1. Introduction
Blockchain is a peer-to-peer distributed storage system with good security performance, high fault tolerance, suitable for encryption and other characteristics [
1,
2]. It is because of these characteristics of blockchain that it has now been combined with four fields of big data [
3], cloud computing [
4] and artificial intelligence [
5] to be called black technology in the information industry. The underlying core, consensus algorithm [
6], is also slowly entering the public vision.
The early consensus algorithm originated from Paxos[
7,
8,
9], a distributed algorithm proposed by Lamport, but it had great limitations and could not be implemented in real life. Then Stanford proposed a practical Raft algorithm [
10] (Replication and Fault Tolerant).Lamport proposed the Byzantine Generals problem [
11], Castro and Liskov et al. proposed a more classical PBFT algorithm to solve this problem [
12]. Satoshi Nakamoto proposed the Proof of Work algorithm [
13,
14,
15] (PoW), but its application in the blockchain has poor performance. The Proof of Stake algorithm [
16] (PoS) has been improved based on this defect, but the centralization is obvious, which does not conform to the decentralized characteristics of the blockchain. In the process of its development, many algorithms have tried to solve this problem, combining PoW and PoS to form a hybrid consensus mechanism, PoW as a method to compete for accounting rights, and PoS as a method to prevent bifurcation. For example, Tendermint[
17] and its improved algorithm HoneyBadger[
18] combined PoS with PBFT, Tangaroa consensus algorithm [
19] combined PBFT with Raft algorithm to unify the advantages of both. The simplicity of Raft and the advantage of PBFT in identifying Byzantine nodes are preserved. Whereas PoW, PoS, and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) can lead to forks [
20] and require the issuance of tokens, PBFT is fork-free, token-free, and tolerant of Byzantine nodes. From this point of view, the PBFT algorithm is an ideal consensus algorithm, but the PBFT algorithm still has shortcomings, such as large communication overhead in the three-phase process, all nodes participate in the consensus process, and it is not suitable for dynamic networks, etc. Therefore, many experts and scholars have improved PBFT [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25].
PBFT algorithm is divided into three protocols, consensus protocol, view switching protocol and checkpoint protocol. Many improved algorithms are based on the optimization of the above three aspects. Literature [
21] proposed an improved PBFT consensus algorithm with random selection of master nodes, which optimized the three-stage process to reduce communication complexity. At the same time, nodes could dynamically join and exit to improve system availability, but the random selection of master nodes made the consensus process lack security and easily triggered the view switching protocol. Literature [
22] proposed an improved PBFT algorithm using ring signature, which used the way of automatically forming rings when nodes signed to increase the dynamics of consensus and optimize the efficiency of view switching. Literature [
23] proposed an improved Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus algorithm of recommended trust model, which added a reward and punishment mechanism, and did not randomly select the master node and consensus node to improve the security of consensus, but the problem of large communication overhead still existed. Literature [
24] also proposed the PBFT consensus algorithm based on trust evaluation model. Although the consensus nodes were grouped to improve the consensus efficiency, the consensus protocol process did not change, and the communication complexity was only slightly less than O (n
2). Literature [
25] proposes an improved PBFT consensus algorithm that classifies nodes by clustering method. According to the response situation of nodes in the consensus process as the data dimension, K-means++ clustering algorithm is combined with it to reduce the number of nodes participating in the consensus process and improve the quality of consensus nodes, but the number of communication in the three stages is not greatly improved.
In order to solve the problems that the improved PBFT algorithm still has large communication overhead, the master node is randomly selected, there are certain limitations that can not complete consensus in the dynamic network, and can not identify the Byzantine nodes in the system, this paper proposes a Fibonacci group consensus algorithm based on node evaluation mechanism (SP-PBFT) based on the overall network and adaptive selection of consensus nodes. The algorithm adopts a speculative method according to the network environment of the system [
26], applies different steps to different network environments to reach consensus, and optimizes the consensus protocol. At the same time, it increases the node evaluation mechanism and groups according to the Fibonacci function [
27], which reduces the number of consensus nodes and fundamentally improves the efficiency. And the nodes participating in the consensus are more reliable to simplify the view switching protocol.
2. Design of SP-PBFT Consensus Algorithm
2.1. Algorithm Idea
In view of the general situation, the traditional PBFT algorithm is rarely attacked by malicious nodes in the consensus, and the Byzantine consensus algorithm will only work when malicious nodes interfere with the consensus process. Therefore, the three-stage communication process of the PBFT algorithm can be simplified, and the optimization idea of speculative algorithm can be used to divide the PBFT algorithm into two modes. (1) In the optimistic mode, nodes behave without delay and hardly apply any protection against malicious nodes. The emphasis on consensus efficiency makes the algorithm in the optimistic mode competitive with the centralized system in terms of speed. (2) Pessimistic mode, optimistic mode is triggered by timeout, and security measures against malicious nodes are added. The only goal is to successfully reach consensus even if there are malicious nodes.
According to the optimization idea shown by the speculative PBFT algorithm, it is found that this consensus algorithm can quickly complete the consensus and improve the efficiency of consensus. In summary, the characteristics of the speculative consensus algorithm are shown in
Table 1.
The specific improvement scheme is divided into the following points:
Firstly, the optimization idea of speculation was proposed, and the algorithm was divided into optimistic mode and pessimistic mode. According to the network environment of the system, the speculative method was adopted, and different steps were applied to different network environments to reach consensus, so as to optimize the consensus protocol. Adding the restriction that a set of nodes cannot participate in consensus twice in a row eliminates forks.
Secondly, a node evaluation mechanism is proposed, which rewards or punishes nodes based on their historical behavior, so that the nodes with higher reputation value are more likely to be the master nodes, and the nodes with poor performance cannot be selected. At the same time, the Byzantine nodes in the system are identified to optimize the view switching protocol.
Finally, the Fibonacci function was used to group the nodes according to their reputation value, and the half of the high reputation value of each group was taken as the consensus node, which reduced the number of nodes participating in the consensus and fundamentally improved the efficiency. At the same time, it prevents the centralization of the consensus process due to the accumulation of reputation value, improves the enthusiasm of nodes, conforms to the decentralized characteristics of blockchain, and makes the consensus process more secure and fair.
2.2. Algorithm Notation
(1) The algorithm contains a total of n nodes, the set of consensus nodes is denoted by R, including master and slave nodes, the ith consensus node is denoted by Ri, and the set of candidate nodes is denoted by s.
(2) The algorithm has certain requirements on the number of nodes, if there are f Byzantine nodes in the system, the total number of all the nodes must be made larger than 3f+1 to accomplish the consensus, which is usually made equal to 3f+1 under experimental conditions to reduce the load on the system.
(3) Meanings of the symbols in the system: v: view number; p: master node; h: block height; B: block; H(B): summary of block B; Bh: block B has height h; Vote(Bh,i): votes on block Bh generated by node i; VoteSet(Bh,i): node i receives a set of votes on block Bh; Cert(Bh): a block certificate, which contains on block Bh at least 2f+1 favorable votes, can be used to verify the validity of block Bh.
2.3. Description of Consensus Process
2.3.1. Optimistic Mode
The best case is network synchronization (all messages are delivered within the maximum delay d), d is less than the timeout threshold t
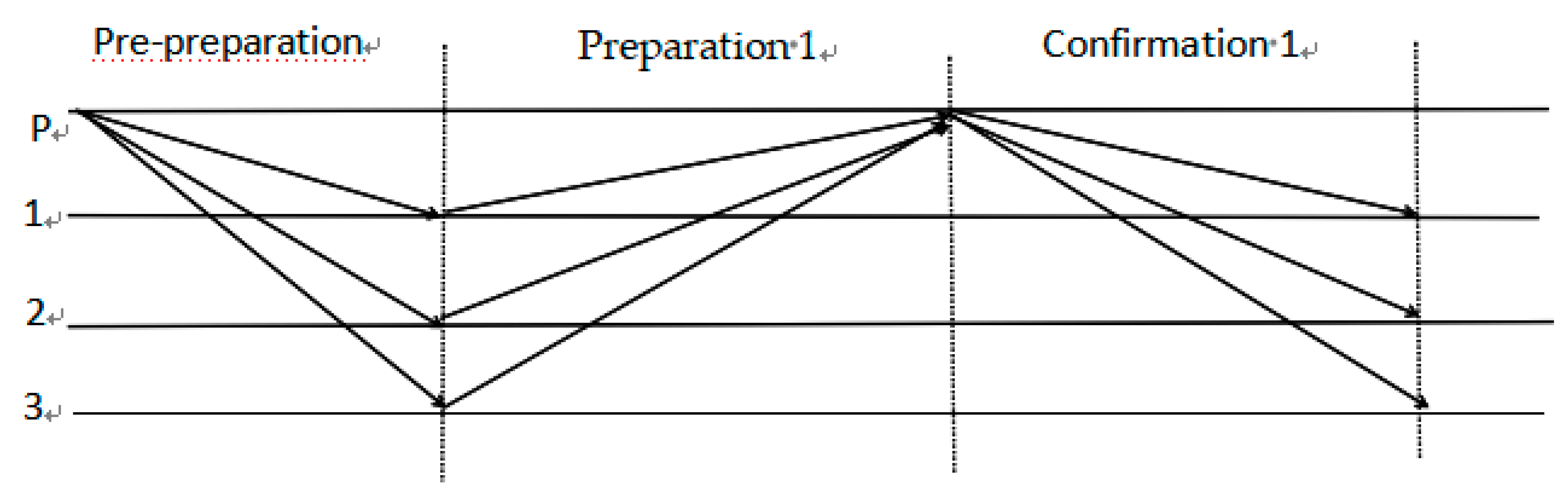
1, simplifying the acknowledgement phase to reduce node interactions in traditional PBFT algorithms, thus reducing the communication overhead in the consistency protocol, generating blocks as fast as possible, and the SP-PBFT algorithm in the optimistic mode, as shown in
Figure 1.
1) Pre-preparation: the master node sends <<Pre-prepare,v,h,H(B),P>,B> message to all the backup nodes and the backup nodes receive the provided Pre-prepare message.
2) Preparation 1: The backup node i returns the <<Prepare-1,v,h,H(B),i>,Votet(Bh,i)> message to the master node after receiving the Prepare message, and the master node receives the provided Prepare-1 message.
3) Confirmation 1: If the master node receives 2f+1 consistent Prepare-1 messages from different backup nodes, i.e., the master node has 2f+1 (possibly including its own) affirmative votes on block Bh, it can immediately synchronize block Bh and broadcast the message <<Commit-1,v,h,H(B),p>,Cert(Bh)>> to all the backup nodes, and if the backup node receives the Commit-1 message before t1, it can synchronize block Bh, and the backup node receives the provided Commit-1 message.
2.3.2. Pessimistic Mode
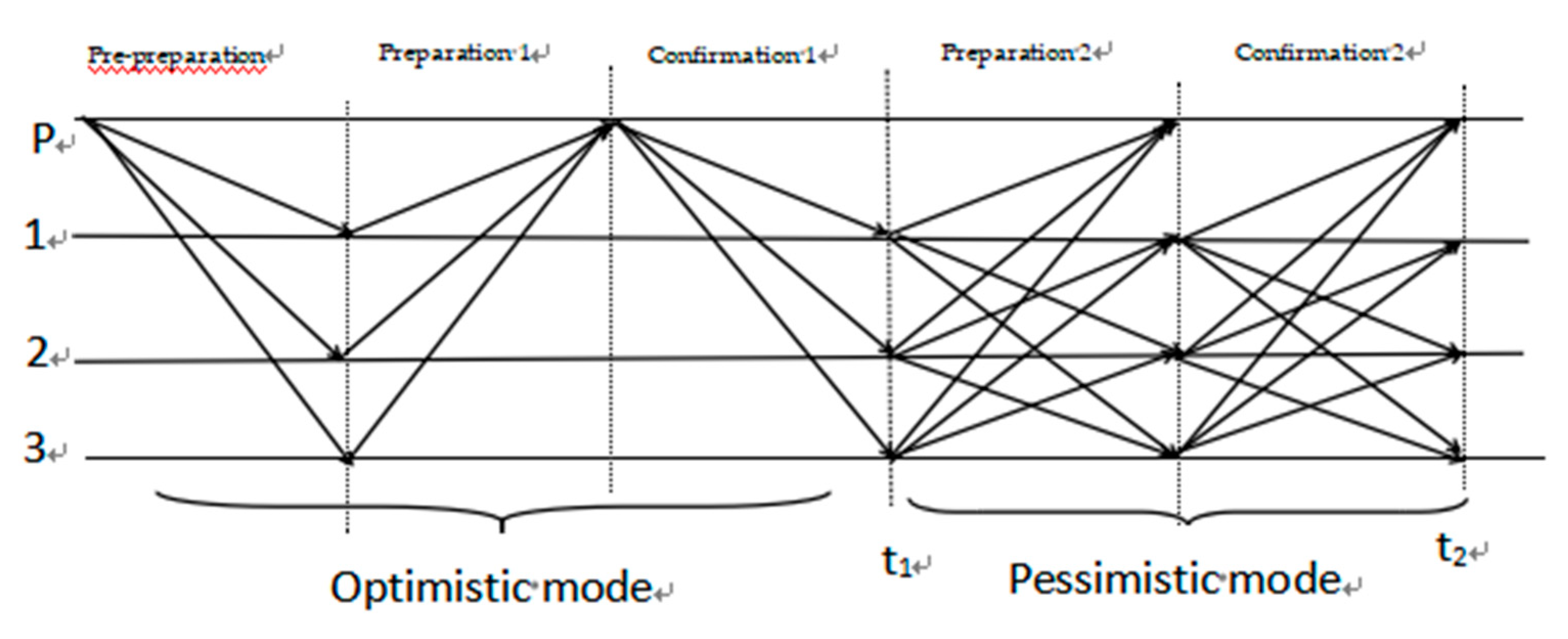
In the optimistic mode the consensus timeout is transferred to the pessimistic mode, the worst case scenario is that while guaranteeing security, f out of 3f+1 nodes are malicious nodes and refuse to generate blocks, the SP-PBFT algorithm still outperforms the PBFT algorithm in the pessimistic mode, adding an additional confirmation phase to enable the system to succeed in the consensus, and at the same time, adding the node evaluation mechanism, which reduces the possibility of the malicious node to become the master node again, and effectively reduces view switching, so that the consensus efficiency is improved, and the consensus process is patched up, as shown in
Figure 2.
4) Preparation 2: If backup node i does not receive a Commit-1 message before t1, it broadcasts a <<Prepare-2,v,h,H(B),i>,Votet(Bh,i)> message to all other consensus nodes, which receive the provided Prepare-2 message.
5) Confirm 2: If backup node i receives a Prepare-2 message and a Commit-1 message, it broadcasts a <<Commit-2,v,h,H(B),i>,Cert(Bh)> message to all other backups, otherwise it waits until it receives at least 2f+1 (possibly including its own) consistent Prepare-2 messages, then broadcasts a << Commit-2,v,h,H(B),i>,VoteSet(Bh,i)> message to all other consensus nodes, and if the backup receives a Commit-2 message containing the block certificate or receives at least 2f+1 consistent Commit-2 messages containing the vote set prior to t2, they can synchronize the block Bh, and the backup node receives the provided Commit-2 message.
The SP-PBFT consensus algorithm is designed with the background of consortium blockchain. In the consortium blockchain, most of the nodes are honest, so the SP-PBFT algorithm will generally execute the optimization PBFT protocol in optimistic mode. When a Byzantine node appears in the master node and executes the optimized consensus protocol, this node re-enters the node evaluation mechanism and its score is reduced. The node with high reputation value in a certain range is regarded as the new consensus node, which ensures the honesty of the consensus node and reduces the attack of malicious nodes. The SP-PBFT algorithm will continue to execute the optimized consistency protocol to complete the next consensus operation.
2.4. Node Evaluation Mechanism
In order to improve the efficiency of the system, it is necessary to reduce the number of view replacement of the master node, so that non-malicious and safe nodes are selected as the master node. The SP-PBFT algorithm applies the node evaluation mechanism, and divides the nodes into two types based on the reputation value. One type is called consensus node, whose function is to participate in the consensus process, and its number is N-f. The other part is the candidate nodes, whose number is f, which do not participate in the consensus process but react to the consensus result. In the SP-PBFT algorithm, each node maintains a node evaluation mechanism, and selects the master node according to the evaluation. A high reputation value of a node means that the node is credible and performs well in the consensus process. In the initial condition, the SP-PBFT algorithm will find the random number, and the time for the node to find the random number, the broadcast degree, the transaction degree and the calculated trust score can be used as the indicators of the node evaluation mechanism. The pseudo-code for the initialization of the node reputation value is as follows (Algorithm 1), where the threshold of the consensus node reputation value is C, and the consensus number is times.
|
Algorithm 1 Node Reputation Value Initialization |
Input: rTime , aReport , aTrade , Credit , C, times , R , S;
1: Begin
2: set R = {Ri| 0≤i≤|R|-1}
3: for Ri ∈R
4: Ri. rTime =0;
5: Ri. aReport =0;
6: Ri. aTrade =0;
7: Ri. Credit =0;
8: Value= aReport + aTrade + Credit - rTime;
9: end for
10: set S = {Si| 0≤i≤|S|-1}
11: for Si∈S
12: Si. rTime=0;
13: Si. aReport=0;
14: Si. aTrade=0;
15: Si. Credit =0;
16: Value= aReport + aTrade +Credit- rTime;
17: end for
18: set C=0;
19: set times=0;
20: end
Output :R ,S, Value ,V, times; |
Definition 1. Finding a random number time. Each node searches for the random number based on the SHA256 hash function [32], and the time of searching for the random number is positively correlated with the computing power of the node. The higher the computing power of the node, the faster it searches for the random number. When a node finds a random number, it can broadcast it to the whole network. In order to reduce the difficulty and improve the efficiency, it takes the last four digits of the hash value of the previous block as the next random number, and takes the time of finding the random number as an important indicator of the node evaluation mechanism, rtime is the ratio of the time it takes for a node to find a random number to the time it takes for the last node to find a random number.
Definition 2. Broadcast degree and transaction degree of a node. After a node completes a transaction, it will broadcast to the whole network. After completing a consensus round, it will record the number of node broadcasts, the number of transactions involved, the total number of broadcasts and the total number of transactions in this consensus. In the consensus process, the broadcast degree of a node is represented by the ratio of the number of broadcasts that the node participates in to the total number of broadcasts, which is denoted as aReport. Similarly, the transaction degree of a node is represented by the ratio of the number of transactions involved in the node to the total number of transactions, which is denoted as aTrade.
Definition 3. Node trust score. In this paper, the regression model logistic is used as the calculation method of trust score. The historical behavior of nodes can be used as the judgment index, the voting reputation value and accounting reputation value can be used as parameters, and the dynamic calculation of trust value (Credit) of nodes can be performed according to the logistic regression function. The formula is as follows.
where, vCredit , bCredit denote the voting reputation function and accounting reputation function, respectively, thus defining the voting reputation value and accounting reputation value.
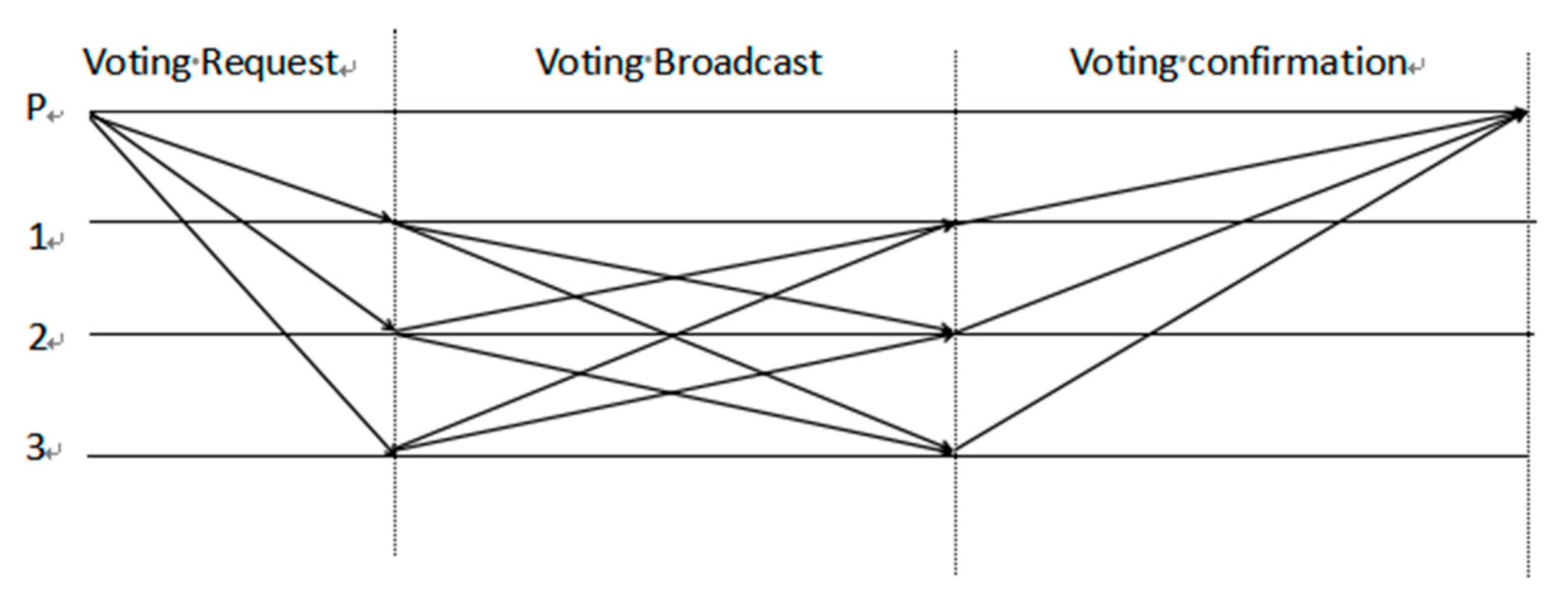
Definition 4. The voting reputation function. In the Byzantine fault tolerance algorithm (PBFT), the number of Byzantine nodes cannot exceed 1/3 of the total number of nodes, and consensus can be successful only when the number of normal nodes is greater than 2/3. In order to make as many nodes as possible participate in the voting, the more nodes participate in the voting, the more nodes are set to increase the reputation value of nodes, and the voting reputation function is as follows.
In the voting reputation function, suppose the number of voting nodes is g, the total number of nodes is n, the consensus round is k, the number of nodes voting i round is X
i, before electing the accounting node, multiple votes can be conducted in the group, the number of nodes not voting in the i round is Y
i, and the voting flow chart of the SP-PBFT algorithm is shown in
Figure 3.
Definition 5. Accounting reputation function. In order to avoid malicious nodes from participating in the consensus, the bookkeeping reputation function is defined, and the historical behavior of whether the bookkeeping is successful is recorded into the next round of the bookkeeping reputation value, as the evaluation index of the bookkeeping reputation function, the bookkeeping reputation function is as follows.
In the accounting reputation function, only one block is generated in each round of consensus, so the accounting reputation value of the non-accounting node is set to be 1, if the node is successful in accounting, m value is 1, if the accounting node is not successful in accounting, m value is 0, and the block time in the ith round of consensus is Ti-1(min).
Definition 6. Node evaluation mechanism. Nodes can find the random number through SHA256 hash function, broadcast and record, and calculate the node reputation value (Value) through the four coefficients of rTime, aReport, aTrade and Credit, the formula for Value is as follows.
When the master node fails, the reputation value of the punishment mechanism will be greatly reduced, and it is difficult to become the master node again for a period of time. Each node saves the block generated by the reputation value of the node evaluation mechanism to the end of the blockchain, and each node broadcast the result of the node evaluation mechanism.
The pseudo-code for selecting consensus nodes based on their reputation values is as follows (Algorithm 2):
|
Algorithm 2 Consensus Node Selection |
Input: rTime , aReport ,aTrade , Credit , C , times , R , S ;
1: Begin
2: for Ri∈R
3: Value= aReport + aTrade + Credit – rTime ;
4: end for
5: if(Ri.Value<C)||(Ri==S&&Ri∉R)
// Determine whether the reputation value of Ri node exceeds the consensus node reputation value threshold
6: set temp=Ri;
7: set Ri=S.max;
8: S.max =temp;
9: times=times+1;
10: for S.max∈S
// Place the eliminated consensus nodes in the candidate node set and sort them by reputation value
11: if(S[i]<S[i-1])
12: S [0] =S[i];
13: for ( j=i-1 ; S [0]<S[j];--j)
14: S[j+1] =S[j];
15: S[j+1] =S [0];
16: end for
17: end if
18: end for
19: end if
20: end
Output: R , S , Value , times; |
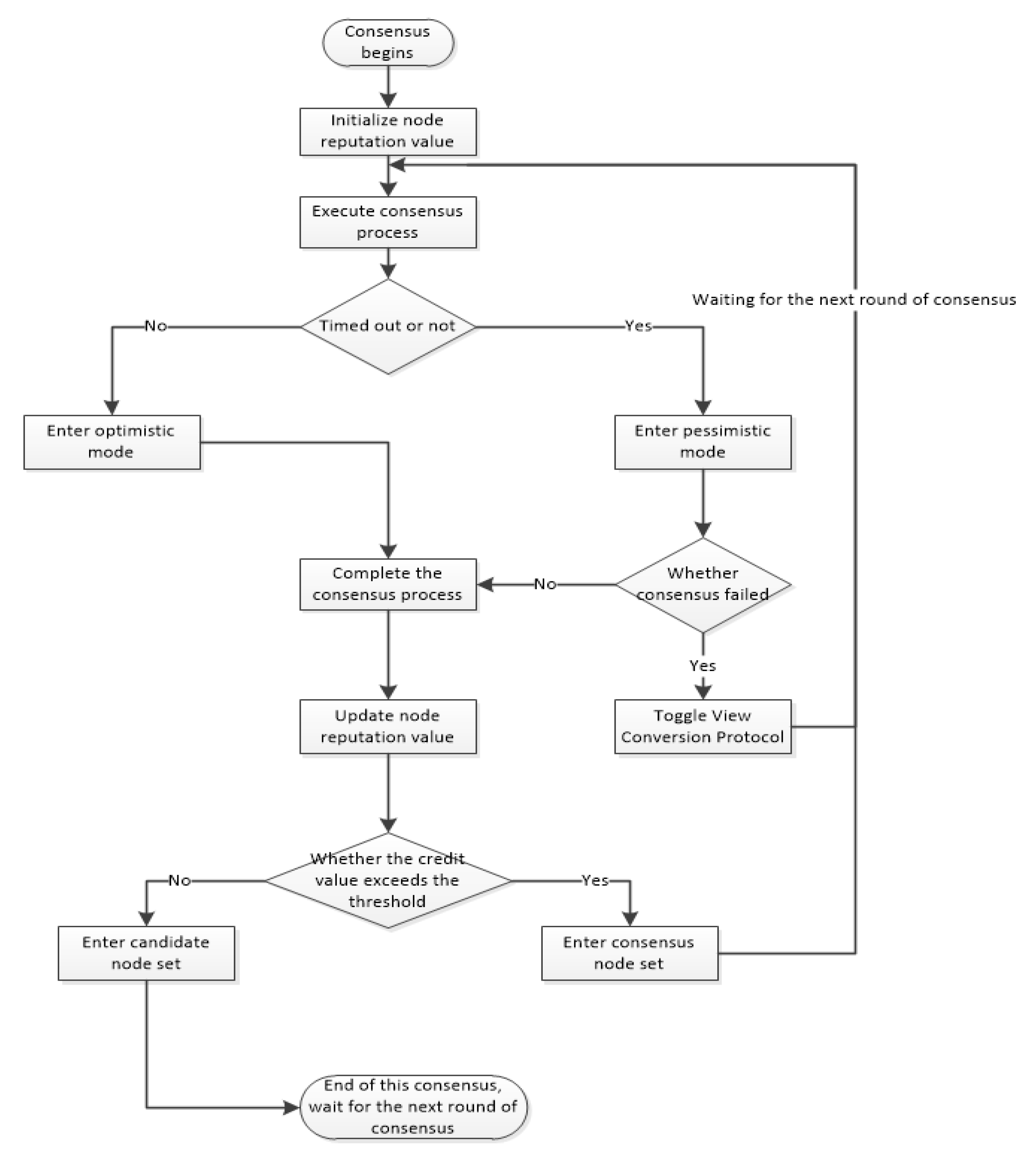
The flow chart of the SP-PBFT algorithm is shown in
Figure 4.
2.5. Fibonacci Grouping
2.5.1. Consensus Node Selection
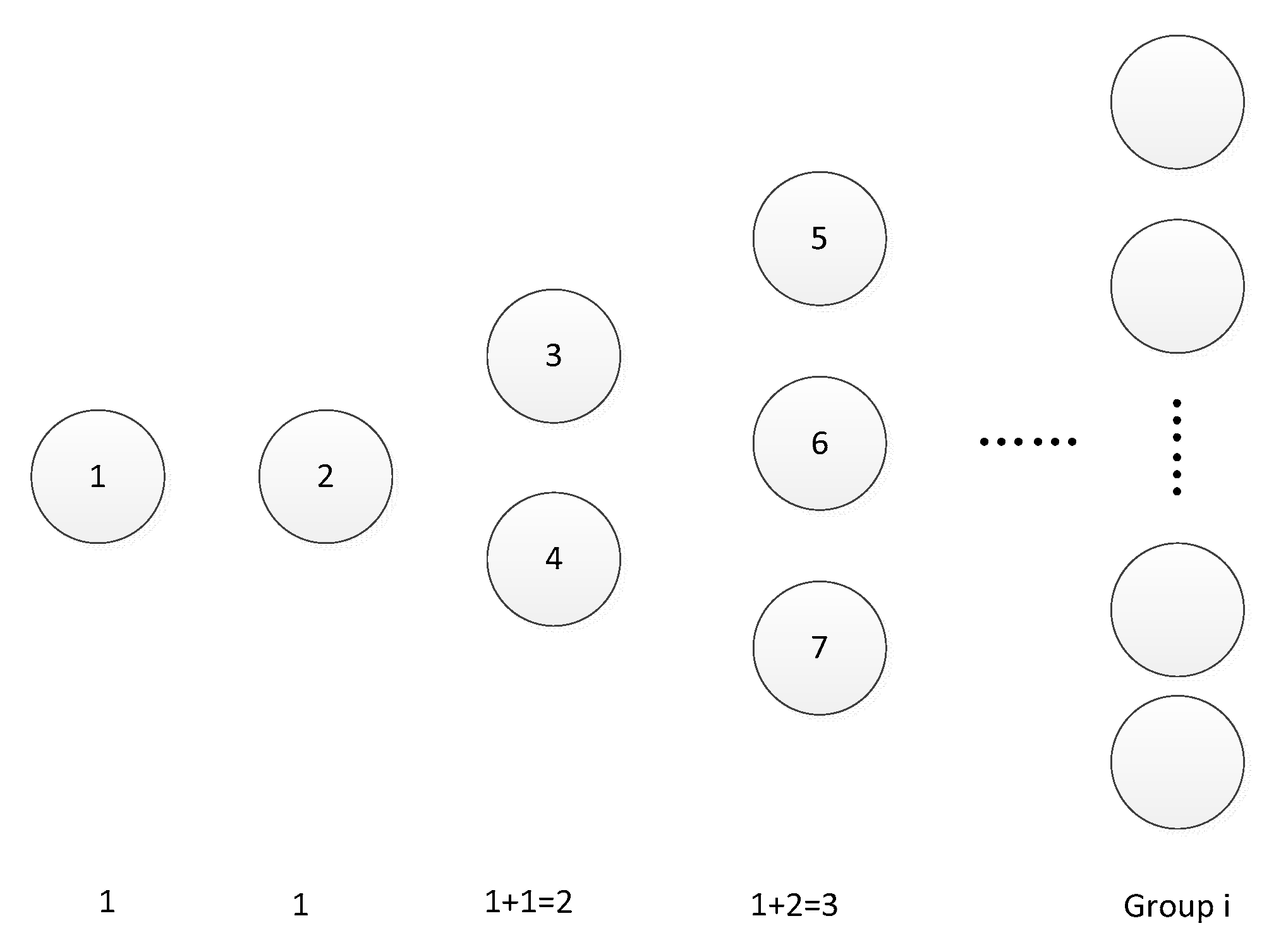
In the SP-PBFT consensus algorithm, the total number of nodes is set to N, the threshold of the reputation value of the consensus node is set to C, and the Fibonacci function is used to group the nodes whose reputation value is greater than or equal to C in order of large to small. The node with the first reputation value is placed in the first group, and the nodes with the second and third reputation value are placed in the second group. According to this order, the nodes are grouped according to their reputation values, and the group number is denoted by Gi, where Gi∈{G1, G2,G3,⋯,GK} means that all nodes exceeding the threshold are divided into k groups, and this node is divided into the ith group. The expression for the Fibonacci function is as follows:
To prevent the problem of fixed consensus nodes and serious centralization of the consensus process caused by the accumulation of reputation values, it is proposed to avoid selecting consensus nodes in the same group, and take the first half of nodes with high reputation values in each group as the consensus nodes of the system, which can improve the enthusiasm of each node to participate in the consensus process, ensure the fairness of the consensus and prevent malicious nodes from attacking nodes with high reputation values. Fibonacci node structure diagram, as shown in
Figure 5.
2.5.2. Master Node Selection
View switching means that if the master node is a Byzantine node and fails to send a consensus request message or the request timeout within the specified time, the remaining slave nodes can issue a request to replace the view, overthrow the master node, and re-select the trusted master node to participate. If the master node is found to be overturned, the new view will be switched again, and the blocks that have completed the consensus in the previous stage will be discarded. After the new master node is elected, the blocks that have been discarded in the previous stage will reach consensus again. When a new view starts, the global node will be synchronized and checked in time to ensure the integrity and consistency of the data, and wait for the next round of consensus. The selection of the view switching master node of the traditional PBFT algorithm is determined according to equation (1).
In this formula, the master node number p for new elections, v for the view number, |R| for the number of the nodes in copy right now is to use the polling way switch traditional view the consistency of the agreement, there is a big probability random way which make malicious nodes into a master node, have a certain risk. In order to solve this problem, this paper uses Fibonacci function to group the nodes, and the nodes in each group vote with each other, in which the weight of the vote is positively correlated with the Value value. The master node starts from the first group of nodes, and the node generated by the second group of voting will be selected if the selection fails, and so on. Because the Fibonacci grouping is implemented according to the order of reputation value from high to low, the node with high reputation value is in the front of the group and has the priority to serve as the master node, which improves the security and stability of the system. This process can quickly select the master node to prevent the slow selection of the master node from causing system delay and stagnation.
3. Analysis of Theoretical and Experimental Results
3.1. Theoretical Analysis
3.1.1. Security Analysis
The traditional PBFT algorithm selects the master node by polling, and there is a certain probability that the Byzantine node will be selected. Once the view switching protocol is triggered, the consensus process will be delayed, and the next master node still selects the master node in this way, the risk does not decrease. The SP-PBFT algorithm proposed in this paper adopts the node evaluation mechanism, calculates the reputation value of each node according to its historical performance, and sorts and groups the nodes according to the reputation value, so that the node with higher reputation value has a high probability to become the master node. The SP-PBFT algorithm is different from the ordinary improved algorithm that only adds the reward and punishment mechanism. After Fibonacci the grouping, the SP-PBFT algorithm only selects half of the nodes with high reputation value in each group, not completely in order of reputation value, to prevent malicious nodes from attacking nodes with high reputation value and cause consensus failure, and improve the security of the consensus process.
3.1.2. Consensus Efficiency Analysis
The traditional PBFT algorithm has a three-stage communication process, and requires all nodes to participate in the consensus process. The nodes interact with each other in pairs, which makes the consensus efficiency low and consumes a lot of resources. The proposed SP-PBFT algorithm improves the consensus efficiency from the following three aspects:
- (1)
The consensus protocol is optimized by using the idea of speculation. When the system has no delay, only the optimistic mode is executed to reduce the communication complexity.
- (2)
Secondly, a node evaluation mechanism is proposed to calculate the reputation value according to the historical behavior of the node, so that the consensus nodes are well-behaved nodes and the probability of view switching is reduced.
- (3)
The Fibonacci group consensus is proposed, and only half of the nodes in each group are selected to participate in the consensus, which reduces the number of nodes participating in the consensus and fundamentally improves the efficiency of consensus.
3.2. Analysis of Experimental Results
3.2.1. Experimental Environment
This experiment uses Docker container simulation multiple nodes to compare the traditional PBFT algorithm and its improved algorithm, and analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of the improved algorithm. The experimental environment is Ubuntu 18.04 operating system, 16GB system memory, CPU is an Intel Core i7 processor, Docker container engine. According to the PBFT consensus algorithm, if there are f Byzantine node, the total number of nodes is not less than 3f+1, From the four aspects of throughput, delay, Fault Tolerance and communication complexity, the PBFT algorithm, PBFT consensus algorithm based on Trust evaluation model in literature [
24] (trust-based Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance ,T-PBFT), an improved PBFT algorithm (Random Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance, RPBFT) algorithm based on random selection of master nodes in reference [
21], and the SP-PBFT algorithm of this paper are compared. The performance of the four algorithms is analyzed by the experimental results.
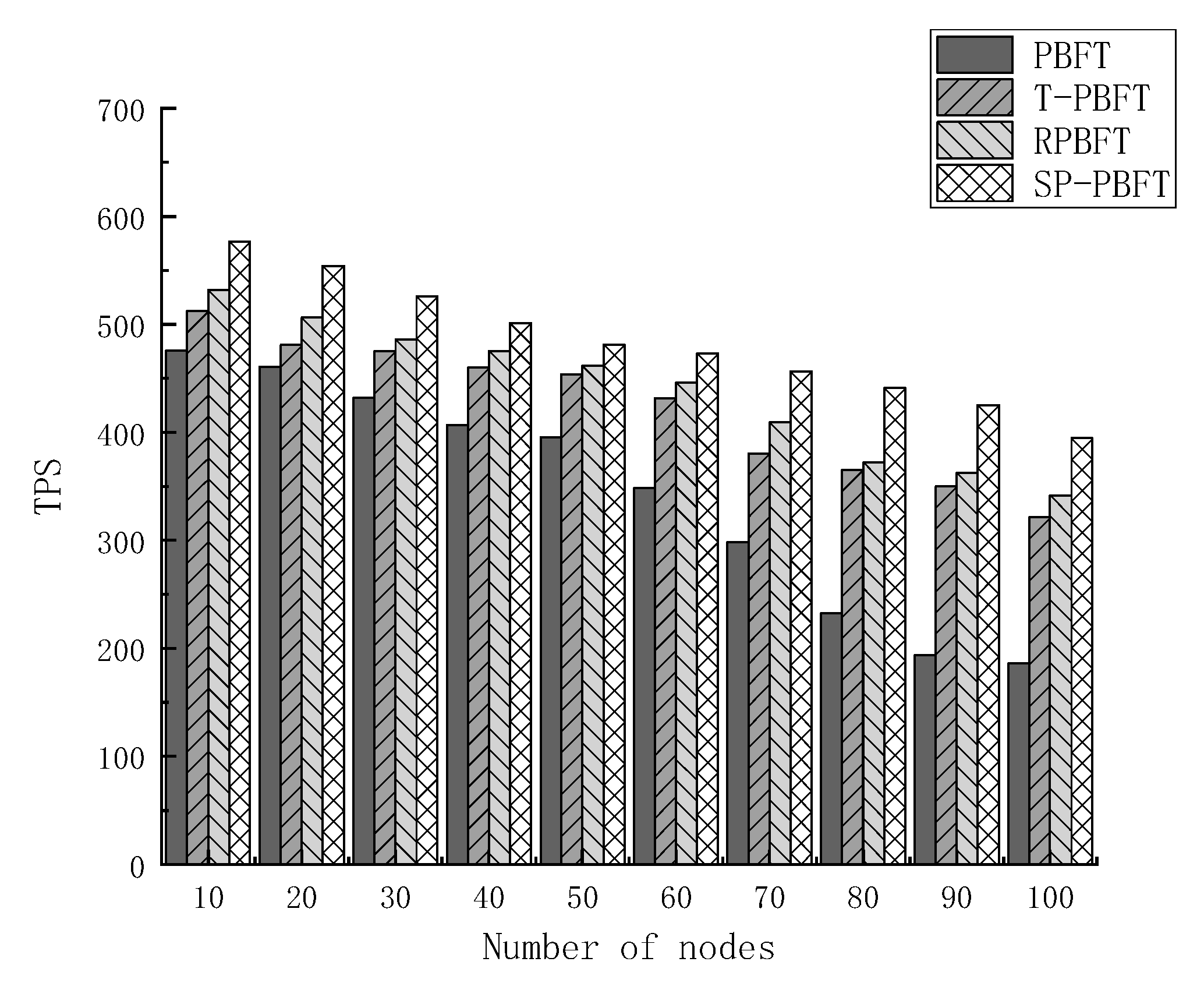
3.2.2. Throughput
Throughput is defined as the number of transactions that the system processes a request in unit time. The higher the throughput, the more the number of transactions will be processed. Set the four consensus algorithms PBFT, T-PBFT, RPBFT and SP-PBFT to complete the same number of transactions in 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 and 100 nodes respectively, and the number of transactions completed per second will be calculated. TPS (Transaction Per Second) represents the system throughput, and the calculation formula is given in (2).
where
represents the time from the transaction information is issued to the completion of block storage, namely block generation time, and
represents the number of transactions completed in each block within the time interval of block generation. The throughput of the system is also related to the network environment and the block size. The larger the block is, the more transactions it can carry, and the corresponding network load will increase. The number of transactions in one second with different number of nodes is counted and all the results are averaged, and the final result is shown in
Figure 6 below.
By analyzing the experimental results and comparing the four algorithms, the throughput of the four algorithms decreases with the increase of the number of nodes, but the throughput of the SP-PBFT algorithm is higher than that of the other three algorithms. Because the traditional PBFT algorithm requires all nodes to participate in the consensus process, the throughput shows a low trend. The RPBFT algorithm only changed the consensus process and relatively optimized the consensus protocol. Although the T-PBFT algorithm groups consensus, it does not reduce the number of nodes participating in the consensus process and the efficiency of the optimized consensus protocol is not as high as that of the SP-PBFT algorithm. After testing, the improved SP-PBFT algorithm has a significant improvement in throughput.
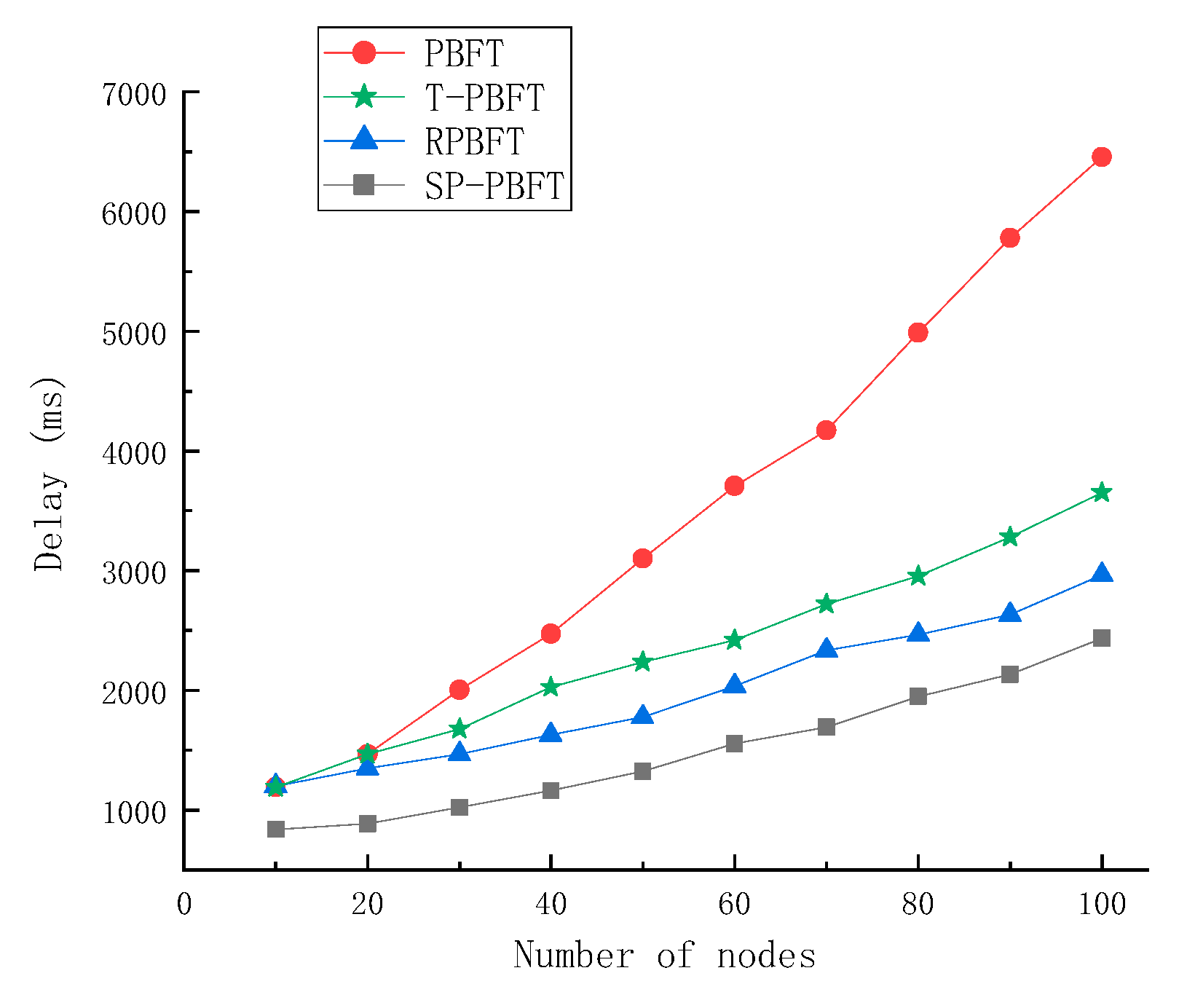
3.2.3. Time Delay Analysis
The throughput of the blockchain is mainly affected by the delay. Under the premise of consistent other aspects, the smaller the delay, the higher the throughput of the blockchain system. In addition, the lower the delay can also improve the speed of blockchain consensus confirmation and the efficiency of the system consensus. Set PBFT,T-PBFT,RPBFT and SP-PBFT four consensus algorithms to complete the same number of transactions in 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 and 100 nodes respectively, and calculate the average delay of the transaction. In this paper, the delay is defined as the time it takes for a block to complete the consensus, as shown in Equation (3).
T
C represents the time of consensus confirmation completion, T
R represents the time of consensus request, and takes the average value of multiple tests using the Caliper tool, and the results are shown in
Figure 7 below.
By analyzing the experimental results and comparing the four algorithms, the more the number of participating nodes, the longer the delay time. At the beginning, the difference between the four algorithms is not big when the number of nodes is small, but the difference is obvious when the number of nodes increases. The traditional PBFT algorithm requires all nodes to participate in the consensus, so the delay is long. The RPBFT algorithm optimized the consensus protocol to reduce the communication complexity and shorten the delay time. Although T-PBFT grouping consensus does not reduce the number of consensus nodes, and the number of broadcasts is still large, the delay time is only slightly improved. The SP-PBFT algorithm has a good improvement in both the consensus protocol and the number of consensus nodes. After testing, the delay of the improved SP-PBFT algorithm is lower than the other three algorithms, which is more stable in delay and has higher consensus efficiency.
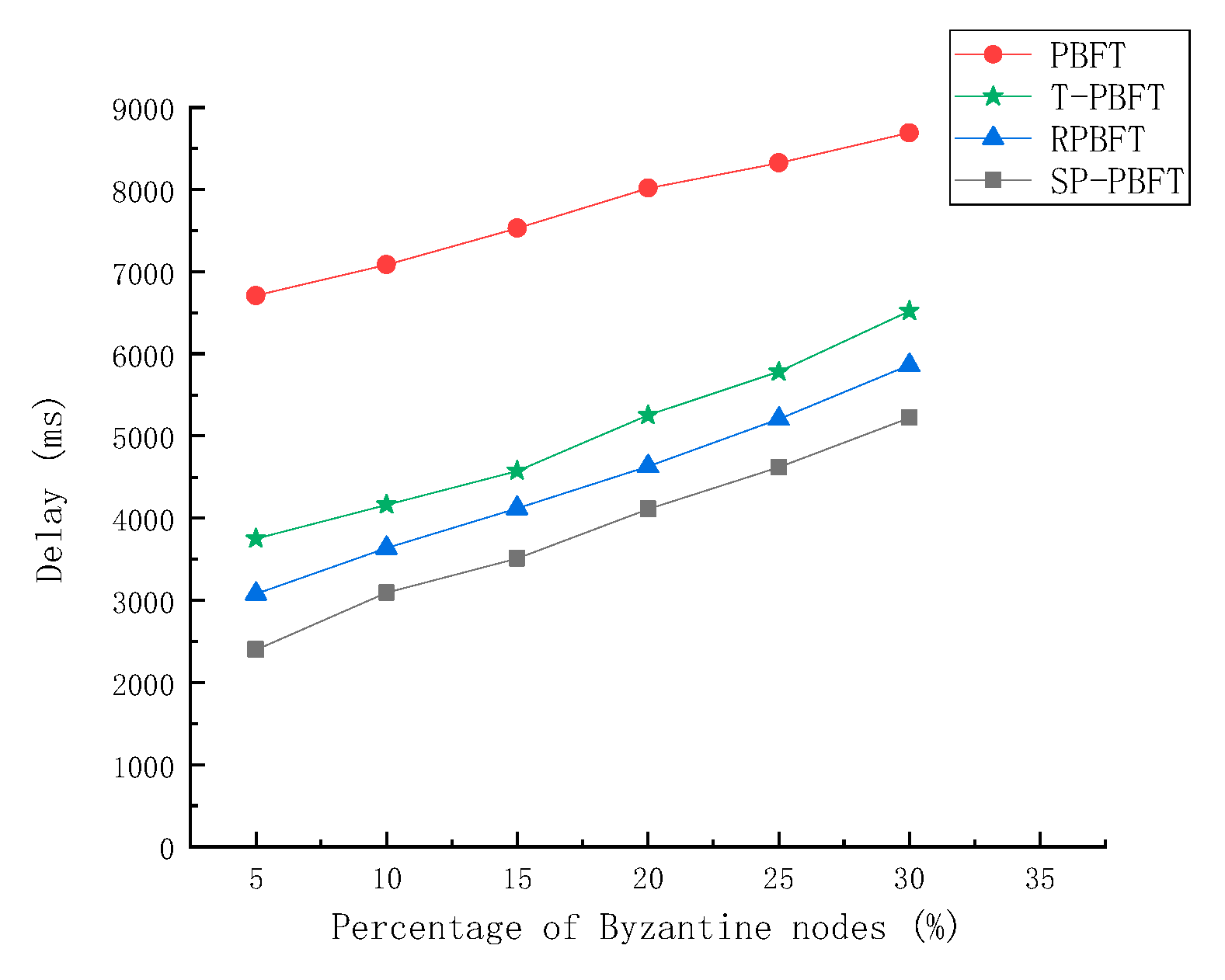
3.2.4. Fault Tolerance
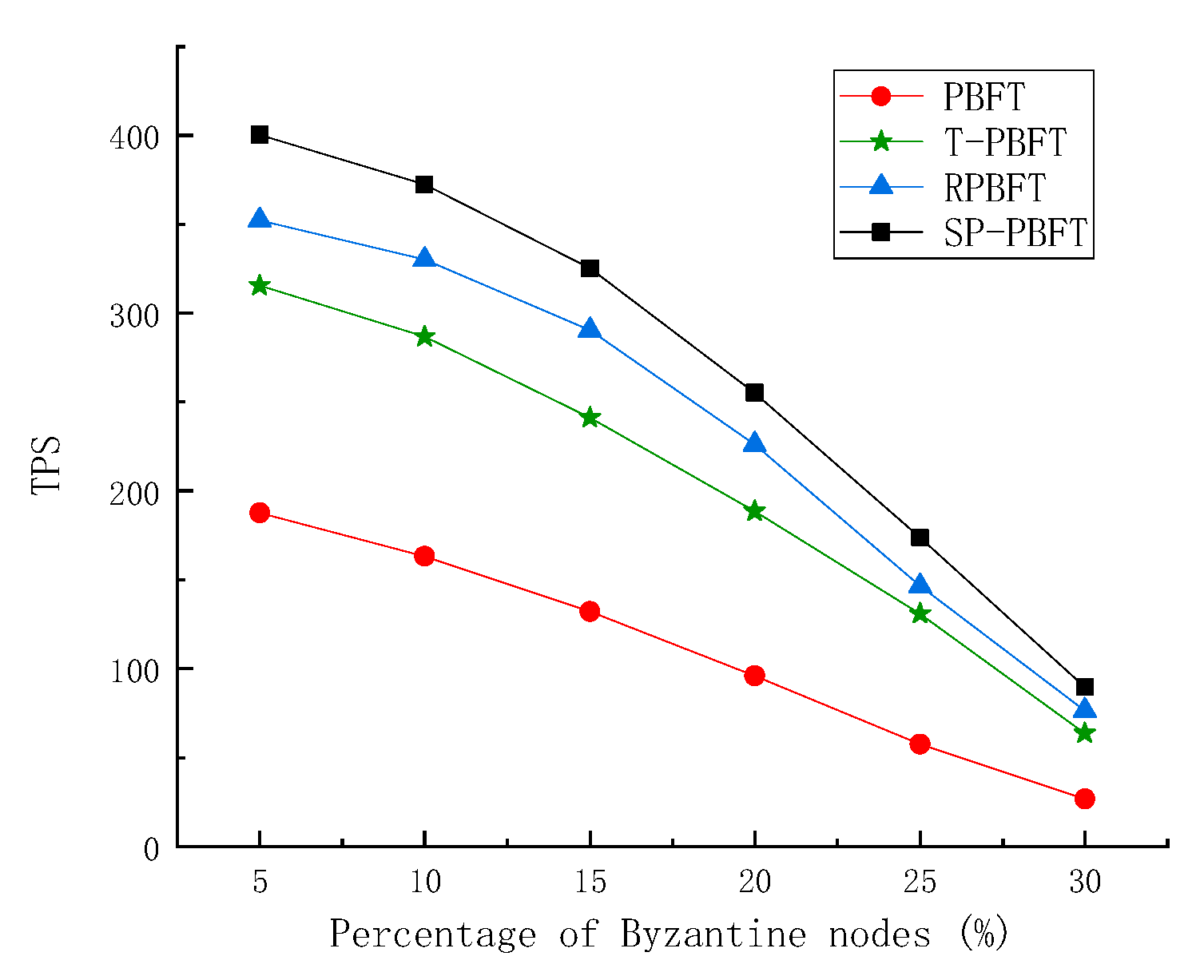
Byzantine fault tolerance is a fault tolerance ability of the distributed network, that is, in the case of malicious nodes, honest nodes can still reach consensus. Byzantine nodes are added to the experiment to test the fault tolerance of the consensus algorithm. The proportion of Byzantine nodes is set to 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, and the total number of nodes is 100. Comparing the delay and throughput of PBFT algorithm, T-PBFT algorithm, RPBFT algorithm and SP-PBFT algorithm with different number of Byzantine nodes to complete the same number of transactions, the results are shown in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9 below.
The experimental results show that the four algorithms have certain fault tolerance. When the number of Byzantine nodes is 33, it does not exceed 1/3 of the number of nodes, and blocks can be normally generated. But when the number of Byzantine nodes is 34, it exceeds 1/3 of the number of nodes, so the block cannot be successfully generated . It can be seen from
Figure 8 that the delay of the four algorithms becomes longer with the increase of the number of Byzantine nodes, but the delay of the SP-PBFT algorithm is lower than that of the other three algorithms. It can be seen in
Figure 9 that the throughput of the algorithm is lower when the number of Byzantine nodes is larger, but the throughput of the SP-PBFT algorithm is always higher than that of the other three algorithms, so the SP-PBFT algorithm is better.
3.2.5. Communication Complexity
The communication complexity of the consensus algorithm represents the interaction of each node in the system to complete the consensus process, which can also be called the number of broadcasts. The higher the communication complexity, the lower the efficiency of the consensus and the greater the consumption of resources. In the pre-preparation process of traditional PBFT algorithm, the master node broadcasts the pre-preparation message to all nodes except itself, and the number of communication is N-1. In the preparation process, the received message was verified and the preparation message was sent, and the number of communication in this process was (N-1)2. Entering the confirmation phase, the verification prepares the message and sends the confirmation message to all nodes, and the number of communications is N(N-1). Combining the above three processes is the number of messages sent by the traditional PBFT algorithm, N-1+(N-1)2+N(N-1)=2N2-2N messages are sent, and the communication complexity is O(n2).
In the SP-PBFT algorithm of this paper, the number of messages sent in the pre-preparation, preparation and acknowledgement phases in optimistic mode is N-1, that is, in the whole process of optimistic mode, N-1+N-1+N-1=3N-3 messages are sent, and the communication complexity is O(n). In the pessimistic mode, the number of messages sent in the preparation phase 2 and the confirmation phase 2 in the optimistic mode are both (N-1)2, and a total of 3N-3+2(N-1)2=2N2-N-1 messages are sent. The communication complexity is O(n2), which is consistent with the traditional PBFT algorithm, but after the screening of the node evaluation mechanism, most of them enter the optimistic mode to complete the consensus, and no longer go through the consensus process of the pessimistic mode. It can be seen that the communication complexity of the improved SP-PBFT algorithm is reduced, the application scope of the algorithm is also wider, and the consensus efficiency is higher, which is optimized.
3.3. Comparison of Related Consensus Algorithms
As shown in
Table 2, the comparison of traditional PBFT algorithms, T-PBFT algorithms, RPBFT algorithms and SP-PBFT algorithms.
It can be seen that the SP-PBFT algorithm has the following advantages over other consensus algorithms.
(1) The SP-PBFT algorithm adds a node evaluation mechanism, which gives rewards or punishments according to the historical behavior of nodes, and increases the security of the consensus process.
(2) The SP-PBFT algorithm can identify Byzantine nodes, reduce the possibility of these Byzantine nodes participating in the consensus process, and increase the robustness of the system, so as to optimize the view switching protocol and improve the speed of consensus.
(3) The SP-PBFT algorithm reduces the communication overhead in the network, adopts the speculative method to optimize the consensus protocol, and the communication complexity required to reach consensus in the optimistic mode is reduced from O(n2) to O(n).
(4) The SP-PBFT algorithm proposes Fibonacci grouping, and combines it with the reputation value in the node evaluation mechanism to select the master node and consensus node, which reduces the number of nodes participating in the consensus and fundamentally improves the efficiency of consensus.
4. Conclusions and Outlook
This paper proposes SP-PBFT consensus algorithms that take a speculative approach depending on the network environment of the system and apply different steps to reach consensus for different network environments. In optimistic mode, the network is secure and stable, the confirmation phase is simplified, and the communication overhead is reduced to reach consensus quickly. When the consensus timeout detects that the system is unsafe, that is, there may be malicious node attacks, the pessimistic mode is triggered, and a new confirmation phase is added to resist malicious node attacks. The node evaluation mechanism is introduced to reward or punish nodes according to their historical behavior, so that the system has the ability to identify Byzantine nodes, the security is guaranteed, and the view switching protocol is optimized. At the same time, Fibonacci function is used to group nodes, and the appropriate master node and consensus node are selected by combining with the reputation value in the node evaluation mechanism, which reduces the number of consensus nodes and fundamentally ensures the efficiency of consensus. The experimental results show that the SP-PBFT algorithm is superior to the traditional PBFT algorithm and its improved algorithm in throughput, delay, fault tolerance and communication complexity. In the case of honest master node and stable network, the advantages of the SP-PBFT algorithm are more obvious. Therefore, the SP-PBFT algorithm is suitable for consortium chains with stable network and more trusted nodes. This algorithm still has some shortcomings. For example, in the case of unstable network and more malicious nodes, the consensus efficiency of pessimistic mode needs to be further improved. The next work focuses on optimizing the pessimistic mode, and discusses how to quickly reach a consensus in the face of many malicious nodes and maximize the consensus efficiency without affecting security and dynamism.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.S. and X.L.; methodology, X.S.; software, X.L.; validation, X.S., and X.L.; formal analysis, X.S.; investigation, X.S.; resources, X.L.; data curation, X.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, X.L.; visualization, X.S.; supervision, X.S.; project administration, X.S.; funding acquisition, X.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 62173171
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the finding of this study are included within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editors and the reviewers for their valuable time and constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yao Shuang, Zhang Dawei, Li Yong, Wang Wei. Overview of research on privacy protection technology of blockchain transaction content. Journal of Cryptography, 2022,9 (04): 596-618.
- Xiao Yao, Feng Yong, Li Yingna, etc. Blockchain transaction data privacy protection scheme based on Homomorphic encryption. Journal of Cryptography, 2022,9 (06): 1053-1066.
- Han Yufang. Research on the Application of Computer Software Technology in the Big data Era. Electronic Technology and Software Engineering, 2023, No.244 (02): 47-51. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Yuchao. Application of Computer Network and Cloud Computing Technology. Integrated Circuit Application, 2023,40 (02): 44-46.
- Guo Xiaoyu, Liu Weibin, Qian Yu. China's Artificial Intelligence Industry and State of the art. Quality and Certification, 2023, No.198 (04): 46-48.
- Jin Shixiong, Zhang Xiaodan, Ge Jingguo, et al. A Review of Blockchain Consensus Algorithms. Journal of Information Security, 2021,6 (02): 85-100.
- Lamport, L. Time, Clocks, and the Ordering of Events in a Distributed System. Communications of the ACM, 1978, 21(7): 558-565. [CrossRef]
- Lamport, L. The Part-time Parliament. ACM Transactions on Computer Systems, 1998, 16(2): 133-169. [CrossRef]
- Pires M, Ravi S, Rodrigues R. Generalized Paxos Made Byzantine (and less Complex). Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 203-218. [CrossRef]
- Kafka official website. https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/. Jan. 2019. [28] Ongaro D, Ousterhout J. K. In search of an understandable consensus algorithm. The usenix annual technical conference, 2014: 305-320.
- Lamport L, Shostak R, Pease M. The Byzantine generals problem. ACM Trans on Programming Languages and Systems, 1982,4 ( 3) : 382-401.
- Sukhwani H,Martínez J M,Chang Xiaolin,et al. Performance modeling of PBFT consensus process for permissioned blockchain network ( Hyperledger Fabric)/Proc of the 36th Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems. Piscataway,NJ: IEEE Press,2017: 253-255..
- Ongaro D, Ousterhout J. K. In search of an understandable consensus algorithm. The usenix annual technical conference, 2014: 305-320.
- Dwork C, Naor M. Pricing via Processing or Combatting Junk Mail[M]. Advances in Cryptology CRYPTO 92. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, : 139-147.
- Back, A. Hashcash - A Denial of Service Counter-Measure. http://www.hashcash.org/papers/hashcash.pdf. Jan. 2019.
- King, S. PPCoin: Peer-to-Peer Crypto-Currency with Proof-of Stake. https://peercoin.net/assets/paper/peercoin-paper.pdf. Nov. 2014.
- Tendermint: Consensus without mining. https://tendermint.com/ static/docs/tendermint.pdf. May. 2019. [38] Miller A, Xia Y, Croman K, et al. The Honey Badger of BFT Protocols.The 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 2016: 31-42.
- Miller A, Xia Y, Croman K, et al. The Honey Badger of BFT Protocols.The 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 2016: 31-42.
- Tangaroa: a byzantine fault tolerant raft. http://www.scs.stanford. edu/14aucs244b/labs/projects/copeland zhong.pdf. May. 2019.
- Zhu Xiaowu, Wei Wenshi. Consensus and Bifurcation of Blockchain: Analysis of the Impact of The DAO Case on Ethereum Bifurcation and Its Enlightenment. Management Review, 2021,33 (11): 324-340.
- Wang Sen, Li Zhihuai, Jia Zhipeng. Improved PBFT consensus algorithm for randomly selecting main nodes. Computer Application and Software, 2022, 39 (10): 299-306.
- Fang Yi, Deng Jianqiu, Jungle Tiger, etc. An improved PBFT blockchain consensus algorithm based on ring signature. Computer engineering, 2019, 45 (11): 32-36.
- Zhang Meng, Wang Baocheng. Improving Byzantine fault tolerance consensus algorithm based on recommended trust model. Computer Application Research, 2023,40 (03): 667-670.
- Ren Xiyu, Tong Xiangrong, Zhang Wei. PBFT consensus algorithm based on trust evaluation model. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2023,46 (01): 108-118.
- Qin Weijie. PBFT Consensus Algorithm Based on Node Partition Clustering. Information Technology and Informatization, 2023, No.274 (01): 65-69.
- Feng Liao, Ding Yan, Liu Kunlin, et al. Progress in Blockchain BFT Consensus Algorithm Research. Computer Science, 2022,49 (04): 329-339.
- Xiao Bingbing, Li Zheng, Li Xiaoruo, etc. Consensus algorithm based on the importance of Fibonacci grouping. Computer and Digital Engineering, 2021,49 (12): 2509-2513+2525.
- Zhao Lijin, Wang Xinsheng, Xia Chunzhong. Research on PBFT consensus mechanism based on trust model. Computer Application and Software, 2022, 39 (07): 304-309.
- Feng Xia, Cui Kaiping, Xie Qingqing, et al. A Distributed Anonymous Authentication Scheme Based on Blockchain in VANET. Journal of Communications, 2022,43 (09): 134-147.
- Wu Teng, Huang Kai, Zhou Linlin, etc. Research on blockchain consistency algorithm with state legitimacy verification. Computer engineering, 2018,44 (01): 160-164.
- FOX G. Peer-to-peer Networks. Computing in Science & Engineering, 2001, 3(3): 75-77.
- APPEL A W. Verification of a Cryptographic Primitive: SHA-256. Proceedings of the Society for Information and Biliology, 2015, 37(2):7.1-7.31.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).