Submitted:
25 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Biochemical Data of the Studied Population
2.2. Allelic and Genotypic Frequencies of the Studied Polymorphisms among DMT2 Patients Undergoing Metformin Treatment
2.3. HbA1c Control by SNPs in SLC22A1, SLC22A2, and SLC22A3.
2.4. Studied Biomarker Values by Genotypic Model
2.5. Metformin Plasmatic Concentrations by Genotype and Genotypic Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sample Description (DMT2 Patients)
Study design
Patient recruitment
4.2. Clinical Evaluation
4.3. Genotyping Procedure
4.4. Plasmatic Metformin Determination
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Inferential analysis.
Genotypic and Allelic Frequency Analysis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Standl, E., Khunti, K., Hansen, T. B., & Schnell, O. The global epidemics of diabetes in the 21st century: Current situation and perspectives. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology (2019). 26(2_suppl), 7–14. [CrossRef]
- Sun H., Pouya P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C.N., Mbanya J.C., Pavkov M. E., Ramachandaran A, Wild S.H., James S., Herman W.H., Zhang P., Bommer C., Kuo S., Boyko E.J., Dianna J., Magliano D.J. IDF DiabetesAtlas:Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice (2022) 183 I09II9, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Romero-Martínez M, Barrientos-Gutiérrez T, Cuevas-Nasu L, Bautista-Arredondo S, Colchero A, Gaona-Pineda E.B, Lazcano-Ponce E, Martínez-Barnetche J, Alpuche-Aranda C, Rivera-Dommarco J, Shamah-Levy T. Metodología de la Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2020 sobre Covid-19. Salud Publica Mex (2021) May 3;63(3):444-451. [CrossRef]
- Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet (1998). 352: 837-853,.
- Diabetes Care Volume 45, Supplement 1, January (2022). Matthew C. Riddle, MD. [CrossRef]
- Diagnóstico y Tratamiento Farmacológico de la Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2 en el Primer Nivel de Atención. Guía de Evidencias y Recomendaciones: Guía de Práctica Clínica. México, Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social. (2018). 55. http://imss.gob.mx/profesionales-salud/gpc (accessed on July 18th 2023).
- LaMoia T. and Shulman G.I. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Metformin Action Endocr Rev. 2021 Feb; 42(1): 77–96. [CrossRef]
- Staiger, H., Schaeffeler, E., Schwab, M., & Häring, H. U. Pharmacogenetics: Implications for modern type 2 diabetes therapy. Review of Diabetic Studies, (2015). 12(3–4), 363–376. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C., & Florez, J. C. Pharmacogenetics in type 2 diabetes: Potential implications for clinical practice. Genome Medicine (2011). 3(11). [CrossRef]
- Weizzman Institute of Science. (2022). Gene cards SLC22A1. https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=SLC22A1(Accessed July 20th 2023).
- Koepsell, H., Lips, K., & Volk, C. Polyspecific organic cation transporters: Structure, function, physiological roles, and biopharmaceutical implications. Pharmaceutical Research (2007) 24(7), 1227–1251. [CrossRef]
- Lai Y. Organic anion, organic cation and zwitterion transporters of the SLC22 and SLC47 superfamily (OATs, OCTs, OCTNs and MATEs). In Transporters in Drug Discovery and Development. (2013). [CrossRef]
- Srijib, G. PharmGKB summary: very important pharmacogene information for SLC22A1. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics (2014). 23(1), 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Becker M.L., Visser L.E., van Schaik, R.H.N., Hofman A., Uitterlinden A.G., Stricker B.H.C. Interaction between polymorphisms in the OCT1 and MATE1 transporter and metformin response. Pharmacogenet. Genom. (2010) 20, 38–44. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.pbidi.unam.mx:2443/19898263/ (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- WHO. Physical Status: The Use of and Interpretation of Anthropometry, Report of a WHO Expert Committee. 1995. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/37003 (accessed on July 21th 2023).
- Shamah Levy T, Cuevas Nasu L, Morales Ruan MC, Mundo Rosas V, Méndez Gómez-Humarán I, Villalpando Hernández S. Profile of the Health and Nutritional Status of Older Adults in Mexico. 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey. J Frailty Aging. 2013;2(4):184-91. [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Ayala A, Rodríguez-Rivera NS, Andrés F. d, LLerena A, Pérez-Silva E, Espinosa-Sánchez AG, Molina-Guarneros JA Pharmacogenetics of Metformin Transporters Suggests No Association with Therapeutic Inefficacy among Diabetes Type 2 Mexican Patients. Pharmaceuticals (2022). 15(7):774. [CrossRef]
- Reséndiz-Abarca C., Flores-Alfaro E., Suárez-Sánchez F., Cruz M., Valladares-Salgado A., Alarcón-Romero L.D.C., Wacher-Rodarte N.A., Gómez-Zamudio J.H. Altered Glycemic Control Associated With Polymorphisms in the SLC22A1 (OCT1) Gene in a Mexican Population With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated With Metformin: A Cohort Study. J. Clin. Pharmacol. (2019), 59 (10) 1384–1390. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.pbidi.unam.mx:2443/31012983/ (accessed on Jul 18th 2023).
- Menjivar M., Sánchez-Pozos K., Jaimes-Santoyo J., Monroy-Escutia J., Rivera- Santiago C., Granados-Silvestre A., Ortiz-López M.G. Pharmacogenetic Evaluation of Metformin and Sulphonylurea Response in Mexican Mestizos with Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Drug Metab. (2020), 21, 291–300. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.pbidi.unam.mx: 2443/32407269/ (accessed on May 2nd 2022).
- Christensen MH , Brasch-Andersenb C , Greene H, Nielsen F , Damkierc P , Beck-Nielsen H and Brosena K. The pharmacogenetics of metformin and its impact on plasma metformin steady-state levels and glycosylated hemoglobin A1c. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics (2011) 21(12):p 837-850. [CrossRef]
- Morris A.D., Boyle D.R. , MacAlpine R, Emslie-Smith A, Jung R.T., Newton RW, MacDonald T. M. for the DARTS/MEMO Collaboration. The diabetes audit and research in Tayside Scotland (darts) study: electronic record linkage to create a diabetes register. BMJ (1997) 315:524.
- Zhou, K., Donnelly, L. A., Kimber, C. H., Donnan, P. T., Doney, A. S. F., Leese, G., Hattersley, A. T., McCarthy, M. I., Morris, A. D., Palmer, C. N. A., & Pearson, E. R. Reduced-function SLC22A1 polymorphisms encoding organic cation transporter 1 and glycemic response to metformin: A GoDARTS study. Diabetes, (2009) 58(6), 1434–1439. [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswaran G, Praveen R.G. Damodaran S. E. Das A.K. Adithan C. Influence of SLC22A1 rs622342 genetic polymorphism on metformin response in South Indian type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Clin Exp Med (2015) 15:511–517.
| Men | Women | ||
| Variable | n= 17 | n= 42 | p value |
| Age (years) | 59.00 (51.00 – 62.00) | 54.50 (46.20 – 61.00) | 0.3354 |
| Height (metres) | 1.64 ±0.05 | 1.54 ±0.05 | <0.001* |
| Weight (kg) | 81.50 ±11.90 | 77.70 ±18.30 | 0.2249 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.20 ±4.04 | 32.6 ±6.93 | 0.0957 |
| BMI clasification Normal weight Overweight Obesity I Obesity II Obesity III |
0 (0.00%) 8 (47.05%) 7 (41.17%) 2 (11.76%) 0 (0.00%) |
4 (9.52%) 12 (28.57%) 11 (26.19%) 10 (23.80%) 5 (11.90%) |
0.2830 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 127 (119 – 136) | 124 (110 – 134) | 0.5135 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 78 (68 – 88) | 77 (70 – 80) | 0.9069 |
| Diagnose date (years) | 3.00 (1.00 – 6.00) | 3.50 (1.62 – 8.00) | 0.4534 |
| Metformin dose(mg/kg/day) | 19.80 (10.50 – 23.80) | 18.4 (12.70 – 26.80) | 0.3839 |
| Metformin dose (mg/day) 500 850 1700 2550 |
0 (0.00%) 7 (43.75%) 7 (43.75%) 2 (12.50%%) |
2 (5.00%) 13 (32.50%) 16 (40.00%) 9 (22.50%) |
0.5878 |
| Metformin concentration (ng/ml) |
650.00 (135.00 – 877.00) |
263.00 (107.00 – 748.00) |
0.3750 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dl) <126 mg/dl >126 mg/dl |
107.00 (102.00 – 134.00) 13 (76.47%) 4 (23.53%) |
121.00 (100.00 – 187.00) 22 (53.65%) 19 (46.35%) |
0.5051 0.1863 |
| HbA1c (%) <7% ≥7% |
6.30 (5.80 – 7.30) 12 (70.58%) 5 (29.42%) |
6.40 (6.10 – 7.85) 31 (73.81%) 11 (26.19%) |
0.3229 1.000 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) <200 ≥200 |
165.00 ±32.40 13 (81.25%) 3 (18.75%) |
179.00 ±41.60 28 (66.66%) 14 (33.33%) |
0.2367 0.4426 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) <150 ≥150 |
185.00 (108.00 –201.00) 6 (42.85%) 8 (57.15%) |
195.00 (132.00 – 239.00) 10 (24.39%) 31 (75.61%) |
0.3339 0.3307 |
| FGR (MDRD-4, ml/min) | 92.80 (80.7 – 113.00) | 94.50 (89.30 – 115.00) | 0.9334 |
| Mean ± (standard deviation), percentile median (25-75), and frequency (%). *Statistic significance (p<0.05). | |||
| Gene | SNP | Genotype | n=59 | Frequency | Allele | n | Frequency | p value |
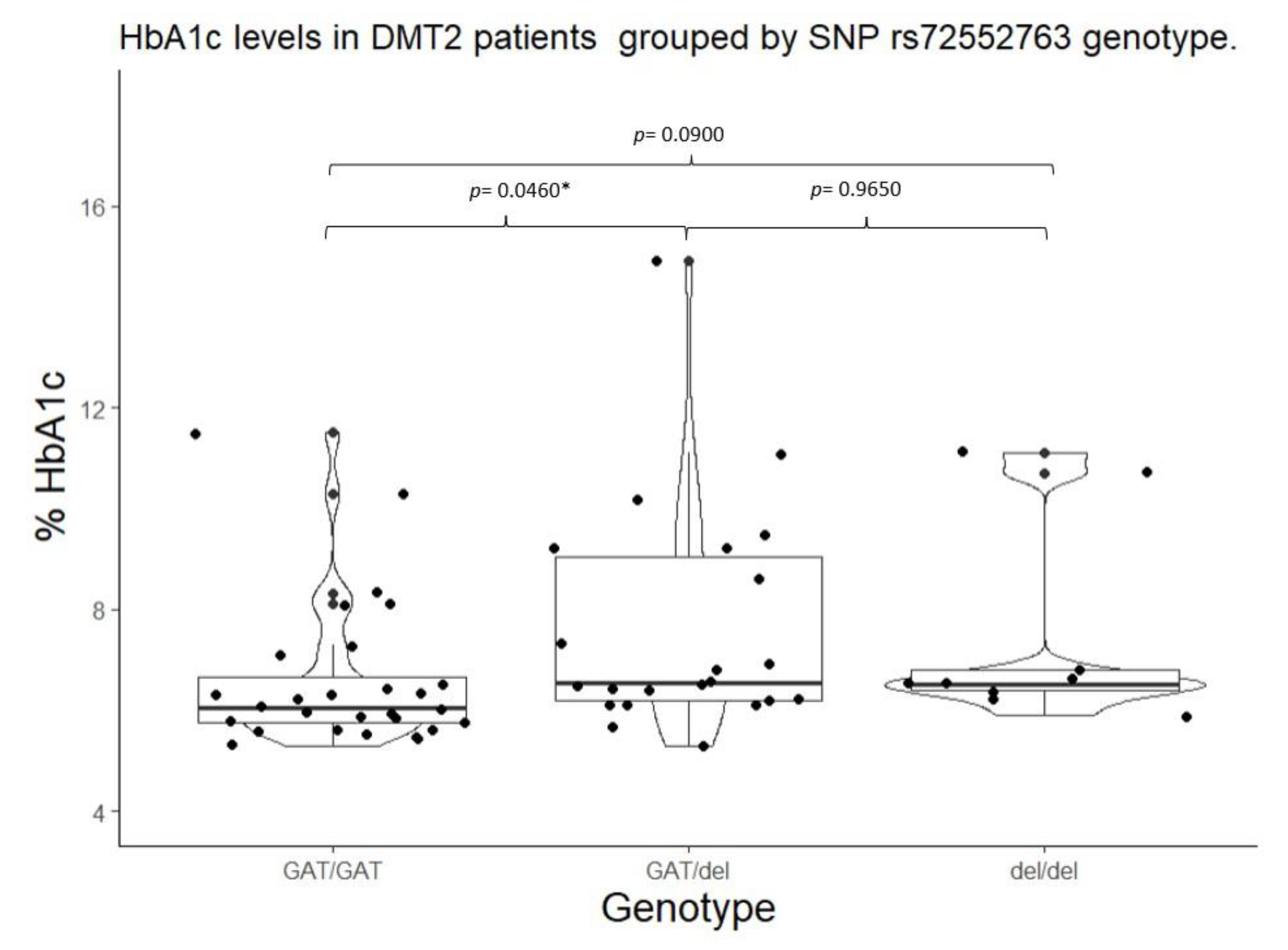
| SLC22A1 | rs72552763 | GAT/GAT | 28 | 0.4745 | GAT | 78 | 0.6610 | 0.6654 |
| GAT/del | 22 | 0.3728 | del | 40 | 0.3389 | |||
| del/del | 9 | 0.1525 | ||||||
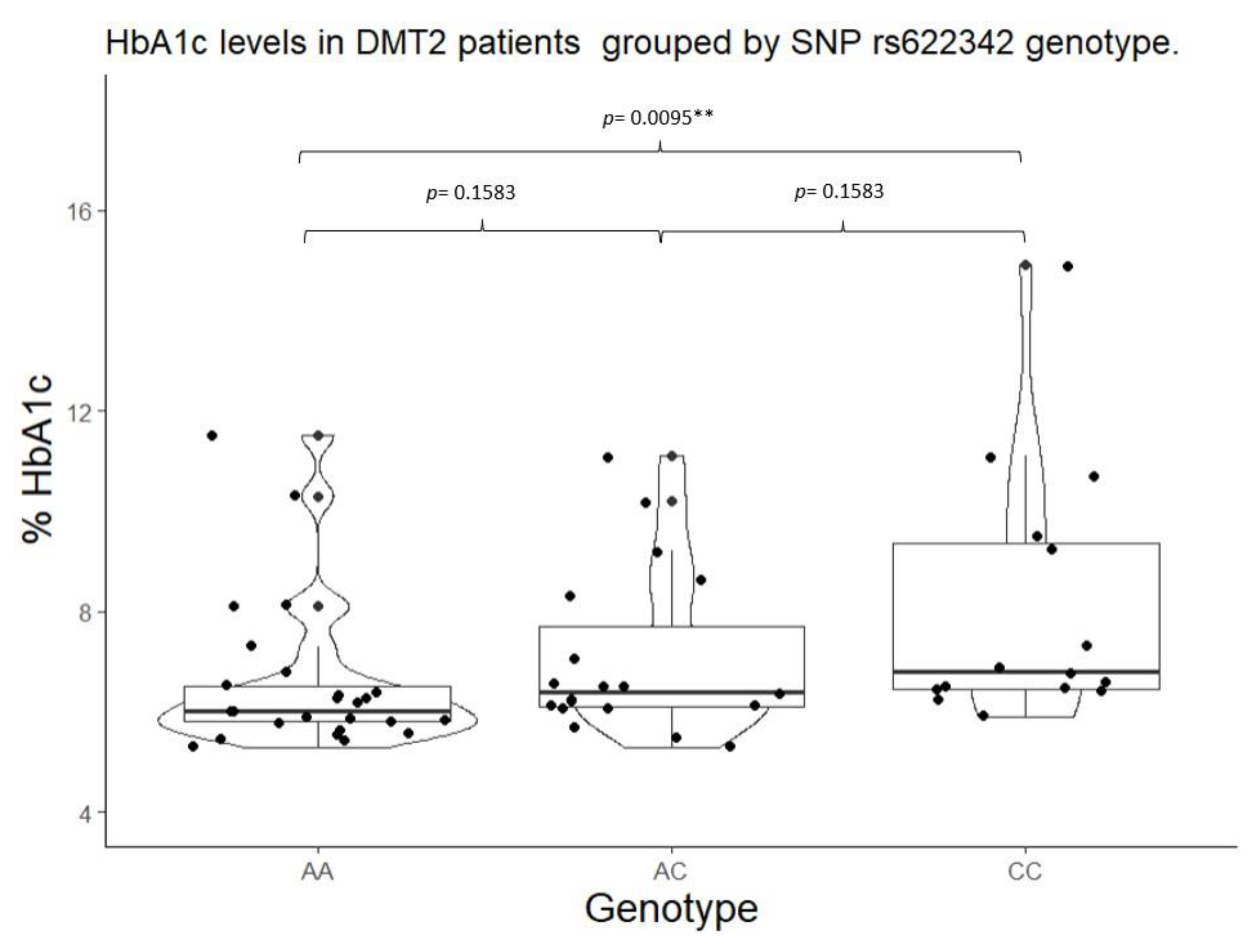
| rs622342 | A/A | 25 | 0.4237 | A | 69 | 0.5847 | 0.1829 | |
| A/C | 19 | 0.3220 | C | 49 | 0.4152 | |||
| C/C | 15 | 0.2542 | ||||||
| SLC22A2 | rs316019 | C/C | 52 | 0.8813 | C | 110 | 0.9322 | 0.7479 |
| C/A | 6 | 0.1016 | A | 8 | 0.0677 | |||
| A/A | 1 | 0.0169 | ||||||
| SLC22A3 | rs2076828 | C/C | 46 | 0.7796 | C | 103 | 0.8728 | 0.7531 |
| C/G | 11 | 0.1864 | G | 15 | 0.1271 | |||
| G/G | 2 | 0.0338 | ||||||
| p value of Pearson’s chi-squared test for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium | ||||||||
| Dominant genotypic model | |||||||||
| Gene | SNP | Genotype | HbA1c<7% n (%) |
HbA1c≥ 7% n (%) |
p value | Genotype | HbA1c<7% n (%) |
HbA1c≥ 7% n (%) |
p value |
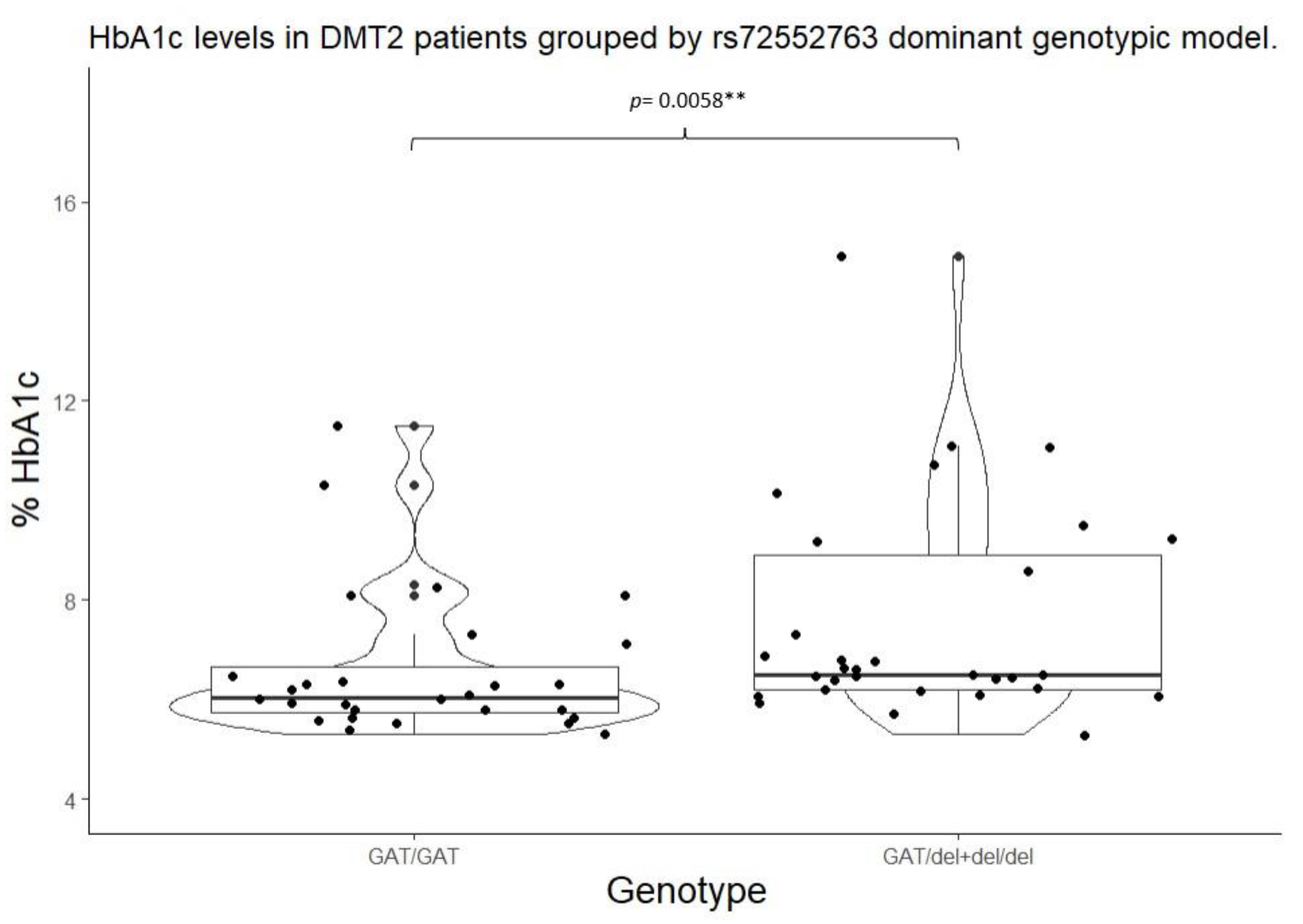
| SLC22A1 | rs72552763 | GAT/GAT | 22 (51.20%) | 6 (37.50%) | 0.4678 | GAT/GAT | 22 (51.16%) | 6 (37.50%) |
0.5215 |
| GAT/del | 14 (32.50%) | 8 (50.00%) | GAT/del + del/del | 21 (48.83%) | 10 (62.50%) | ||||
| del/del | 7 (16.30%) | 2 (12.50% | |||||||
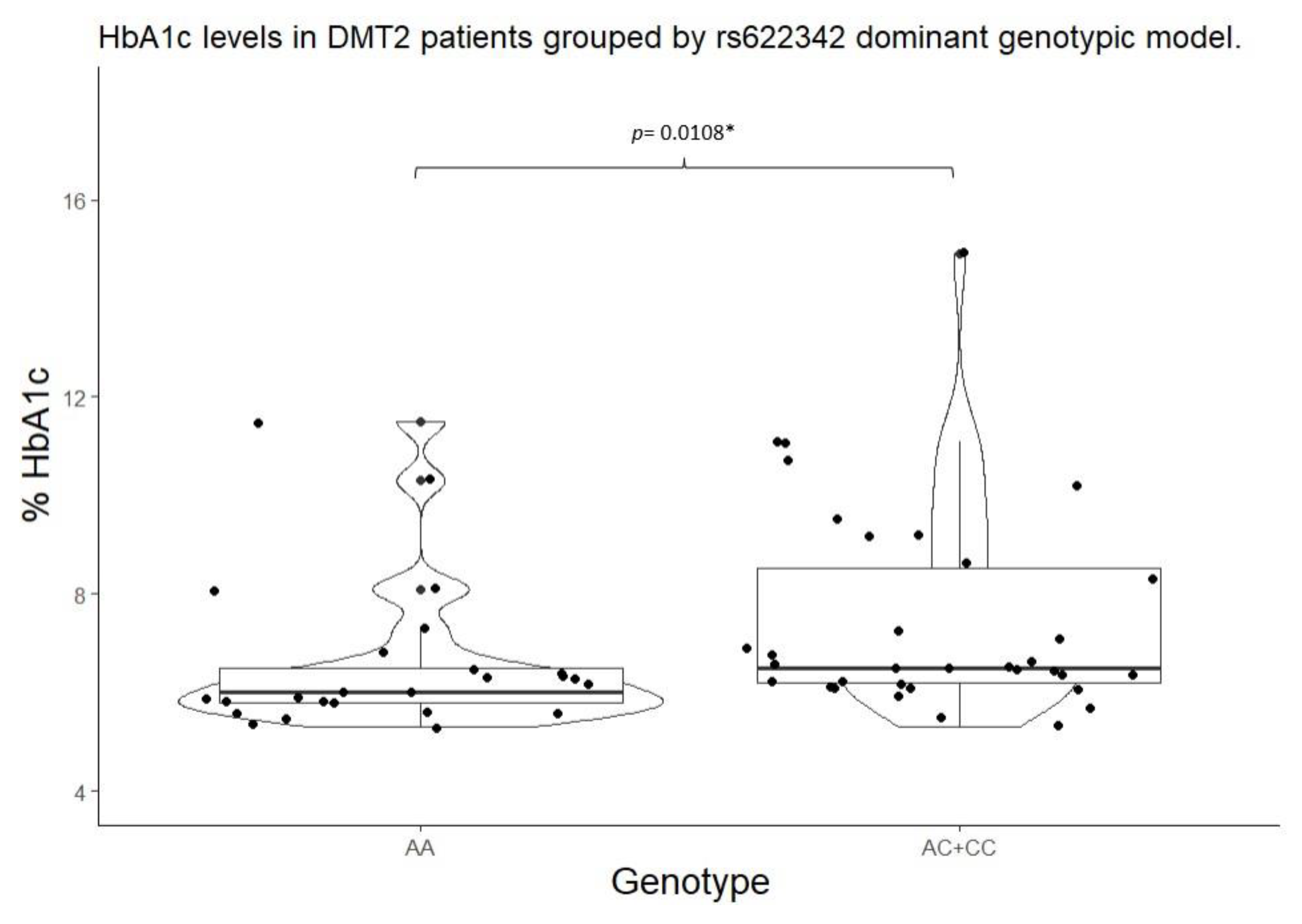
| rs622342 | A/A | 21 (48.83%) | 4 (25.00%) | 0.2215 | A/A | 21 (48.83% | 4 (25.00%) |
0.1767 |
|
| A/C | 13 (30.23%) | 6 (37.50%) | A/C + C/C | 22 (51.16%) | 12 (75.00%) | ||||
| C/C | 9 (20.93%) | 6 (37.50%) | |||||||
| SLC22A2 | rs316019 | C/C | 38 (88.37%) | 14 (87.5%) | 0.2209 | C/C | 38 (88.37%) | 14 (87.50%) | 1.000 |
| C/A | 5 (11.62%) | 1 (6.25%) | C/A + A/A | 5 (11.62%) | 2 (12.50%) | ||||
| A/A | 0 (0%) | 1 (6.25%) | |||||||
| SLC22A3 | rs2076828 | C/C | 36 (83.72%) | 10 (62.50%) | 0.215 | C/C | 36 (83.72%) | 10 (62.50%) | 0.163 |
| C/G | 6 (13.95%) | 5 (31.25%) | C/G + G/G | 7 (16.28%) | 6 (37.50%) | ||||
| G/G | 1 (2.32%) | 1 (6.25%) | |||||||
| In display: frequency and percentage (%). | |||||||||
| Genotype | Dominant genotypic model | ||||||||||
| Gene | SNP | Genotype | HbA1c (%) | p value | Fasting glucose | p valor | Genotype | HbA1c (%) |
p value | Fasting glucose (mg/dl) | p value |
| SLC22A1 | rs72552763 | GAT/GAT | 6.05 (5.75 – 6.65) |
0.0220* | 103.00 (100.00 – 133.20) |
0.0822 | GAT/GAT | 6.05 (5.75 – 6.65) |
0.0058** | 103.00 (100.00 – 133.25) |
0.0260** |
| *** GAT/del |
6.55 (6.20 – 9.05) |
127.00 (106.00 – 195.00 |
GAT/del + del/del |
6.50 (6.20 – 8.90) |
127.00 (107.20 – 193.00) |
||||||
| del/del | 6.5 (6.4 – 6.8) |
127.00 (116.00 – 146.00) |
|||||||||
| rs622342 | A/A | 6.00 (5.80 – 6.50) |
0.0093* | 105.00 (102.00 – 133.00) |
0.0864 | A/A | 6.00 (5.80 – 6.50) |
0.0108** | 105.00 (102.00 – 133.00) |
0.1551 | |
| A/C | 6.4 (6.10 – 7.70) |
113.00 (100.00 – 133.00) |
A/C + C/C |
6.50 (6.20 – 8.50) |
127.00 (104.00 – 187.00) |
||||||
| *** C/C |
6.8 (6.45 – 9.35) |
135.00 (118.50 – 205.00) |
|||||||||
| SLC22A2 | rs316019 | C/C | 6.4 (5.97 – 7.15) |
0.6097 | 115.00 (101.00 – 140.00) |
0.3138 | C/C | 6.40 (5.90 – 7.10) |
0.888 | 115.00 (101.00 – 140.5) |
0.210 |
| C/A | 6.25 (5.90 – 7.65) |
139.00 (107.50 – 207.20) |
C/A + A/A |
6.30 (6.00 – 8.10) |
157.00 (112.00 – 223.50) |
||||||
| A/A | 8.1 | 223 | |||||||||
| SLC22A3 | rs2076828 | C/C | 6.3 (5.90 – 6.80) |
0.3356 | 115.00 (102.00 – 152.00) |
0.507 | C/C | 6.30 (5.90 – 6.80) |
0.3552 | 115.00 (102.00 – 152.00) |
0.8156 |
| C/G | 6.40 (5.90 – 8.20) |
107.00 (100.00 – 167.00) |
C/G + G/G |
6.60 (6.10 – 9.20) |
121.00 (100.00 – 204.00) |
||||||
| G/G | 8.60 (7.60 – 9.60) |
175.00 (151.00 – 199.00) |
|||||||||
| Mean ± (standard deviation), percentile median (25-75), and frequency (%) *Statistical significance (p<0.05) for Kruskal-Wallis test. **Statistical significance (p<0.05) for Mann Whitney’s U test. ***Statistical significance (p<0.05) for Wilcoxon’s signed-rank test with continuity correction vs Wild type genotype. | |||||||||||
| Genotype | Dominant genotypic model | ||||||
| Gene | SNP | Genotype | Metformin concentration (ng/ml) | p value | Genotype | Metformin concentration (ng/ml) | p value |
| SLC22A1 | rs72552763 | GAT/GAT | 504.04 (131.65 – 900.16) |
0.4628 |
GAT/GAT | 504.04 (131.65 – 900.16) |
0.2384 |
| GAT/del | 262.17 (57.23 – 765.18) |
GAT/del + del/del |
236.48 (86.76 – 785.24) |
||||
| del/del | 146.14 (119.93 – 792.97) |
||||||
| rs622342 | A/A | 451.65 (128.01 – 848.18) |
0.6390 | A/A | 451.65 (128.01 – 848.18) |
0.4548 |
|
| A/C | 270.56 (61.85 – 747.55) |
A/C + C/C |
263.24 (95.18 – 807.73) |
||||
| C/C | 237.55 (126.04 – 934.38) |
||||||
| SLC22A2 | rs316019 | C/C | 327.96 (105.88 – 812.59) |
0.7780 | C/C | 283.43 (250.93 – 446.05) |
0.7780 |
| C/A | 283.43 (250.93 – 446.05) |
C/A + A/A |
6.3 (6.0 – 8.1) |
||||
| A/A | - | ||||||
| SLC22A3 | rs2076828 | C/C | 146.14 (102.66 – 810.16) |
0.4560 | C/C | 146.14 (102.66 – 810.16) |
0.1748 |
| C/G | 481.75 (264.30 – 687.45) |
C/G + G/G |
618.85 (320.64 – 848.03) |
||||
| G/G | - | ||||||
| Mean ± (standard deviation), percentile median (25-75), and frequency (%) *Statistical significance (p<0.05) for Kruskal-Wallis test. **Statistical significance (p<0.05) for Mann-Whitney’s posthoc test vs. Wild type genotype. | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





