1. Introduction
Training to become an independently practicing physician is a seven-to-eleven-year process that involves retention and understanding of a continuously expanding mass of information. Textbook reading is becoming obsolete as trainees favor using podcasts, videos, and app-based learning strategies. [
1] There are many well-known information retention strategies including but not limited to pneumonics, flashcards, spaced repetition, and the method of loci. This paper is a review of a powerful new learning algorithm that engages the user through gamification and evidence proven retention algorithms, Anki.
Anki is an innovative tool for information retention gaining popularity among medical students nationwide. This web-based open-sourced flashcard deck application synchs between laptop and mobile devices. The mobility of the application allows for studying within the time-constrained clinical environment. Decks used to study can be pre-made and downloaded off the internet or decks can be custom created by the user tailored specifically to educational needs. The program uses an evidence based spaced repetition algorithm to increase retention and promote engagement of the user. This is best described as an expanded retrieval platform. The interval between testing of subject matter is gradually increased over time (spaced repetition) .[
2] Applied memory research in the field of cognitive and educational psychology has generated a large body of data to support the use of spacing and testing to promote long-term or durable memory. [
3]
With increasing quantity and variety of Anki use being reported, there is gap in large-scale evidence validating its efficacy. This review acts to summarize current use and corresponding data available. Although relatively little research has been conducted on this topic, the utility of spaced repetition applications has the potential to transform medical education. Using evidence-based practices to optimize and expand this educational platform may greatly benefit knowledge acquisition and retention while addressing severe time management restraints.
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
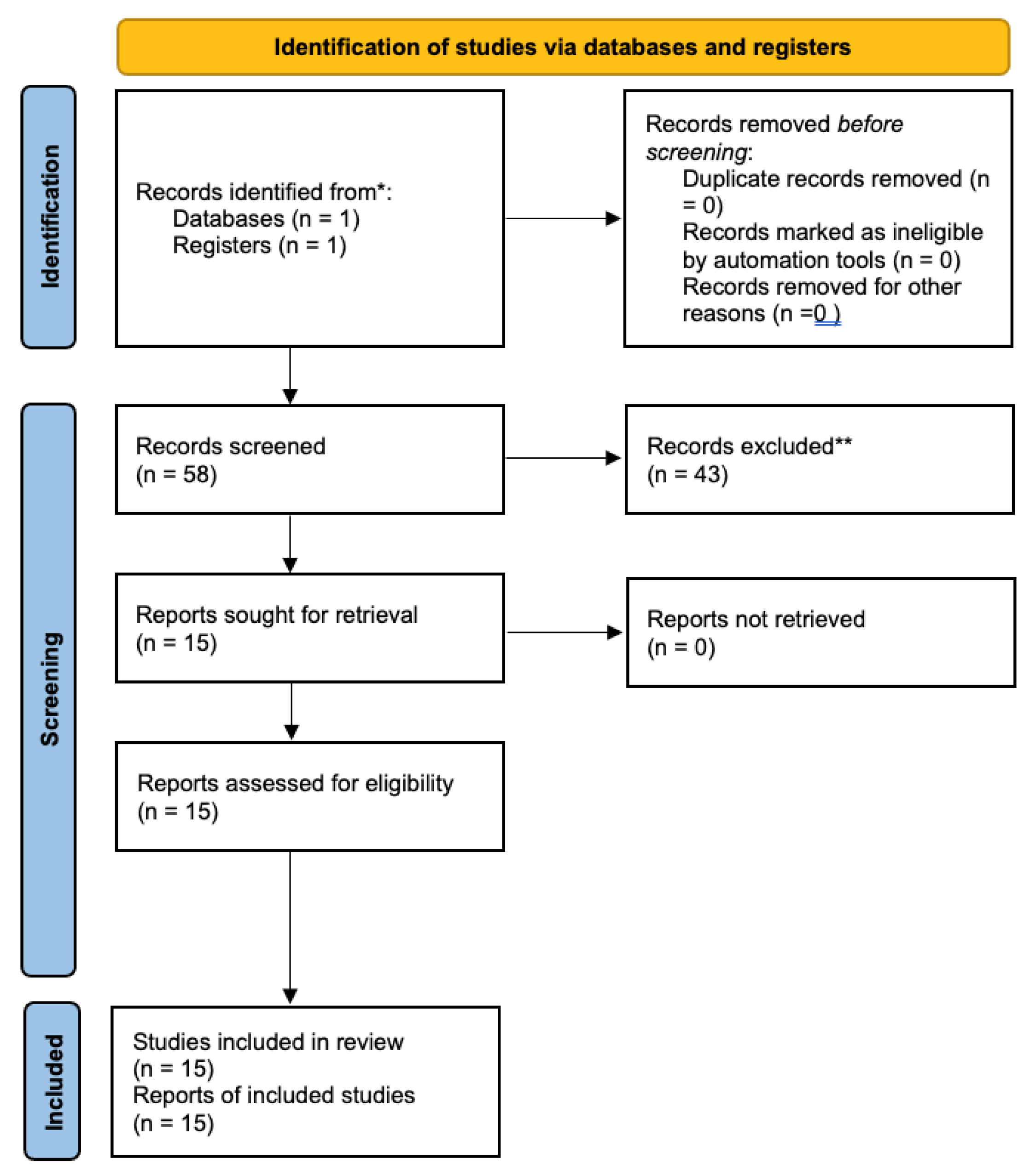
The use of the search term (Anki) revealed 58 peer-reviewed publications. Abstracts were read and all papers including the topic of Anki related to medical education were included in this review. Of the search results, 4 had some form of reportable outcome measures and their data was recorded (see
Table 1).
The use of the search term (spaced repetition residency) revealed 15 results. Abstracts were read and all papers including the topic of Anki and medical education were included in this review. Of the 15 search results, 8 studies included relevant topics pertaining to Anki’s utility in medical education were included in this review. Half of the 8 relevant studies had some form of reportable outcome measures, and their data was recorded in table 1 following the first search. One was a review concerning radiologist training that mentioned benefits of Anki. One was a study on Anki use by otolaryngology residents but had no objective data reported. One study was on the need for future Anki use among plastic surgeon residents but had no objective data reported.
3.2. Medical Student Education
The first study describing Anki efficacy was in 2015 by Deng at Washing State University Medical School. At that time 49% of respondents reported using either Anki or Firecracker flashcard applications. The results showed for every 1,700 unique Anki flashcards incorporated into studying, there was an associated additional point on Step 1 when controlling for other academic and psychological factors. [
4]
A recent 2022 study done by Harris on first-year medical students at the University of Central Florida demonstrated an interval increase in usage and how rapidly first-year students integrate Anki into their education. Results showed 70% of first-year medical students were utilizing Anki in conjunction with formal lectures by the 13
th week. [
5] Authors of the study proposed that faculty consider methods of incorporating Anki into university created education.
Compared with Deng’s 2015 data (49%), Harris’ updated numbers (70%) of Anki usage reflect an increase in usage in medical education. Prior to their study, it was known high numbers of medical students adopt Anki to prepare for the United States Medical Licensing Exam (USMLE) Step 1 exam, but no data had been collected on early adoption of the app.
Another 2022 study done by Jape provided further evidence of medical student enthusiasm toward Anki utilization. Students were given a basic 1,208 pharmacology deck and found benefits to Anki use. In focus groups students shared remarked Anki as “comprehensive and well formatted”. The authors proposed Anki utilization addressed a significant unmet need for time-efficient strategies regarding the ongoing revision of medical pharmacology. [
6]
The deck size used in all discovered studies is minuscule compared to popular decks circulating nationally. The Anking deck, aimed to prepare students for STEP-1, contains over 40,000 flash cards. Considering the study by Deng showed a dose-dependent increase in board scores correlating with unique Anki flashcard addition, there are obvious advantages to adding cards to your study resources.
3.3. Resident Education
As Anki-trained medical students progress into residency, they have naturally continued utilizing learning strategies that improved efficiency in medical school. Their review only yielded papers on a select few specialties detailed below. Each review reported Anki being well accepted and effective in resident education warranting further research expanding on the concept.
Orthopedic Surgery. Orthopedic surgery residents must acquire a considerable amount of knowledge, develop complex surgical skills, and hone crucial clinical thinking in a relatively short period of time. [
7]. A recent study of twelve orthopedic surgery residents demonstrated Anki’s utility for studying for the OPBS exam under typical time constraints of a surgical resident. There was a 92% pass rate among the residents studied, far superior to the national pass rate of 67%. The Anki deck used was basic containing 1,400 practice questions. This study demonstrated Anki to be an effective study strategy in surgical residency and authors proposed Anki should be further developed in other areas of surgery.
Obstetrics and Gynecology. Another study on Duke University obstetrics and gynecology residents provided additional benefits of Anki in resident training. The study evaluated resident usage and satisfaction with the Anki application and again demonstrated it was a well-accepted and valued tool among residents. Residents remarked liking the convenience and accessibility of the study flashcards, which allowed them to incorporate studying between day-to-day activities. This study additionally showed improvement in scores on the Council on Resident Education in Obstetrics and Gynecology (CREOG) exam, but this finding did not reach statistical significance [
8].
Diagnostic radiology. Diagnostic radiology was the only residency within the scope of the review that had multiple papers regarding Anki. A review from 2019 by Morin investigated the use of spaced repetition among radiology residents. This review highlighted Anki’s advantages compared with other applications available at the time. Anki uniquely has the capability to incorporate non-image-based faction information radiology trainees are required to learn. This study went on to demonstrate how their independently developed space repetition software was an effective tool for trainees to create and share flashcard decks. The Anki platform has similar sharing abilities and its global open-sourced platform is under continual development. Another 2019 study by Ayoob evaluated the feasibility of Anki to act as a comprehensive resource specifically targeted to first-year radiologist residents. This study involved creating a web-based curriculum incorporating Anki-decks and a system for monitoring intern use of the resource is feasible. Users perceived the course as a useful resource and reported high satisfaction with the curriculum. [
9]
Otolaryngology. A study done in 2018 by Kuperstock investigating Anki use in 11 second- to fifth-year otolaryngology residents at one academic center. Analysis showed that app usage was associated with a 2.92% improvement on overall in-service scores. Some subsections showed even more impressive improvements with Anki use (allergy 11.3% and pediatrics 15.2%). This demonstrated Anki was effective at resident education despite high-stress levels and time restraint. [
10]
Plastic Surgery. There is currently no widely available Anki deck for plastic surgery residents, but many have argued a pressing need for this resource. Koenig et al. are currently spearheading a comprehensive digital flashcard deck at West Virginia University, but it is not widely available for all trainees. While it is hypothesized that this resource can improve in-service examination scores and clinical knowledge, further studies are warranted after distribution to understand the effects of its implementation.
3.4. Therapeutic Intervention
An unexpected result of our search was the potential use of Anki within specific patient populations. A study done by Evans and Quimby utilized Anki as a novel treatment for a patient with semantic variant Primary Progressive Aphasia (svPPA). This case demonstrated an anomic patient could use Anki-based interventional therapy independently at home and retain far more words than is typically targeted in prior interventions. [
11] With our continuously aging population, Anki has great potential for memory intervention. Decks could be created for necessary acidity of daily living (ADL) information such as home address and phone numbers. Future research should investigate alternative Anki-based therapeutic interventions and verify its efficacy in svPPA.
4. Discussion
The modern day medical student is faced with the stresses of a catastrophic debt burden, highly competitive residency positions, and the need to keep pace with an exponential increase in medical knowledge. [
12] Medical students consistently turn to e-learning resources that include video lectures, visual mnemonics, and flashcard systems. [
5]
The dogma of medical education is in flux as student and organizational preferences continuously evolve. The COVID-19 pandemic served as a catalyst for this change as virtual education and student independence was a sudden necessity.
Recent studies provide further evidence of students’ willingness to accept alternative educational structures. The movement towards a ‘lecture-free’ curriculum has been deemed necessary to advance medical education and prepare students to become life-long learners. Once residency begins, there is an inevitable transition to self-directed learning. [
13] It is logical integrating these principles early in medical education will benefit future physicians.
Blended learning is defined as applying more than one method, strategy, or media in education. [
14] This method of teaching increases students’ knowledge, satisfaction, and attention. [
14] Use of an open-sourced memory retention tool such as Anki is an ideal tool to incorporate into blended learning curriculums. Use of spaced repetition flashcard applications has the potential to decrease text anxiety [
16] and mediate burnout.
With studies showing as many as 70% of students adopt Anki early in their medical careers, it is clear students have cast their vote in favor of the software. This same data showed students utilized Anki to supplement studies as opposed to replacing formal instruction. [
5] Students are already utilizing Anki as a form of blended learning.
The scope of flashcard applications is now expanding beyond standard curriculum-centered fact memorization. A recent study investigated a flash card-based tool to help develop introspective career habits. Their tool helped students reflect on early clinical experiences and guided them to form their own professional identities. [
15]
Plastic surgery requires an in-depth knowledge of anatomy, physiology, biomaterials, and microbiology, in addition to understanding and implementing complex surgical techniques and non-operative interventions [
17]. Moreover, plastic surgery residents are required to take an in-service examination every year that tests knowledge across all plastic surgery domains including, but not limited to hand, breast, craniofacial, cosmetics, and microsurgery. Other surgical fields such as neurosurgery and general surgery have similar demands that Anki has the potential to help with.
Spaced repetition has proven to be a superior method of knowledge acquisition and retention compared to grouping study sessions together, [
18] yet to date there is no widely available spaced repetition resource for many surgery trainees. Creating this model could improve examination scores and enhance clinical knowledge, as has been proven for other similarly complex specialties such as orthopedic surgery, otolaryngology, and obstetrics and gynecology [
17].
The prevalence and awareness of burnout among trainees has increased over recent years. A meta-analysis of trainees showed that burnout rates are as high as 22%-52% among orthopedic surgeons and between 22%-51% [
19] among OBGYN residents. Anki was reported to decrease test-related anxiety and may help mitigate resident burnout.
Rounds should be a vital portion of the resident teaching experience. It allows for faculty to assess resident knowledge and share insights from years of experience. In modern residential environments, attention is pulled in a multitude of directions. Daily attending rounds are a cornerstone of teaching and essential for resident education. [
20] Trainees must attend to pages, electronic medical record direct messaging, lab values, test results, and charting simultaneously. Attending rounds may be educationally compromised due to non-urgent interruptions.
Physicians have reported a loss of focus, missed information, and increased stress secondary to round interruptions. [
20] Between clerical duties, residents must somehow find time to prepare for upcoming cases (if surgical) and delineate time for board review. Anki study resources have been reported to be a convenient and well-accepted study resource. Giving residents the ability to increase study efficiency may give back some valuable free time. Having a nationally shared and validated study tool could help fill gaps in resident education not covered during teaching rounds and other didactics.
Medical students and residents have a massive selection of study resources to choose from. Highly effective study tools usually come with a steep paywall. During pre-clinical education resources such as question banks, online lectures, and books will set students back hundreds of dollars. Sketchy Medicine is a popular memory aid utilized by students across the country, despite an annual cost of
$399 [
21]. Likewise, residential educational tools can also be quite expensive.
One advantage of Anki is its open-sourced software available for all to use free of charge. Shared decks are openly downloaded and spread across the internet for interested users. The lack of financial barriers to educational materials allows for equal educational opportunity and levels the playing field for financially challenged students.
Residency programs are responsible for providing trainees with adequate clinical and didactic training. Programs traditionally create didactic experiences individually, requiring tremendous resources with variable content exposure and quality. Anki utilization would permit students and teachers across the country to create a shared study resource covering all material needed for licensing examinations. With recent updates to the Anki platform, decks can be continuously updated by users nationwide. Although this software comes at a small cost (5
$ per month) [
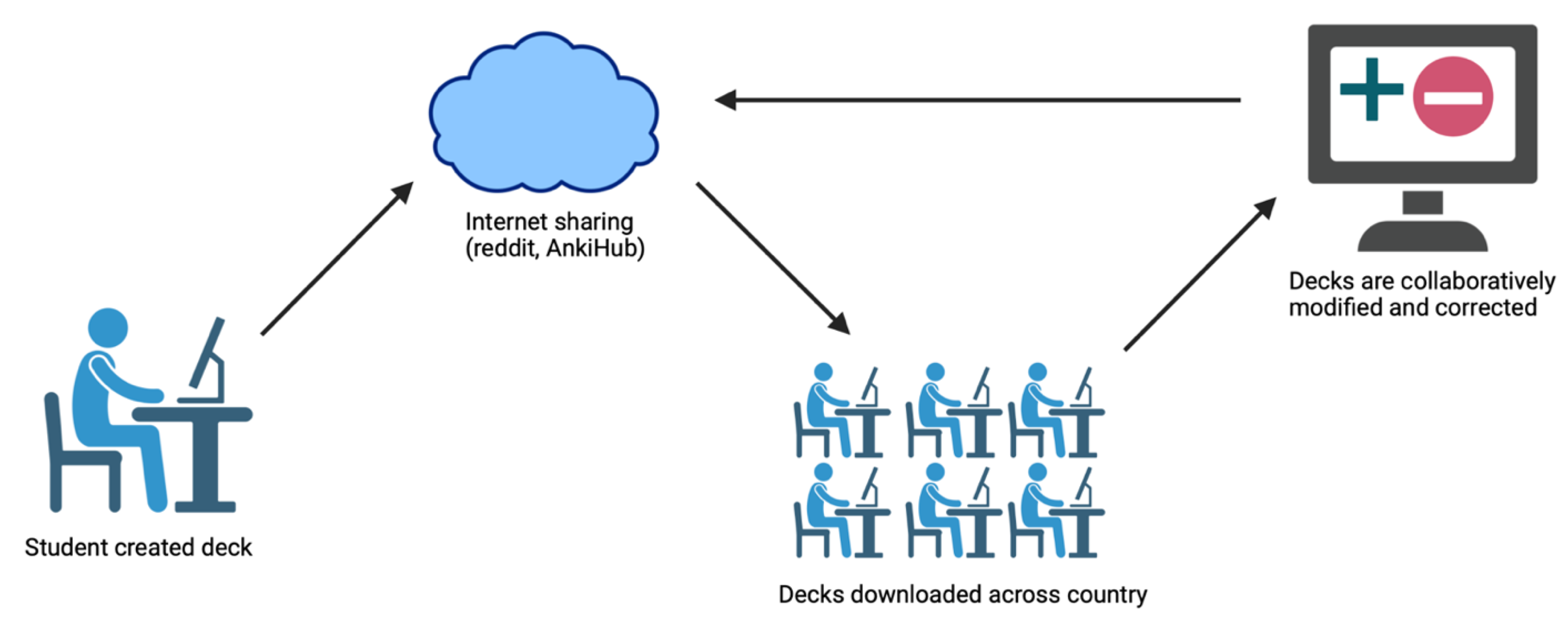
22]. A free alternative is using online forums such as Reddit to share and update decks. Decks are created, uploaded to the internet, and downloaded across the country. Any additions, corrections, or improvements made from widespread use is then re-uploaded and combined into a new version of the deck (see
Figure 1). Standardizing, validating, and sharing open study resources like Anki across residency programs and medical schools alike may improve networking amongst programs in addition to test scores.
5. Future Directions
Anki usage continues to steadily increase among medical students and there is continued evidence demonstrating its benefits in test performance. This paper detailed numerous accounts of objective and subjective evidence of Anki’s utility. Spaced repetition models for learning are well-accepted by learners and have been shown in randomized controlled trials to improve knowledge acquisition and retention [
20]. The use of the Anki platform specifically has been shown to be independently associated with higher Step 1 board exam scores in medical school and improved in-service examination scores and curricula satisfaction in residency [
4,
9,
10].
Despite this evidence, Anki is not widely used in most residency training programs. Efforts for future resident education should utilize repetition models, such as Anki, to effectively enhance long-term retention. Lack of awareness has been considered a barrier to utilization. [
5] More publications are needed to further support available evidence.
Being up to date on cutting-edge research is an essential part of a physician's career. Emerging data helps to accurately assess risk and guide clinical decision making. Keeping up with the literature is essential, but time consuming. It has been proposed that future research could focus on incorporating peer-reviewed research into an expanded-retrieval platform such as Anki. [
2]
Although the available research is promising, extensive validation and expansion of the literature is warranted. The software itself facilitates simple objective data extraction which can be used to fuel further research in the field. Anki™ software automatically records the number of reviews, review times, review intervals, and percentage of correct reviews. Further analysis of how the study resource is being utilized could be the target of future research [
6]. Differing usage schedules and efficacy among diverse cohorts are also areas that require additional studies. [
4]