Submitted:
18 July 2023
Posted:
19 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and ecology
2.2. Physiology and Chemotaxonomy
2.3. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA and rpoB genes
2.4. Genome Features
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physiology and Chemotaxonomy
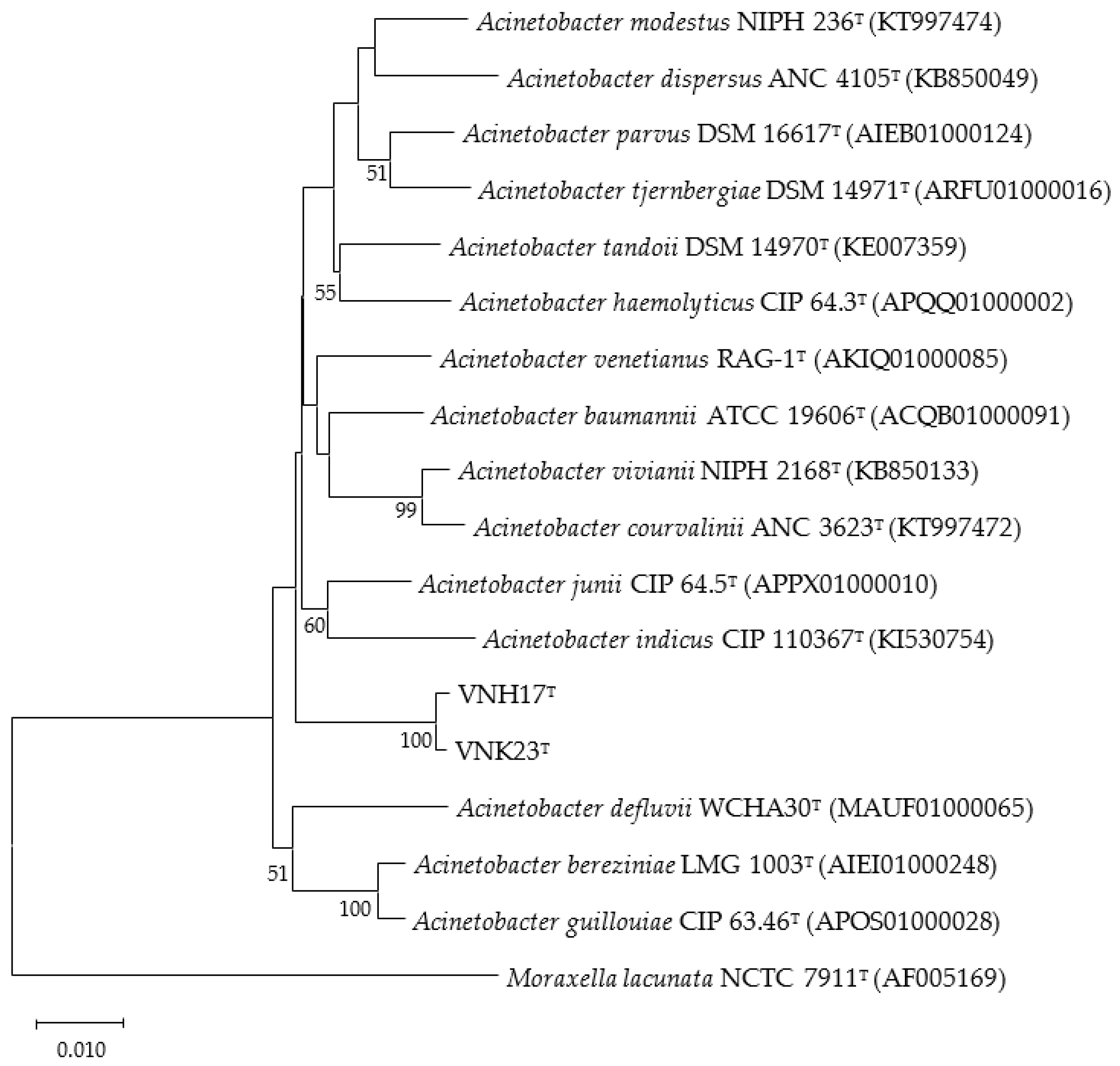
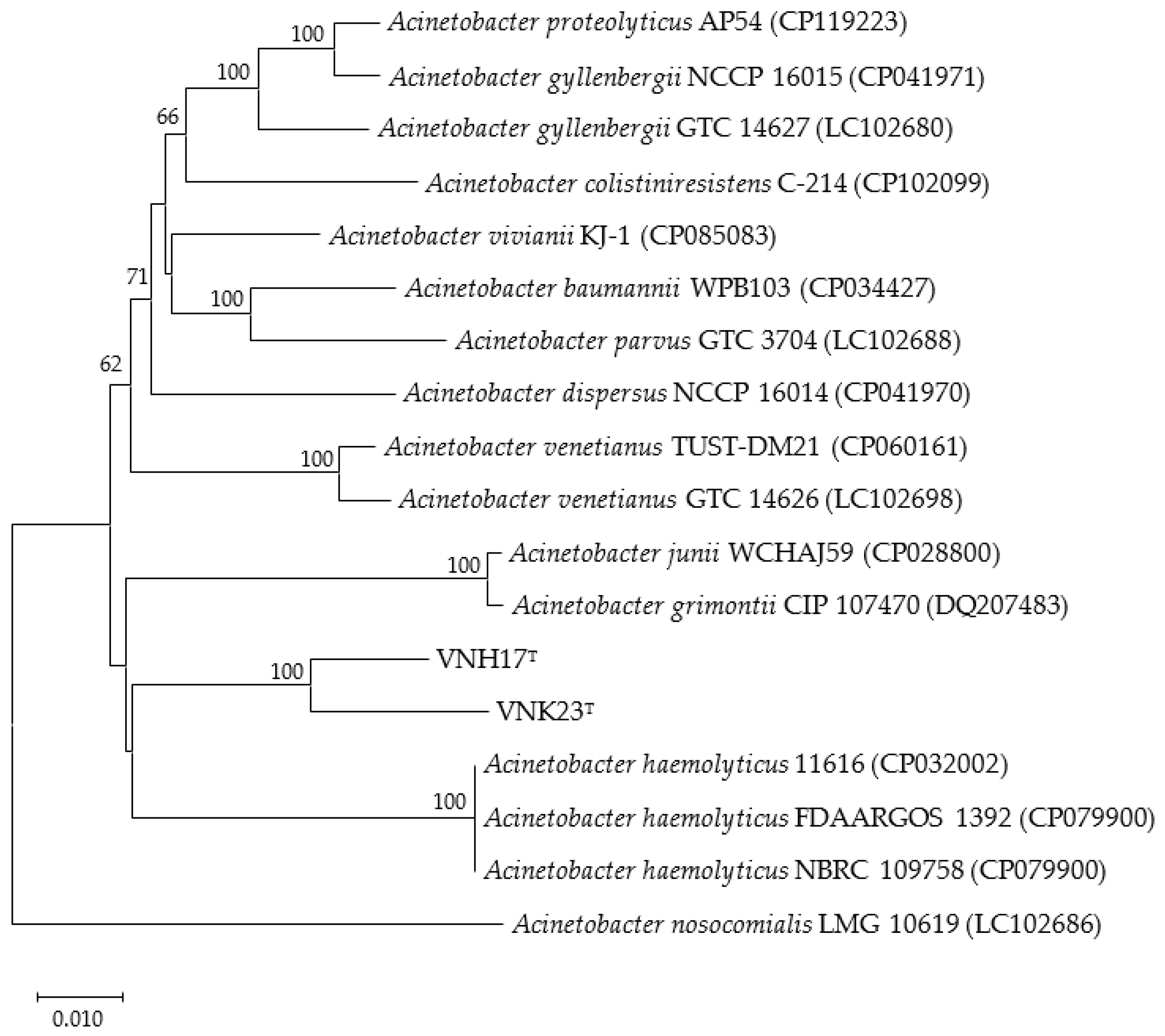
3.2. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA and rpoB genes
3.3. Genome Features
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beijerinck, MW. Pigments as products of oxidation by bacterial action. Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie Van Wetenschappen Proc Ser B Phy Sci, 1910, 13, 1066–77. [Google Scholar]
- Brisou J, Prevot AR. Etudes de Systematique Bacterienne. X. Revision des especes reunies dans le genre Achromobacter. Ann Inst Pasteur, 1954, 86, 722–728. [Google Scholar]
- Parte, AC. LPSN—List of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature (bacterio.net), 20 years on. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2018, 68, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz-Moreira I, Novo A, Hantsis-Zacharov E, Lopes AR, Gomila M et al. Acinetobacter rudis sp. nov., isolated from raw milk and raw wastewater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2011, 61, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marí-Almirall M, Cosgaya C, Pons MJ, Nemec A, Ochoa TJ et al. Pathogenic Acinetobacter species including the novel Acinetobacter dijkshoorniae recovered from market meat in Peru. Int J Food Microbiol, 2019, 305, 108248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalheira A, Gonzales-Siles L, Salva-Serra F, Lindgren A, Svensson-Stadler L, Thorell K, Pineiro-Iglesias B, Karlsson R, Silva J, Teixeira P, et al. Acinetobacter portensis sp. nov. and Acinetobacter guerrae sp. nov., isolated from raw meat. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2020, 70, 4544–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemec A, Musilek M, Maixnerova M, De Baere T, van der Reijden TJ, Vaneechoutte M, Dijkshoorn L. Acinetobacter beijerinckii sp. nov. and Acinetobacter gyllenbergii sp. nov., haemolytic organisms isolated from humans. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2009, 59, 118–124.
- Yacouba A, Sissoko S, Tchoupou Saha OF, Haddad G, Dubourg G, Gouriet F, Tidjani Alou M, Alibar S, Million M, Lagier JC, et al. Description of Acinetobacter ihumii sp. nov., Microbacterium ihumii sp. nov., and Gulosibacter massiliensis sp. nov., three new bacteria isolated from human blood. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 2022, 369, 0. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Perez S, Lievens B, Jacquemyn H, Herrera CM. Acinetobacter nectaris sp. nov. and Acinetobacter boissieri sp. nov., isolated from floral nectar of wild Mediterranean insect-pollinated plants. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2013, 63, 1532–1539. [CrossRef]
- Krizova L, Maixnerova M, Sedo O, Nemec A. Acinetobacter bohemicus sp. nov. widespread in natural soil and water ecosystems in the Czech Republic. Syst Appl Microbiol, 2014, 37, 467–473. [CrossRef]
- Radolfova-Krizova L, Maixnerova M, Nemec A. Acinetobacter celticus sp. nov., a psychrotolerant species widespread in natural soil and water ecosystems. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2016, 66, 5392–5398. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radolfova-Krizova L, Maixnerova M, Nemec A. Acinetobacter pragensis sp. nov., found in soil and water ecosystems. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2016, 66, 3897–3903. [CrossRef]
- Yamahira K, Hirota K, Nakajima K, Morita N, Nodasaka Y, Yumoto I. Acinetobacter sp. strain Ths, a novel psychrotolerant and alkalitolerant bacterium that utilizes hydrocarbon. Extremophiles, 2008, 12, 729–734. [CrossRef]
- Dahal RH, Chaudhary DK, Kim J. Acinetobacter halotolerans sp. nov., a novel halotolerant, alkali tolerant, and hydrocarbon degrading bacterium, isolated from soil. Arch Microbiol, 2017, 199, 701–710. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarny J, Staninska-Pięta J, Piotrowska-Cyplik A, Juzwa W, Wolniewicz A, Marecik R, Lawniczak L, Chrzanowski L. Acinetobacter sp. as the key player in diesel oil degrading community exposed to PAHs and heavy metals. J Hazard Mater, 2020, 383, 121168. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai Y, Wang R, Rao P, Wu B, Yan L, Hu L, Park S, Ryu M, Zhou X. Bioremediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons Using Acinetobacter sp. SCYY-5 Isolated from Contaminated Oil Sludge: Strategy and Effectiveness Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 19, 18(2):819. [Google Scholar]
- Xia M, Liu Y, Taylor AA, Fu D, Khan AR, Terry N. Crude oil depletion by bacterial strains isolated from a petroleum hydrocarbon impacted solid waste management site in California. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad, 2017, 123, 70–77. [CrossRef]
- Lányi, B. Classical and Rapid Identification Method for Medically Important Bacteria. In Method in Microbiology 19; Cowell R, Ed.; Academic Press: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1987; pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer AB, Fulton M. A simplified method of staining endospores. Science, 1933, 77, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RA, Krieg NR. Phenotypic Characterization and the Principles of Comparative Systematics. In Methods for General and Molecular Microbiology; Reddy CA, Ed, Ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 330–393. [Google Scholar]
- Smibert RM, Krieg NR. Phenotypic characterization. In Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology; Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR, Ed.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 607–654. [Google Scholar]
- Dahal RH, Kim J. Rhabdobacter roseus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2016, 66, 308–314.
- Minnikin D, O'Donnell A, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, et al. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 1984, 2, 233–241. [CrossRef]
- Sasser, M. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. Technol. Note 2001, 101, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Frank JA, Reich CI, Sharma S, Weisbaum JS, Wilson BA, Olsen GJ. Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically United database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol, 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Scola B, Gundi VA, Khamis A, Raoult D. Sequencing of the rpoB gene and flanking spacers for molecular identification of Acinetobacter species. J Clin Microbiol, 2006, 44, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol, 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na SI, Kim YO, Yoon SH, Ha SM, Baek I, Chun J. UBCG: Up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol, 2018, 56, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform, 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, et al. The RAST server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom, 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res, 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juni, E. Interspecies transformation of Acinetobacter: genetic evidence for a ubiquitous genus. J Bacteriol, 1972, 112, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso-da-Rocha C, Vaz-Moreira I, Svensson-Stadler L, et al. Diversity and antibiotic resistance of Acinetobacter spp. in water from the source to the tap. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2013, 97, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter M, Rossello-Mora R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source of isolation | Forest soil | Paddy soil | Sediment from an acidic hot spring and pyritic mine drainage | The thalli of Cladonia arbuscula and Cladonia stellaris lichens | Acidic mine drainage | Acidic northern wetlands |
| Cell shape | Ovals, Rods | Ovals, rods | Cocci, short rods | Spherical to ovoid | Rods | Coccobacilli |
| Cell size (µm) | 0.8-1.1 x1.5-3.2 | 2.0-3.0 x3.0-10 | 0.7-0.9 x0.9-1.6 | 0.8-1.6 x0.9-2.26 | 1.3-1.5 x3.2-3.3 | 0.7-1.5 x1.4-4.1 |
| Colony color | White, Mucoid | Red brown | Salmon pink | pink or salmon pink | Light yellow | White, cream |
| Motility | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| Anaerobic phototrophy | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| Bacteriochlorophyll a | - | + | + | + | - | - |
| Temperature range for growth (°C) | 20-40 | 20-40 | 20-40 | 5-30 | 20–45 | 2–30 |
| Optimal growth temperature (°C) | 30-35 | 30–35 | 20-35 | 10-15 | 37 | 18–22 |
| pH range for growth | 6-9 | 5.0–8.5 | 3.5-6.0 | 3.0–7.5 | 2.5–5 | 3.7–7.5 |
| pH optimum for growth | 7-8 | 6.0–6.5 | 4.5-5.0 | 4.5–5.5 | 4.0 | 5.0–5.7 |
| Tolerance of >2.5 (%w/v) NaCl | - | - | + | + | - | - |
| Electron donor/ carbon source | ||||||
| Acetate | - | ++ | - | - | nd | - |
| Lactate | - | + | + | - | nd | + |
| Mannose | +/- | + | - | + | - | + |
| Sorbitol | +/- | + | + | + | + | + |
| Glycerol | +/- | - | + | - | - | + |
| Asparagine | + | + | - | - | + | + |
| Aspartate | - | + | - | nd | + | - |
| Glutamate | - | ++ | - | - | nd | nd |
| Glutamine | ++ | ++ | - | - | nd | nd |
| Citrate | ++ | - | +/- | - | nd | - |
| Nitrogen fixation | - | + | nd | - | nd | nd |
| Major quinone(s) | Q-10 | Q-10, RQ-10 | Q-10 | Q-10 | Q-10 | Q-10 |
| DNA G+C content (mol%) | 68.7 | 67.8 | 69.1-69.8 | 69.1–69.8 | 65.9 | 60.5–61.9 |
| Fatty acid | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated | ||||||||
| C10:0 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 0.33 | 1.35 | 0.67 | 0.13 | - | 1.35 |
| C11:0 | - | - | - | 0.11 | - | - | - | |
| C12:0 | 2.92 | 3.34 | 6.21 | 2.80 | 5.88 | 6.55 | 9.31 | 5.18 |
| C14:0 | 0.98 | 1.19 | 0.52 | 0.57 | 1.27 | 0.81 | 0.78 | |
| C16:0 | 18.96 | 22.53 | 9.02 | 15.59 | 17.12 | 14.05 | 20.46 | 24.43 |
| N alcohol C16:0 | - | - | - | 0.14 | 1.10 | - | 0.17 | - |
| C17:0 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.37 | 0.92 | 0.54 | 0.22 | - | 0.29 |
| Iso C17:0 | - | 0.23 | 1.04 | 0.15 | - | - | - | |
| C18:0 | 2.12 | 0.33 | - | 1.68 | 1.31 | 1.85 | 1.19 | 0.97 |
| 10-methyl C17:0 | - | - | - | - | 0.47 | - | - | - |
| anteiso -C17:0 | 0.17 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Unsaturated | ||||||||
| C14:1 ω5c | 0.10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| C16:1 ω5c | - | - | - | 0.10 | - | - | - | - |
| C16:1 ω7c alcohol | - | - | - | - | 0.49 | - | - | - |
| C16:1 ω9c | - | - | - | 0.9 | - | - | - | - |
| C17:1 ω8c | 0.60 | 0.77 | 2.49 | 2.86 | 0.95 | 0.58 | 0.22 | 1.22 |
| C18:1 ω9c | 49.42 | 36.56 | 39.37 | 38.41 | 31.21 | 29.76 | 30.14 | 29.68 |
| C18:1 ω5c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.11 |
| C18:3 ω6c | 0.11 | - | - | 0.22 | 1.28 | - | 0.21 | - |
| Iso I C19:1 | 0.14 | 0.31 | - | - | 0.15 | - | 0.18 | 0.17 |
| Hydroxy | ||||||||
| C8:0 3OH | - | - | 0.13 | - | - | - | - | - |
| C12:0 2OH | 2.15 | 2.33 | 3.63 | 2.89 | 1.51 | 0.57 | 0.63 | 2.25 |
| C12:0 3OH | 3.79 | 4.18 | 6.73 | 4.75 | 4.68 | 3.04 | 5.59 | 5.19 |
| Summed features* | ||||||||
| Summed Feature 1 | - | - | - | 0.13 | - | - | - | - |
| Summed Feature 2 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.3 | 0.16 | 2.61 | 0.10 | 0.22 |
| Summed Feature 3 | 16.39 | 25.89 | 29.75 | 23.70 | 28.15 | 36.84 | 28.41 | 26.90 |
| Summed Feature 8 | 1.18 | 1.48 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 3.54 | 2.49 | 2.40 | 1.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





