Submitted:
28 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
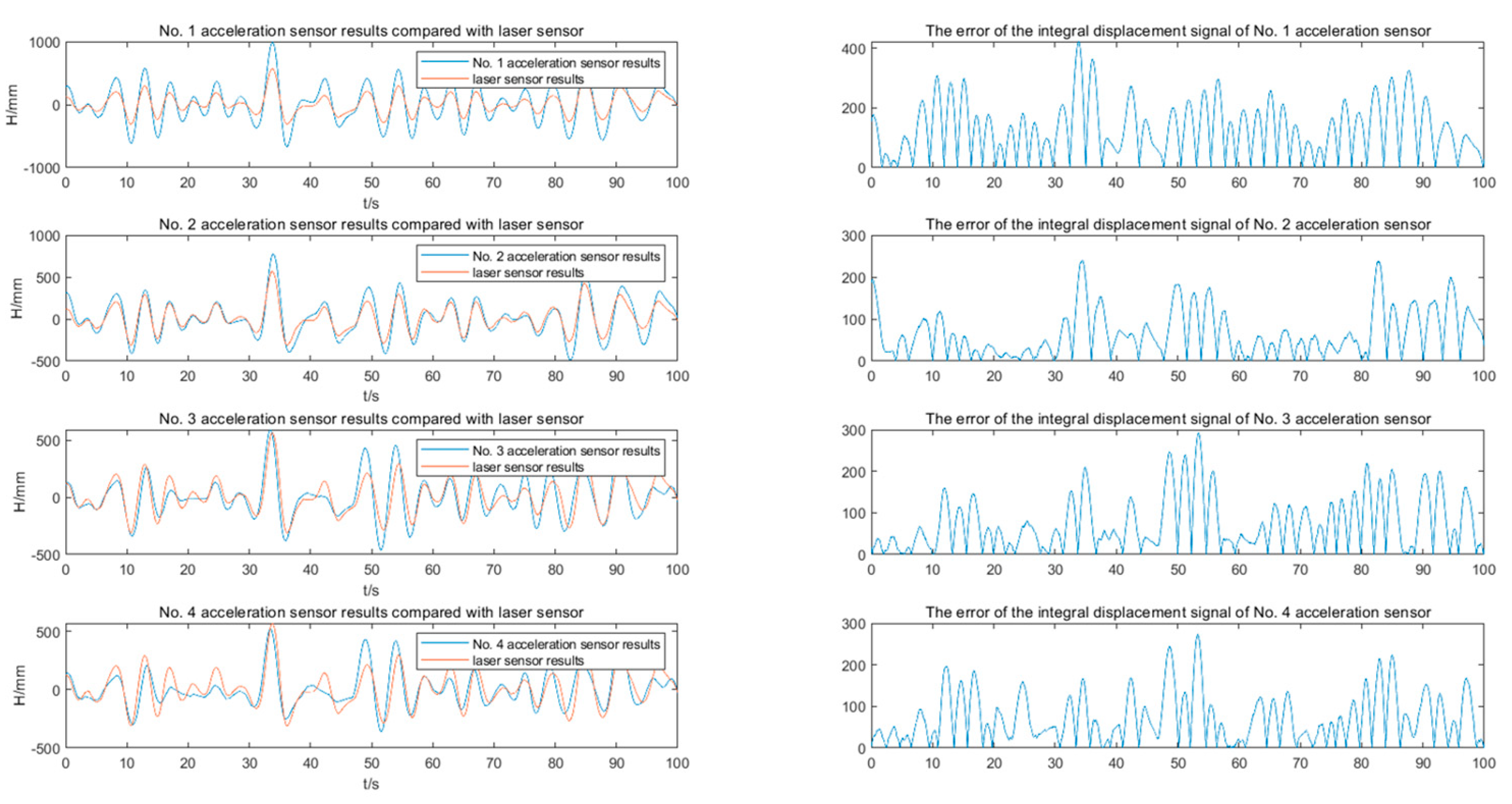
- A method for measuring and correcting the heave direction of ship-borne mechanical platform motion based on multi-acceleration-sensor fusion is proposed. The heave displacement signal of the platform under unknown tilt angle is calculated by the outputs of 4 sets of acceleration sensors with improved accuracy.
- A method for measuring the change of inclination angle of ship-borne mechanical platform motion based on Kalman filtering technique using sensor fusion of acceleration sensor and angle sensor is proposed. The calculated tilt angle of the platform in roll and pitch direction calculated by 4 sets of acceleration sensors is used as the estimation value, and the inclination angle signal measured by the angle sensor is used as the observation value. Innovation-based adaptive Kalman filtering is used to obtain the inclination angle and the heave displacement of the platform with higher accuracy.
2. Preliminary Work
- Capacitance is seriously interfered by the marine environment, such as temperature, humidity and other factors. Generally, it needs to be shielded and filtered, otherwise it will affect the measurement accuracy.
- Capacitive sensors need to be installed on the hull, which is easily subjected to vibration and shock from the hull.
- In marine environments, capacitive sensors are susceptible to seawater corrosion and water pressure, requiring special protection methods.
3. Proposed Algorithm
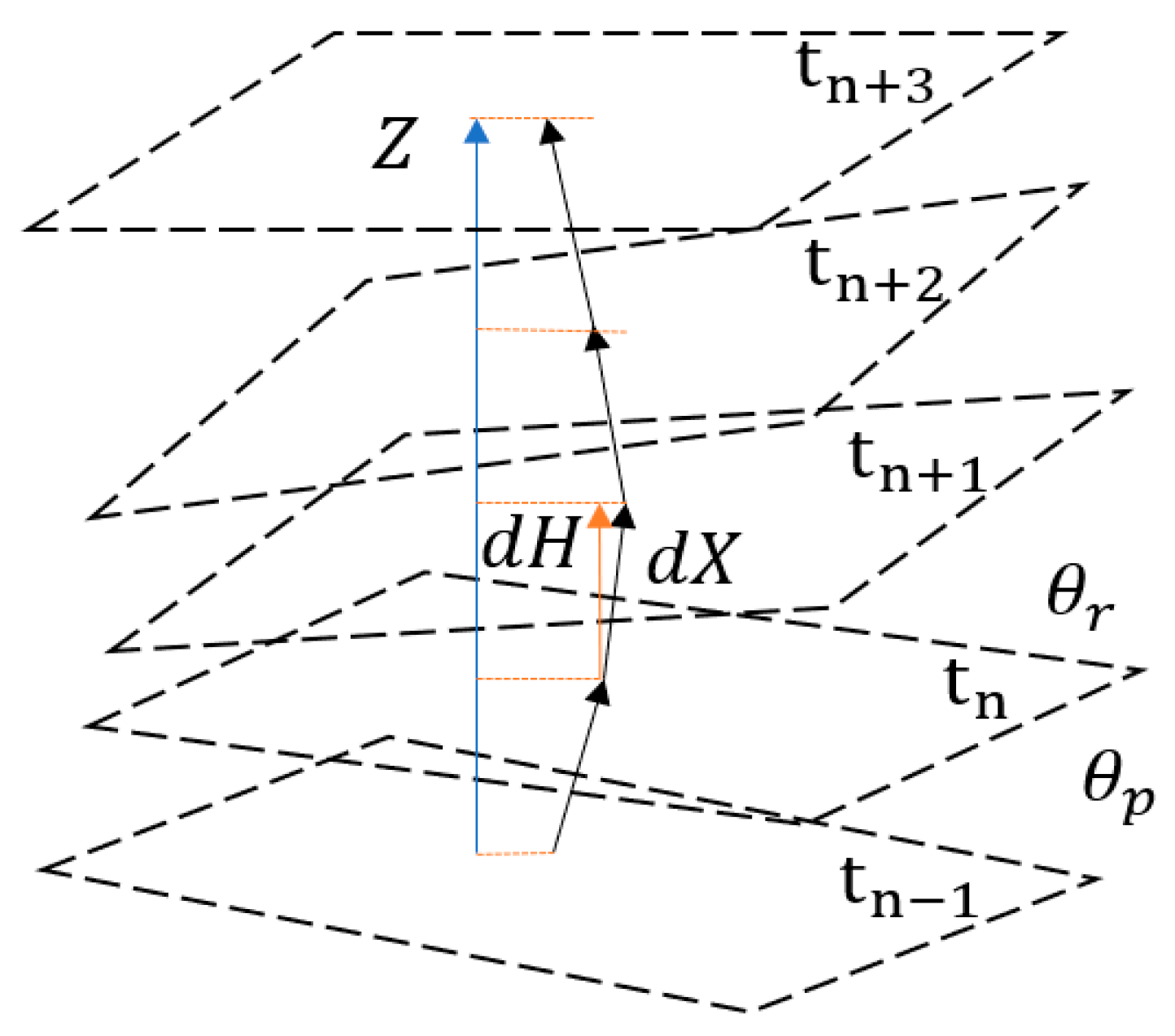
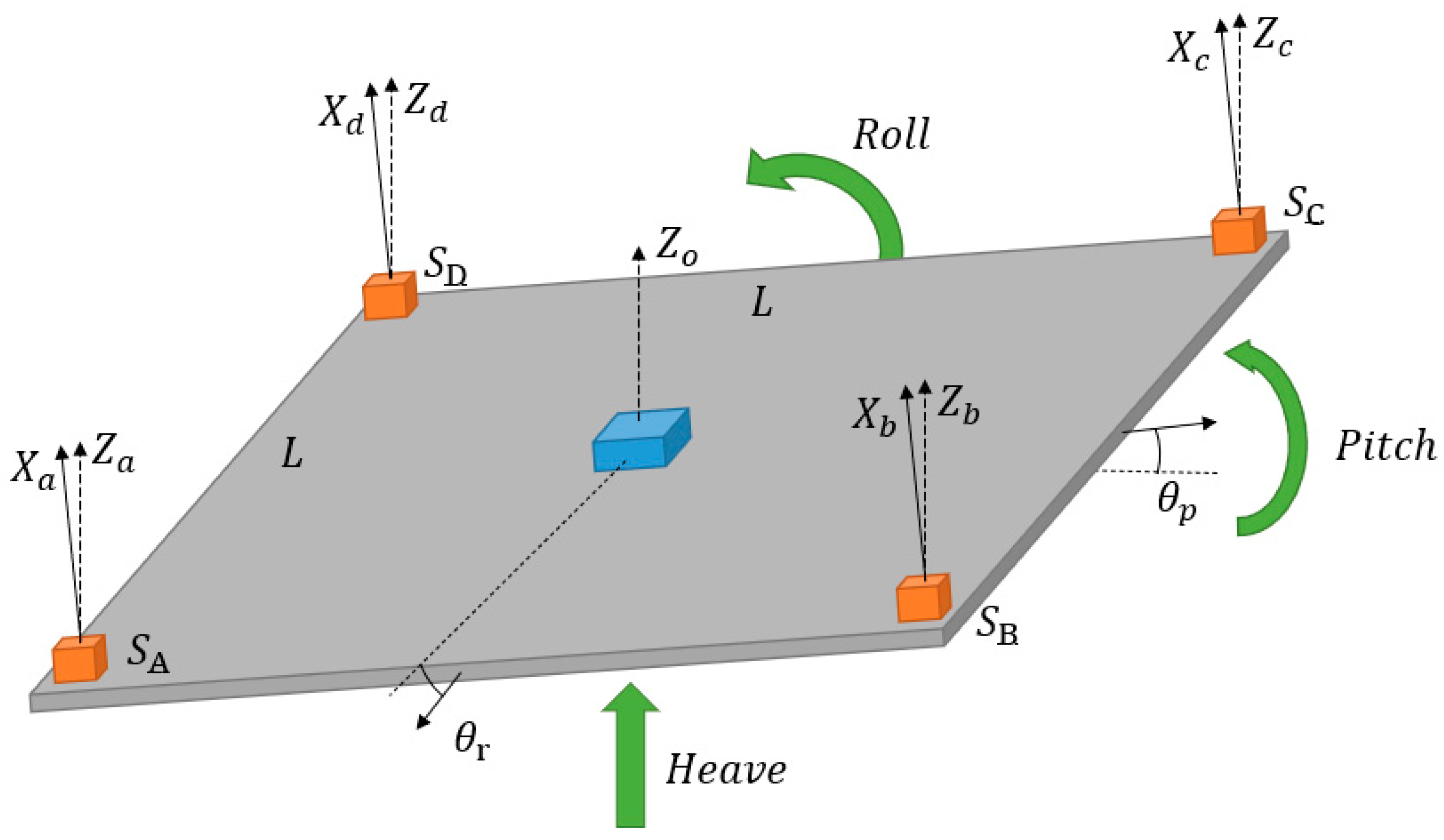
3.1. Multi-Sensor Fusion of Acceleration Sensor Sets
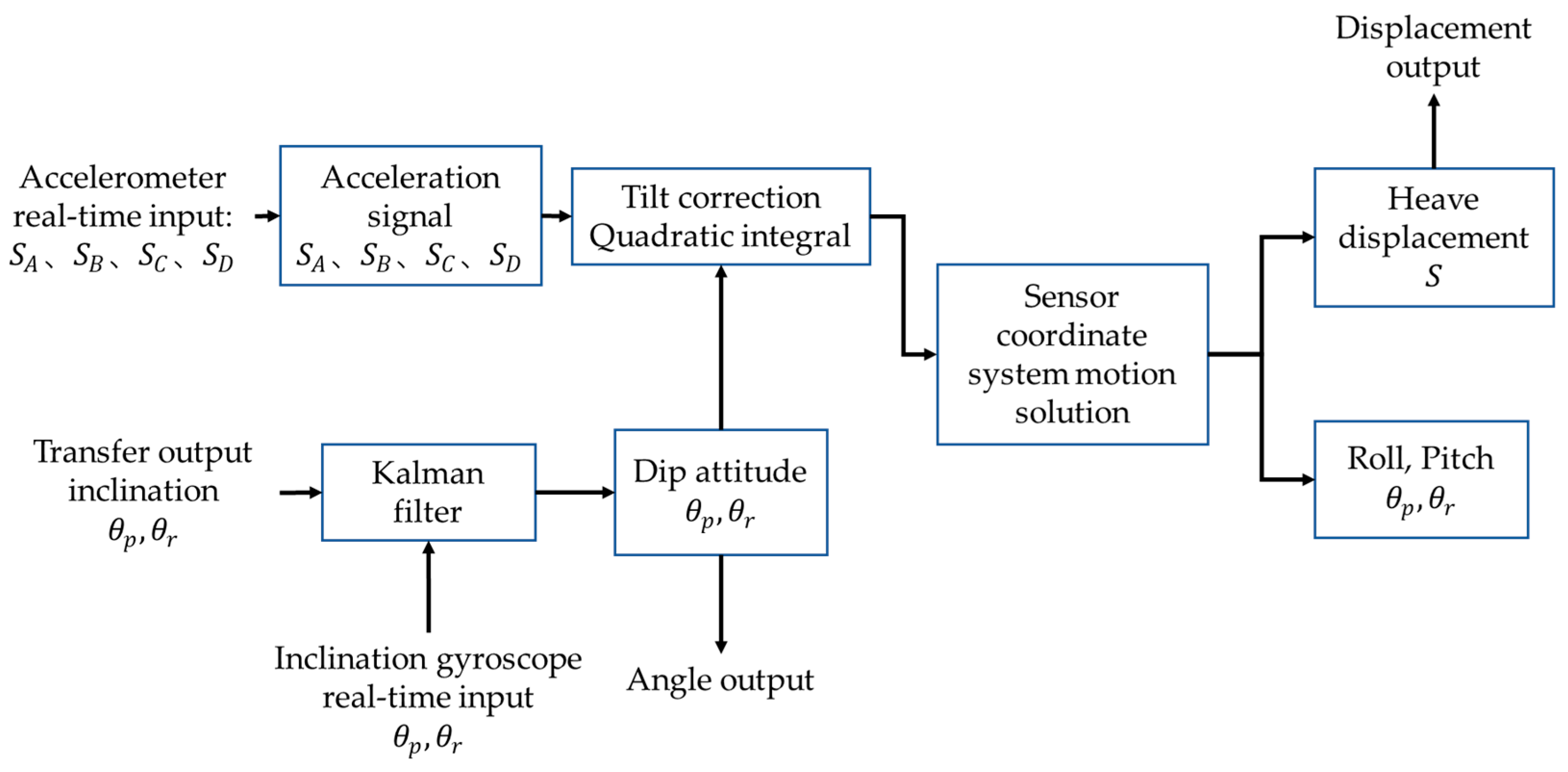
3.2. Motion estimation based on Kalman filtering
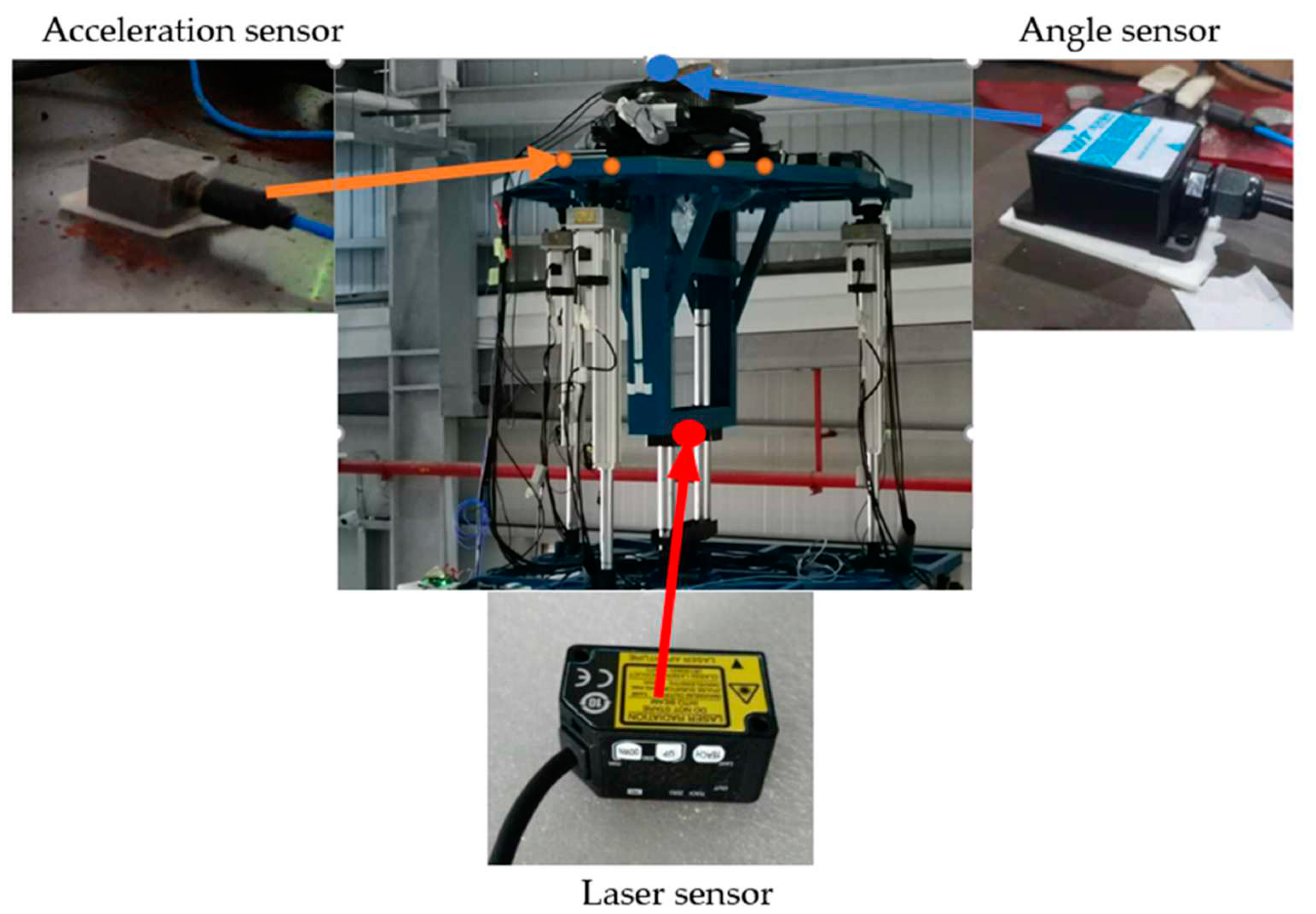
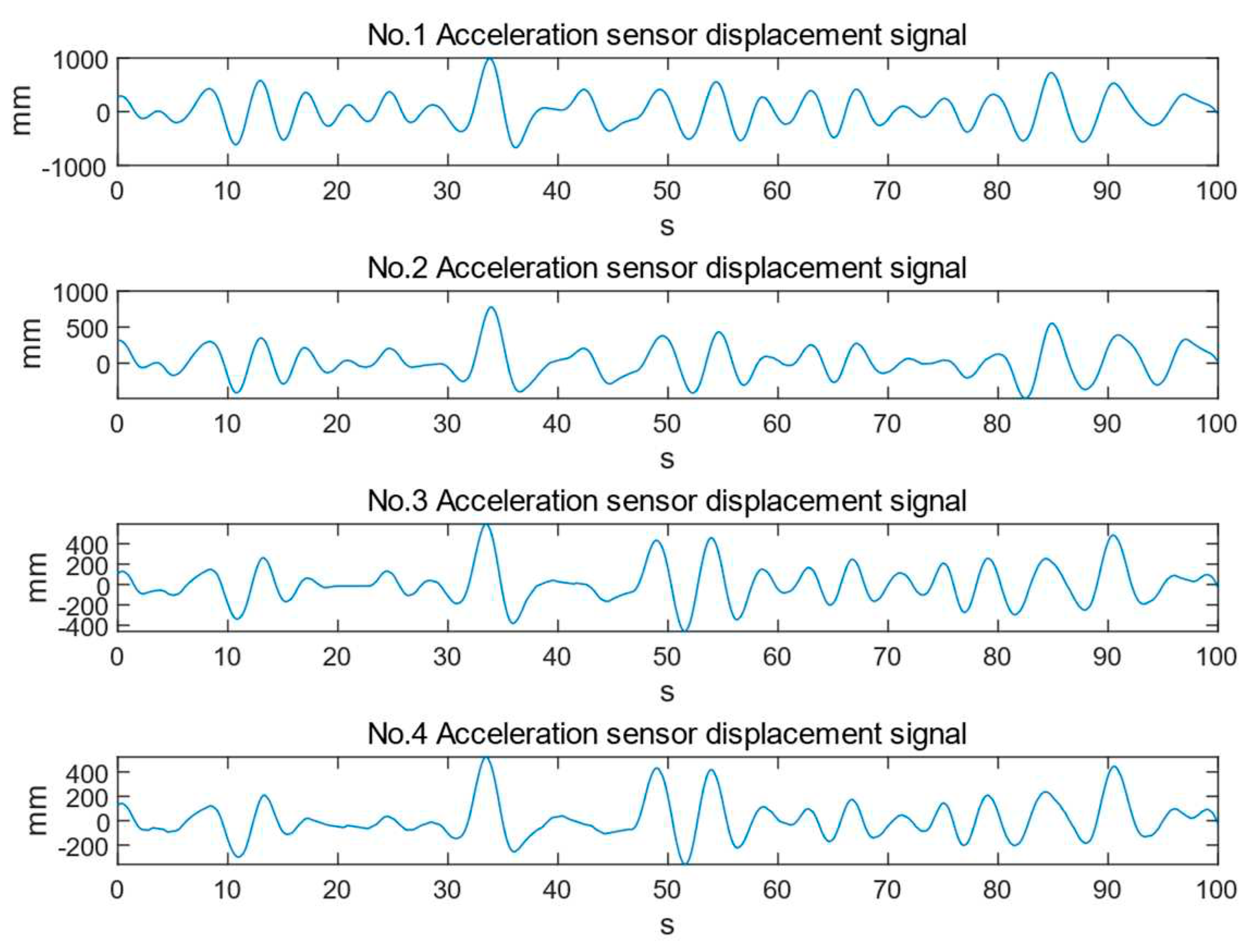
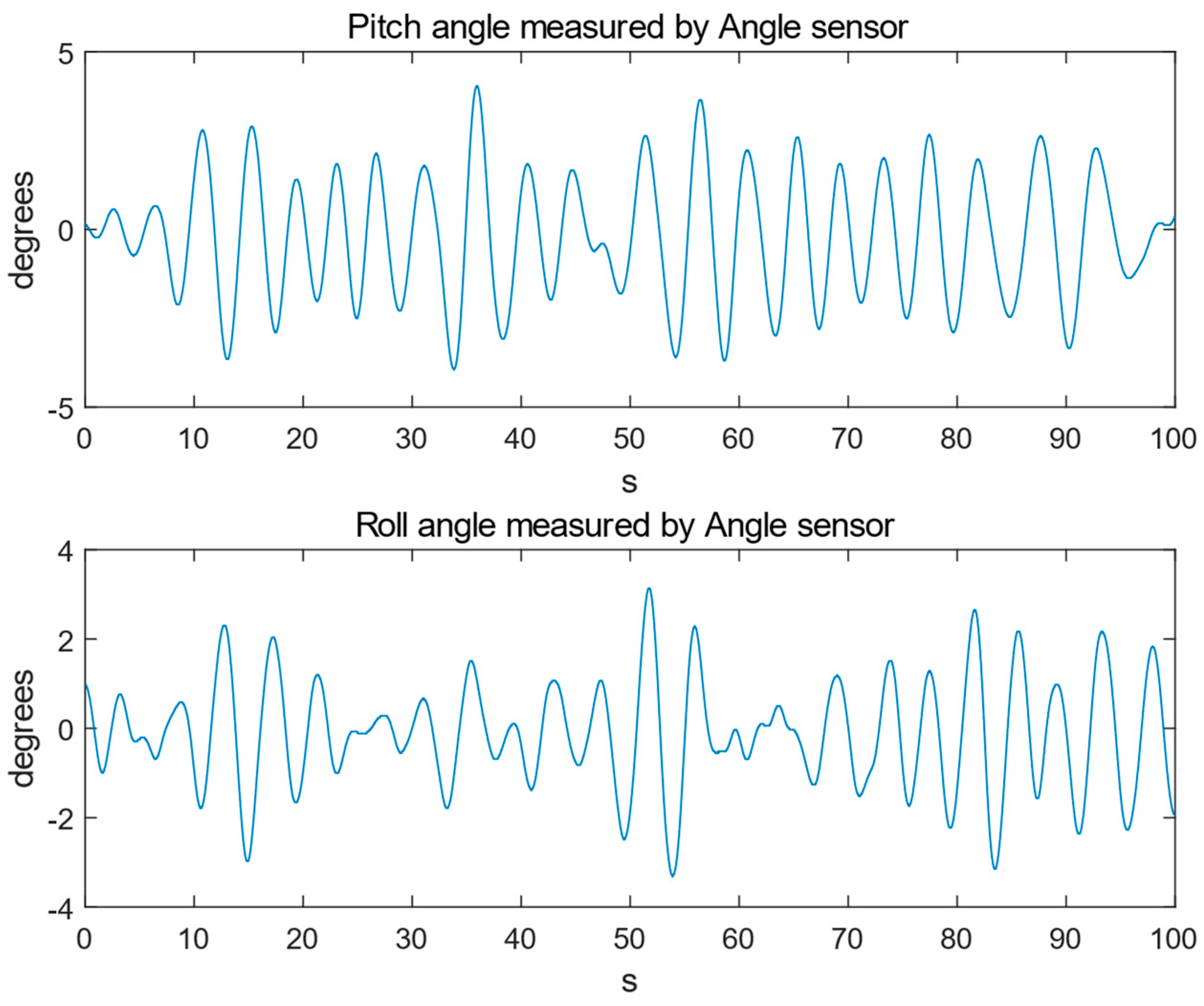
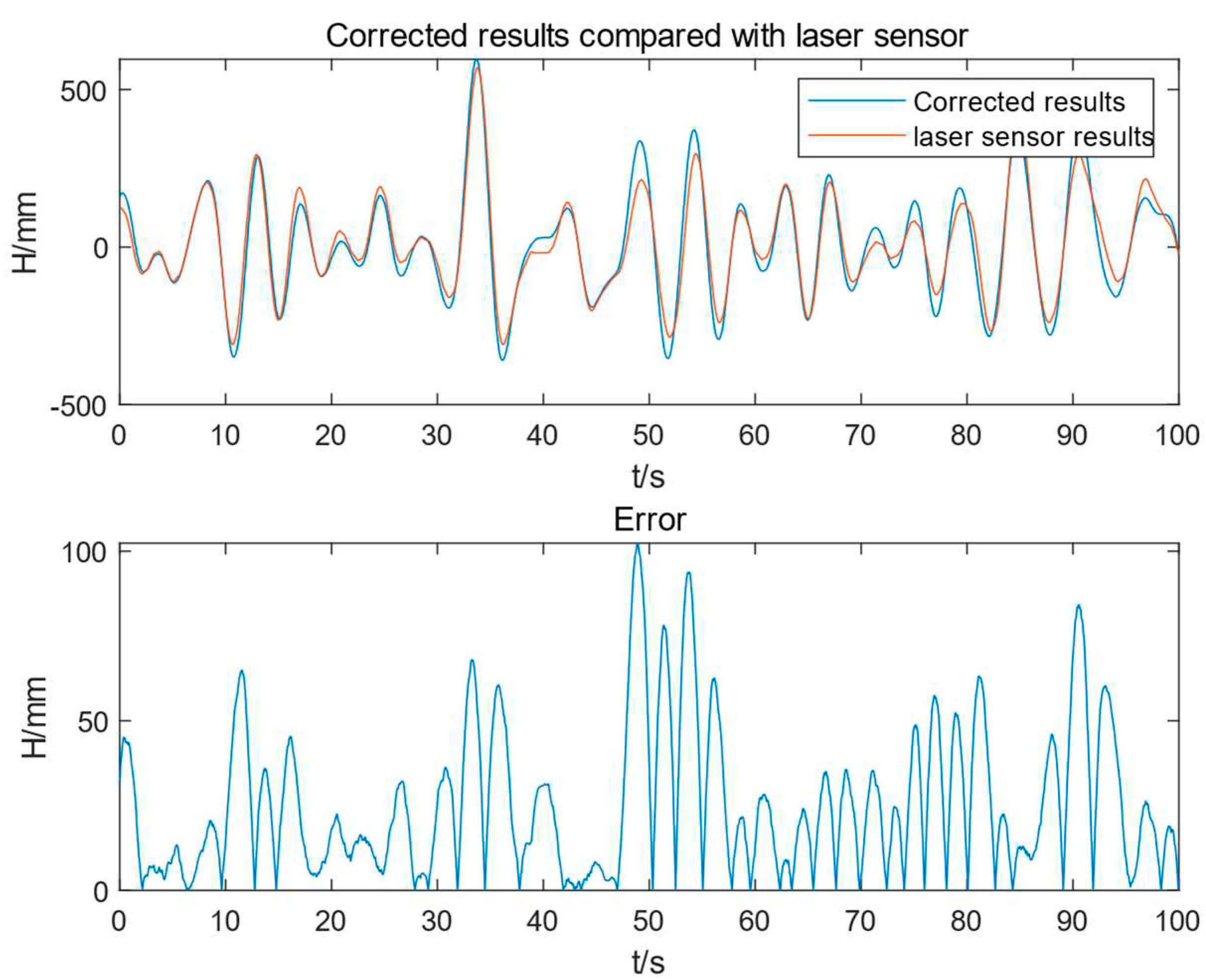
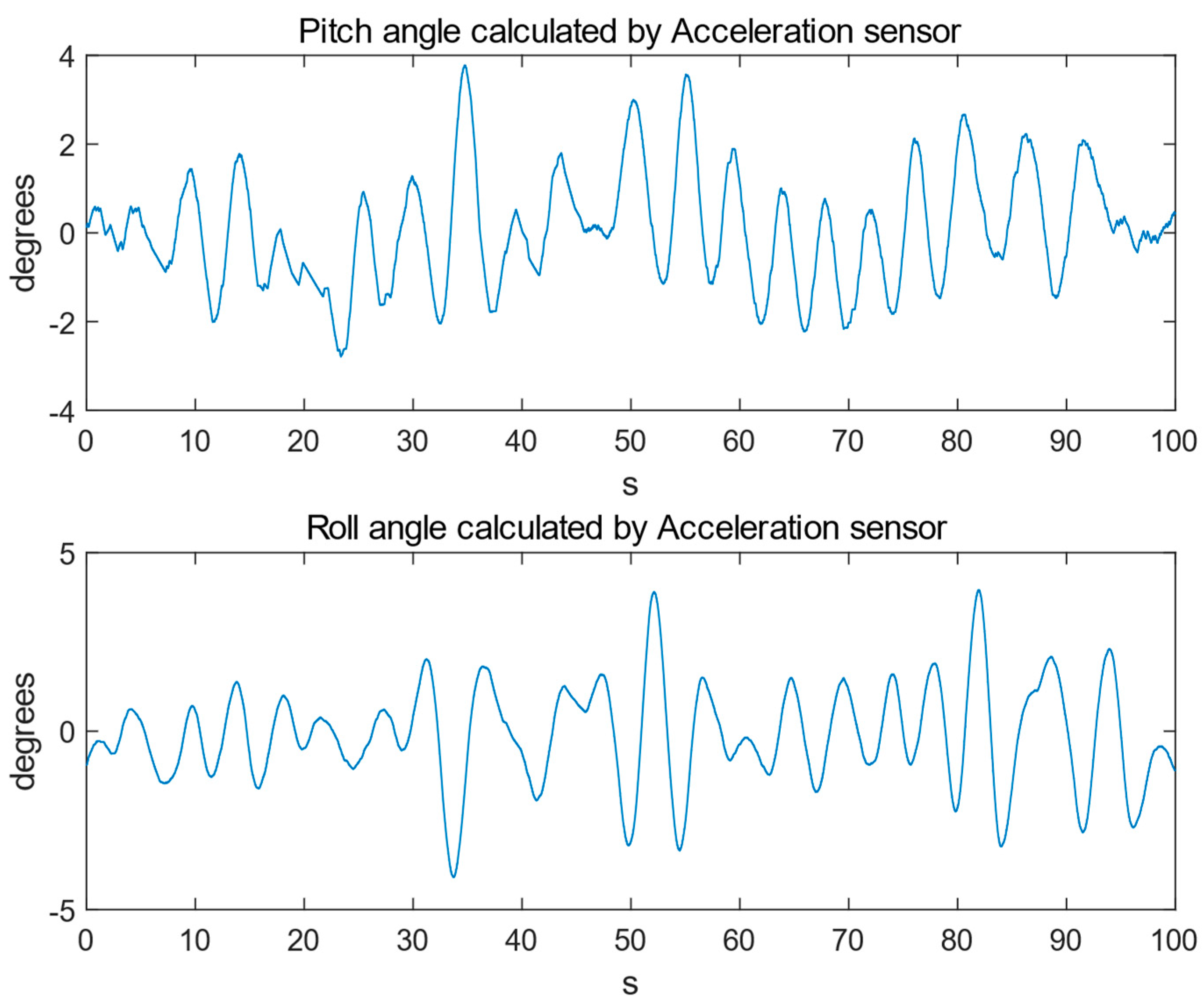
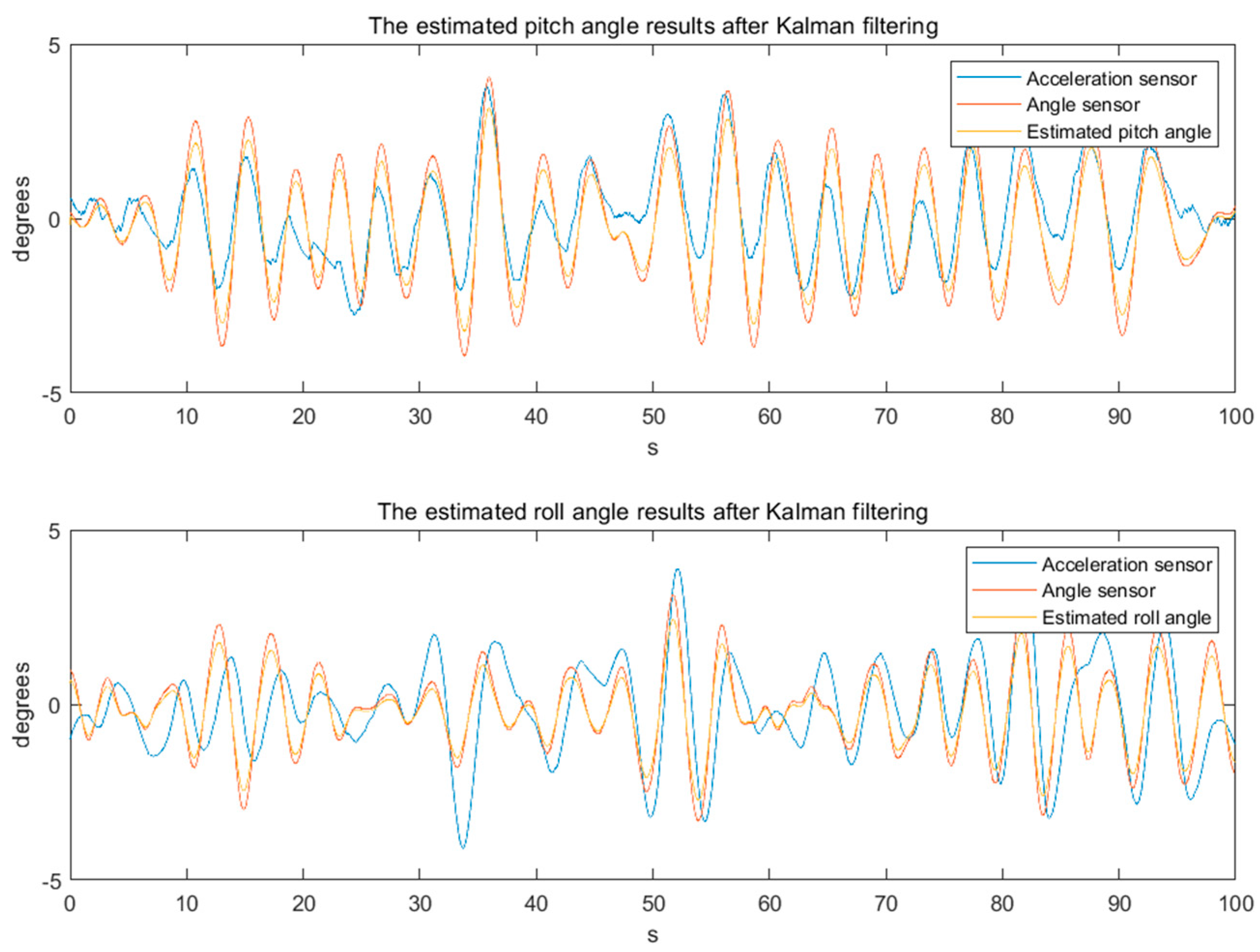
4. Experimental Results
- Reduce influence of noise and error. The angle signal calculated by the acceleration sensor usually has large noise and error. Meanwhile, the angle signal measured by the angle sensor may also be affected by external interference. Through Kalman filtering, these noises and errors can be filtered out, so as to obtain more accurate angle signals.
- Improved response speed. The angle signal calculated by the acceleration sensor has a faster response speed, but there are large noises and errors. On the other hand, the angle signal measured by the angle sensor has a slower response speed, but possess higher precision. Through Kalman filtering, the advantages of the two can be combined, which not only improves the response speed, but also improves the accuracy.
- Improve system stability. Since the angle signal calculated by the acceleration sensor has large noise and errors, the system may jitter or become unstable. Through adaptive Kalman filtering, these noises and errors can be filtered out, thereby improving the stability of the system.
- Reduced cost: the cost of the angle signal calculated by acceleration sensors is lower than that of the angle signal measured by advanced angle sensors. Through the Kalman filter, the angle signal calculated by the acceleration sensor can be filtered to obtain a result comparable to or even better than the angle signal measured by the angle sensor, thereby reducing the cost of using expensive gyroscopes.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, R.C.; Lin, M.-H.; Scherp, R.S. Dynamic Multi-Sensor Data Fusion System for Intelligent Robots. IEEE Journal on Robotics and Automation 1988, 4, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant-Whyte, H.F.; Rao, B.Y.S.; Hu, H. Toward a Fully Decentralized Architecture for Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the Proceedings., IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; IEEE; 1990; pp. 1331–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, W.; Durrant-Whyte, H.F. Model-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 1992 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation; IEEE; 1992; pp. 1720–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.J.; Bailey, A.; Dodd, T.J. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion in Defence and Aerospace. The Aeronautical Journal 1998, 102, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinas, J.; Hall, D.L. An Introduction to Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the ISCAS’98. Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (Cat. No. 98CH36187); IEEE, 1998; Vol. 6, pp. 537–540.
- Chen, S.; Bao, H.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Y. A Fire Detecting Method Based on Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the SMC’03 Conference Proceedings. 2003 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. Conference Theme-System Security and Assurance (Cat. No. 03CH37483); IEEE, 2003; Vol. 4, pp. 3775–3780.
- Herpel, T.; Lauer, C.; German, R.; Salzberger, J. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion in Automotive Applications. In Proceedings of the 2008 3rd International Conference on Sensing Technology; IEEE; 2008; pp. 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Manjunatha, P.; Verma, A.K.; Srividya, A. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion in Cluster Based Wireless Sensor Networks Using Fuzzy Logic Method. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE region 10 and the third international conference on industrial and information systems; IEEE; 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Zhuang, D.; Huang, Y.; Fu, J. Advances in Multi-Sensor Data Fusion: Algorithms and Applications. Sensors 2009, 9, 7771–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolter, P.T.; Townsend, P.A. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion for Estimating Forest Species Composition and Abundance in Northern Minnesota. Remote Sens Environ 2011, 115, 671–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjahed, H.; Istrate, D.; Boudy, J.; Baldinger, J.-L.; Dorizzi, B. A Pervasive Multi-Sensor Data Fusion for Smart Home Healthcare Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems (FUZZ-IEEE 2011); IEEE; 2011; pp. 1466–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, T.P.; Das, S. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Using Support Vector Machine for Motor Fault Detection. Inf Sci (N Y) 2012, 217, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frikha, A.; Moalla, H. Analytic Hierarchy Process for Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Based on Belief Function Theory. Eur J Oper Res 2015, 241, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimirad, E.; Haddadnia, J.; Izadipour, A.L.I. A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW OF THE MULTI-SENSOR DATA FUSION ARCHITECTURES. J Theor Appl Inf Technol 2015, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Fortino, G.; Galzarano, S.; Gravina, R.; Li, W. A Framework for Collaborative Computing and Multi-Sensor Data Fusion in Body Sensor Networks. Information Fusion 2015, 22, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.; Rawat, S. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion by a Hybrid Methodology–A Comparative Study. Comput Ind 2016, 75, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duro, J.A.; Padget, J.A.; Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A.; Nassehi, A. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Framework for CNC Machining Monitoring. Mech Syst Signal Process 2016, 66, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitijiang, M.; Ghulam, A.; Sidike, P.; Hartling, S.; Maimaitiyiming, M.; Peterson, K.; Shavers, E.; Fishman, J.; Peterson, J.; Kadam, S. Unmanned Aerial System (UAS)-Based Phenotyping of Soybean Using Multi-Sensor Data Fusion and Extreme Learning Machine. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2017, 134, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, M.; Wang, P. An Adaptive Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Method Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Fault Diagnosis of Planetary Gearbox. Sensors 2017, 17, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Gauba, H.; Roy, P.P.; Dogra, D.P. Coupled HMM-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion for Sign Language Recognition. Pattern Recognit Lett 2017, 86, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouain, M.; Ali, K.M.A.; Berdjag, D.; Fakhfakh, N.; Atitallah, R. Ben An Embedded Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Design for Vehicle Perception Tasks. J. Commun. 2018, 13, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Qin, B. A Weighted Combination Method for Conflicting Evidence in Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. Sensors 2018, 18, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ning, Y.; Suo, C. A Method Based on Multi-Sensor Data Fusion for UAV Safety Distance Diagnosis. Electronics (Basel) 2019, 8, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Farias, C.M.; Pirmez, L.; Fortino, G.; Guerrieri, A. A Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Technique Using Data Correlations among Multiple Applications. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 92, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Based on the Belief Divergence Measure of Evidences and the Belief Entropy. Information Fusion 2019, 46, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. Evidence Combination Based on Prospect Theory for Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. ISA Trans 2020, 106, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammal, M.; Talat, R.; Sodhro, A.H.; Pirbhulal, S. A Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Enabled Ensemble Approach for Medical Data from Body Sensor Networks. Information Fusion 2020, 53, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Gebraeel, N.; Lei, Y.; Fang, X.; Cai, X.; Yan, T. Remaining Useful Life Prediction Based on a Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Model. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 2021, 208, 107249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashinath, S.A.; Mostafa, S.A.; Mustapha, A.; Mahdin, H.; Lim, D.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Al-Rimy, B.A.S.; Fudzee, M.F.M.; Yang, T.J. Review of Data Fusion Methods for Real-Time and Multi-Sensor Traffic Flow Analysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 51258–51276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.; Hassan, M.A.; Xiao, Y.; Su, X.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Duan, F.; Chen, R.; Ma, Y. UAV-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion and Machine Learning Algorithm for Yield Prediction in Wheat. Precis Agric 2023, 24, 187–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Hu, X. An Absolute Displacement Measurement Method and Its Application in Ship Motion Measurement. J Mar Sci Eng 2023, 11, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



