1. Introduction
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells of the eye contain three types of pigment granules: melanosomes, lipofuscin granules, and melanolipofuscin granules. Melanosomes are specialized organelles of RPE cells containing a protein part and a eumelanin-type polymer. All melanosomes in RPE are formed right at the time of embryonic development and perform their functions throughout the life of an individual, while lipofuscin and melanolipofuscin granules are formed much later and accumulate in RPE cells as a function of age. Changes in the density of melanosomes and lipofuscin granules in RPE are considered to be hallmarks of aging or the development of various retinal diseases, including Stargardt’s disease and age-related macular degeneration [
1]. Melanosomes perform the function of screening photoreceptor cells from excessive illumination and the function of antioxidant protection of the cell from free-radical oxidation caused by irradiation and reactive oxygen species [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. With age, there is a significant decrease in the number of melanosomes in RPE cells. Whereas melanosomes occupy up to 8% of the RPE cell volume before the age 20 years, this volume gradually decreases to 3.5% between the ages of 40–90 years [
9,
10]. At the same time, the total concentration of melanin in the RPE cell decreases by 2.5 times [
10]. Simultaneously with age, the density of lipofuscin and melanolipofuscin granules increases in RPE [
9,
11]. A decrease in the density of melanosomes with age may be due to the fact that they conjugate with lipofuscin granules [
12,
13,
14,
15] or with partially degraded phagosomes [
16,
17,
18,
19]. This results in the formation mixed melanolipofuscin granules which, along-with lipofuscin granules, can occupy up to a third of the cytoplasmic space of RPE cells in people over 70 years old [
9]. However, this process alone cannot lead to a decrease in the total concentration of melanin in the RPE cell.
Melanin content has been suggested to decrease due to its photooxidative and/or oxidative degradation [
10,
20]. Oxidative degradation of RPE melanosomes leads, on the one hand, to a decrease in their antioxidant activity, and, on the other hand, to the appearance of prooxidant properties and an increase in photoreactivity [
7,
21,
22,
23,
24].
However, specific mechanisms of melanosome biodegradation in RPE cells are still not known. The most probable is the oxidative degradation of melanosomes as a result of their interaction with reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS, such as superoxide radicals and/or hydrogen peroxide, are known to cause degradation of the melanin polymer [
20,
25,
26,
27,
28] with the formation of water-soluble fluorescent products [
20,
29,
30,
31,
32]. In RPE cells of the eye, reactive oxygen species can arise from both normal metabolic processes and photoinduced oxidation. A well-known light-induced generator of reactive oxygen species in the RPE cell is lipofuscin bisretinoids, such as N-retinylidene-retinyl ethanolamine (A2E). When irradiated with visible light, especially in the blue range, lipofuscin granules from RPE cells reduce oxygen to superoxide radicals [
33,
34,
35,
36]. At the same time, the intensity of superoxide generation by lipofuscin should increase with age, since the number of lipofuscin granules increases sharply with aging.
We have previously shown that upon irradiation with blue light (450 nm; 4 mW/cm
2) of RPE melanosomes, fluorescent melanin degradation products are virtually not formed, whereas irradiation of a mixture of melanosomes and lipofuscin granules leads to the appearance of melanin degradation products [
20]. On this basis, it was suggested [
20] that age-related destruction of melanin by superoxide radicals occurs under the action of light in melanolipofuscin granules containing a source of superoxide radicals, lipofuscin. In this case, the age-related decrease in the concentration of melanin in the RPE cell would result from a decrease in the number of melanosomes due to their fusion with lipofuscin granules and the subsequent degradation of melanin already inside these complex granules. Therefore, due to the degradation of melanin, the specific gravity of melanolipofuscin granules will decrease, which will lead to the accumulation of mixed granules with small admixtures of melanin, which has not yet had time to be destroyed by superoxide radicals. This process will lead to a general decrease in the concentration of melanin in the RPE cell.
In the present study, we showed that blue light irradiation of melanolipofuscin granules from RPE cells of the human eye, in contrast to irradiation of lipofuscin granules and melanosomes, resulted in the accumulation of products of oxidative degradation of melanin caused by superoxide radicals. It has also been shown that the products of oxidative degradation of RPE melanosomes are photoinducible generators of superoxide and contain carbonyl compounds. We propose a scheme of oxidative degradation of melanin and lipofuscin inside melanolipofuscin granules under the action of light.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Spectral fluorescence studies of melanin oxidative degradation products
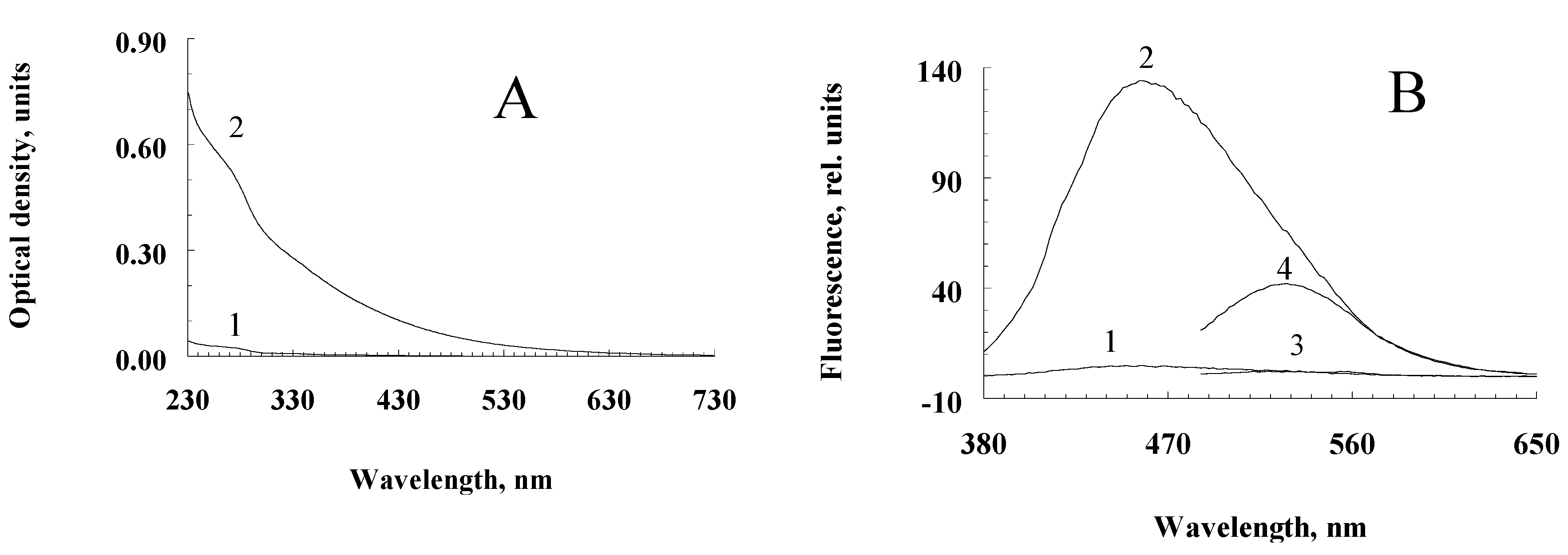
Incubation of a suspension of human RPE melanosomes with relatively low concentrations of potassium superoxide results in the accumulation of water-soluble products with relatively high absorption values in the short-wavelength region of the spectrum (less than 400 nm;
Figure 1A, curve 2). Water-soluble products obtained from intact, non-oxidized melanosomes do not absorb in the long-wavelength region and absorb poorly in the short-wavelength region of the spectrum (
Figure 1A, curve 2). This is probably due to the process of melanin oxidation by superoxide radicals, which leads to the accumulation of water-soluble, low-molecular products of its destruction in the incubation medium. Indeed, as can be seen from
Figure 1B, melanosome oxidation with superoxide radicals results in products with emission maxima at 460–480 nm (curve 2; excitation at 365 nm) and 530 nm (curve 4; excitation at 470 nm). At the same time, the water-soluble fractions obtained from the initial, non-oxidized suspension of melanosomes showed almost no fluorescent properties (
Figure 1B, curves 1 and 3, respectively).
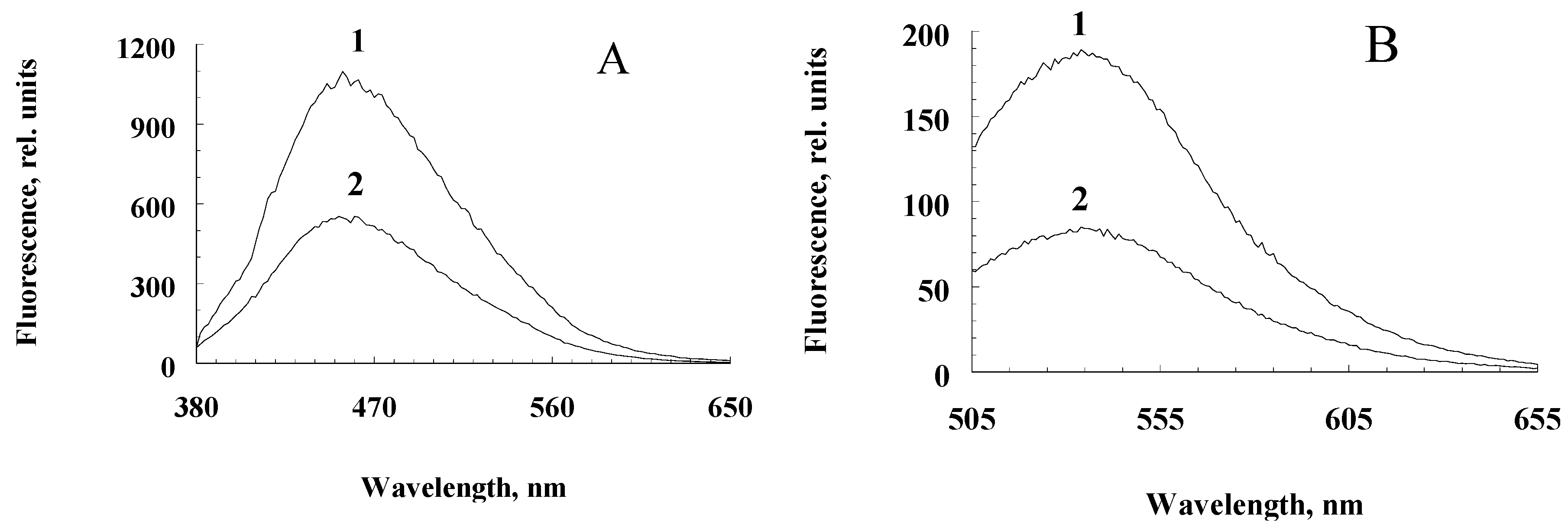
Incubation of a suspension of melanolipofuscin granules with potassium superoxide also leads to the appearance of fluorescent melanin degradation products, though to a lesser extent, which is apparently due to the lower melanin content in these granules compared to melanosomes (
Figure 2A,B, curves 1 for water-soluble products melanosome destruction and curves 2 for water-soluble destruction products of melanolipofuscin granules).
2.2. Characterization and potential phototoxicity of melanin oxidative degradation products of RPE pigment granules
The next stage of the work was to study the nature and physicochemical properties of water-soluble products formed during the oxidative degradation of RPE melanosomes induced by potassium superoxide. Potassium superoxide at millimolar concentrations disrupts RPE melanosome with the formation of fluorescent products with an emission maximum of 520-525 nm.
Figure 3A shows the kinetics of accumulation of melanin degradation products by melanosomes. The degradation products formed during the oxidative degradation of melanin contain carbonyl compounds. This is evidenced by the data obtained using time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry. As can be seen from the diagram (
Figure 3C), under the action of potassium superoxide on melanosomes, there is a significant increase in carbonyl ions (m/z = 29 – CHO
+ ion, m/z = 60 – C
2H
4O
2+ ion, m/z = 69 – C
4H
7O
+ ion). Ions with m/z = 60 give the greatest increase in concentration (an increase of about 1.5 times). The obtained results indicate the presence of aldehydes in the products formed during the oxidation of melanosomes by superoxide radicals. These results are confirmed by experiments on the content of carbonyl compounds that react with thiobarbituric acid (TBA-reactive products) (
Figure 3C). As can be seen, the water-soluble fractions obtained from oxidized samples (
Figure 3B, columns 2 and 3) contain significantly more TBA-reactive products than the supernatants of control, non-oxidized samples (
Figure 3B, column 1), and the higher the dose of KO
2, the more TBA-reactive products are formed (
Figure 3B, columns 2 and 3).
The products of oxidative degradation of melanin from RPE melanosomes exhibited the ability for light-induced generation of superoxide radicals (
Figure 3D). When irradiated with blue light (450 nm), they catalyze the reduction of cytochrome
c (transition of Fe
3+ to Fe
2+ form) and nitro blue tetrazolium to formazan (not shown in the figures). The process is inhibited in the presence of superoxide dismutase.
The obtained results indicate that the oxidation of melanosomes with potassium superoxide results in the formation of carbonyl products that are readily soluble in the aqueous phase. The degree of melanin degradation depends on the melanin/superoxide ratio. Increasing the superoxide concentration leads to increased accumulation of TBA-reactive products (
Figure 3B). Calculations show that in one RPE cell with a volume of 2x10
-9 ml, containing about 10-20 picograms of melanin, when completely destroyed, up to 0.3 nmol of TBA-reactive products can accumulate. This is quite a lot for the manifestation of the toxic effect of carbonyls. Aldehydes and ketones contained in the water-soluble fraction obtained as a result of the oxidative degradation of melanosomes were also found to be quite stable, since the content of TBA-reactive products in them remained virtually unchanged (not shown in the figure). The appearance of such long-lived and active chemicals during oxidative degradation of RPE by melanosomes may contribute to the development of various eye pathologies. The revealed ability of the products of oxidative degradation of melanosomes to light-dependent generation of superoxide radicals indicates their potential phototoxicity.
2.3. Spectral fluorescence studies of melanin photooxidative degradation products
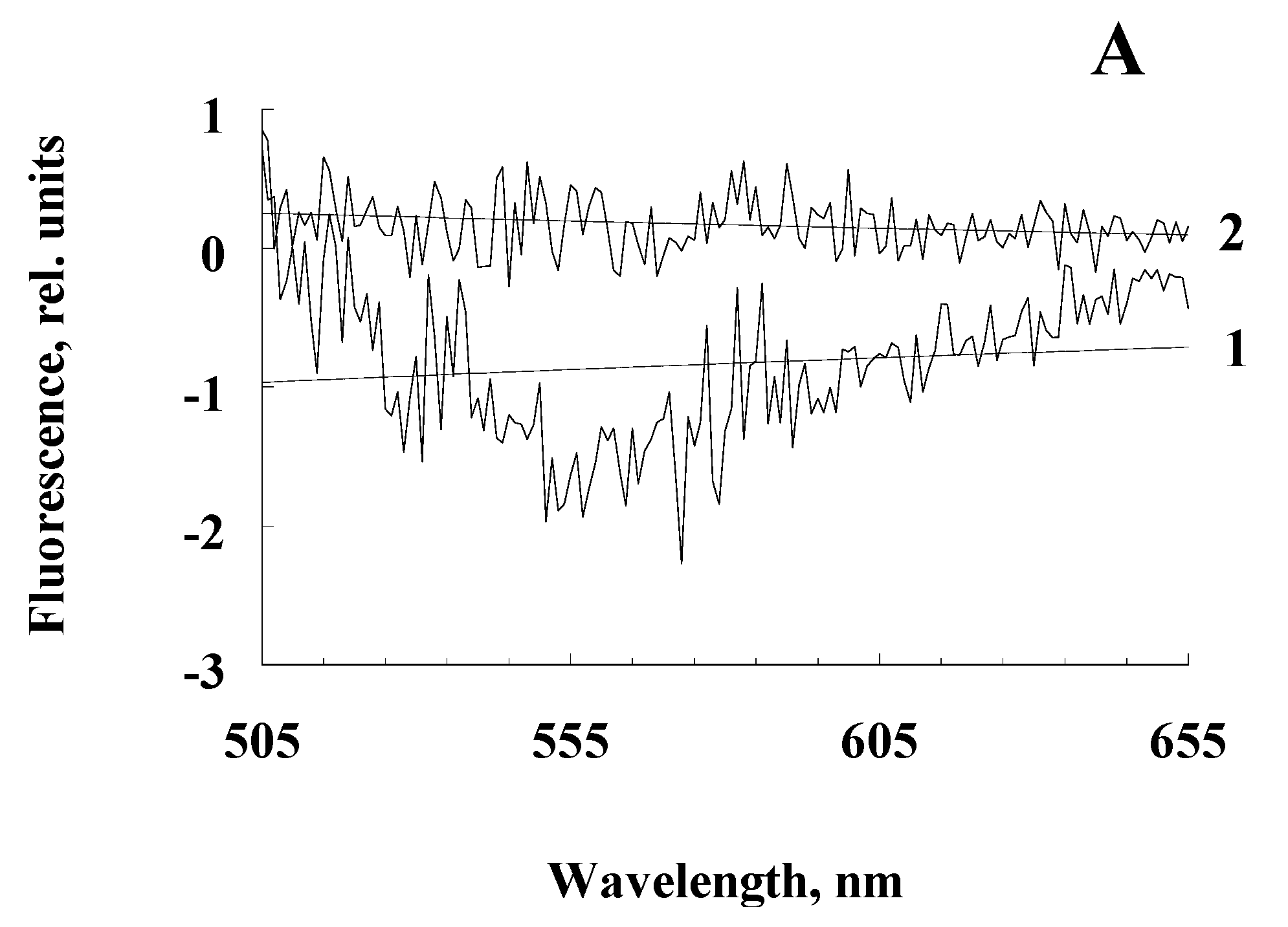
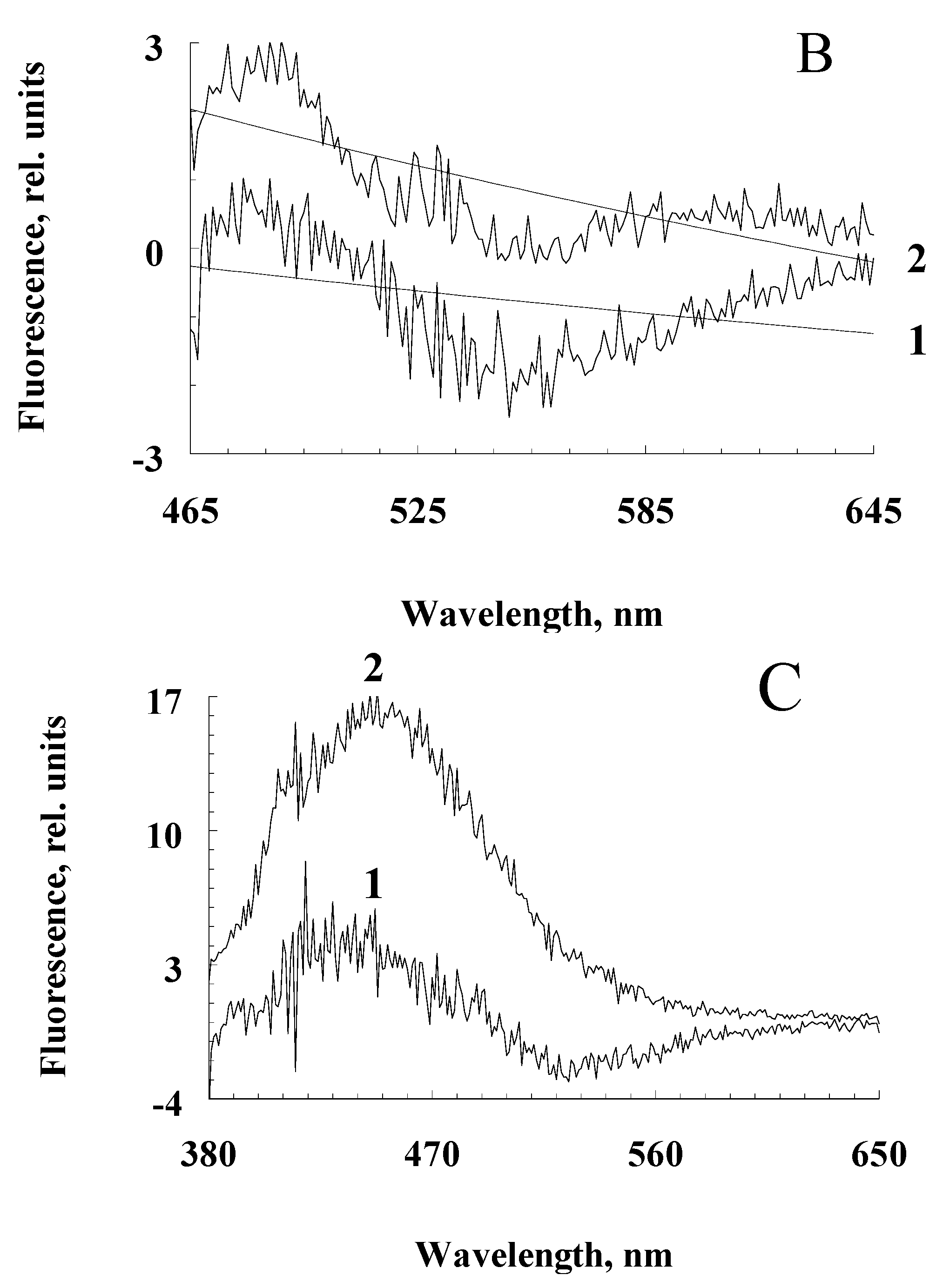
We hypothesize that when melanolipofuscin granules are irradiated with blue light, the melanin contained in them can be destroyed, by the action of superoxide radicals generated by lipofuscin bisretinoids during photoexcitation. We assume that blue light irradiation of melanosomes would not lead to a noticeable accumulation of melanin degradation products due to its high resistance to irradiation and the absence of lipofuscin fluorophores and other photosensitizers in melanosomes. Experiments on the comparative irradiation of RPE melanosomes and melanolipofuscin granules with blue light showed that only upon irradiation of melanolipofuscin granules, a significant excess of fluorescence intensity of water-soluble products was observed compared to unirradiated granules (
Figure 4, curves 2). This was observed at all excitation wavelengths but was especially pronounced for excitation at 365 nm (
Figure 4C).
The average value of the emission intensity (535 nm) for the decay products of irradiated melanolipofuscin granules was + 0.15; for melanosomes, this value is significantly negative.
The average value of the emission intensity (525 nm) for the decay products of irradiated melanolipofuscin granules was + 1.20; for melanosomes, this value is significantly negative.
The average value of the emission intensity (460 nm) for the decay products of irradiated melanolipofuscin granules was + 16.0; for melanosomes - +4.0.
This indicates the appearance of melanin degradation products upon irradiation of melanolipofuscin granules. In contrast to melanolipofuscin granules, irradiation of melanosomes under the same conditions led to a decrease in the fluorescence intensity of the resulting products, so that the differential spectra were in the negative region (
Figure 4A,B, curves 1), except for the excitation wavelength of 365 nm (
Figure 4C, curves 1). At this excitation wavelength, the appearance of melanin degradation products was observed, which may be associated either with the presence of a slight admixture of lipofuscin in melanosomes, or with an admixture of prooxidant degradation products of melanin itself (see below).
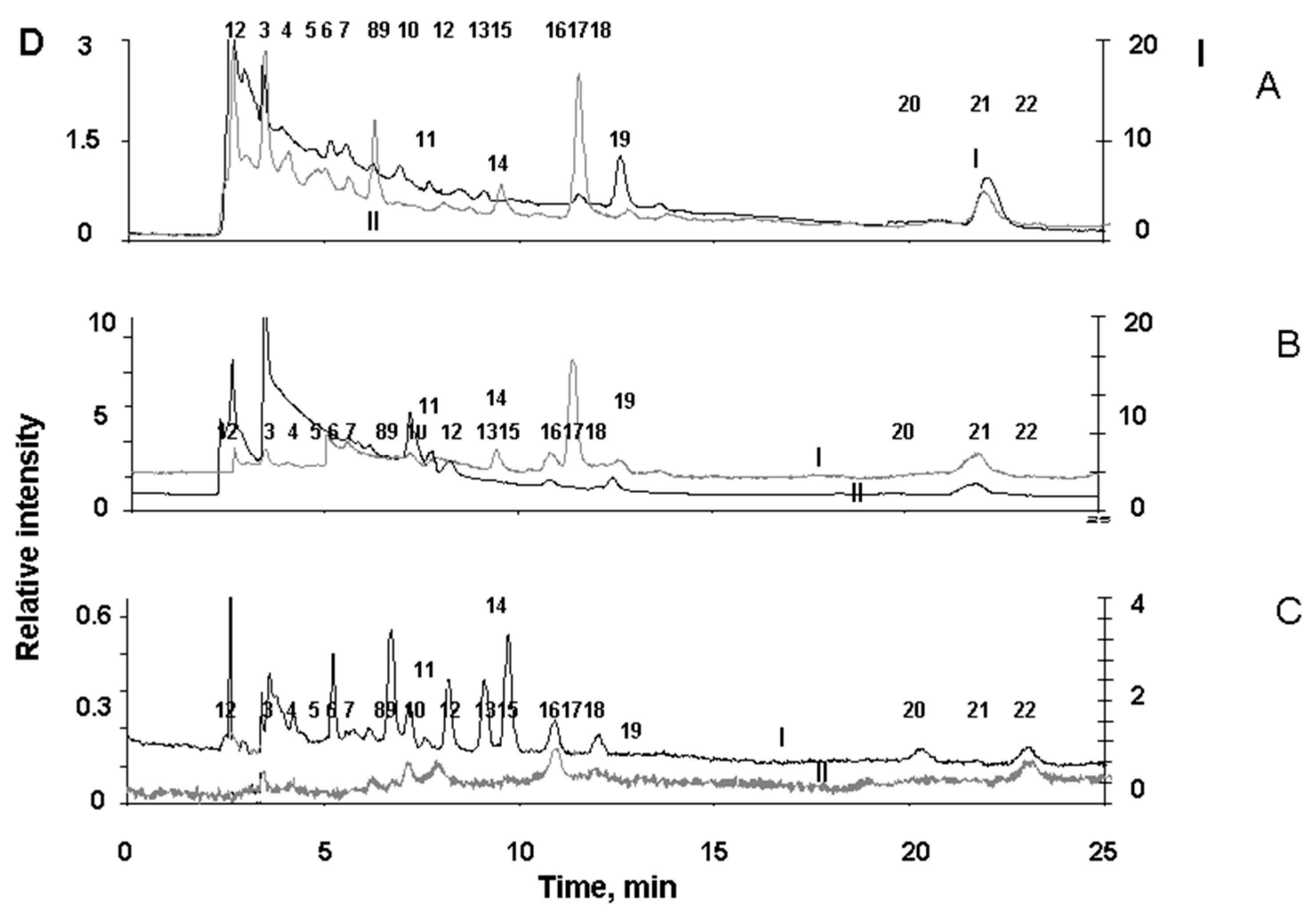
However, with an increase in the intensity of irradiation of RPE melanosomes with visible light, an increase in melanin degradation is observed (
Figure 5). The appearance of degradation products of melanosomes upon their irradiation with high-intensity light is clearly seen from the chromatogram (
Figure 5C).
2.4. Detection of products of oxidative degradation of melanin in melanolipofuscin granules
2.4.1. HPLC analysis
To detect melanin degradation products in the water-soluble fraction of melanolipofuscin granules irradiated with visible light, we analyzed the chromatograms of supernatants of all three types of RPE pigment granules, melanosomes, melanolipofuscin granules, and lipofuscin granules. It was important to show that during irradiation of melanolipofuscin granules with visible light, it formed products characteristic of the oxidative degradation of melanin under the action of superoxide radicals. For this purpose, chromatography experiments were carried out on the products formed during the oxidative degradation of RPE melanosomes by potassium superoxide. These data were compared with chromatograms of water-soluble products of light-induced degradation of RPE melanolipofuscin and lipofuscin granules.
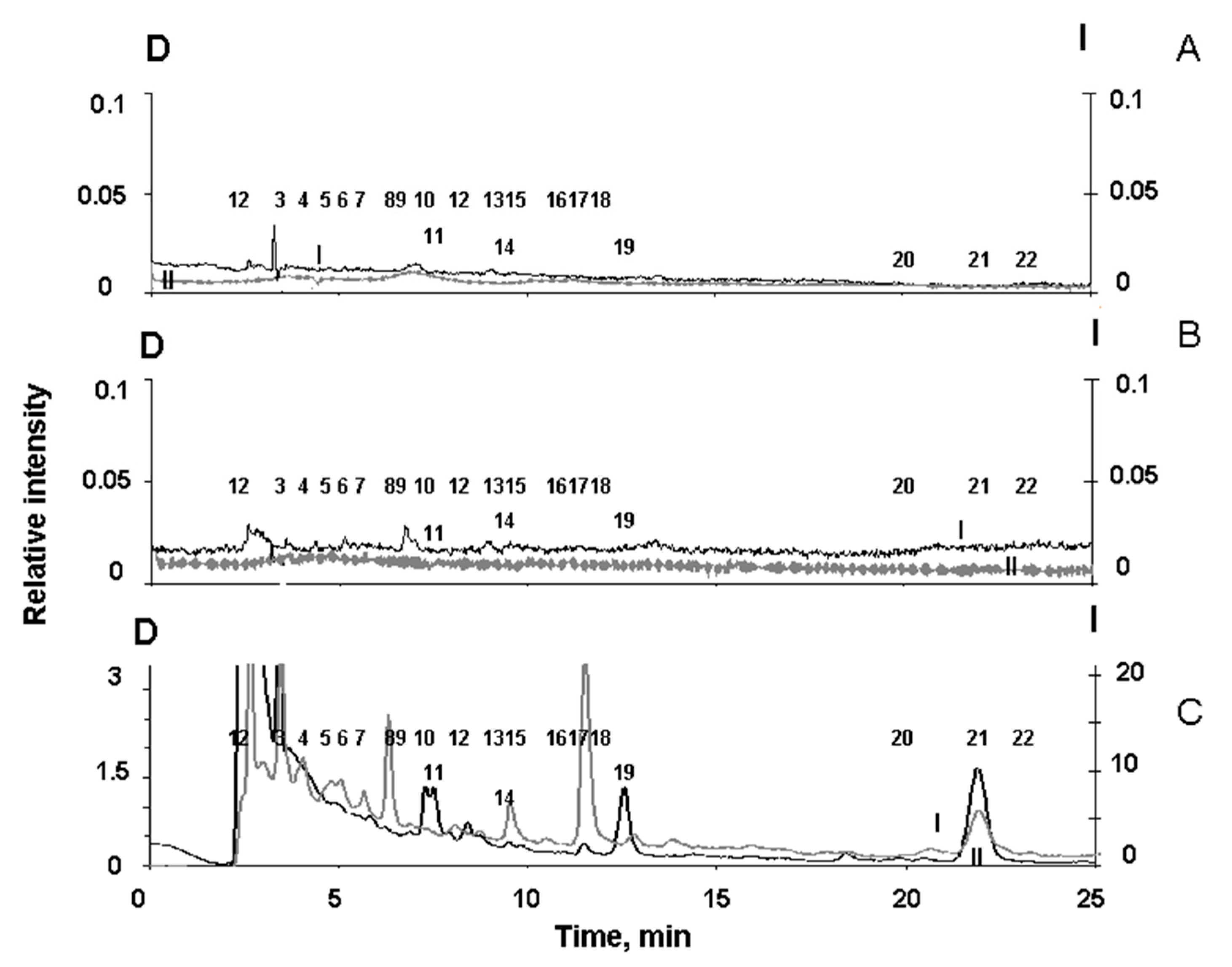
Figure 6 shows typical chromatograms superoxide-oxidized supernatants of melanosomes (A), as well as melanolipofuscin granules (B) and lipofuscin granules (C) irradiated with blue LED light.
Figure 6C shows that the water-soluble products formed upon irradiation of RPE lipofuscin granules are characterized by peaks designated by numbers 6, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 16, 18, 20 and 22. On the contrary, the water-soluble degradation products of RPE melanosomes, formed during the oxidation of granules with superoxide, are characterized by peaks designated with numbers 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 11, 14, 17, 19, and 21 (
Figure 6A). The standards for specific melanin degradation products, pyrrole-2,2-dicarboxylic acid (PDCA, peak № 17) and pyrrole-2,3,5-tricarboxylic acid (PTCA, peak № 21), are released at 11.5 min. and at 22.1 minutes, respectively, which is in good agreement with the literature data [
37].
It is important to note that among the degradation products of RPE melanosomes, we observed peaks of both PDCA and PTCA, which are considered to be the main products of oxidative degradation of melanin and characterize its initial structure, as well as other compounds that are formed during the degradation of melanosomes when they are irradiated with intense visible light (
Figure 5C). This indicates the existence of two different groups of melanin degradation: the first group is PDCA and PTCA, and the second group is melanin degradation fragments exhibiting longer wavelength fluorescence.
The water-soluble fraction obtained from irradiated melanolipofuscin RPE granules shows the presence of peaks characteristic of degradation products of both melanosomes and lipofuscin granules (
Figure 6B). Thus, the water-soluble products of light-induced degradation of melanolipofuscin RPE granules irradiated with blue light from an LED lamp (450 nm, 4 mW/cm
2), in contrast to lipofuscin RPE granules, contain products characteristic of the oxidative degradation of melanin caused by superoxide radicals (
Figure 6 B).
The results confirm the assumption that bisretinoid fluorophores present in the melanolipofuscin granules, which generate superoxide radicals under the action of blue light, cause oxidative degradation of the melanin contained in these granules.
2.4.2. Mass spectrometric analysis
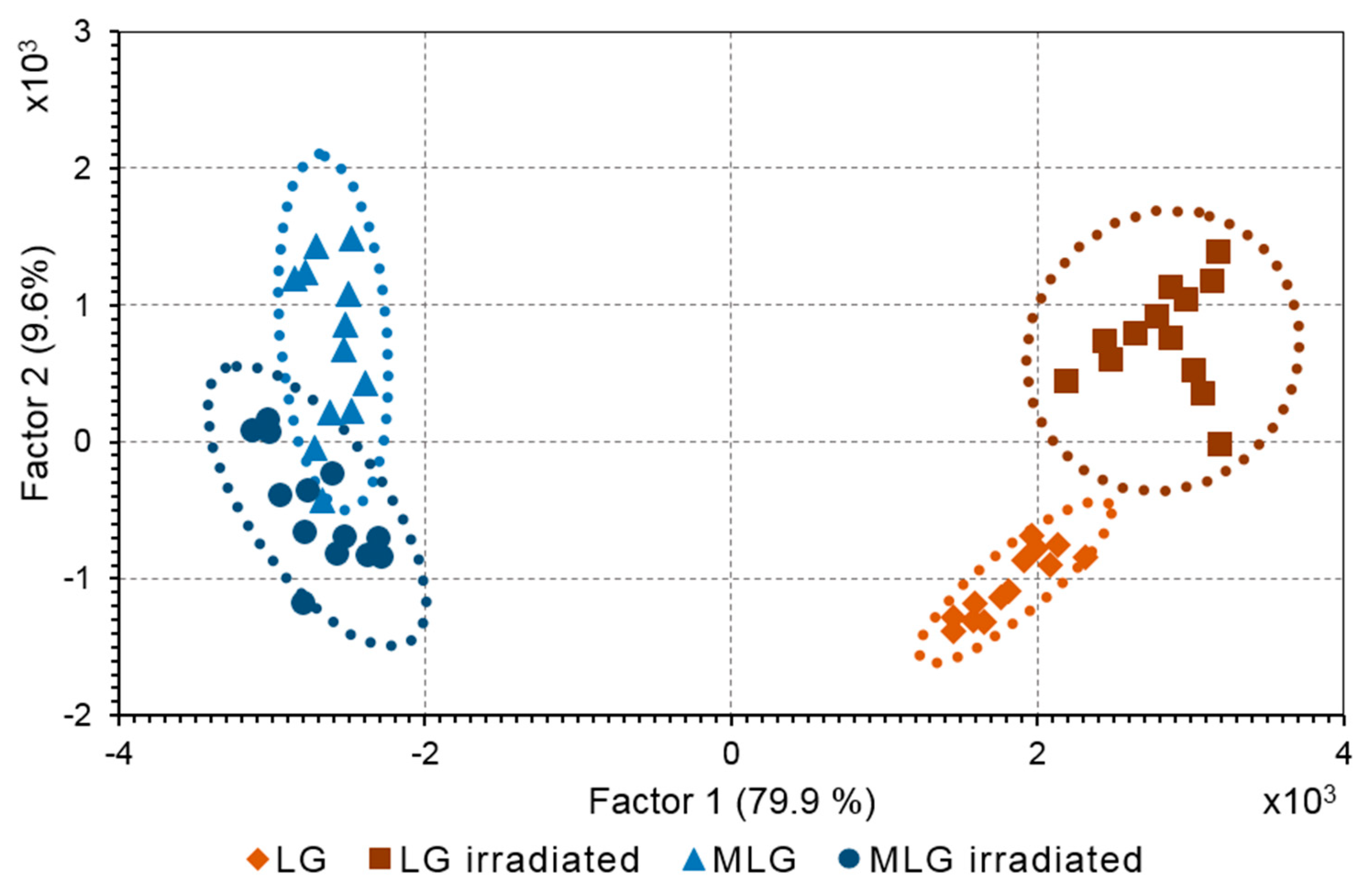
The compounds formed as a result of light-induced degradation of RPE pigment granules were characterized using principal component analysis (PCA) for mass spectra obtained by the ToF-SIMS. Mass spectra of samples of melanosomes, melanolipofuscin and lipofuscin granules were obtained before and after their irradiation with visible light. The peaks that are related to melanin degradation products were identified both in the composition of melanosomes and in the composition of melanolipofuscin granules. PCA is routinely applied for ToF-SIMS data to distinguish the differences in sample composition [
38]. PCA score plot revealed a significant difference between the samples of melanolipofuscin and lipofuscin granules (
Figure 7).
Principal component 1 (PC1) was mainly related to the difference between melanolipofuscin and lipofuscin while PC2 could be attributed to the difference between non-irradiated and irradiated states of RPE granules. PC loadings analysis was applied to make a list of photodegradation fragments that have enlarged ion yield in melanolipofuscin granules.
However, it was unclear did these fragments originated from the supernatant or melanin polymer structure. In order to understand the source of photodegradation products a suspension of melanosomes containing melanin degradation products was subjected to centrifugation. Two samples were acquired: a precipitate containing melanosomes with an intact melanin polymer structure and a supernatant, where small molecules of melanin degradation products were present in water solution. Mass spectra were analyzed by PCA in the same manner. As a result, the fragments corresponding to the products of melanin degradation in the supernatants from oxidized melanosomes were revealed and compared with ions found in the melanolipofuscin. The resulting
Table 1 shows the masses responsible for the photodegradation products of melanin in both melanosomes and melanolipofuscin granules. The assignments were proposed according to the exact mass value (
Table 1).
The obtained results indicate the presence of melanin degradation products in the water-soluble fraction of melanolipofuscin granules irradiated with blue light. Previously, we found that the concentration of melanin in human RPE melanosomes does not change with age [
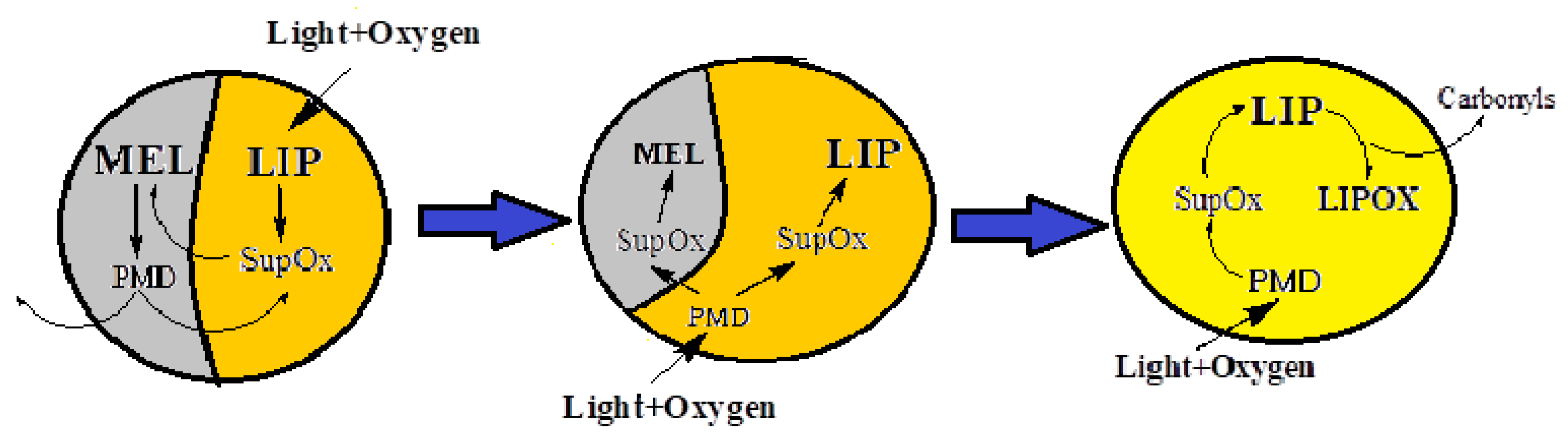
39]. We can assume that the decrease in melanin concentration with age is not due to its destruction in RPE melanosomes, but is caused by its degradation by superoxide radicals generated by lipofuscin bisretinoids localized in melanolipofuscin granules. In the present study, we have shown that it is superoxide radicals that cause melanin degradation in melanolipofuscin granules, and the resulting products, in turn, are photosensitive generators of superoxide. Considering these facts, a scheme of the mechanism of melanin and lipofuscin degradation in melanolipofuscin granules is proposed, to explain the reasons for the decrease in melanin concentration in RPE cells with age (
Figure 8).
Light in the presence of oxygen activates the generation of superoxide (SupOx) mediated by lipofuscin fluorophores (LIPs). The superoxide reacts with the melanin (MEL) in the melanolipofuscin granule, causing its degradation and the formation of photosensitive degradation products (PMD). The latter can partially leave the granule, partially remain in it, in turn causing additional formation of superoxide under the action of light. This leads to further degradation of melanin and oxidation of lipofuscin. The toxic products of lipofuscin oxidation, carbonyls, can exit the granule into the cell and damage cytoplasmic proteins in the dark.
3. Materials and methods
3.1. Preparing products of oxidative degradation of RPE pigment granules during oxidation by superoxide radicals.
Pigment granules were isolated from RPE cells of human cadaveric eyes. Human cadaveric eyes were obtained from the Eye Tissue Bank of the S.N. Fedorov Institute of Eye Microsurgery of the Ministry of Health of Russia from donors without ophthalmic pathologies, aged 40 to 75 years. A total of 40 donor eyes were used. Pigment granules were isolated from retinal pigment epithelium cells according to the method described in [
40,
41]. RPE cells in 0.1 M K-phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, when cooled to 4° C, were sonicated twice for 40 s at maximum resonance, followed by removal of undamaged cell membranes by centrifugation at 100g for 15 min. The resulting supernatant was centrifuged at 6,000g for 15 min, the precipitate was suspended in 0.3 M sucrose and centrifuged in an ultracentrifuge in a sucrose density gradient (2.0; 1.8; 1.6; 1.5; 1.4; 1.2; 1.0; 0.3 M) at 103,000g for 1 hour. Then, pigment granules separated into fractions were selected and washed from sucrose with 0.1 M K-phosphate buffer. Melanosomes formed a dark brown precipitate, lipofuscin granules formed a layer in the region of sucrose density of 1.2, and melanolipofuscin granules were localized in the region of 1.6 - 1.8. The granules were suspended in phosphate buffer and stored in a freezer at –18°C. Granule concentration counting was carried out in a Goryaev chamber using a “LOMO MikMed-2” fluorescent microscope equipped with a camera.
Oxidative degradation of granules was carried out by incubating a suspension of granules in 0.1 M K-phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, (1.0x108 – 5.0x108 granules/ml) with dry potassium superoxide (3–8 mg) at room temperature for 1–2 hours. At the end of the reaction, the water-soluble products were separated by centrifugation in a Beckman Allegra 64R centrifuge at 12,000g for 20 min.
Photoinduced degradation of RPE pigment granules was carried out by irradiating them with blue light from an LED source with irradiation energy of 4 mW/cm2 for 1-2 hours. In some experiments, the products of RPE melanosome photodegradation were obtained by irradiating them with visible light of a halogen lamp with an energy of 100 mW/cm2 for at least two hours. At the end of the reaction, the water-soluble products were separated by centrifugation in a Beckman Allegra 64R centrifuge at 12,000g for 20 min.
3.2. Investigation of the Spectral Characteristics of Degradation Products of Pigment Granules
The degradation products of the melanin-containing pigment granules were recorded fluorometrically by measuring the emission intensity at the excitation wavelength of 365 nm, 450 nm, 470 nm, and 488 nm. The emission intensity was measured on a Shimadzu RF5301PC Spectro fluorophotometer (Japan). To estimate the concentration of melanin degradation products, we used a calibration curve of the dependence of the emission intensity at 520–525 nm on the concentration of synthetic DOPA melanin completely oxidized by KO2. The control samples were incubated for the same time in the dark. When the reaction was completed, the water-soluble degradation products of the granules were obtained by centrifugation at 15,000g for 20 min. Differential fluorescence spectra (light-dark) were plotted to analyze the obtained products.
3.3. Measurement of photoinduced generation of superoxide radicals by water-soluble products of oxidative destruction of melanosomes and melanolipofuscin granules
The process of light-induced generation of superoxide radicals by water-soluble products of oxidative destruction of melanin was estimated by measuring the kinetics of the reduction of cytochrome
c (Fe
3+) inhibited by superoxide dismutase using a modified method [
42]. The reaction mixture contained 0.1 M K-phosphate buffer, pH 7.6, 100 μM cytochrome
c, 0.05% cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, and various amounts of water-soluble melanin oxidative degradation products. The mixture was irradiated with blue light from an LED source with an irradiation energy of 4 mW/cm
2 and an irradiation wavelength of 450 nm with constant stirring, followed by measuring of the absorption maximum at a wavelength of 550 nm (molar absorption coefficient 21 mM
–1cm
–1) [
43]. Samples incubated in the dark and samples containing no melanin degradation products, served as controls.
3.4. Measurement of products that react with thiobarbituric acid (TBA-reactive products).
Water-soluble degradation products of melanosomes and melanolipofuscin RPE granules were evaluated for the content of reactive carbonyls reacting with thiobarbituric acid [
44]. The concentration of TBA-reactive products was determined spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 532 nm [
45] on a Shimadzu UV-1700 spectrophotometer (Japan). Water-soluble products obtained from native, non-oxidized pigment granules served as controls.
3.5. Mass Spectrometry of Pigment Granule Destruction Products by ToF-SIMS
Mass spectra were obtained on a TOF.SIMS.5 time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer (ION-TOF, Germany) with a bismuth cluster beam, which is regularly used for biological studies [
46]. The 300×300 μm (64×64 pixels) analysis area was probed with primary Bi
3+ ions with an energy of 30 keV at a primary ion dose density of ~4×10
11 ions/cm
2 in each measurement. At least 10 measurements were recorded for each sample, in both positive and negative ion modes. During the analysis, the electron gun was activated. Ions processing and identification was carried out using SurfaceLab 7 software.
3.6. Chromatographic analysis of melanin degradation products
Chromatographic separation of melanin degradation products in supernatants from melanosomes, melanolipofuscin and lipofuscin granules of the human eye was carried out on a Knauer chromatograph (Germany) with a Diasfer 120 C18 column (4x250 mm, sorbent size 5 μm), according to the modernized method described in the work [
37]. PDCA and PTCA, - were kindly provided by Prof. Dr. Kazumasa Wakamatsu (Institute for Melanin Chemistry, Fujita Health University, Toyoake, Japan). A mixture of a 1% solution of formic acid in water (pH, 2.8) and methanol in a ratio of 97:3, by volume, was used as an eluent [
37]. The eluent flow rate was 0.8 ml/min. The chromatographic separation products were measured using a Knauer K-2501 photometric detector and a fluorometric detector (RF-10A-xl, Shimadzu). Detection was performed at 270 nm by absorption as well as by fluorescence at different excitation and detection wavelengths.
4. Conclusions
The obtained results indicate that during the oxidative degradation of RPE melanosomes under the action of superoxide radicals, water-soluble carbonyls - aldehydes and ketones, exhibiting TBA activity, are formed. It was found for the first time that water-soluble melanin degradation products are photosensitive and generate superoxide radicals under blue light irradiation. Consequently, the toxicity of melanin oxidative degradation products for cells can be due to both the content of reactive aldehydes and the ability to generate light-dependent superoxide radicals. Since superoxide radicals cause the oxidation and degradation of melanin, as well as the oxidation and degradation of lipofuscin fluorophores, this can lead to increased light-induced degradation of both lipofuscin and melanin in the melanolipofuscin granule (
Figure 8). This fact may also explain the important role of melanin in the process of lipofuscin degradation in the RPE cell [
19].
Melanin degradation products formed as a result of its reaction with superoxide radicals were identified and characterized using HPLC and mass spectrometry. The same products were found in samples of melanolipofuscin granules irradiated with blue light. This indicates the degradation of melanin by superoxide radicals in these granules. Superoxide radicals in melanolipofuscin granules can be generated during the irradiation of granules with both bisretinoids, which are part of the lipofuscin part of the granule, and photosensitive degradation products of the melanin part of the granule.
Thus, it can be concluded that when melanolipofuscin granules are irradiated with blue light (450 nm, 4 mW/cm2), the melanin included in their composition will be destroyed as a result of its reaction with superoxide radicals. This process probably leads to an age-related decrease in the concentration of melanin in RPE cells of the human eye.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.D., M.O. and V.N.; methodology, A.D., M.Y., A.A. and A.G.; investigation, A.D., M.Y., A.A., A.V. and A.G.; data curation, A.D., M.Y., A.V., A.A., V.N. and A.G.; writing—review and editing, A.D.; M.Y., and A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.D., M.Y. M.O. and A.G.; funding acquisition, M.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Russia and carried out for Research Project No 075-15-2020-795 (local identifier 13.1902.21.0027).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Experiments on human cadaver eye tissues were performed in compliance with officially accepted procedures, specifically the Russian Federation law N 4180-I dated 22 December 1992, “On human organs or tissue transplantation” (with the most recent modifications and additions dated 8 December 2020) (
http://base.garant.ru/136366 (accessed on 11 January 2021)). On the basis of the Russian Federal Service on Surveillance in Healthcare (Roszdravnadzor) licenses No. 99-01-005317 dated 30.04.2008 and No. FS-99-01-008251 dated 18.02.2013, the Eye Tissue Bank located in the S. Fyodorov Eye Microsurgery Federal State Institution (Beskudnikovsky bld. 59a, Moscow, Russia, 127486) obtained human cadaver eyes from the mortuary departments of the Moscow Forensic Medical Examination Bureau. These licenses permit the use of tissue isolated from human cadaver eyes for transplantation and scientific research. The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article and on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Kazumasa Wakamatsu from Fujita Health University, Japan, for kindly provided reagents (PDCA, PTCA) and Prof. S. Borzenok and Dr. M. Khubetsova from the S. Fyodorov Eye Microsurgery Federal State Institution, who contributed human cadaver eye samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Meleppat, R.K.; Ronning, K.E.; Karlen, S.J.; Burns, M.E.; Pugh, E.N. Jr; Zawadzki, R.J. In vivo multimodal retinal imaging of disease-related pigmentary changes in retinal pigment epithelium. Nature portfolio. 2021, 11, 16252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, M.A.; Sakina, N.L.; Dontsov, A.E. Antioxidative role of eye screening pigments. Vision Res. 1987, 27, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dontsov, A.E.; Ostrovsky, M.A. The antioxidant role of screening eye pigments – melanins and ommochromes, and physicochemical mechanism of their action. In Chemical and Biological Kinetics. New Horizons. Varfolomeev, S.D., Burlakova, E.B., Eds.; CRC Press: Danvers; MA, USA; 2005; v. 2, pp. 133–150. ISBN 9067644293.
- Wang, Z.; Dillon, J.; Gaillard, E. R. Antioxidant Properties of Melanin in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2006, 82, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.M.; Kaczara, P.; Skumatz, C.M.; Zareba, M.; Raciti, M.W.; Sarna, T. Dynamic analyses reveal cytoprotection by RPE melanosomes against non-photic stress. Mol. Vision. 2011, 17, 2864–2877. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrovsky, M.A.; Zak, P.P.; Dontsov, A.E. Vertebrate eye melanosomes and invertebrate eye ommochromes as screening cell organelles. Biology Bulletin. 2018, 45, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacout, S.M.; McIlwain, K.L.; Mirza, S.P.; Gaillard, E.R. Characterization of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Melanin and Degraded Synthetic Melanin Using Mass Spectrometry and In Vitro Biochemical Diagnostics. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, M.A.; Dontsov, A.E. Vertebrate Eye Melanosomes and Invertebrate Eye Ommochromes as Antioxidant Cell Organelles: Part 2. Biol. Bulletin. 2019, 46, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney-Burns, L.; Hilderbrand, E.S.; Eldridge, S. Aging human RPE: morphometric analysis of macular, equatorial, and peripheral cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1984, 25, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sarna, T.; Burke, J.M.; Korytowski, W.; Rózanowska, M.; Skumatz, C.M.B.; Zareba, A.; Zareba, M. Loss of melanin from human RPE with aging: possible role of melanin photooxidation. Exp Eye Res. 2003, 76, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney-Burns, L.; Burns, R.P.; Gao, C.L. Age-related Macular Changes in Humans Over 90 Years old. American J. Ophthalmol. 1990, 109, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, L. Lipofuscin and melanin of human retinal pigment epithelium: fluorescence, enzyme cytochemical, and ultrastructural studies. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1978, 17, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delori, F.C.; Goger, D.G.; Dorey, C.K. Age-related accumulation, and spatial distribution of lipofuscin in RPE of normal subjects. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taubitz, T.; Tschulakow, A.V.; Tikhonovich, M.; Illing, B.; Fang, Y.; Biesemeier, A.; Julien-Schraermeyer, S.; Schraermeyer, U. Ultrastructural alterations in the retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptors of a Stargardt patient and three Stargardt mouse models: indication for the central role of RPE melanin in oxidative stress. PeerJ. 2018, 6, e5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollreisz, A.; Neschi, M.; Sloan, K.R.; Pircher, M.; Mittermueller, T.; Dacey, D.M.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Curcio, C.A. Atlas of human retinal pigment epithelium organelles significant for clinical imaging. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraermeyer, U.; Stieve, H. A newly discovered pathway of melanin formation in cultured retinal pigment epithelium of cattle. Cell Tissue Res. 1994, 276, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraermeyer, U.; Heimann, K. Current understanding on the role of retinal pigment epithelium and its pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 1999, 12, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wavre-Shapton, S.T.; Meschede, I.P.; Seabra, M.C.; Futter, C.E. Phagosome maturation during endosome interaction revealed by partial rhodopsin processing in retinal pigment epithelium. J Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 3852–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Tschulakow, A.V.; Schraermeyer, U. Melanosomes degrade lipofuscin and precursors that are derived from photoreceptor membrane turnover in the retinal pigment epithelium—an explanation for the origin of the melanolipofuscin granule. BioRxiv, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dontsov, A.E.; Sakina, N.L.; Ostrovsky, M.A. Loss of melanin by eye retinal pigment epithelium cells is associated with its oxidative destruction in melanolipofuscin granules. Biochemistry (Moscow). 2017, 82, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadlo, A.; Rozanowska, M.B.; Burke, J.M.; Sarna, T.J. Photobleaching of retinal pigment epithelium melanosomes reduces their ability to inhibit iron induced peroxidation of lipids. Pigment Cell Res. 2007, 20, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rózanowski, B.; Burke, J.M.; Boulton, M.E.; Sarna, T.; Rózanowska, M. Human RPE melanosomes protect from photosensitized and iron-mediated oxidation but become pro-oxidant in the presence of iron upon photodegradation. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadlo, A.; Burke, J.M.; Sarna, T. Effect of untreated and photobleached bovine RPE melanosomes on the photoinduced peroxidation of lipids. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2009, 8, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olchawa, M.M.; Szewczyk, G.M.; Zadlo, A.C.; Krzysztynska-Kuleta, O.I.; Sarna, T.J. The effect of aging and antioxidants on photoreactivity and phototoxicity of human melanosomes: in vitro study. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2020, 34, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dontsov, A.E.; Sakina, N.L.; Koromyslova, A.D.; Ostrovsky, M.A. Effect of UV radiation and hydrogen peroxide on the antiradical and antioxidant activities of DOPA-melanin and melanosomes from retinal pigment epithelium cells. Russian Chemical Bulletin, 2015, 64, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Kikuta, M.; Koike, S.; Szewczyk, G.; Sarna, M.; Zadlo, A.; Sarna, T.; Wakamatsu, K. Roles of reactive oxygen species in UVA-induced oxidation of 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid-melanin as studied by differential spectrophotometric method. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Sarna, T. Photodegradation of Eumelanin and Pheomelanin and Its Pathophysiological Implications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadlo, A.; Ito, S.; Sarna, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Mokrzyński, K.; Sarna, T. The role of hydrogen peroxide and singlet oxygen in the photodegradation of melanin. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2020, 19, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzhova, L.P.; Frolova, E.V.; Romakov, Iu.A.; Kuznetsova, N.A. Photo-induced destruction of DOPA-melanin. Biochemistry (Moscow), 1989, 54, 992–998. [Google Scholar]
- Kayatz, P.; Thumann, G.; Luther, T.T.; Jordan, J.F.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.V.; Esser, P.J.; Schraermeyer, U. Oxidation causes melanin fluorescence. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Elleder, M.; Borovansky, J. Autofluorescence of melanin induced by ultraviolet radiation and near ultraviolet light. A histochemical and biochemical study. Histochem. J., 2001, 33, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovansky, J.; Elleder, M. Melanosomes degradation: fact or fiction. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, M.; Dontsov, A.; Jarvis-Evans, J.; Ostrovsky, M.; Svistunenko, D. Lipofuscin is a photoinducible free radical generator. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. Biol. 1993, 19, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozanowska, M.; Jarvis-Evans, J.; Korytowski, W.; Boulton, M.E.; Burke, J.M.; Sarna, T. Blue light-induced reactivity of retinal age pigment: In vitro generation of oxygen-reactive species. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270, 18825–18930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Montenegro, D.; Zhao, J.; Sparrow, J.R. Bisretinoids of the Retina: Photo-Oxidation, Iron-Catalyzed Oxidation, and Disease Consequences. Antioxidants, 2021, 10, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, T.B.; Dontsov, A.E.; Yakovleva, M.A.; Ostrovsky, M.A. Photobiology of lipofuscin granules in the retinal pigment epithelium cells of the eye: norm, pathology, age. Biophys. Rev. 2022, 14, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarelli, M.; Passamonti, P.; Renieri, C. Purification, characterization and analysis of sepia melanin from commercial sepia ink (Sepia Officinalis) Purificación, caracterización y análisis de la melanina de sepia a partir de la tinta de sepia (Sepia Officinalis). Rev CES Med Vet Zootec. 2010, 5, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Jia, F.; Ye, J.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, F. Cisplatin-induced alteration on membrane composition of A549 cells revealed by ToF-SIMS. SIA. 2020, 52, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaev, A.B.; Dontsov, A.E.; Ilyasova, V.B.; Ostrovsky, M.A. Determination of the melanin level in human melanosomes in the pigment epithelium of the eye depending on age. Reports Acad. Sci. 1993, 333, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, M.; Marshall, J. Re-pigmentation of human retinal pigment epithelial cell in vitro. Exp. Eye Res. 1985, 41, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, T.B.; Yakovleva, M.A.; Arbukhanova, P.M.; Borzenok, S.A.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Popov, I.A.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Ostrovsky, M.A. Changes in spectral properties and composition of lipofuscin fluorophores from human retinal pigment epithelium with age and pathology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCord, J.M.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 6049–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T. Selective inhibition by the sulfhydryl reagent maleimide of zymosan particle phagocytosis by neutrophils. FEBS Letters, 1982, 141, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterbauer, H.; Cheeseman, K.H. Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: Malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimolina, L.; Gulin, A.; Ignatova, N.; Druzhkova, I.; Gubina, M.; Lukina, M.; Snopova, L.; Zagaynova, E.; Kuimova, M.K.; Shirmanova, M. The role of plasma membrane viscosity in the response and resistance of cancer cells to oxaliplatin Cancers, 2021, 13, 616513. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Spectral characteristics of water-soluble destruction products of human RPE melanosomes. A – Optical absorption (curves 1 and 2 – water-soluble products from non-oxidized and superoxide-oxidized melanosomes, respectively; B – fluorescence spectrum upon excitation at 365 nm (1, 2) and 470 nm (3, 4) (curves 1, 3 and 2, 4 – water-soluble products from non-oxidized and superoxide-oxidized melanosomes, respectively.
Figure 1.
Spectral characteristics of water-soluble destruction products of human RPE melanosomes. A – Optical absorption (curves 1 and 2 – water-soluble products from non-oxidized and superoxide-oxidized melanosomes, respectively; B – fluorescence spectrum upon excitation at 365 nm (1, 2) and 470 nm (3, 4) (curves 1, 3 and 2, 4 – water-soluble products from non-oxidized and superoxide-oxidized melanosomes, respectively.
Figure 2.
Differential fluorescence spectra of water-soluble fractions obtained from RPE pigment granules oxidized and non- oxidized with potassium superoxide at excitation lengths of 365 nm (A) and 488 nm (B). 1 – melanosomes, 2 – melanolipofuscin granules.
Figure 2.
Differential fluorescence spectra of water-soluble fractions obtained from RPE pigment granules oxidized and non- oxidized with potassium superoxide at excitation lengths of 365 nm (A) and 488 nm (B). 1 – melanosomes, 2 – melanolipofuscin granules.
Figure 3.
Physicochemical characteristics of the products formed during the interaction of RPE melanosomes with potassium superoxide. A. Kinetics of accumulation of fluorescent decay products. The incubation medium contained 0.1 M K-phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 1.5x108 melanosome granules/ml, and 70 mM KO2. Curves 1-5 – incubation time 0, 30, 60, 90 and 180 min, respectively. Excitation wavelength – 450 nm; B. Concentration of TBA-reactive products in water-soluble fractions obtained by oxidation of melanosomes with potassium superoxide. Column 1 – original, non-oxidized melanosomes, 2 – 15 mg KO2 added, 3 – 30 mg KO2 added; C. Comparative histogram of carbonyl ion signals in samples of non-oxidized (grey bars) and oxidized KO2 (blue bars) RPE melanosomes; student T test, P-value ˂ 0.05; D. Kinetics of superoxide formation upon irradiation with blue light of the products of oxidative degradation of RPE melanosomes. The reaction mixture contained 0.1 M K-phosphate buffer, pH 7.6, 100 μM cytochrome c, 0.05% cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, and 100 μl of water-soluble melanin oxidative degradation products. The concentration of superoxide dismutase added is 10 µg/ml.
Figure 3.
Physicochemical characteristics of the products formed during the interaction of RPE melanosomes with potassium superoxide. A. Kinetics of accumulation of fluorescent decay products. The incubation medium contained 0.1 M K-phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 1.5x108 melanosome granules/ml, and 70 mM KO2. Curves 1-5 – incubation time 0, 30, 60, 90 and 180 min, respectively. Excitation wavelength – 450 nm; B. Concentration of TBA-reactive products in water-soluble fractions obtained by oxidation of melanosomes with potassium superoxide. Column 1 – original, non-oxidized melanosomes, 2 – 15 mg KO2 added, 3 – 30 mg KO2 added; C. Comparative histogram of carbonyl ion signals in samples of non-oxidized (grey bars) and oxidized KO2 (blue bars) RPE melanosomes; student T test, P-value ˂ 0.05; D. Kinetics of superoxide formation upon irradiation with blue light of the products of oxidative degradation of RPE melanosomes. The reaction mixture contained 0.1 M K-phosphate buffer, pH 7.6, 100 μM cytochrome c, 0.05% cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, and 100 μl of water-soluble melanin oxidative degradation products. The concentration of superoxide dismutase added is 10 µg/ml.
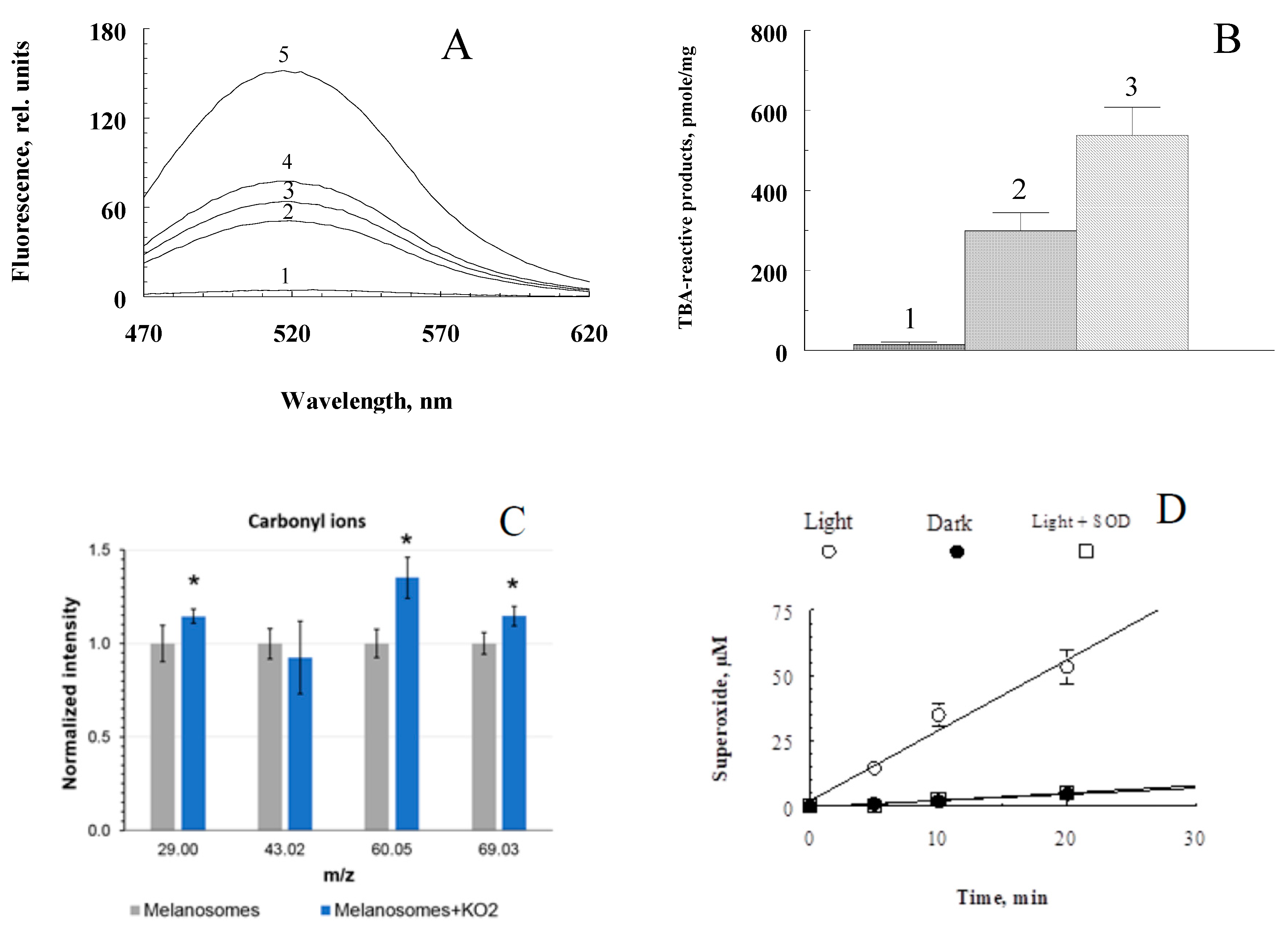
Figure 4.
Differential fluorescence spectra of water-soluble products obtained from the RPE pigment granules irradiated and not irradiated with blue light. Excitation wavelength: A - 488 nm, B - 450 nm, C - 365 nm. Curves 1, 2 are the fluorescence of water-soluble products obtained by irradiation with melanosome and melanolipofuscin granules, respectively.
Figure 4.
Differential fluorescence spectra of water-soluble products obtained from the RPE pigment granules irradiated and not irradiated with blue light. Excitation wavelength: A - 488 nm, B - 450 nm, C - 365 nm. Curves 1, 2 are the fluorescence of water-soluble products obtained by irradiation with melanosome and melanolipofuscin granules, respectively.
Figure 5.
Comparative chromatograms of water-soluble fractions of RPE melanosomes irradiated with light of different intensity. Water-soluble fractions were obtained from: A – initial (dark) melanosomes; (b) melanosomes irradiated with blue light from a LED source with energy of 4 mW/cm2 for 1.5 hours; C - melanosomes irradiated with visible light of a halogen lamp with an energy of 100 mW/cm2 for 2.5 hours. Scale D (left)—detection by absorption at 270 nm (curves 1); scale I (right) – fluorescence detection (excitation wavelength 270 nm, emission 380 nm (curves 2). Numerals (1-22) indicate the peaks in the chromatograms.
Figure 5.
Comparative chromatograms of water-soluble fractions of RPE melanosomes irradiated with light of different intensity. Water-soluble fractions were obtained from: A – initial (dark) melanosomes; (b) melanosomes irradiated with blue light from a LED source with energy of 4 mW/cm2 for 1.5 hours; C - melanosomes irradiated with visible light of a halogen lamp with an energy of 100 mW/cm2 for 2.5 hours. Scale D (left)—detection by absorption at 270 nm (curves 1); scale I (right) – fluorescence detection (excitation wavelength 270 nm, emission 380 nm (curves 2). Numerals (1-22) indicate the peaks in the chromatograms.
Figure 6.
Chromatograms of water-soluble fractions of RPE pigment granules. A. Products of degradation of melanosomes oxidized by superoxide; B and C are destruction products of melanolipofuscin and lipofuscin granules, respectively, formed upon irradiation of the granules with blue light from an LED lamp. Scale D (left, curves I) - detection by absorption at 270 nm; scale I (right, curves II)—fluorescence detection at an excitation wavelength of 270 nm and emission at 380 nm. The numbers (1-22) indicate the peaks in the chromatograms.
Figure 6.
Chromatograms of water-soluble fractions of RPE pigment granules. A. Products of degradation of melanosomes oxidized by superoxide; B and C are destruction products of melanolipofuscin and lipofuscin granules, respectively, formed upon irradiation of the granules with blue light from an LED lamp. Scale D (left, curves I) - detection by absorption at 270 nm; scale I (right, curves II)—fluorescence detection at an excitation wavelength of 270 nm and emission at 380 nm. The numbers (1-22) indicate the peaks in the chromatograms.
Figure 7.
PCA score plot of RPE pigment granules. Suspension of lipofuscin (LG) melanolipofuscin (MLG) granules were irradiated by a white light LED source with energy of 20 mW/cm2 for 2.5 hours. Ellipse marked 95% confidence interval.
Figure 7.
PCA score plot of RPE pigment granules. Suspension of lipofuscin (LG) melanolipofuscin (MLG) granules were irradiated by a white light LED source with energy of 20 mW/cm2 for 2.5 hours. Ellipse marked 95% confidence interval.
Figure 8.
Scheme of the mechanisms of melanin degradation in the melanolipofuscin granule.
Figure 8.
Scheme of the mechanisms of melanin degradation in the melanolipofuscin granule.
Table 1.
The ions with enlarged yields in melanolipofuscin granules according to mass spectra data.
Table 1.
The ions with enlarged yields in melanolipofuscin granules according to mass spectra data.
| Ions |
m/z |
Ions |
m/z |
Ions |
m/z |
| CH2N+
|
28,02 |
C3H3O+
|
55,02 |
C2H6N3+
|
72,05 |
| C2H4+
|
28,03 |
C3H6N+
|
56,05 |
C2H7N3+
|
73,06 |
| CH4N+
|
30,04 |
CH6N3+
|
60,06 |
C4H6NO+
|
84,04 |
| C2H3O+
|
43,02 |
C4H6N+
|
68,05 |
C5H10N+
|
84,08 |
| CH2NO+
|
44,01 |
C4H5O+
|
69,03 |
C4H5O2+
|
85,04 |
| C2H6N+
|
44,05 |
C5H10+
|
70,07 |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).