Submitted:
23 July 2023
Posted:
25 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
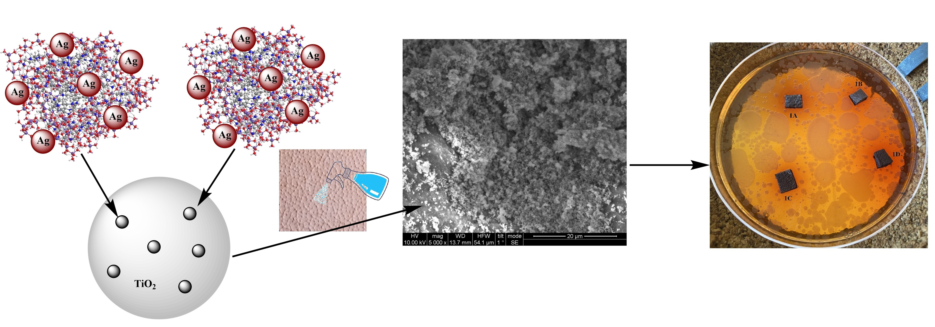
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3. IR Spectroscopy
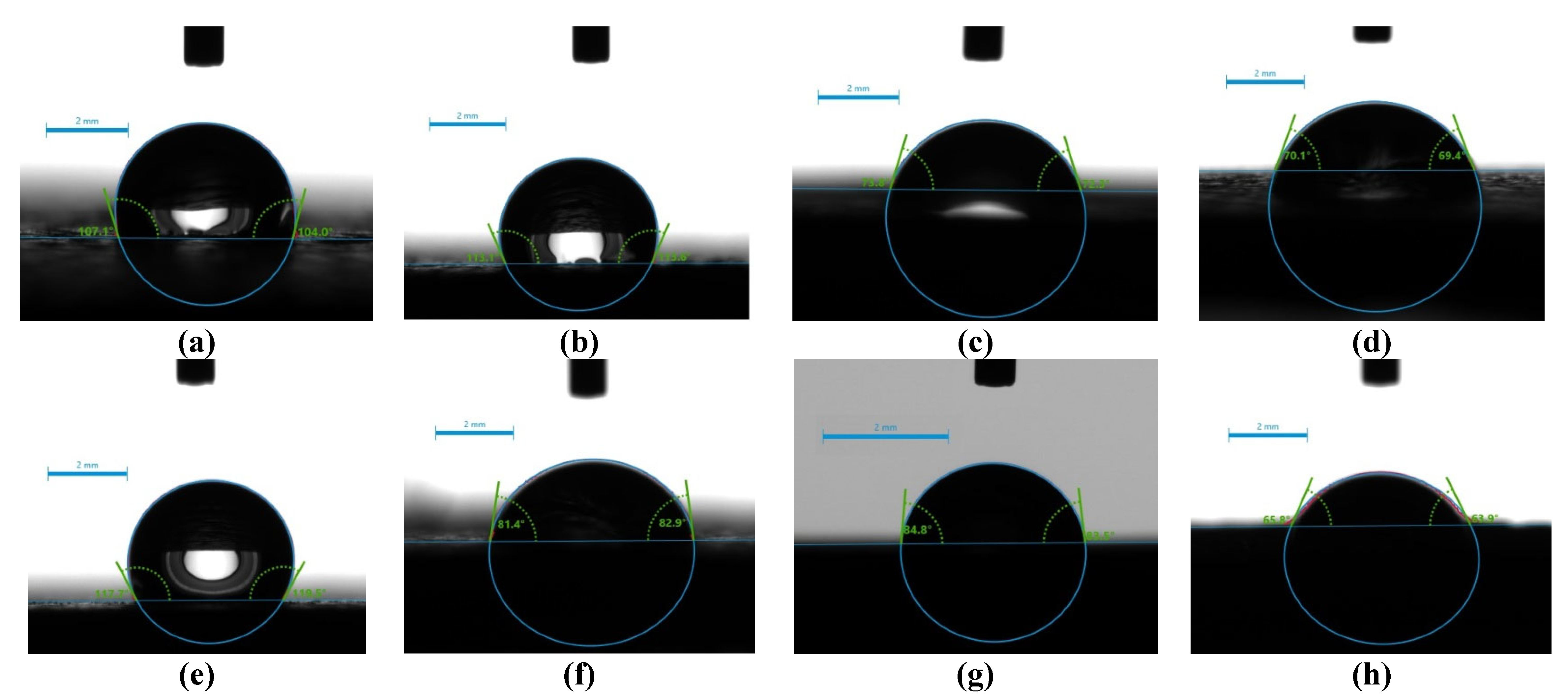
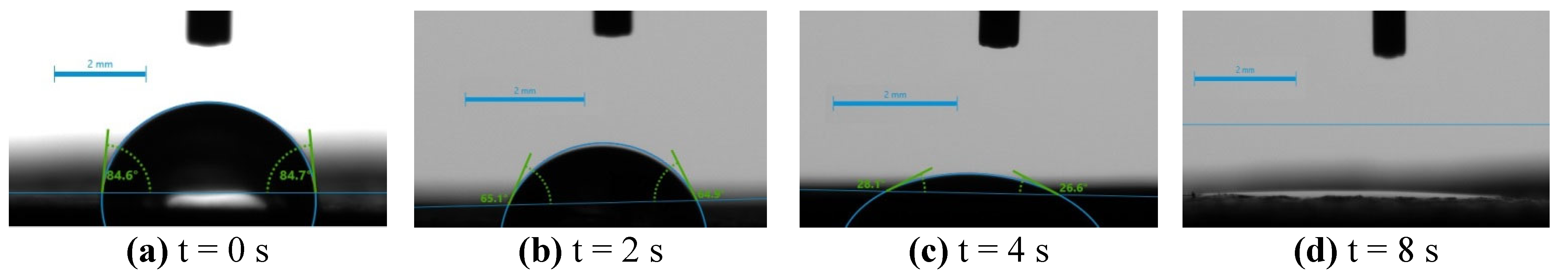
2.4. Surface Hydrophilicity/Hydrophobicity – Water Wettability
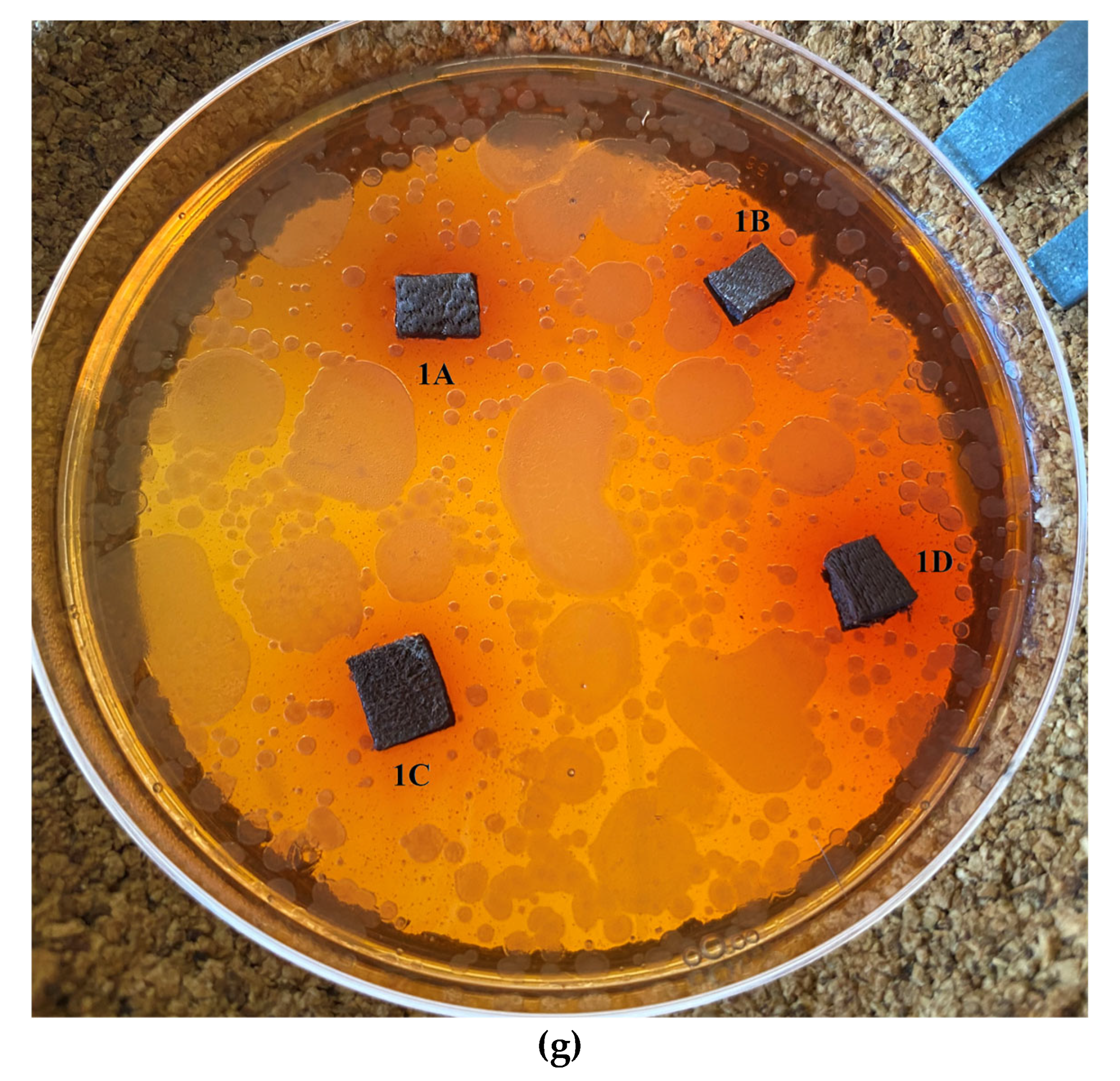
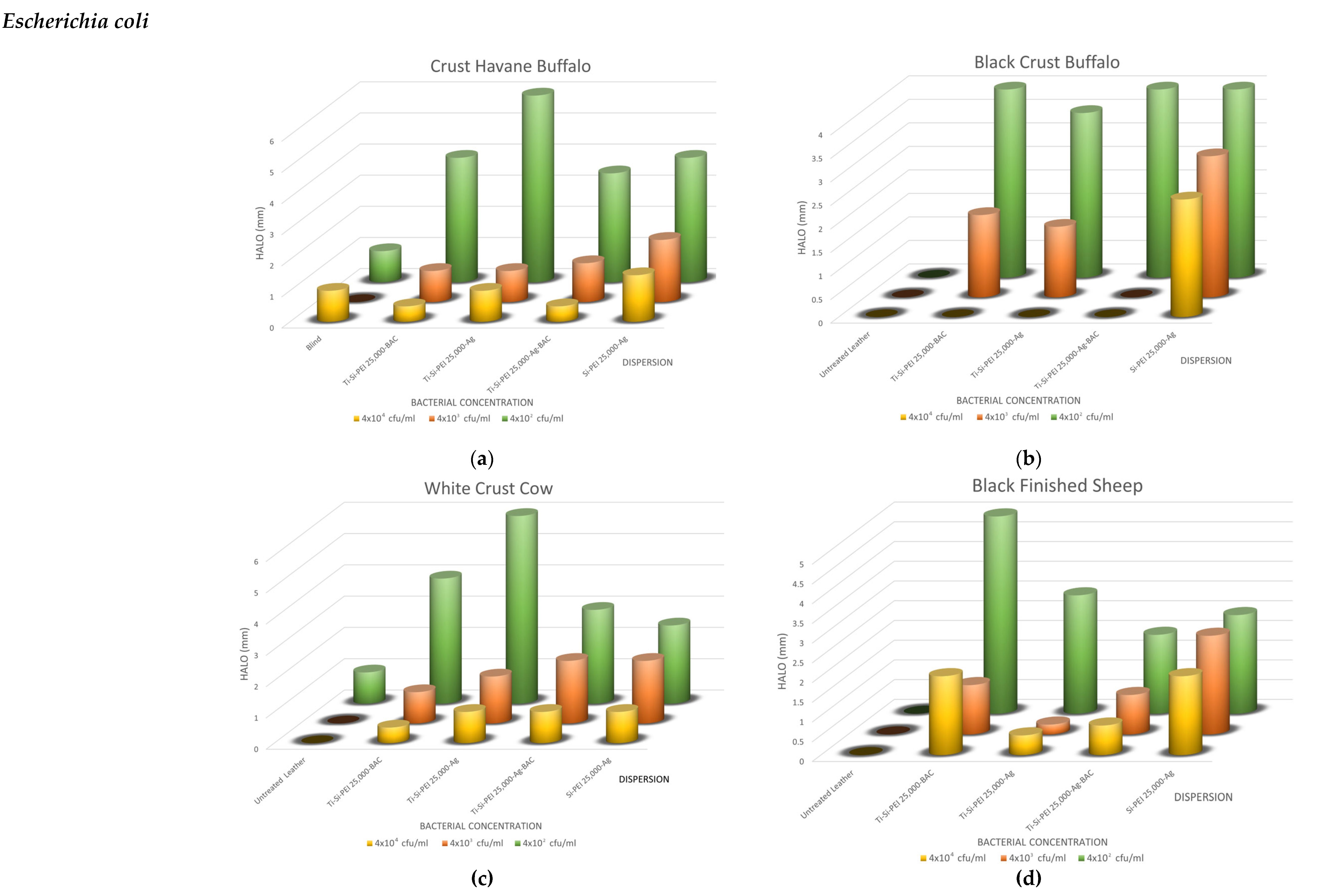
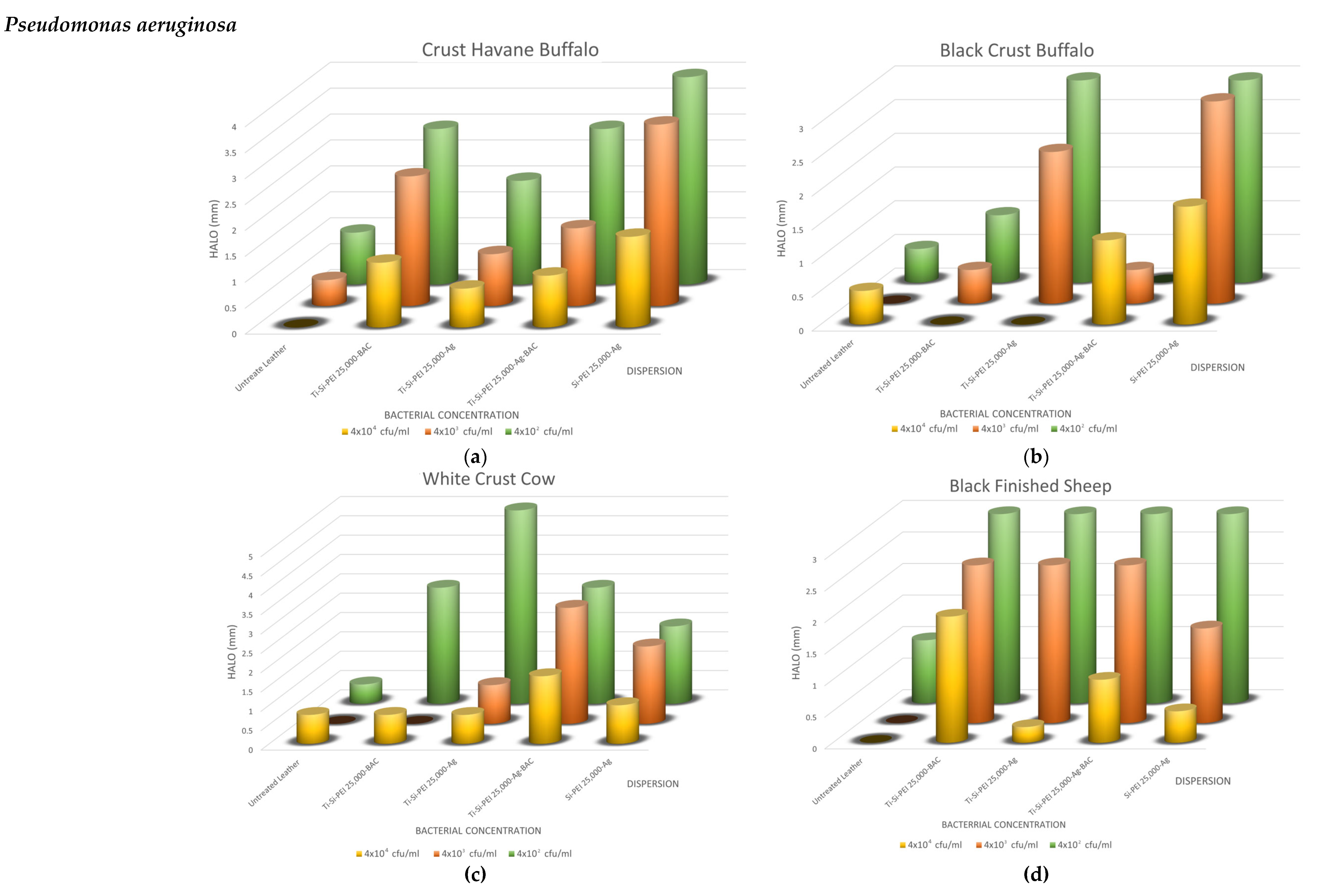
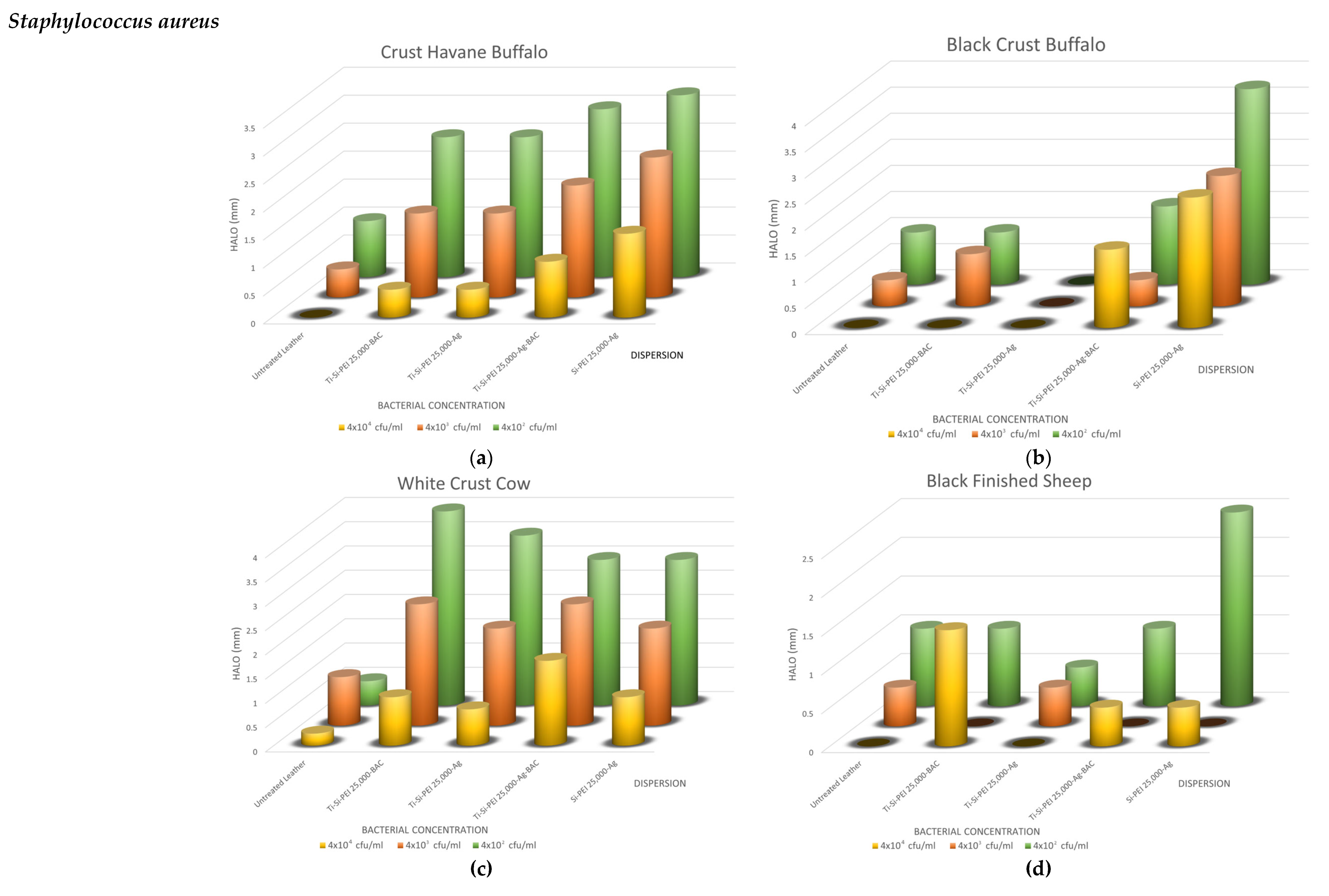
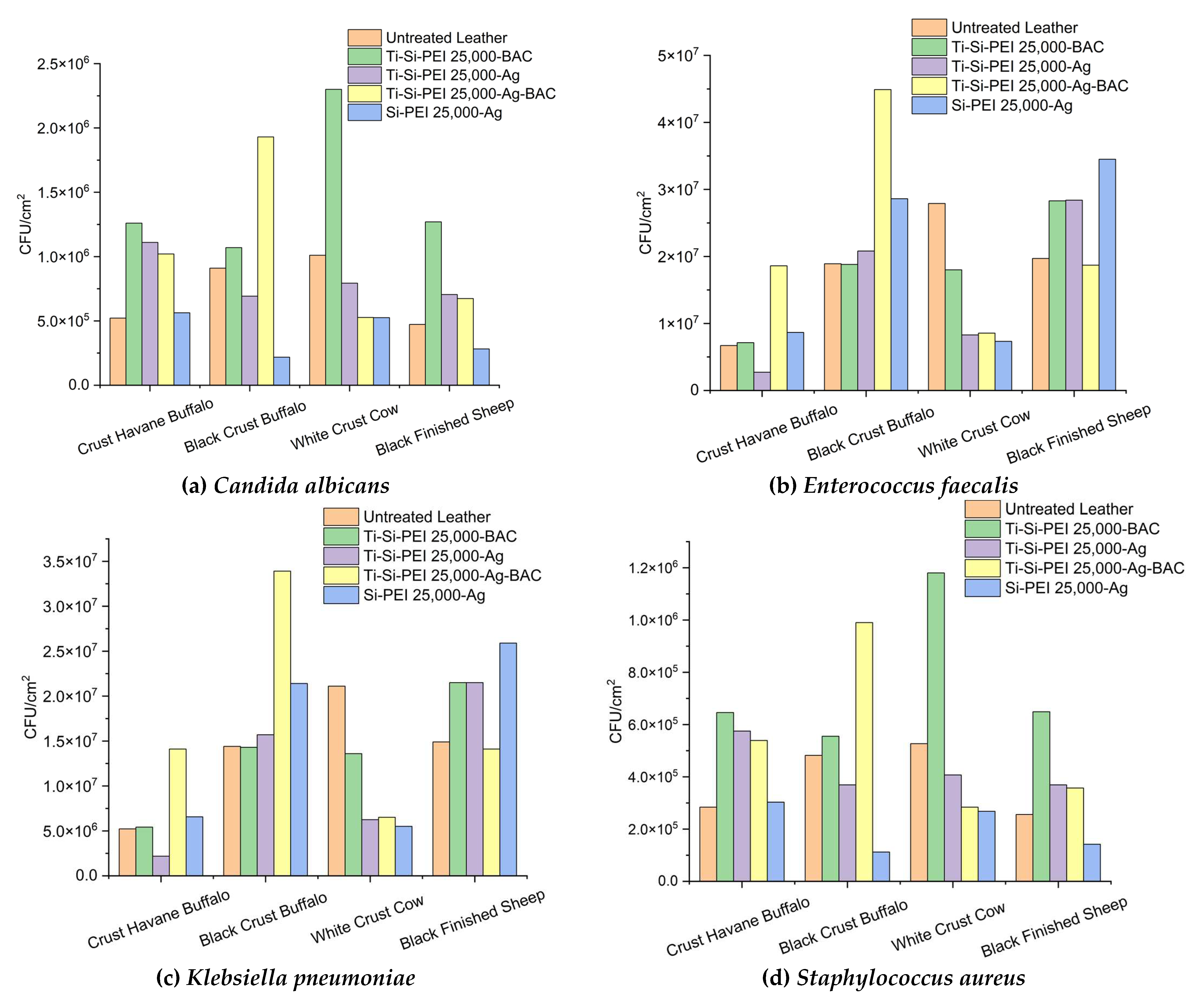
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5.1. Disk-Diffusion Method
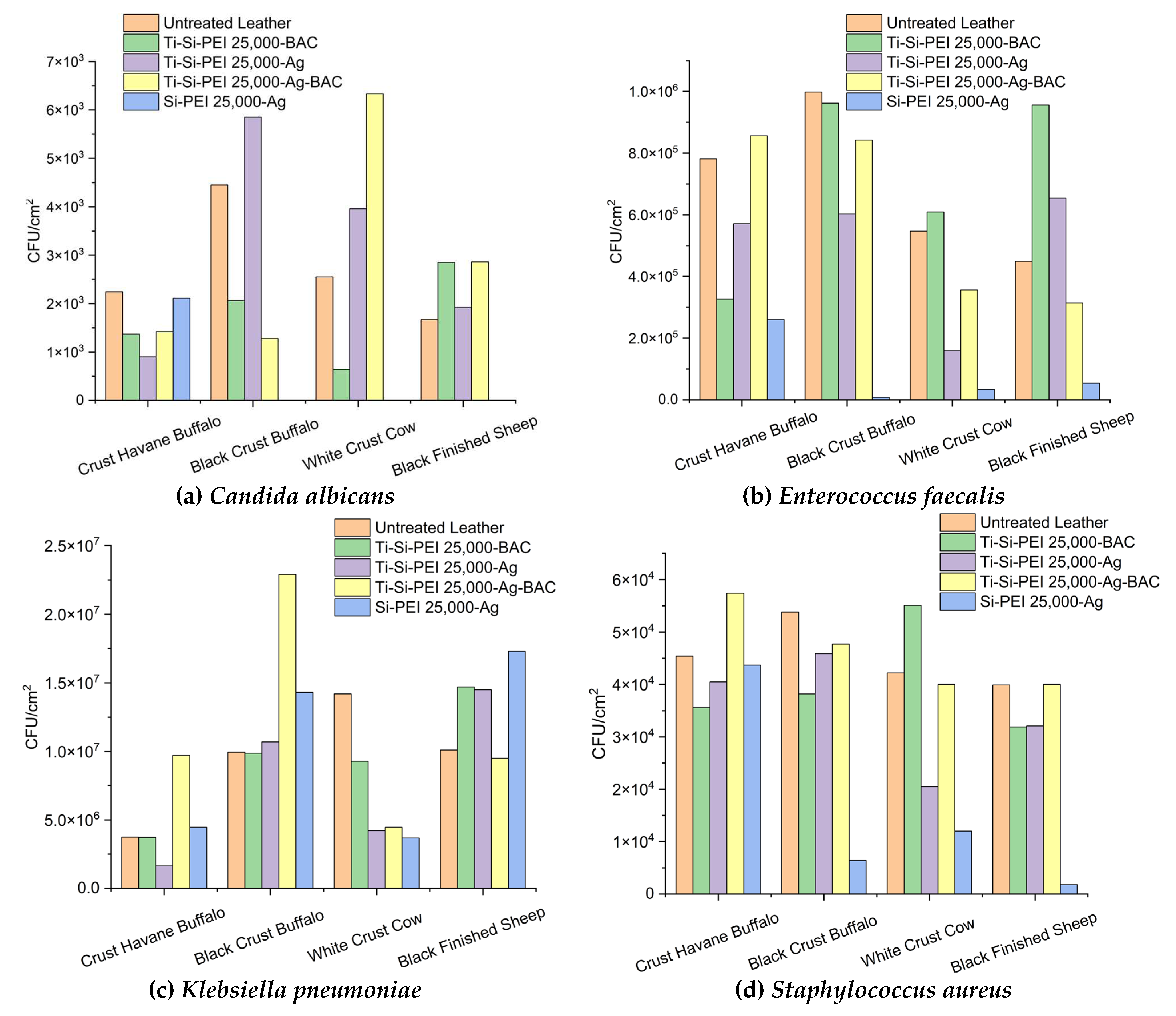
2.5.2. Anti Adherence Activity
2.5.2. Antibiofilm Activity of Leather Samples
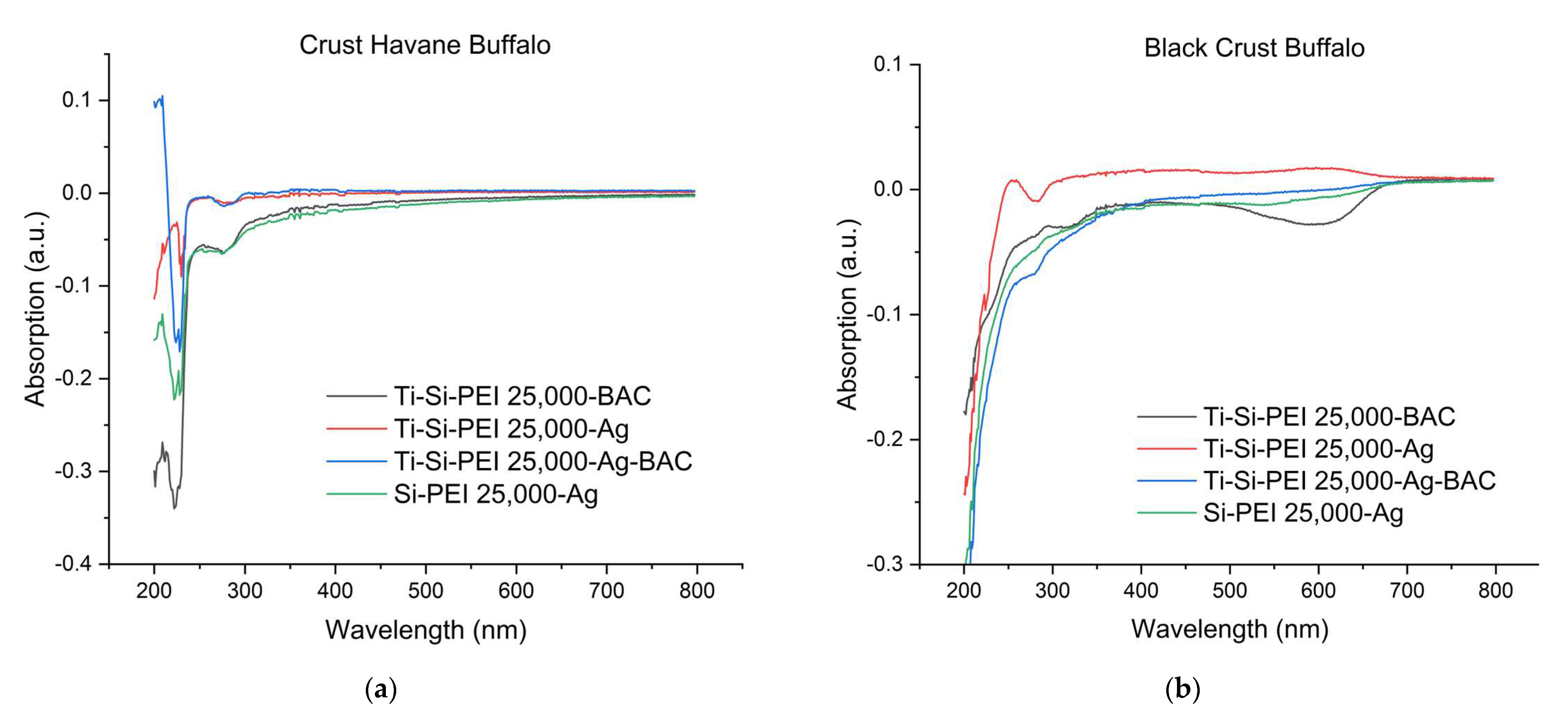
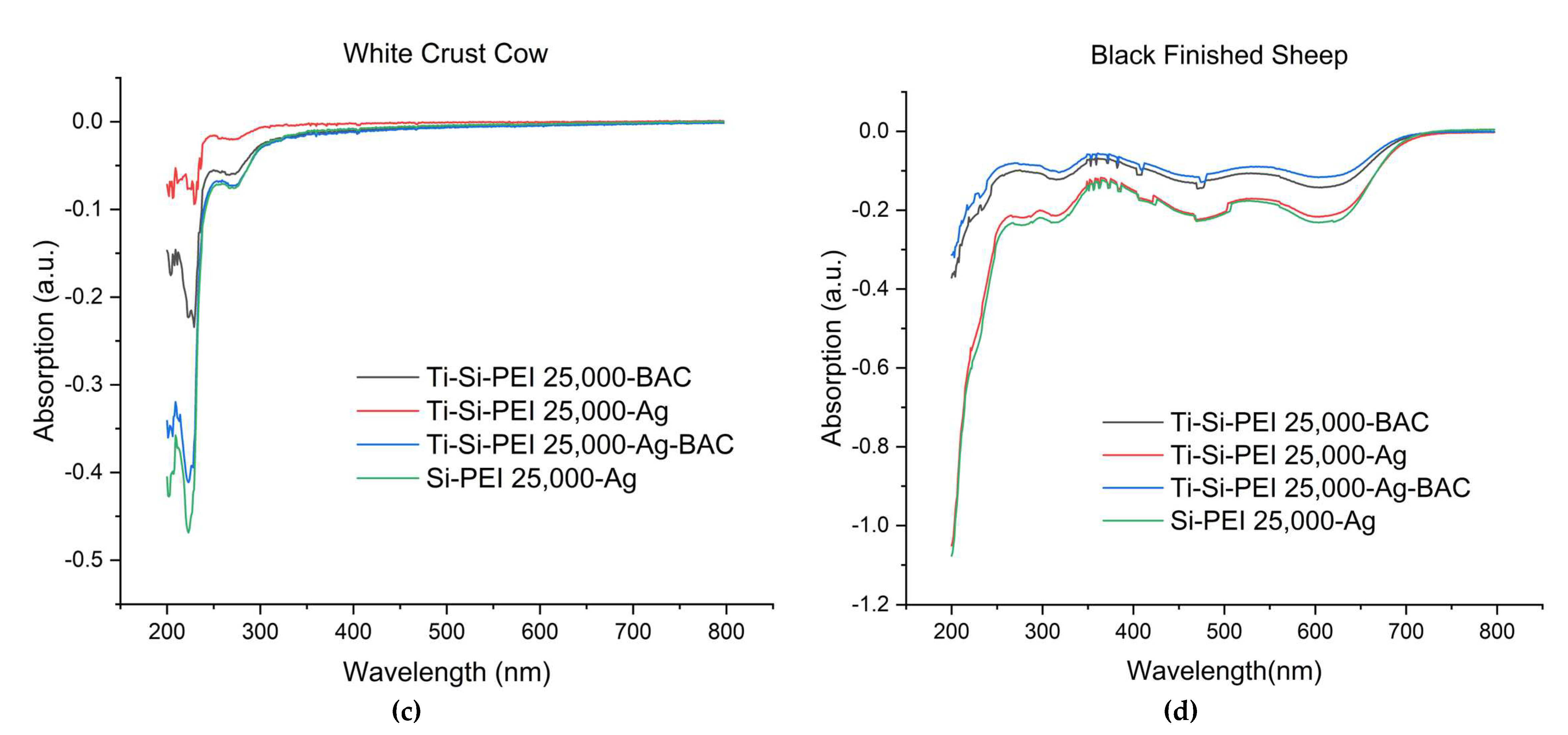
2.3. Difusion of leather components in water
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instrumentation
4.3. Pretreatment of Raw Bovine Buffalo and Sheep Hides
4.4. Synthesis of Xerogels and Coating of Leathers
4.4.1. Preparation of the Silica Xerogel-Silver Nanoparticle Dispersion (Si-PEI 25,000-Ag)
4.4.2. Preparation of the Titania-Silica Xerogel-Silver Nanoparticle Dispersion (Ti-Si-PEI 25,000-Ag)
4.4.3. Preparation of the Titania-Silica Xerogel-BAC Dispersion (Ti-Si-PEI 25,000-BAC)
4.4.4. Preparation of the Titania-Silica Xerogel- Silver Nanoparticle-BAC Dispersion (Ti-Si-PEI 25,000-Ag-BAC)
4.5. Disk-Diffusion Method
4.6. Anti-adherence Properties of Leather Samples
4.7. Antibiofilm Properties of Leather Samples
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, R.R.; Sathish, M.; Rao, J.R. Research advances in the fabrication of biosafety and functional leather: A way-forward for effective management of COVID-19 outbreak. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127464. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, S.; Yadav, A.; Dwivedi, P.D.; Das, M. Toxic hazards of leather industry and technologies to combat threat: a review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2015, 87, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenti, R.; Redwood, M.; Puig, R.; Frostell, B. Measuring the environmental footprint of leather processing technologies. Journal of Industrial Ecology 2017, 21, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Lee, T.-J.; Hsiao, C.-S.; Chen, S.-Y.; Liu, D.-M. Characterization and drug release behavior of chip-like amphiphilic chitosan-silica hybrid hydrogel for electrically modulated release of ethosuximide: An in vitro study. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16077–16085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Z. A pH-Responsive Hydrogel Based on a Tumor-Targeting Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposite for Sustained Cancer. Labeling Ther. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radin, S.; El-Bassyouni, G.; Vresilovic, E.J.; Schepers, E.; Ducheyne, P. In vivo tissue response to resorbable silica xerogels as controlled-release materials. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahola, M.; Rich, J.; Kortesuo, P.; Kiesvaara, J.; Seppala, J.; Yli-Urpo, A. In vitro evaluation of biodegradable s-caprolactone-co-D,Llactide/silica xerogel composites containing toremifene citrate. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 181, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C. Lok, C. Ho, R. Chen, Q. He, W. Yu, H. Sun, P.K. Tam, J. Chiu, C. Che, Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles research articles. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 916–924. [CrossRef]
- J.S. Kim, E. Kuk, K.N. Yu, J.H. Kim, S.J. Park, H.J. Lee, S.H. Kim, Y.K.Park, Y.H. Park, C.Y. Hwang, Y.K. Kim, Y.S. Lee, D.H. Jeong, M.H. Cho, Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol.Med. 2007, 3, 95–101.
- S. Jaiswal, P. McHale, B. Duffy, Preparation and rapid analysis of antibacterial silver, copper and zinc doped sol-gel surfaces. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2012, 94, 170–176. [CrossRef]
- U. Samuel, J.P. Guggenbichler, Prevention of catheter-related infections: the potential of a new nano-silver impregnated catheter. Int.J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 75–78. [CrossRef]
- K. Chaloupka, Y. Malam, A.M. Seifalian, Nanosilver as a new generation of nanoproduct in biomedical applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 580–288. [CrossRef]
- A, Petica, C. Gaidau, J. Ma, D. Simion, Q. Xu, M. Niculescu, Antimicrobial electrochemically obtained nanosilver solutions for leather and fur skin treatment. Rev. Chim. 2013, 64, 1329–1334.
- I.M. Lopez, M.F. Payà-Nohales, J.N. Cuesta-Garrote, F. Arán-Ais, M.Á.Martinez-Sánchez, C. Orgilés-Barceló, M. Bertazzo, Antimicrobial effect of coated leather based on silver nanoparticles and nanocomposites: synthesis, characterisation and microbiological evaluation. J. Biotechnol.Biomater. 2015, 5, 1–10.
- M.M. Sanchez-Navarro, M.A. Perez-Liminana, N. Cuesta-Garrote, M.I.Maestre-Lopez, M. Bertazzo, M.A. Martinez-Sanchez, C. Orgiles-Barcelo, F. Aran-Ais, Latest developments in antimicrobial functional materials for footwear. Microbial Pathogens and Strategies for Combating Them: Science, Technology and Education 2013, 102–113.
- Petica A., Gaidau C., Ignat M., Sendrea C., Anicai L. Doped TiO2 nanophotocatalysts for leather surface finishing with self-cleaning properties. J Coat Technol Res. 2015, 12, 1153–1163. [CrossRef]
- Xu Q., Fan Q., Ma J., Yan Z. Facile synthesis of casein-based TiO2 nanocomposite for self-cleaning and high covering coatings: insights from TiO2 dosage. Prog Org Coat. 2016, 99, 223–229. [CrossRef]
- A. Fujishima, X. Zhang, D.A. Tryk, TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2008, 63, 515–582. [CrossRef]
- S.M. Gupta, M. Tripathi, A review of TiO2 nanoparticles. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 1639–1657. [CrossRef]
- V.I. Shapovalov, Nanopowders and films of titanium oxide for photo-catalysis: a review. Glas. Phys. Chem. 2010, 36, 121–157. [CrossRef]
- J.W. Liou, H.H. Chang, Bactericidal effects and mechanisms of visible light-responsive titanium dioxide photocatalysts on pathogenic bacteria. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 2012, 60, 267–275. [CrossRef]
- Yasa, I., Lkhagvajav N., Koizhaiganova M., Çelik E., Sari Ö., Assessment of antimicrobial activity of nanosized Ag-TiO2 prepared by sol-gel method. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2531–2539.
- Kim, H.Y., Kim J.H., Kwon S.C., Jeong S.H., A study on multifunctional wool textiles treated with nanosized silver. J. Mater. Sci 2007, 42, 8020–8024. [CrossRef]
- Lee M., S., Hong S.,S., Mohseni M., Synthesis of photocatalytic nanosized TiO2–Ag particles with sol–gel method using reduction agent. J. Mol. Catal. A. Chem 2005, 242, 135–140. [CrossRef]
- Fréchet, J.M.J.; Tomalia, D.A. Dendrimers and Other Dendritic Polymers, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vögtle, F.; Gestermann, S.; Hesse, R.; Schwierz, H.; Windisch, B. Functional Dendrimers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 987–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newkome, G.R.; Moorefield, C.N.; Vögtle, F. Dendrimers and Dendrons. Concepts, Syntheses, Perspectives, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bosman, A.W.; Janssen, H.M.; Meijer, E.W. About Dendrimers: Structure, Physical Properties, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 1665–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Mackay, J.A.; Frechet, J.M.; Szoka, F.C. Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalia, D.A.; Frechet, J.M.J. Discovery of dendrimers and dendritic polymers: A brief historical perspective. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2002, 40, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréchet, J.M.J.; Hawker, C.J.; Gitsov, I.; Leon, J.W. Dendrimers and Hyperbranched Polymers: Two Families of Three-Dimensional Macromolecules with Similar but Clearly Distinct Properties. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 1996, 33, 1399–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkas, M.; Eleades, L.; Paleos, C.M.; Tsiourvas, D. Alkylated hyperbranched polymers as molecular nanosponges for the purification of water from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 2299–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allabashi, R.; Arkas, M.; Hörmann, G.; Tsiourvas, D. Removal of some organic pollutants in water employing ceramic membranes impregnated with cross-linked silylated dendritic and cyclodextrin polymers. Water Res. 2007, 41, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marple, B.; Roland, P.; Benninger, M. Safety review of benzalkonium chloride used as a preservative in intranasal solutions: An overview of conflicting data and opinions. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuo, T.; Masahiro, I.; Kyoji, K.; Yukio, S. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of copolymers having a quaternary ammonium salt side group. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1989, 37, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, J.A.; Froelich, E.J. Inactivation of Viruses by Benzalkonium Chloride. Appl. Microbiol. 1964, 12, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, O.I.; Scrivano, L.; Sinicropi, S.; Puoci, F. Polymeric nanoparticle constructs as devices for antibacterial therapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 36, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkas, M.; Anastopoulos, I.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Pashalidis, I.; Katsika, T.; Nikoli, E.; Panagiotopoulos, R.; Fotopoulou, A.; Vardavoulias, M.; Douloudi, M. Catalytic Neutralization of Water Pollutants Mediated by Dendritic Polymers. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiourvas, D.; Tsetsekou, A.; Papavasiliou, A.; Arkas, M.; Boukos, N. A novel hybrid sol–gel method for the synthesis of highly porous silica employing hyperbranched poly(ethyleneimine) as a reactive template. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 175, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakli, F.; Arkas, M.; Tsetsekou, A. α-Alumina nanospheres from nano-dispersed boehmite synthesized by a wet chemical route. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 3508–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsou, I.; Arkas, M.; Tsetsekou, A. Synthesis and characterization of ceria-coated silica nanospheres: Their application in heterogeneous catalysis of organic pollutants. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiourvas, D.; Tsetsekou, A.; Arkas, M.; Diplas, S.; Mastrogianni, E. Covalent attachment of a bioactive hyperbranched polymeric layer to titanium surface for the biomimetic growth of calcium phosphates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 22, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douloudi, M.; Nikoli, E.; Katsika, T.; Vardavoulias, M.; Arkas, M. Dendritic Polymers as Promising Additives for the Manufacturing of Hybrid Organoceramic Nanocomposites with Ameliorated Properties Suitable for an Extensive Diversity of Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsou, I.; Panagopoulos, P.; Maggos, T.; Arkas, M.; Tsetsekou, A. Development of SiO2@TiO2 core-shell nanospheres for catalytic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 441, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkas, M., Douloudi, M., Nikoli, E., Karountzou, G., Kitsou, I., Kavetsou, E., Korres, D., Vouyiouka, S., Tsetsekou, A., Giannakopoulos, K. and Papageorgiou, M. Investigation of two bioinspired reaction mechanisms for the optimization of nano catalysts generated from hyperbranched polymer matrices. Reactive and Functional Polymers 2022, 174, 105238.
- Arkas, M.; Tsiourvas, D. Organic/inorganic hybrid nanospheres based on hyperbranched poly (ethylene imine) encapsulated into silica for the sorption of toxic metal ions and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkas, M., Giannakopoulos, K., Favvas, E.P., Papageorgiou, S., Theodorakopoulos, G.V., Giannoulatou, A., Vardavoulias, M., Giannakoudakis, D.A., Triantafyllidis, K.S., Georgiou, E. and Pashalidis, I. Comparative Study of the U (VI) Adsorption by Hybrid Silica-Hyperbranched Poly (ethylene imine) Nanoparticles and Xerogels. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1794.
- Martin, C.A.; Lin, Z.; Kumar, A.; Dinneen, S.R.; Osgood, I.R.M.; Deravi, L.F. Biomimetic Colorants and Coatings Designed with Cephalopod-Inspired Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 4, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfand, R.; Tomalia, D.A. Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers: From biomimicry to drug delivery and biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2001, 6, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.K., Jensen, H.E., Blirup-Plum, S.A., Bue, M., Hanberg, P., Kvich, L., Aalbæk, B., López, Y., Soto, S.M., Douloudi, M. and Papageorgiou, M. Coating of bone implants with silica, hyperbranched polyethyleneimine, and gentamicin prevents development of osteomyelitis in a porcine model. Materialia 2022, 24, 101473.
- Arkas, M., Vardavoulias, M., Kythreoti, G. and Giannakoudakis, D.A. Dendritic Polymers in Tissue Engineering: Contributions of PAMAM, PPI PEG and PEI to Injury Restoration and Bioactive Scaffold Evolution. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 524. [CrossRef]
- Arkas, M., Kythreoti, G., Favvas, E.P., Giannakopoulos, K., Mouti, N., Arvanitopoulou, M., Athanasiou, A., Douloudi, M., Nikoli, E., Vardavoulias, M. and Dimitriou, M. Hydrophilic antimicrobial coatings for medical leathers from silica-dendritic polymer-silver nanoparticle composite xerogels. Textiles 2022, 2, 464–485.
- Arkas, M., Douloudi, M., Nikoli, E., Karountzou, G., Kitsou, I., Kavetsou, E., Korres, D., Vouyiouka, S., Tsetsekou, A., Giannakopoulos, K. and Papageorgiou, M., Additional data on the investigation of the reaction mechanisms for the production of silica hyperbranched polyethylene imine silver nanoparticle composites. Data in Brief 2022, 43, 108374.
- Bellamy, L.J. The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules; Methuen & Co Ltd.: London, UK, 1966; p. 341. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiourvas, D.; Arkas, M. Columnar and smectic self-assembly deriving from non ionic amphiphilic hyperbranched polyethylene imine polymers and induced by hydrogen bonding and segregation into polar and non polar parts. Polymer 2013, 54, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M., Naffa, R., Maidment, C., Holmes, G. and Waterland, M. Raman and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy towards classification of wet blue bovine leather using ratiometric and chemometric analysis. Journal of Leather Science and Engineering 2020, 2, 1–15.
- Shao, Y., 2005. Chemical analysis of leather. Chemical testing of textiles. Abington, Woodhead Publishing, pp.47-73.
- Arkas, M.; Kithreoti, G.; Boukos, N.; Kitsou, I.; Petrakli, F.; Panagiotaki, K. Two completely different biomimetic reactions mediated by the same matrix producing inorganic/organic/inorganic hybrid nanoparticles. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 14, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoranová, D., Brezová, V., Mazúr, M. and Malati, M.A. Investigations of metal-doped titanium dioxide photocatalysts. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2022, 37, 91–105.


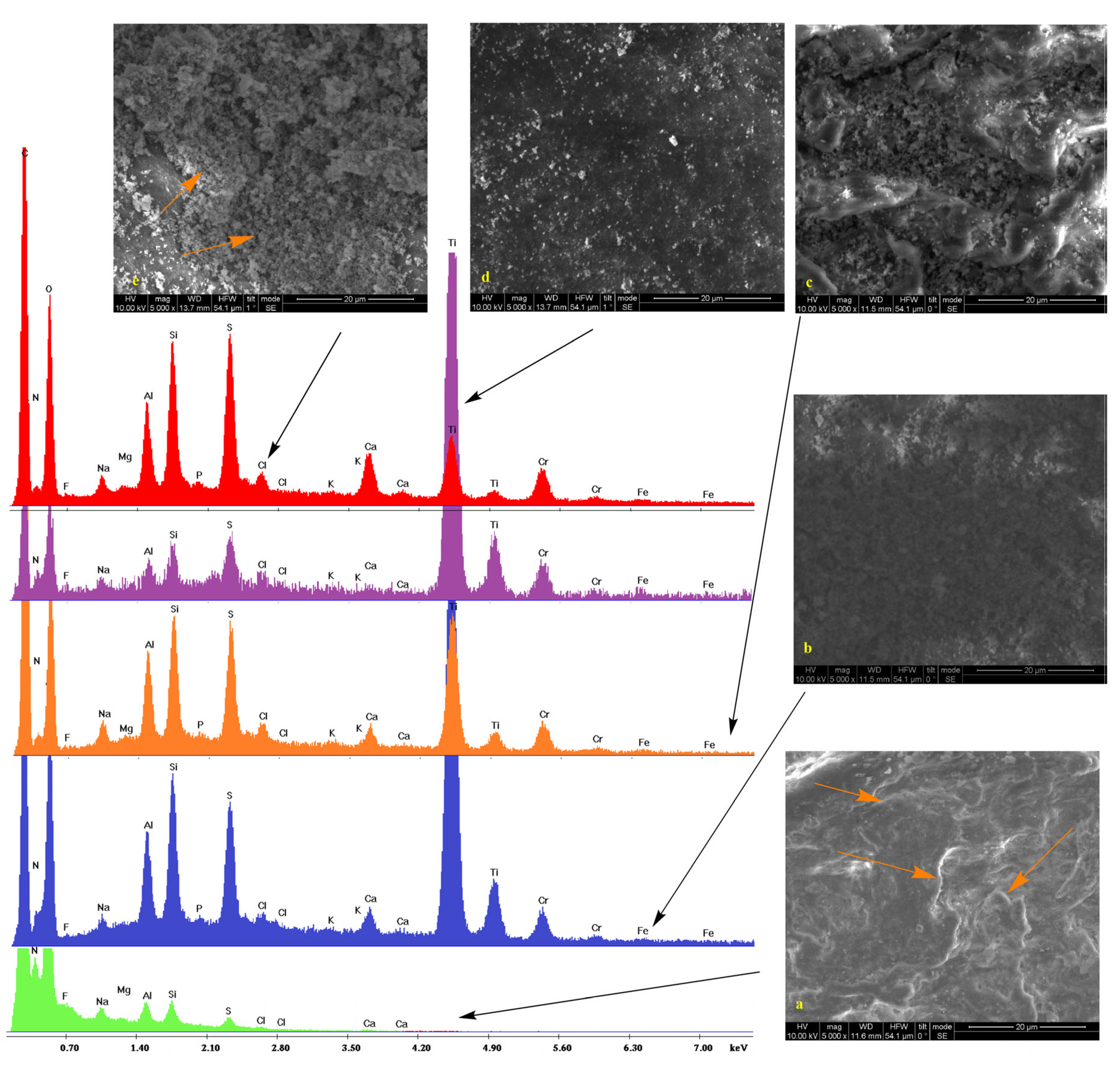
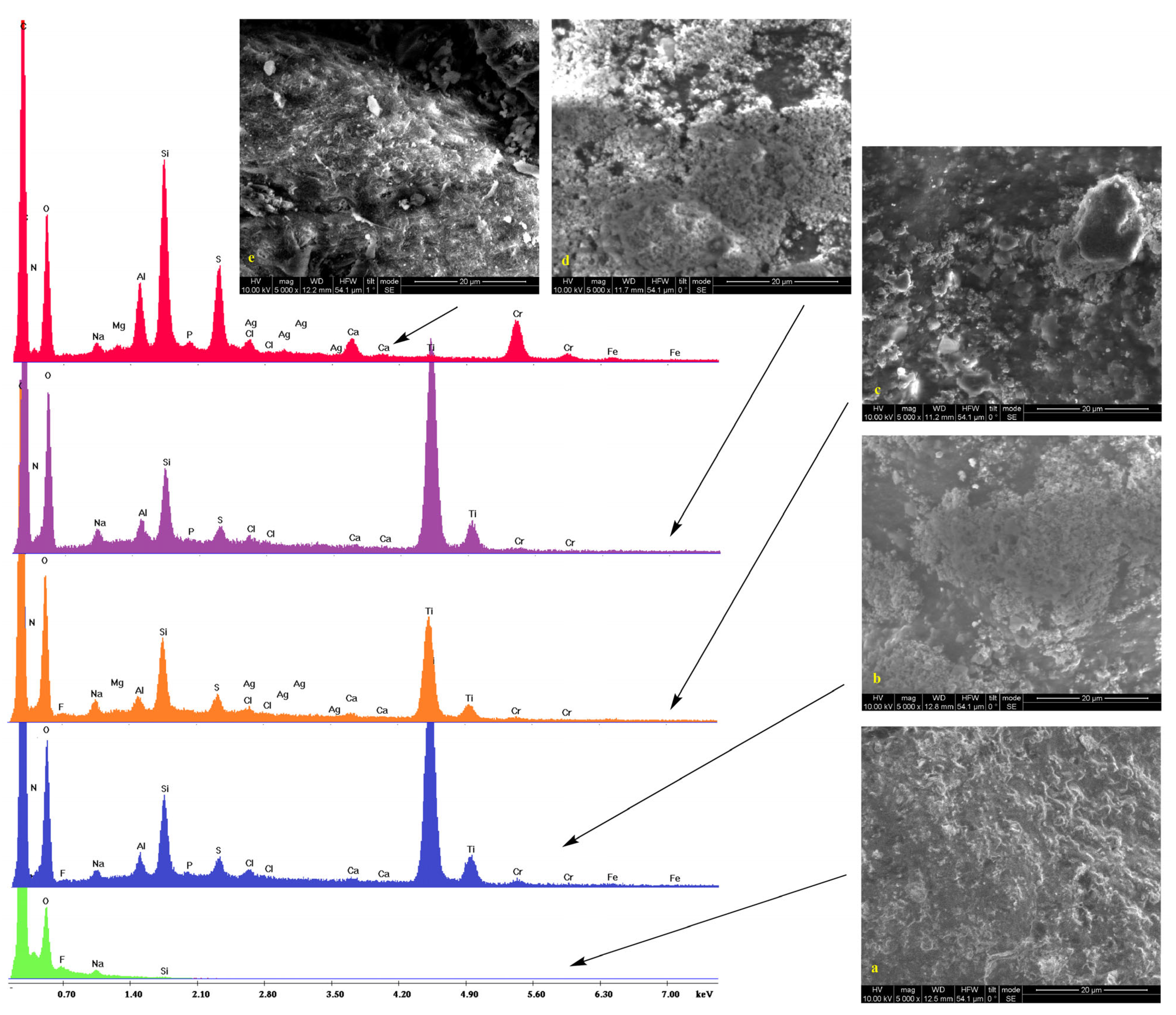
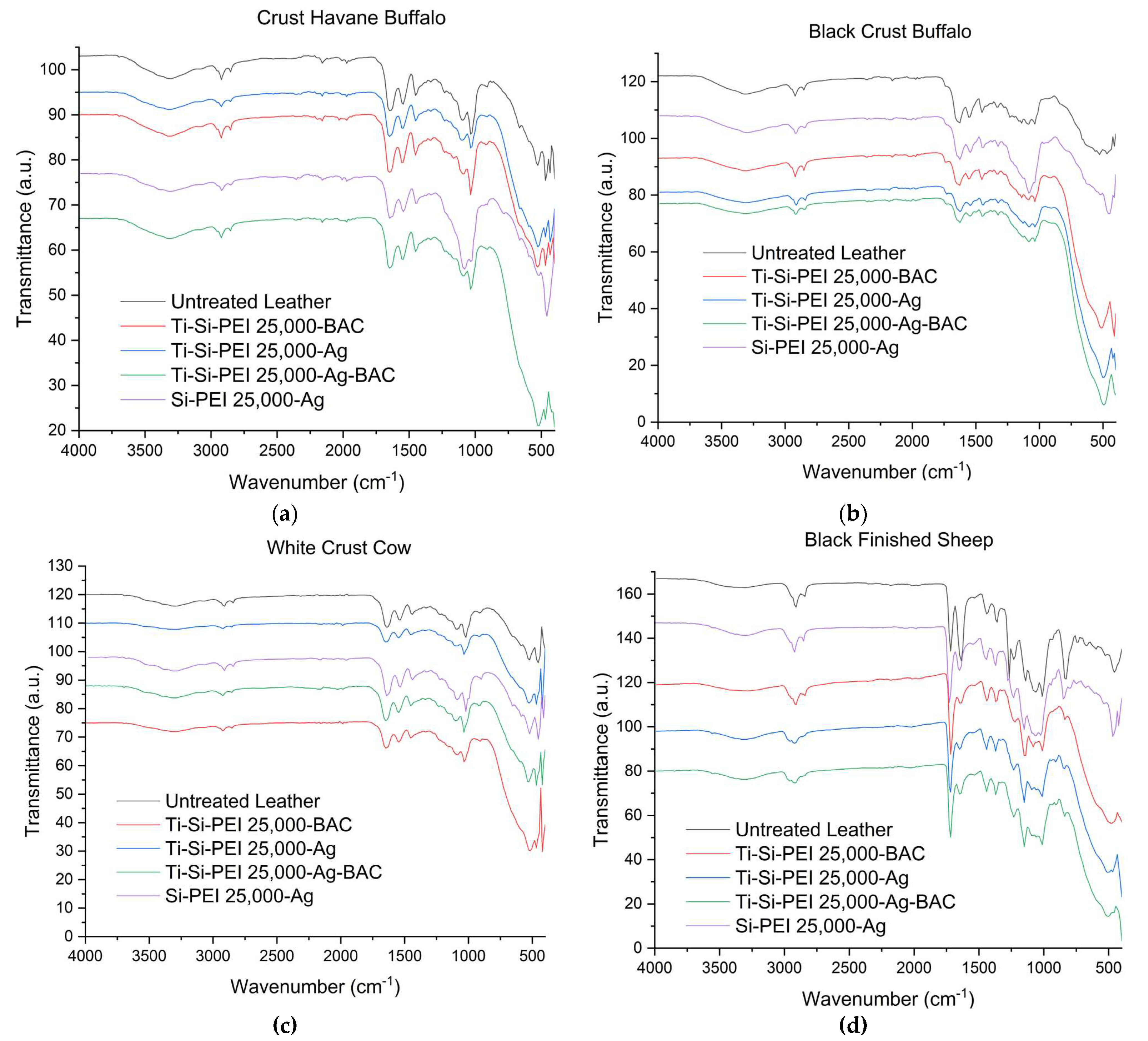
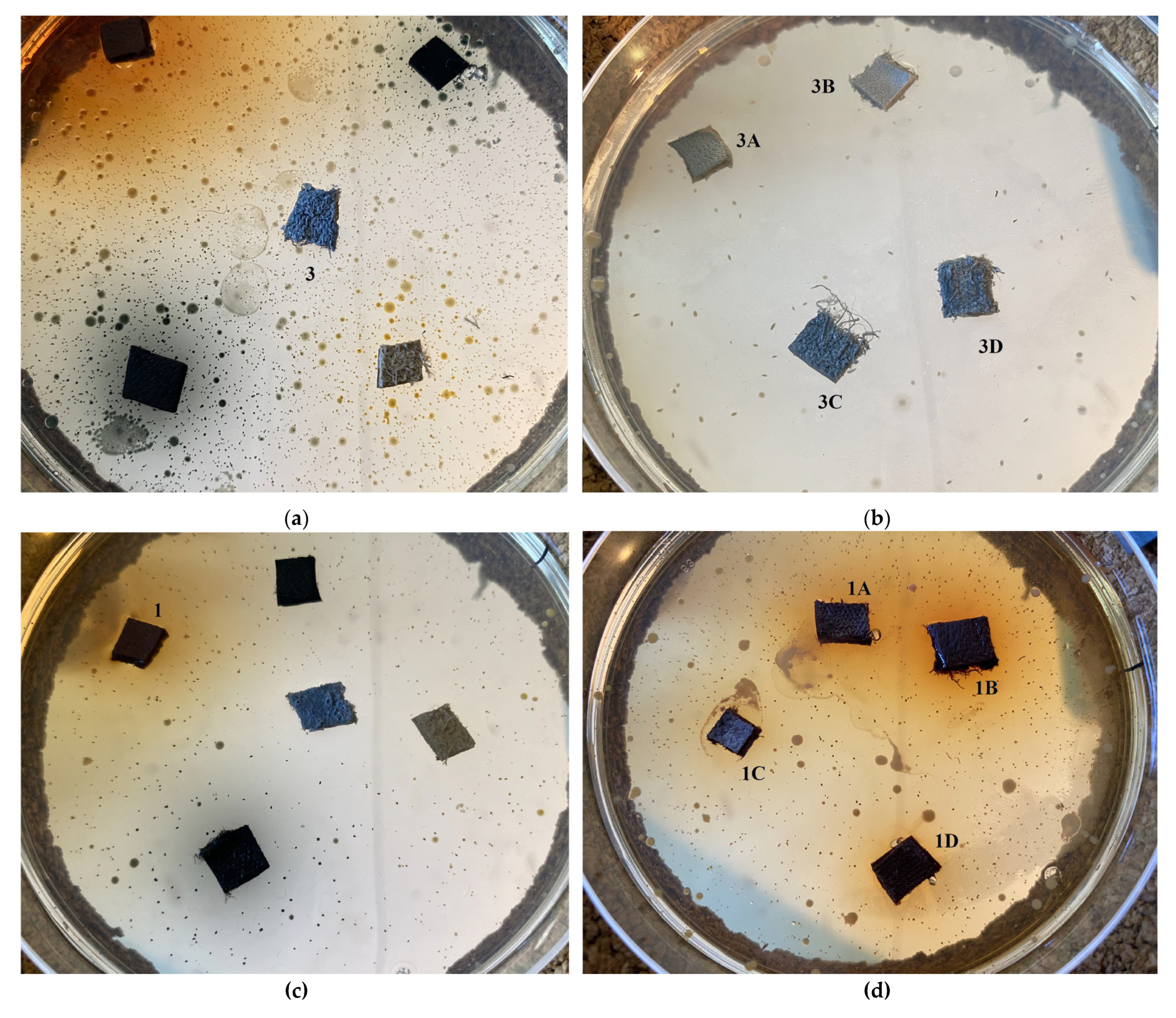

| Dispersion | ||||
| Leather Type | Crust Havane Buffalo | Black Crust Buffalo | White Crust Cow | Black Finished Sheep |
| Blind (untreated) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Ti-Si-PEI 25,000-BAC | 1A | 2A | 3A | 4A |
| Ti-Si-PEI 25,000-Ag | 1B | 2B | 3B | 4B |
| Ti-Si-PEI 25,000-Ag-BAC | 1C | 2C | 3C | 4C |
| Si-PEI 25,000-Ag | 1D | 2D | 3D | D4 |
| Sample Name | t(sec) = 0 | t(sec) = 15 | t(sec) = 30 | t(sec) = 60 | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 104.5 | 105.6 | 104.8 | stable drop | |
| 2 | 113.4 | 104.9 | 109.7 | stable drop | |
| 3 | 73.05 | 27.5 | disappeared | fully adsorbed | |
| 4 | 69.75 | 64.35 | 62.85 | unstable drop | |
| 1A | 99.05 | 88.0 | 83.5 | unstable drop | |
| 2A | 41.85 | 19.3 | disappeared | fully adsorbed | |
| 3A | 65.0 | 37.3 | 27.5 | disappeared | fully adsorbed |
| 4A | 102.35 | 88.4 | 83.35 | 84.65 | unstable drop |
| 1B | 96.75 | 86.75 | 81.2 | 78.65 | unstable drop |
| 2B | 82.15 | 10.8 | disappeared | fully adsorbed | |
| 3B | 58.85 | 37.7 | disappeared | fully adsorbed | |
| 4B | 95.4 | 87.5 | 85.65 | 85.45 | unstable drop |
| 1C | 110.8 | 104.5 | 99.1 | unstable drop | |
| 2C | 67.9 | 52.5 | 49.1 | 25.8 | adsorbed |
| 3C | 84.15 | 67.0 | 43.35 | 27.35 | adsorbed |
| 4C | 84.75 | 75.5 | 74.6 | 73.5 | unstable drop |
| 1D | 118.6 | 119.2 | 119.2 | stable drop | |
| 2D | 78.45 | 67.6 | 60.5 | unstable drop | |
| 3D | 84.65 | 65.0 | 27.35 | disappeared | fully adsorbed |
| 4D | 64.85 | 50.55 | 54.0 | 44.3 | adsorbed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





