Submitted:
24 July 2023
Posted:
25 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
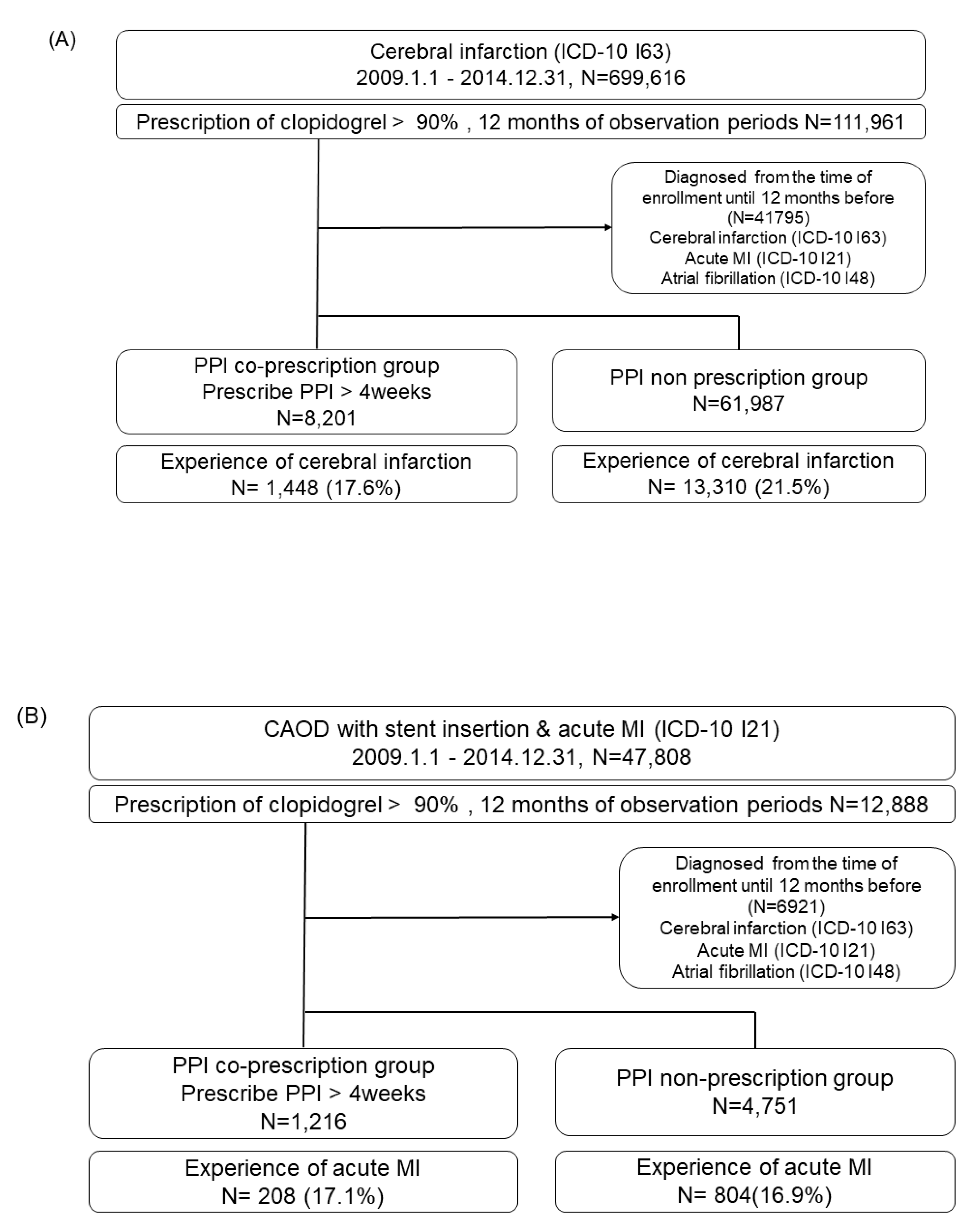
Data sources
Study design and population
Self-controlled case series study
Cohort Study
Statistical analyses
Results
Self-controlled case series design
| Stroke | Myocardial infarction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | PPI co-prescription groups (n=8,201) |
PPI non-prescription group (n=61,987) |
P-value | PPI co-prescription group (n=1,216) |
PPI non-prescription group (n=4,751) |
P-value |
| Sex | ||||||
| Women, n (%) | 3,742 (45.8) | 25,662 (41.4) | <0.001 | 670 (55.1) | 3,043 (64.0) | <0.001 |
| Age | 67.28 ± 10.99 | 66.14 ± 11.86 | <0.001 | 69.64 ± 10.26 | 68.06 ± 11.51 | <0.001 |
| Aspirin co-prescription | 3,094 (37.8) | 22,810 (36.8) | 0.069 | 982 (80.8) | 3,608 (75.9) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity | ||||||
| Hypertension | 6,357 (77.7) | 46,388 (74.8) | <0.001 | 1,080 (58.1) | 4,103 (86.4) | 0.023 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4,041 (49.4) | 32,432 (52.3) | <0.001 | 707 (58.1) | 2,662 (56.0) | 0.185 |
| Dyslipidemia | 5,499 (67.3) | 38,245 (61.7) | <0.001 | 917 (75.4) | 3,534 (74.4) | 0.463 |
| Smoking history | ||||||
| Never smoker | 2,610 (31.9) | 16,837 (27.1) | <0.001 | 341(28.0) | 1,146 (24.1) | 0.020 |
| Ex-smoker | 728 (8.9) | 4,643 (7.5) | 106 (8.7) | 389 (8.2) | ||
| Current smoker | 1,137 (13.9) | 8,531 (13.8) | 159 (13.1) | 625 (13.2) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.43± 3.09 | 24.39 ± 3.05 | 0.479 | 24.11±3.1 | 24.41±3.08 | 0.032 |
| Total cholesterol level (mg/dL) | 202.52 ± 42.01 | 204.96 ± 45.07 | <0.001 | 205.94 ±44.95 | 207.52± 53.37 | 0.460 |
Relative risk of recurrent stroke in the PPI co-prescription group
Relative risk of recurrent MI in the PPI co-prescription group
Cohort study
Incidence of recurrent stroke in the PPI co-prescription group
Incidence of recurrent MI in the PPI co-prescription group
Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scally, B.; Emberson, J.R.; Spata, E.; Reith, C.; Davies, K.; Halls, H.; Holland, L.; Wilson, K.; Bhala, N.; Hawkey, C.; et al. Effects of gastroprotectant drugs for the prevention and treatment of peptic ulcer disease and its complications: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, P.O.; Dunbar, K.B.; Schnoll-Sussman, F.H.; Greer, K.B.; Yadlapati, R.; Spechler, S.J. ACG Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. The American journal of gastroenterology 2022, 117, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakiri, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Manabe, N.; Ihara, E.; Kuribayashi, S.; Akiyama, J.; Kondo, T.; Yamashita, H.; Ishimura, N.; Kitasako, Y.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for gastroesophageal reflux disease 2021. J Gastroenterol 2022, 57, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.K.; Tae, C.H.; Song, K.H.; Kang, S.J.; Park, J.K.; Gong, E.J.; Shin, J.E.; Lim, H.C.; Lee, S.K.; Jung, D.H.; et al. 2020 Seoul Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2021, 27, 453–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, N.S.; Hlatky, M.A.; Antman, E.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bjorkman, D.J.; Clark, C.B.; Furberg, C.D.; Johnson, D.A.; Kahi, C.J.; Laine, L.; et al. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2010 expert consensus document on the concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and thienopyridines: a focused update of the ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use. A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010, 56, 2051–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Kandulski, A.; Venerito, M. Proton-pump inhibitors: understanding the complications and risks. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 14, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.F.; Yang, Y.X.; Howden, C.W. Complications of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, V.; Marabotto, E.; Zentilin, P.; Furnari, M.; Bodini, G.; De Maria, C.; Pellegatta, G.; Coppo, C.; Savarino, E. Proton pump inhibitors: use and misuse in the clinical setting. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 2018, 11, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthiah, M.D.; Zheng, H.L.; Chew, N.W.S.; Xiao, J.L.; Lim, L.G.; Tan, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Low, A.F.; Foo, L.L.; Richards, A.M.; et al. Outcomes of a multi-ethnic Asian population on combined treatment with clopidogrel and omeprazole in 12,440 patients. J Thromb Thrombolys 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Cryer, B.L.; Contant, C.F.; Cohen, M.; Lanas, A.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Shook, T.L.; Lapuerta, P.; Goldsmith, M.A.; Laine, L.; et al. Clopidogrel with or without omeprazole in coronary artery disease. The New England journal of medicine 2010, 363, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Cannon, C.P.; Cryer, B.L.; Liu, Y.; Hsieh, W.H.; Doros, G.; Cohen, M.; Lanas, A.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Shook, T.L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Proton-Pump Inhibitors in High-Risk Cardiovascular Subsets of the COGENT Trial. The American journal of medicine 2016, 129, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Goh, K.L. East Asian perspective on the interaction between proton pump inhibitors and clopidogrel. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology 2017, 32, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.G.; Clare, R.; Pieper, K.S.; Nicolau, J.C.; Storey, R.F.; Cantor, W.J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Angiolillo, D.J.; Husted, S.; Cannon, C.P.; et al. Association of proton pump inhibitor use on cardiovascular outcomes with clopidogrel and ticagrelor: insights from the platelet inhibition and patient outcomes trial. Circulation 2012, 125, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, K.; Katsanos, A.H.; Bilal, M.; Ishfaq, M.F.; Goyal, N.; Tsivgoulis, G. Cerebrovascular Outcomes With Proton Pump Inhibitors and Thienopyridines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2018, 49, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.M.; Maddox, T.M.; Wang, L.; Fihn, S.D.; Jesse, R.L.; Peterson, E.D.; Rumsfeld, J.S. Risk of adverse outcomes associated with concomitant use of clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors following acute coronary syndrome. Jama 2009, 301, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassen, J.A.; Choudhry, N.K.; Avorn, J.; Schneeweiss, S. Cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients using clopidogrel with proton pump inhibitors after percutaneous coronary intervention or acute coronary syndrome. Circulation 2009, 120, 2322–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, I.J.; Evans, S.J.; Hingorani, A.D.; Grosso, A.M.; Timmis, A.; Hemingway, H.; Smeeth, L. Clopidogrel and interaction with proton pump inhibitors: comparison between cohort and within person study designs. BMJ 2012, 345, e4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, T.Z.; Xiang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Tan, H.; Huang, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of clopidogrel only vs. clopidogrel added proton pump inhibitors in the treatment of patients with coronary heart disease after percutaneous coronary intervention: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc 2019, 23, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.J.; Thomas, C.D.; Barbarino, J.; Desta, Z.; Van Driest, S.L.; El Rouby, N.; Johnson, J.A.; Cavallari, L.H.; Shakhnovich, V.; Thacker, D.L.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C19 and Proton Pump Inhibitor Dosing. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2021, 109, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbing, D.; Morath, T.; Stegherr, J.; Braun, S.; Vogt, W.; Hadamitzky, M.; Schömig, A.; Kastrati, A.; von Beckerath, N. Impact of proton pump inhibitors on the antiplatelet effects of clopidogrel. Thromb Haemost 2009, 101, 714–719. [Google Scholar]
- Siller-Matula, J.M.; Spiel, A.O.; Lang, I.M.; Kreiner, G.; Christ, G.; Jilma, B. Effects of pantoprazole and esomeprazole on platelet inhibition by clopidogrel. Am Heart J 2009, 157, 148–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, N.; Haddad, N.; Crispo, J.; Birkett, N.; McNair, D.; Momoli, F.; Wen, S.W.; Mattison, D.R.; Krewski, D. Trends in concomitant clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitor treatment among ACS inpatients, 2000-2016. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2019, 75, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.O.; Jung, C.H.; Song, Y.D.; Park, C.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Cha, B.S.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Ko, K.S.; Lee, B.W. Background and data configuration process of a nationwide population-based study using the korean national health insurance system. Diabetes Metab J 2014, 38, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Han, K.; Ko, S.H.; Ko, K.S.; Lee, K.U. Data Analytic Process of a Nationwide Population-Based Study Using National Health Information Database Established by National Health Insurance Service. Diabetes Metab J 2016, 40, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.C.; Lee, S.; Cho, S.Y.; Park, H.; Jung, S.; Cho, J.; Yoon, D.; Park, R.W. Conversion of National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC) Database into Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership-Common Data Model (OMOP-CDM). Studies in health technology and informatics 2017, 245, 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Hripcsak, G.; Duke, J.D.; Shah, N.H.; Reich, C.G.; Huser, V.; Schuemie, M.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Park, R.W.; Wong, I.C.; Rijnbeek, P.R.; et al. Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI): Opportunities for Observational Researchers. Studies in health technology and informatics 2015, 216, 574–578. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.I.; Park, C.H.; You, S.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, J.J.; Seo, W.W.; Lee, H.S.; et al. Association between proton pump inhibitor use and gastric cancer: a population-based cohort study using two different types of nationwide databases in Korea. Gut 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.H.; Seo, S.I.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, W.W.; Lee, H.S.; Shin, W.G.; Yoo, J.J. Long-term proton pump inhibitor use and risk of osteoporosis and hip fractures: A nationwide population-based and multicenter cohort study using a common data model. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022, 37, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.I.; Park, C.H.; Kim, T.J.; Bang, C.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.H.; You, S.C.; Shin, W.G. Aspirin, metformin, and statin use on the risk of gastric cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea with systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med 2022, 11, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, H.J.; Hocine, M.N.; Farrington, C.P. The methodology of self-controlled case series studies. Stat Methods Med Res 2009, 18, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Schuemie, M.J.; Suchard, M.A. Evaluating large-scale propensity score performance through real-world and synthetic data experiments. International journal of epidemiology 2018, 47, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundhun, P.K.; Teeluck, A.R.; Bhurtu, A.; Huang, W.Q. Is the concomitant use of clopidogrel and Proton Pump Inhibitors still associated with increased adverse cardiovascular outcomes following coronary angioplasty?: a systematic review and meta-analysis of recently published studies (2012 - 2016). BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2017, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.C.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.G.; Yu, M.Y. Ethnic variance on long term clinical outcomes of concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and clopidogrel in patients with stent implantation A PRISMA-complaint systematic review with meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, B.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Kim, D.B.; Ahn, H.S. Influence of individual proton pump inhibitors on clinical outcomes in patients receiving clopidogrel following percutaneous coronary intervention. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021, 100, e27411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Schuemie, M.J.; Blei, D.M.; Hripcsak, G. Adjusting for indirectly measured confounding using large-scale propensity score. Journal of biomedical informatics 2022, 134, 104204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.C.; Rho, Y.; Bikdeli, B.; Kim, J.; Siapos, A.; Weaver, J.; Londhe, A.; Cho, J.; Park, J.; Schuemie, M.; et al. Association of Ticagrelor vs Clopidogrel With Net Adverse Clinical Events in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Jama 2020, 324, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchard, M.A.; Schuemie, M.J.; Krumholz, H.M.; You, S.C.; Chen, R.; Pratt, N.; Reich, C.G.; Duke, J.; Madigan, D.; Hripcsak, G.; et al. Comprehensive comparative effectiveness and safety of first-line antihypertensive drug classes: a systematic, multinational, large-scale analysis. Lancet (London, England). [CrossRef]
- Requena, G.; Douglas, I.J.; Huerta, C.; de Abajo, F. Impact of pre-exposure time bias in self-controlled case series when the event conditions the exposure: Hip/femur fracture and use of benzodiazepines as a case study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2020, 29, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stroke | Myocardial infarction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of events | Relative risk (95% CI) | Number of events | Relative risk (95% CI) | |
| Total events | 1448 | 208 | ||
| RR of PPIs exposed periods (PPIs co-prescribed periods only) | ||||
| PPIs unexposed | 795 | 1 (reference) | 113 | 1 (reference) |
| Overall | 653 | 2.09 (1.83-2.38) | 95 | 1.47 (1.02-2.11) |
| 0~2 weeks | 254 | 1.76 (1.50-2.07) | 32 | 1.30 (0.83-2.04) |
| 2~4 weeks | 187 | 2.02 (1.68-2.43) | 16 | 0.95 (0.54-1.69) |
| 4~6 weeks | 90 | 3.02 (2.36-3.86) | 19 | 2.33 (1.32-4.13) |
| 6~8 weeks | 47 | 2.81 (2.02- 3.92) | 11 | 1.99 (0.98-4.03) |
| >8 weeks | 75 | 5.57 (4.06-7.64) | 17 | 3.80 (1.93-7.45) |
| RR of PPIs exposed periods (included PPIs washout periods) | ||||
| Non-risk periods | 594 | 1 (reference) | 85 | 1 (reference) |
| Risk-periods | 854 | 2.47 (2.16-2.81) | 123 | 1.87 (1.31-2.65) |
| Type of PPIs | Stroke | Myocardial infarction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of events | Relative risk (95% CI) | Number of events | Relative risk (95% CI) | ||
| Omeprazole | PPIs unexposed | 83 | 1 (reference) | 7 | 1 (reference) |
| Overall | 54 | 1.84 (1.18-2.86) | 2 | 0.33 (0.47-2.34) | |
| Non-risk periods | 64 | 1 (reference) | 5 | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 73 | 2.03 (1.34-3.08) | 4 | 1.04 (0.13-8.40) | |
| Esomeprazole | PPIs unexposed | 181 | 1 (reference) | 29 | 1 (reference) |
| Overall | 192 | 2.75 (2.12-3.57) | 21 | 0.89 (0.36-2.18) | |
| Non-risk periods | 128 | 1 (reference) | 23 | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 245 | 3.18 (2.45-4.11) | 27 | 1.18 (0.52-2.65) | |
| Pantoprazole | PPIs unexposed | 213 | 1 (reference) | 42 | 1 (reference) |
| Overall | 151 | 1.61 (1.21-2.13) | 40 | 2.56 (1.46-4.50) | |
| Non-risk periods | 175 | 1 (reference) | 35 | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 189 | 1.80 (1.37-2.35) | 47 | 2.53 (1.47-4.36) | |
| Rabeprazole | PPIs unexposed | 295 | 1 (reference) | 39 | 1 (reference) |
| Overall | 197 | 1.88 (1.49-2.36) | 19 | 1.11(0.54–2.24) | |
| Non-risk periods | 232 | 1 (reference) | 32 | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 260 | 2.02 (1.62-2.52) | 24 | 1.14 (0.54-1.98) | |
| Lansoprazole | PPIs unexposed | 121 | 1 (reference) | 21 | 1 (reference) |
| Overall | 49 | 1.32 (0.87-2.01) | 11 | 0.58 (0.22-1.52) | |
| Non-risk periods | 99 | 1 (reference) | 16 | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 71 | 1.63 (1.12-2.38) | 16 | 0.87 (0.33-2.24) | |
| Dexlansoprazole | PPIs unexposed | 9 | 1 (reference) | 0 | 1 (reference) |
| Overall | 3 | 1.08 (0.18-6.49) | 2 | NA | |
| Non-risk periods | 6 | 1 (reference) | 0 | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 6 | 3.65 (0.71-8.78) | 2 | NA | |
| Outcome | Cohort | Patients, n | Observation, person-years | Events | Incidence ratea | HR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke | PPI | 373 | 240 | 81 | 337.5 | 1.34 (1.01-1.76) | 0.04 |
| Non-PPI | 1,051 | 740 | 189 | 255.2 | Reference | ||
| Myocardial infarction | PPI | 179 | 133 | 23 | 171.7 | 1.42 (0.79-2.49) | 0.23 |
| Non-PPI | 439 | 336 | 43 | 127.8 | Reference |
| Analysis | Observation period | Stroke HR (95% CI) |
Myocardial infarction HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PS matching 1:4(main analysis) | 12 months | 1.34 (1.01-1.76) | 1.42 (0.79-2.49) |
| 1:4 | 6 months | 1.42 (1.05-1.90) | 2.15 (1.10-4.13) |
| 1:1 | 12 months | 1.52 (1.06-2.20) | 1.33 (0.69-2.65) |
| 1:1 | 6 months | 1.56 (1.07-2.30) | 2.12 (0.95-5.21) |
| PS stratification | 12 months | 1.37 (1.08-1.73) | 1.15 (0.71-1.81) |
| 6 months | 1.43 (1.10-1.84) | 1.69 (0.96-2.92) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





