Submitted:
21 July 2023
Posted:
25 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods / Research Methodology
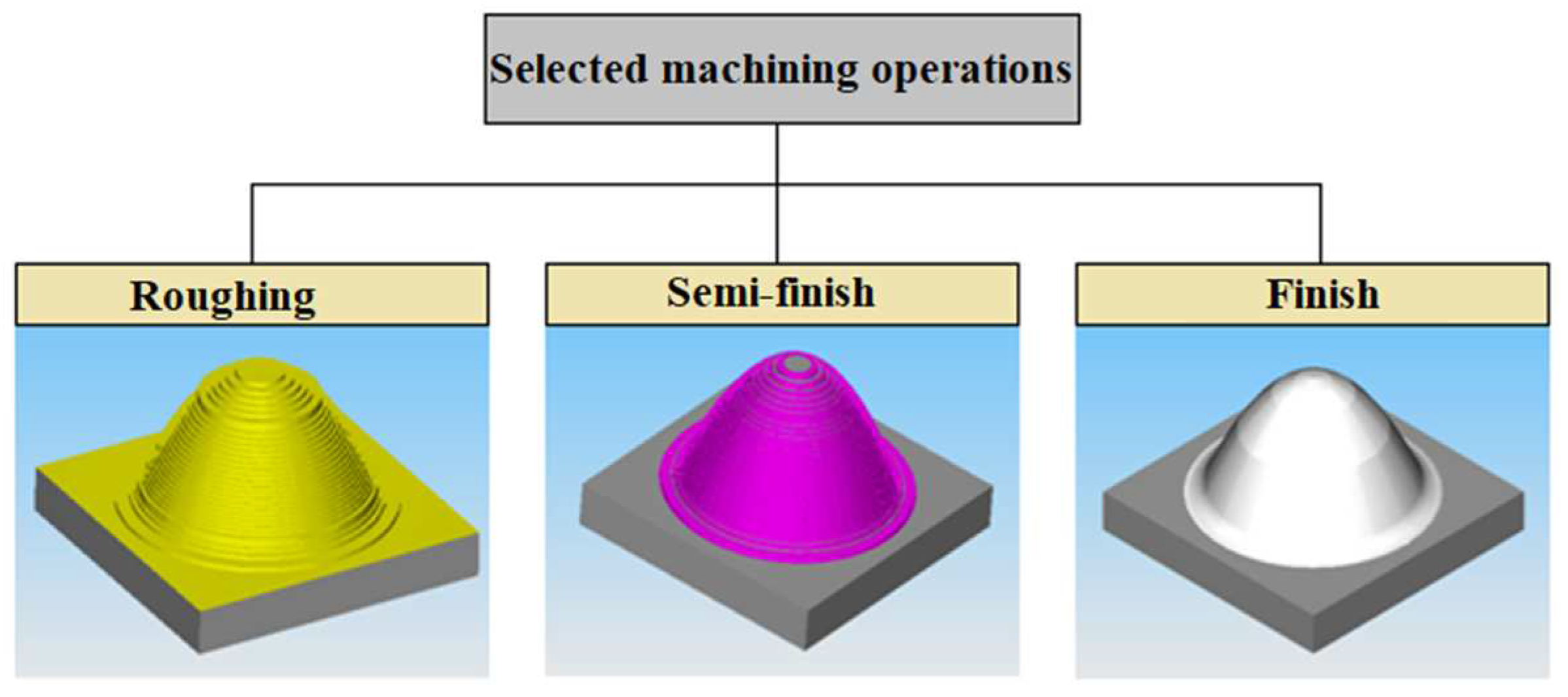
- Roughing operation – end mill tool D18 mm, two interchangeable plates marked APXT11T3PDR-MA, manufactured by Korloy, depth of cut ap = 3 mm, side step ae = 3 mm, toolpath tolerance T = 0.1 mm, surface allowance P = 0.5 mm
- Semi-finish operation – end mill D 8 mm with two-flute cutters marked as 273618.080, cutting material HSS Co8, depth of cut ap = 0.5 mm, side step ae = 0.5 mm, strategy Constant Z, toolpath tolerance T = 0.1 mm, surface allowance P = 0.2 mm
- Finishing operation - ball end mill D 6 mm with two-flute cutters marked as 511418.060, cutting material HSS Co8, side step ae = 0.25 mm, toolpath tolerance T = 0.01 mm, scallop height SH = 0.01 mm
- Comparison and evaluation of surface topography using a Keyence VHX-5000 digital microscope (Keyence International, Mechelen, Belgium).
- Roughness evaluation using device Alicona InfiniteFocus G5 (Alicona Imaging GmbH, Raaba/Graz, Austria).
- Evaluation of shape deviations using coordinate measuring machine ZEISS Duramax HTG (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
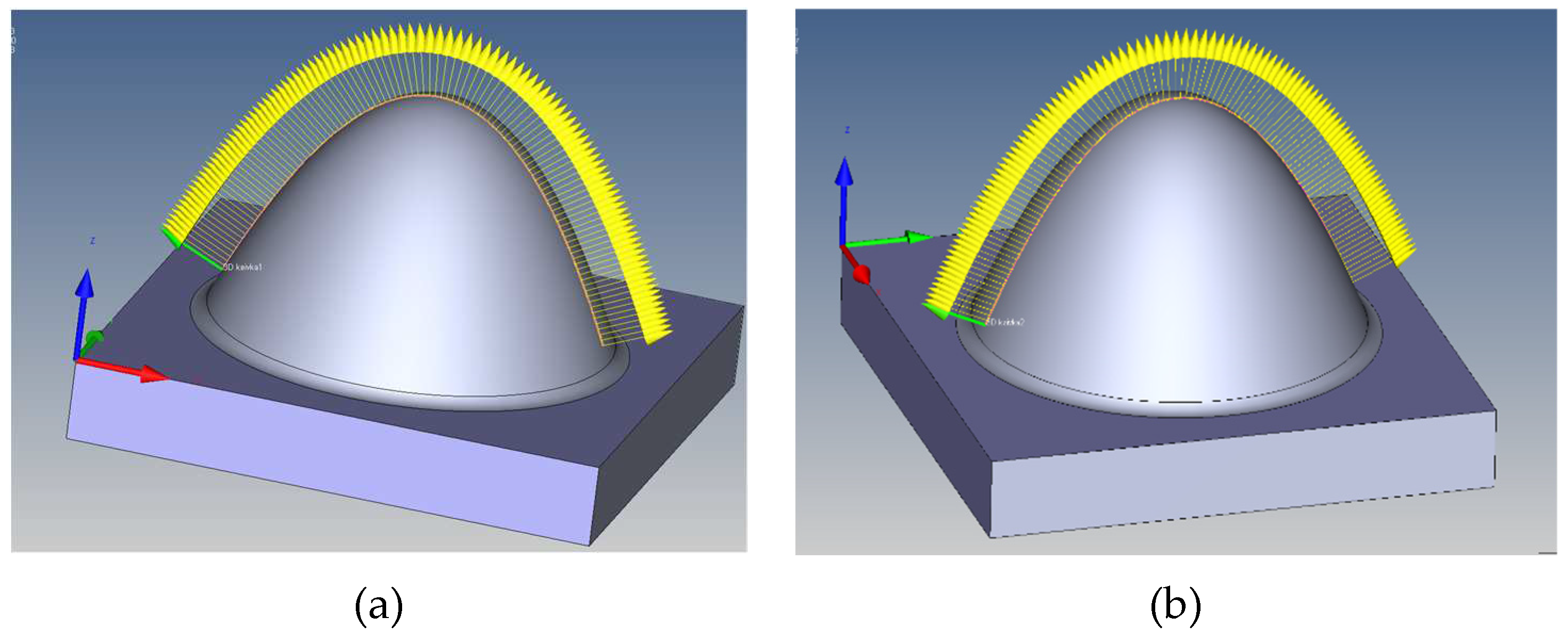
2.1. Topography observation methodology
2.2. Surface roughness analysis methodology
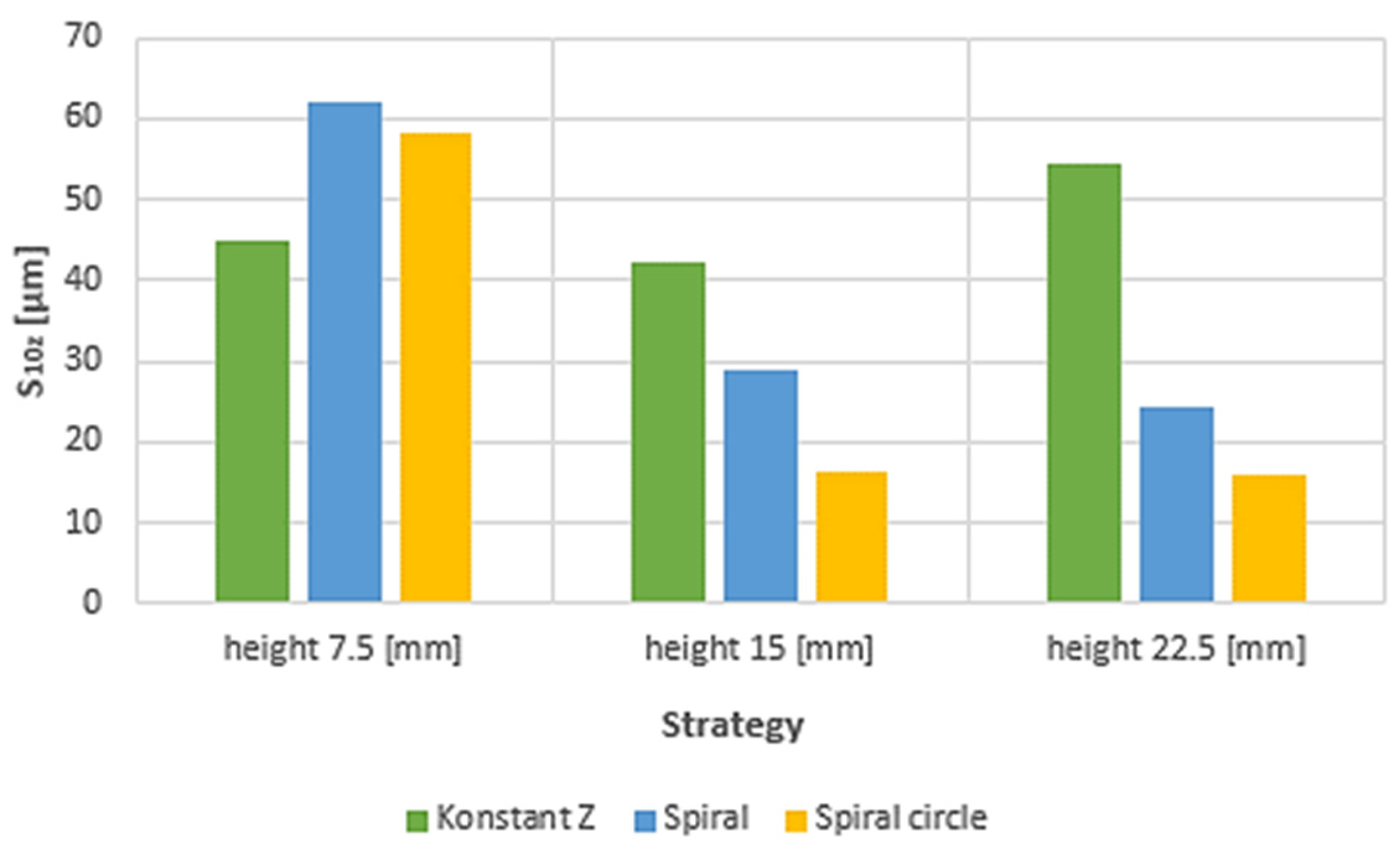
- S10z - is sensitive to changes in the topography of the observed surface; an important parameter in evaluating of the surface functionality (affects dimensional accuracy of fitted surfaces, tightness of joints, etc.).
- Sa - is a powerful statistical parameter that is used to regulate and control pro-duction.
- Ssk - gives us information about the protrusions and depressions of the topography of the observed surface. If it takes a positive value protrusion dominate and if it takes a negative value depressions dominate.
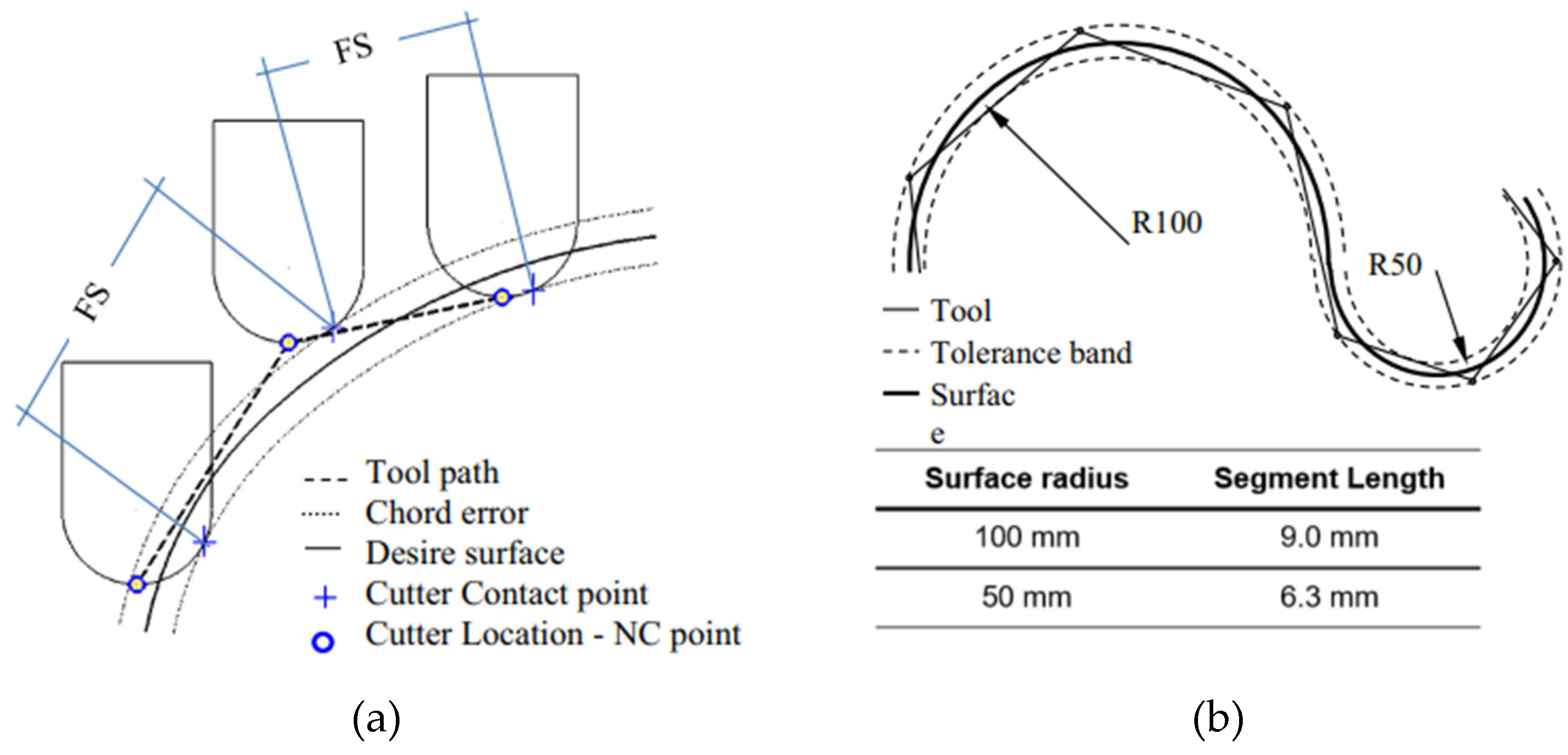
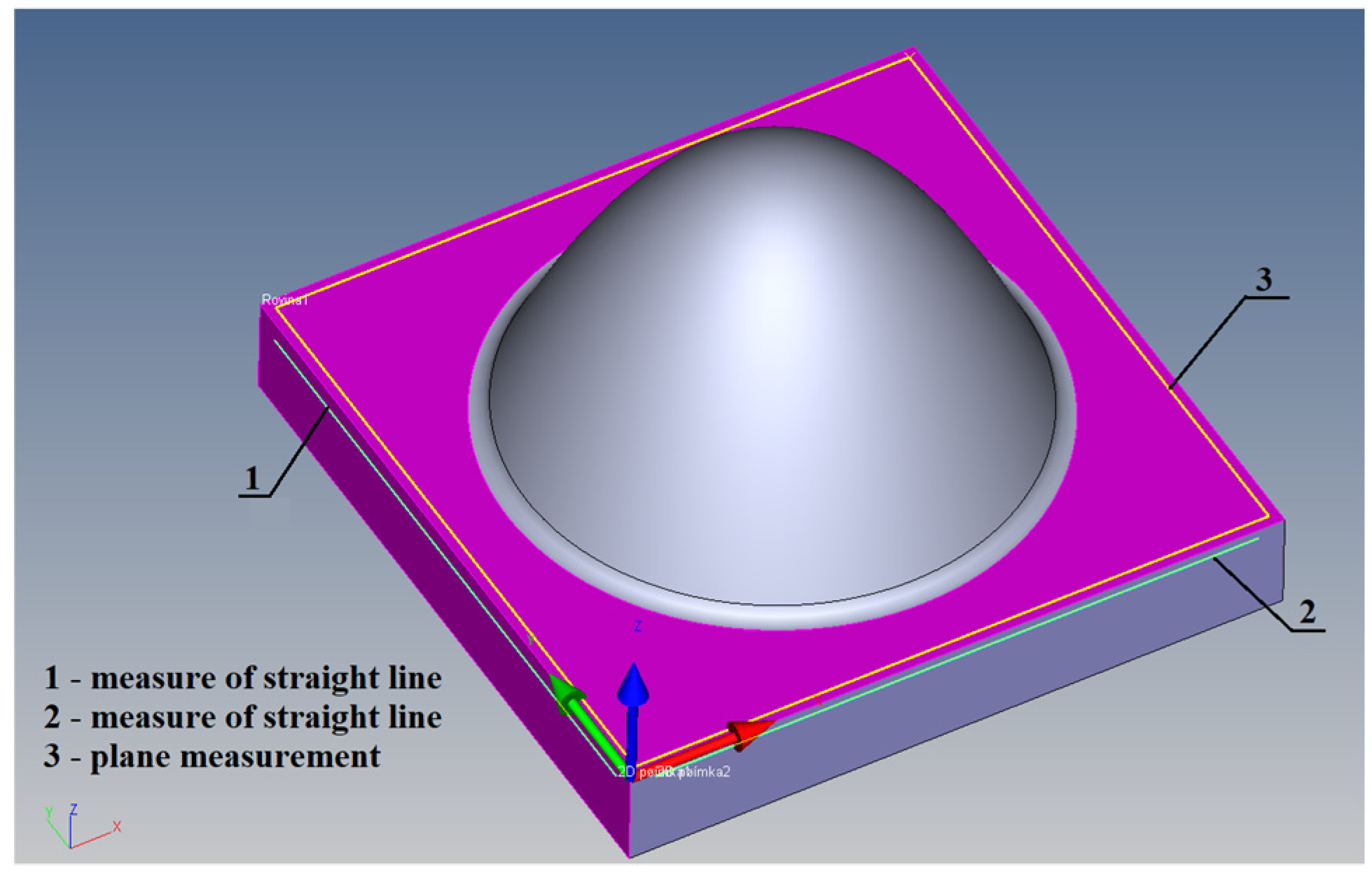
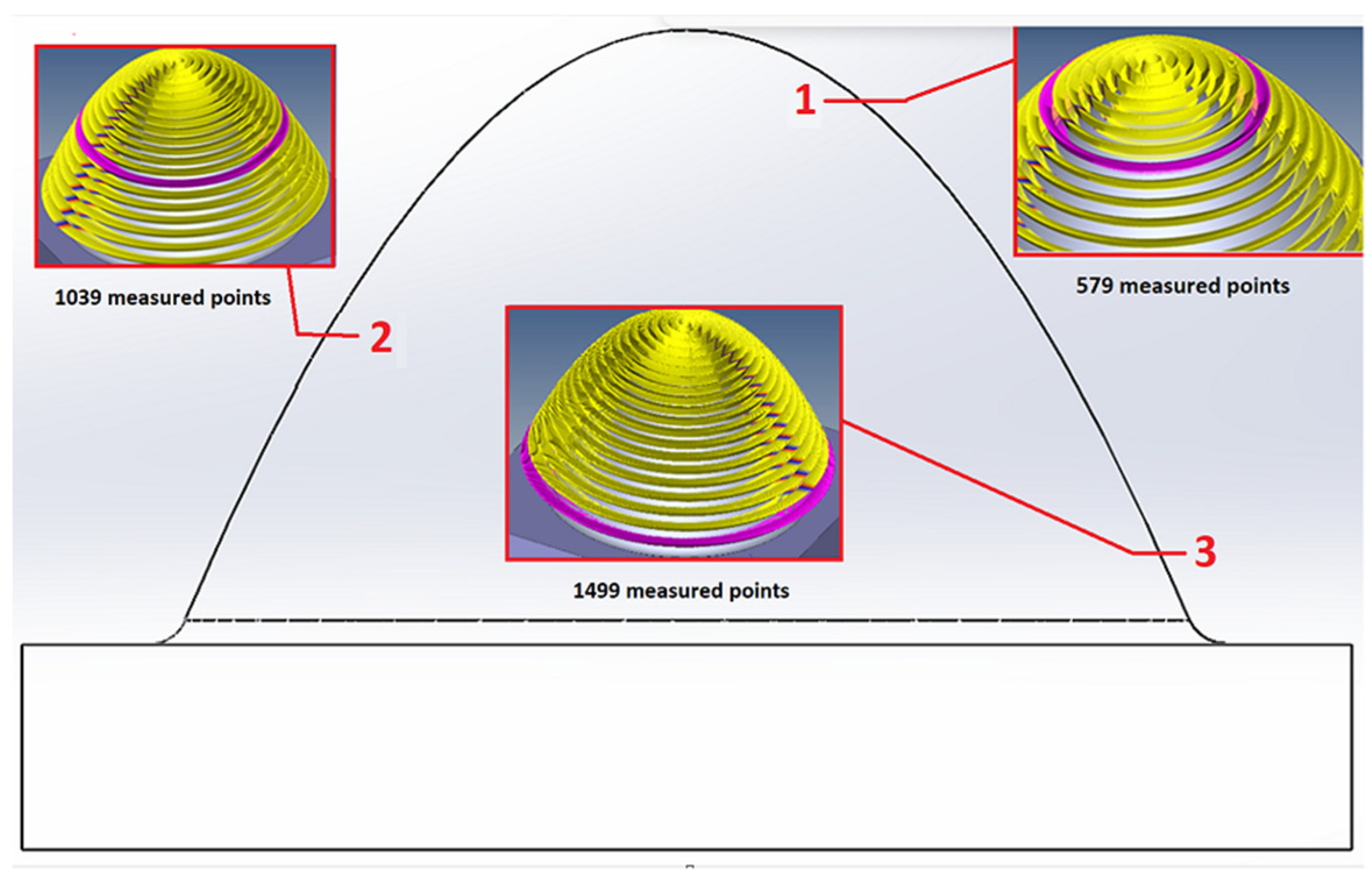
2.3. Methodology of the shape deviation
3. Results
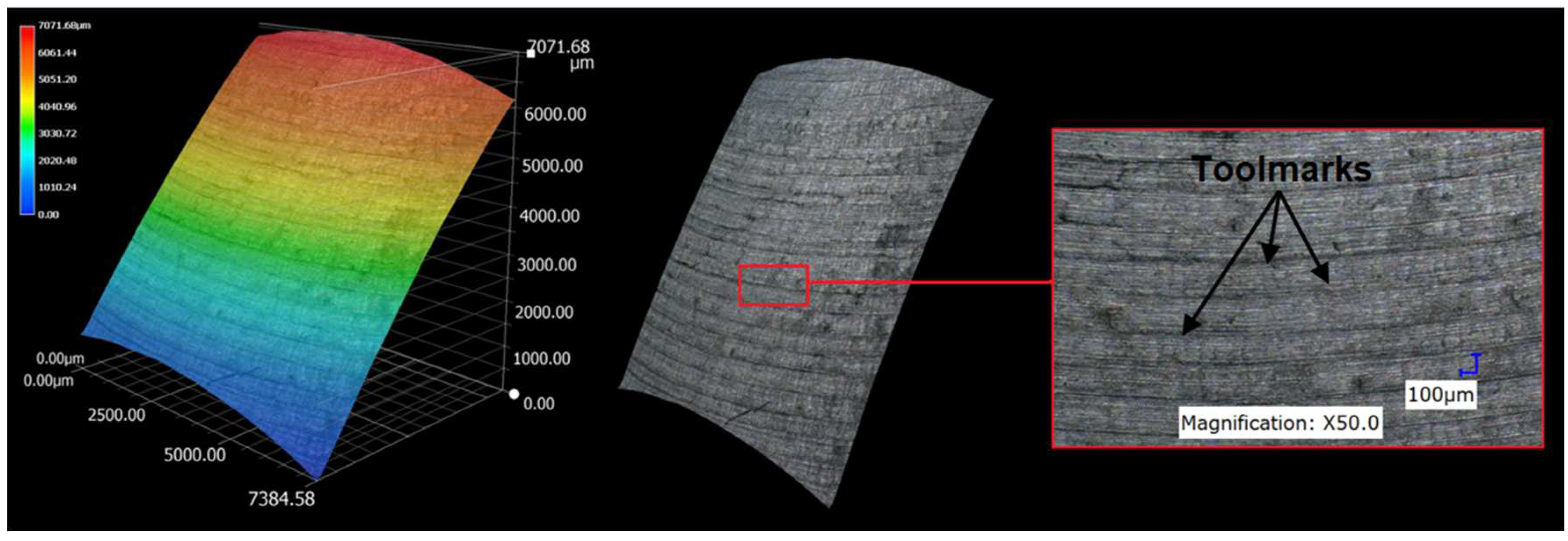
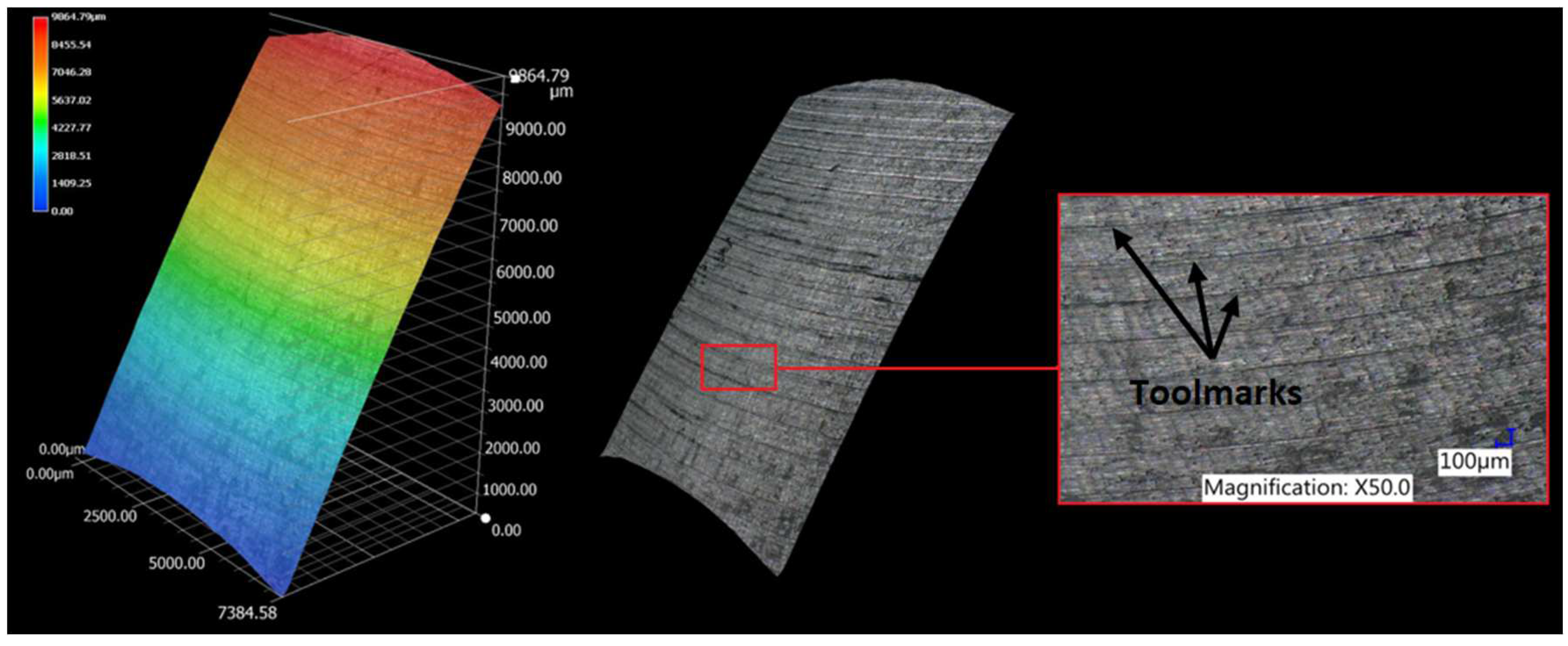
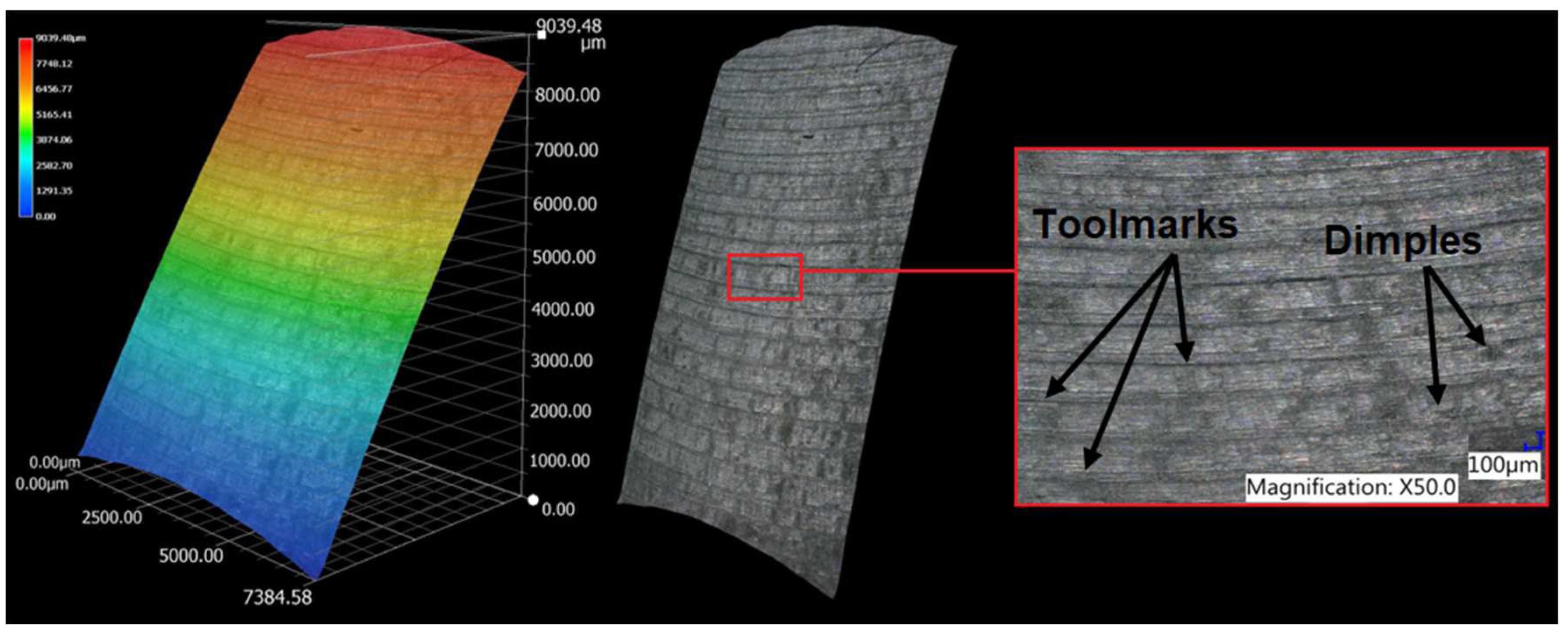
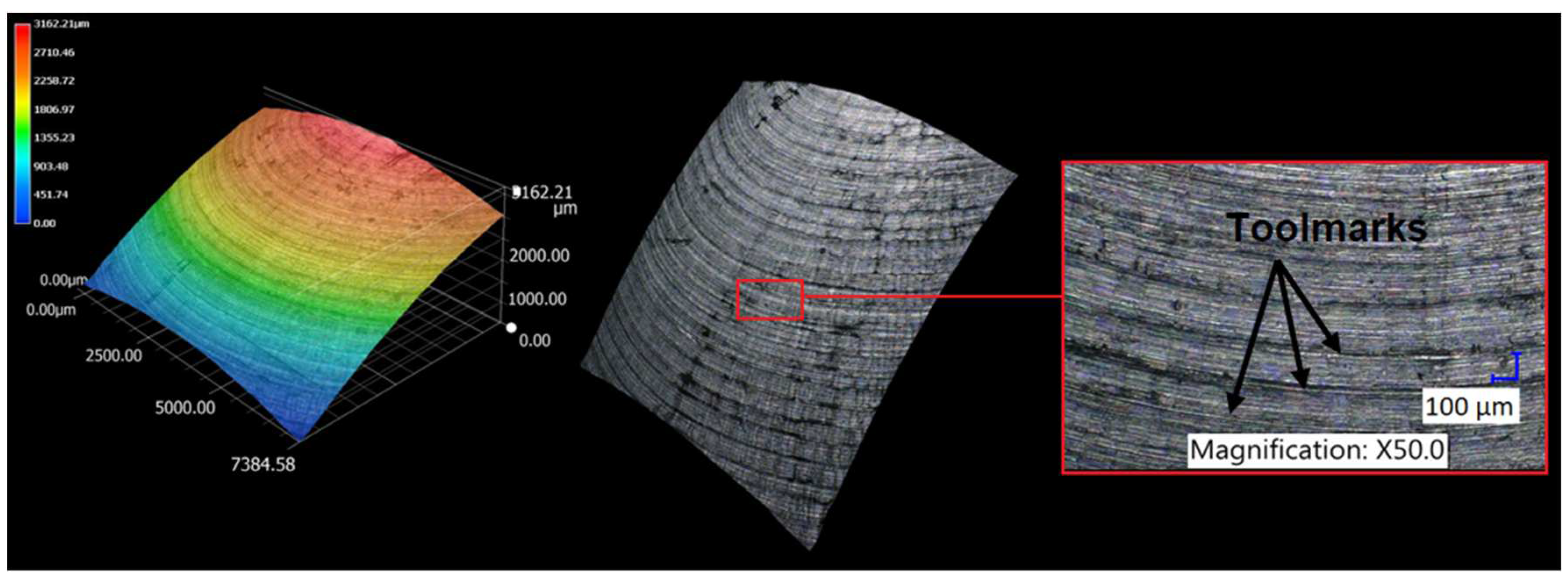
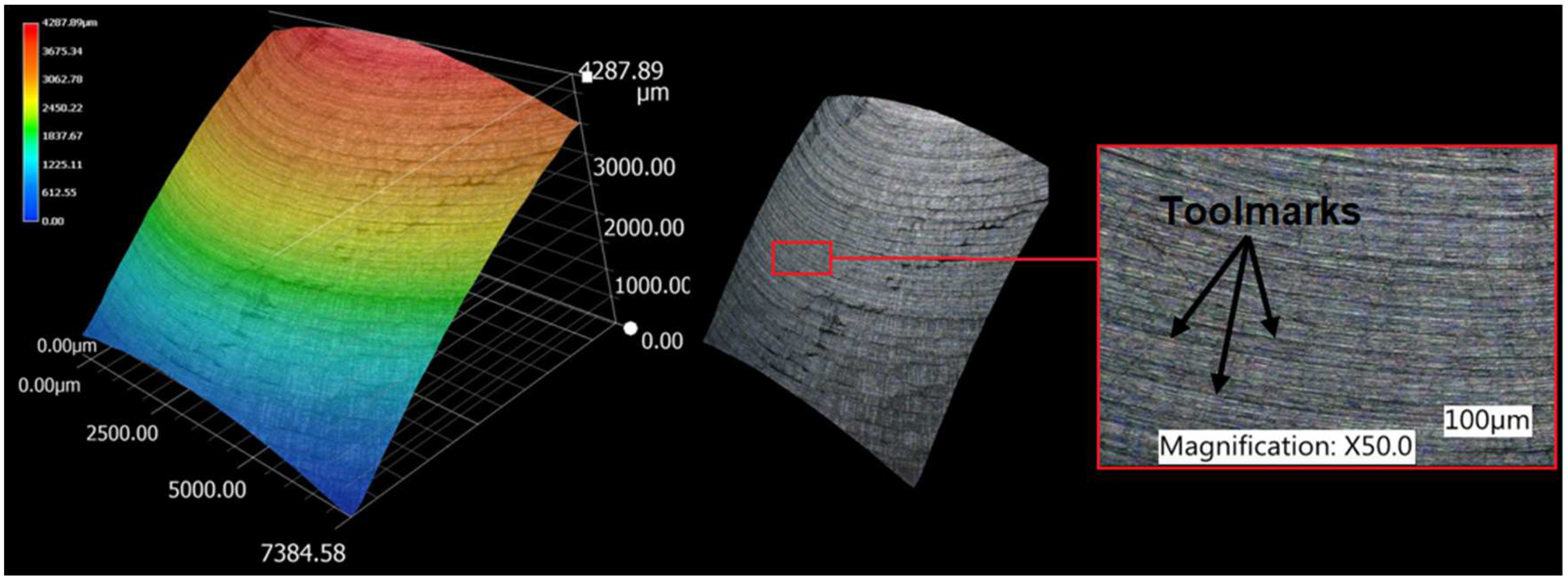
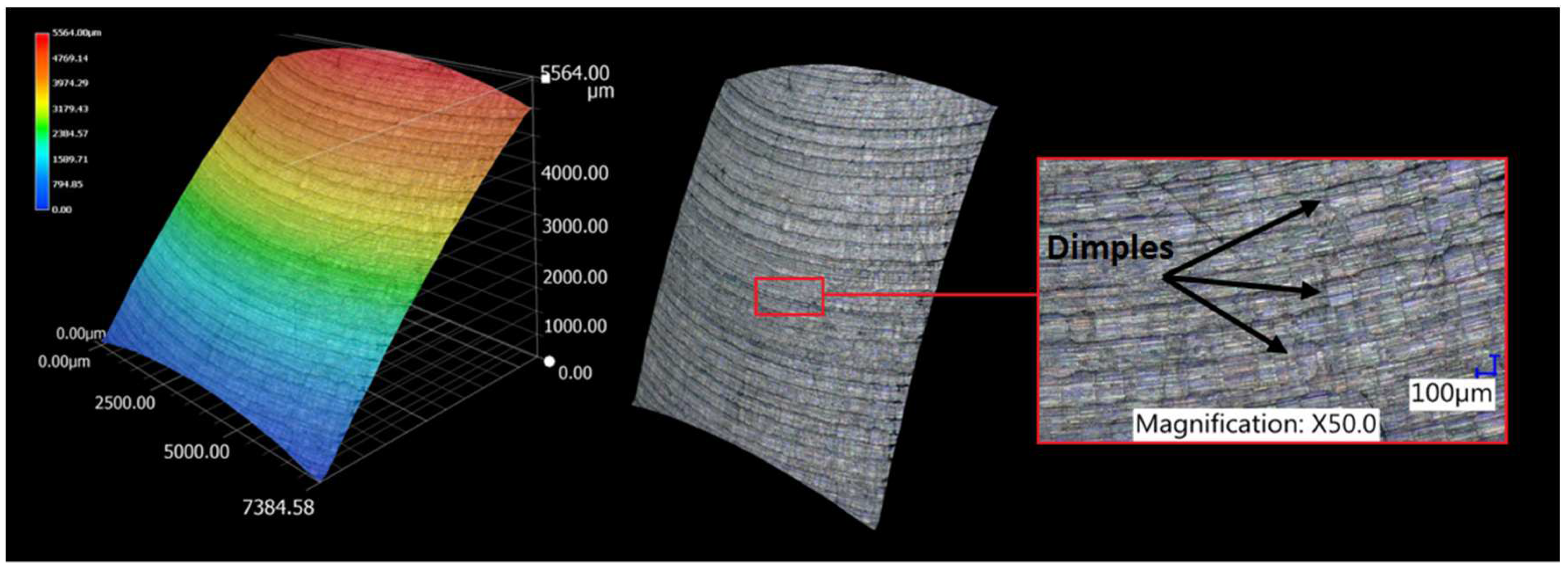
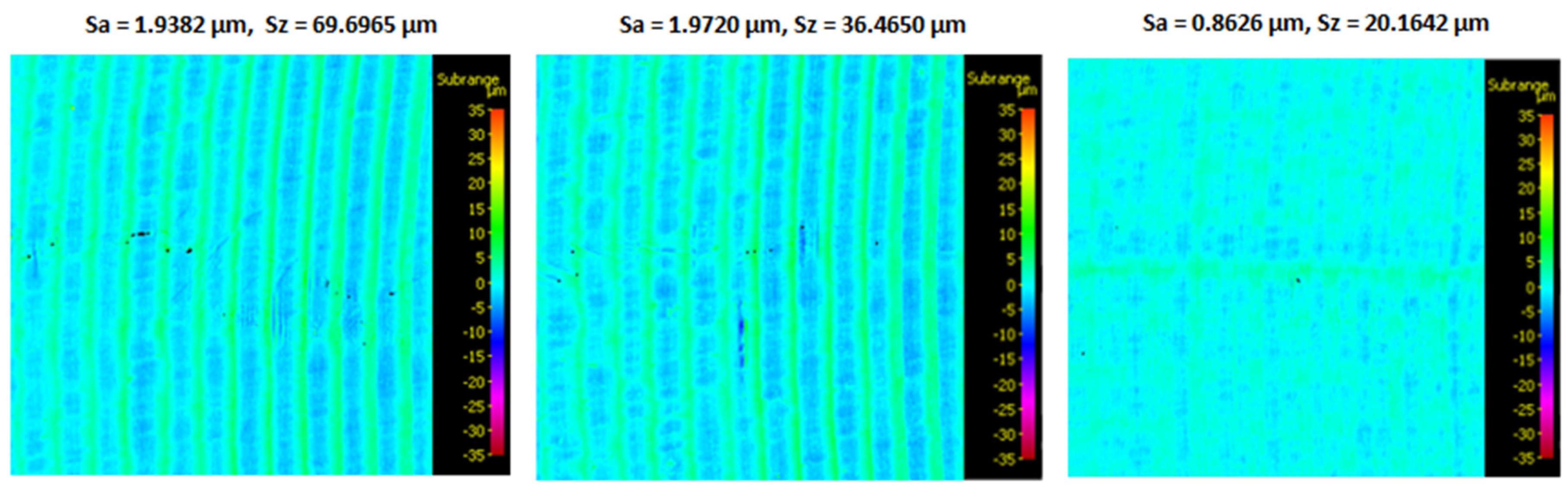
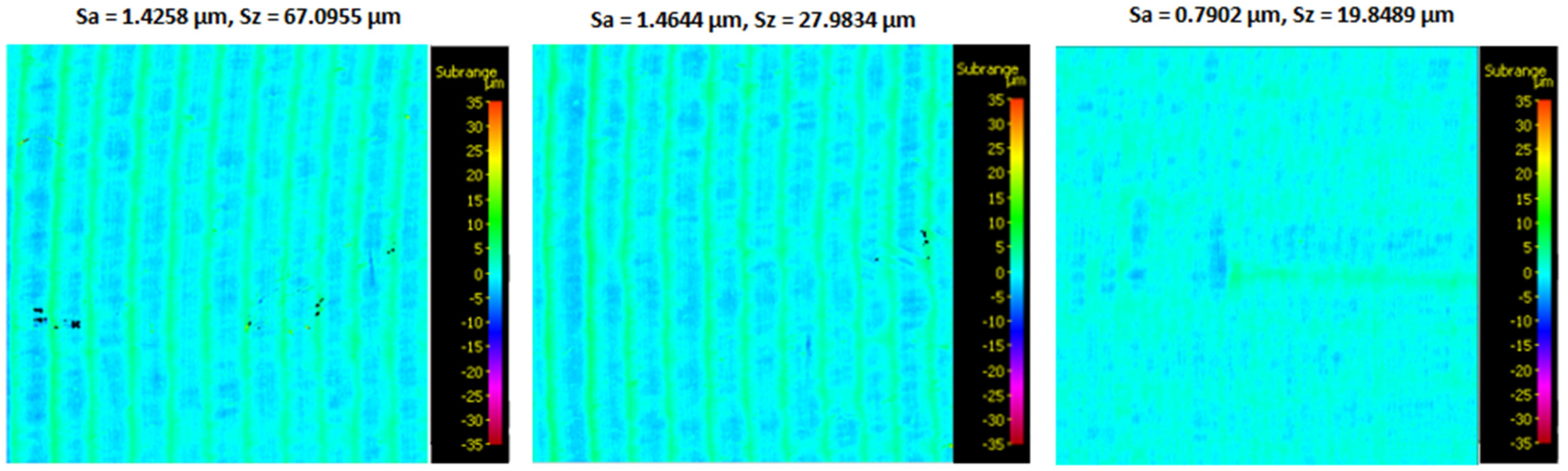
3.1. Surface topography evaluation
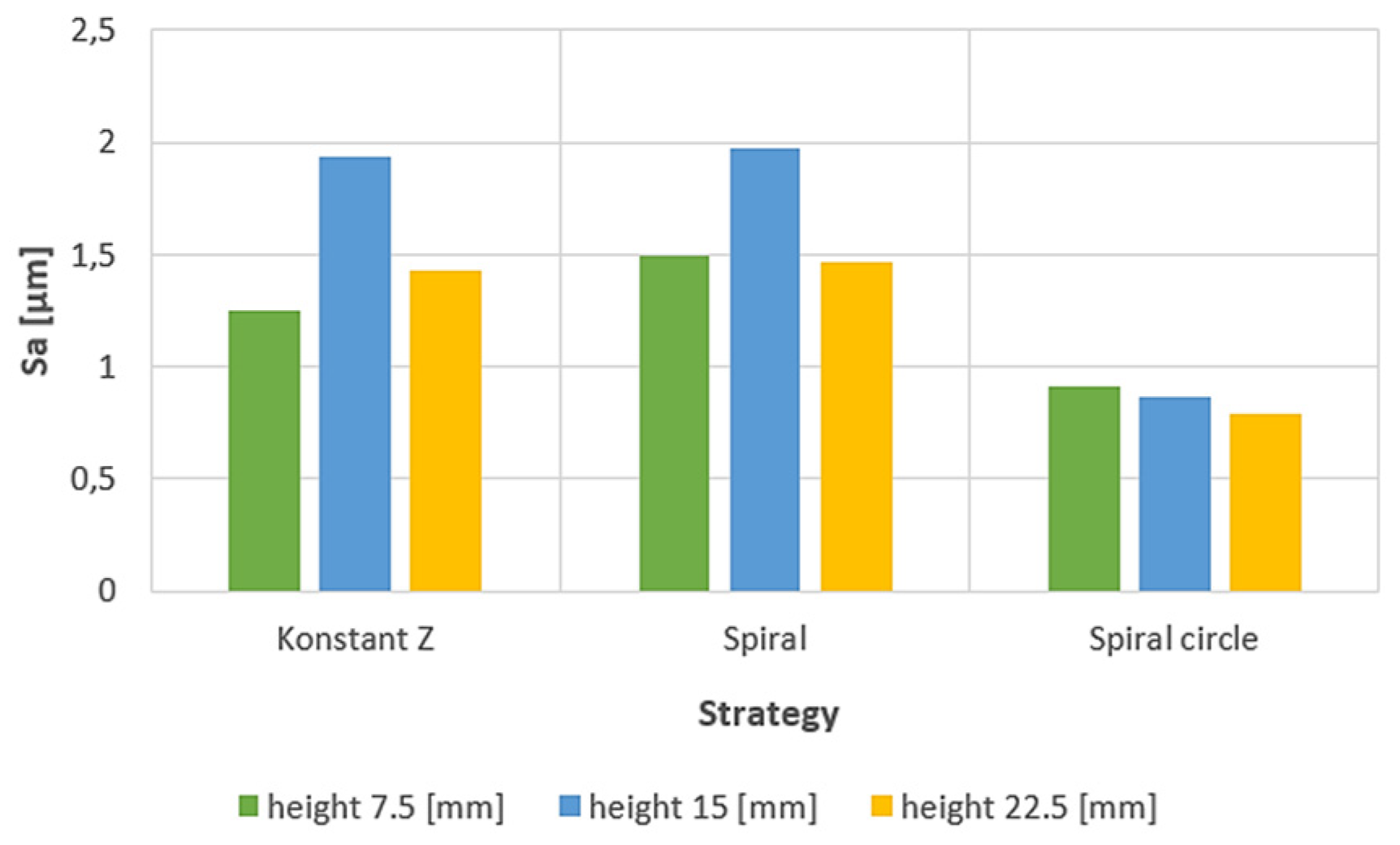
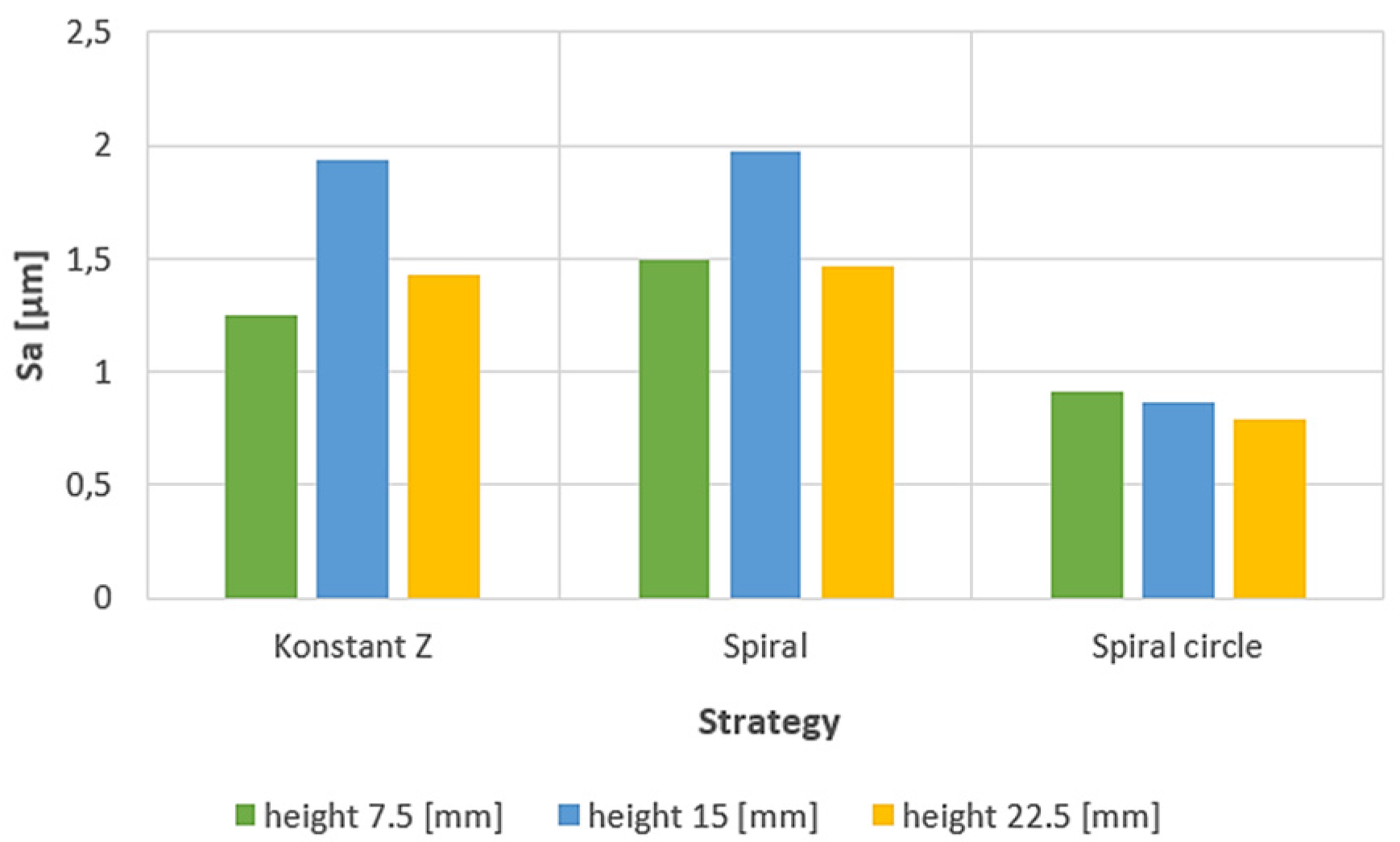
3.2. Roughness evaluation
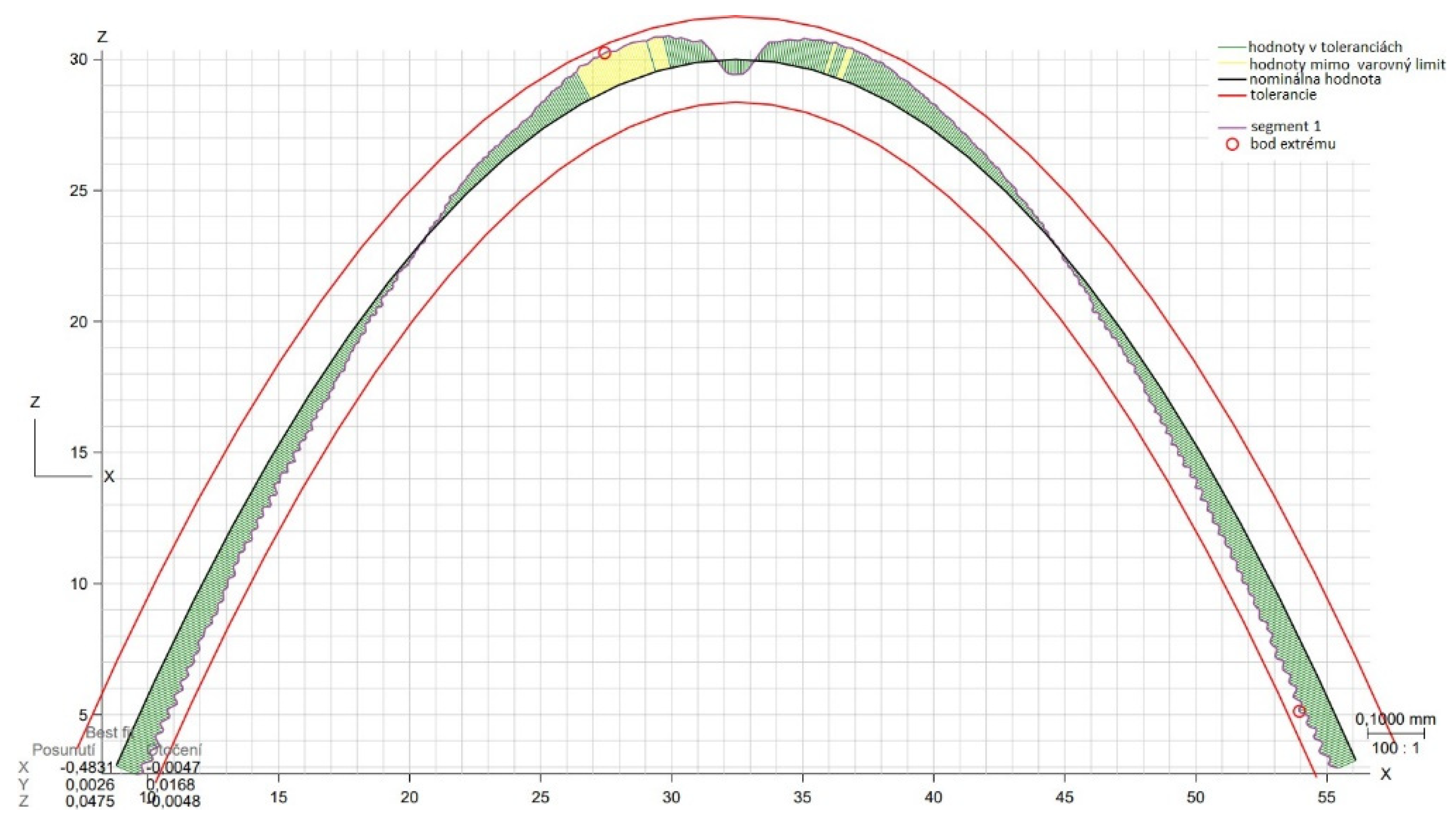
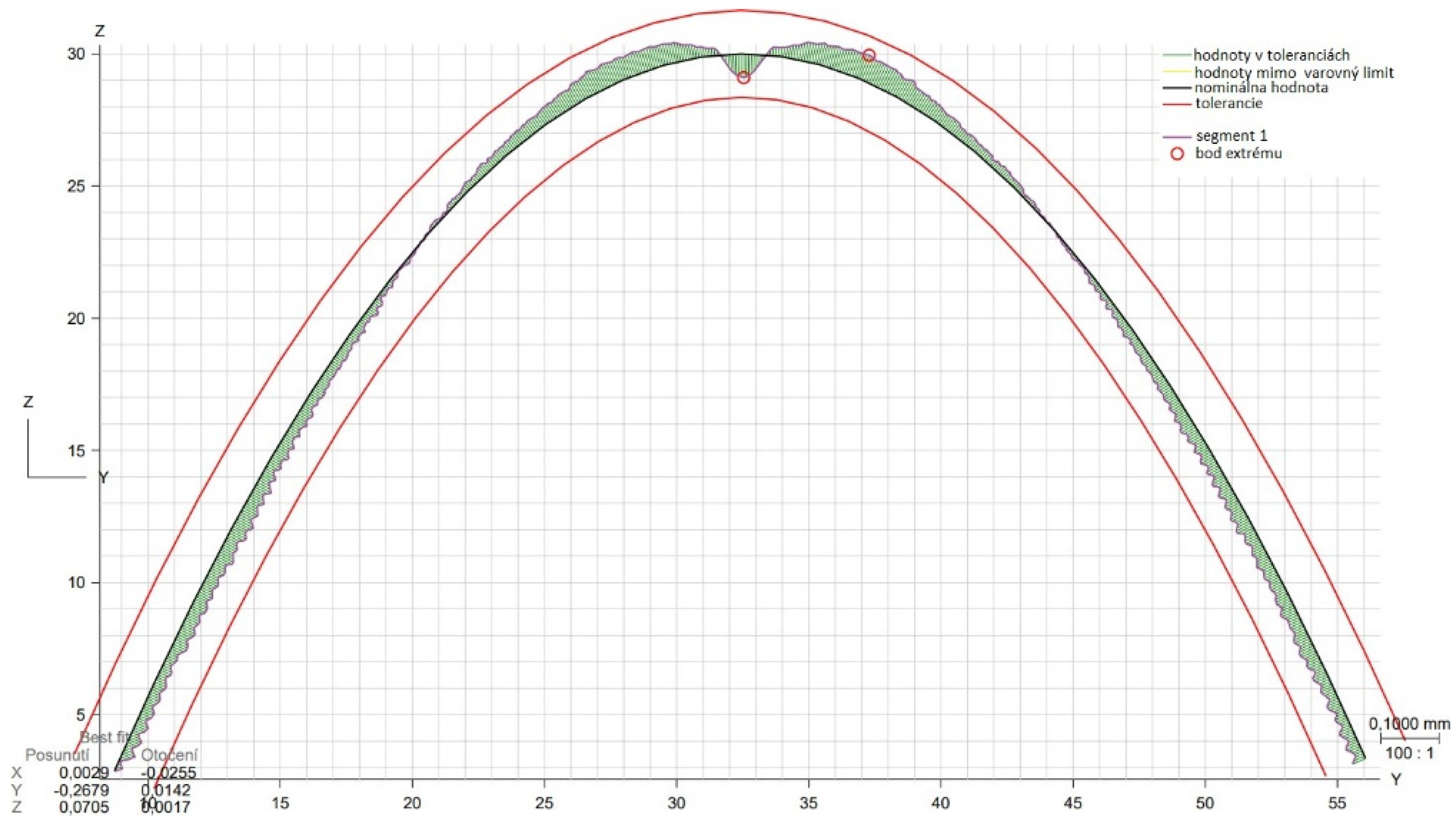
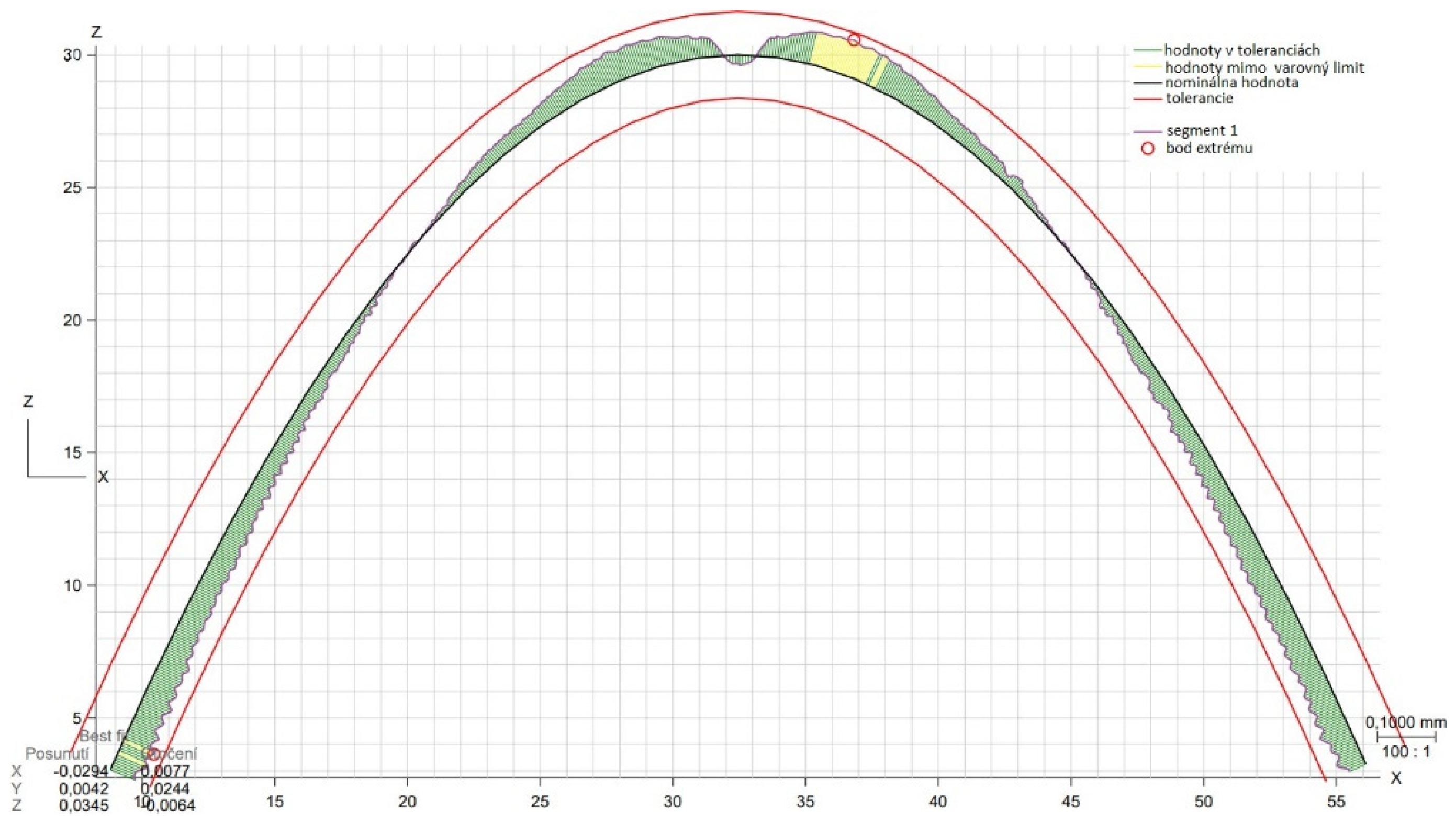
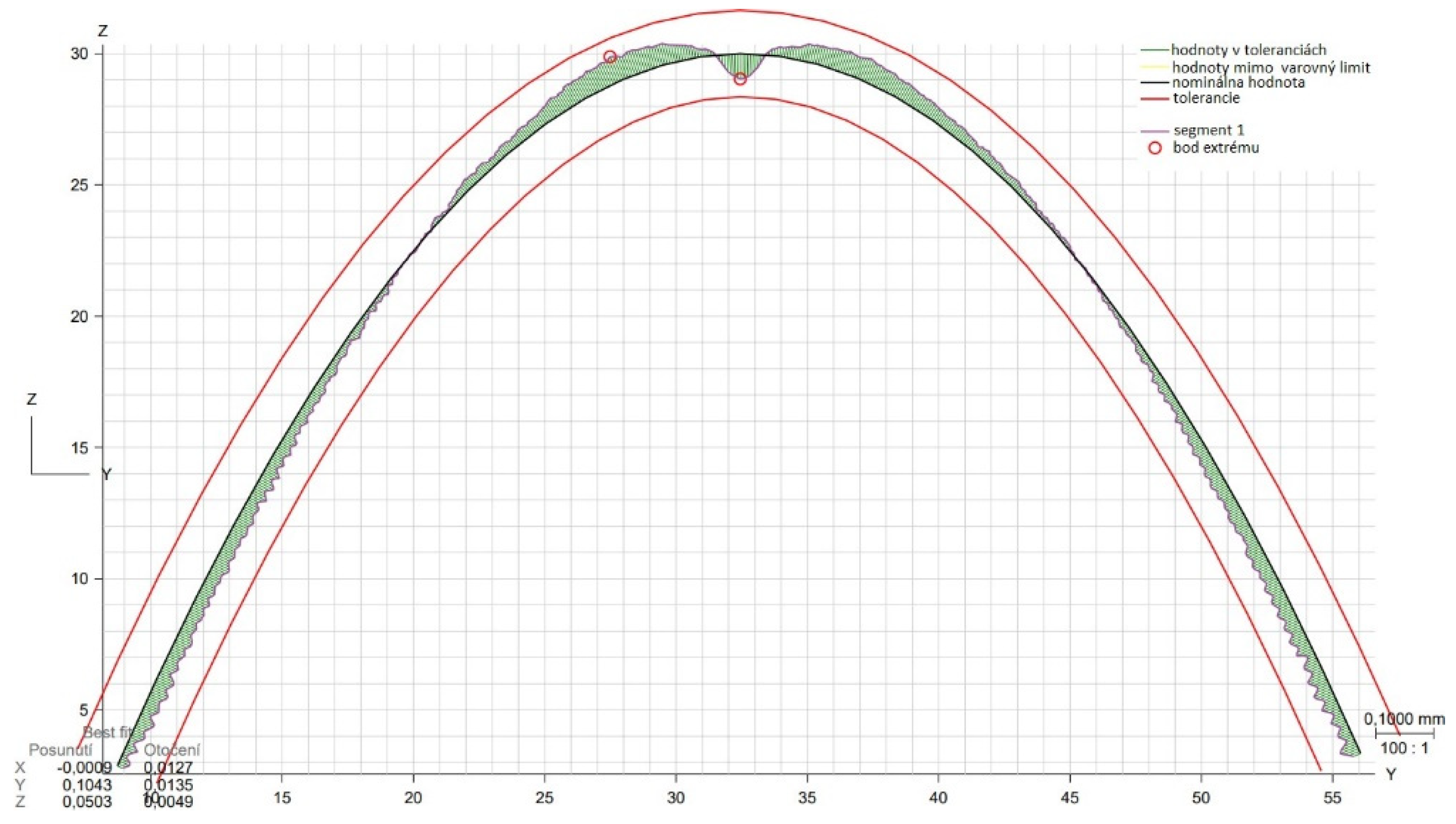
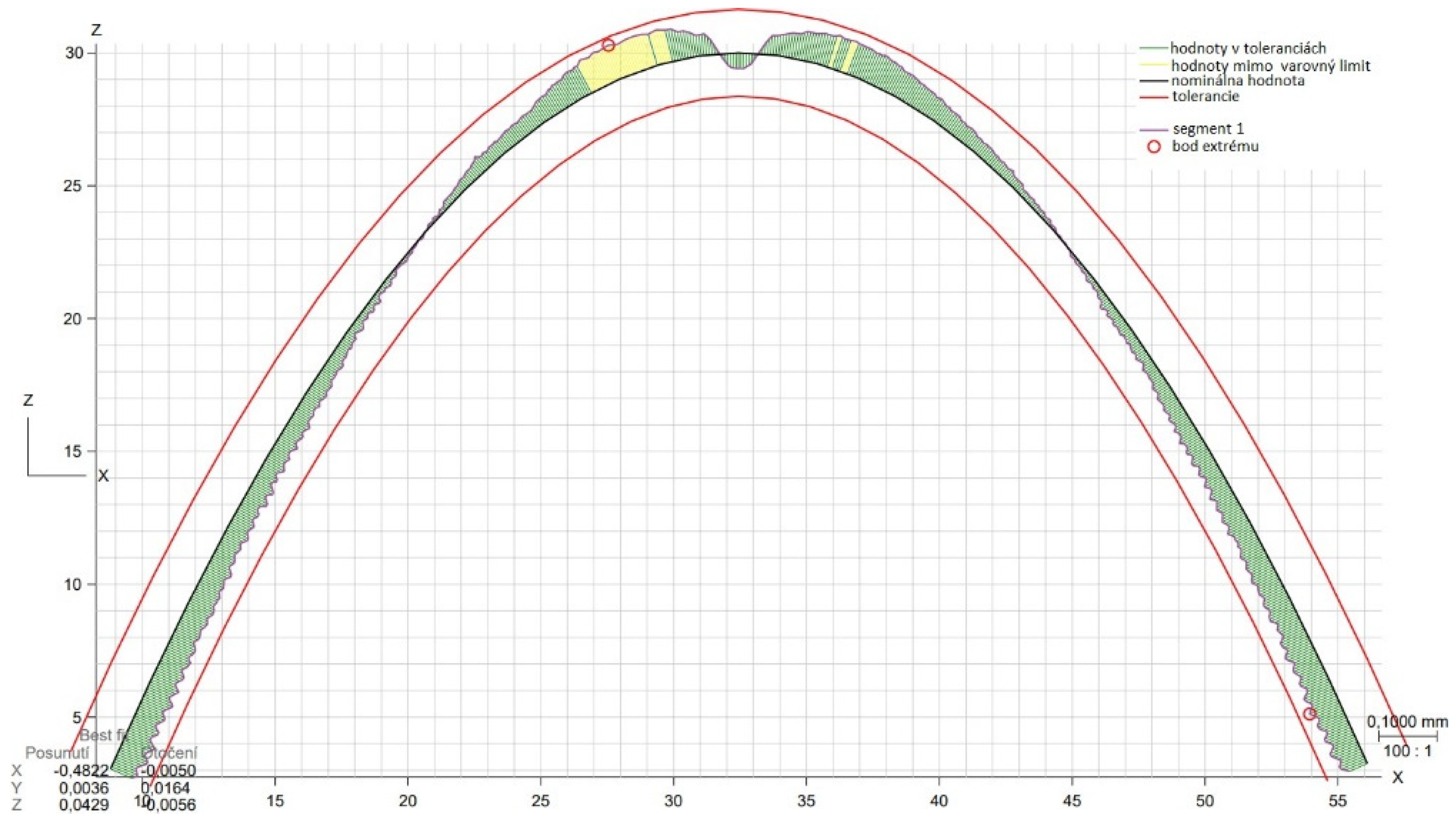
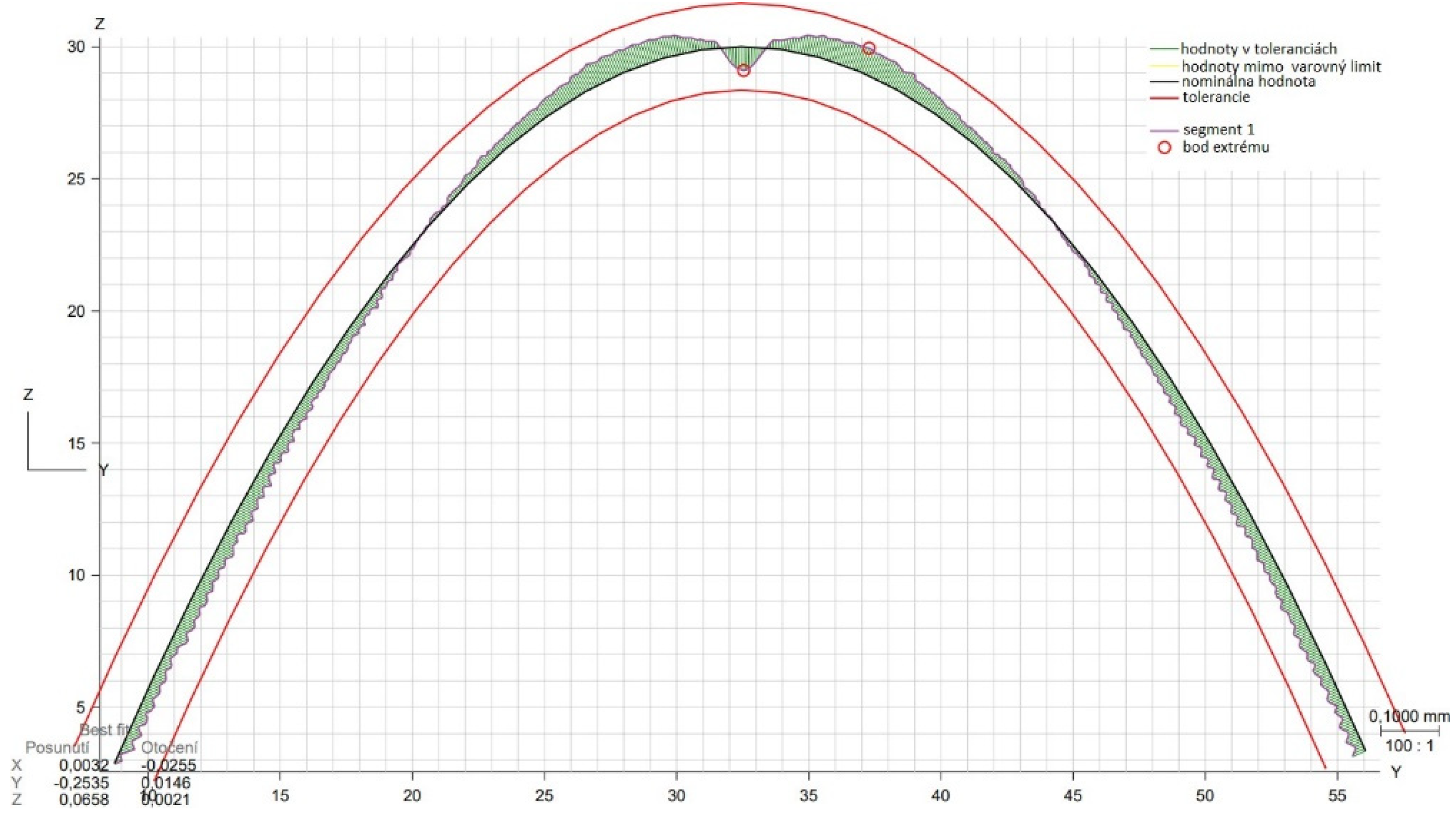
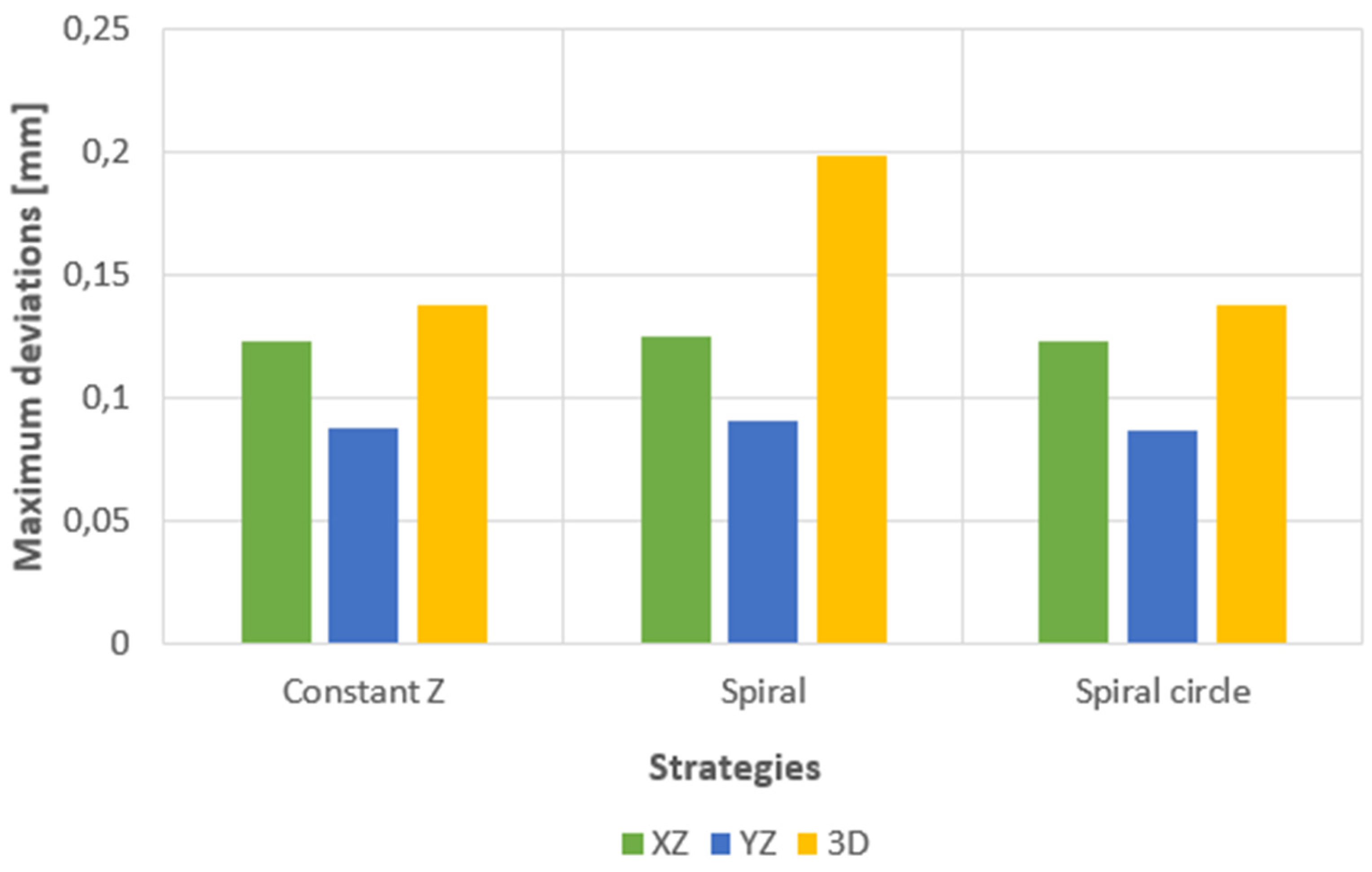
3.3. Shape deviation evaluation
4. Discussion
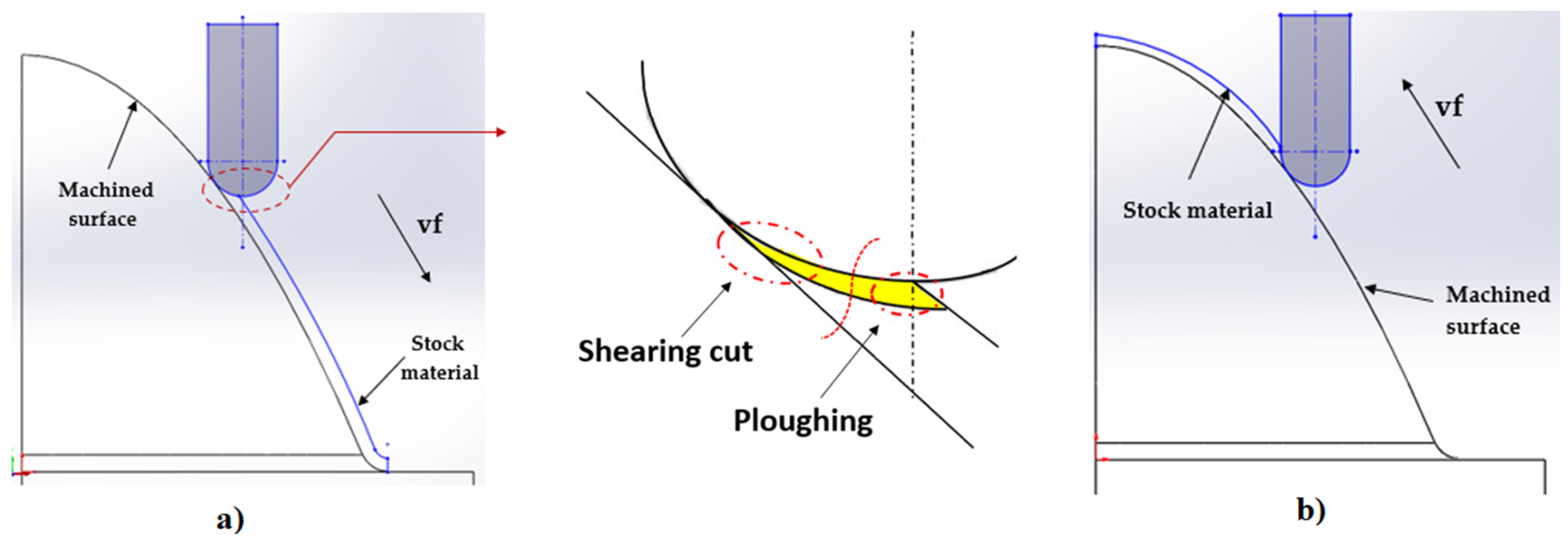
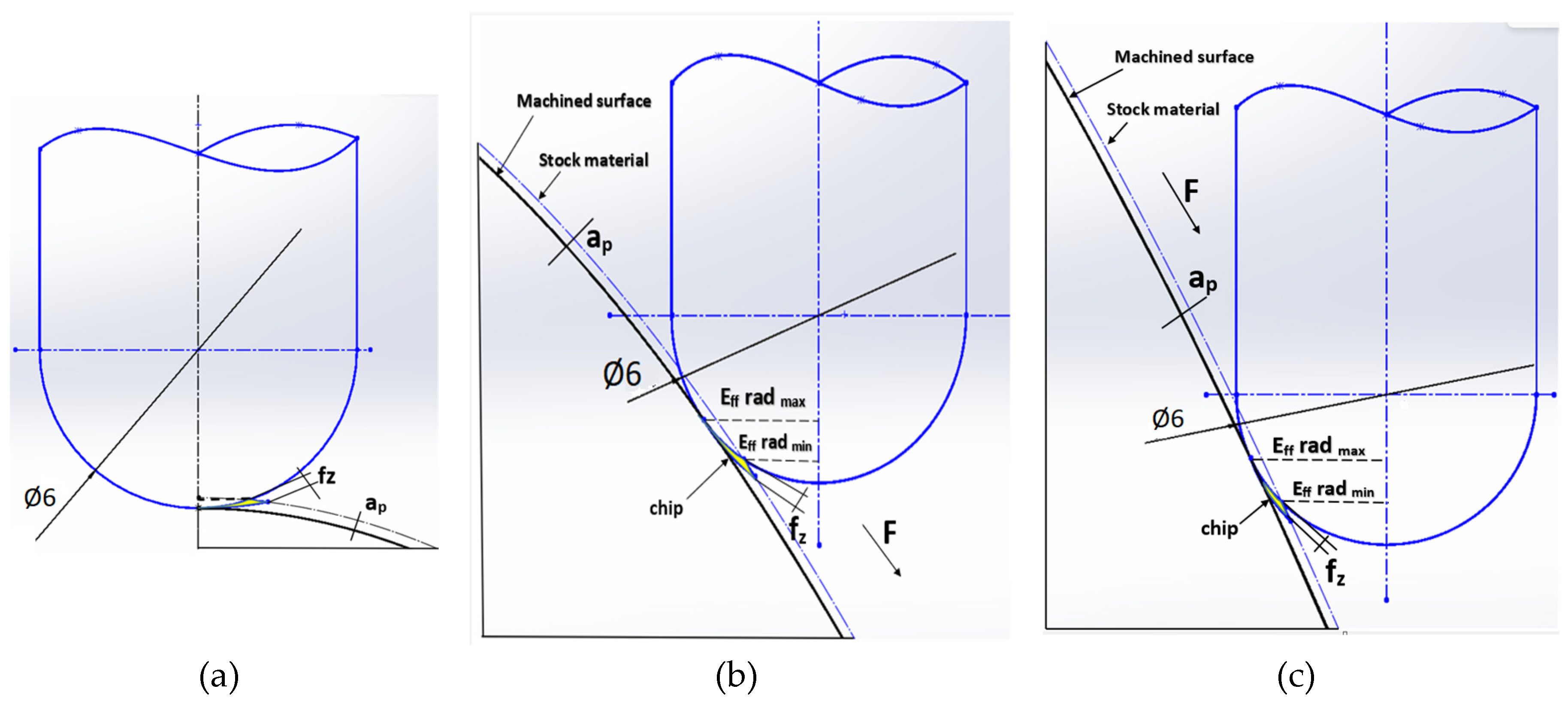
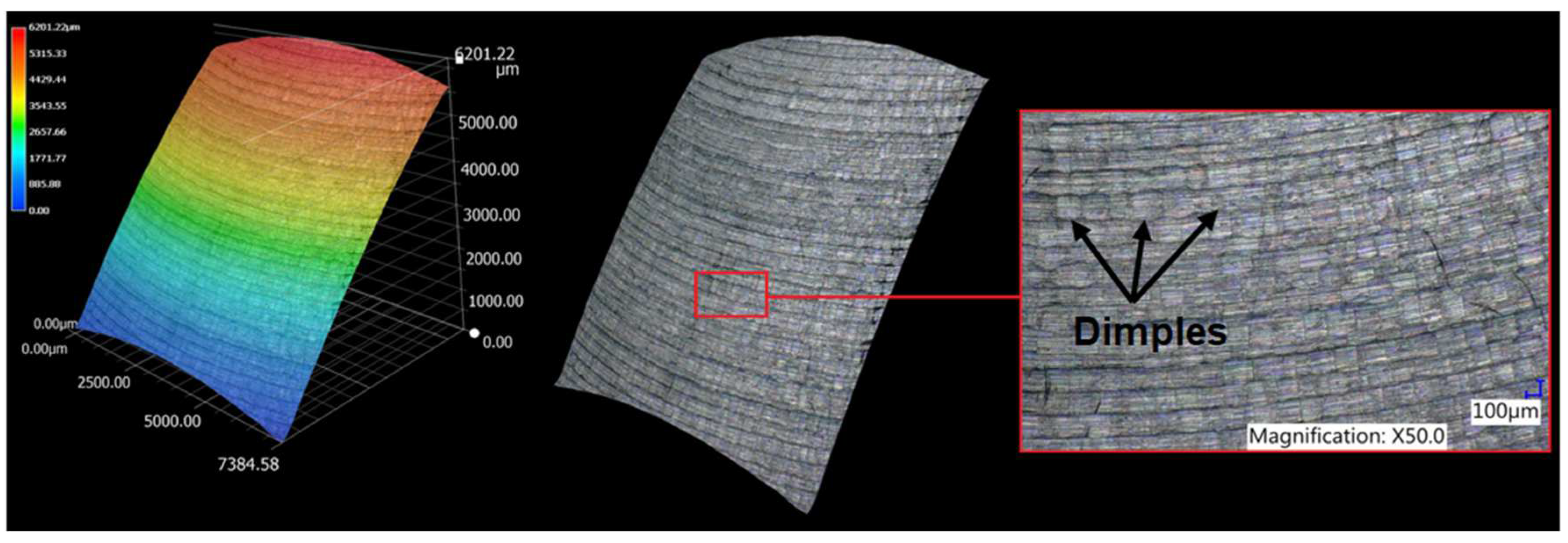
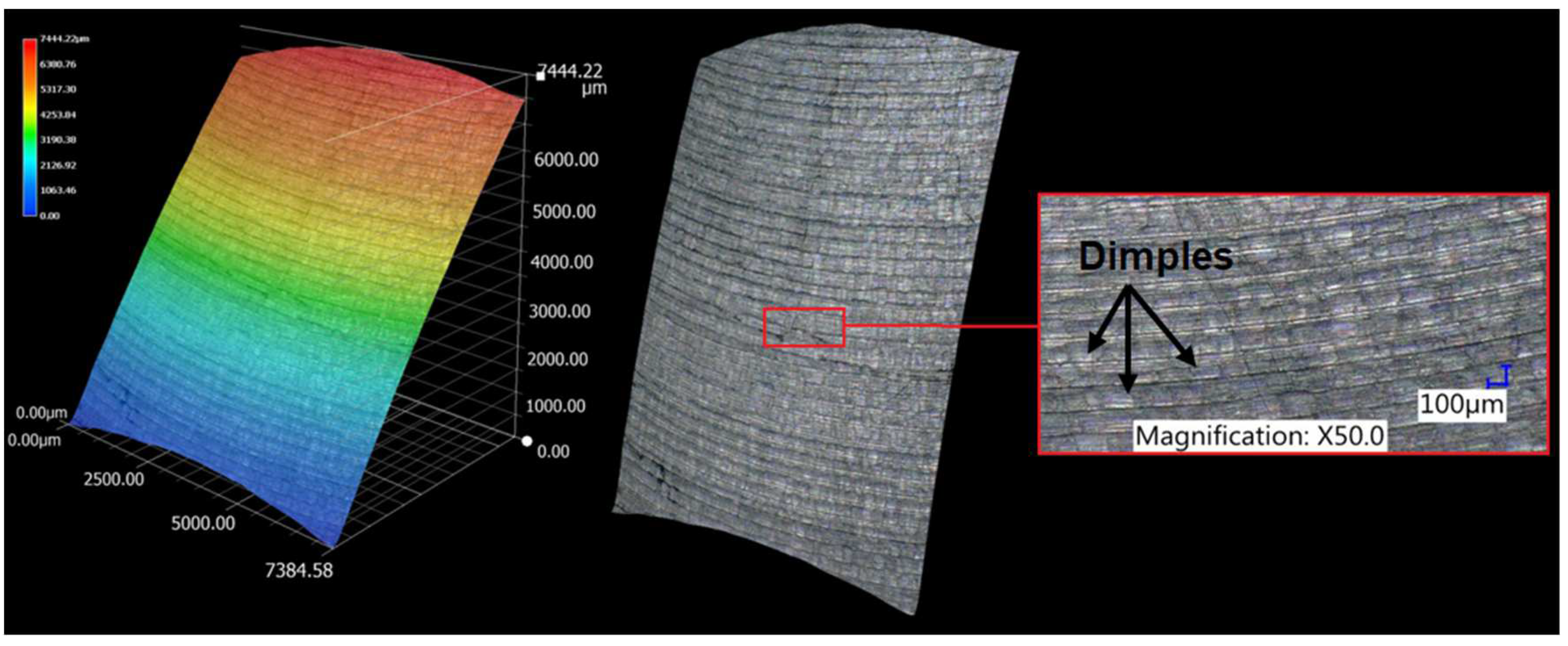
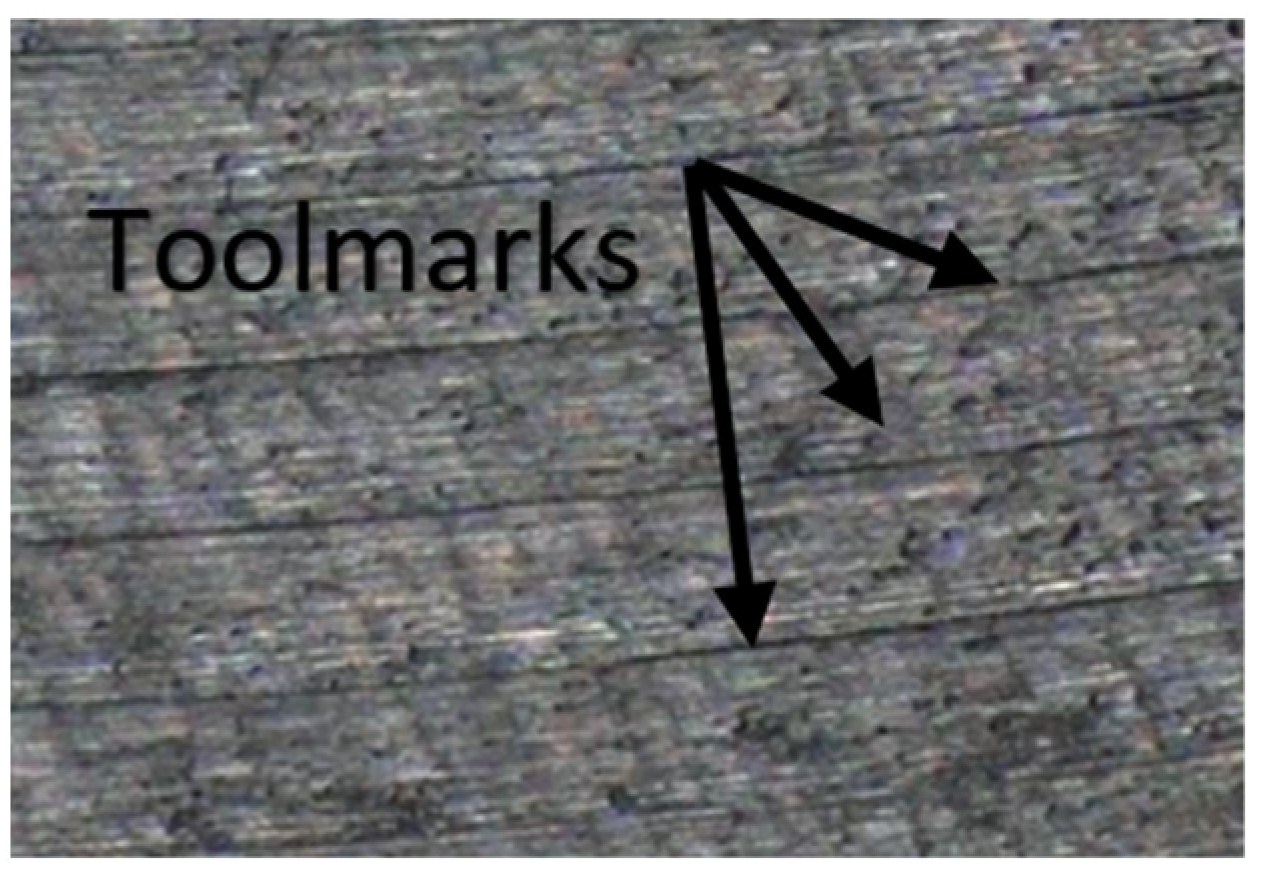
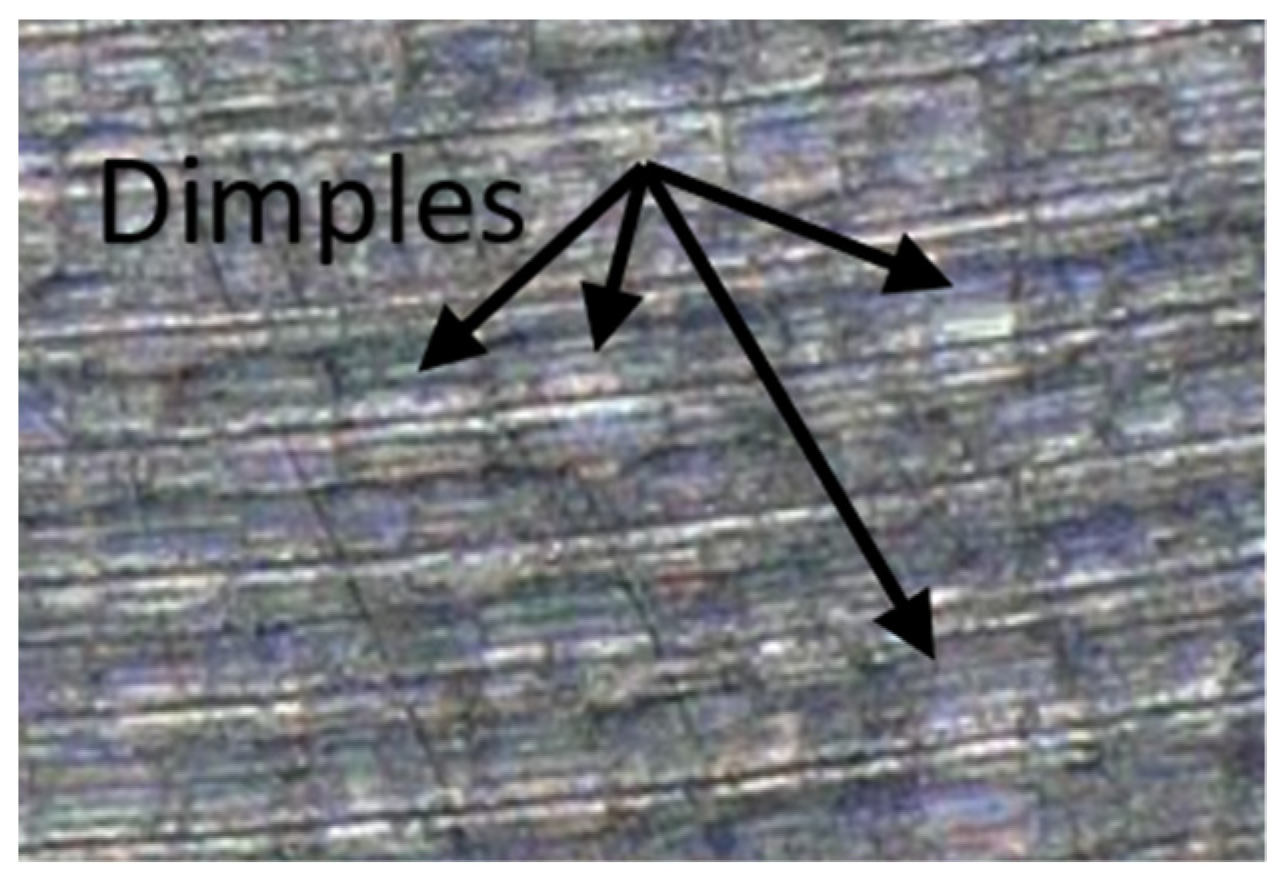
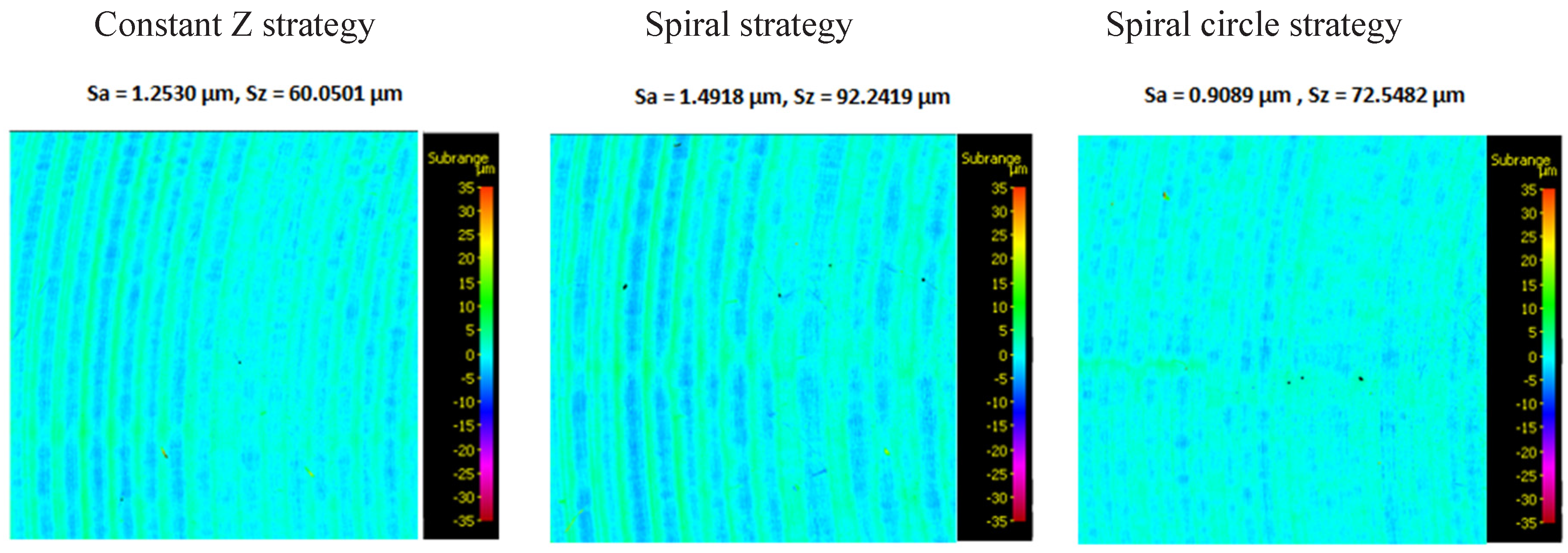
- From the details it is possible to see the variation of toolpaths due to the influence of the tool contact in the relationship between the tool and the machined surface. This is due to the changing effective diameter of the tool with respect to the curvature of the surface. The constant Z strategy demonstrated better surface quality with respect to topography than the Spiral circle strategy. The cause of the defects on the machined surface in the form of dimples was due to the vibrations generated in the cutting process, which resulted in repeated deviations from the programmed path.
- The individual details indicate that under ideal conditions (no cutting vibration and tool deformation), the toolpath obtained by the Constant Z strategy showed an ideal machined surface, which made it possible to observe uniform surface topography on the surface along the feed. This results in tool grooves aligned along contours that are clearly visible.
- The errors in the form of dimples are the result of an inadequate control system of the CNC milling machine. The overall machining process involves a so-called cycle time, in which the control system reads the generated NC code line and then converts this data from the code line into a tool position change. Thus, in the case of creating a toolpath consisting of multiple small segments, the machine control system must recalculate a number of NC blocks in a short time. If the control system is not able to handle a given volume of calculations related to the required toolpaths and the cutting conditions in the cutting process, it will adapt to its calculation capabilities in the form of a reduced feed rate.
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toh, C.K. A study of the effects of cutter path strategies and orientations in milling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 152, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daymi, A.; Boujelbene, M.; Linares, J.M.; Bayraktar, E.; Amara, A.B. Influence of workpiece inclination angle on the surface roughness in ball end milling of the titanium alloy Ti-6Al- 4V. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2009, 35, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Václav, Š.; Mareš, A.; Legutko, S.; Košťál, P.; Delgado Sobrino, D.R. Proposal of a system for estimating the assembly time in small and medium-sized enterprises. Tech. Gaz. 2020, 27, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavykia, A.; Iranmanesh, S.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. The Effect of Tool Path Strategy on Surface and Dimension in High-Speed Milling. Int. J. Mech. Aerosp. Ind. Mechatron. Manuf. Eng. 2017, 35, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, J.; Spišák, E.; Gajdoš, I.; Mulidrán, P. Comparison of milling strategies in the production of shaped surfaces. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2022, 16, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grešová, Z.; Ižol, P.; Vrabeľ, M.; Kaščák, Ľ.; Brindza, J.; Demko, M. Influence of ball-end milling strategy on the accuracy and roughness of free form surfaces. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boujelbene, M.; Moisan, A.; Tounsi, N.; Brenier, B. Productivity enhancement in dies and molds manufacturing by the use of C1 continuous tool path. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Relvas, C.; Simoes, J.A. The influence of finishing milling strategies on texture, roughness and dimensional deviations on the machining of complex surfaces. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 136, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, B.V.; Raviswaran, N. Tool path generation algorithm and 3D tolerance analysis for free-form surfaces. Ethiop. J. Sci. Technol. 2006, 4, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D.; Sundararajan, V.; Wright, P.K. Zig-zag tool path generation for sculptured surface. Geom. Algorithmic Asp. Comput. -Aided Des. Manuf. 2003, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, C.K. Surface topography analysis in high speed finish milling inclined hardened steel. Precis. Eng. 2004, 28, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ižol, P.; Brindza, J.; Vrabeľ, M.; Demko, M.; Basilio, S.E. Effect of optimization software on part shape accuracy and production times during rough milling of aluminum alloy. Machines 2022, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asilturk, I.; Akkus, H. Determining the effect of cutting parameters on surface roughness in hard turning using the Taguchi method. Measurement 2011, 44, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Tóth, T.; Kaščák, Ľ.; Spišák, E. The effect of the machining strategy on the surface accuracy when milling with a ball end cutting tool of the aluminum alloy AlCu4Mg. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.; Tsai, C.; Lee, A. Analysis of cutting forces in ball end milling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1995, 47, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Tóth, T.; Frankovský, P.; Dulebová, Ľ.; Spišák, E.; Zajačko, I.; Živčák, J. The influence of automated machining strategy on geometric deviations of machined surfaces. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.F.; Bodziak, B. Advanced free form manufacturing by computer aided systems Book Mechanical Engineering. April 2012. [CrossRef]
- Boujelbene, M.; Moisan, A.; Torbaty, S. Study of the tool inclination in multi-axes milling. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Manufacturing Systems – ICMaS, Bucharest, Romania, 26–27 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, E.; Tunc, L.T.; Budak, E. Investigation of lead and tilt angle effects in 5-axis ball-end milling processes. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandiffio, I.; Diniz, A.E.; Souza, A.F. Evaluating surface roughness, tool life, and machining force when milling free-form shapes on hardened AISI D6 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 82, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.F.; Berkenbrock, E.; Rodriguez, A.R.; Diniz, A.E. Influences of the tool path strategy on the 75 machining force when milling free form geometries with a ball-end cutting tool. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2014, 37, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissacco, G.; Hansen, H.N.; Chiffre, L. Size effect on surface generation in micromilling of hardened tool steel. CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol. 2006, 555, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducobu, F.; Filippi, E.; Rivière, L.E. Chip formation and minimum chip thickness in micro-milling. Processings of the 12th CIRP Conference on modeling of machining operations, Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain, 9−14 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tuysuz, O.; Altintas, Y.; Feng, H.Y. Prediction of cutting forces in three and five-axis ball-end milling with tool indentation effect. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2013, 66, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.T.; Tsai, Ch.M.; Lee, A.Ch. Analysis of cutting forces in ball-end milling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1995, 47, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Loftus, M.; Whitten, A. Surface finish visualization in high speed, ball nose milling applications. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinwall, D.K.; Dewes, R.C.; Ng, E.G.; Sage, C. The influence of cutter orientation and workpiece angle on machinability when high-speed milling Inconel 718 under finishing conditions. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, S.; Wiackiewicz, G.M.; Krolczyk, G.M. Study on metrological relations between instant tool displacements and surface roughness during precise ball end milling. Measurement 2018, 129, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghayegh, S.; Sadeghi, M.H.; Hassanpour, H. The Influence of Tool Path Strategies on Cutting Force and Surface Texture during Ball End Milling of Low Curvature Convex Surfaces. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käsemodel, R.B.; Souza, A.F.; Voigt, R.; Basso, I.; Rodrigues, A.R. CAD/CAM interfaced algorithm reduces cutting force, roughness, and machining time in free-form milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 1883–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.F.; Diniz, A.E.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Coelho, R.T. Investigating the cutting phenomena in free-form milling using a ball-end cutting tool for die and mold manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuysuz, O.; Altintas, Y.; Feng, H.Y. Prediction of cutting forces in three and five-axis ball-end milling with tool indentation effect. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2013, 66, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, E.; Kurt, A.; Şeker, U. The Effects of the Feed Rate on the Cutting Tool Stresses in Machining of Inconel 718. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 231, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, H.; Hock, S. High-Speed Milling of Dies and Moulds — Cutting Conditions and Technology. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1995, 44, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhangiang, L.; Shi, Z.; Song, Q. Optimum end milling tool path and machining parameters for micro Laval nozzle manufacturing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 231, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, A.; Bilalis, N.; Balouktsis, A.; Savakis, C. Prediction of Surface Topomorphy and Roughness in Ball-End Milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2003, 21, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunović, G.; Šimunović, K.; Šarić, T. Modelling and simulation of surface roughness in face milling. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2013, 12, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukelic, D.; Tadic, B.; Miljanic, D. Novel workpiece clamping method for increased machining performance. Teh. Vjesn. -Tech. Gaz. 2012, 19, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antic, A.; Kozak, D.; Kosec, B.; Šimunović, G.; Šarić, T.; Kovačevič, D.; Čep, R. The influence of tool wear on the chip-forming mechanism and tool vibrations. Teh. Vjesn. -Tech. Gaz. 2013, 20, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, C.K. Design, evaluation, and optimization of cutter path strategies when high speed milling hardened mold and die materials. Mater. Des. 2005, 26, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelnaga, A.M.; Dardiry, M.A. Optimization methods for metal cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tool Des. Res. 1997, 24, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.; Houshyar, A. Quality and optimum parameter selection in metal cutting. Comput. Ind. 1992, 20, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajari, S.; Sadeghi, M.H.; Hassanpour, H. The Influence of Tool Path Strategies on Cutting Force and Surface Texture during Ball End Milling of Low Curvature Convex Surfaces. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikua, B.W.; Tanaka, H.; Obata, F.; Sakamoto, S.; Kishi, T.; Ishii, T. Prediction of cutting forces and machining error in ball end milling of curved surfaces—II experimental verification. Precis. Eng. 2002, 26, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matras, A.; Kowalczyk, R. Analysis of machining accuracy during free form surface milling simulation for different milling strategies. Proc. SPIE - Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2014, 9290, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Yue, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Modeling of Convex Surface Topography in Milling Process. Met. - Open Access Metall. J. 2020, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoles, X.; Landon, Y.; Rubio, W. Kinematic modelling of a 3-axis NC machine tool in linear and circular interpolation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 47, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monreal, M.; Rodriguez, C.A. Infuence of tool path strategy on the cycle time of high-speed milling. Comput. -Aided Des. 2003, 35, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, H.T.; Kuo, M.J. NURBS machining and feed rate adjustment for high-speed cutting of complex sculptured surfaces. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2001, 39, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, R.T.; Souza, A.F.; Roger, A.R. Mechanistic approach to predict real machining time for milling free-form geometries applying high feed rate. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 46, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.F.; Käsemodel, R.B.; Arias, M.; Marin, F.; Rodriguez, A.R. Study of tool paths calculated by diferent commercial CAM systems and infuences on the real machining time and surface roughness for milling free-form geometries. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 363, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siller, H.; Rodriguez, C.A.; Ahuett, H. Cycle time prediction in high-speed milling operations for sculptured surface finishing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 174, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasemi, A.; Xue, D.; Gu, P. Recent development in CNC machining of freeform surfaces: A state-of-the-art review. Comput. Aided Des. 2010, 42, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Václav, Š.; Sivtsev, N.S.; Senderská, K. Investigation of stress-strain state of a workpiece at gauge burnishing of its holes. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2017, 11, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymakci, M.; Lazoglu, I. Tool path selection strategies for complex sculptured surface machining. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2008, 12, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, P.; Peterka, J.; Václav, Š. The task of 5-axis milling. Tech. Gaz. 2012, 19, 147–150. [Google Scholar]





| Tool Diameter [mm] | Cutting speed [m.min- 1] | Feed per tooth [mm] | Spindle frequency [RPM] | Tool producer | Tool code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| End Mill D 18 | 270 | 0.125 | 4800 | Korloy | AMS2018S |
| End Mill D8 | 123 | 0.029 | 4900 | ZPS-FN | 273618.080 |
| Ball End Mill D6 | 92.4 | 0.022 | 4900 | ZPS-FN | 511418.060 |
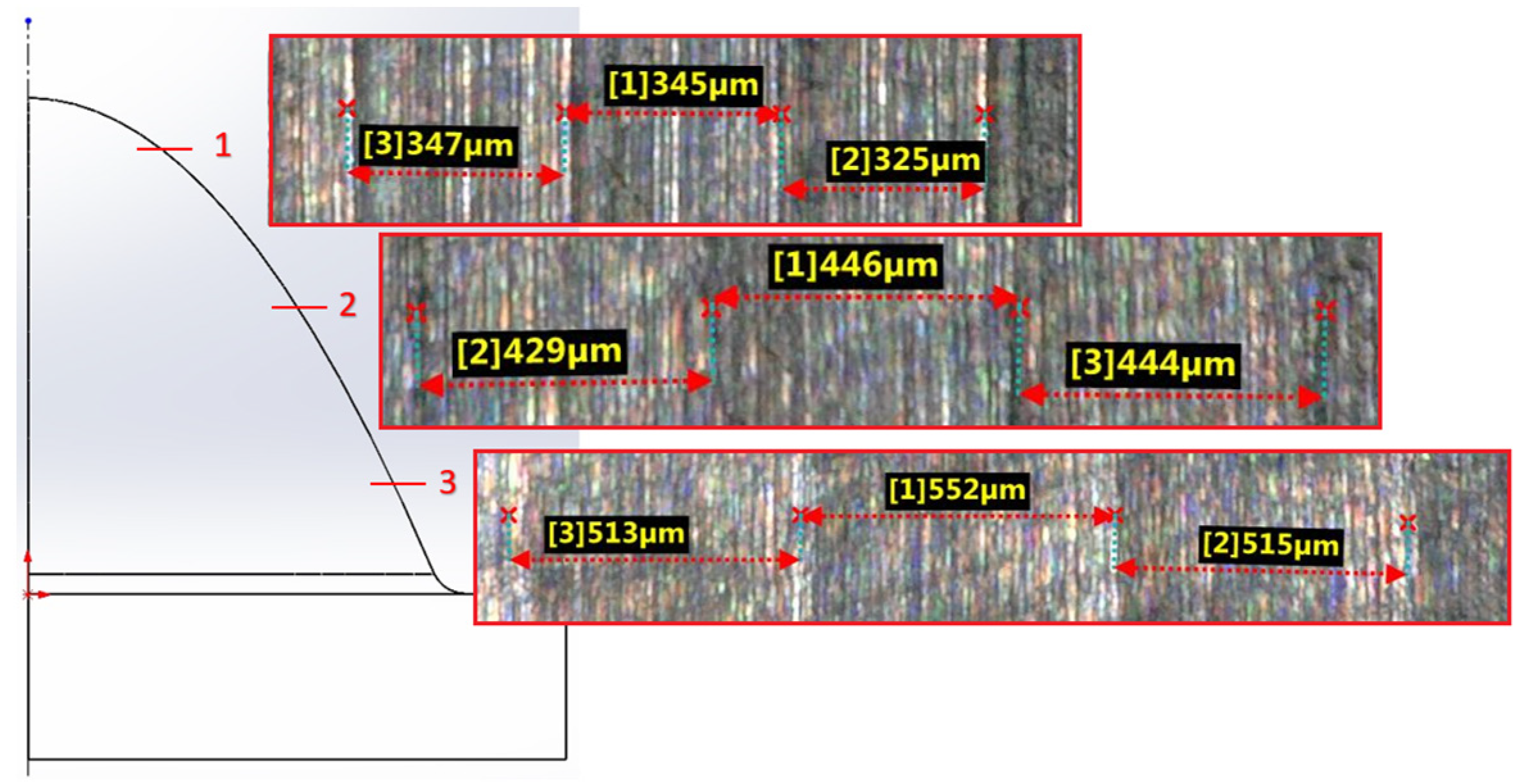
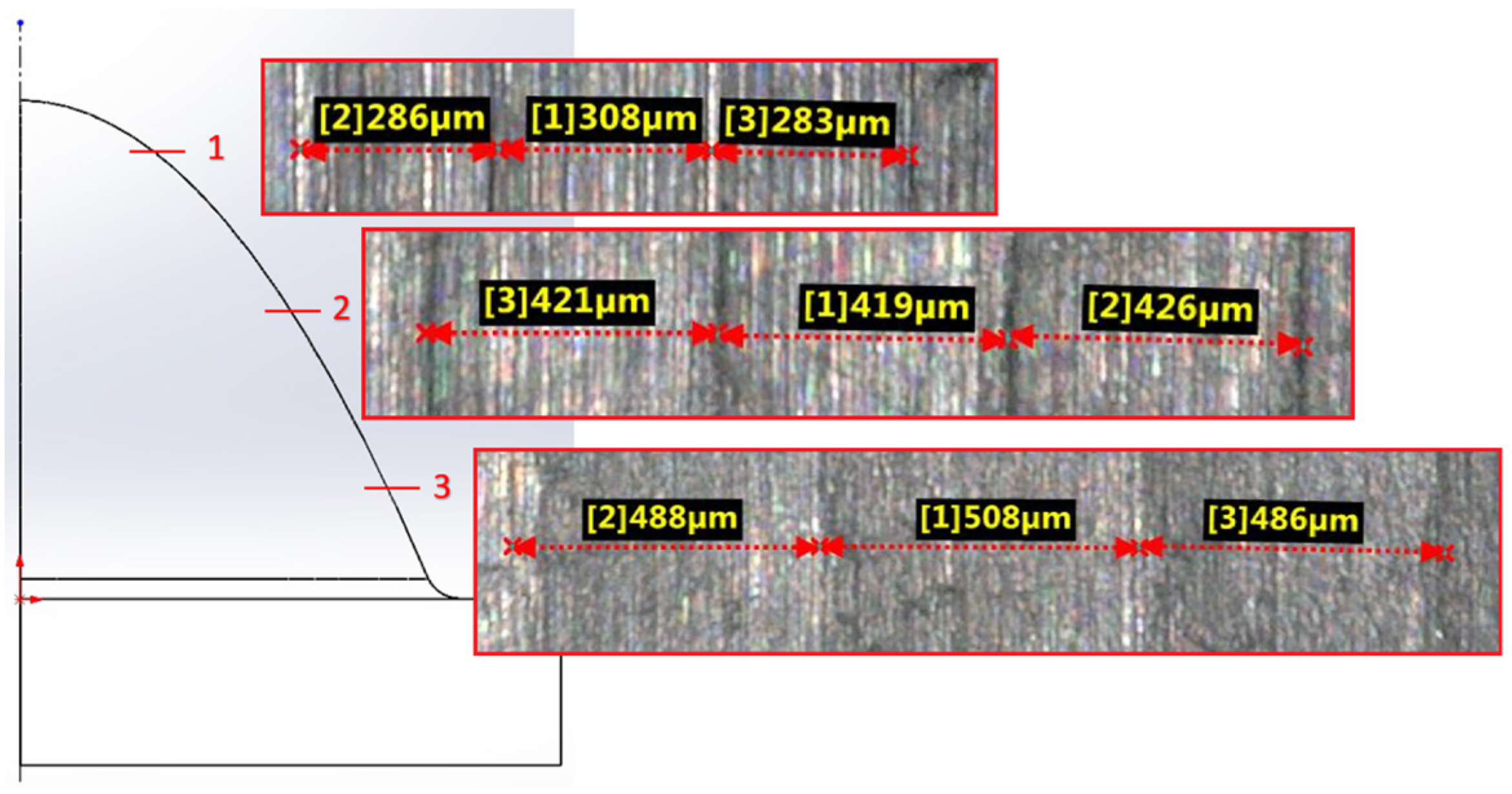
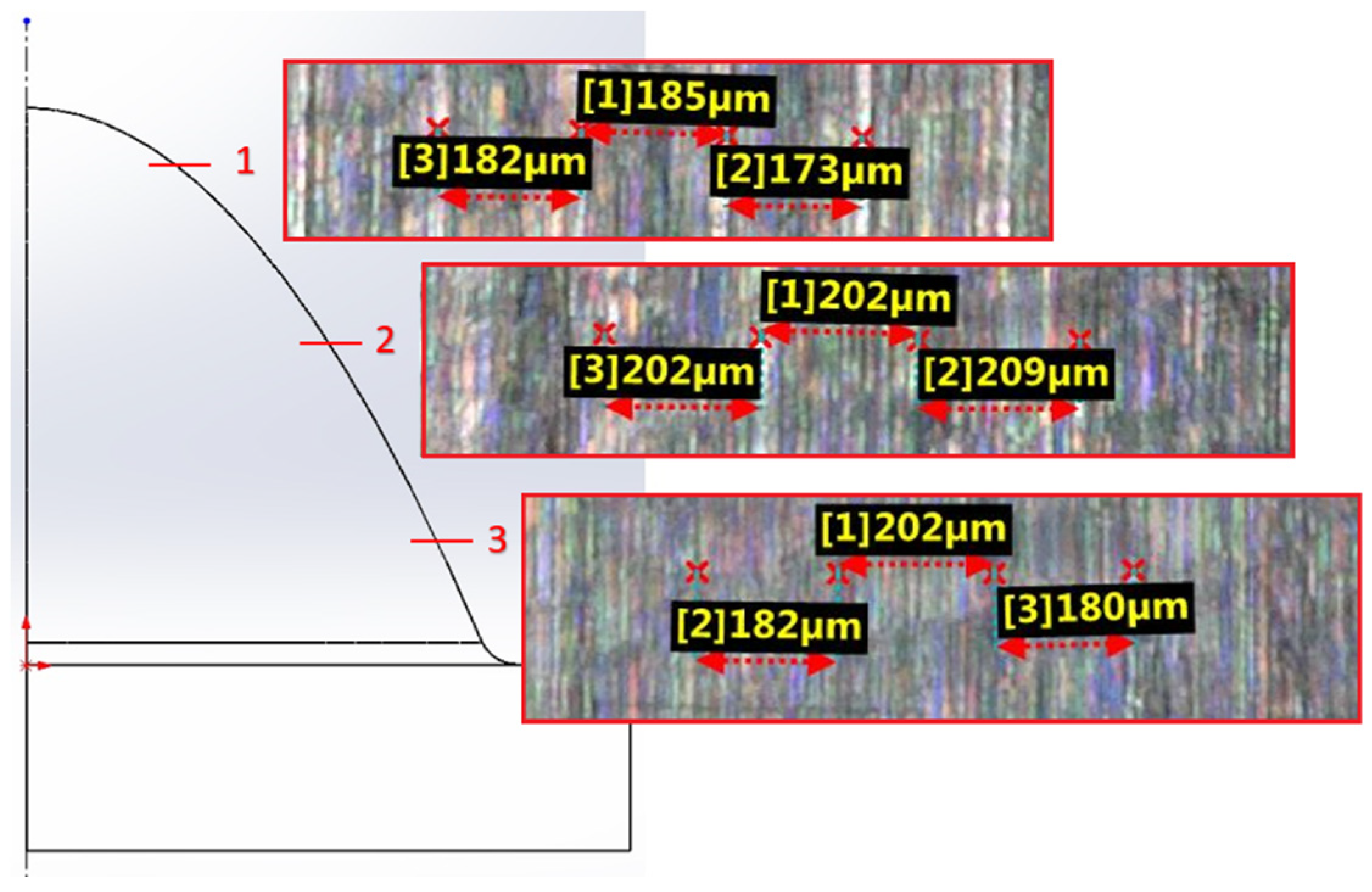
| Strategy | Radial depth of cut ae [µm] of 7.5mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement 1 | Measurement 2 | Measurement 3 | |
| Constant Z | 347 | 345 | 325 |
| Spiral | 286 | 308 | 283 |
| Spiral circle | 182 | 185 | 173 |
| Strategy | Radial depth of cut ae [µm] of 15mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement 1 | Measurement 2 | Measurement 3 | |
| Constant Z | 429 | 446 | 444 |
| Spiral | 421 | 419 | 426 |
| Spiral circle | 202 | 202 | 209 |
| Strategy | Radial depth of cut ae [µm] of 22.5mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement 1 | Measurement 2 | Measurement 3 | |
| Constant Z | 513 | 552 | 515 |
| Spiral | 488 | 508 | 486 |
| Spiral circle | 182 | 202 | 180 |
| Area evaluated | Calculated deviation [mm] |
Set tolerance [mm] | Maximum negative deviation [mm] |
Maximum positive deviation [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D profile XZ | 0.1231 | 0.15 | -0.0549 | 0.0616 |
| 2D profile YZ | 0.0874 | 0.15 | -0.0411 | 0.0437 |
| 3D area profile | 0.1372 | 0.15 | -0.0686 | 0.0665 |
| Area evaluated | Calculated deviation [mm] |
Set tolerance [mm] | Maximum negative deviation [mm] |
Maximum positive deviation [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D profile XZ | 0.1249 | 0.15 | -0.0580 | 0.0625 |
| 2D profile YZ | 0.0905 | 0.15 | -0.0440 | 0.0453 |
| 3D area profile | 0.1983 | 0.15 | -0.0561 | 0.0991 |
| Area evaluated | Calculated deviation [mm] |
Set tolerance [mm] | Maximum negative deviation [mm] |
Maximum positive deviation [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D profile XZ | 0.1228 | 0.15 | -0.0557 | 0.0614 |
| 2D profile YZ | 0.0868 | 0.15 | -0.0411 | 0.0434 |
| 3D area profile | 0.1371 | 0.15 | -0.0686 | 0.0670 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





