1. Introduction
Lung cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in the world, and its incidence and mortality are increasing every year [
1]. About 80% lung cancer patients are diagnosed with non-small lung cancer (NSCLC) [
2]. Currently, platinum-based chemotherapeutics are the main chemotherapeutic methods for the treatment of lung cancer, among which cisplatin is a common chemotherapy drug [
3,
4]. During the treatment with cisplatin, patients often develop drug resistance, resulting in poor chemotherapy effect and tumor recurrence [
5,
6]. Therefore, how to overcome cisplatin resistance, enhance the sensitivity of cancer cells to cisplatin, and develop new therapeutic strategies are urgent clinical problems.
Z-ligustilide belongs to the phthalide class of compounds, and is mostly in the Angelica sinensis and Chuangxiong. Z-Ligustilide has been found to have anti-tumor activity in many tumors. For example, in glioblastoma, Z-ligustilide reduces cell migration by decreasing the expressions of the Rho GTPases [
7]. In breast cancer, Z-ligustilide inhibits autophagy and accumulates DNA damages to overcome tamoxifen resistance [
8]. In lung cancer, Z-ligustilide inhibits cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis by glycolysis [
9]. But whether Z-ligustilide can reverse cisplatin resistance in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer has not yet been reported.
Metabolic reprogramming is a hallmark of malignancy [
10]. Lipid metabolism reprogramming has gradually been recognized as a key mechanism for promoting cancer cell survival and proliferation [
11,
12], and is closely related to the development of drug resistance [
13]. Gefitinib-resistant and gefitinib-sensitive NSCLC cells exhibited distinct phospholipids compositions, revealing phospholipid remodeling during drug resistance [
14].
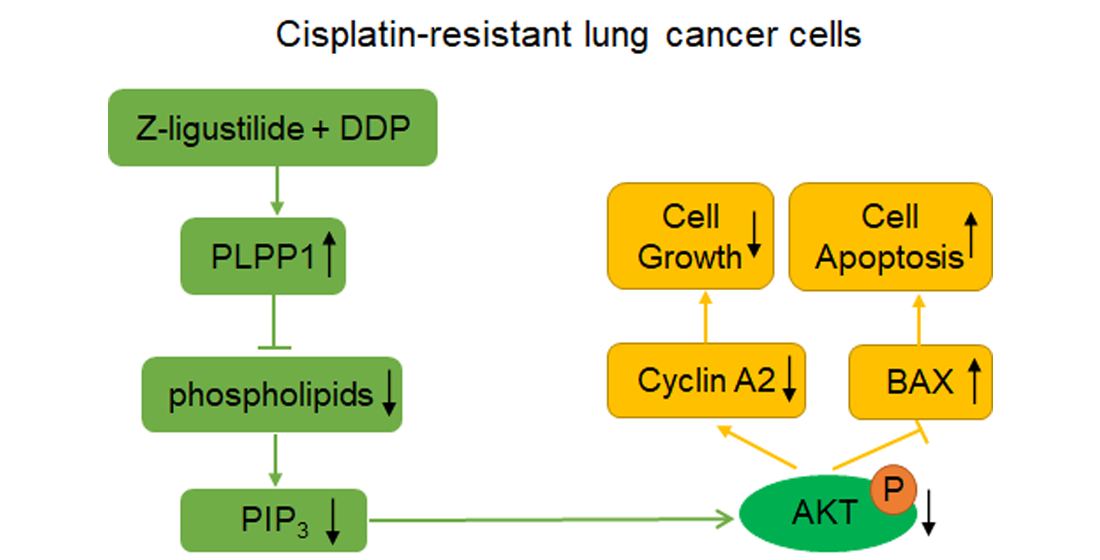
In this study, through molecular biology experiments, we confirmed that Z-ligustilide combined with cisplatin (Z-ligustilide+cisplatin) reduced the resistance of cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. Through lipid metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis, we revealed that PLPP1-mediated phospholipid synthesis participated in the reversal of resistance.
3. Discussion
Lung cancer is the malignant tumor with the highest morbidity and mortality in the world, and its five-year survival rate is less than 20% [
24,
25]. The early stage of lung cancer is relatively insidious, and the course of lung cancer develops rapidly. Most of the patients have been in the middle and late stages when they are diagnosed, they cannot undergo surgical resection due to the missed best treatment time [
26]. At present, the treatment of NSCLC mostly adopts platinum drug-based combination chemotherapy. The most widely used chemotherapy drug is cisplatin, and cisplatin has the advantages of wide anti-cancer range and strong effect in the treatment of lung cancer. In the process, cisplatin shows a good therapeutic effect, but long-term application will cause tumor cells to develop resistance, resulting in poor therapeutic effect [
27]. Therefore, in order to improve clinical treatment effect of patients with lung cancer, it is very important to find new drug against drug resistance.
Z-Ligustilide, also known as 3-butenyl-4,5-dihydro-1 (3H)-isobenzofuranone, is the main active ingredient of Chinese medicine Angelica volatile oil. In recent years, it is found that Z-ligustilide has anti-tumor activity in various tumors. For example, Z-ligustilide can induce cell death and oxidative stress by epigenetically transcriptional regulation of Nrf2 in prostate cancer [
28]. In addition, Z-ligustilide can increase the sensitivity of breast cancer to tamoxifen and reduce chemoresistance during breast cancer treatment by inhibiting autophagy and promoting caspase-independent cell death [
29]. However, the role of Z-ligustilide in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer has not been reported. In this study, we found that cell viability was obviously reduced, cell proliferation was inhibited and cell apoptosis was increased in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells with the treatment of Z-ligustilide+cisplatin.
PLPP1 catalyzed the formation of diacylglycerol (DAG) from phosphatidic acid (PA), and participated in lipid metabolism and signal transduction. It has been reported that loss of the phospholipid phosphatase Pah1 in yeast reduced DAG production, resulting in reducing level and synthesis of TGs and increasing level and synthesis of phospholipids [
18,
19]. Phospholipids are composed of glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelins. Glycerophospholipids include PC, PE, PS, PG, PI and PA. Changes in PC, PE, and PS can alter the properties of cell membranes and affect signal transduction and biological processes, thereby affecting tumor development and drug resistance [
30,
31,
32]. We discovered that PLPP1 was upregulated in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells with the treatment of Z-ligustilide+cisplatin compared with cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. Low expression of PLPP1 was strongly associated with poor prognosis. PLPP1 silence alleviated the effects on cell viability, cell cycle, cell apoptosis and phospholipid synthesis mediated by Z-ligustilide+cisplatin. Altered phospholipids are closely related to the activation of the AKT signaling pathway [
21]. We observed the inhibition of p-AKT expression and the decrease of PIP
3 levels in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer treated with Z-ligustilide+cisplatin, however, the knockdown of PLPP1 reversed the effects. The results demonstrated that the decrease in phospholipids mediated by PLPP1 reduced the levels of PIP
3, ultimately inhibiting the activation of AKT.
In summary, our study provided a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of cisplatin-resistant lung cancer, and elucidated the specific action mechanism of Z-ligustilide+cisplatin.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell culture
A549 (human lung adenocarcinoma cell line) was purchased from Shanghai Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China), and A549/DDP (cisplatin-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cell line) was purchased from BeNa Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Hebei, China). H460 (human lung cancer cell line) and H460/DDP (cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cell line) were purchased from YaJi Biological (Shanghai, China). These cells were cultured in DMEM/high glucose medium or RPMI 1640, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 units/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin in an incubator with 5% CO2, 37 °C.
4.2. Reagents and antibodies
Cisplatin and Z-ligustilide were purchased from MedChemExpress Company (Shanghai, China). The following primary antibodies for BAX (Proteintech Technology, Wuhan, China ), PI3K (Proteintech Technology, Wuhan, China), PLPP1 (Proteintech Technology, Wuhan, China) and Cyclin A2 (Proteintech Technology, Wuhan, China), AKT (Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, USA), phosphor-Akt (Ser473) (Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, USA), Cleaved-Caspase 3 (Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, USA) and GAPDH (Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, USA), PI3K p85α (phospho-Tyr607) (Bioworld Technology, Minnesota, USA), Cyclin E1 (HUABIO Technology, Hangzhou, China) and PPAP2A (PLPP1) (Novus Technology, Colorado, USA) were used.
4.3. Cell counting kit-8 assay
Cell viability was detected by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). Briefly, cells were seeded in 96-well plates containing 3x103 cells and 100 μL medium per well. After the cells adhered, different doses of Z-ligustilide and cisplatin were added to stimulate the cells for 24 h. 10 μL CCK-8 solution was added to each well, and placed in a 37 °C incubator for 1 h in the dark. Then the absorbance was measured at 450 nm.
4.4. Cell apoptosis assay
PE Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit (BD Pharmingen, San Diego, CA) was used to assess the percentage of apoptotic cells. Firstly, the cells were treated with cisplatin and Z-ligustilide alone or in combination for 24 h. Then, the cells were washed with PBS, digested with trypsin, and centrifuged. Next, 200 μL 1X Binding Buffer was added to disperse the cells, and 5 μL PE Annexin V and 5 μL 7-AAD were added to mix gently, the cells were incubated at room temperature for 15 min away from light. Finally, the apoptotic cell rates were analyzed by flow cytometry.
4.5. Cell cycle assay
Cisplatin- and Z-ligustilide-stimulated cells were fixed with prechilled 70% ethanol overnight, and then the cells were analyzed by Cycle and Apoptosis Analysis Kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s instruction.
4.6. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis
The cells were seeded in 10 cm dishes and stimulated with cisplatin and Z-ligustilide alone or in combination for 24 h. The cells were washed three times with 10 mL PBS, and quenched with liquid nitrogen. Next, cells were collected with 1 mL extractant (80% methanol containing internal standard), and added to chloroform and ultrapure water sequentially, and vortexed for 30 s. Centrifuge at 13000 g for 15 min at 4 °C. 400 μL hydrophobic layer was aspirated and then lyophilized. Quality control (QC) samples were lyophilized in the same volume. Add 30 μL chloroform/methanol (2: 2, v: v) solution, vortex for 30 s to reconstitute, and then add 70 μL acetonitrile/isopropanol/MilliQ water (65: 30: 5) containing 5 mM ammonium acetate, vortex for 30 s to dilute.
UPLC-Q-Exactive HF MS was used for nontargeted lipidomic analysis. The column was an ACQUITY UPLC C8 Column (100 x 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm). The column temperature was 60℃ and the flow rate was 0.3 mL/min. The injection chamber temperature was 10℃. Injection volume was 5 μL. Mobile phase A was 60% acetonitrile/MilliQ water containing 10 mM ammonium acetate, and phase B was 10% acetonitrile/isopropanol containing 10 mM ammonium acetate. Mass spectrometry ion source sheath gas flow rate was 45 arb, and auxiliary gas flow rate was 10 arb. Spray voltage was 3.5 kV (ESI+) and 3.0 kV (ESI-). Capillary temperature was 320℃, and auxiliary gas temperature was 350 °C. Resolution was 12e4. The full scanning modes was used, and scan ranges was 200-1100 m/z (ESI+) and 120-1600 m/z (ESI-).
4.7. RNA sequencing
Total RNA was isolated using a TRIzol total RNA extractibn kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China), which yielded > 2 μg of total RNA per sample. RNA quality was examined by 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis and spectrophotometry. Illumina HiSeq library construction was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions (Illumina, California, USA). Oligo-dT primers were used to transverse mRNA to obtain cDNA (APExBIO, Houston, USA). The second cDNA strand was synthesized by amplifying the cDNA, and was purified using magnetic beads. After library construction, library fragments were enriched by PCR amplification and selected according to a fragment size of 350-550 bp. The library was quality-assessed using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, California, USA). The library was sequenced using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 sequencing platform (Paired end150) to generate raw reads.
4.8. Western blot
Cells were harvested and lysed with RIPA (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) containing protein and phosphatase inhibitors (APExBIO, Houston, USA). Total protein extract (20 μg) was loaded in 4-20% SDS-PAGE. The protein was transferred to PVDF membrane, and was blocked with 5% milk. Subsequently, the protein was incubated with primary antibodies and second HRP linked antibodies. Finally, the protein was visualized using ECL Chemiluminescence Chromogenic Solution (Tanon, Shanghai, China).
4.9. Real-time PCR
Total RNA was isolated with Trizol Reagent Kit (Takara, Tokyo, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The cDNA was generated by using PrimeScript RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Takara, Tokyo, Japan). Real-time PCR was carried out by using TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (Takara, Tokyo, Japan) operating on LightCycler 96 Real-time PCR system. The primers sequencings were as follows:
GAPDH (forward): TCCAAAATCAAGTGGGGCGA
GAPDH (reverse): TGATGACCCTTTTGGCTCCC
Cyclin A2 (forward): GATTTCGTCTTCCAGCAGCAG
Cyclin A2 (reverse): ATCTGACAAGCATCGGGACC
Cyclin E1 (forward): AGAGGAAGGCAAACGTGACC
Cyclin E1 (reverse): GAGGCTTGCACGTTGAGTTT
BCL2 (forward): GAACTGGGGGAGGATTGTGG
BCL2 (reverse): CCGTACAGTTCCACAAAGGC
BAX (forward): GACATTGGACTTCCTCCGGG
BAX (reverse): GGGACATCAGTCGCTTCAGT
PLPP1 (forward): CTGGCTGGATTGCCTTTTGC
PLPP1 (reverse): AACAGACAGGGTTTCTCCAAGA
4.10. Immunohistochemistry
Human lung cancer tissue chip was purchased from Outdo Biotech (Shanghai, China). The tissue chip used was HLugA180Su04. Immunohistochemical procedures and evaluation methods were performed [
15].
4.11. PIP3 measurements
PIP3 levels were analyzed by Human PIP3 ELISA Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (COIBO BIO, Shanghai, China).
4.12. PI3K kinase assay
PI3K kinase activity was examined by Human PI3K ELISA Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (COIBO BIO, Shanghai, China).
4.13. Statistical analysis
The experiments are repeated three or more times. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was measured by Student’s t-test (unpaired, two-tailed) with
p<0.05 indicating significance. Statistical analysis was performed with Prism software (La Jolla, CA, USA), FlowJo software (TreeStar, Ashland, OR), SIMCA-P software (Umetrics, Umea, Sweden) and Multi Experiment Viewer (
http://www.tm4.org).
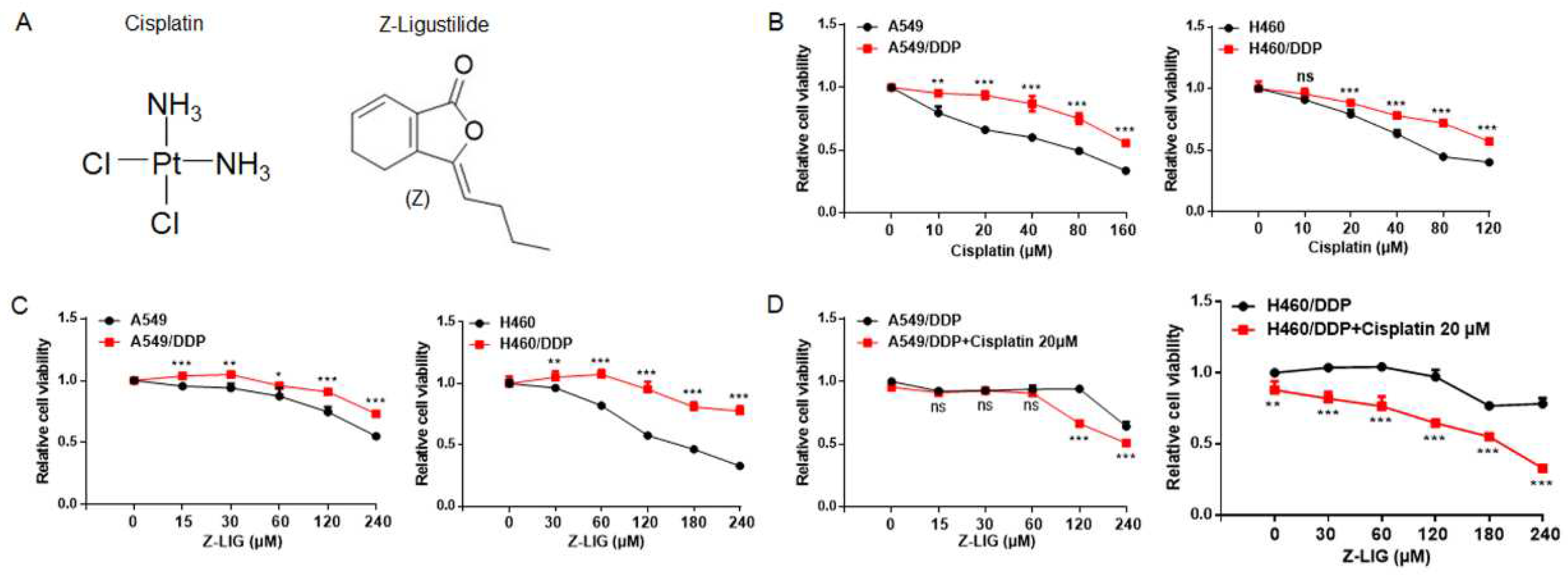
Figure 1.
Z-ligustilide inhibited cell viability of cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. (A) Chemical structures of Cisplatin and Z-ligustilide (Z-LIG). (B) Cell viability of A549 cells and cisplatin-resistant A549 (A549/DDP) cells, H460 cells and cisplatin-resistant H460 (H460/DDP) cells after treatment with cisplatin. (C) Cell viability of A549 cells and A549/DDP, H460 cells and H460/DDP cells after treatment with Z-ligustilide. (D) Cell viability of A549/DDP cells and H460/DDP cells after treatment with Z-ligustilide+cisplatin. ns, no significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.
Figure 1.
Z-ligustilide inhibited cell viability of cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. (A) Chemical structures of Cisplatin and Z-ligustilide (Z-LIG). (B) Cell viability of A549 cells and cisplatin-resistant A549 (A549/DDP) cells, H460 cells and cisplatin-resistant H460 (H460/DDP) cells after treatment with cisplatin. (C) Cell viability of A549 cells and A549/DDP, H460 cells and H460/DDP cells after treatment with Z-ligustilide. (D) Cell viability of A549/DDP cells and H460/DDP cells after treatment with Z-ligustilide+cisplatin. ns, no significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.
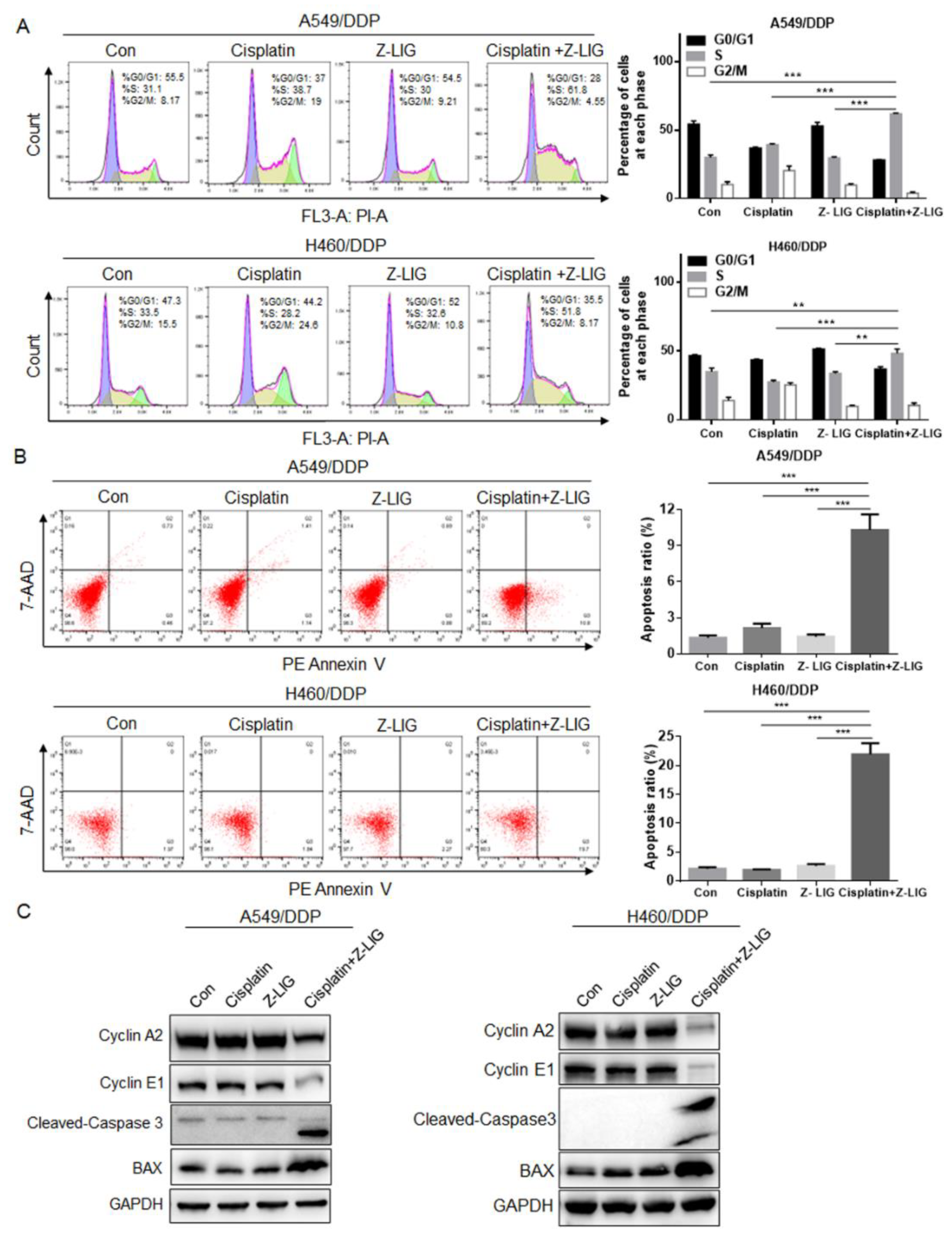
Figure 2.
Z-ligustilide+cisplatin induced S phase arrest and promoted cell apoptosis. (A) Cell cycle analysis of A549/DDP and H460/DDP, A549/DDP and H460/DDP treated with cisplatin and Z-ligustilide alone or in combination for 24h. (B) PE Annexin V apoptosis analysis of A549/DDP and H460/DDP, A549/DDP and H460/DDP treated with cisplatin and Z-ligustilide alone or in combination for 24h. (C) Protein expression of Cyclin A2, Cyclin E1, Cleaved-Caspase 3 and BAX in A549/DDP and H460/DDP, A549/DDP and H460/DDP treated with cisplatin and Z-ligustilide alone or in combination. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.
Figure 2.
Z-ligustilide+cisplatin induced S phase arrest and promoted cell apoptosis. (A) Cell cycle analysis of A549/DDP and H460/DDP, A549/DDP and H460/DDP treated with cisplatin and Z-ligustilide alone or in combination for 24h. (B) PE Annexin V apoptosis analysis of A549/DDP and H460/DDP, A549/DDP and H460/DDP treated with cisplatin and Z-ligustilide alone or in combination for 24h. (C) Protein expression of Cyclin A2, Cyclin E1, Cleaved-Caspase 3 and BAX in A549/DDP and H460/DDP, A549/DDP and H460/DDP treated with cisplatin and Z-ligustilide alone or in combination. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.
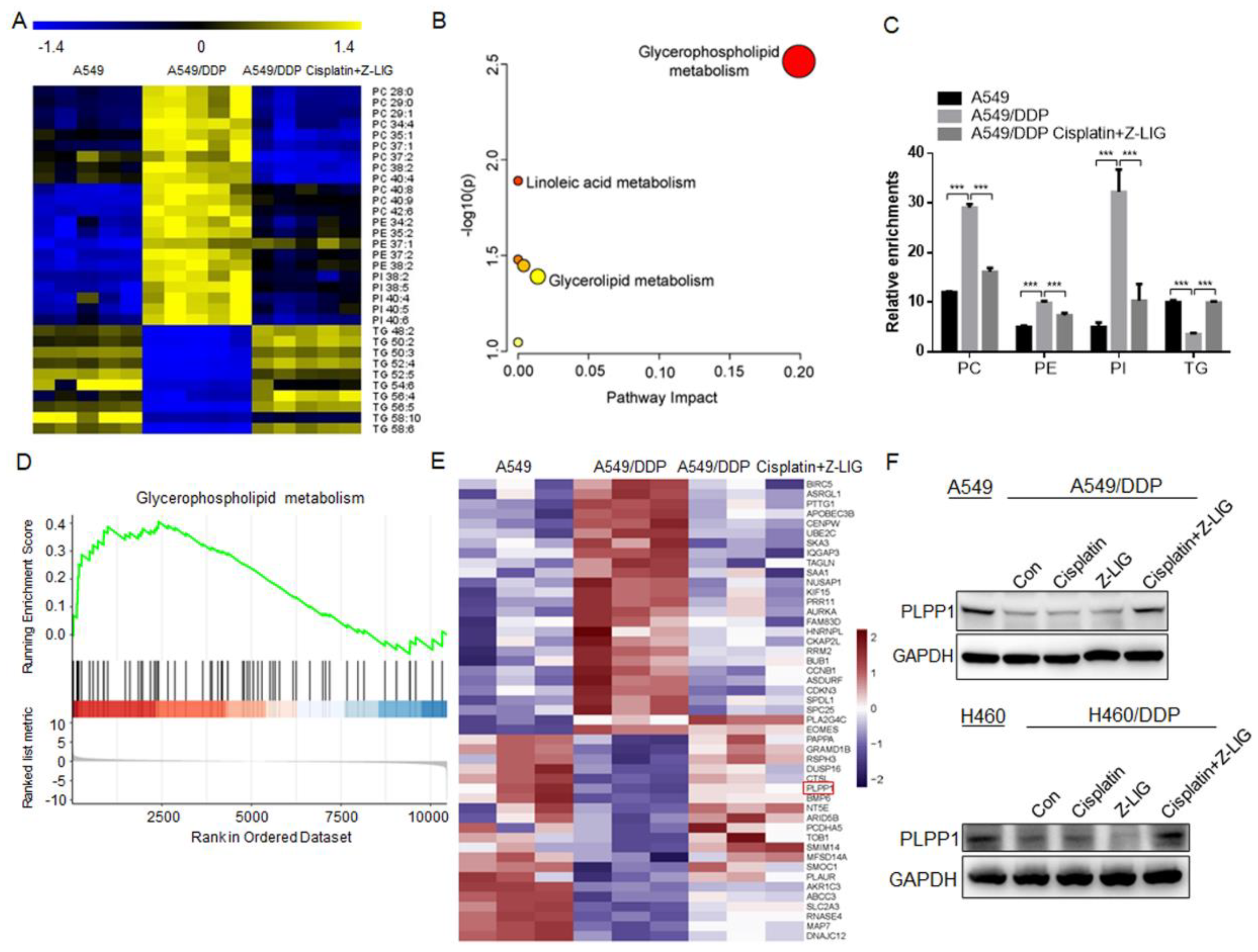
Figure 3.
Z-ligustilide+cisplatin reduced phospholipids contents and upregulated PLPP1 expression. (A) Heat map of the differential lipids in A549, A549/DDP cells and A549/DDP cells Z-ligustilide+cisplatin. (B) Pathway enrichment analysis. (C) Relative enrichment of each lipid class. ***p < 0.001. (D) GSEA analysis of the RNA-seq data. The glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway-targeted genes shows significant overlap. (E) Heat map for RNA-Seq analysis of significantly differentially expressed genes in A549 cells vs A549/DDP cells vs A549/DDP cells treated with Z-ligustilide+cisplatin. (F) Protein level of PLPP1 determined by the western blot.
Figure 3.
Z-ligustilide+cisplatin reduced phospholipids contents and upregulated PLPP1 expression. (A) Heat map of the differential lipids in A549, A549/DDP cells and A549/DDP cells Z-ligustilide+cisplatin. (B) Pathway enrichment analysis. (C) Relative enrichment of each lipid class. ***p < 0.001. (D) GSEA analysis of the RNA-seq data. The glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway-targeted genes shows significant overlap. (E) Heat map for RNA-Seq analysis of significantly differentially expressed genes in A549 cells vs A549/DDP cells vs A549/DDP cells treated with Z-ligustilide+cisplatin. (F) Protein level of PLPP1 determined by the western blot.
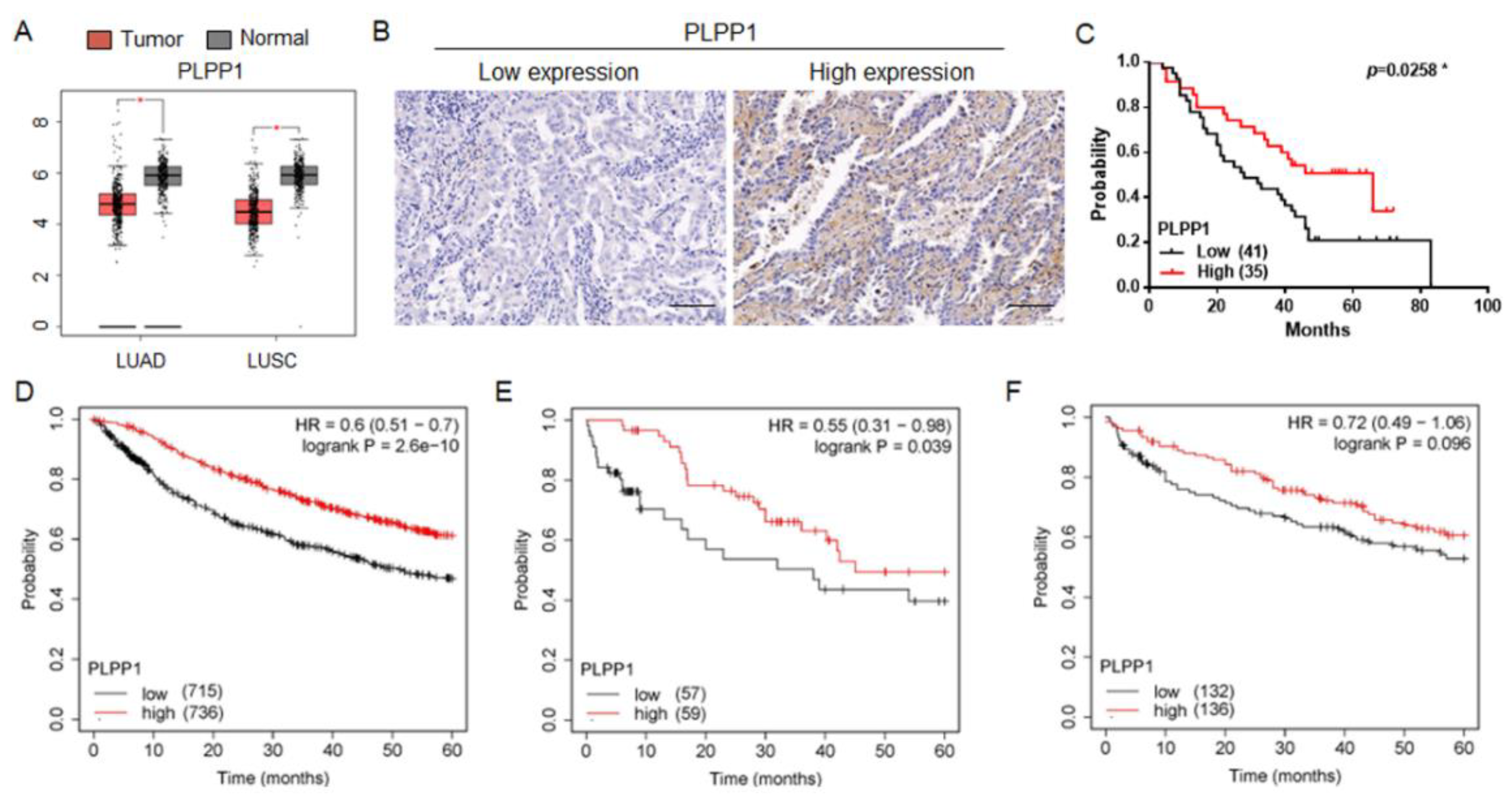
Figure 4.
PLPP1 was low expressed and associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer. (A) PLPP1 expression was detected in LUAD, LUSC, and corresponding normal tissues in the TCGA cohort. LUAD (num (T)=483; num (N)=347). LUSC (num (T)=486; num (N)=338). (B) Representative images of the immunohistochemical staining of PLPP1 in lung cancer samples. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) The association between the PLPP1 protein expression and overall survival in patients with lung cancer. Low PLPP1 expression (n=41), high PLPP1 expression (n=35). *p < 0.05. (D) The correlation between PLPP1 expression and overall survival in 1451 lung cancer patients. (E) The correlation between PLPP1 expression and overall survival in 116 lung cancer patients administered chemotherapy. (F) The correlation between PLPP1 expression and overall survival in 268 lung cancer patients without chemotherapy.
Figure 4.
PLPP1 was low expressed and associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer. (A) PLPP1 expression was detected in LUAD, LUSC, and corresponding normal tissues in the TCGA cohort. LUAD (num (T)=483; num (N)=347). LUSC (num (T)=486; num (N)=338). (B) Representative images of the immunohistochemical staining of PLPP1 in lung cancer samples. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) The association between the PLPP1 protein expression and overall survival in patients with lung cancer. Low PLPP1 expression (n=41), high PLPP1 expression (n=35). *p < 0.05. (D) The correlation between PLPP1 expression and overall survival in 1451 lung cancer patients. (E) The correlation between PLPP1 expression and overall survival in 116 lung cancer patients administered chemotherapy. (F) The correlation between PLPP1 expression and overall survival in 268 lung cancer patients without chemotherapy.
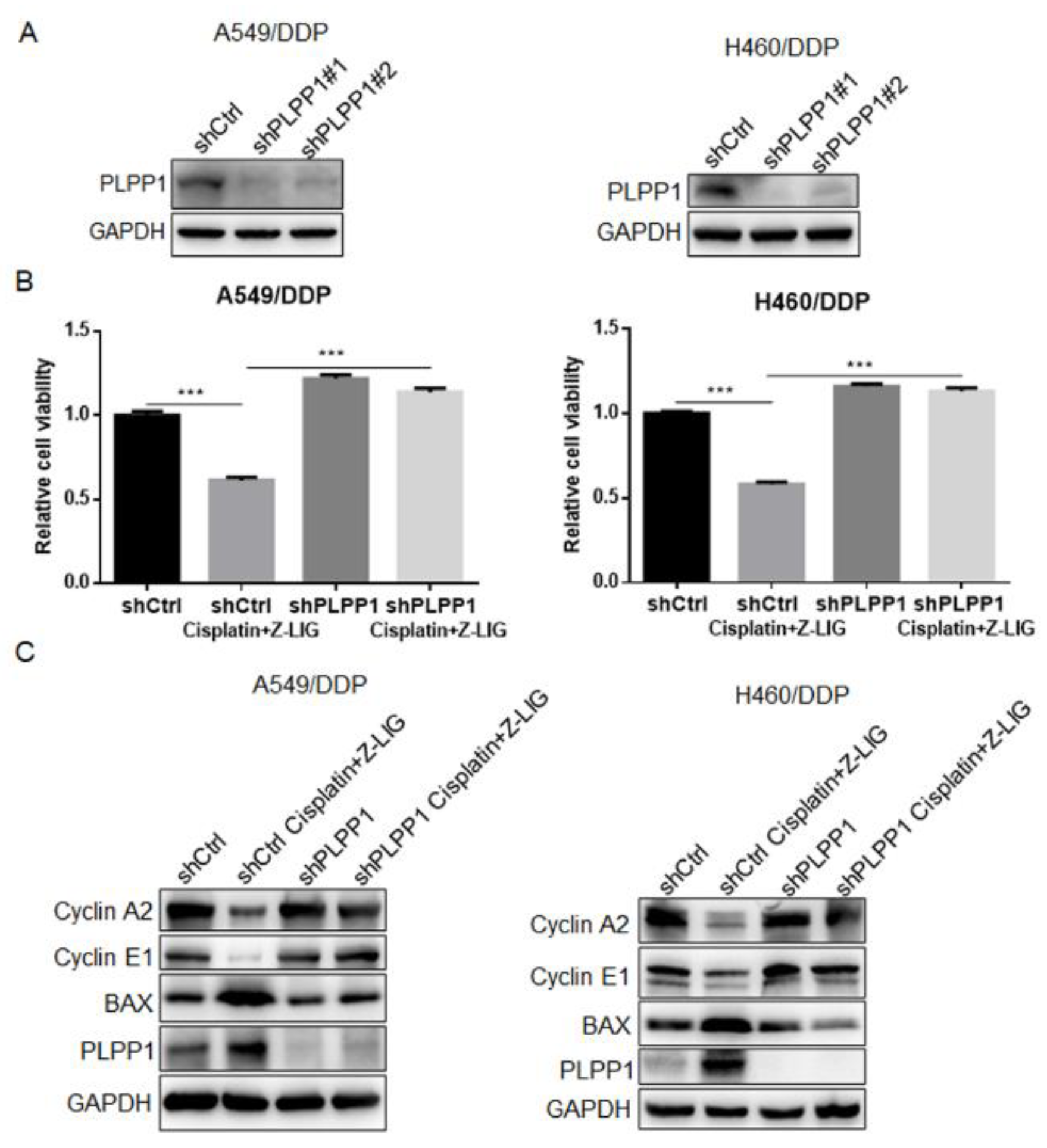
Figure 5.
Z-ligustilide+cisplatin induced the reversal of resistance mediated by PLPP1. (A) Protein expression of PLPP1 in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells, respectively. (B) Cell viability was measured in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment, ***p < 0.001. (C) Relative protein expressions in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment.
Figure 5.
Z-ligustilide+cisplatin induced the reversal of resistance mediated by PLPP1. (A) Protein expression of PLPP1 in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells, respectively. (B) Cell viability was measured in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment, ***p < 0.001. (C) Relative protein expressions in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment.
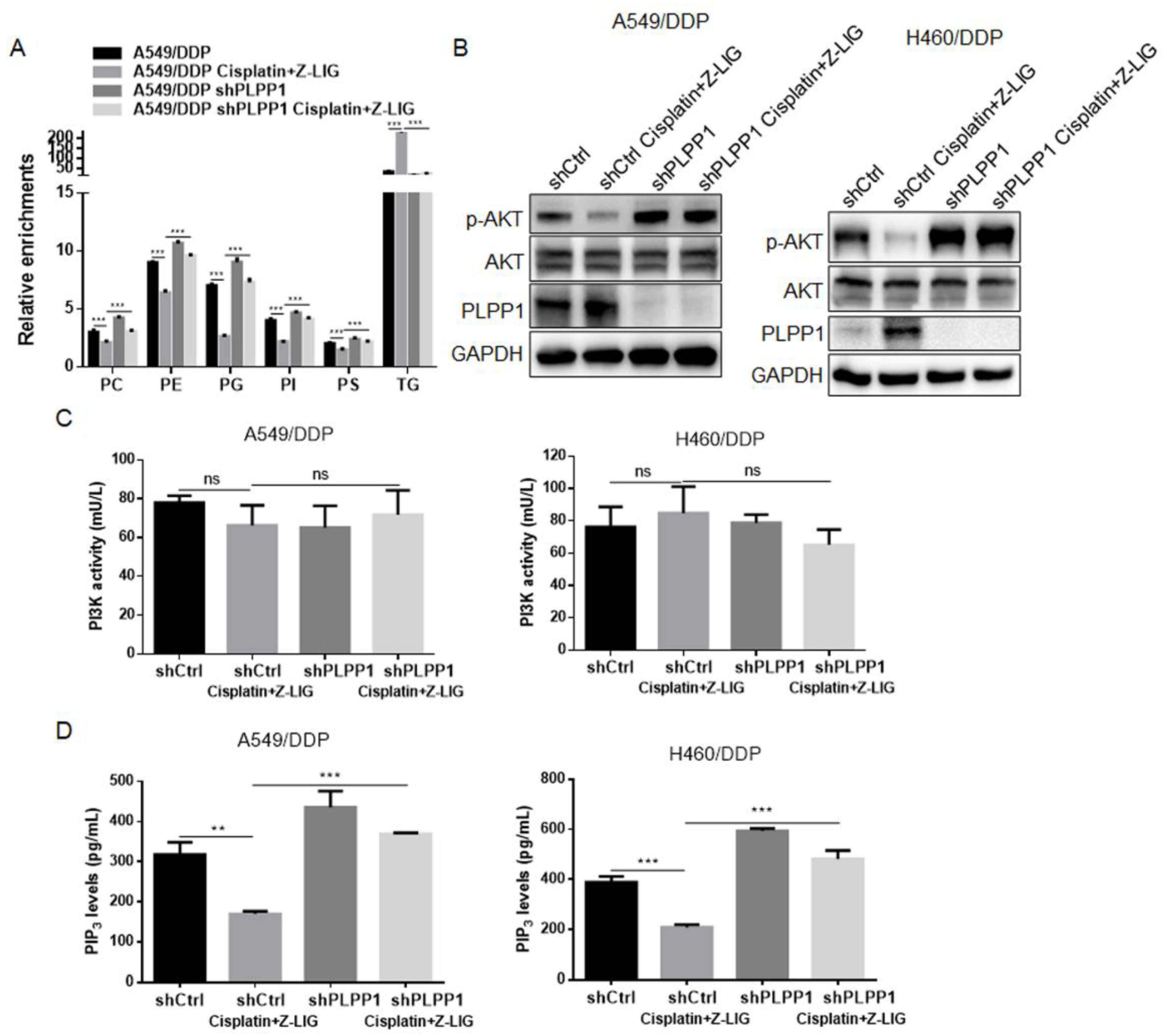
Figure 6.
Z-ligustilide+cisplatin induced the inactivation of AKT by inhibiting PLPP1-mediated phospholipid synthesis. (A) Relative enrichments of each lipid class in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment. ns, no significant, ***p < 0.001. (B) Protein expression of p-AKT in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment. (C) and (D) PI3K kinase activity assay and PIP3 levels measurements in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment. ns, no significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.
Figure 6.
Z-ligustilide+cisplatin induced the inactivation of AKT by inhibiting PLPP1-mediated phospholipid synthesis. (A) Relative enrichments of each lipid class in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment. ns, no significant, ***p < 0.001. (B) Protein expression of p-AKT in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment. (C) and (D) PI3K kinase activity assay and PIP3 levels measurements in shCtrl and PLPP1 knockdown A549/DDP and H460/DDP cells with or without Z-ligustilide and cisplatin combination treatment. ns, no significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.