1. Introduction
Bioactive lipids regulate cellular functions and contribute to tissue homeostasis and pathology [
1]. Four families of bioactive lipids are involved in inflammation and immune regulation; eicosanoids, specialized pro-resolving mediators, lysoglycerophospholipids/ sphingolipids and endocannabinoids, which are generated from ω-3 or ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). Eicosanoids are key elements in inflammation, and have been linked with diseases, such as viral infections, neurodegenerative disorders [
2], rheumatoid arthritis [
3], atherosclerosis [
4,
5], acute coronary syndrome [
6], cancer [
7,
8], systemic lupus erythematosus [
9], multiple sclerosis [
10], liver injury [
11], celiac disease [
12], diabetes [
13], cystic fibrosis [
14], renovascular disease [
15], asthma [
16] and muscle dysfunction [
17]. In addition, fatty acids, the common components of complex lipids, often act as immunomodulatory factors [
18,
19].
In general, lipids are challenging molecules to characterize due to the limited analytical capacity to identify, quantify, and annotate them in biological samples, which has been an impediment to the advancement of discovering molecular mechanisms of disease, biomarker discovery and drug development. Mass spectrometry (MS) approaches, predominantly in combination with liquid chromatography (LC), are widely used for analysis of biomolecules [20-23], including eicosanoids [24, 25] . More recently, LC coupled with dynamic multiple-reaction monitoring (dMRM) workflows for targeted detection of specific subsets of eicosanoids [26, 27], and high-resolution (MRMHR) methods to generate a library of high-resolution fragmentation spectra [
28] , have been developed. In addition, eicosanoid profiling by LC-MS has previously been performed on human plasma [
29], clinical samples [
30] and mouse models of pathophysiological states [
31]. However, such analyses remain challenging due to limitations in the accurate assignment and detection of endogenous species [32, 33]. One reason is a lack of thoroughness in optimising truly representative sample matrix variations, instead of using “surrogate matrices” (such as BSA in sample buffer, which would be a matrix approximation), and applying more efficient extraction methodologies adapted to specific lipid subsets within specific sample types (e.g. cell and cell supernatant samples).
In this study, an intracellular and extracellular analysis (the media in which the respective cells are cultured) of eicosanoids and fatty acids was performed using a tailored extraction and dMRM method to maximize the sensitivity of detecting endogenous species. Since bioactive lipids such as eicosanoids have important roles in inflammation and cancer, we performed a proof-of-concept experiment to study the effect of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interferon α 2 (IFNα-2b; hereafter IFN-I) on HAP1 cells. HAP1 cells were derived from a chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) patient and have been extensively used in different translational studies [34-36]. IFN-I is a cytokine secreted by most cells in response to viral infection, and with known immunostimulatory and anti-cancer properties [
37]. The IFN-I subtype IFNα2 has been approved, alone and in combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), for the treatment of CML [
38].
Here, we found that IFN-I affected intra- and extracellular concentrations of 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), the intracellular concentration of Arachidonic Acid (AA), and the extracellular concentrations of Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α), 5-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HETE), Palmitic acid (PA, C16:0) and Stearic acid (SA, C18:0), suggesting a role of these lipids in the inflammatory state of tumours.
3. Discussion
The primary objective of this article was to establish the importance of investigating the appropriate extraction technique for the specific sample type (e.g. cells or cell supernatant), in addition to considering the matrix effect of every lipid analysed within the specific sample type, and applying the methodology to unravelling the effect of interferon treatment upon the lipidome in the context of inflammation, cancer and specifically CML. We have used HAP1 cells as a model for CML, as HAP1 cells are derived from a CML patient cells and have the BCR-ABL gene, which is common in leukaemia’s, turning the myeloid cell into a chronic myeloid cell [40, 41].
Due to intrinsic molecular differences, innate variation and organic solvent preferences during extraction, there is no agreement on the best sample preparation and analysis of lipids. As a consequence, analysing different subclasses simultaneously is challenging. In this study, we have optimised extraction, chromatography and MS parameters which provide the best conditions for the identification and quantitation of a set of eicosanoids and fatty acids with well-established roles in inflammation.
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) methods, can be used to reduce the complexity, and to concentrate the samples prior to analysis. However, we found that SPE is unreliable for concentrating a variety of lipids simultaneously, resulting in the loss of some metabolites (unpublished observations). Therefore, we opted to optimise LLE methods, and concentrate samples subsequently by resuspension of the dried lipids into smaller volumes. Due to differences in natural abundance of these metabolites, and the MS response, we were able to dilute the sample for those lipids with a higher natural concentration and/or a higher ion intensity (such as intracellular 2-AG). A separate method could be implemented for the analysis of 2-AG, LTC
4, and PGF
2α, as even at low on-column concentrations as these lipids have a large AUC. For instance, the standards and samples could be diluted further than reported here. Pre-analytical influences may change lipid concentrations or matrices which is why we prefer to use extensive matrix-dependent normalisations, for each analyte within a “true” matrix (e.g. not a surrogate matrix), and demonstrate its application tailored to specific endogenous lipid (eicosanoids and fatty acids) detection in clinically relevant biological samples. However, to bypass normalisation calculations, to provide information on the regulatory network and to identify important metabolite conversions within the pathway, ratios between metabolites could be used instead (e.g. PGE
2:PGF
2α). In this analysis, there is variability in response curves for the lipids (R
2 values, from 0.950 to 0.999;
Table S5), and variation in the matrix effects (RF values from 0.34 to 40.06), highlighting the need to determine the responses for every lipid quantified, as the results would otherwise vary significantly from the observed amounts. Nonetheless, the reproducibility of detection for our method achieved technical CV values of less than 20% and were within 5-10% for most species (
Figure 3). Our intraday variation for all lipids analysed was below 20% CV, with 5-oxo-ETE, SA, 2-AG, PA, and 5-HETE being below 5%.
Recommended options for future development of this analysis could include chemical derivatization of the lipids, exploring an analysis in negative mode electrospray ionization (ESI-), using an ultrafast LC, and a complementary proteomics analysis. Derivitisation has been implemented for enhanced lipidomic analysis by MS [
42], and it may boost the MS response for some lipids. However, it would need to be considered that derivatization itself is laborious, time-consuming, different metabolites have differing derivatization efficiencies, and batch effects are common. It has also been described that lipids with carboxylic acid moieties, will benefit from being analysed in negative polarity [43, 44]. However, this may not be suitable for the simultaneous analysis of all the lipids reported here. For instance, and in line with our observations, ionisation of LTC
4 has been already shown to be very efficient in positive polarity [
45]. MS fast-switching between polarity modes could potentially further improve sensitivity of detection. It is important to consider that PUFAs are easily oxidized and this may lead to erroneous concentration reporting for some lipids. Using an ultrafast-LC could reduce the total analysis time, increasing throughput, reducing the cost per sample and labour time (samples would not need to be added daily). In addition, sample quality could be improved as they would not need to be stored as long in the autosampler. Integrating complementary proteomics data would lead to greater understanding and enhance confidence of the changes observed within the studied pathways. For instance, changes in the expression of some of the enzymes involved in the metabolism of eicosanoids and fatty acids have been associated with cancer development [46-49]. Pinpointing which enzymes are modified upon interferon treatment, using proteomics, may corroborate our findings and expand our knowledge of the effect of interferon treatment in CML patients.
The pro-inflammatory tumour microenvironment [50-54], and immune ‘hot’ tumours show increased levels of inflammation and anticancer immune responses, such as T cell infiltration and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interferons. Defects in Interferon signaling pathways during cancer treatment have been linked to immunotherapy resistance [
55]. Our results suggest that IFN-I treatment significantly reduces the intracellular concentration of the eicosanoid precursors 2-AG and AA. However, the underlying molecular mechanism is as yet still unknown. We hypothesise that this reduction may be through decreased production of their precursors (2-AG-LPA or DAG), a decreased presence or activity of the respective enzymes which produce 2-AG-LAP and DAG (for example; 2-LPAP or DAGL) or by increased metabolism to downstream eicosanoids (such as PGF
2α). The latter seems to be the case as both, intracellular, and extracellular concentration of PGF
2α are increasing. This may suggest that cells treated with IFN-I are secreting excess PGF
2α out of the intracellular space. Increased concentrations of PGF
2α have been indicated as a driver of particular cancers [56-58], although its role in CML remains unclear. Secretion of SA and PA also appear increased upon IFN-I exposure, possibly through enhanced export. These fatty acids could contribute to the tumour microenvironment, act as key metabolites in reducing tumorigenicity, and affect the interplay between tumour and immune cells. 5-oxo-ETE, PGD
2 and PGE
2 were not identified in the samples, indicating either their absence, that they fell below the lower limit of detection (LLOD, a signal-to-noise ratio of >3), and/or the matrix caused considerable ionisation suppression. Alternatively, perhaps there was unexpected in-source fragmentation, leading to differing parent or product ions from those that we monitored. 5-oxo-ETE could be rapidly metabolised to either 5-HETE or to Di-endoperoxidase [59, 60], and therefore with the current treatment of 36 hours, it is very likely that the changes, if happening upon IFN-I treatment, will not be observed.
We were unable to chromatographically separate standards of the isobaric species PGD
2 and PGE
2. However, separation is possible though, with a method specifically dedicated to the analysis of these particular lipids. Employing normal-phase chiral chromatography, and/or alternative MS approaches (employing additional separation techniques, such as ion mobility), will isolate isobaric prostaglandins based on their chirality, mobility, and/or collisional cross section value. PGD
2 can undergo dehydration to form Prostaglandin J
2, and other Prostaglandin metabolites, with dehydration of PGD
2 being accelerated in the presence of serum albumin [61-63]. Since our tissue culture media contains serum albumin, it might be contributing to the absence of PGD
2 in our analysis. Previous studies have suggested that PGE
2 is reduced in CML patients [
64], hence this may be why our method was unable to detect PGE
2 in samples. Upon IFN-treatment, intracellular production of 5-HETE appears to be maintained, possibly through metabolism from AA, or by the reduction of 5-oxo-ETE (and NADP+) to 5-HETE (and NADPH) [
60]. In addition, the extracellular quantity of 5-HETE significantly increases, which to our knowledge is novel biology and an area of CML research yet to be explored. Changes in LTC
4 amount and activity, and LTC
4 concentration are cell specific [65-67]. With CML researchers suggesting that there can be a steady state, an increase or a decrease in Leukotrienes in patients compared to healthy controls. Nonetheless, despite these disparities, inhibitors of Leukotriene signaling have reduced cancer growth in CML [68, 69]. When these Leukotriene inhibitors have been used in combination with traditional methods to treat CML (Tyrosine kinase inhibitors), the reduction of tumour growth was further increased [
70]. Interestingly, our results, although not significant, show a slight decrease in intracellular LTC
4 levels upon IFN-I stimulation. However, Leukotrienes can be readily metabolised [
71], with LTC
4 potentially being converted to Leukotriene D
4, therefore we cannot confirm that LTC
4 concentrations are affected or not by 36 hours of IFN-I treatment.
In conclusion, the present study describes an original, ultra-sensitive methodology, whereby LC and MS parameters are modified for a specific set of lipids, the extraction of these lipids from different sample types is modified accordingly and extensive matrix considerations, both in terms of the matrix effect upon each individual lipid and the matrix effect of the different sample types (cells and cell supernatant) are applied. for accurate and simultaneous analysis of a range of eicosanoids and fatty acids. Our optimization of sample preparation, technical parameters and data normalization for different sample types, plus the application of dMRM transitions maximises the sensitivity of detection, allowing detection at endogenous levels, even for very low abundance species. The observed improvements in detection and sensitivity are the hallmark of this analytical method, permitting us to resolve changes of relevant bioactive lipids in response to treatment with a pro-inflammatory cytokine in a cancer cell model. Translational application examples include the profiling of bioactive lipids in patient samples, for monitoring inflammation levels caused by pathology, or to treatment with immunodulators (i.e. immunotherapy). In closing, we believe this emphasises the benefits of using targeted MS in understanding pathophysiological states, to unravel yet unknown mechanisms of diseases.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Abbreviations
2-AG; 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, 2-AG-LPA; 2-Arachidonoyglycerol lysophosphatidic acid, 2LPAP; 2-Lysophosphatidic acid phosphatase, 5-HETE; 5-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 5-HPETE; 5-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 5-oxo-ETE; 5-Oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid, AA; Arachidonic acid, ACN: Acetonitrile, AUC; area under the curve, BLM; bioactive lipid mix, CBR1; Carbonyl reductase 1, CE; collisional energy, CHCl3; chloroform, CML; chronic myeloid leukaemia, COX 1/2; Cytochrome C oxidase 1 or 2, CV; coefficient of variation, DAGL; Diacylglycerol lipase, dMRM; dynamic multiple-reaction monitoring, ESI; electrospray ionization, eV; electron volts, FBS; fetal bovine serum, GPX; Glutathione peroxidase, H2O; water, HMDB; Human Metabolome Database, IFNα; Interferon alpha, IMDM; Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's Medium, IPA; isopropanol, LC-MRM-QQQ; Liquid chromatography- multiple reaction monitoring- triple quadrupole, LC-MS; liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, LLE; liquid-liquid extraction, LLOD; lower limit of detection, LLOQ; lower limit of quantification, LOX; Lysyl Oxidase, LTA4; Leukotriene A4, LTC4; Leukotriene C4, LTC4S; Leukotriene C4 synthase, LTC4S; LTC4 synthase, m/z; mass to charge ratio, MAGL; Monoacylglycerol lipase, MeOH; Methanol, MRMHR; multiple reaction monitoring high-resolution, MTBE; Methyl tert-butyl ether, NADP+ / NADPH; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, NT; non-treated, PA; Palmitic acid, PGD2; Prostaglandin D2, PGDS; Prostaglandin D2 synthase, PGE2; Prostaglandin E2, PGES; Prostaglandin E2 synthase, PGF2α; Prostaglandin F2α, PUFA’s; polyunsaturated fatty acids, QC; quality control, QTOF; quadrupole time of flight, RF; response factor, SD; standard deviation, S/N; signal-to-noise ratio, SA; Stearic acid, SPE; solid-phase extraction, TIMS-TOF; Trapped ion mobility – time of flight, UPLC-MS/MS; ultra-performance liquid chromatography - tandem mass spectrometry.
4.2. Figures
Figures 1a, 1b, 4a, 5a, 6 and 7d were generated in Biorender.
4.3. Reagents
Lipid standards; PGE2 (catalogue # sc-201225), PGF2α (catalogue # sc-201227), 5-HETE (catalogue # sc-205136), 5-oxo-ETE (catalogue # sc-203783) and PGD2 (catalogue # sc-201221) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. SA (catalogue # 10011298-500 mg-CA), LTC4 (catalogue # 20210-25 ug-CAY) and PA (catalogue # 10006627-10 g-CAY) were acquired from Cayman Chemicals. AA (catalogue # ab120916) is from Abcam. 2-AG (catalogue # A8973) was purchased from Sigma. LC-MS grade water (Catalogue # 115333) and MeOH (Catalogue # 106035) was available from Merck. Amm onium acetate (Catalogue # 10365260) and IPA (Catalogue # 15686670) were from Fisher Scientific. MTBE was acquired from Acros organics (Catalogue # 3787 20010) and ACN was from Honeywell Riedel-de Haën (Catalogue # 348512.5L). IMDM was from Gibco at Thermo Fisher Scientific (reagent # 12440053) and IFN-I was from Biotechne R&D systems (catalogue # 11105-1).
4.4. Standard solutions
Stock concentrations of all lipid standards were prepared as individual aliquots at 100 µmol/L in 100% MeOH. These stocks were then pooled and serially diluted to a concentration of 100 nmol/L in 50% (v/v) MeOH to create an equimolar standard mixture, the bioactive lipid mix (BLM). The BLM was used as a spike, which was added to pooled samples (a fraction of all samples combined) to determine the matrix effects.
4.5. Tissue culture
HAP1 cells were cultured as previously described [
72]. In brief, cells were cultured in IMDM media containing 10% FBS and were grown until 60-70% confluency. Cells were then treated with 1000 U/mL of IFNα-2b for 36 hours, until ~80% confluent. The surrounding media (the cell supernatant) was collected and used for analysis of extracellular lipids. Both cell supernatant and cell plates were stored at -80 °C until lipid extraction.
4.6. Lipid extraction
A simultaneous lysis and LLE was performed. For cells, the lysis was performed by scraping with 100% MeOH. The lysate was then added to 50% CHCl3 and 50% MBTE, which was then vortexed briefly and then spun at 12 rpm for 20 minutes at 4 °C. The sample was then centrifuged at 17 x G for 5 minutes at 4 °C and the resulting organic fraction was removed and stored on ice. The remaining pellet underwent another round of vortexing, spinning and centrifuging in 50% CHCl3 and 50% MTBE with the resulting organic fraction being pooled with the previous fraction. The final extraction step was performed with 50% MeOH and the sample was vortexed, spun and centrifuged again with the organic fraction being pooled with the previous fractions. Once all organic fractions were collected for each sample, a small portion of each was removed and pooled together for a pooled sample. The samples and the pooled samples were then dried in a speedvac at 30 °C until dry and then stored at -20 °C until LC-MS analysis.
To the dried lipid extracts 50% MeOH or the same volume of the BLM was added prior to analysis. The samples were briefly vortexed and then shaken at 400 rpm at 4 °C until homogenous. Cell-supernatant samples were diluted 1 in 20. Cell samples were diluted 1 in 10 for analysis of AA, PGF2α, SA and 5-HETE or diluted 1 in 100 for analysis of 2-AG, PA and LTC4. Diluted samples were then transferred to LC-MS autosampler vials.
4.7. LC-MS method
Levels of 2-AG, AA, PGD2, PGE2, PGF2α, 5-HETE, 5-oxo-ETE, LTC4, PA and SA were analysed. Metabolites were quantified using an optimised dMRM method on a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with a JetStream ESI source (Agilent 6490) coupled to a 1290 Agilent LC system.
Lipids were separated on an ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 column (1.7 µm, 100 x 2.1 mm i.d., Waters) with mobile phase A of 2 % IPA with 5 mM Ammonium Acetate, and mobile phase B of 100 % IPA with 5 mM Ammonium Acetate at 40 °C. The flow rate was set to 0.21 mL min-1 and sample injection volume was 1 µL, 10 µL or 15 µL (depending of the response of the metabolites). The following gradient (% mobile phase B) was used: 0 - 1.5 min at 50% B, 1.5 - 9 min 70% B, 9 - 13 min 100% B. A wash with 100% mobile phase B and a wash with 100% mobile phase A was performed to clean the column before re-equilibration to starting conditions. The autosampler was maintained at 4 °C.
The following ESI+ source parameters were used: gas temp at 280 °C, gas flow 14 L/min, nebulizer at 20 psi, sheath gas temp at 250 °C, sheath gas flow at 11 L/min, capillary voltage 3000 V, nozzle voltage 1500 V, high-pressure RF at 150 V and low-pressure RF at 60V. Transitions used in the dMRM analysis are shown in
Table 1, LC and MS parameters used are shown in
Table 2.
4.8. Data analysis
Initial data processing was performed using Agilent MassHunter Quantitative software. Post-processing was performed in Excel and GraphPad Prism:
The MRM AUC’s were corrected with the matrix response factor (matrix RF) (
Figure 6). To determine the matrix RF, the response of the analyte as a standard is needed, as is the response in the sample (the intrinsic contribution, the matrix) and the response of the standard mixture spiked into the matrix. To calculate the matrix RF, the response of the intrinsic contribution in the sample (the matrix) is subtracted from the response of the standard spiked into the matrix, to give the effect of the matrix upon the standard (response of the standard mixture in the matrix). The response of the standard by itself divided by the response of the standard mixture in the matrix gives a matrix response factor.
To account for matrix effects in biological samples, the response of an analyte in a (biological) sample is multiplied by the corresponding matrix RF value to give the ‘real’ response of the analyte (i.e., to eliminate ionization enhancement/suppression effects on an analyte). This matrix RF corrected response can subsequently be used to calculate analyte concentration from a standard curve trendline equation (y = Mx+C). Standard curves are generated by injection of increasing concentrations of the BLM, calculating the AUC at each concentration, and plotting AUC values against the corresponding concentration
Statistical analysis of the two sample (or unpaired) t-test is used to validate difference between no treatment (NT) and treated with IFNα (+IFNα) for 36 hours. A p-value less than 0.05 (***) indicates the results have highly significant differences.
4.9. Method validation
The LLOD was calculated as a S/N ratio of >3, the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was a S/N ratio of >10. Intraday precision was calculated using three replicates of two concentrations over the course of one day and results are reported as CV % between replicates of one concentration. To monitor instrument performance over time and check that batches that span inter-day analysis were consistent (quality control, QC), the BLM (1 pmol/L on-column) was routinely injected. If total sample analysis time was over multiple days, the samples were briefly vortexed at the start of each day to avoid precipitation.
Figure 1.
Eicosanoid pathway and methodology workflow. (a) Metabolic pathways of selected bioactive lipids. Converting enzymes are in boxes and lipids in this study are circled in grey. De novo lipogenesis leading to fatty acid synthesis, which results in the elongation of fatty acids, produces Palmitic acid and Stearic acid. Exogenous fatty acid uptake is via transmembrane transporters. (b) Optimised experimental workflow for the analysis of eicosanoids and fatty acids using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-dMRM-MS (UPLC-dMRM-MS). Cells were cultured in IMDM media, containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and grown until 60-70% confluent. Cells were then treated with 1000 U/ml of IFNα-2b for 36 hours, reaching ~80% confluence. The surrounding media (the cell supernatant) was collected from the plates and cells were lysed. Lipid extraction from cells and cell supernatants was performed with Methanol/ Methyl Tert-Butyl Ether/ Chloroform (MeOH/MTBE/CHCl3), and acetonitrile (ACN), respectively. Lipid extracts were subsequently dried and reconstituted in 50% (v/v) MeOH (in H2O) prior to LC-MS analysis.
Figure 1.
Eicosanoid pathway and methodology workflow. (a) Metabolic pathways of selected bioactive lipids. Converting enzymes are in boxes and lipids in this study are circled in grey. De novo lipogenesis leading to fatty acid synthesis, which results in the elongation of fatty acids, produces Palmitic acid and Stearic acid. Exogenous fatty acid uptake is via transmembrane transporters. (b) Optimised experimental workflow for the analysis of eicosanoids and fatty acids using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-dMRM-MS (UPLC-dMRM-MS). Cells were cultured in IMDM media, containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and grown until 60-70% confluent. Cells were then treated with 1000 U/ml of IFNα-2b for 36 hours, reaching ~80% confluence. The surrounding media (the cell supernatant) was collected from the plates and cells were lysed. Lipid extraction from cells and cell supernatants was performed with Methanol/ Methyl Tert-Butyl Ether/ Chloroform (MeOH/MTBE/CHCl3), and acetonitrile (ACN), respectively. Lipid extracts were subsequently dried and reconstituted in 50% (v/v) MeOH (in H2O) prior to LC-MS analysis.
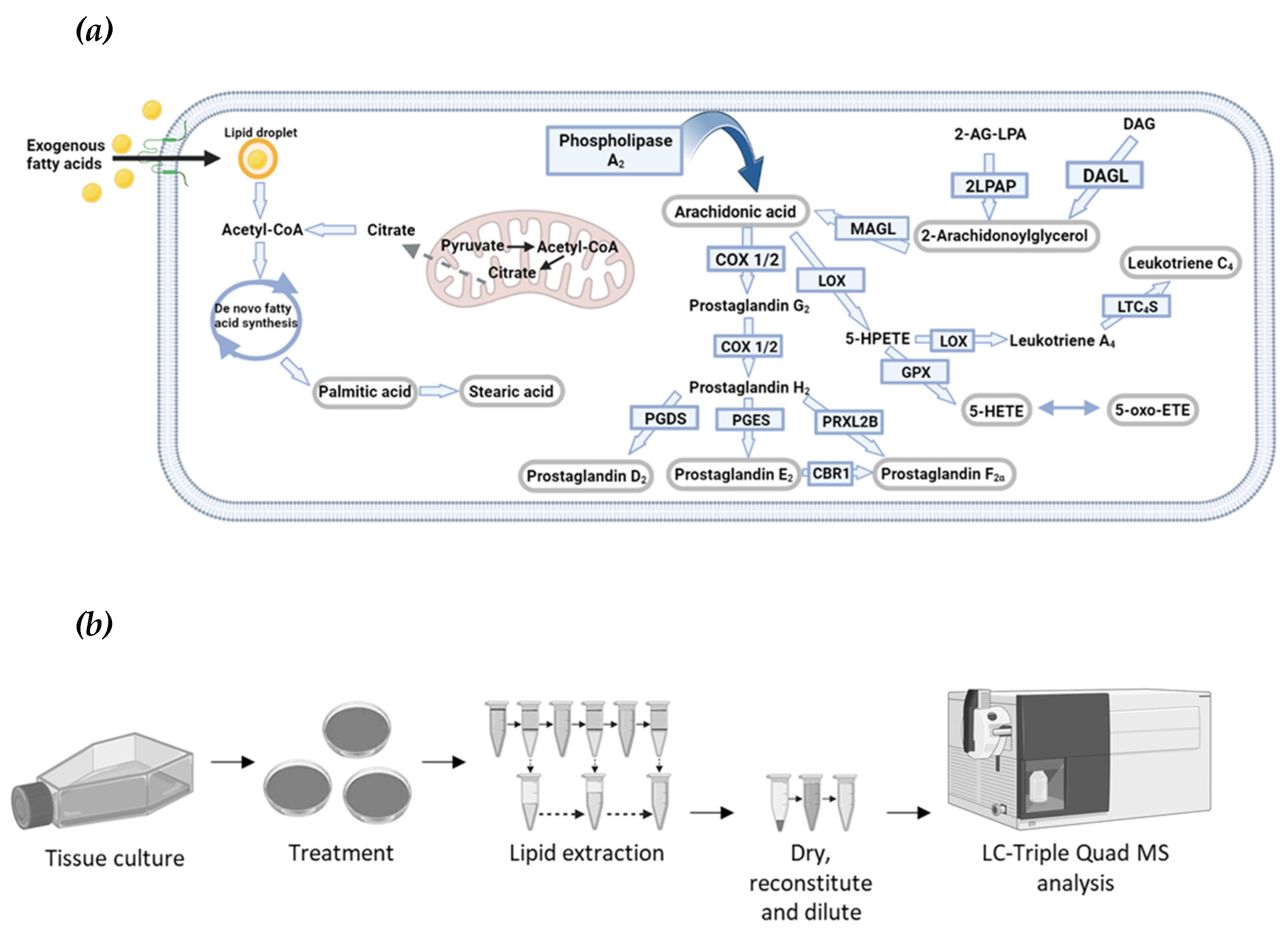
Figure 2.
Optimised eicosanoid and fatty acid profiling by targeted MS. (a) The MS2 ion spectra of PGF2α (molar mass of 354.48) using electrospray ionization in positive mode (ESI+), identifying the sodium adduct ([M+Na]+), potassium adduct ([M+K]+), dimer ([2M+H]+), and the sodiated dimer ([2M+Na]+) adduct of PGF2α. The fragments at m/z 319.2 and m/z 265.1, caused by in-source fragmentation, have formulas and structures as shown. (b) dMRM chromatogram of PGF2α. The sodium adduct (precursor ion) is exposed to a CE of 4 eV to obtain the product ion of m/z 360.3, 12 eV for product ion 342.2 m/z, 48 eV for product ion 57 m/z and a 64 eV for product ion 43.3 m/z. The product ion, 360.3 m/z is the most abundant species and is therefore used as the quant ion for determining concentration. (c) dMRM ion spectra of PGF2α. The precursor ion is indicated by the red star at m/z 377.2 The product ions are shown. (d) Product ion chromatograms of eicosanoid and fatty acid standards. Standards are in an equimolar ratio and an on-column concentration of 300 fmol/L. The chromatogram is not scaled to the largest in the chromatogram, which would make each peak have the same height (normalise the counts to the largest peak in the chromatogram). For each lipid, the most intense peak is the quant ion, the other three peaks are the respective qual ions.
Figure 2.
Optimised eicosanoid and fatty acid profiling by targeted MS. (a) The MS2 ion spectra of PGF2α (molar mass of 354.48) using electrospray ionization in positive mode (ESI+), identifying the sodium adduct ([M+Na]+), potassium adduct ([M+K]+), dimer ([2M+H]+), and the sodiated dimer ([2M+Na]+) adduct of PGF2α. The fragments at m/z 319.2 and m/z 265.1, caused by in-source fragmentation, have formulas and structures as shown. (b) dMRM chromatogram of PGF2α. The sodium adduct (precursor ion) is exposed to a CE of 4 eV to obtain the product ion of m/z 360.3, 12 eV for product ion 342.2 m/z, 48 eV for product ion 57 m/z and a 64 eV for product ion 43.3 m/z. The product ion, 360.3 m/z is the most abundant species and is therefore used as the quant ion for determining concentration. (c) dMRM ion spectra of PGF2α. The precursor ion is indicated by the red star at m/z 377.2 The product ions are shown. (d) Product ion chromatograms of eicosanoid and fatty acid standards. Standards are in an equimolar ratio and an on-column concentration of 300 fmol/L. The chromatogram is not scaled to the largest in the chromatogram, which would make each peak have the same height (normalise the counts to the largest peak in the chromatogram). For each lipid, the most intense peak is the quant ion, the other three peaks are the respective qual ions.
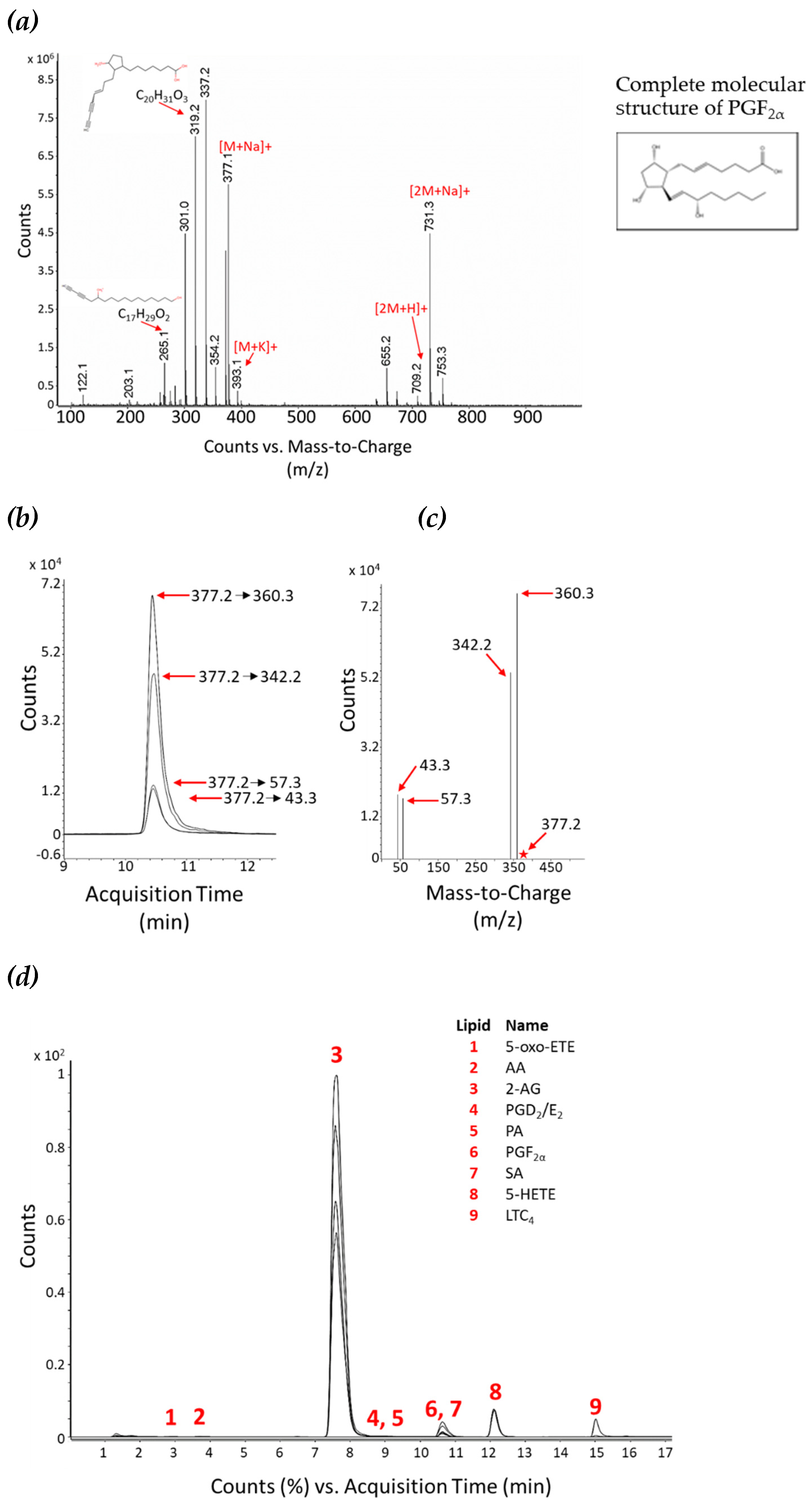
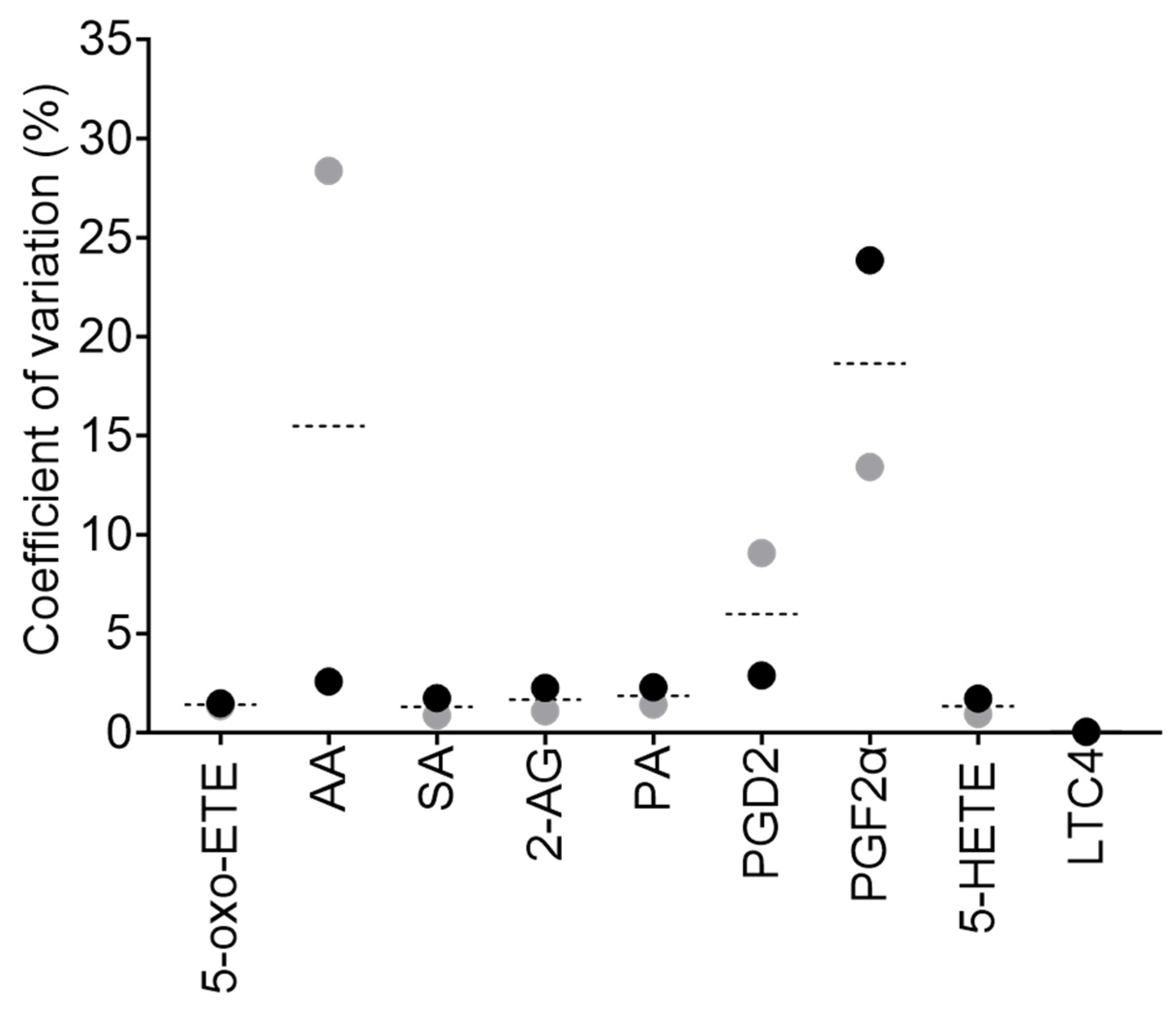
Figure 3.
Method intraday reproducibility. Lipid standards were combined and analysed in technical triplicate at two concentrations, 0.3 pmol (grey dots) and 3 pmol (black dots) on-column, respectively. The CV between technical triplicates was calculated (as %) for each standard, as a mean of the two concentrations (dashed line) or individually (dots).
Figure 3.
Method intraday reproducibility. Lipid standards were combined and analysed in technical triplicate at two concentrations, 0.3 pmol (grey dots) and 3 pmol (black dots) on-column, respectively. The CV between technical triplicates was calculated (as %) for each standard, as a mean of the two concentrations (dashed line) or individually (dots).
Figure 4.
Comparison of liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) methods for cellular lipids. (a) Three LLE techniques were tested. In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 1 cells are lysed with 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 1), followed by lipid extraction with MTBE (steps 2 and 3) and finally 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 4). In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 2 cells are lysed with 100% MeOH (step 1), followed by lipid extraction with MTBE:CHCl
3 (1:1, v/v)(steps 2 and 3), and 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 4). In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 3 cell lysis and all lipid extraction steps are performed with 100% ACN. Three biological replicates were used for each technique.
(b) The graph represents the mean of three biological replicates. Light grey bars are the results from Extraction Method 1, dark grey bars are results from Extraction Method 2, and black bars are from Extraction Method 3. Results are normalised. Normalisation parameters: 100% is defined as the largest mean in each data set and the results are given as percentages. For area under the curve (AUC) for each result (not normalised results), see
Table S1a.
Figure 4.
Comparison of liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) methods for cellular lipids. (a) Three LLE techniques were tested. In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 1 cells are lysed with 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 1), followed by lipid extraction with MTBE (steps 2 and 3) and finally 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 4). In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 2 cells are lysed with 100% MeOH (step 1), followed by lipid extraction with MTBE:CHCl
3 (1:1, v/v)(steps 2 and 3), and 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 4). In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 3 cell lysis and all lipid extraction steps are performed with 100% ACN. Three biological replicates were used for each technique.
(b) The graph represents the mean of three biological replicates. Light grey bars are the results from Extraction Method 1, dark grey bars are results from Extraction Method 2, and black bars are from Extraction Method 3. Results are normalised. Normalisation parameters: 100% is defined as the largest mean in each data set and the results are given as percentages. For area under the curve (AUC) for each result (not normalised results), see
Table S1a.
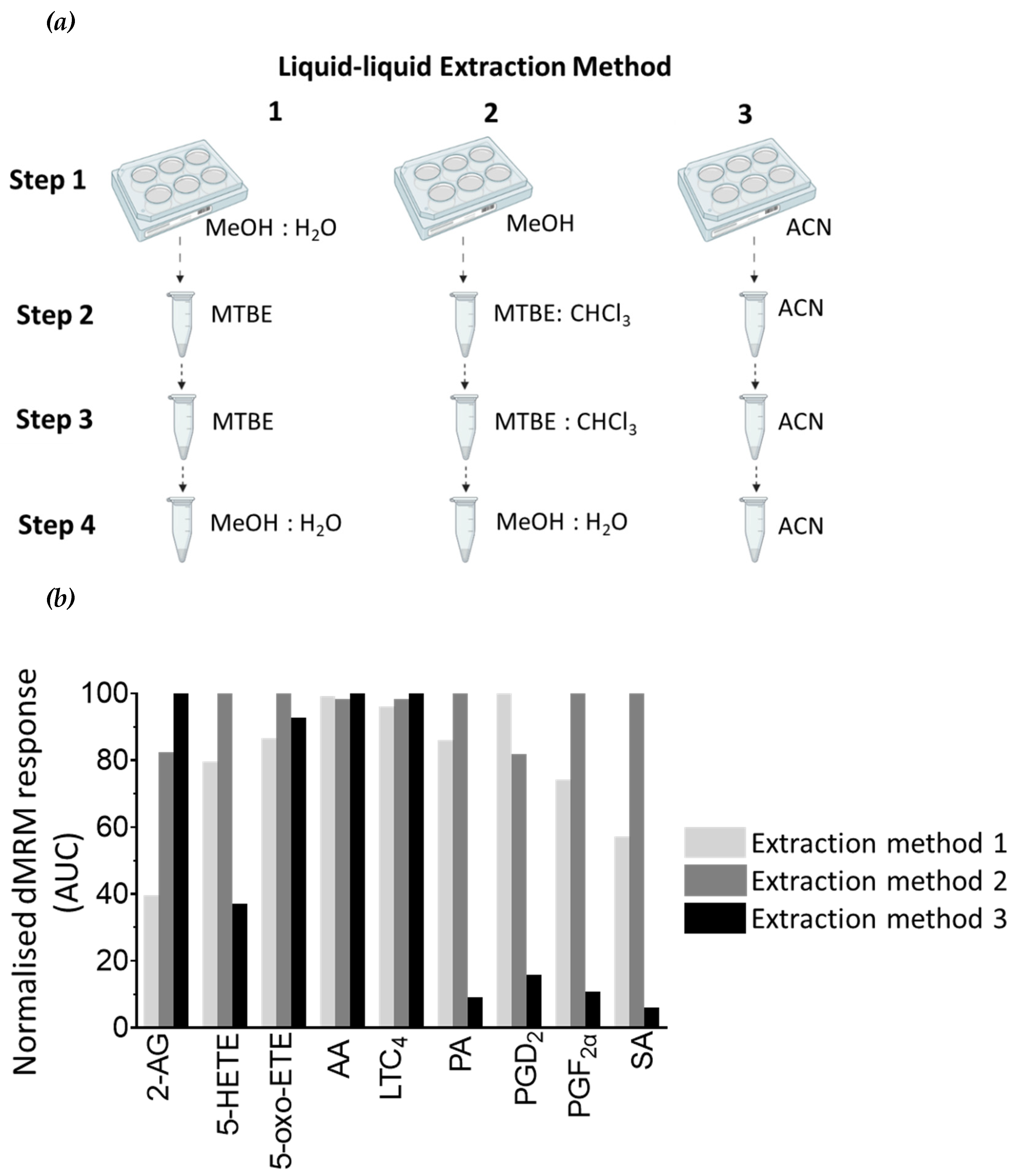
Figure 5.
Comparison of LLE techniques for secreted lipids in cell supernatant material. (a) Three LLE techniques were tested. In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 1 lipids are first extracted with MeOH:H
2O:MBTE (1:1:2, v:v:v), followed by extraction with MTBE (step 2) and 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 3). In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 2 lipids are first extracted with MeOH:MTBE:CHCL
3 (2:1:1, v:v:v), followed by extraction step with MTBE:CHCl
3 (step 2), and 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 3). In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 3 all lipid extract steps are performed with 100% ACN. Three biological replicates were used for each technique.
(b) The graph represents the mean of three biological replicates. Light grey bars are the results from Extraction Method 1, dark grey bars are results from Extraction Method 2, and black bars are from Extraction Method 3. Results are normalised. Normalisation parameters: 100% is defined as the largest mean in each data set and the results are given as percentages. For area under the curve (AUC) for each result (not normalised results), see
Table S1b.
Figure 5.
Comparison of LLE techniques for secreted lipids in cell supernatant material. (a) Three LLE techniques were tested. In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 1 lipids are first extracted with MeOH:H
2O:MBTE (1:1:2, v:v:v), followed by extraction with MTBE (step 2) and 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 3). In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 2 lipids are first extracted with MeOH:MTBE:CHCL
3 (2:1:1, v:v:v), followed by extraction step with MTBE:CHCl
3 (step 2), and 50% (v/v) MeOH in H
2O (step 3). In liquid-liquid Extraction Method 3 all lipid extract steps are performed with 100% ACN. Three biological replicates were used for each technique.
(b) The graph represents the mean of three biological replicates. Light grey bars are the results from Extraction Method 1, dark grey bars are results from Extraction Method 2, and black bars are from Extraction Method 3. Results are normalised. Normalisation parameters: 100% is defined as the largest mean in each data set and the results are given as percentages. For area under the curve (AUC) for each result (not normalised results), see
Table S1b.
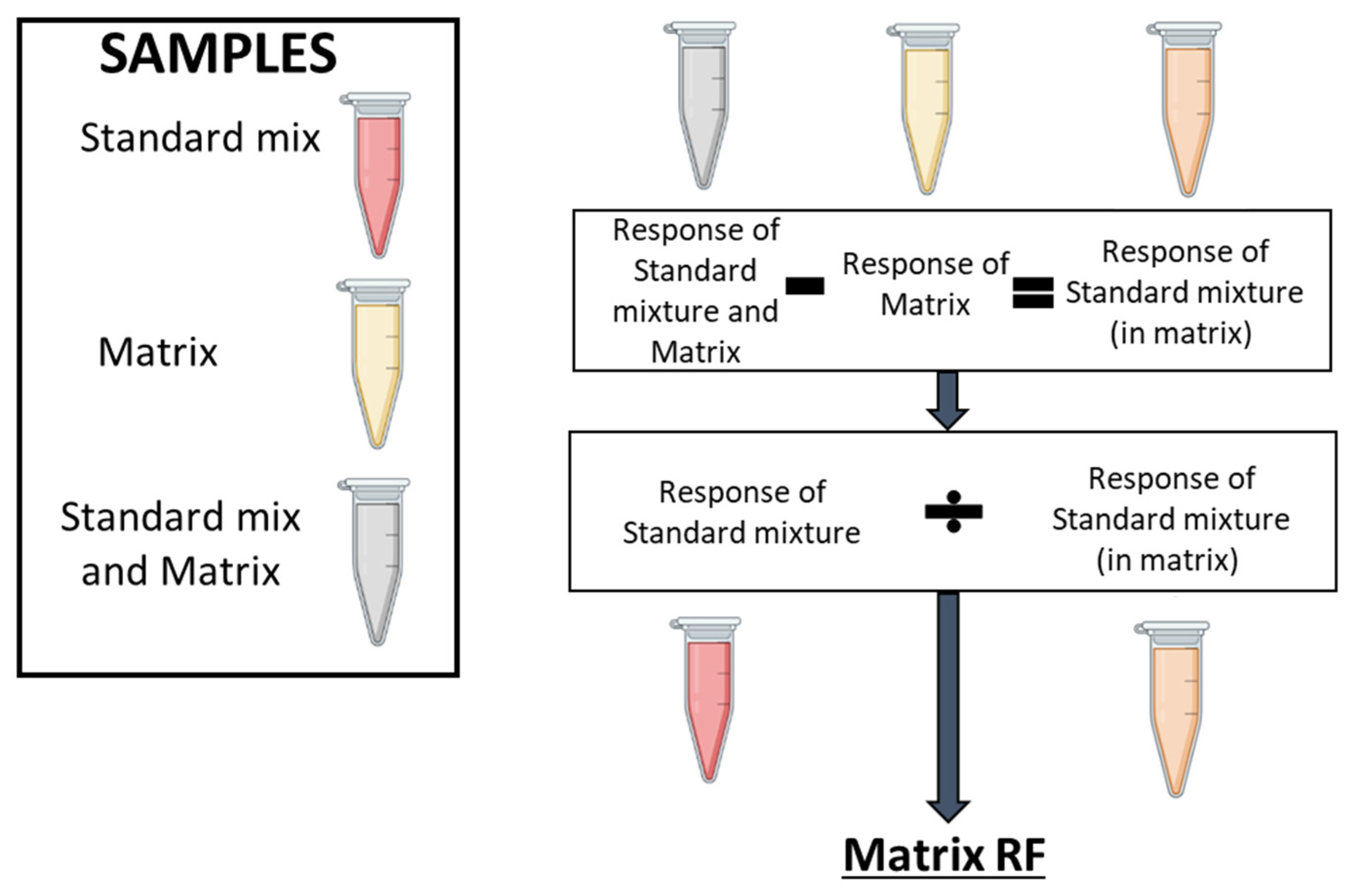
Figure 6.
Matrix effect on lipid detection. The workflow followed for determining the matrix effect for each lipid. Three types of samples must be prepared: a pool of all samples (matrix, yellow tube), a standard mixture (the BLM, red tube) and the standard mixture spiked into the matrix (grey tube). First, the intrinsic contribution of the lipid response from the matrix itself (yellow tube) is removed from the standard mixture spiked into the matrix (grey tube) by subtracting the MRM AUC for each metabolite found in the matrix. This calculation gives the BLM response when present in the matrix (orange tube). A matrix RF value is subsequently obtained by dividing the MRM AUC value for the standard mixture (red tube) by the MRM AUC value for the standard mixture when present in the matrix (orange tube). Numeric values for measured matrix RFs are provided in
Table S2.
Figure 6.
Matrix effect on lipid detection. The workflow followed for determining the matrix effect for each lipid. Three types of samples must be prepared: a pool of all samples (matrix, yellow tube), a standard mixture (the BLM, red tube) and the standard mixture spiked into the matrix (grey tube). First, the intrinsic contribution of the lipid response from the matrix itself (yellow tube) is removed from the standard mixture spiked into the matrix (grey tube) by subtracting the MRM AUC for each metabolite found in the matrix. This calculation gives the BLM response when present in the matrix (orange tube). A matrix RF value is subsequently obtained by dividing the MRM AUC value for the standard mixture (red tube) by the MRM AUC value for the standard mixture when present in the matrix (orange tube). Numeric values for measured matrix RFs are provided in
Table S2.
Figure 7.
Interferon alpha modulates eicosanoid and fatty acid pathways. (a) Analysis of bioactive lipids in HAP1 cells and cell supernatants after 36 hours treatment with IFN-I. (a) Graphs represent the mean with the standard error of the mean (SEM). Cell results are graphs on the left, the corresponding cell supernatant is on the right. Grey bars are for the not treated sample (NT) and grey with a white stripe pattern are results for IFN-I treated samples. The statistical analysis is the two sample (or unpaired) t-test. A p-value less than 0.05 suggests the results have highly significant differences. If there is no significance difference it is not labelled. (b) Mean percentage change of bioactive lipids in HAP1 cells, not treated (NT) and treated with IFNα for 36 hours (+ IFNα) (c) Cell supernatant from HAP1 cells, not treated (NT) and treated with IFNα for 36 hours (+ IFNα). Heat maps display normalized lipid abundances relative to the mean concentration of the nontreated samples (NT), which is represented by grey. For IFN-treatment, blue results are for a decrease in concentration, in percentage, grey is no change and red is for an increase in concentration in percentage. (d) Metabolic pathways of selected lipids after IFN-treatment. Converting enzymes are in boxes and lipids in this study are circled. Lipids circled in grey, have no change compared to non-treated cells, blue have decreased concentration compared to non-treated cells, lipids circled in red have an increased concentration compared to non-treated. Lipids discovered in the cell supernatant are outside of the cell lipid membrane. Lipids with a significant difference between non-treated and treated (a p-value of less than 0.05) are indicated by a yellow star.
Figure 7.
Interferon alpha modulates eicosanoid and fatty acid pathways. (a) Analysis of bioactive lipids in HAP1 cells and cell supernatants after 36 hours treatment with IFN-I. (a) Graphs represent the mean with the standard error of the mean (SEM). Cell results are graphs on the left, the corresponding cell supernatant is on the right. Grey bars are for the not treated sample (NT) and grey with a white stripe pattern are results for IFN-I treated samples. The statistical analysis is the two sample (or unpaired) t-test. A p-value less than 0.05 suggests the results have highly significant differences. If there is no significance difference it is not labelled. (b) Mean percentage change of bioactive lipids in HAP1 cells, not treated (NT) and treated with IFNα for 36 hours (+ IFNα) (c) Cell supernatant from HAP1 cells, not treated (NT) and treated with IFNα for 36 hours (+ IFNα). Heat maps display normalized lipid abundances relative to the mean concentration of the nontreated samples (NT), which is represented by grey. For IFN-treatment, blue results are for a decrease in concentration, in percentage, grey is no change and red is for an increase in concentration in percentage. (d) Metabolic pathways of selected lipids after IFN-treatment. Converting enzymes are in boxes and lipids in this study are circled. Lipids circled in grey, have no change compared to non-treated cells, blue have decreased concentration compared to non-treated cells, lipids circled in red have an increased concentration compared to non-treated. Lipids discovered in the cell supernatant are outside of the cell lipid membrane. Lipids with a significant difference between non-treated and treated (a p-value of less than 0.05) are indicated by a yellow star.
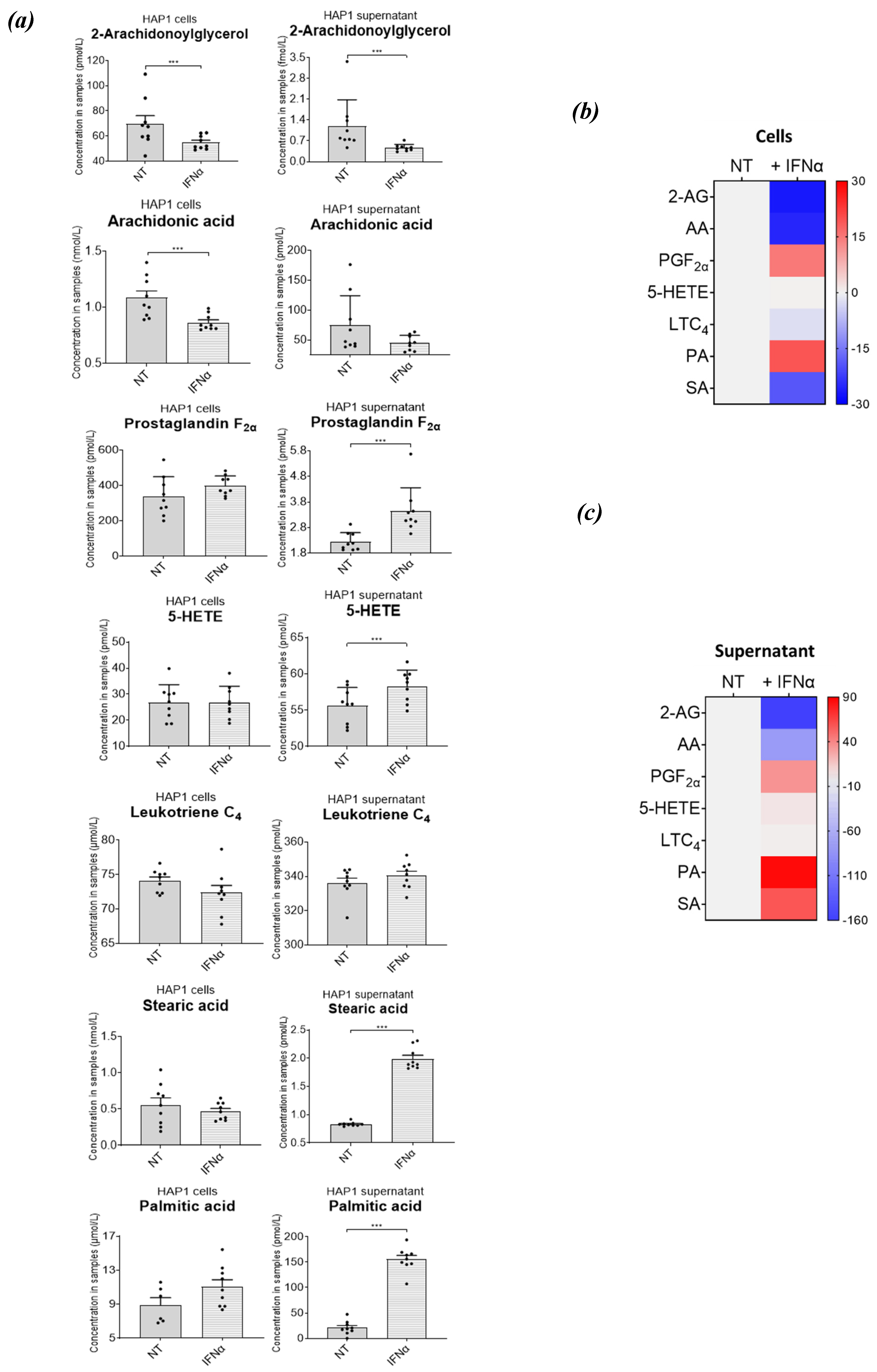
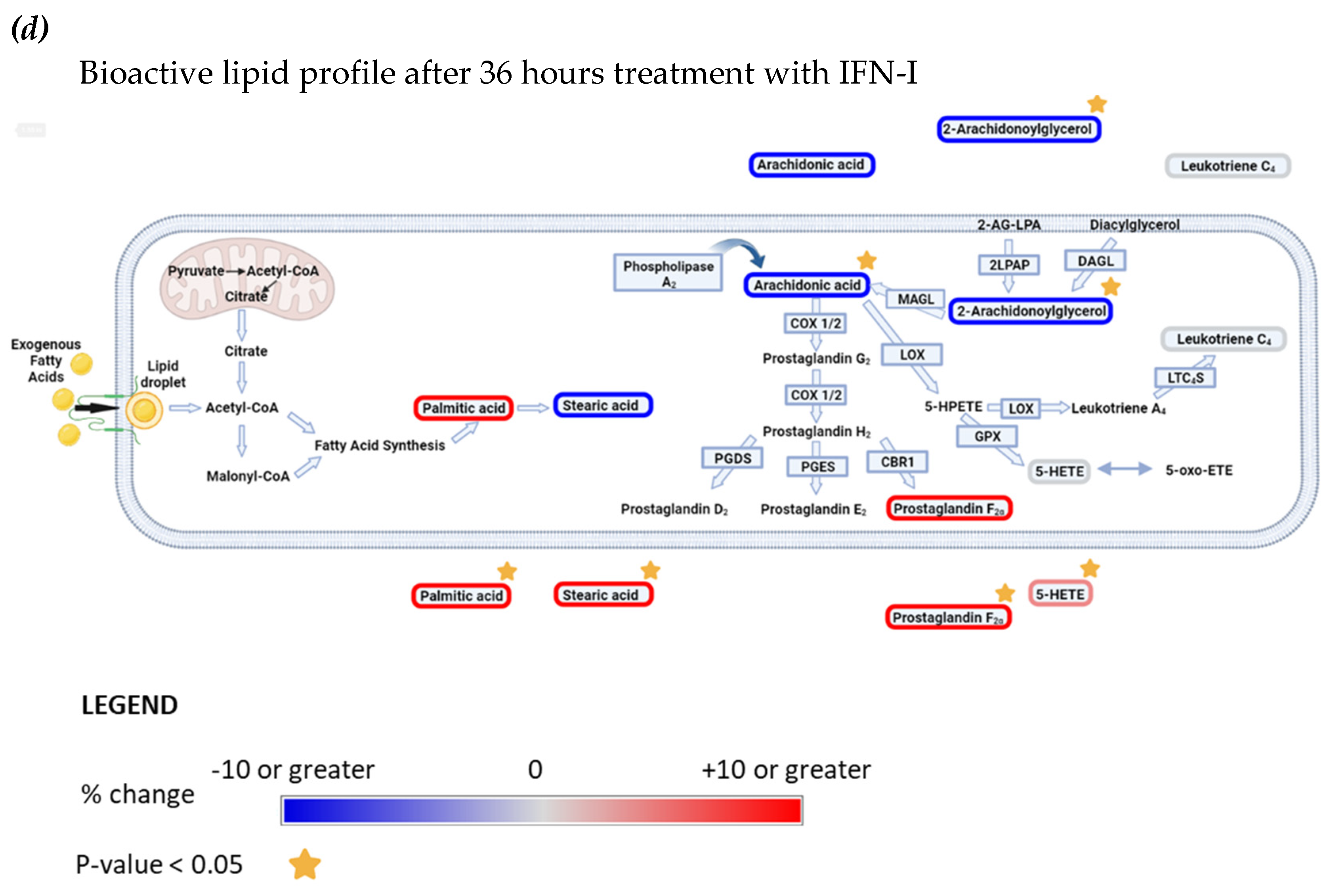
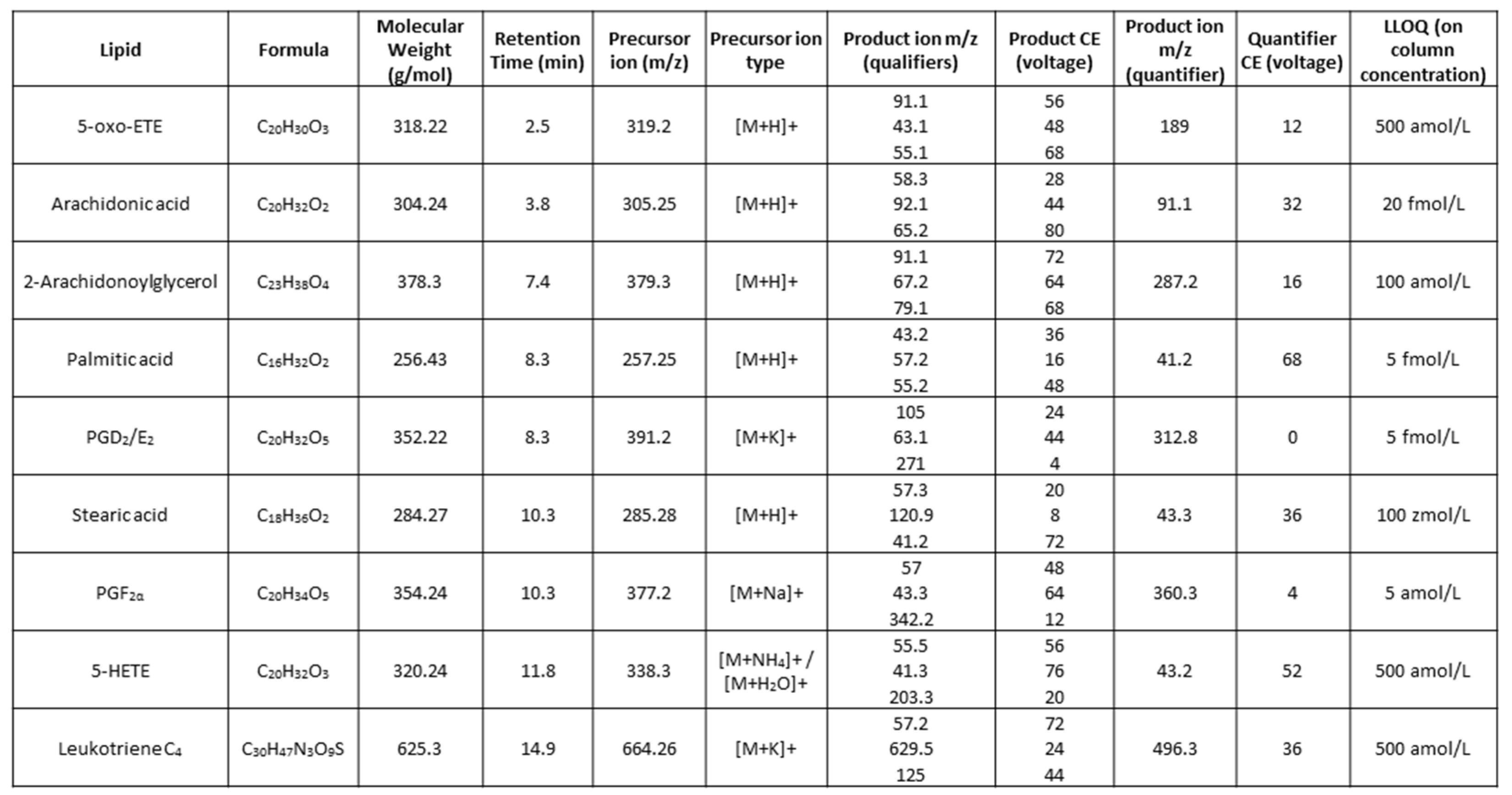
Table 1.
Optimised transitions for LC-dMRM-MS. Lipid names, dMRM parameters and lower limits of quantification (LLOQ) are listed for all eicosanoid and fatty acid standards analysed. The CE used from precursor to product ion transitions are indicated in electron volts (eV).
Table 1.
Optimised transitions for LC-dMRM-MS. Lipid names, dMRM parameters and lower limits of quantification (LLOQ) are listed for all eicosanoid and fatty acid standards analysed. The CE used from precursor to product ion transitions are indicated in electron volts (eV).
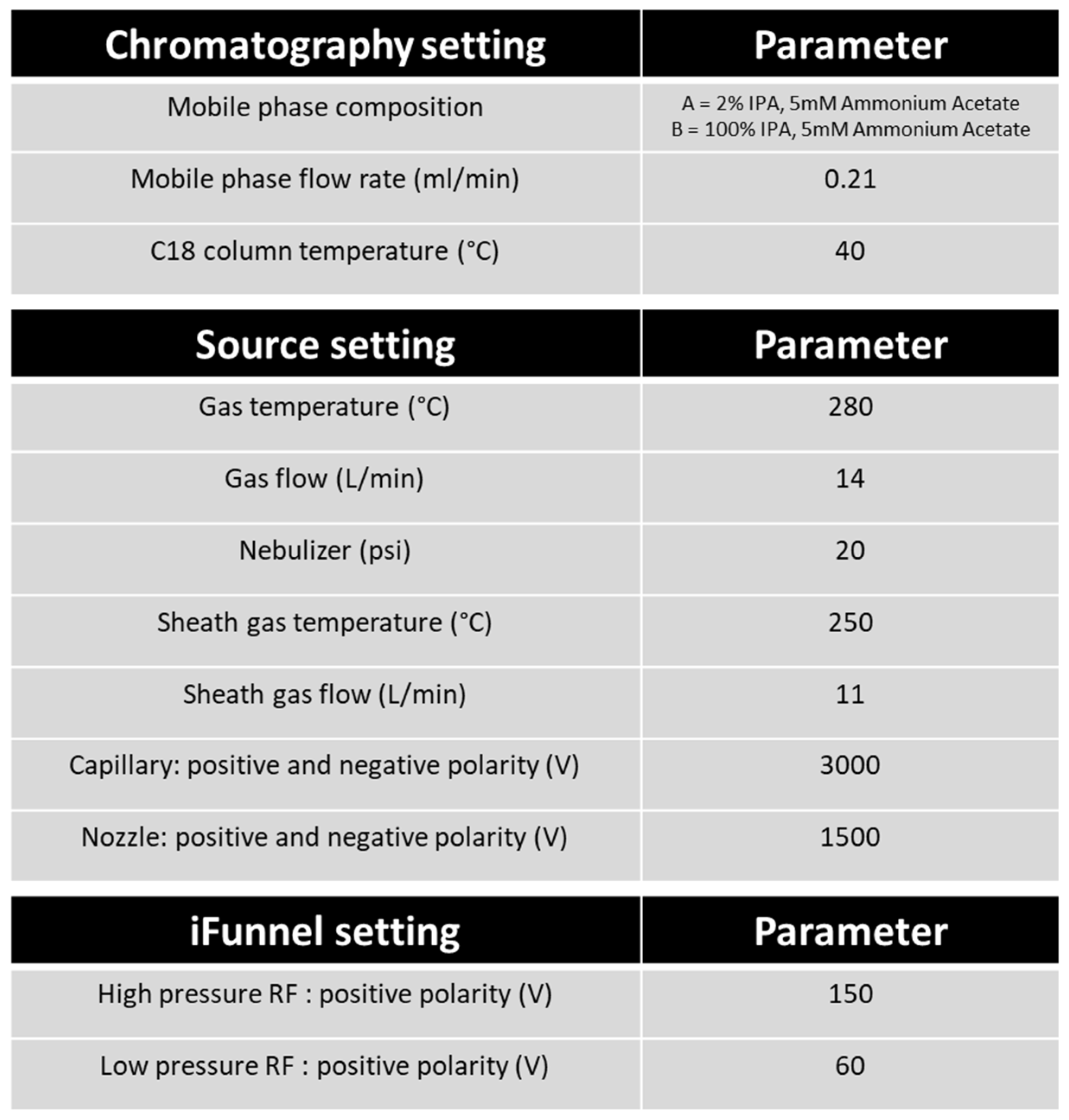
Table 2.
Chromatography and mass spectrometry parameters. This table represents the instrumentation settings used in the analysis method and parameters applied. Settings are selected for the most favourable separation and ionisation of eicosanoids and fatty acids.
Table 2.
Chromatography and mass spectrometry parameters. This table represents the instrumentation settings used in the analysis method and parameters applied. Settings are selected for the most favourable separation and ionisation of eicosanoids and fatty acids.