Submitted:
27 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study site
2.2. Trends in govering pressures
2.3. Land use and other catchment characteristics
2.4. Biochemical analysis
2.5. Derived parameters and statistical analysis
3. Results and discussions
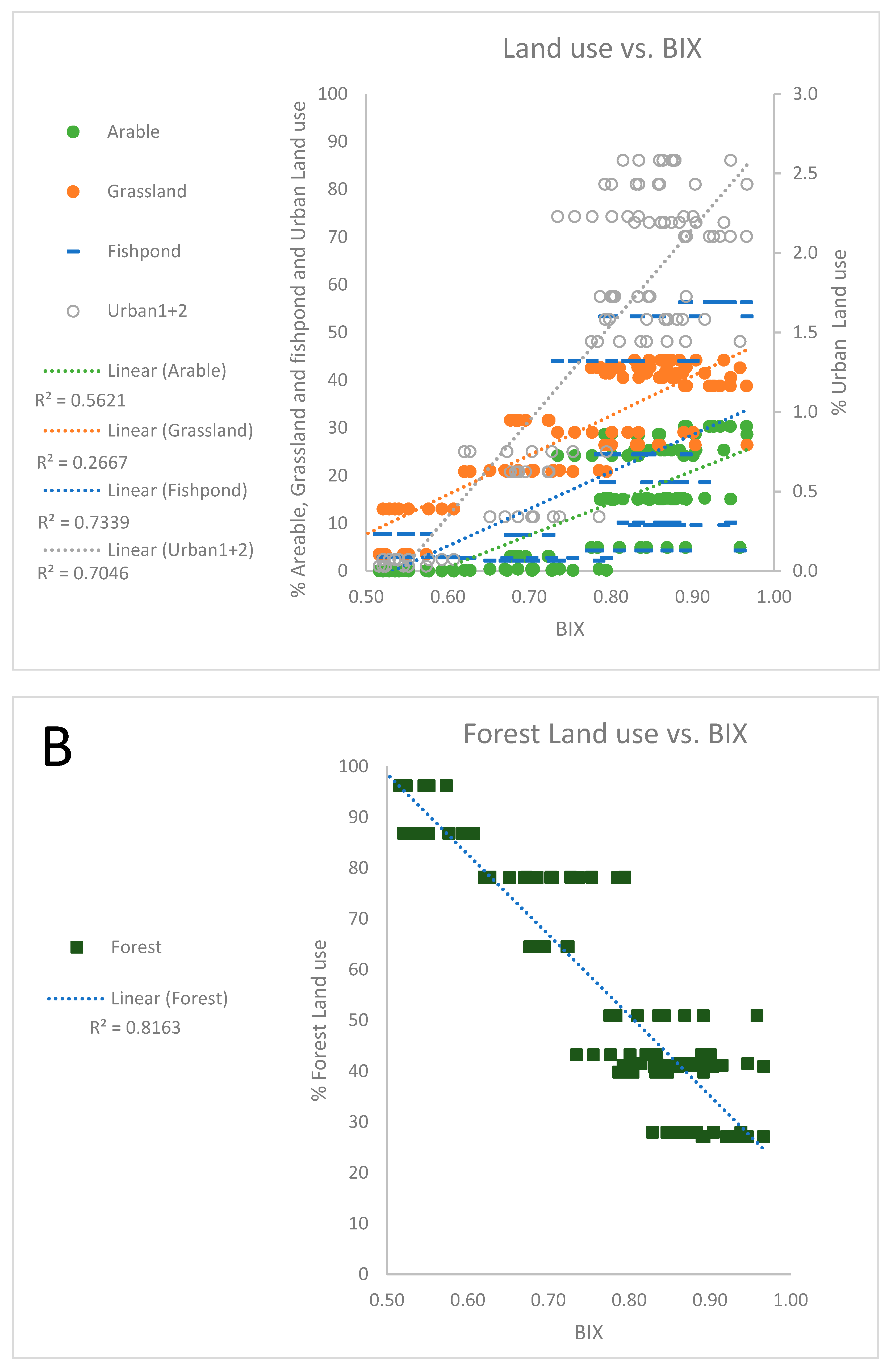
3.1. Land use as governing factor on spatial differences in water chemistry
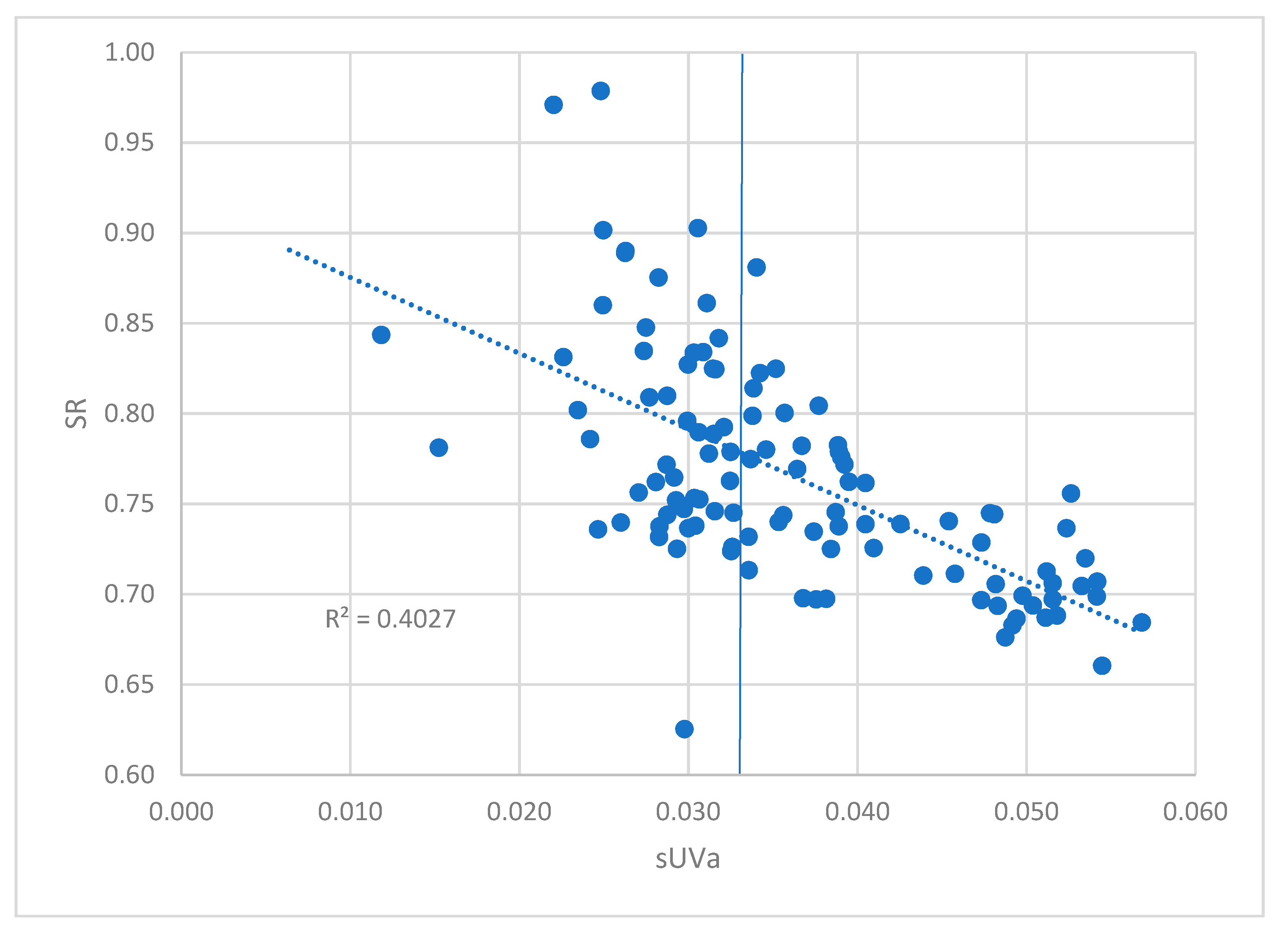
3.2. Governing factors on DOM
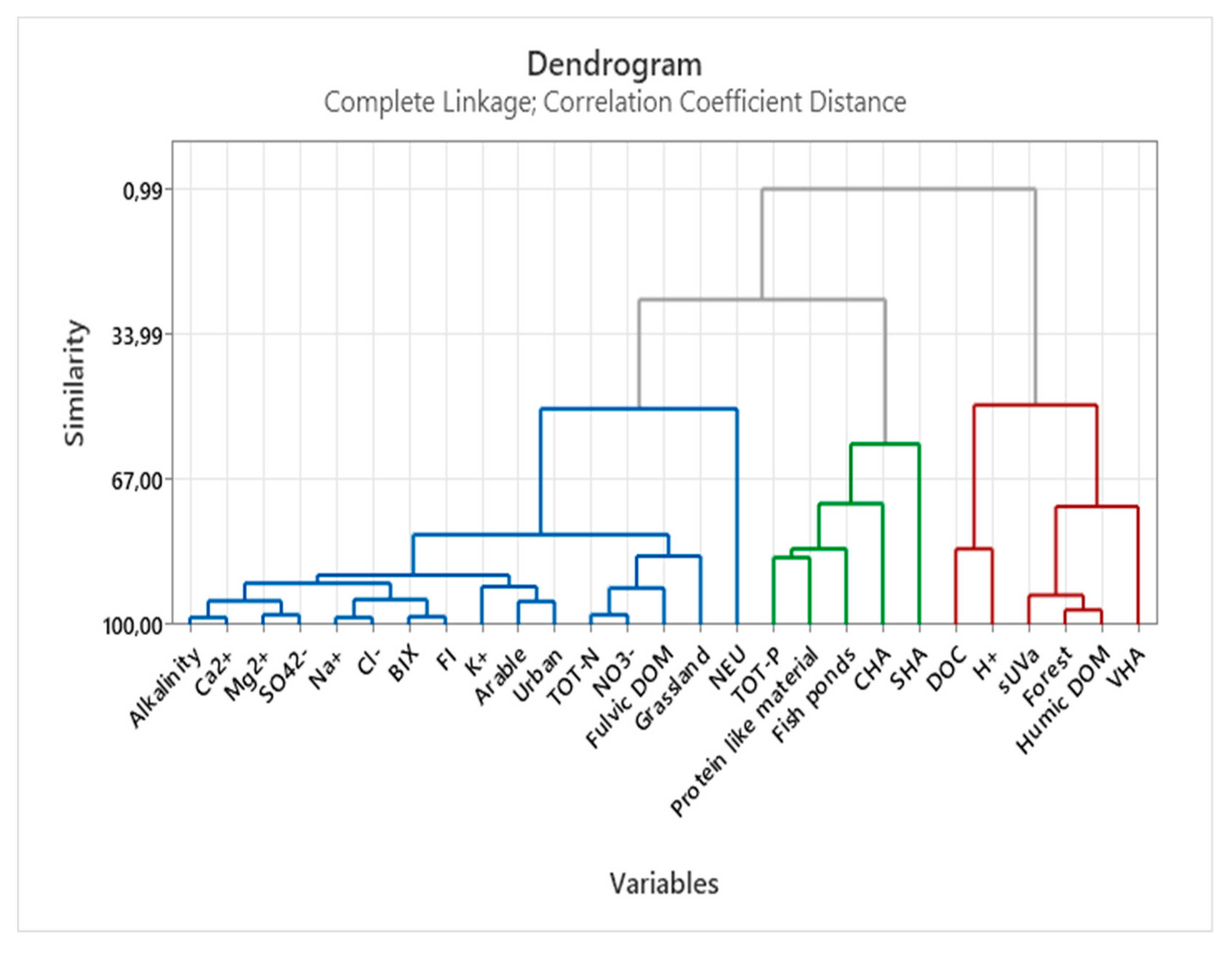
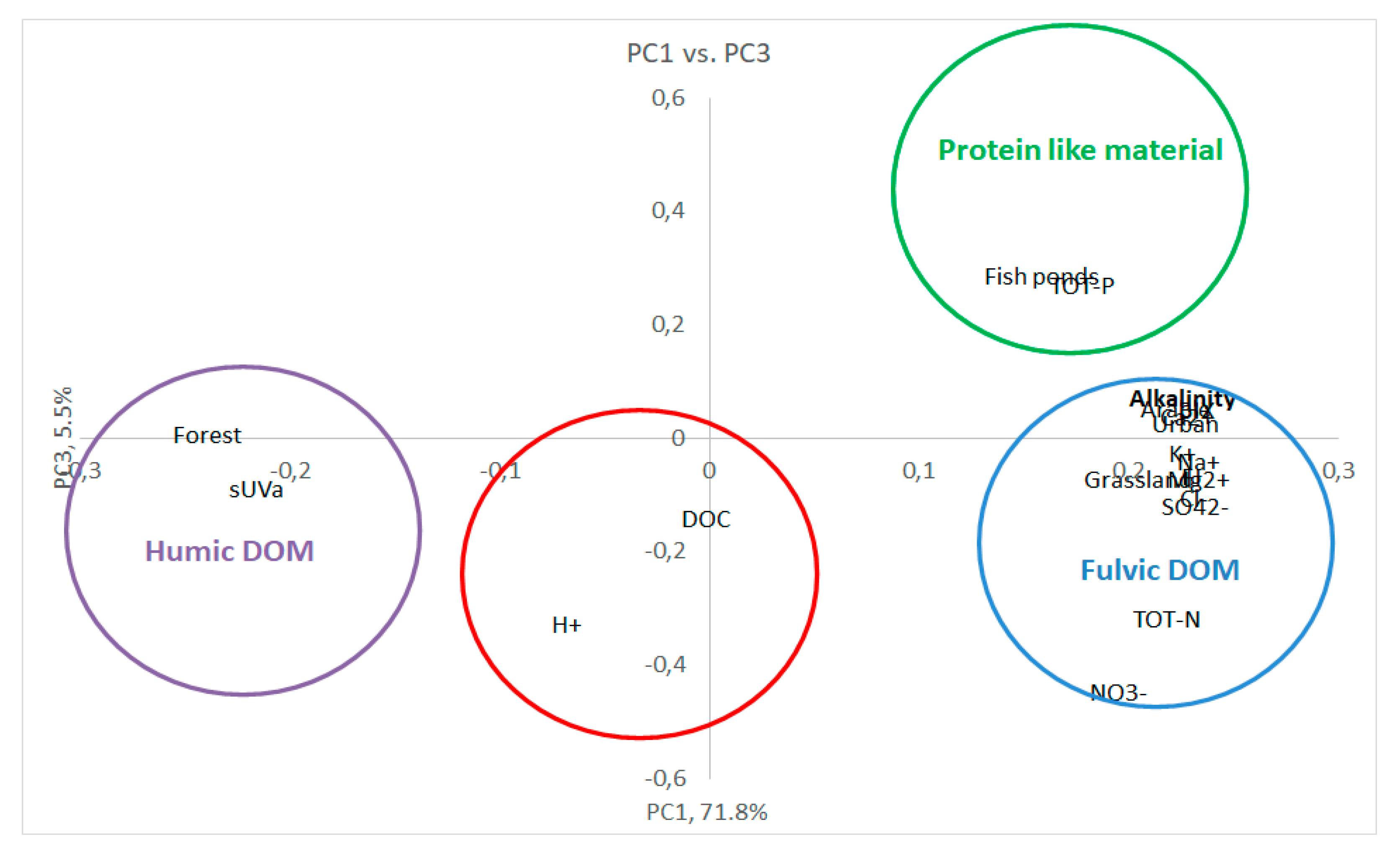
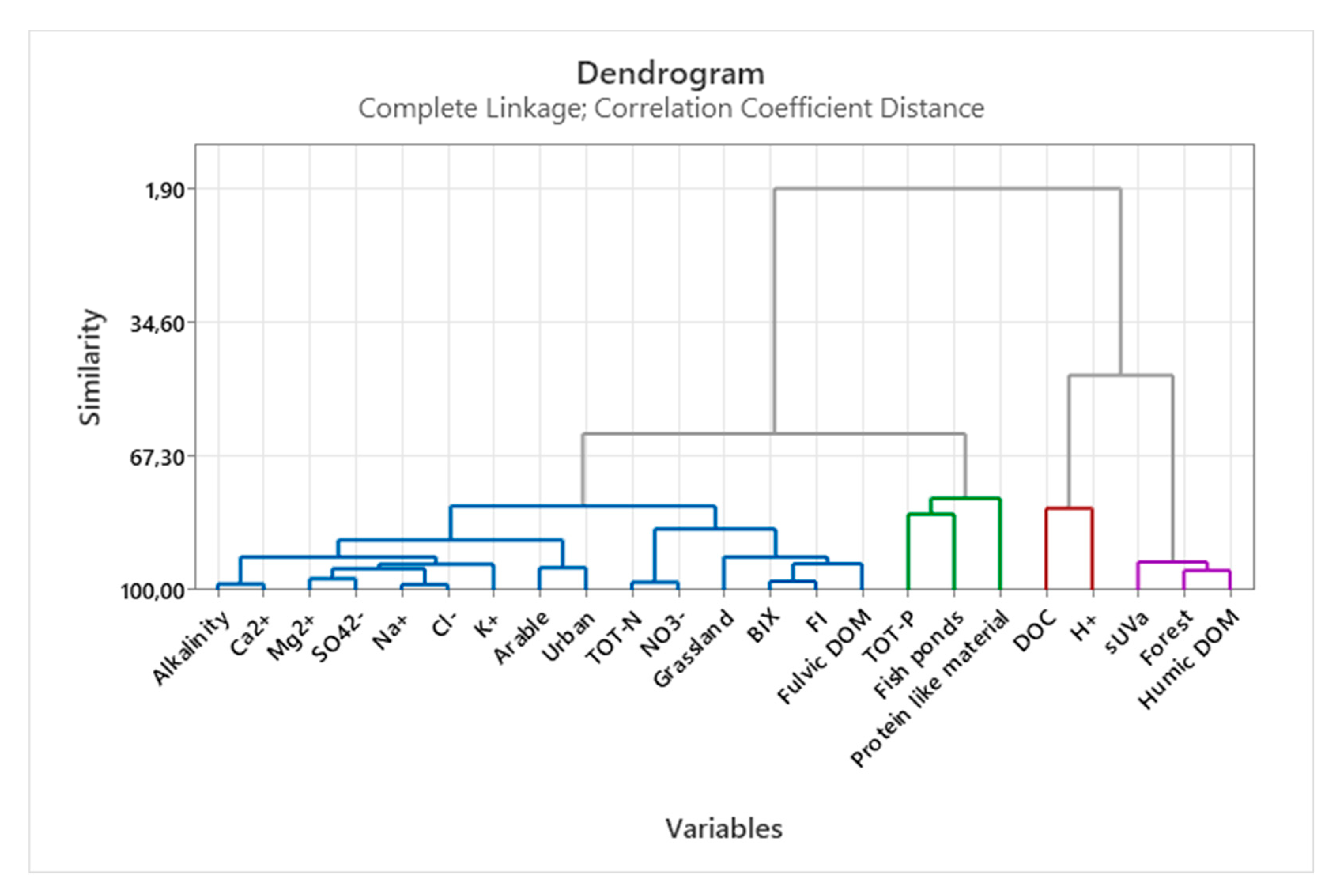
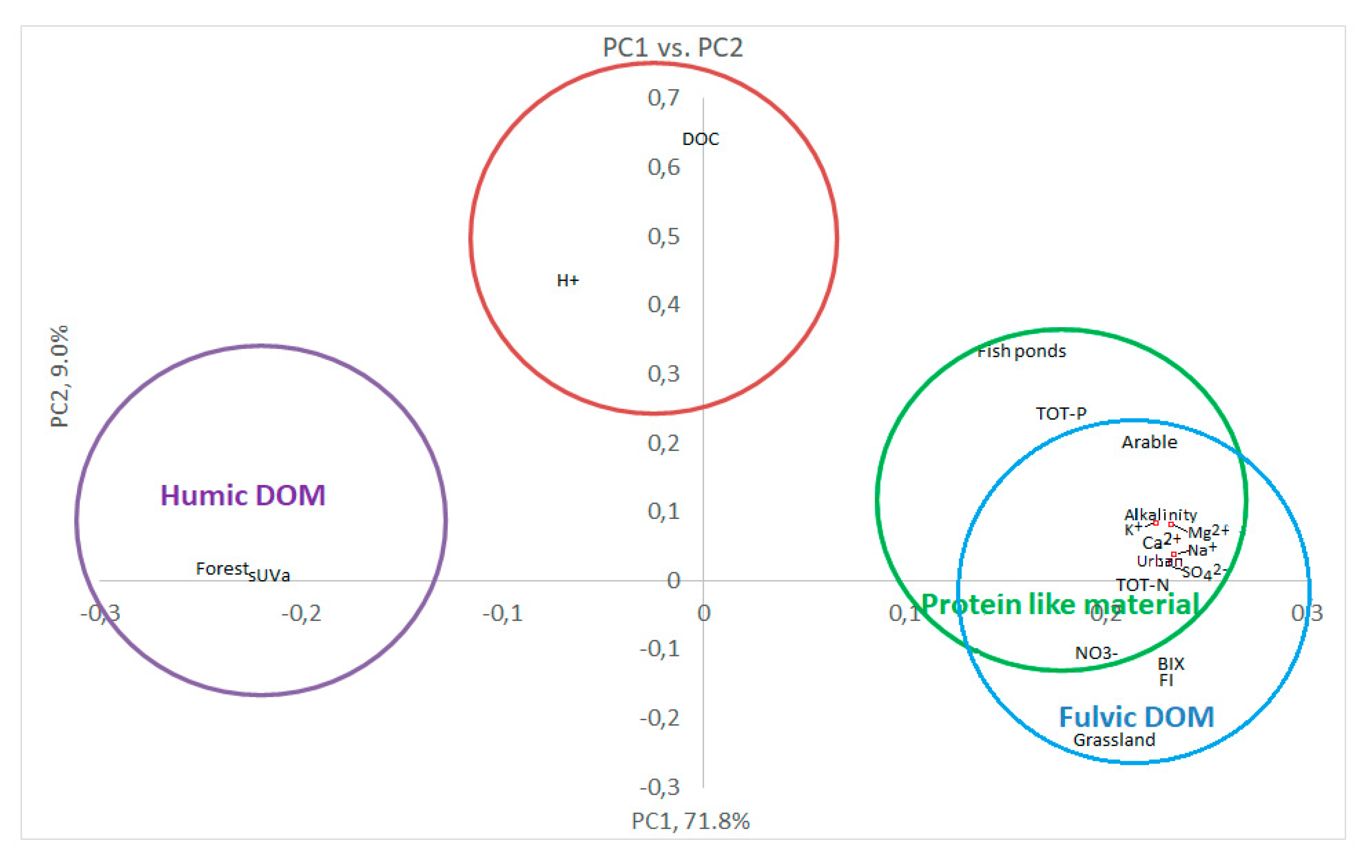
3.3. Multivariate statistics
3.4. Fishpond study
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Appendix A
| Parameter | Method of analysis/instrument | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| pH | Probe YSI 6600 V2-4 (Xylem Inc.) | ‒ |
| Suspended solids (mg L−1) | Gravimetry after drying at 105 °C | 49 |
| Alkalinity | Titrimetric determination of acid neutralizing capacity to pH 4.5 (ANC4.5) | 50 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand after 5 days (BOD5, mg L−1) | Electrochemical or optical probe methods | 51 |
| Chemical oxygen demand by permanganate (CODMn, mg L−1) | Titrimetric determination after digestion with permanganate | 52 |
| Chemical oxygen demand by dichromate method (CODCr, mg L−1) | Spectrophotometric test-tube method | 53 |
| UV absorbency (Abs. @UVλ254) | Spectrometry (Shimadzu UV-1650 PC) | 54 |
| TOT-P (mg L−1) | Inductive coupled plasma spectrometry (Agilent 8800 ICP-MSQ) | 55 |
| PO43- (mg L−1) | Spectrophotometric ammonium molybdate method (Shimadzu UV-1650 PC) | 56 |
| TOT-N (mg L−1) | High-temperature combustion (Multi N/C 2100 analyser, Analytik Jena AG, Germany) with unfiltered water samples | 57 |
| N-NH4+ (mg L−1) | Spectrophotometry (Shimadzu UV-1650 PC) | 58 |
| SO42-, N-NO3-, Cl-, (mg L−1) | Ion chromatography (Dionex ICS-1000) | 59 |
| Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+ (mg L−1) | Ion chromatography (Dionex ICS-1000) | 60 |
| Chl-a (µg L−1) | Spectrometry (Shimadzu UV-1650 PC) | 61 |
| TC (mg L−1) | High-temperature combustion method (Multi N/C 2100 analyser, Analytik Jena AG, Germany) | 62 |
| TIC (mg L−1) | Low temperature acidification method (Multi N/C 2100 analyser, Analytik Jena AG, Germany) | 62 |
| TOC (mg L−1) | TOC = TC – TIC | 62 |
| DC (mg L−1) | High temperature combustion method (Multi N/C 2100 analyser, Analytik Jena AG, Germany) | 62 |
| DIC (mg L−1) | Low temperature acidification method (Multi N/C 2100 analyser, Analytik Jena AG, Germany) | 62 |
| DOC (mg L−1) | DOC = DC – DIC | 62 |
| Parameter | Method of analysis/instrument | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| pH | TIM865, Radiometer | ‒ |
| Suspended solids (mg L−1) | Gravimetry after drying at 105 °C | 63 |
| Alkalinity | Titrimetric determination of acid neutralizing capacity according to Gran using TIM865, Radiometer | 50 |
| UV absorbency (Abs. @UVλ254) |
Spectrometry (Shimadzu UV-2700) | 54 |
| TOT-P (mg L−1) | Spectrophotometric molybdate method (Kopáček and Hejzlar, 1993) | 56 |
| PO43- (mg L−1) | Spectrophotometric ammonium molybdate method (Specord 50, Analytik Jena) Murphy and Riley (1962) |
56 |
| Tot-N (mg L−1) | High-temperature combustion (Shimadzu TOC-L) with unfiltered water samples | 57 |
| N-NH4+ (mg L−1) | Spectrophotometry (Specord 50, Analytik Jena) | 58 |
| N-NO3-, Cl-, SO42- (mg L−1) | Ion chromatography (Dionex ICS-5000+) | 59 |
| Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+ (mg L−1) | Ion chromatography (Dionex IC25) | 60 |
| TOC (mg L−1) | Nonpurgable total organic carbon (Shimadzu TOC-5000A) | 62 |
| DOC (mg L−1) | Nonpurgable dissolved organic carbon (Shimadzu TOC-L) | 62 |
Appendix B
| Site | pH | Alkalinity | SS | TOT-N | TOT-P | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | SO42- | NO3- | Cl- | PO43- | N-NH4+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | mmol L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | |
| 1 | 7.53 | 0.83 | 8.55 | 2.45 | 0.10 | 14.5 | 5.60 | 7.51 | 3.07 | 22.2 | 1.73 | 11.6 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| 2 | 7.45 | 1.14 | 19.18 | 2.89 | 0.15 | 24.05 | 8.83 | 15.12 | 4.65 | 33.34 | 1.99 | 22.94 | 0.05 | 0.11 |
| 3 | 7.58 | 0.99 | 7.43 | 3.19 | 0.14 | 22.45 | 7.06 | 14.92 | 3.61 | 24.73 | 2.60 | 25.37 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| 4 | 7.51 | 1.36 | 10.02 | 4.71 | 0.14 | 28.53 | 9.88 | 13.61 | 4.54 | 35.43 | 3.74 | 21.44 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| 5 | 7.80 | 2.23 | 19.55 | 3.75 | 0.20 | 40.26 | 14.20 | 15.45 | 5.13 | 44.83 | 2.61 | 19.07 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
| 6 | 7.76 | 1.61 | 16.61 | 3.74 | 0.14 | 35.32 | 9.38 | 11.51 | 3.41 | 29.42 | 2.67 | 18.70 | 0.10 | 0.28 |
| 7 | 7.45 | 0.89 | 16.79 | 2.63 | 0.07 | 14.94 | 6.17 | 8.72 | 2.80 | 21.14 | 2.14 | 13.35 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| 8 | 7.53 | 0.85 | 7.15 | 2.04 | 0.05 | 18.31 | 4.59 | 7.50 | 2.71 | 17.38 | 1.75 | 10.36 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| 9 | 7.00 | 0.22 | 2.10 | 0.78 | 0.03 | 3.80 | 1.00 | 2.59 | 0.69 | 4.41 | 0.78 | 1.64 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| 10 | 7.18 | 0.39 | 5.87 | 1.38 | 0.06 | 8.58 | 2.41 | 4.30 | 1.49 | 11.40 | 1.08 | 4.28 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 11 | 6.57 | 0.12 | 2.54 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 1.84 | 0.53 | 2.03 | 0.57 | 3.05 | 0.24 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 12 | 5.72 | 0.10 | 1.28 | 0.68 | 0.02 | 1.47 | 0.43 | 1.43 | 0.31 | 1.45 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| 13 | 7.14 | 0.26 | 3.79 | 1.13 | 0.04 | 2.78 | 1.71 | 4.38 | 1.63 | 11.99 | 0.76 | 3.57 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| 14 | 7.45 | 0.44 | 8.25 | 1.68 | 0.04 | 6.28 | 3.99 | 13.35 | 1.66 | 12.41 | 1.23 | 6.19 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| Sort | DOC | sUVa | BOD5 | CODCr | CODMn | Chl-a | BIX | FI | HIX | VHA | SHA | CHA | NEU | HPO | HPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | mg L−1 | cm−1/ mg C/L) |
mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | % | % | % | % | % | % | |||
| 1 | 6.94 | 0.033 | 2.92 | 21.03 | 7.65 | 13.57 | 0.81 | 1.29 | 0.84 | 69.5 | 3.0 | 4.7 | 22.9 | 72.5 | 27.5 |
| 2 | 9.52 | 0.028 | 3.62 | 25.74 | 7.32 | 44.12 | 0.86 | 1.33 | 0.84 | 68.1 | 8.3 | 5.3 | 18.3 | 76.4 | 23.6 |
| 3 | 4.87 | 0.031 | 2.47 | 16.24 | 4.73 | 6.05 | 0.87 | 1.34 | 0.85 | 69.0 | 3.7 | 0.8 | 26.5 | 72.7 | 27.3 |
| 4 | 6.44 | 0.028 | 2.43 | 19.20 | 5.99 | 9.83 | 0.88 | 1.37 | 0.88 | 70.6 | 4.6 | 5.2 | 19.6 | 75.2 | 24.8 |
| 5 | 8.77 | 0.025 | 4.07 | 28.65 | 8.44 | 22.08 | 0.92 | 1.38 | 0.84 | 58.2 | 16.4 | 8.7 | 16.7 | 74.6 | 25.4 |
| 6 | 4.78 | 0.030 | 2.96 | 17.31 | - | 6.21 | 0.86 | 1.33 | 0.85 | 59.8 | 12.6 | 4.2 | 23.5 | 72.3 | 27.7 |
| 7 | 5.43 | 0.032 | 2.13 | 13.40 | 4.26 | 3.39 | 0.83 | 1.33 | 0.84 | 62.8 | 12.4 | 1.1 | 23.6 | 75.3 | 24.7 |
| 8 | 2.60 | 0.031 | 1.74 | 8.68 | 2.93 | 3.28 | 0.85 | 1.32 | 0.82 | 55.3 | 13.8 | 0.0 | 30.9 | 69.1 | 30.9 |
| 9 | 5.25 | 0.048 | - | - | 6.47 | - | 0.60 | 1.11 | 0.86 | 80.4 | 3.9 | 0.6 | 15.0 | 84.3 | 15.7 |
| 10 | 3.59 | 0.029 | 1.70 | 10.29 | 3.87 | - | 0.71 | 1.20 | 0.84 | 72.2 | 2.2 | 0.9 | 24.7 | 74.4 | 25.6 |
| 11 | 7.03 | 0.052 | - | - | - | - | 0.56 | 1.10 | 0.87 | 84.7 | 5.2 | 0.9 | 9.2 | 90.0 | 10.0 |
| 12 | 9.49 | 0.051 | 1.66 | 26.31 | 12.55 | - | 0.53 | 1.07 | 0.87 | 84.3 | 7.9 | 1.2 | 6.5 | 92.2 | 7.8 |
| 13 | 4.05 | 0.037 | 1.51 | 13.70 | 4.92 | - | 0.71 | 1.24 | 0.87 | 69.9 | 8.1 | 1.8 | 20.3 | 78.0 | 22.0 |
| 14 | 5.53 | 0.039 | 1.72 | 15.75 | 5.33 | 3.07 | 0.69 | 1.21 | 0.88 | 69.1 | 9.0 | 2.7 | 19.1 | 78.1 | 21.9 |
Appendix C
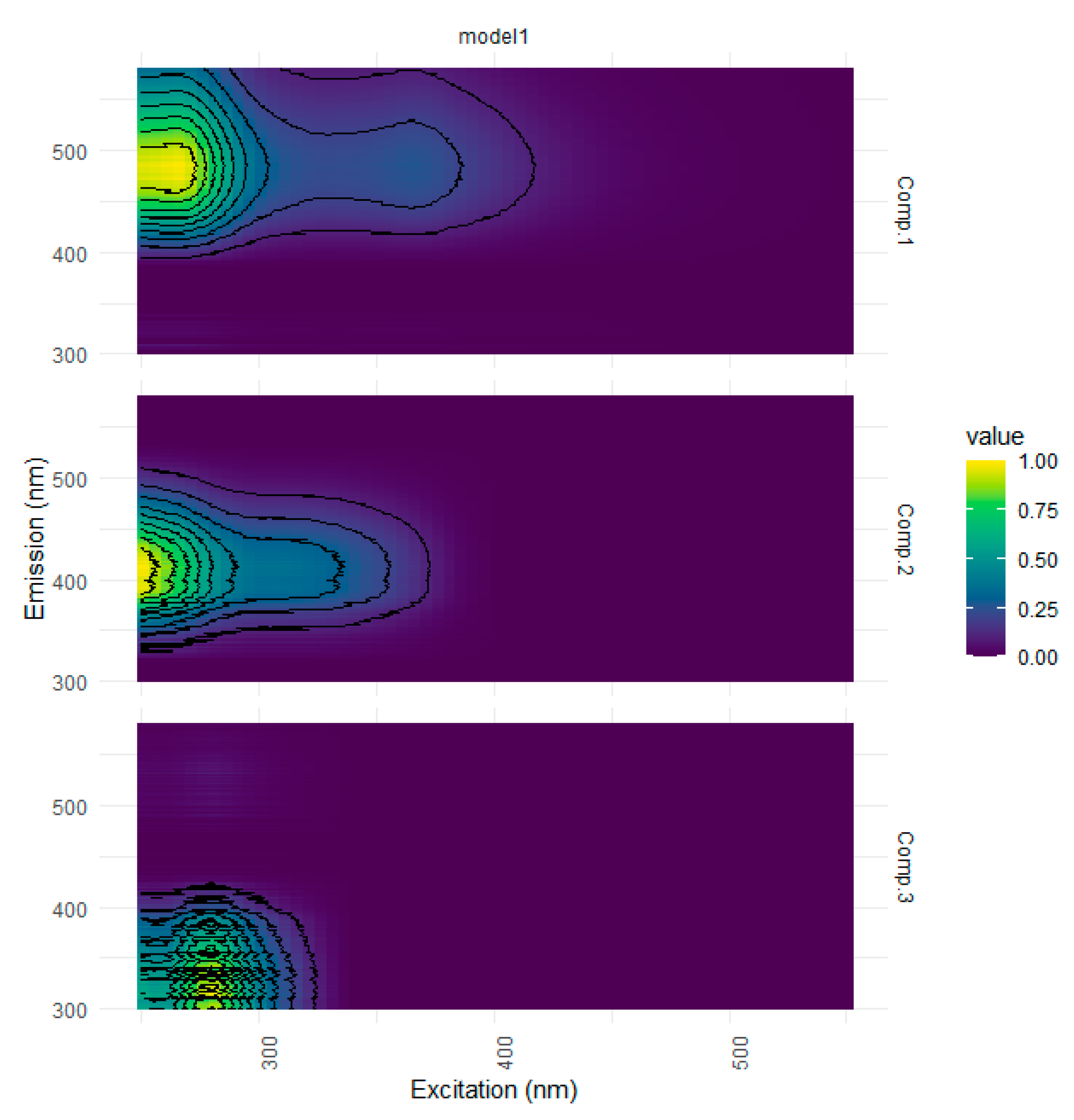

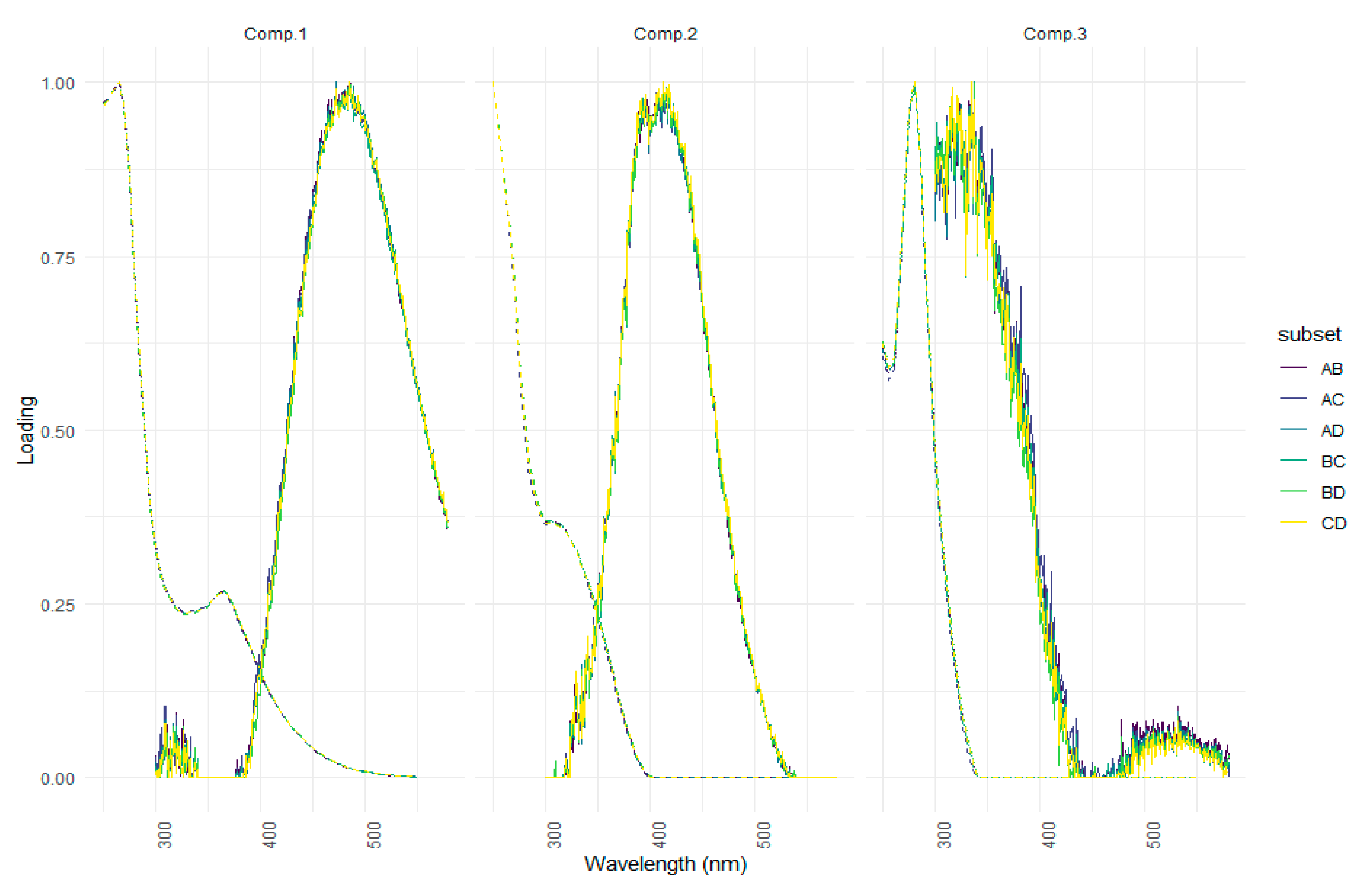
| Ref. | Component assignment and description | Location | Sample type | Excitation/emission similarity score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component 1: λexcitation, max/λemission, max = 265 (365)/487 | |||||
| 1 | 43 RaskaDOM |
C2: Humic-like; large sized; characteristics of soil, sediment, and freshwater environments. | Cropping system, Montana, USA | Soil water extractable DOM | 0.9920/0.9946 |
| 2 | 64 Wheat |
C2: Humic-like; large sized; characteristics of soil, sediment, and freshwater environments | Cropping system, Montana, USA | Soil water extractable DOM | 0.9876/0.9972 |
| 3 | 65 Recycle |
C1: Terrestrial humic-like fluorescence in high nutrient and wastewater-impacted environments. | Water recycling plant, Australia | Water recycling DOM | 0.9808/0.9986 |
| 4 | 66 Galveston bay |
C1: similar to Coble peak C; humic like | Texas, USA | Riverine/Estuarine DOM | 0.9802/0.9975 |
| 5 | 67 Gueguen_Nelson |
C1: Humic-like; terrestrially derived; Coble peak C; some photobleaching | Beaufort Sea, experiments | Estuarine DOM | 0.9792/0.9933 |
| 6 | 68 Macaronesia |
C3: humic like | Sao Vicente, Cape Verde to Gran Canaria, Canary Island | Marine DOM | 0.9753/0.9968 |
| 7 | 69 | C1: Coble peak C+A; Humic-like; terrestrially derived | Australia | Water treatment plant DOM | 0.9723/0.9988 |
| 8 | 42 | C2: humic-like; terrestrially derived material identified in a variety of aquatic environments; photosensitive | Various freshwater environments across Quebec, Canada | Boreal freshwater DOM | 0.9965/0.9728 |
| 9 | 40 | C1: terrestrial and marine DOM | Fjordsystem, Norway | Experimental marine DOM | 0.9798/0.9861 |
| 10 | 41 | C2: aromatic; high molecular weight organic matter (humic-like) with terrestrial character and correlated to lignin phenol concentrations; humic-like substance, enriched in terrestrial DOM sources; ubiquitous in DOM. | Experiments | SRHA DOM standard from the International Humic Substances Society | 0.9832/0.9724 |
| Component 2: λexcitation, max/λemission, max = 250 305/413 | |||||
| 1 | 70 | C4: UVA humic-like component frequently found in lentic freshwater; associated with bacterial planktonic activity. | The Sau Reservoir and its tributary the Ter River, Spain | Freshwater DOM | 0.9823/0.9924 |
| 2 | 41 | C3: combined Coble peaks A+M; microbial humic-like substances; produced by microbial degradation of organic matter. | Experiments | SRHA DOM standard from the International Humic Substances Society | 0.9887/0.9842 |
| 3 | 67 | C2: Humic-like; terrestrially derived; Coble peak A; susceptible to photobleaching. | Beaufort Sea, experiments | Estuarine DOM | 0.9790/0.9898 |
| 4 | 44 | C2: humic-like, ubiquitous humic component related with fulvic acids and re-processed humics | Montseny Natural Park, Spain | Headwater forested catchment freshwater DOM | 0.9717/0.9968 |
| 5 | 45 | C1: terrestrial humic-like, microbial-humic-like. | The Baltimore sewer system, Baltimore, USA | Wastewater DOM | 0.9810/0.9865 |
| 6 | 66 Galveston bay |
C2: similar to Coble peak M. | Texas, USA | Riverine/Estuarine DOM | 0.9834/0.9826 |
| 7 | 69 | C2: Coble peaks C+A; Humic-like; terrestrial delivered reprocessed OM | Australia | Water treatment plant DOM | 0.9733/0.9886 |
| 8 | 43 | C1: Humic-like; medium sized; characteristics of soil, sediment, and freshwater environments. | Cropping system, Montana, USA | Soil water extractable DOM | 0.9718/0.9548 |
| 9 | 64 | C2: Humic-like; medium sized; characteristics of soil, sediment, and freshwater environments. | Cropping system, Montana, USA | Soil water extractable DOM | 0.9826/0.9761 |
| 10 | 65 | C2: Microbial humic-like. | Water recycling plant, Australia | Water recycling DOM | 0.9826/0.9679 |
| Component 3: λexcitation, max/λemission, max = 280/336 | |||||
| 1 | 71 | C7: protein-like; both tyrosine- and tryptophan-like properties. | Southern Onterio, Canada | Stormwater pond DOM | 0.9951/0.9961 |
| 2 | 72 | C5: Coble peak T; tryptophan-like. | Mackenzie, Lena, Kolyma, Ob, and Yenisei Rivers | Arctic river DOM | 0.9878/0.9947 |
| 3 | 73 | C5: Coble T peak; protein-like/tryptophan-like material with a recent, probably microbial origin. | Drinking water treatment plant, Sweden | Drinking water treatment plant water DOM | 0.9935/0.9867 |
| 4 | 74 | C2: tryptophan-like; protein-like | Maryland, USA | Leaf litter leachate | 0.9877/0.9924 |
| 5 | 69 | C4: Coble peaks T+B, Protein-like; microbial delivered. | Australia | Water treatment plant DOM | 0.9885/0.9886 |
| 6 | 46 | C4: tryptophan-like and protein-like material; generally contributes the highest intensity peaks in wastewaters, even in treated effluents; indicates recent production; often found in anthropogenically affected watersheds. | Coastal drainage basins of Miami, FL, USA | Coastal DOM | 0.9913/0.9845 |
| 7 | 75 | C3: protein-like; fresh production; biological production; higher in surface water layer. | Indian ocean | Marine DOM | 0.9978/0.9781 |
| 8 | 76 | C4: Tryptophan-like; both photodegraded and produced during photodegradation, depending on sample type. | Subtropical Minjiang watershed, China | Wastewater, leaf litter leachates, river water DOM. | 0.9864/0.9836 |
| 9 | 42 | C6: associated with freshly produced protein-like material; tryptophan-like; strongest predictor of BDOC. | Various freshwater environments across Quebec, Canada | Boreal freshwater DOM | 0.9663/0.9825 |
| 10 | 45 | C4: tryptophan-like; wastewater indicator. | The Baltimore sewer system, Baltimore, USA | Wastewater DOM | 0.9953/0.9538 |
Appendix D
References
- Thurman, E. M. Organic geochemistry of natural waters. Martinus Nijhoff/Dr. W. Junk Publishers Springer, Netherlands, 1985. [CrossRef]
- Chudoba, J.; Hejzlar, J.; Doležal, M. Microbial polymers in the aquatic environment - III. Isolation from river, potable and ground water and analysis. Water Res, 1986, 20, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdue, E. M. Natural Organic matter. In G. E. Likens (Ed.), Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences, from Encyclopedia of Inland Waters. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Swyngedouw, E. Modernity and Hybridity: Nature, Regeneracionismo, and the Production of the Spanish Waterscape, 1890-1930. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 1999, 89, 443–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, R.W. Environmental Literacy in Science and Society. From Knowledge to Decisions, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2011.
- Moore, J.W. Capitalism in the Web of Life. London: Verso. 2015.
- Bonneuil, C.; Fressoz J-B. The Shock of the Anthropocene. London: Verso. 2017.
- Winter K., B.; Lincoln, N. K.; Berkes, F. The Social-Ecological Keystone Concept: A Quantifiable Metaphor for Understanding the Structure, Function, and Resilience of a Biocultural System. Sustainability, 2018, 10, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejzlar, J.; Chudoba, J. Microbial polymers in the aquatic environment - II. Isolation from biologically non-purified and purified municipal waste water and analysis. Water Res. 1986, 20, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, D.T.; Stoddard, J.L.; Evans, C.D.; De Wit, H.A.; Forsius, M.; Høgåsen, T.; Wilander, A.; Skjelkvåle, B.L.; Jeffries, D.S.; Vuorenmaa, J.; Keller, B.; Kopáček, J.; Veselý, J. Dissolved organic carbon trends resulting from changes in atmospheric deposition chemistry. Nature 2007, 450, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, H.A.; Mulder, J.; Hindar, A.; Hole, L. Long-term increase in dissolved organic carbon in streamwaters in Norway is response to reduced acid deposition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7706–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteith, D.T.; Henrys, P.A.; Hruška, J.; de Wit, H.A.; Krám, P.; Moldan, F.; Posch, M.; Räike, A.; Stoddard, J.L.; Shilland, E.M.; Pereira, M.G.; Evans, C.D. Long-term rise in riverine dissolved organic carbon concentration is predicted by electrolyte solubility theory. Sci Adv 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, R. D.; de Wit, H.; Koponen, K. Case study on impacts of large-scale re-/afforestation on ecosystem services in Nordic regions. Report series Quantifying and deploying responsible negative emissions in climate resilient pathways. Horizon 2020, Grant Agreement no. 869192. 2022. https://www.negemproject.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/NEGEM_D3.6_Case-study-on-impacts-of-large-scale-re-afforestation-on-ecosystem-services-in-Nordic-regions.pdf.
- Kopáček, J.; Evans, C.D.; Hejzlar, J.; Kaňa, J.; Porcal, P.; Šantrůčková, H. Factors affecting the leaching of dissolved organic carbon after tree dieback in an unmanaged European mountain forest. Environ Sci and Technol 2018, 52, 6291–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, H.A.; Garmo, ØA.; Jackson-Blake, L.; Clayer, F.; Vogt, R.D.; Kaste, Ø; Gundersen, C.B.; Guerrerro, J.L.; Hindar, A. Changing Water Chemistry in One Thousand Norwegian Lakes During Three Decades of Cleaner Air and Climate Change. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2023, 37. [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.; Lawrence, D.; Lang, M.; Martinkova, M.; Kjeldsen, T.R. Review of trend analysis and climate change projections of extreme precipitation and floods in Europe. J. Hydrol 2014, 519, 3634–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grennfelt, P.; Engleryd, A.; Forsius, M.; Hov, Ø.; Rodhe, H.; Cowling, E. Acid rain and air pollution: 50 years of progress in environmental science and policy. Ambio 2020, 49, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte-Uebbing, L.; de Vries, W. Global-scale impacts of nitrogen deposition on tree carbon sequestration in tropical, temperate, and boreal forests: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang Biol. 2018. 24, 416–431. [CrossRef]
- Kaste, Ø.; Skarbøvik, E.; Vogt, R. D. Assessment of parameters for suspended solids and organic matter can be included in the water classification system (in Norwegian). NIVA-rapport 7860 2023. https://hdl.handle.net/11250/3067437.
- Hansen, A. M.; Kraus, T. E. C.; Pellerin, B. A.; Fleck, J. A.; Downing, B. D.; Bergamaschi, B. A. Optical properties of dissolved organic matter (DOM): Effects of biological and photolytic degradation. Limnol Oceanogr 2016, 61, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, J.E.; Jackson-Blake, L.; Vogelsang, C.; Kaste, Ø.; Vogt, R.D. TEOTIL3: A coefficient-based export model for simulation of river inputs (in Norwegian). NIVA rapport. In Prep. 2023.
- Zsolnay, A.; Baigar, E.; Jimenez, M.; Steinweg, B.; Saccomandi, F. Differentiating with fluorescence spectroscopy the sources of dissolved organic matter in soils subjected to drying. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J. M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org Geochem 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K. R.; Stedmon, C. A.; Wenig, P.; Bro, R. OpenFluor– an online spectral library of auto-fluorescence by organic compounds in the environment [10.1039/C3AY41935E]. Analytical Methods, 2014, 6, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Kang, J.; Shen, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. EEM–PARAFAC characterization of dissolved organic matter and its relationship with disinfection by-products formation potential in drinking water sources of northeastern China. Sci Total Environ 2021, 774, 145297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.D.; Akkanen, J.; Andersen, D.O.; Bruggemann, R.; Chatterjee, B.; Gjessing, E.; Kukkonen, J.V.K.; Larsen, H.E.; Luster, J.; Paul, A.; Pflugmacher, S.; Starr, M.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Zsolnay, Á. Key site variables governing the functional characteristics of dissolved natural organic matter (DNOM) in Nordic forested catchments. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 66, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykkelbost, T.C.; Vogt, R.D.; Seip, H.M.; Riise, G. Organic carbon fractionation applied to lake-and soil water at the HUMEX site. Environ. Int. 1995, 21, 849–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopáček, J.; Hejzlar, J.; Porcal, P.; Posh, M. Trends in riverine element fluxes: A chronicle of regional socio-economic changes. Water Res 2017, 125, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselý, J.; Hruška, J.; Norton, S.A.; Johnson, C.E. Trends in water chemistry of acidified Bohemian lakes from 1984 to 1995: I. Major solutes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1998. 108, 107–127. [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M. Mapping of causes for increase in dissolved organic matter in a Czech watershed. Master Thesis. University of Oslo, Norway, 06.2021. https://www.duo.uio.no/handle/10852/93531.
- Schmidt, S.I.; Hejzlar, J.; Kopáček, J.; Paule-Mercado, M.C.; Porcal, P.; Vystavna, Y.; Lanta, V. Forest damage and subsequent recovery alter the water composition in mountain lake catchments. Sci Total Environ 2022, 827, 154293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, C. W. K.; Fabris, R.; Drikas, M. A rapid fractionation technique to characterise natural organic matter for the optimisation of water treatment processes. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 2004, 53, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T. Fluorescence Inner-Filtering Correction for Determining the Humification Index of Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ Sci Technol 2002, 36, 742–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellman, J.B.; Hood, E.; and Spencer, R.G.M. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Opens New Windows into Dissolved Organic Matter Dynamics in Freshwater Ecosystems: A Review. Limnol Oceanogr 2010, 55, 2452–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hur, J. Utilization of UV-Vis spectroscopy and related data analyses for dissolved organic matter (DOM) studies: A review. Critical Reviews in Environ Sci Technol 2017, 47, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.M.; Boyer, E.W.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Doran, P.T.; Kulbe, T.; Andersen, D.T. Spectrofluorometric Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter for Indication of Precursor Organic Material and Aromaticity. Limnol Oceanogr 2001, 46, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M. P.; Sander de Carvalho, L. A.; Novo, E.; Jorge, D. S. F.; Barbosa, C. C. F. Use of optical absorption indices to assess seasonal variability of dissolved organic matter in Amazon floodplain lakes. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 5355–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucher, M.; Wünsch, U.; Weigelhofer, G.; Murphy, K.; Hein, T.; Graeber, D. staRdom: Versatile Software for Analyzing Spectroscopic Data of Dissolved Organic Matter in R’, Water, 2019, 11, 2366. [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2023. https://www.R-project.org/.
- Stedmon, C.; Bro, R. Characterizing Dissolved Organic Matter Fluorescence with Parallel Factor Analysis: A Tutorial. Limnol Oceanogr 2008, 6, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; He, H.; Lürling, M.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y. Composition of dissolved organic matter controls interactions with La and Al ions: Implications for phosphorus immobilization in eutrophic lakes. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 248, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, J. F.; del Giorgio, P. A. Partial coupling and differential regulation of biologically and photochemically labile dissolved organic carbon across boreal aquatic networks. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 5969–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C. M.; Engel, R. E.; D’Andrilli, J.; Miller, P. R.; Wallander, R. Compositional tracking of dissolved organic matter in semiarid wheat-based cropping systems using fluorescence EEMs-PARAFAC and absorbance spectroscopy. Journal of Arid Environments 2019, 167, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.; Lupon, A.; Catalán, N.; Castelar, S.; Martí, E. Decoupling of dissolved organic matter patterns between stream and riparian groundwater in a headwater forested catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci 2018, 22, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista-Andrade, J. A.; Diaz, E.; Iglesias Vega, D.; Hain, E.; Rose, M. R.; Blaney, L. Spatiotemporal analysis of fluorescent dissolved organic matter to identify the impacts of failing sewer infrastructure in urban streams. Water Research 2023, 229, 119521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M. A.; Kominoski, J. S.; Gaiser, E. E.; Price, R. M.; Troxler, T. G. Stormwater Runoff and Tidal Flooding Transform Dissolved Organic Matter Composition and Increase Bioavailability in Urban Coastal Ecosystems. J Geohys Res, B 2021, 126, e2020JG006146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikebrokk, B.; Haaland, S. L.; Jarvis, P.; Riise, G.; Vogt, R. D.; Zahlsen, K. NOMiNOR: Natural Organic Matter in drinking waters within the Nordic Region. Norsk Vann report 2018, 231. https://va-kompetanse.no/butikk/a-231-nominor-natural-organic-matter-in-drinking-waters-within-the-nordic-region-kun-digital/.
- Crapart, C.; Andersen, T.; Hessen, D. O.; Valiente, N.; Vogt, R. D. Factors Governing Biodegradability of Dissolved Natural Organic Matter in Lake Water. Water 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ČSN EN 12880. Water quality, determination of dry residue and water content of sludges and sludge products. Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing, Prague, 2000.
- ČSN EN ISO 9963-1. Water quality. Determination of alkanity. Part 1: Determination of total and composite alkanity. Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing, Prague, 1995.
- ČSN EN ISO 5815-1. Water quality – Determination of biochemical oxygen demand after n days (BODn) –Part 1: Dilution and seeding method with allylthiourea addition. Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing, Prague, 2020.
- ČSN EN ISO 8467. Water quality - Determination of chemical oxygen demand by permanganate (CODMn). Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing, Prague, 1997.
- ČSN ISO 157085. Geometrical product specifications (GPS) - Surface texture: Profile method - Terms, definitions and surface texture parameters. Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing, Prague, 2008.
- ČSN 757360. Water quality, determination of absorbance. Direct measurement of absorption of UV radiation at wavelength 254 nm. Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing, Prague, 2013.
- ISO 17294-2. Water quality-application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS)-Part 2: determination of 62 elements (Vol. 2). Int. Organ. for Standardisation (ISO), Geneva, 2003.
- ISO 6878. Water quality — Determination of phosphorus — Ammonium molybdate spectrometric method. Int. Organ. for Standardisation (ISO), Geneva. 2004.
- DIN EN 12260. Water quality. Determination of nitrogen. Determination of bound nitrogen (TNb), following oxidation to nitrogen oxides. Deutches Institut fur Normung, Berlin. 2003.
- ISO 7150-1. Water quality-determination of ammonium. Part 1: manual spectrometric method. Int. Organ. for Standardisation (ISO), Geneva,1984.
- ISO10304-1. Water quality-determination of dissolved anions by liquid chromatography of ions-Part 1: determination of bromide, chloride, fluoride, nitrate, nitrite, phosphate and sulfate (Vol. 1). Int. Organ. for Standardisation (ISO), Geneva, 2007.
- ČSN EN ISO 14911. Water quality - Determination of dissolved Li+, Na+, NH4+, K+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ using ion chromatography - Method for water and waste water. Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing, Prague, 2000.
- ISO 10260. Water quality, measurement of biochemical parameters; spectrometric determination of chlorophyll-a concentration (ISO: 1992). Int. Organ. for Standardisation (ISO), Geneva, 1992.
- ISO 8245. Water quality-Guidelines for the determination of total organic carbon (TOC) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC). Int. Organ. for Standardisation (ISO), Geneva. 1999.
- ČSN EN 12880. Characterization of sludges - Determination of dry residue and water content. Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing, Prague, 2000.
- Romero, C. M.; Engel, R. E.; D’Andrilli, J.; Chen, C.; Zabinski, C.; Miller, P. R.; Wallander, R. Bulk optical characterization of dissolved organic matter from semiarid wheat-based cropping systems. Geoderma 2017, 306, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K. R.; Stedmon, C. A.; Graeber, D.; Bro, R. Fluorescence spectroscopy and multi-way techniques. PARAFAC [10.1039/C3AY41160E]. Analytical Methods 2013), 5, 6557-6566. [CrossRef]
- Gold-Bouchot, G.; Polis, S.; Castañon, L. E.; Flores, M. P.; Alsante, A. N.; Thornton, D. C. O. Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in a subtropical estuary (Galveston Bay, USA) and the impact of Hurricane Harvey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2021, 28, 53045–53057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, C.; Mokhtar, M.; Perroud, A.; McCullough, G.; Papakyriakou, T. Mixing and photoreactivity of dissolved organic matter in the Nelson/Hayes estuarine system (Hudson Bay, Canada). J Mar Syst 2016, 161, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Casiano, J. M.; González-Santana, D.; Devresse, Q.; Hepach, H.; Santana-González, C.; Quack, B.; Engel, A.; González-Dávila, M. Exploring the Effects of Organic Matter Characteristics on Fe(II) Oxidation Kinetics in Coastal Seawater. Environ Sci Technol 2022, 56, 2718–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutova, Y.; Baker, A.; Bridgeman, J.; Henderson, R. K. Spectroscopic characterisation of dissolved organic matter changes in drinking water treatment: From PARAFAC analysis to online monitoring wavelengths. Water Res 2014, 54, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcé, R.; Verdura, L.; Leung, N. Dissolved organic matter spectroscopy reveals a hot spot of organic matter changes at the river–reservoir boundary. Aquatic Sci 2021, 83, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C. J.; Frost, P. C.; Xenopoulos, M. A. Beyond best management practices: pelagic biogeochemical dynamics in urban stormwater ponds. Ecol Appl 2013, 23, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S. A.; Amon, R. M. W.; Stedmon, C. A. Variations in high-latitude riverine fluorescent dissolved organic matter: A comparison of large Arctic rivers. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 2013, 118, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moona, N.; Holmes, A.; Wünsch, U. J.; Pettersson, T. J. R.; Murphy, K. R. Full-Scale Manipulation of the Empty Bed Contact Time to Optimize Dissolved Organic Matter Removal by Drinking Water Biofilters. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, K. I.; Levia, D. F.; Hudson, J. E. Tracking senescence-induced patterns in leaf litter leachate using parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) modeling and self-organizing maps. Journal of Geophysical Research. Biogeosciences 2017, 122, 2233–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Kang, H.-W.; Kim, S. H.; Rho, T.; Kang, D.-J. Tracing water mass fractions in the deep western Indian Ocean using fluorescent dissolved organic matter. Mar Chem 2020, 218, 103720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.-E.; Chen, W.; Yang, L. Effects of Photodegradation on the Optical Indices of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter from Typical Sources. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 14268. https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/21/14268.
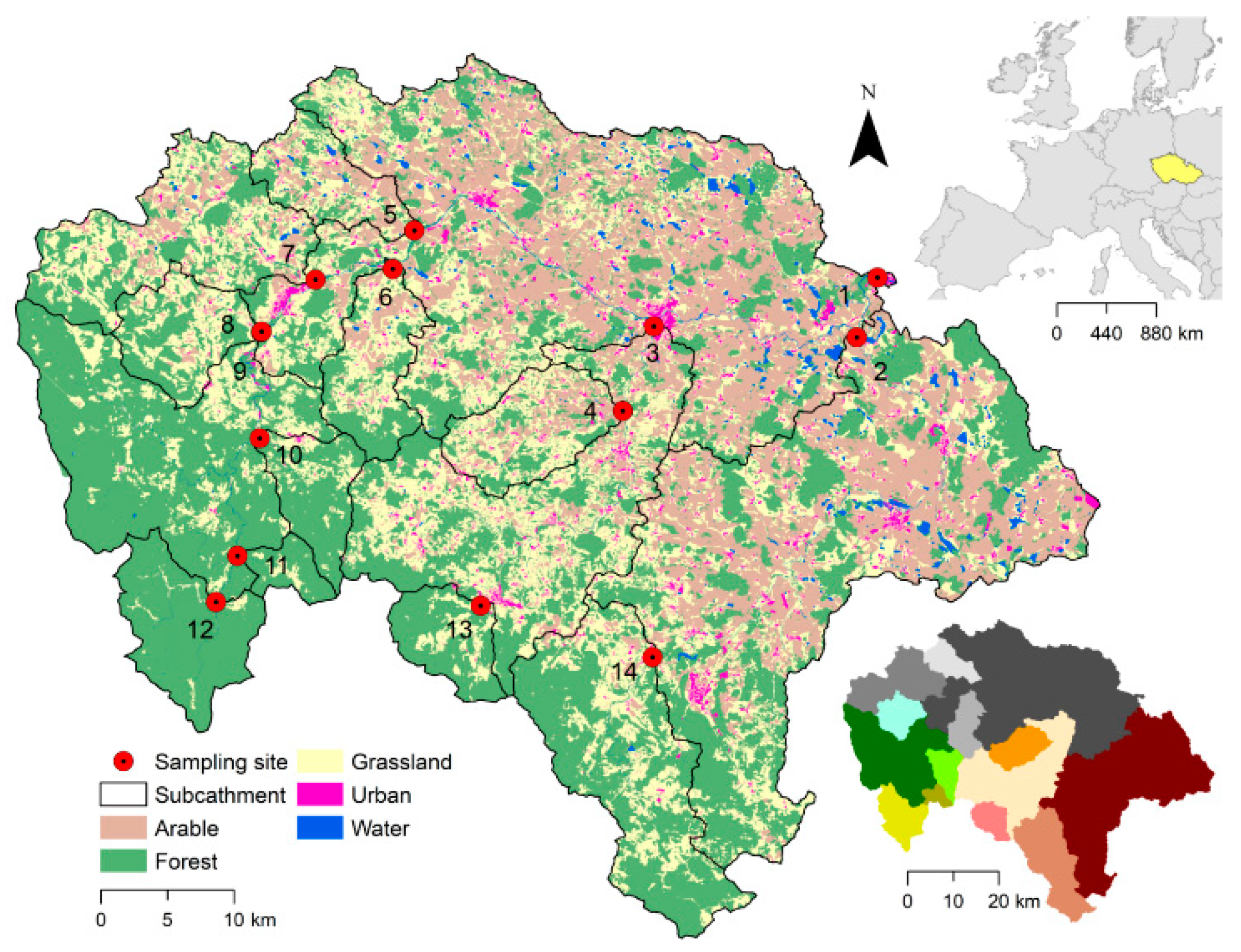
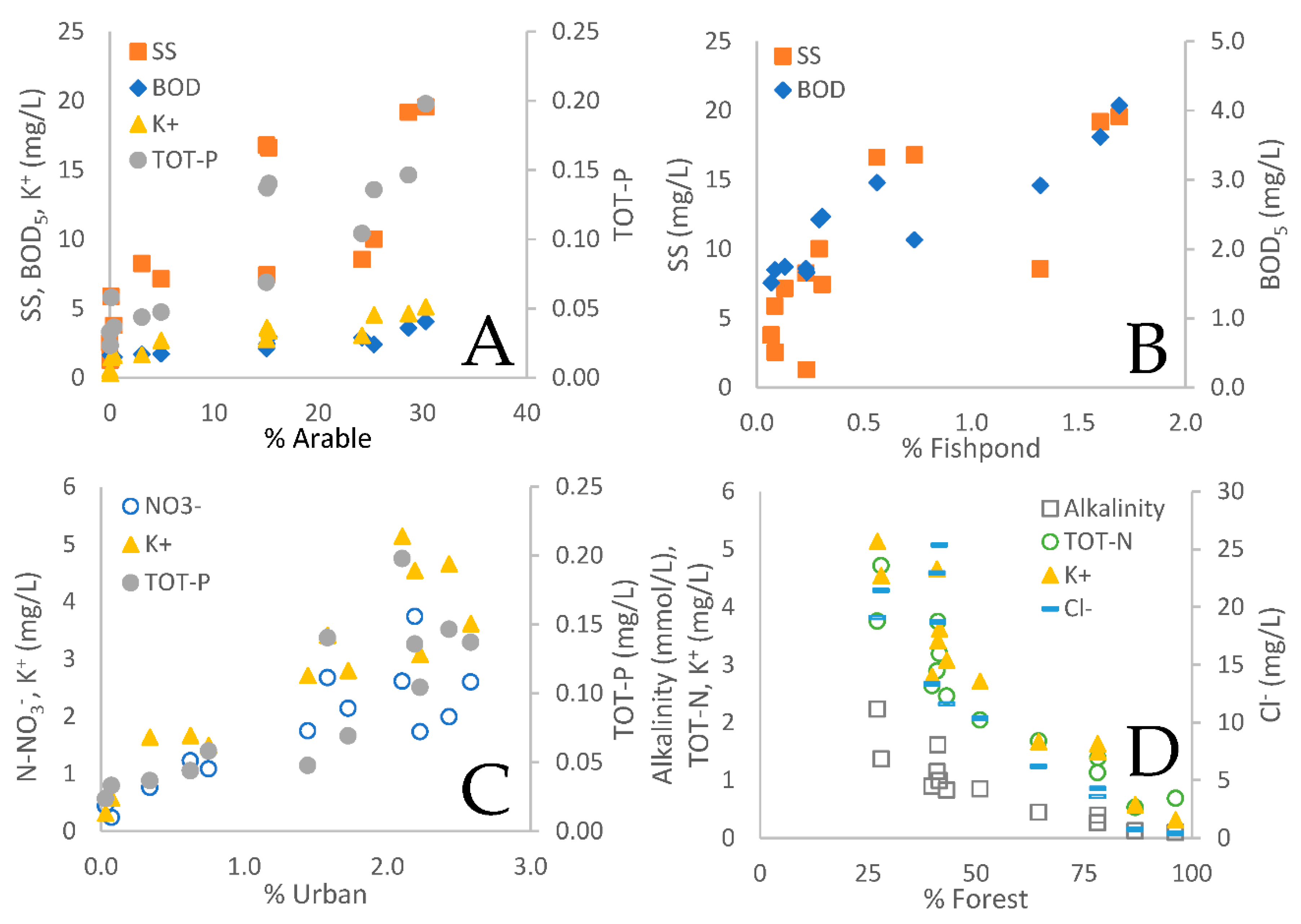
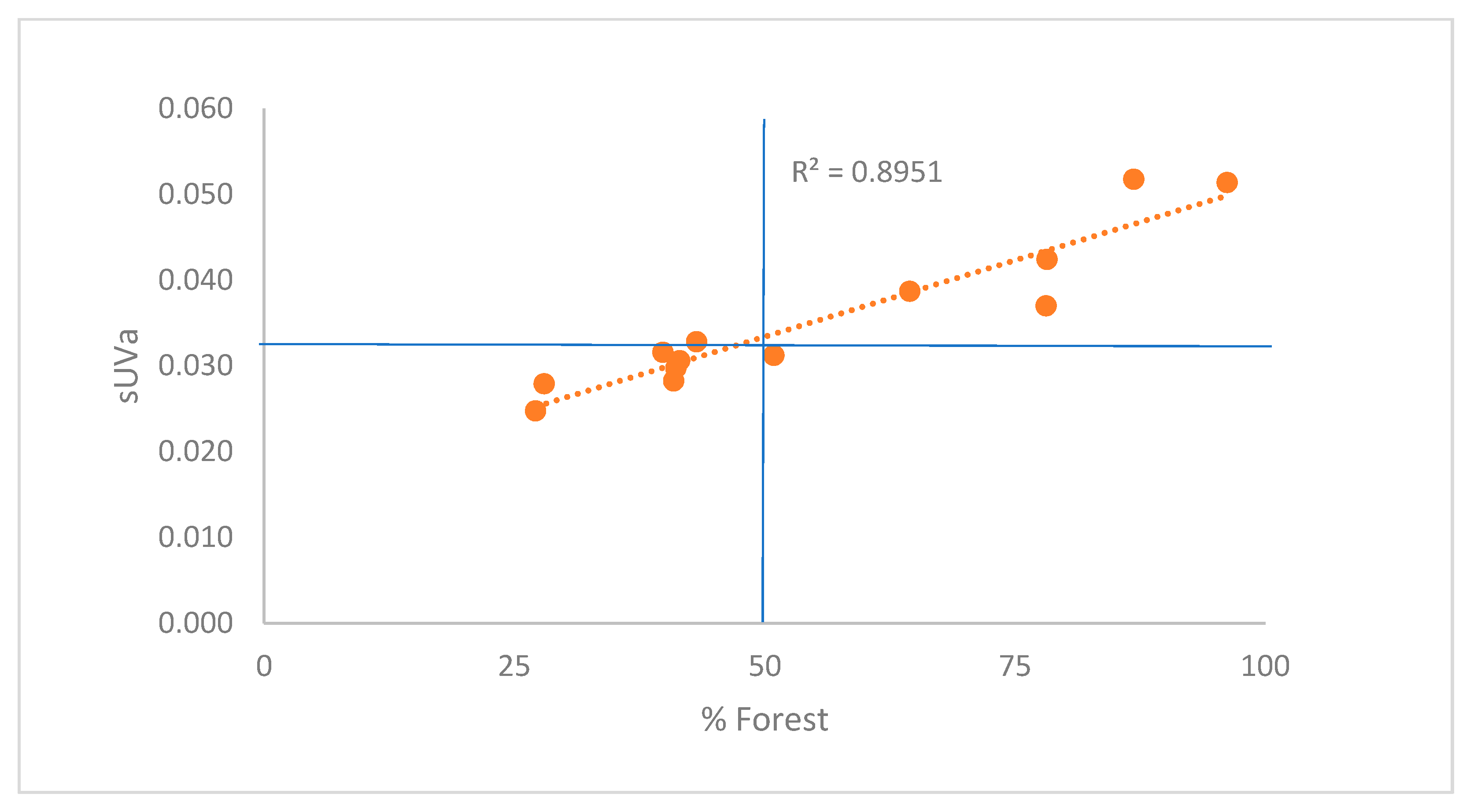
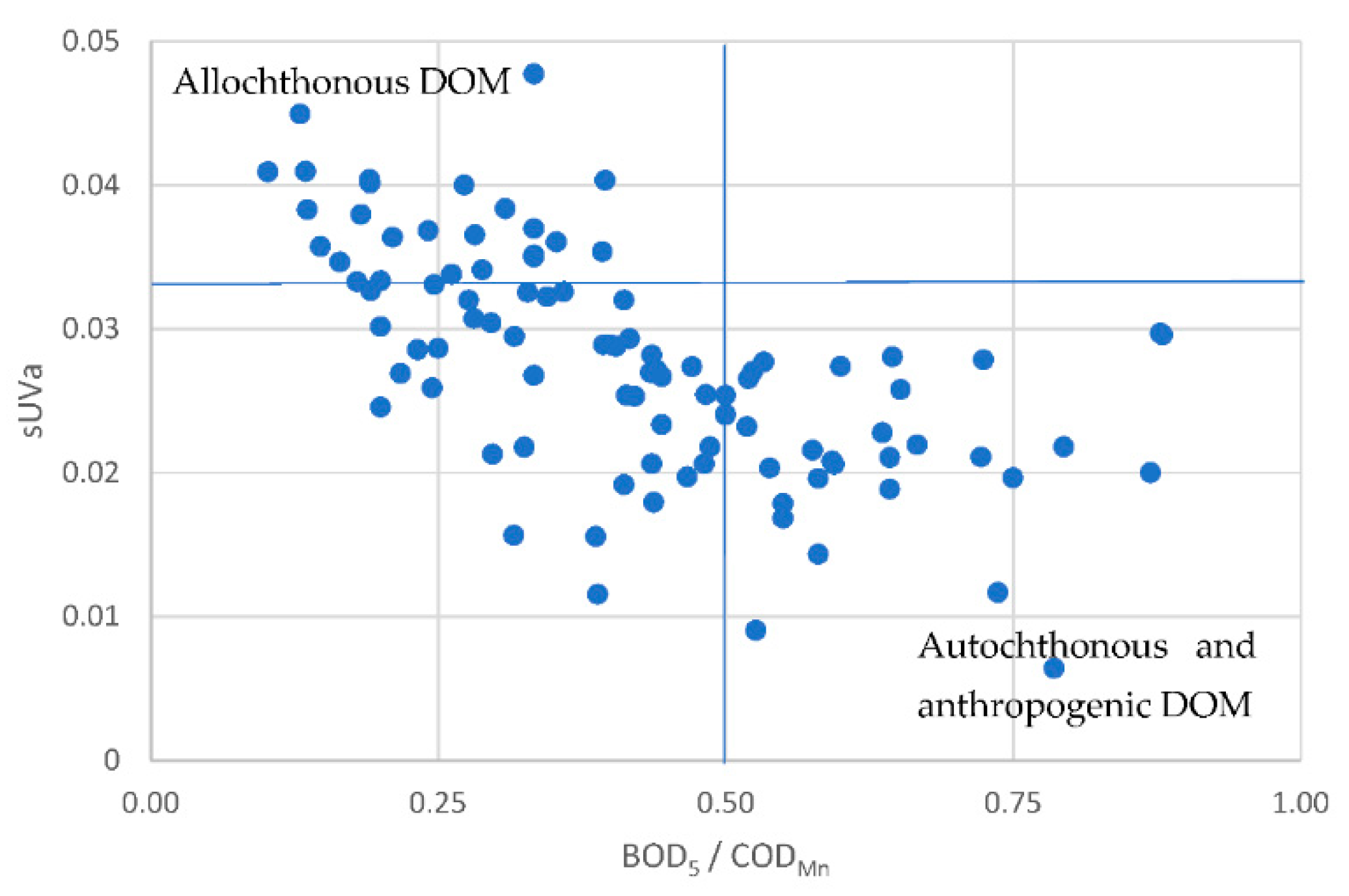
| Site # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Otava Písek |
Blanice Putim |
Volyňka Strakonice | Peklov Nemětice |
Černíčský potok Bojanovice |
Nezdický potok Žichovice |
Ostružná Sušice | Volšovka Červené Dvorce | Otava nad Volšovkou |
Losenice Rejštejn |
Hamerský potok Antýgl |
Vydra Modrava |
Volyňka Vimperk | Blanice Pode-dvory |
| Location () | 49.3083 14.1250 |
49.2663 14.1127 |
49.2541 13.9032 |
49.1947 13.8839 |
49.2948 13.6435 |
49.2670 13.6273 |
49.2521 13.5499 |
49.2120 13.5026 |
49.2115 13.5022 |
49.1405 13.5170 |
49.0597 13.5120 | 49.0267 13.4974 | 49.0506 13.7676 | 49.0328 13.9504 |
| Altitude m a.s.l. |
360 | 364 | 400 | 428 | 429 | 435 | 452 | 482 | 465 | 558 | 900 | 980 | 710 | 545 |
| Catchment area km2 |
2885 | 860 | 427 | 80.3 | 61.5 | 75.8 | 172 | 74.4 | 456 | 53.7 | 20.7 | 89.7 | 48.4 | 210 |
| Land use, %: | ||||||||||||||
| Forest | 43.2 | 40.92 | 41.5 | 28.0 | 27.1 | 41.1 | 39.8 | 50.9 | 82.1 | 78.2 | 86.9 | 96.2 | 78.1 | 64.5 |
| Arable | 24.2 | 28.6 | 15.1 | 25.3 | 30.3 | 15.3 | 15.0 | 4.93 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 3.07 |
| Grassland1 | 29.1 | 26.4 | 40.5 | 44.2 | 38.8 | 41.5 | 42.7 | 42.6 | 16.7 | 20.8 | 13.0 | 3.49 | 21.1 | 31.6 |
| Urban | 2.23 | 2.43 | 2.58 | 2.19 | 2.10 | 1.58 | 1.73 | 1.44 | 0.45 | 0.75 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.62 |
| Water2 | 1.32 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 0.29 | 1.69 | 0.56 | 0.73 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.23 |
| Population density, person km⁻2 |
50.0 | 48.4 | 57.3 | 32.0 | 29.0 | 22.8 | 27.3 | 59.8 | 9.5 | 30.7 | 3.2 | 0.64 | 4.2 | 11.4 |
| %DOM fractions |
vs. |
R2 |
|---|---|---|
|
HPI |
Fishponds | 0.712 |
| BOD5 | 0.810 | |
| Rel. RR | 0.691 | |
| VHA | sUVa | 0.669 |
|
CHA |
Urban | 0.689 |
| CODMn | 0.729 | |
| K+ | 0.676 | |
| NO3- | 0.729 | |
| BIX | 0.757 | |
| FI | 0.805 | |
| HIX | 0.704 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





