Introduction
Low back pain (LBP) is a common complaint among adults with approximately 39 percent of Americans experiencing LBP in 2019.[
1] Pharmacological intervention, such as acetaminophen and non-steroidal inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), is the first line treatment for LBP.[
2] Pharmaceuticals as the primary treatment for LBP can be costly and less accessible, especially for the 44.8 percent of individuals that struggle with back pain and live below the federal poverty level.[
1] Additionally, opioids are commonly prescribed for low back pain and more than half of opioid users have reported LBP despite these medications showing limited efficacy for this condition.[
3]
Prior work in human subjects indicates that soft tissue manipulation (STM) such as massage may accelerate return-to-function, improve mental and emotional wellbeing, and reduce the need for opioid medication usage.[
4] However, heterogeneity of lifestyles and body conditions, potential co-morbidities, and the inherent mind-body aspect of manual therapies complicate our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying these findings.
Instrument-assisted STM (IASTM) is a manual therapy modality that stimulates painful areas of soft tissue with a rigid instrument. A recent study indicates that IASTM improves gait patterns in rats with induced LBP,[
5] suggesting that IASTM may promote pain relief and/or functional recovery from LBP. This same study revealed that IASTM modulates serum levels of cytokines involved in inflammatory response including reduced levels of RANTES, which is a generally pro-inflammatory cytokine.[
5]
Despite these findings, the molecular changes associated with STM in the tissue itself remain uncertain. This knowledge gap may prevent future therapeutic potential and widespread adoption of this non-invasive approach to pain management and inflammation. Thus, we sought to extend prior work on IASTM in a rat model of induced LBP to examine for potential changes in tissue levels of more than thirty pro- or anti-inflammatory cytokines following IASTM. Our results indicate that IASTM is associated with reduced soft tissue levels of RANTES and increased soft tissue levels of IL-4, which are pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, respectively. These findings advance the mechanistic understanding of tissue-level responses to IASTM and provide rationale for future studies involving STM in human subjects with LBP.
Materials and Methods
Animal Model and Soft Tissue Biopsies
All soft tissue biopsies utilized in this study were collected from rats involved in a prior report and full details of the animal husbandry, injury model, and IASTM intervention may be found therein.[
5] Briefly, adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (11 to 16 weeks old) were subjected to induced chronic inflammatory LBP by injection of 50 μL Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) unilaterally while animals were under isoflurane anesthesia. Samples discussed in the present study were obtained at sacrifice 14 days post-injury from rats randomized to the following groups: (1), sham treatment (
n=5/group) or (2), three IASTM sessions/week to the region of injury over two weeks (6 IASTM sessions total) (n=10/group) performed while conscious. All IASTM sessions were administered by a single examiner, who was trained and experienced in IASTM, using an IASTM device designed for treating small areas to manipulate the injured tissue.[
4] Sham treatment was carried out using light stroke from a soft bristled paint brush. IASTM treatment lasted 5 minutes/session at a pressure within subject tolerance – for example, no withdrawal response, no furigmentation/discoloration, or vocalization – using an average force of 2.46N
±0.42N (i.e., 0.55
±0.09 lbs).[
5] Rats were euthanized by asphyxiation using carbon dioxide, and immediately post-mortem, muscle biopsies were collected from the region of injury and subsequently snap-frozen. Rats in Group 2 were sacrificed within 30 minutes post-IASTM (n=5) or two hours post-IASTM (n=5) to compare the immediate and delayed effects of soft tissue manipulation. All animal procedures were performed in alignment with a protocol approved by the Indiana University Institutional Animal Care & Use Committee and national standards.
Muscle biopsies were homogenized in 1X RIPA buffer (Cell Signaling, Danvers, Massachusetts, USA) with 1X Halt Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) using a Bullet Blender (Next Advance, Troy, New York, USA). Protein concentration was determined using a BCA Assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) on a FilterMax F3 plate reader (Molecular Devices, San Jose, California, USA).
Cytokine Membrane Array
Pooled tissue homogenates were analyzed using the Proteome Profiler Rat Cytokine Array Kit Panel A (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA) as directed by the manufacturer and as reported previously.[
6] Briefly, 80 µg total protein was pooled for each individual rat within the respective treatment group (n=5 per treatment group) resulting in 400 µg total protein sample loaded onto each membrane. The arrays were developed using WesternBright Quantum reagent (Advansta, San Jose, California, USA) on a C-Digit scanner (LI-COR, Lincoln, Nebraska, USA) and signal densities were determined using Image Studio software package (LI-COR). Data for each target were expressed relative to the average reference spot density on the respective membrane and normalized to the untreated sample.
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
Individual tissue homogenates were analyzed using a custom-made GeniePlex Multiplex Assay (AssayGenie, Dublin, Ireland) to quantify levels of CXCL10, GM-CSF, IL-4, IL-6, LIX, TNF-α, TIMP-1, and RANTES. The assay was performed as directed by the manufacturer except for 1X RIPA plus Halt Protease Inhibitor Cocktail being substituted for the tissue lysis buffer included with the kit. Assays were run on an Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey, USA) using 300 µg total protein per sample. Quantification of results was performed by AssayGenie using FCAP Array Software Version 3.0 (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey, USA) by a scorer that was blinded to sample identity.
Statistical Analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 as described in each respective figure legend. A p-value of <0.05 was considered significant.
Results
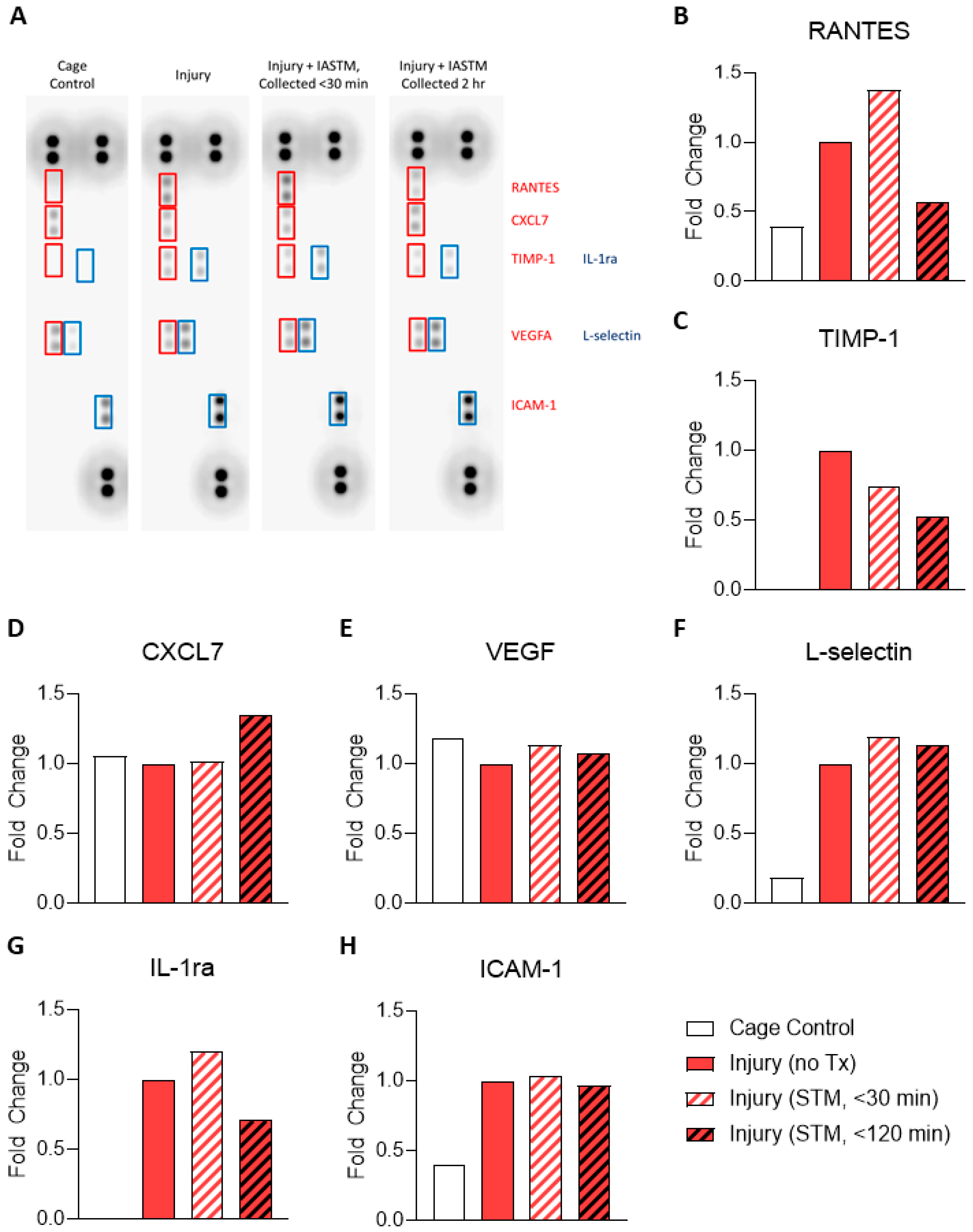
To examine the tissue-specific changes associated with IASTM, homogenates from muscle biopsies were pooled within treatment groups and subjected to membrane-based cytokine arrays which examine expression levels of nearly thirty targets simultaneously (
Figure 1A). These assays detected seven targets in at least one condition whereas the other targets were below the detection limit (
Figure 1A). Of these seven, only RANTES/CCL5 (
Figure 1B) and TIMP-1 (
Figure 1C) were altered by ≥50% in IASTM-treated samples compared to untreated injury controls, with levels of both cytokines being reduced in samples obtained 120 minutes following IASTM; the other targets – CXCL7 (
Figure 1D), VEGF (
Figure 1E), L-selectin (
Figure 1F), IL1-ra (
Figure 1G), and ICAM-1(
Figure 1H) – did not significantly differ between treatment groups.
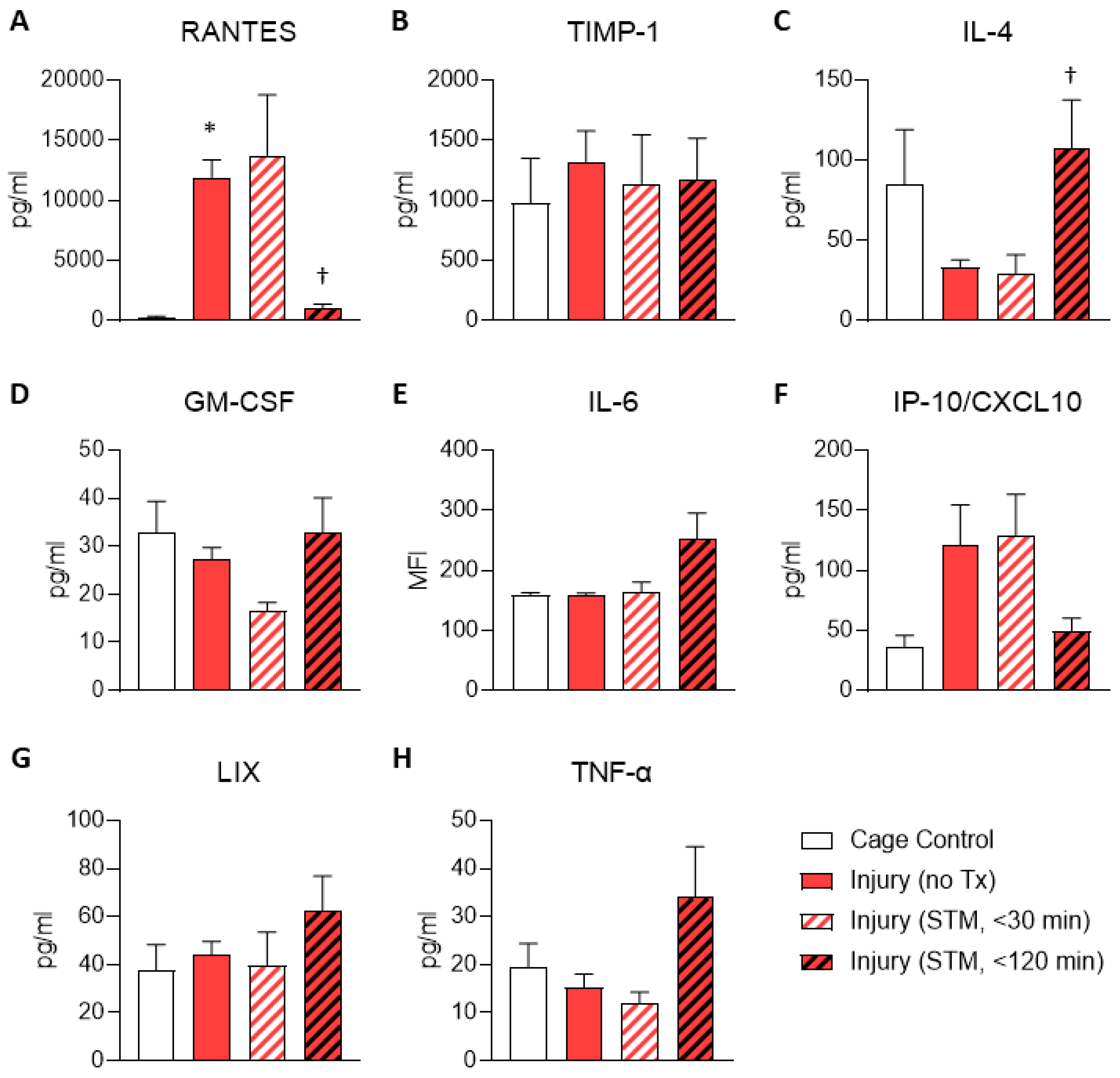
Given that the results for the membrane arrays were generated using pooled samples, we next sought to validate the findings for RANTES/CCL5 and TIMP-1 using ELISA on individual samples to enable statistical testing. These results confirmed that the level of RANTES was higher in untreated injury samples compared to cage controls and were reduced within 120 minutes following IASTM (
Figure 2A). In contrast, TIMP-1 levels were more variable between samples and did not reach statistical significance in this assay (
Figure 2B).
ELISAs were also utilized to interrogate levels of several other cytokines/chemokines of interest that were not detected on the membrane array, including IL-4, GM-CSF, IL-6, IP-10/CXCL10, LIX, and TNF-α (
Figure 2C-H). Among these, only IL-4 levels were altered in samples subjected to IASTM compared to untreated injury controls, with levels of this cytokine being elevated approximately 3-fold in samples obtained 120 minutes following IASTM (
Figure 2C).
Discussion
LBP is one of most common problems affecting people of all ages and can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, poor posture, and underlying medical conditions. This makes it difficult to determine the effective course of treatment, consequently making LBP challenging to manage. The prevalence and challenge of managing LBP has encouraged research into non-pharmacological and noninvasive therapies in an effort to find a less expensive, non-addictive, but yet effective form of treatment. The financial burden of healthcare costs associated with prescription medication and more invasive treatments like surgery may be reduced by alternatives like STM and massage. Althouth these alternatives are not one-size-fits-all treatments for LBP, these noninvasive treatments have known to have benefits to LBP by reducing pain, improving range of motion, increasing circulation, etc.[
4] One of the potential mechanisms of the benefits is via regulating inflammation, as suggested in our previous report.[
5] Therefore, we further hypothesized that better understanding of molecular changes of more inflammatory cytokines could open up wide adoption of STM and/or massage to manage LBP.
Our study analyzed tissue homogenates from muscle biopsies in several groups: uninjured cage controls, injured without treatment, injured + IASTM (sampled collected within 30 minutes of treatment), and injured + IASTM (sampled collected within 120 minutes of treatment). Our results indicate that this model of chronic LBP leads to elevated soft tissue levels of the chemokine RANTES and that IASTM decreases those levels of RANTES in rats within 120 minutes of treatment. This is consistent with a prior report demonstrating that IASTM decreases serum levels of RANTES in this same model.[
5] Given that RANTES exerts generally pro-inflammatory effects,[
7] these findings provides important molecular level information on a potential role for IASTM in reducing inflammation in vivo. Additionally, we found that, at the same time point, IASTM increases tissue levels of IL-4, which has been shown to suppress the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-1β while also stimulating the production of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra).[
8] IL-4 has also been linked to macrophage activation which counteracts inflammation by releasing IL-1ra, IL-10, and TGF-β.[
8] Thus, our observation of increased tissue levels of IL-4 following IASTM are supportive of a potential anti-inflammatory effect of this treatment modality.
TIMP-1 is another inflammation-related protein that inhibits the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), potentially leading to preventing MMPs from breaking down the extracellular matrix.[
9] TIMP-1 also has cytokine-line functions, such as binding to receptors on the surface of immune cells and regulates signaling pathways that influence cell behavior.[
9] Many inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and psoriasis, show upregulated levels of TIMP-1, suggesting that this protein could be a promising therapeutic target for the development of new anti-inflammatory treatment.[
10] Our findings regarding TIMP-1 were variable between methodologies but it is worth noting that this protein has mRNA splice variants which may alter the amino acid sequence.[
11,
12] Since the assays contain proprietary information, the manufacturers were unwilling to disclose details regarding the specific immunogen used in developing the antibodies; thus, we are unable to comment on the discrepancy between techniques.
We additionally investigated tissue levels of several other proteins that have been associated with pro- or anti-inflammatory effects and may play a role in various types of LBP, including CXCL5/LIX (the murine homolog of IL-8), GM-CSF, ICAM-1, IL1-ra, IL-6, IP-10/CXCL10, TNF-α, and VEGF.[
13,
14,
15] However, our analyses were unable to detect any IASTM-mediated effects on levels of these cytokines in this model. These findings may be representative of the limitations in our current study, which include evaluation of only male rats at a single time point (two weeks post-injury) in a single model of chronic, induced LBP using Freund’s adjuvant. Thus, it is possible that these and/or other factors are altered earlier or later in the time course of induced LBP or with IASTM. That said, taken with Loghmani et al,[
5] our study is supportive of the notion that IASTM exerts anti-inflammatory effects in LBP and could be a promising treatment option for individuals suffering from musculoskeletal inflammation or injury.
Conclusions
Our study found that IASTM is associated with reduced soft tissue levels of RANTES/CCL5 and increased soft tissue levels of IL-4 in rats with chronic, induced LBP. Combined with our prior report demonstrating IASTM improved gait patterns in rats with induced LBP,[
5] the present findings suggest that IASTM exerts effects involving changes in pro/anti-inflammatory cytokines in circulation and at the tissue level. Future studies are needed to confirm these findings in human subjects and to investigate the long-term effects of IASTM on soft tissue levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T.L. and J.W.L.; Methodology, C.L.M, T.A.H., M.T.L. and J.W.L.; Validation, C.L.M, T.A.H., M.T.L. and J.W.L; Formal Analysis, C.L.M, T.A.H., M.T.L. and J.W.L; Investigation, C.L.M., T.A.H, K.L.J., S.S., C.M., A.E., J.M.H., M.T.L., T.G.C, K.S.K., and J.W.L.; Resources, M.T.L. and J.W.L.; Data Curation, M.T.L. and J.W.L.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, C.L.M, T.A.H., M.T.L. and J.W.L.; Writing – Review & Editing, C.L.M., T.A.H, K.L.J., S.S., C.M., A.E., J.M.H., M.T.L., T.G.C, K.S.K., and J.W.L.; Visualization, C.L.M, T.A.H., and J.W.L.; Supervision, M.T.L. and J.W.L.; Project Administration, M.T.L. and J.W.L.; Funding Acquisition, M.T.L. and J.W.L.
Funding
Funding was provided by a Marian University College of Osteopathic Medicine Faculty Research Development award (issued to JWL) and other intramural funds.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not involve human subjects and IRB approval is not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge members of the Marian University Bone & Muscle Research Group and the Indiana Center for Musculoskeletal Health for critical feedback on this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lucas, J. W.; Connor, E. M.; Bose, J. , Back, Lower Limb, and Upper Limb Pain Among U.S. Adults, 2019. NCHS Data Brief 2021, ((415)), 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Last, A. R.; Hulbert, K. , Chronic low back pain: evaluation and management. Am Fam Physician 2009, 79(12), 1067–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyo, R. A.; Von Korff, M.; Duhrkoop, D. , Opioids for low back pain. BMJ 2015, 350, g6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Beaton, K.; Hughes, T. , The effectiveness of massage therapy for the treatment of nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review of systematic reviews. Int J Gen Med 2013, 6, 733–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loghmani, M. T.; Tobin, C.; Quigley, C.; Fennimore, A. Soft Tissue Manipulation May Attenuate Inflammation, Modulate Pain, and Improve Gait in Conscious Rodents With Induced Low Back Pain. Military Medicine 2021, 186 (Supplement_1), 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anloague, A.; Mahoney, A.; Ogunbekun, O.; Hiland, T. A.; Thompson, W. R.; Larsen, B.; Loghmani, M. T.; Hum, J. M.; Lowery, J. W. , Mechanical stimulation of human dermal fibroblasts regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines: potential insight into soft tissue manual therapies. BMC Res Notes 2020, 13(1), 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, R. E.; Guabiraba, R.; Russo, R. C.; Teixeira, M. M. , Targeting CCL5 in inflammation. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2013, 17(12), 1439–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woodward, E. A.; Prele, C. M.; Nicholson, S. E.; Kolesnik, T. B.; Hart, P. H. , The anti-inflammatory effects of interleukin-4 are not mediated by suppressor of cytokine signalling-1 (SOCS1). Immunology 2010, 131(1), 118–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ries, C. Cytokine functions of TIMP-1. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 2014, 71, 659–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knight, B. E.; Kozlowski, N.; Havelin, J.; King, T.; Crocker, S. J.; Young, E. E.; Baumbauer, K. M. , TIMP-1 Attenuates the Development of Inflammatory Pain Through MMP-Dependent and Receptor-Mediated Cell Signaling Mechanisms. Front Mol Neurosci 2019, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Usher, P. A.; Sieuwerts, A. M.; Bartels, A.; Lademann, U.; Nielsen, H. J.; Holten-Andersen, L.; Foekens, J. A.; Brunner, N.; Offenberg, H. , Identification of alternatively spliced TIMP-1 mRNA in cancer cell lines and colon cancer tissue. Mol Oncol 2007, 1(2), 205–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obro, N. F.; Lademann, U.; Birkenkamp-Demtroder, K.; Holten-Andersen, L.; Brunner, N.; Offenberg, H. , A TIMP-1 splice variant transcript: possible role in regulation of TIMP-1 expression. Cancer letters 2008, 262(1), 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shnayder, N. A.; Ashhotov, A. V.; Trefilova, V. V.; Nurgaliev, Z. A.; Novitsky, M. A.; Vaiman, E. E.; Petrova, M. M.; Nasyrova, R. F. Cytokine Imbalance as a Biomarker of Intervertebral Disk Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24((3)). [Google Scholar]
- Risbud, M. V.; Shapiro, I. M. , Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nature reviews. Rheumatology 2014, 10(1), 44–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J. E.; Zhao, K. H.; Qu, Y.; Zou, Y. C. , Increased serum CXCL10 levels are associated with clinical severity and radiographic progression in patients with lumbar disc degeneration. Clin Chim Acta 2022, 525, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).