromising its function (
Supplementary Table S6). No known mutations related to efflux overexpression were detected.
Detection of virulence determinants
All three isolates exhibited virulence factors related to adherence and motility, including flagella, type IV pili biosynthesis, and twitching motility. Alginate biosynthesis genes known for promoting bacterial resilience against harsh conditions and host immune responses (Franklin
et al., 2011) were detected in all isolates. However, certain antimicrobial-related factors (
phzC2, phzD2,
phzE2,
phzF2, and
phzG2) were absent compared to the reference strain PA01. Phospholipases C and D were identified, including
plcH, known for its hemolytic activity (Vasil
et al., 2009). Siderophore production genes were present in Paer3541 and Paer3796A, while the
pvdD gene, responsible for pyoverdine production, was lacking in Paer4782MK, indicating impaired pyoverdine synthesis (Meldrum, no date). Additional virulence factors, including alkaline protease (AprA), elastase (LasA and LasB), Protease IV (PrpL), and exotoxin A (ToxA) were also detected. Quorum sensing components such as acylhomoserine lactone synthase (HdtS), transcription factors (LasI, RhlI), receptors (LasR, RhlR), as well as the GacS/GacA two-component system and type VI secretion system (H-T6SS) components were found in all three isolates. Rhamnolipid biosynthesis genes (
rhlA,
rhlB, and
rhlC), associated with host cell infiltration and biofilm formation (McClure and Schiller, 1996; Zulianello
et al., 2006) were identified. The isolates exhibited T3SS effectors, including
exoS,
exoT, and
exoY, involved in manipulating host cell signaling pathways and immune responses, along with T3SS genes such as
pcrV,
popB,
popD, and
pscF, indicating the presence of a functional T3SS machinery capable of delivering effector molecules into host cells. The isolates harboured genes associated with hydrogen cyanide production (HcnA, HcnB, and HcnC), a potent toxic compound known to disrupt cellular processes and impact aerobic respiration (Ryall
et al., 2008). Furthermore, the MDR plasmid p4782-IMP in Paer4782MK harbored the
katG gene, which is involved in oxidative stress protection (Manca
et al., 1999). A summary of the virulence screening results can be found in
Supplementary Table S7.
Plasmid analysis
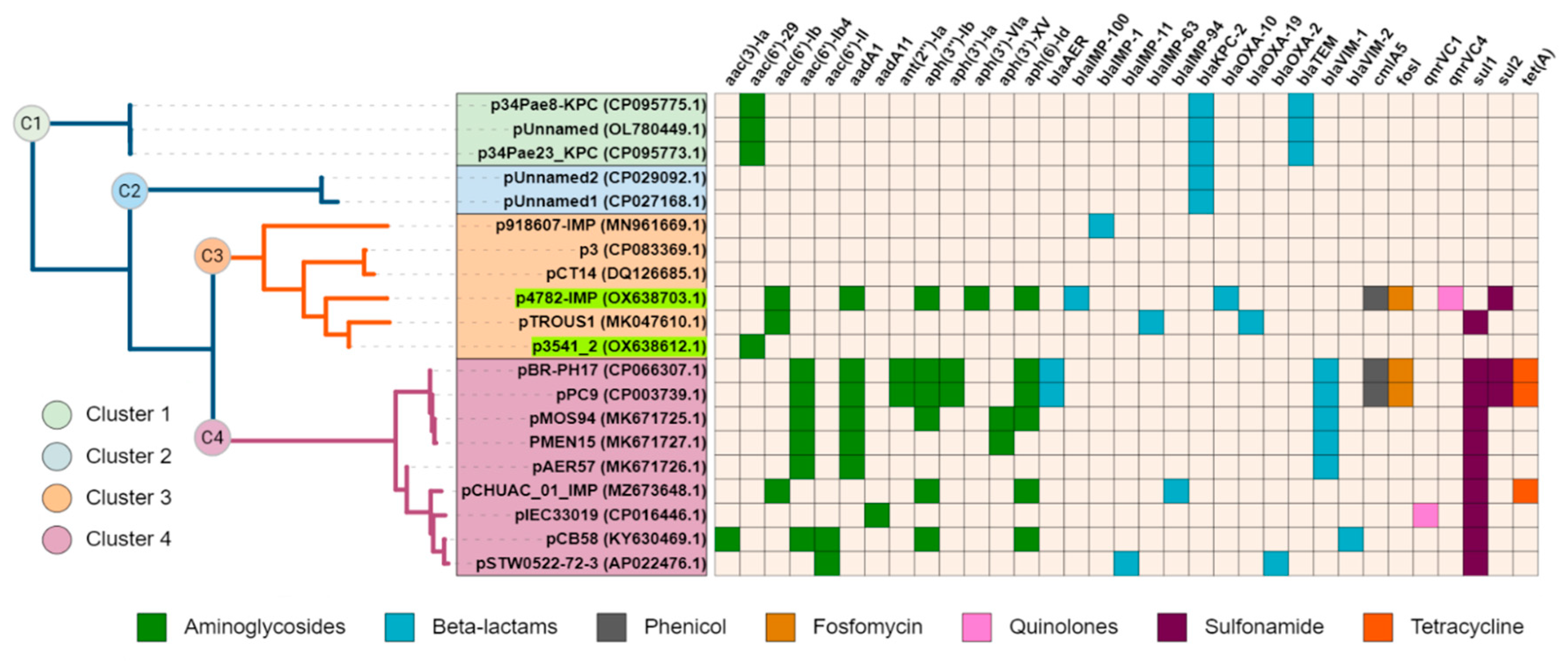
The complete sequence of plasmid p4782-IMP was subjected to a BLAST search against the nr/nt database of NCBI, and a neighbor-joining tree was constructed with the most similar plasmids (n=19). Interestingly, plasmid p3541_2 was identified as closely related to p3782-IMP. Additionally, all plasmids were screened for AMR genes and the results were illustrated as a heatmap and linked to the phylogenetic tree (
Figure 2.).
Upon observation, cluster C1 was found to encompass three plasmids with unknown MOB type that encoded KPC enzymes. The remaining clusters C2-C4 comprised plasmids from the MOBF and MPFT families. C2 was similar to C3 plasmids, but unlike them carried only KPC enzyme. C3 and C4 both exhibited relatedness to the pMOS94-like plasmids (Pilato et al., 2019a). Interestingly, C3 plasmids had lower density of AMR-associated genes compared to C4. Despite the high abundance of AMR genes found on plasmid p4782-IMP similar to C4 plasmids, it was grouped within the lower-resistance cluster C3.
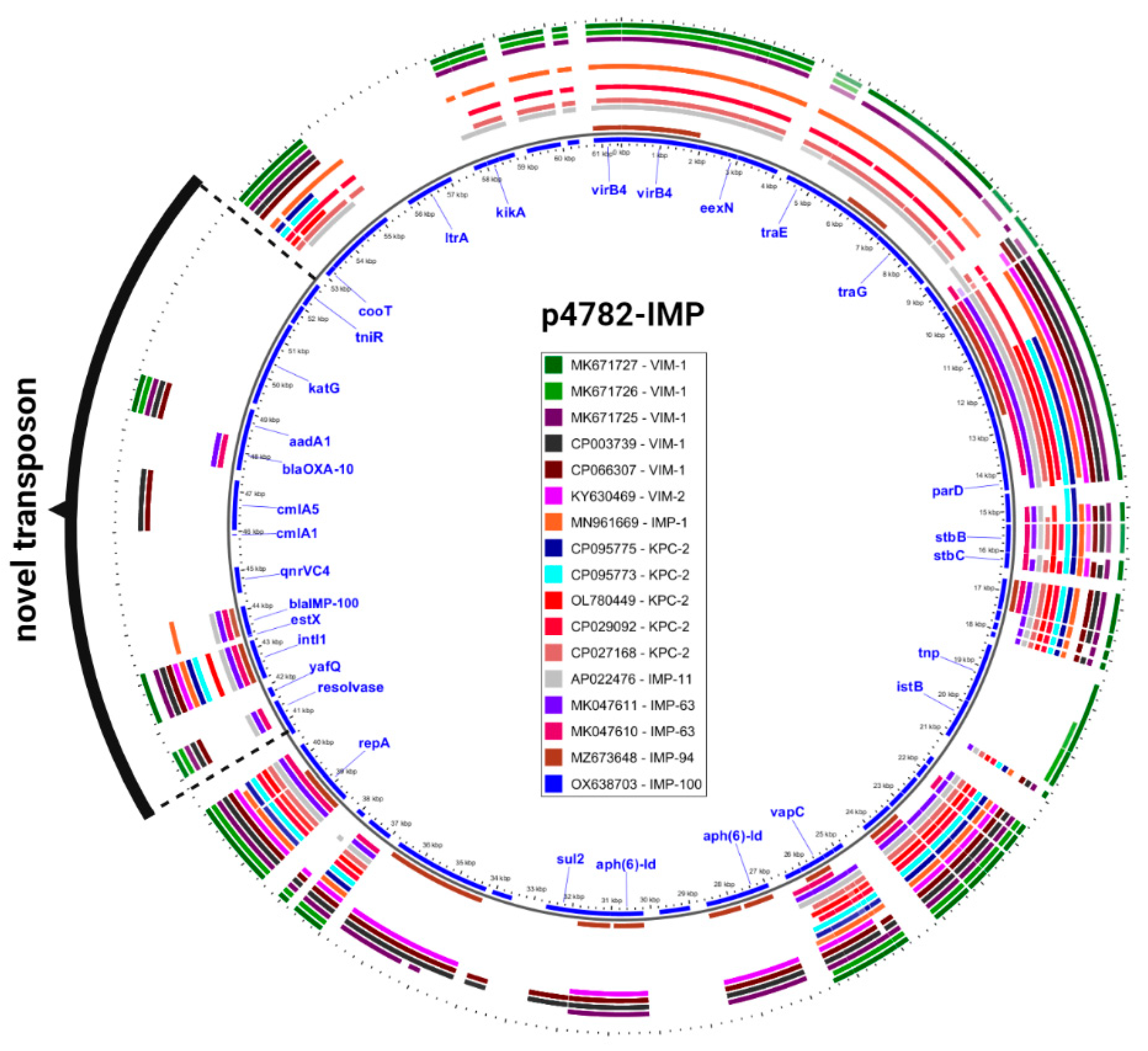
Additionally, an in-depth comparison was conducted between the most phylogenetically related carbapenemase-harboring plasmids and p4782-IMP using the Gview server’s BLAST Atlas. The analysis unveiled a distinctive transposon insertion within the MOB
F/MPF
T family plasmid backbone, as illustrated in
Figure 3. This novel transposon carried the novel
blaIMP-100 allele, as well as multiple AMR determinants, which accounted for the atypical abundance of resistance genes observed in p4782-IMP.
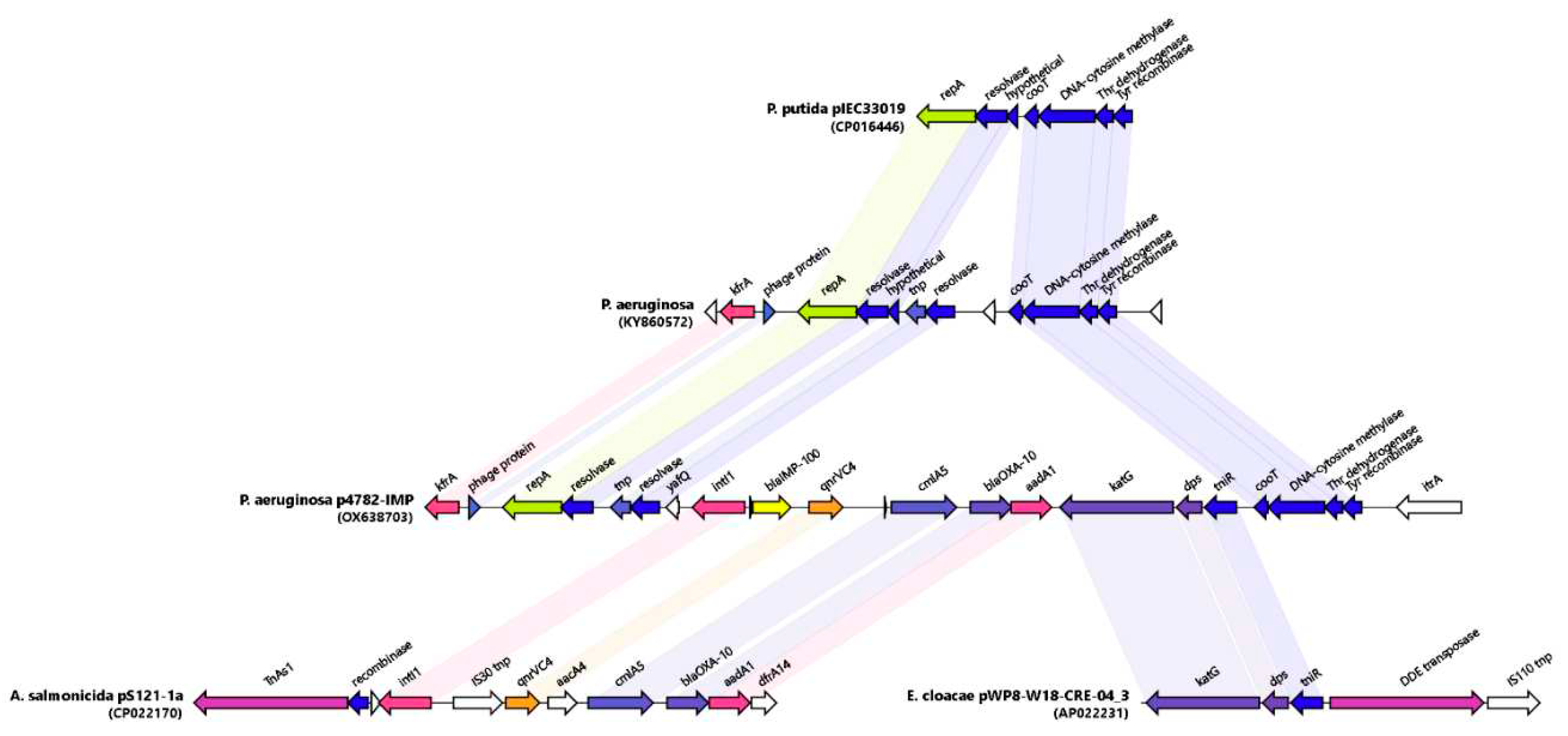
Phylogeny and Genetic environment of blaIMP-100 in Paer4782MK
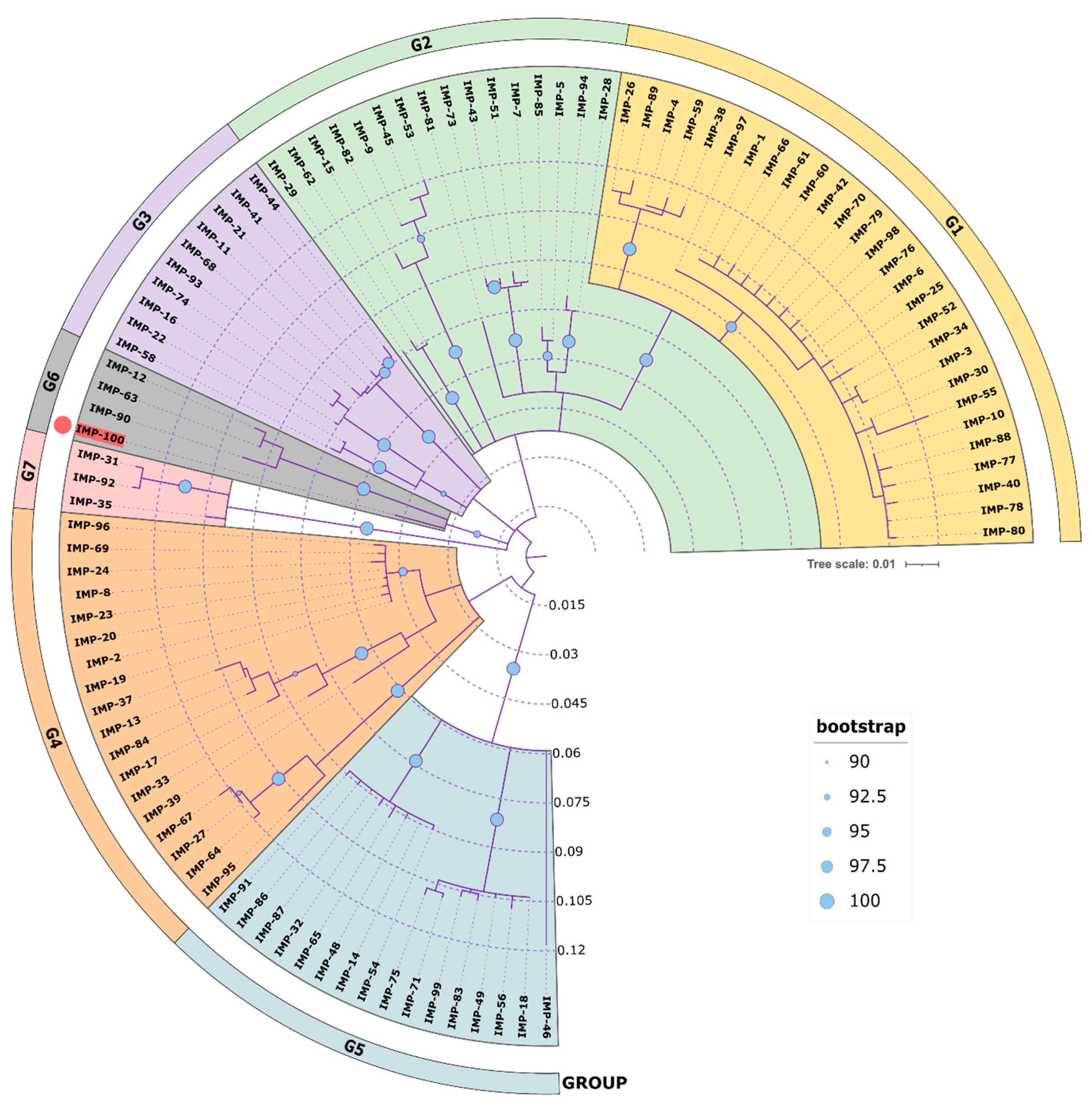
A phylogenetic analysis of all IMP variants was conducted through protein sequence alignment and subsequent construction of a phylogenetic tree (
Figure 4). The clustering of IMP alleles and the labeling of the resulting groups was completed according to a clustering scheme suggested previously (Li
et al., 2023), thus maintaining consistency. The novel allele IMP-100 falls into the G6 cluster revealing closest similarity to IMP-63, IMP-12 and IMP-90. The
blaIMP-100 gene was positioned as the first cassette under weak PcW+P2 promotor (Wei
et al., 2011) in a novel
In1300-like Tn402 type integron platform and followed by
qnrVC4,
cmlA5, and
blaOXA-10 cassettes (
Figure 5).
Similar cassette array (
In1300) was previously reported in
Aeromonas salmonicida MDR plasmid pS121-1a (CP022170). The p4782-IMP integron was preceded by a novel putative IS, hereby referred to as
IS4782 flanked by imperfect 25bp inverted repeats IRL (TGTCATTTTCAGAAG
GCGACTGCAC) and IRR (TGTCATTTTCAGAAG
ACGACTGCAC) closely resembling those of
ISPa17 and
Tn402. IRR was also found on the far 3′ end of the
Tn402 integron as well (
Figure 4). The
IS4782 harbored three genes: the
yafQ toxin gene, putative resolvase (188AA) and short transposase (128AA). This putative IS was lacking any significant homologues within the ISFinder or TnCentral databases (Siguier
et al., 2006; Ross
et al., 2021). BLAST search was able to find eight identical hits (all plasmid borne and one being p3541_2 plasmid reported here) only matching the resolvase and transposase genes and not the whole IS. It was hypothesized that this element is capable of horizontal dissemination either alone or with the
Tn402 integron due to sharing the same inverted repeats. Next, we managed to identify and map related mobile elements in order to detect a hypothetical origin of the novel transposon (
Figure 5). The 5′ end most closely resembled the tnp/resolvase combination found in a
P.aeruginosa transposon from the Czech Republic (KY860572) (Papagiannitsis
et al., 2017) followed by an integron carrying the IMP-100 that was highly similar to the one from
Aeromonas salmonicida MDR plasmid pS121-1a (
Figure 5). The 3′ end of the transposon resembled a remnant from another one found in
Enterobacter cloaceae plasmid (AP022231) containing the
katG,
dps and the
tniR. Similar structures have been reported in most pMOS94-like plasmids where
ISPa17 preceded carbapenemase carrying
Tn402 integrons (Pilato
et al., 2019a). Recently it was hypothesized that the
ISPa17 transposase might be capable of mobilization of adjacent
Tn402 integrons resulting in distinct transposon elements (Papa-Ezdra
et al., 2023). The IMP-100 transposon had 5bp direct repeats (AAAAC) located up to 26bp apart from each IR, which although unexpected might be suggestive of past transposition events. Finally, we also discovered a probable ancestral insertion site of the whole IS4782-
Tn402 structure located in a
P. putida plasmid from Brazil (CP016446) (Souza
et al., 2023).
For the remaining two strains we found that IMP-13 (Paer3541) and IMP-84 (Paer3796) were located chromosomally in class I integrons embedded in Tn5051-like transposons, whereas VIM-4 (in Paer4782) was found in In237-like integron. Importantly, all these MBLs were components of self-transmissible T4SS-type ICEs meaning they are capable of dissemination by horizontal gene transfer (Supplemental Figure S8). Lastly, all putative novel mobile genetic elements were submitted to the respective databases (ISFinder, TnRegistry and INTEGRALL) (Siguier et al., 2006; Moura et al., 2009; Tansirichaiya, Rahman and Roberts, 2019).
Discussion
Between 2018 and 2022, three epidemiologically unrelated MDR P. aeruginosa strains were obtained from diverse clinical sources. Surprisingly, the modified CarbaNP test and the PCR for carbapenemase detection yielded conflicting results for strains Paer3541 and Paer3796A with PCR being negative. Furthermore, WGS analysis revealed the presence of blaIMP-13 in Paer3541 and blaIMP-84 in Paer3796A. These findings were suggestive that the primers used to target blaIMP genes were ineffective and had to be replaced. Paer4782MK was the most recent isolate of the three and the blaIMP was therefore successfully detected with the updated PCR assay (Goudarzi et al., 2019). It is important to note that the availability of several alternative methods for carbapenemase detection may prove useful as well as regular updates of the methodologies are required to correctly detect the presence of rare gene variants.
Among the carbapenemases detected in Bulgaria, VIM-type enzymes are frequently observed (Schneider et al., 2008; Strateva, Setchanova and Peykov, 2021), but occurrence of NDM-1, GES-5, and OXA-50 carbapenemases were also documented (Petrova et al., 2019; Kostyanev et al., 2020). To our knowledge, this study represents the first report of blaIMP detection in three clinical MDR isolates from Bulgaria. Additionally, we identified a novel allele of the blaIMP gene, designated blaIMP-100, located on a MDR plasmid (p4782-IMP) within Paer4782MK. This strain also carried a chromosomally-encoded blaVIM-4 carbapenemase and was categorized as ST233, a globally prevalent multidrug-resistant clone (Aguilar-Rodea et al., 2017), often associated with blaVIM-2 production (del Barrio-Tofiño, López-Causapé and Oliver, 2020). Paer3541 (IMP-13) and Paer3796A (IMP-84) were classified as ST621, an epidemic clone known for its association with blaIMP production and a higher prevalence of pldA, a trans-kingdom phospholipase T6SS effector (Boulant et al., 2018). This effector is associated with the H2 Type VI secretion system (H2-T6SS) and involved in bacterial endocytosis (Russell et al., 2013).
In line with previous research demonstrating a correlation between ST233 and the exoS+ (exoU-) genotype (del Barrio-Tofiño, López-Causapé and Oliver, 2020), our virulence analysis revealed that Paer4782MK (ST233) exhibited this specific genotype. ExoU and ExoS are mutually exclusive T3SS effectors, with ExoS leading to delayed apoptotic cell death, while ExoU induces rapid host cell lysis (Hauser, 2009). Regarding serotypes, our findings align with existing literature (Recio et al., 2020), demonstrating a strong association between serotypes O4 and O11 and MDR phenotypes. Typically, the O4 serotype is associated with the exoU-negative genotype, while the O11 serotype is linked to the exoU-positive genotype. Interestingly, Paer4782MK tested negative for exoU and exhibited the exoS genotype. Furthermore, despite recent studies suggesting an association between ST233 and serotype O6 (Pottier et al., 2023), our classification of Paer4782MK as ST233:O11 deviates from this anticipated relationship.
Upon analyzing the WGS data, it was determined that the observed negative expression of oprD in the expression assay was due to an identical 10 amino acid indel, which prevented primer binding across all three isolates, thereby rendering the results invalid. Additionally, PorinPredict tool confirmed the presence of an intact and functional oprD porin in Paer3541, which likely contributed to its susceptibility to and lowest MIC values of meropenem, imipenem, meropenem/vaborbactam, and imipenem/relebactam of all three strains. Despite the occurrence of a missense mutation S325F, the oprD integrity in Paer3796A remained unaffected. In fact, the presence of this mutation has been associated in a potential increase in the MIC of imipenem (Khoury et al., 2019). However, further investigations are necessary to determine its precise impact. Lastly, both our observation and PorinPredict concluded that the oprD gene in Paer4782MK is truncated, therefore its functionality was compromised, consistent with the higher reported MIC values for meropenem, imipenem, meropenem/vaborbactam, and imipenem/relebactam in this particular strain.
Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated a close genetic association between the plasmid p4782-IMP, harboring the novel blaIMP-100 allele, and the pMOS94-like plasmid family. The pMOS94 plasmid family was recently recognized as an emerging lineage involved in dissemination of MBL genes among Pseudomonas species, also commonly carry blaVIM and blaIMP genes, and recently blaBIM, and some of them were found to display disruptions in the transfer module (trw), thus impeding conjugation (Pilato et al., 2019b). In the genetic environment of the trw transfer module of p4782-IMP we could not identify any disruption, so the observed unsuccessful mating experiments could be due to other reasons. Next, the comparison with the nearest carbapenemase-harboring plasmids revealed an insertion of unique transposon in p4782-IMP, carrying multiple AMR determinants. The transformation of PA01 with the p4782-IMP plasmid resulted in a resistance profile similar to that of the Paer4782MK strain, demonstrating the impact of p4782-IMP in reducing susceptibility to important antibiotic classes and conferring multiple drug resistance. Furthermore, the transfer of the entire plasmid into the PA01 conferred resistance to CFDC. On the other hand, in the case of the E. coli NEB10 transformant carrying only the blaIMP-100 gene, there was no significant increase in the CFDC MIC suggesting that the CFDC resistance was a result of complex interplay between multiple genes present on the plasmid, in addition to blaIMP-100.
Conclusion
Our study is the first to our knowledge to document the blaIMP in clinical P. aeruginosa from Bulgaria. We also discovered a novel blaIMP-100 allele located on a MDR plasmid (p4782-IMP). The plasmid in turn conferred resistance to multiple antibiotics including CFDC, as shown by the similar MDR pattern revealed in PA01 transformant. However, by examining transformants carrying only the blaIMP-100 gene, we observed that CFDC MIC values did not show a substantial increase, further implying the involvement of other plasmid genes in the development of resistance to this novel agent. Lastly, our study emphasizes the importance of employing multiple methods for carbapenemase screening, given that conventional methods, apart from WGS, might show reduced sensitivity and neglect carbapenemase activity or genes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org., S1. Carba mPCR; S2. Cloning protocol template; S3. Clonning schematic; S4. Expression analysis; S5. Genome Quality; S6. MOB Suite results; S7. oprD analysis; S8. Virulence factors; S9. ICEs.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed in different aspects. Conceptualization, methodology and validation - I. I., R.H., S.S. and I.S. Software, formal analysis, investigation – I.S., D.D., I.I., D.T., E.D.; resources S.S, E.D, R.H, data curation – D.D., D.T., S.S.; writing—original draft preparation – I.S., I.I., D.D., writing—review and editing – I.S., I.I., S.S., D.T., E.D., visualization – D.D., I.S., supervision, project administration, funding acquisition – I.I.All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by The Bulgarian National Science Fund under Grant КП-06-Н23/5 and the European Regional Development Fund through the Operational Program Science and Education for Smart Growth 2014–2020; Grant BG05M2OP001-1.002-0001-C04 “Fundamental Translational and Clinical Research in Infection and Immunity”.
Data Availability Statement
All used data is included in the main text and in the supplementary materials. Relevant links and/or references to other sources are included in the main text. The generated information and/or datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. This study was partially reported as a poster M193 at the 10th FEMS Congress of European Microbiologists, 9-13 June 2023, Hamburg, Germany
References
- Aguilar-Rodea, P. et al. (2017) ‘Identification of extensive drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains: New clone ST1725 and high-risk clone ST233′, PLoS ONE, 12(3). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0172882. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Arevalo, M. et al. (2022) ‘Extraction and Oxford Nanopore sequencing of genomic DNA from filamentous Actinobacteria’, STAR protocols, 4(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.XPRO.2022.101955. [CrossRef]
- del Barrio-Tofiño, E., López-Causapé, C. and Oliver, A. (2020) ‘Pseudomonas aeruginosa epidemic high-risk clones and their association with horizontally-acquired β-lactamases: 2020 update’, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 56(6), p. 106196. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJANTIMICAG.2020.106196. [CrossRef]
- Biggel, M. et al. (2023) ‘PorinPredict: In Silico Identification of OprD Loss from WGS Data for Improved Genotype-Phenotype Predictions of P. aeruginosa Carbapenem Resistance’, Microbiology spectrum, 11(2). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/SPECTRUM.03588-22. [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V. et al. (2020) ‘ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes’, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 75(12), pp. 3491–3500. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/JAC/DKAA345. [CrossRef]
- Boulant, T. et al. (2018) ‘Higher Prevalence of PldA, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Trans-Kingdom H2-Type VI Secretion System Effector, in Clinical Isolates Responsible for Acute Infections and in Multidrug Resistant Strains’, Frontiers in Microbiology, 9. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2018.02578. [CrossRef]
- Cabot, G. et al. (2011) ‘Overexpression of AmpC and Efflux Pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from Bloodstream Infections: Prevalence and Impact on Resistance in a Spanish Multicenter Study’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 55(5), p. 1906. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01645-10. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. et al. (2018) ‘fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor’, Bioinformatics, 34(17), pp. i884–i890. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTY560. [CrossRef]
- Clausen, P.T.L.C., Aarestrup, F.M. and Lund, O. (2018) ‘Rapid and precise alignment of raw reads against redundant databases with KMA’, BMC Bioinformatics, 19(1), pp. 1–8. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/S12859-018-2336-6/TABLES/2. [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.M. et al. (2009) ‘Development and Evaluation of a Real-Time PCR Assay for Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase Genes’, Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 47(2), p. 322. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01550-08. [CrossRef]
- Daikos, G.L. et al. (2021) ‘Review of Ceftazidime-Avibactam for the Treatment of Infections Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa’, Antibiotics, 10(9). Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIBIOTICS10091126. [CrossRef]
- Feldgarden, M. et al. (2021) ‘AMRFinderPlus and the Reference Gene Catalog facilitate examination of the genomic links among antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence’, Scientific Reports 2021 11:1, 11(1), pp. 1–9. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91456-0. [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.J. et al. (2011) ‘Biosynthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Extracellular Polysaccharides, Alginate, Pel, and Psl’, Frontiers in microbiology, 2(AUG). Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2011.00167. [CrossRef]
- Giani, T. et al. (2018) ‘Italian nationwide survey on Pseudomonas aeruginosa from invasive infections: activity of ceftolozane/tazobactam and comparators, and molecular epidemiology of carbapenemase producers’, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 73(3), pp. 664–671. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/JAC/DKX453. [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, H. et al. (2019) ‘Rapid detection and molecular survey of blaVIM, blaIMP and blaNDM genes among clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii using new multiplex real-time PCR and melting curve analysis’, BMC Microbiology, 19(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/S12866-019-1510-Y. [CrossRef]
- Gröbner, S. et al. (2009) ‘Emergence of carbapenem-non-susceptible extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates at the university hospital of Tübingen, Germany’, Journal of Medical Microbiology, 58(7), pp. 912–922. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1099/JMM.0.005850-0/CITE/REFWORKS. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V. (2008) ‘Metallo beta lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter species’, http://dx.doi.org/10.1517/13543784.17.2.131, 17(2), pp. 131–143. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.17.2.131. [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.R. (2009) ‘The Type III Secretion System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Infection by Injection’, Nature reviews. Microbiology, 7(9), p. 654. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/NRMICRO2199. [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.J. et al. (2015) ‘Epidemiology and Characteristics of Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa’, Infection & Chemotherapy, 47(2), p. 81. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3947/IC.2015.47.2.81. [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A. et al. (2012) ‘Ribosomal multilocus sequence typing: universal characterization of bacteria from domain to strain’, Microbiology (Reading, England), 158(Pt 4), pp. 1005–1015. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1099/MIC.0.055459-0. [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.Y. El et al. (2019) ‘Chemogenomic Screen for Imipenem Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria’, mSystems, 4(6). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/MSYSTEMS.00465-19. [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M. et al. (2019) ‘Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs’, Nature Biotechnology 2019 37:5, 37(5), pp. 540–546. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0072-8. [CrossRef]
- Kostyanev, T. et al. (2020) ‘Emergence of ST654 Pseudomonas aeruginosa co-harbouring blaNDM-1 and blaGES-5 in novel class I integron In1884 from Bulgaria’, Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance, 22, pp. 672–673. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JGAR.2020.06.008. [CrossRef]
- Li, C. et al. (2011) ‘FastCloning: A highly simplified, purification-free, sequence- and ligation-independent PCR cloning method’, BMC Biotechnology, 11(1), pp. 1–10. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-11-92/FIGURES/6. [CrossRef]
- Li, X. et al. (2023) ‘Characterization of Three Novel IMP Metallo-β-Lactamases, IMP-89, IMP-91, and IMP-96, and Diverse blaIMP-Carrying Accessory Genetic Elements from Chinese Clinical Isolates’, Microbiology spectrum, 11(3). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/SPECTRUM.04986-22. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. et al. (2022) ‘VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors’, Nucleic acids research, 50(D1), pp. D912–D917. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKAB1107. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M. et al. (2019) ‘ICEberg 2.0: an updated database of bacterial integrative and conjugative elements’, Nucleic Acids Research, 47(D1), pp. D660–D665. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKY1123. [CrossRef]
- Livermore, D.M. and Jones, C.S. (1986) ‘Characterization of NPS-1, a novel plasmid-mediated β-lactamase, from two Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 29(1), pp. 99–103. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.29.1.99. [CrossRef]
- Manca, C. et al. (1999) ‘Mycobacterium tuberculosis catalase and peroxidase activities and resistance to oxidative killing in human monocytes in vitro’, Infection and immunity, 67(1), pp. 74–79. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.67.1.74-79.1999. [CrossRef]
- Manni, M. et al. (2021) ‘BUSCO Update: Novel and Streamlined Workflows along with Broader and Deeper Phylogenetic Coverage for Scoring of Eukaryotic, Prokaryotic, and Viral Genomes’, Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38(10), pp. 4647–4654. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/MOLBEV/MSAB199. [CrossRef]
- Mazel, D. (2006) ‘Integrons: agents of bacterial evolution’, Nature Reviews Microbiology 2006 4:8, 4(8), pp. 608–620. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1462. [CrossRef]
- McClure, C.D. and Schiller, N.L. (1996) ‘Inhibition of macrophage phagocytosis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids in vitro and in vivo’, Current microbiology, 33(2), pp. 109–117. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/S002849900084. [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, A.J. (no date) ‘Regulation of Pyoverdine Biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa’.
- Mendes, R.E. et al. (2007) ‘Rapid Detection and Identification of Metallo-β-Lactamase-Encoding Genes by Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay and Melt Curve Analysis’, Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 45(2), p. 544. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01728-06. [CrossRef]
- Mikheenko, A. et al. (2018) ‘Versatile genome assembly evaluation with QUAST-LG’, Bioinformatics, 34(13), pp. i142–i150. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTY266. [CrossRef]
- Moura, A. et al. (2009) ‘INTEGRALL: a database and search engine for integrons, integrases and gene cassettes’, Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 25(8), pp. 1096–1098. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTP105. [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P., Poirel, L. and Dortet, L. (2012) ‘Rapid Detection of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae’, Emerging Infectious Diseases, 18(9), p. 1503. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3201/EID1809.120355. [CrossRef]
- Papa-Ezdra, R. et al. (2023) ‘Novel Resistance Regions Carrying TnaphA6, blaVIM-2, and blaPER-1, Embedded in an ISPa40-Derived Transposon from Two Multi-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates’, Antibiotics, 12(2), p. 304. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIBIOTICS12020304/S1. [CrossRef]
- Papagiannitsis, C.C. et al. (2017) ‘Molecular Characterization of Carbapenemase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa of Czech Origin and Evidence for Clonal Spread of Extensively Resistant Sequence Type 357 Expressing IMP-7 Metallo-β-Lactamase’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 61(12). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01811-17. [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H. et al. (2015) ‘CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes’, Genome Research, 25(7), pp. 1043–1055. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1101/GR.186072.114. [CrossRef]
- Petrova, A. et al. (2019) ‘First detected OXA-50 carbapenem-resistant clinical isolates Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Bulgaria and interplay between the expression of main efflux pumps, OprD and intrinsic AmpC’, Journal of medical microbiology, 68(12), pp. 1723–1731. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1099/JMM.0.001106/CITE/REFWORKS. [CrossRef]
- Pilato, V. Di et al. (2019a) ‘Identification of a novel plasmid lineage associated with the dissemination of metallo-β-lactamase genes among pseudomonads’, Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, p. 464887. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2019.01504/BIBTEX. [CrossRef]
- Pilato, V. Di et al. (2019b) ‘Identification of a novel plasmid lineage associated with the dissemination of metallo-β-lactamase genes among pseudomonads’, Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, p. 1504. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01504. [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L., Naas, T. and Nordmann, P. (2006) ‘Pyrosequencing as a rapid tool for identification of GES-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamases’, Journal of clinical microbiology, 44(8), pp. 3008–3011. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02576-05. [CrossRef]
- Pottier, M. et al. (2023) ‘A 10-year microbiological study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains revealed the circulation of populations resistant to both carbapenems and quaternary ammonium compounds’, Scientific Reports 2023 13:1, 13(1), pp. 1–16. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-29590-0. [CrossRef]
- Quale, J. et al. (2006) ‘Interplay of Efflux System, ampC, and oprD Expression in Carbapenem Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 50(5), p. 1633. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.50.5.1633-1641.2006. [CrossRef]
- Recio, R. et al. (2020) ‘Predictors of Mortality in Bloodstream Infections Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Impact of Antimicrobial Resistance and Bacterial Virulence’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 64(2). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01759-19. [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P. et al. (2008) ‘Revised Nomenclature for Transposable Genetic Elements’, Plasmid, 60(3), pp. 167–173. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLASMID.2008.08.001. [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. and Nash, J.H.E. (2018) ‘MOB-suite: software tools for clustering, reconstruction and typing of plasmids from draft assemblies’, Microbial Genomics, 4(8). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1099/MGEN.0.000206. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M., Poirel, L. and Nordmann, P. (2009) ‘Molecular Epidemiology and Mechanisms of Carbapenem Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 53(11), p. 4783. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00574-09. [CrossRef]
- Ross, K. et al. (2021) ‘TnCentral: a Prokaryotic Transposable Element Database and Web Portal for Transposon Analysis’, mBio, 12(5). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/MBIO.02060-21. [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.B. et al. (2013) ‘Diverse type VI secretion phospholipases are functionally plastic antibacterial effectors’, Nature, 496(7446), p. 508. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/NATURE12074. [CrossRef]
- Ryall, B. et al. (2008) ‘Pseudomonas aeruginosa, cyanide accumulation and lung function in CF and non-CF bronchiectasis patients’, European Respiratory Journal, 32(3), pp. 740–747. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00159607. [CrossRef]
- Sakuda, A. et al. (2018) ‘Divalent cations increase the conjugation efficiency of the incompatibility P-7 group plasmid pCAR1 among different Pseudomonas hosts’, Microbiology (Reading, England), 164(1), pp. 20–27. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1099/MIC.0.000583. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, I. et al. (2008) ‘VIM-15 and VIM-16, Two New VIM-2-Like Metallo-β-Lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from Bulgaria and Germany’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 52(8), p. 2977. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00175-08. [CrossRef]
- Schwengers, O. et al. (2021) ‘Bakta: Rapid and standardized annotation of bacterial genomes via alignment-free sequence identification’, Microbial Genomics, 7(11), p. 000685. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1099/MGEN.0.000685/CITE/REFWORKS. [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K. and Rao, T.S. (2017) ‘An Improved Crystal Violet Assay for Biofilm Quantification in 96-Well Microtitre Plate’, bioRxiv, p. 100214. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1101/100214. [CrossRef]
- Siguier, P. et al. (2006) ‘ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences’, Nucleic acids research, 34(Database issue). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKJ014. [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.O. et al. (2023) ‘Genetic and biochemical characterization of BIM-1, a novel acquired subgroup B1 MBL found in a Pseudomonas sp. strain from the Brazilian Amazon region’, The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy, 78(6), pp. 1359–1366. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/JAC/DKAD077. [CrossRef]
- Strateva, T., Setchanova, L. and Peykov, S. (2021) ‘Characterization of a Bulgarian VIM-2 metallo-β-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate belonging to the high-risk sequence type 111′, https://doi.org/10.1080/23744235.2021.1934531, 53(11), pp. 883–887. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/23744235.2021.1934531. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. (2021) ‘Cefiderocol: A Review in Serious Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections’, Drugs, 81(13), p. 1559. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/S40265-021-01580-4. [CrossRef]
- Tansirichaiya, S., Rahman, M.A. and Roberts, A.P. (2019) ‘The Transposon Registry’, Mobile DNA, 10(1), pp. 1–6. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/S13100-019-0182-3/FIGURES/3. [CrossRef]
- Thrane, S.W. et al. (2016) ‘Application of whole-genome sequencing data for o-specific antigen analysis and in silico serotyping of pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates’, Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 54(7), pp. 1782–1788. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00349-16/SUPPL_FILE/ZJM999095025SO3.XLSX. [CrossRef]
- Toleman, M.A. et al. (2005) ‘Italian metallo-beta-lactamases: a national problem? Report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Programme’, The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy, 55(1), pp. 61–70. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/JAC/DKH512. [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q. et al. (2016) ‘Room temperature electrocompetent bacterial cells improve DNA transformation and recombineering efficiency’, Scientific reports, 6. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/SREP24648. [CrossRef]
- Vasil, M.L. et al. (2009) ‘A Complex Extracellular Sphingomyelinase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Inhibits Angiogenesis by Selective Cytotoxicity to Endothelial Cells’, PLOS Pathogens, 5(5), p. e1000420. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PPAT.1000420. [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.R. et al. (2005) ‘Metallo-β-lactamases: The quiet before the storm?’, Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 18(2), pp. 306–325. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.18.2.306-325.2005/ASSET/1879A073-59B5-4686-BE7F-2512B2959689/ASSETS/GRAPHIC/ZCM0020521330004.JPEG. [CrossRef]
- Walter, M. V, Porteous, A. and Seidler, R.J. (1987) ‘Measuring Genetic’, 53(1), pp. 105–109.
- Wang, M.G. et al. (2021) ‘Retrospective Data Insight into the Global Distribution of Carbapenemase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa’, Antibiotics, 10(5). Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIBIOTICS10050548. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M. et al. (1991) ‘Transferable imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 35(1), pp. 147–151. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.35.1.147. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q. et al. (2011) ‘Transcription of integron-harboured gene cassette impacts integration efficiency in class 1 integron’, Molecular Microbiology, 80(5), pp. 1326–1336. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1365-2958.2011.07648.X. [CrossRef]
- Wi, Y.M. et al. (2018) ‘Activity of Ceftolozane-Tazobactam against Carbapenem-Resistant, Non-Carbapenemase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Associated Resistance Mechanisms’, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 62(1). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01970-17. [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R. and Holt, K.E. (2022) ‘Polypolish: Short-read polishing of long-read bacterial genome assemblies’, PLOS Computational Biology, 18(1), p. e1009802. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PCBI.1009802. [CrossRef]
- Zavascki, A.P. et al. (2006) ‘The influence of metallo-β-lactamase production on mortality in nosocomial Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections’, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 58(2), pp. 387–392. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/JAC/DKL239. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H. and Hu, Z.Q. (2010) ‘β-Lactamases identified in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa’, http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2010.481763, 36(3), pp. 245–258. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2010.481763. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H. and Hu, Z.Q. (2011) ‘IMP-type metallo-β-lactamases in Gram-negative bacilli: distribution, phylogeny, and association with integrons’, Critical reviews in microbiology, 37(3), pp. 214–226. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2011.559944. [CrossRef]
- Zimin, A. V. and Salzberg, S.L. (2020) ‘The genome polishing tool POLCA makes fast and accurate corrections in genome assemblies’, PLOS Computational Biology, 16(6), p. e1007981. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PCBI.1007981. [CrossRef]
- Zulianello, L. et al. (2006) ‘Rhamnolipids Are Virulence Factors That Promote Early Infiltration of Primary Human Airway Epithelia by Pseudomonas aeruginosa’, Infection and Immunity, 74(6), p. 3134. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.01772-05. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).