Submitted:
17 July 2023
Posted:
18 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
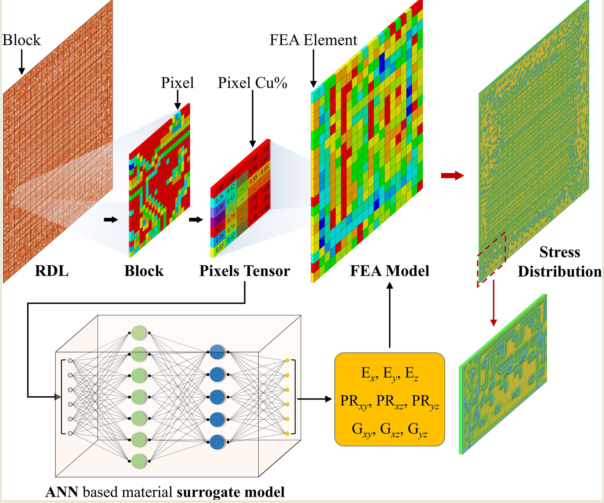
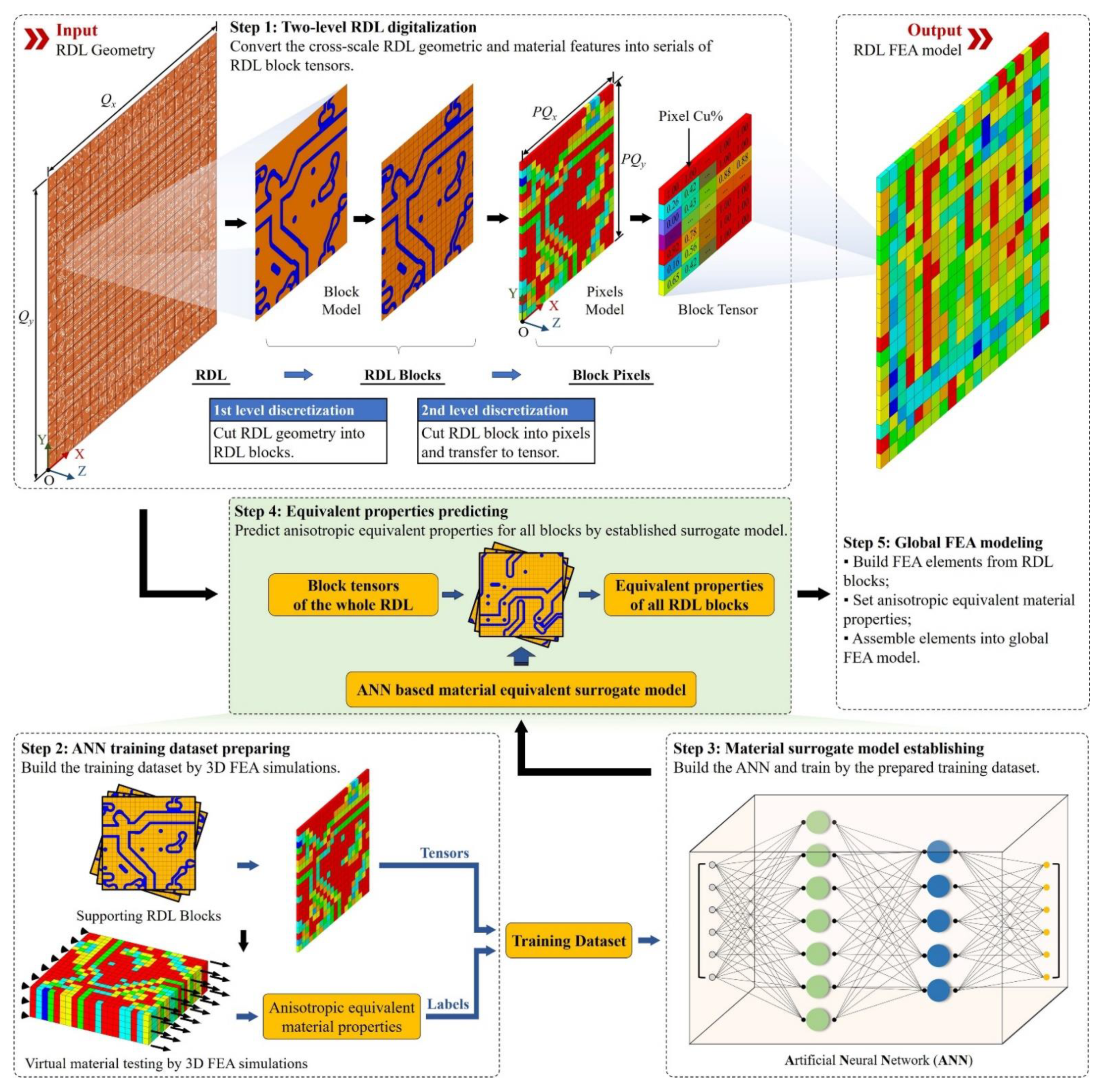
2. Methods
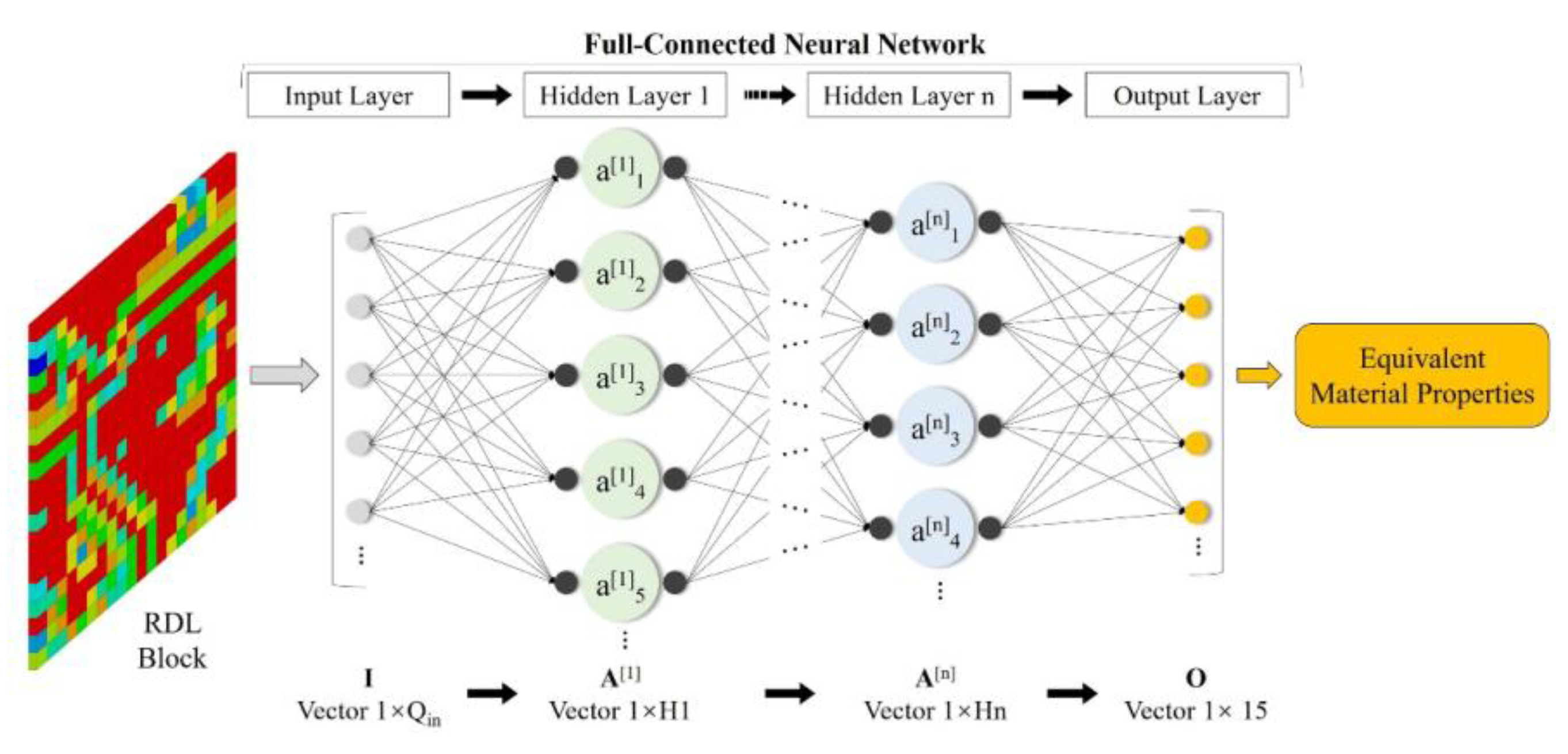
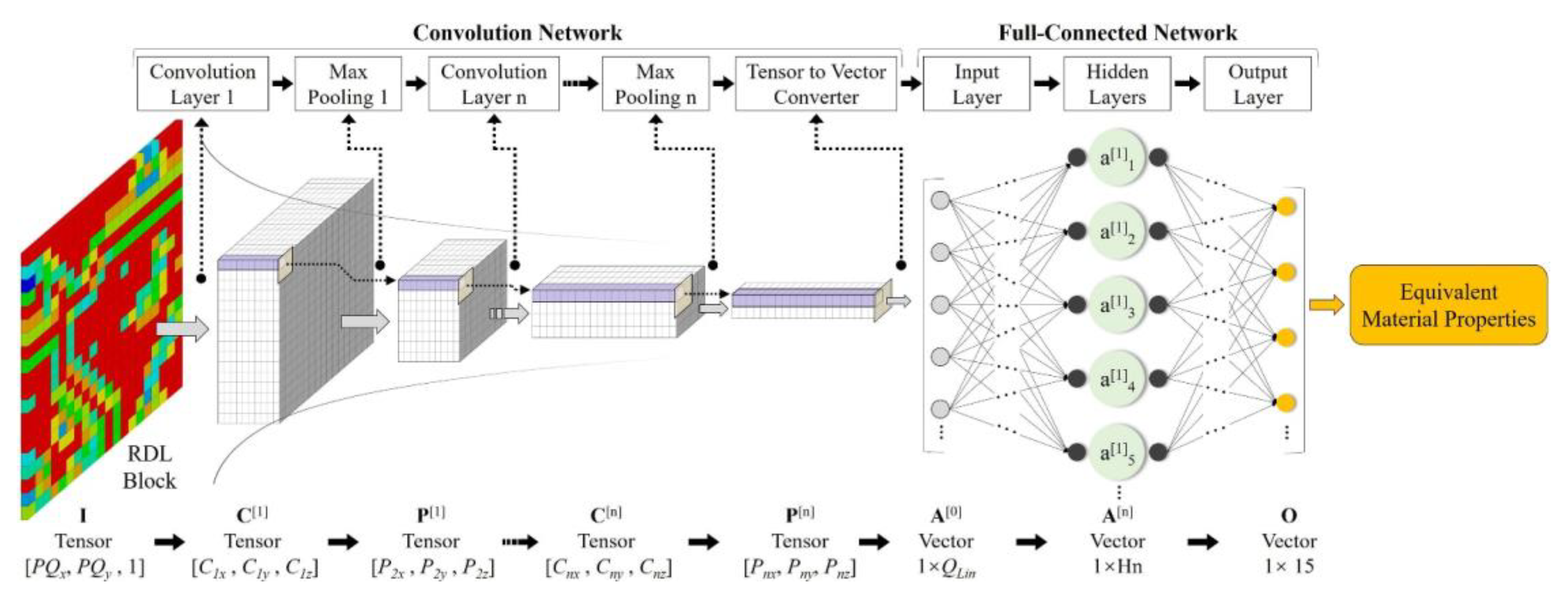
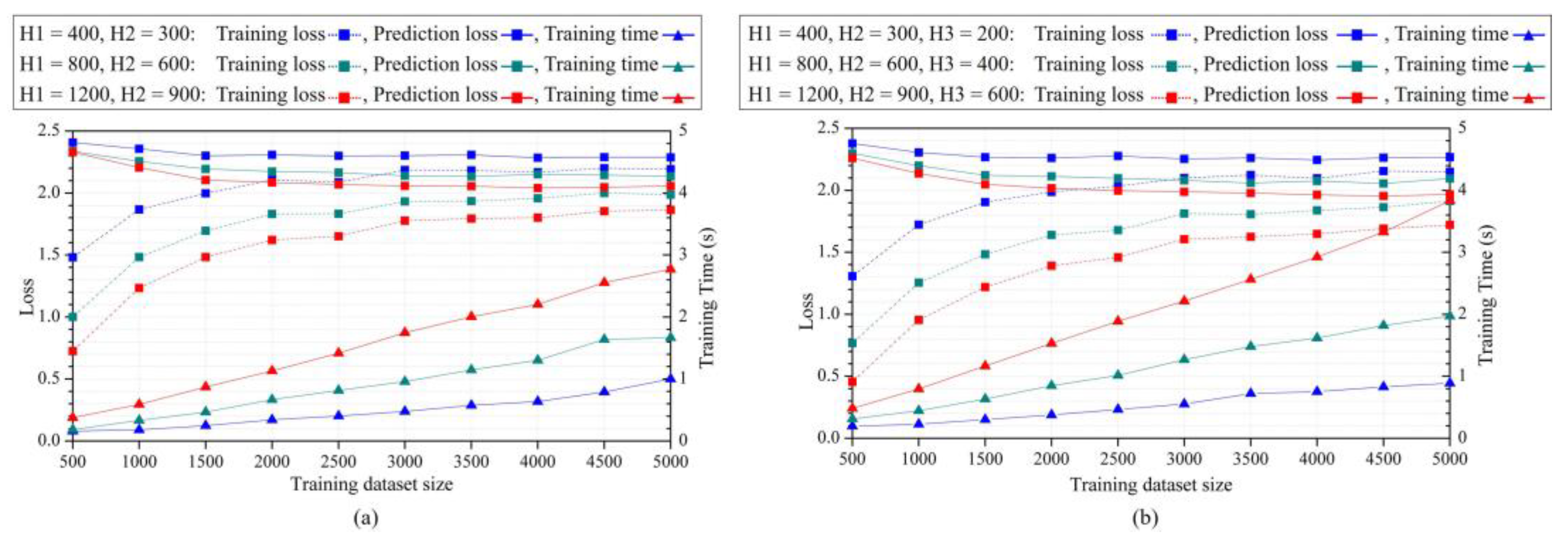
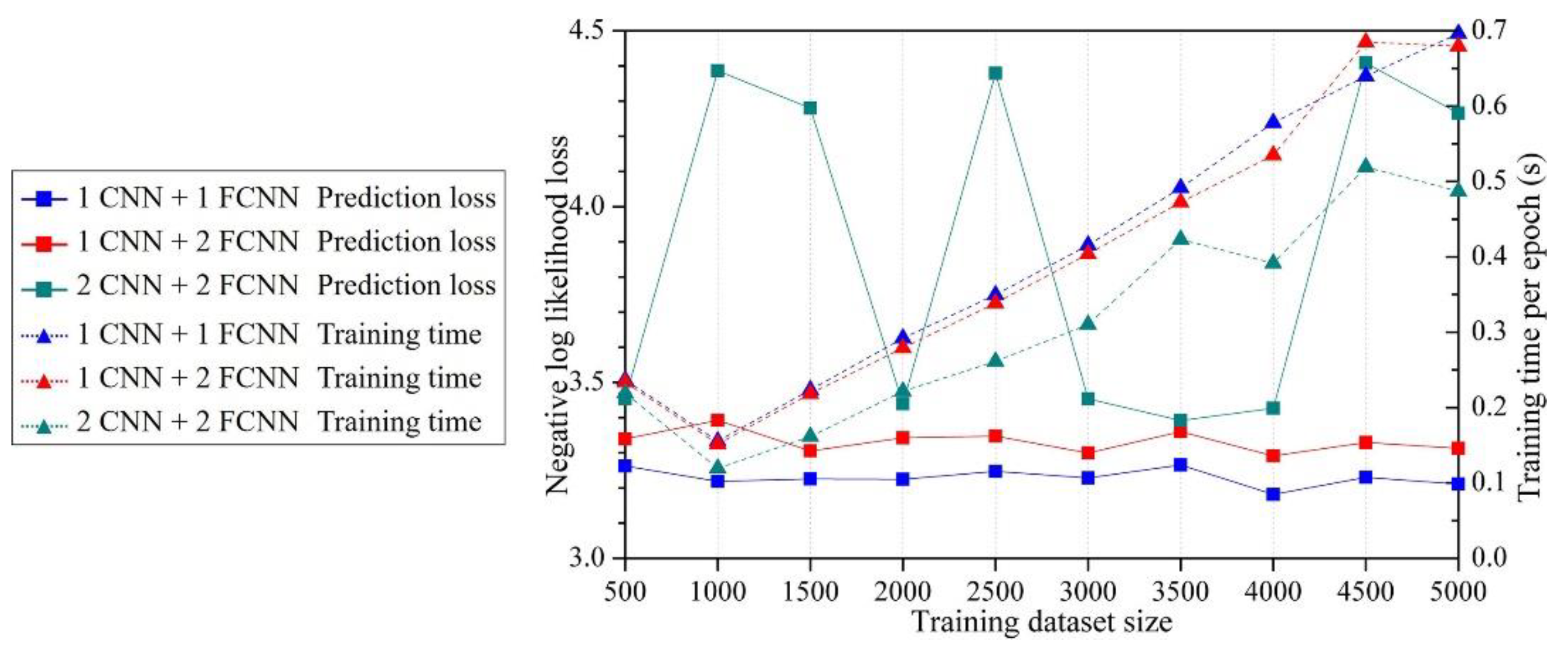
2.1. ANN Architectures
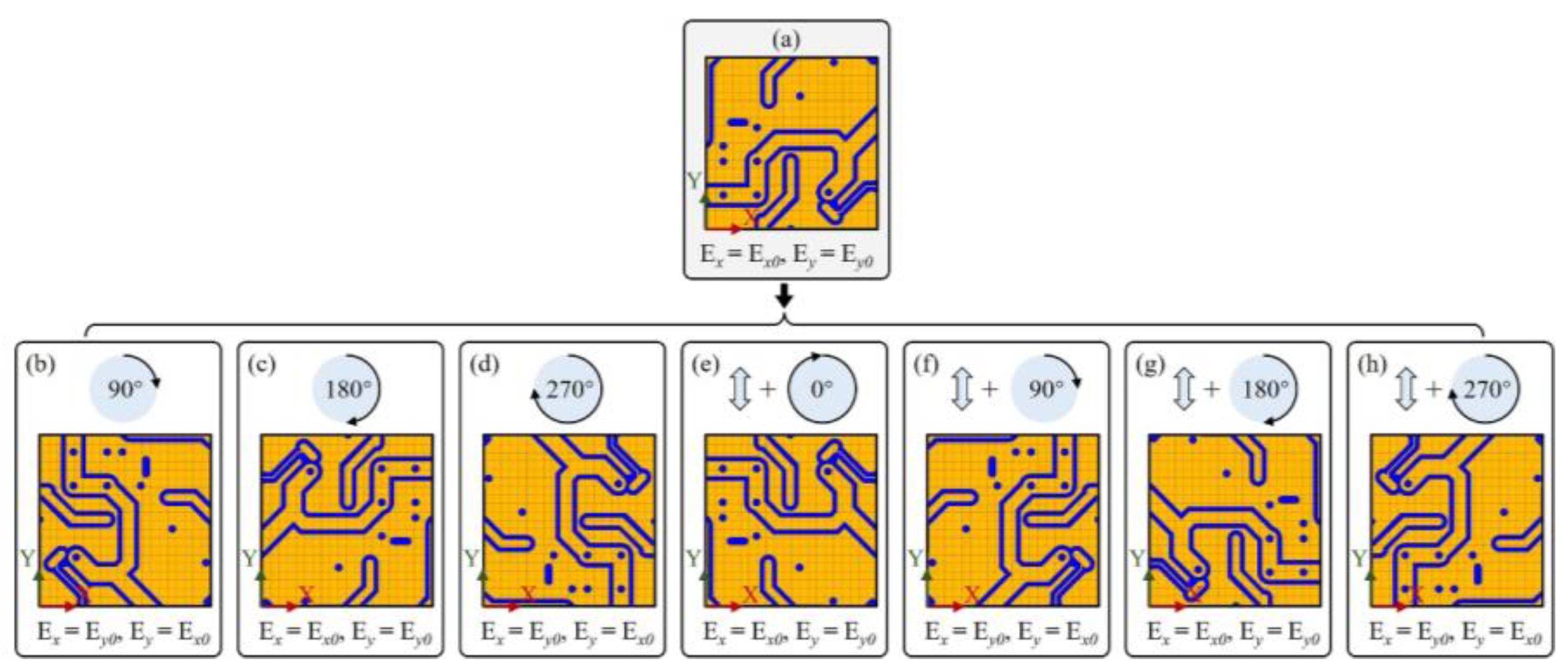
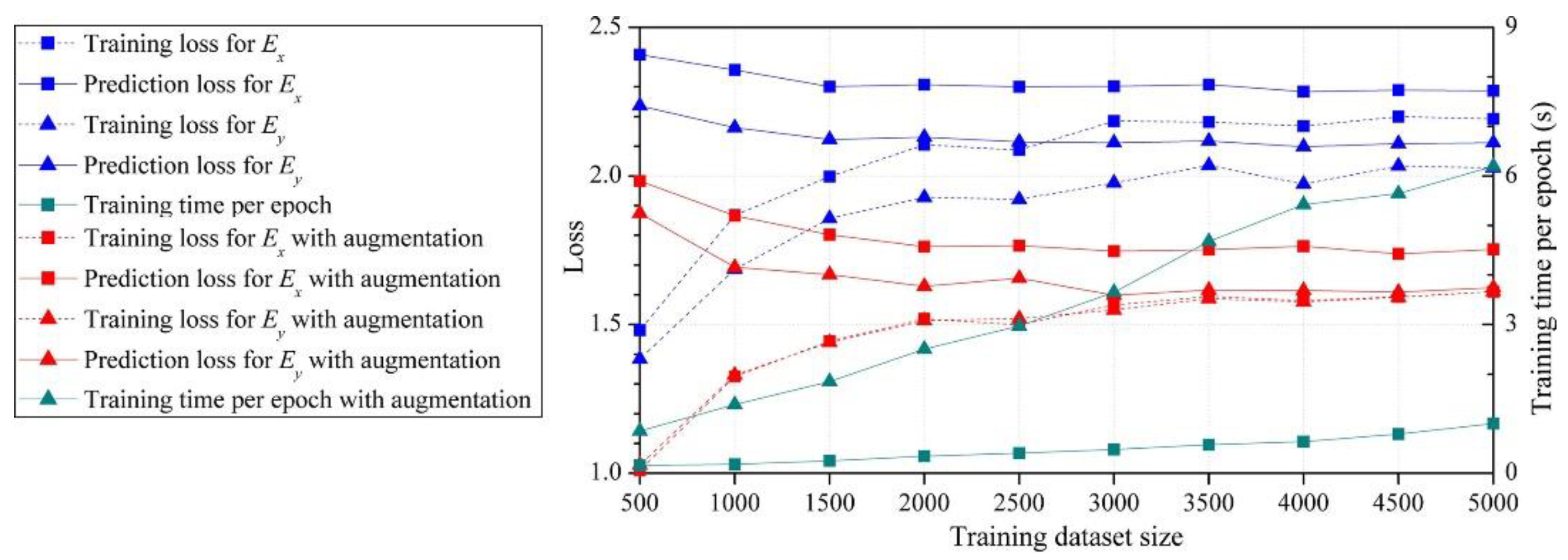
2.2. Training dataset augmentation
3. Result and discussions
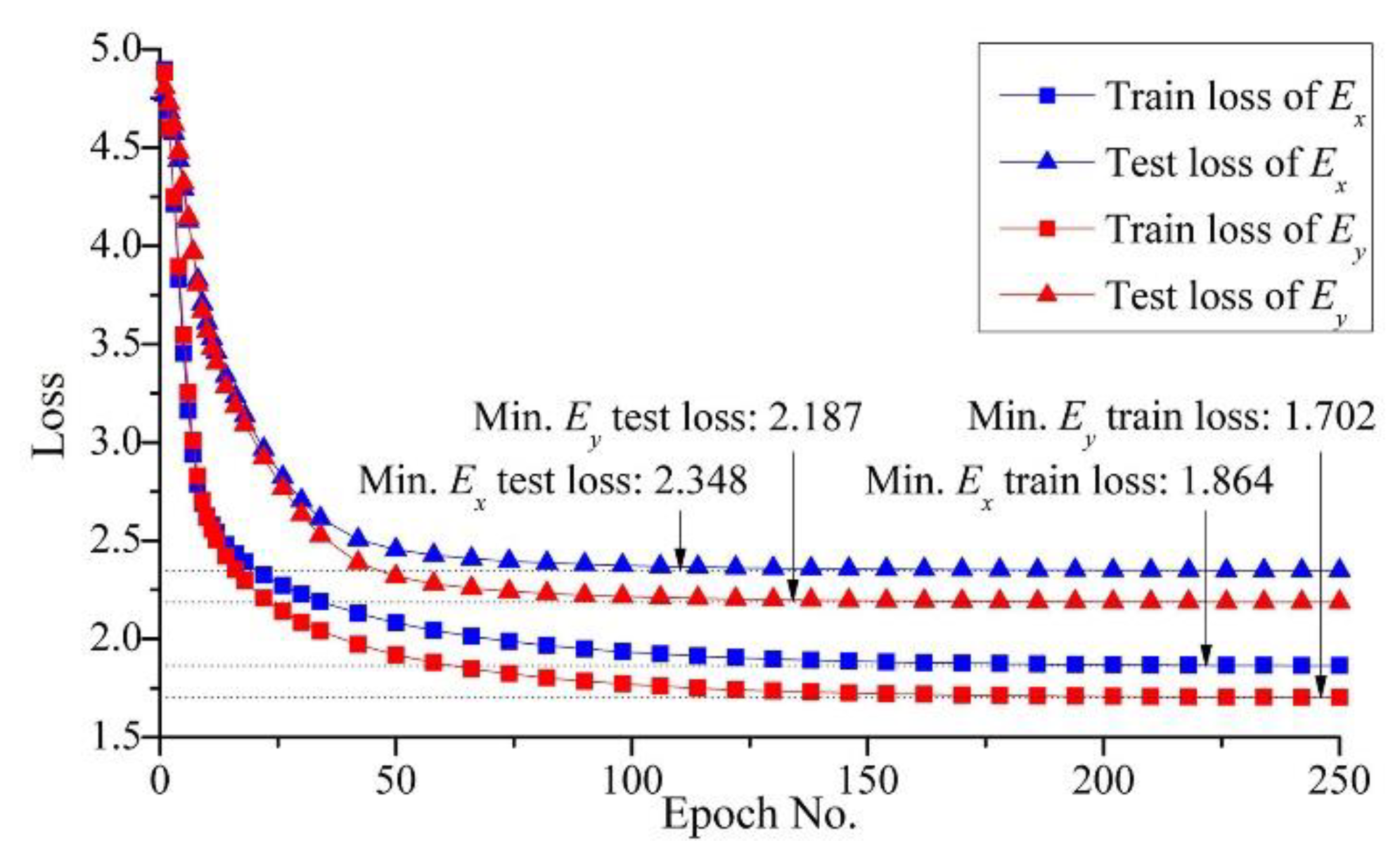
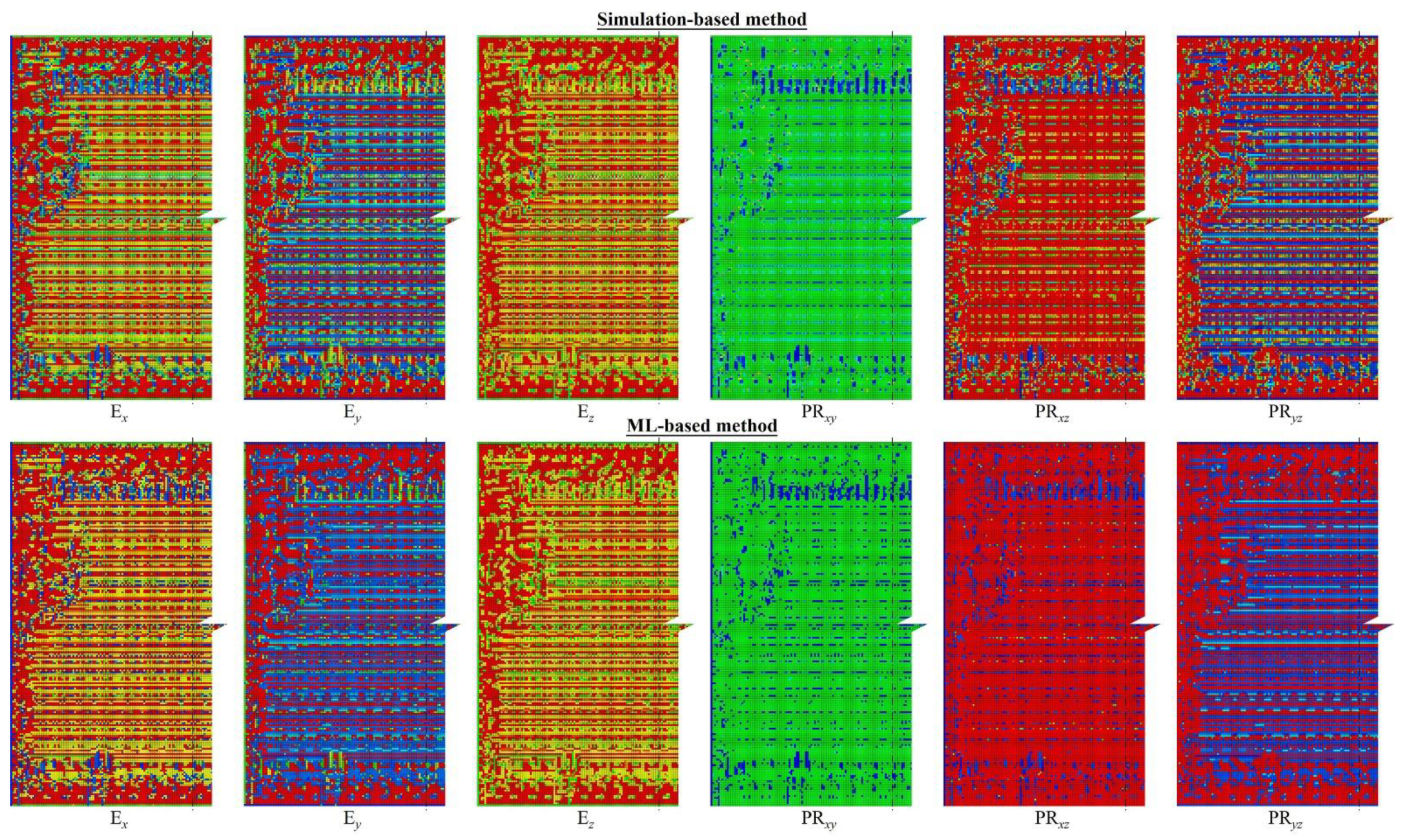
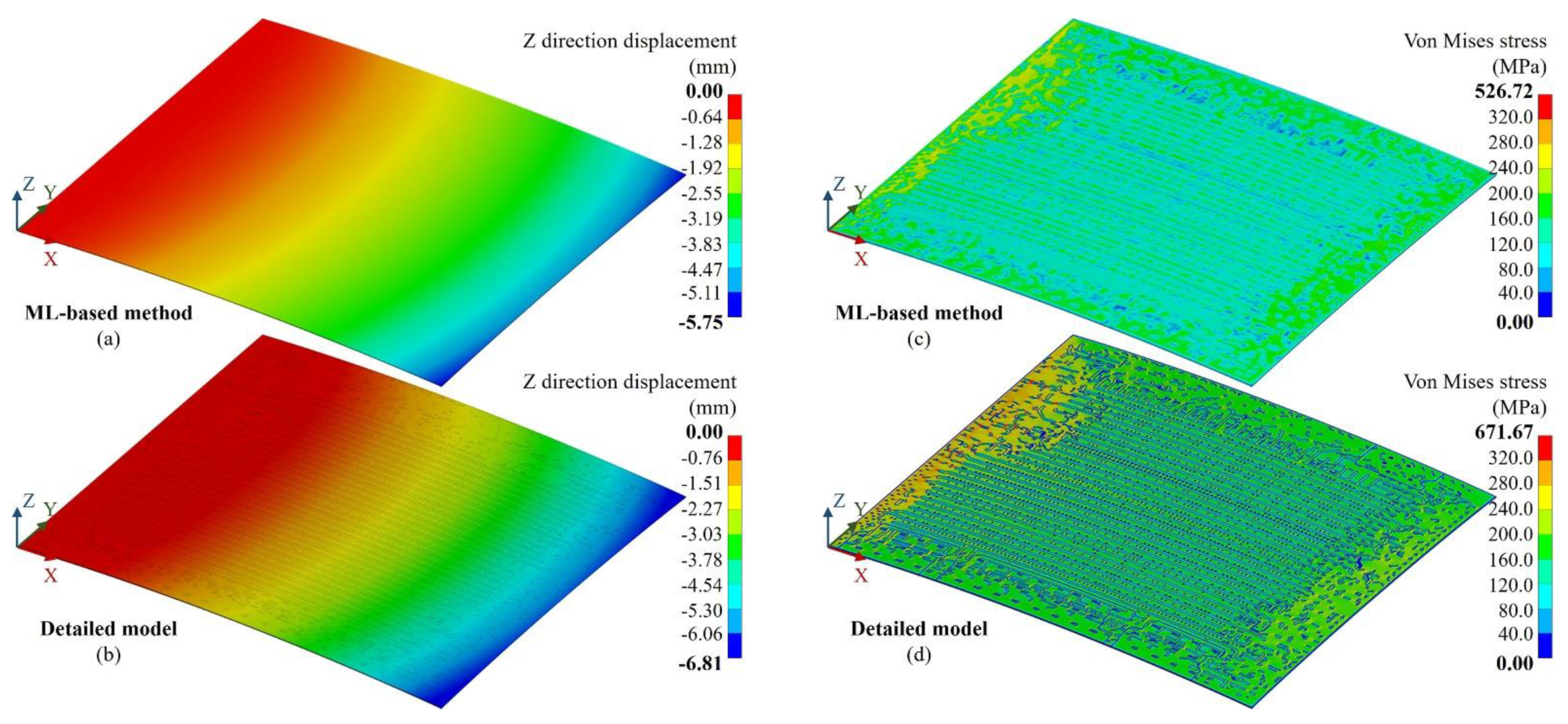
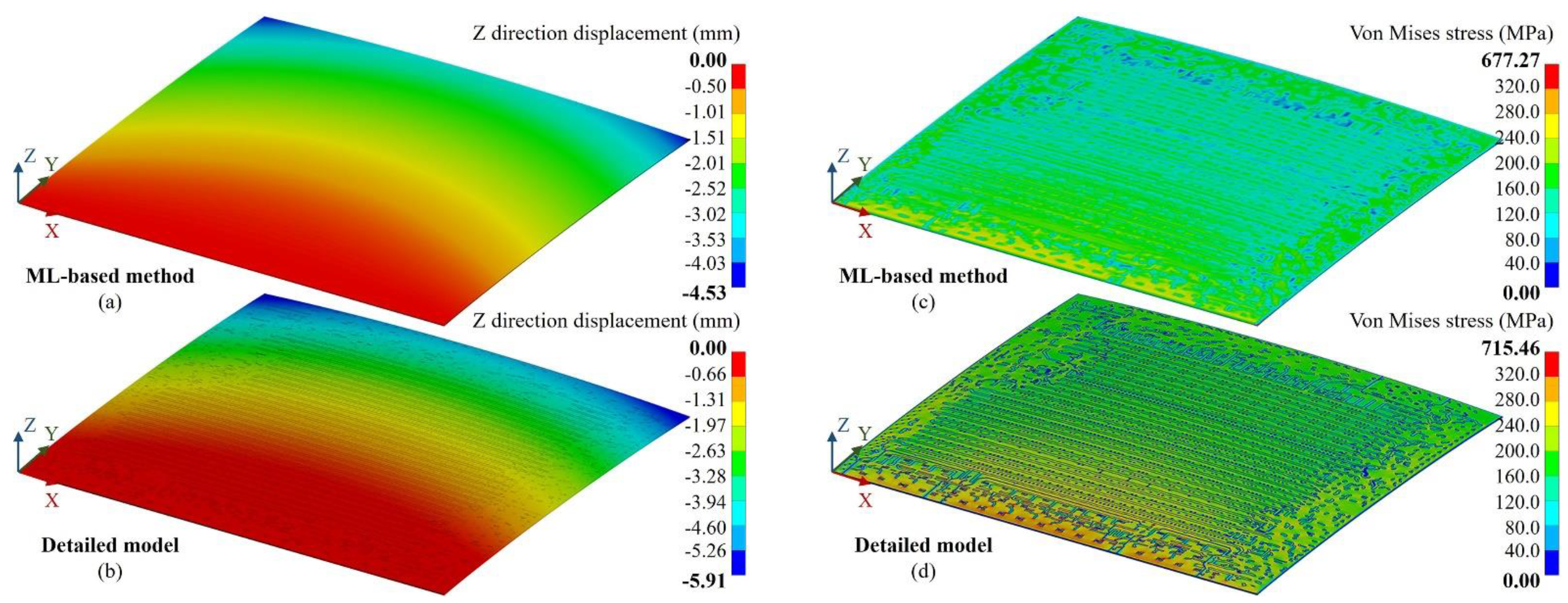
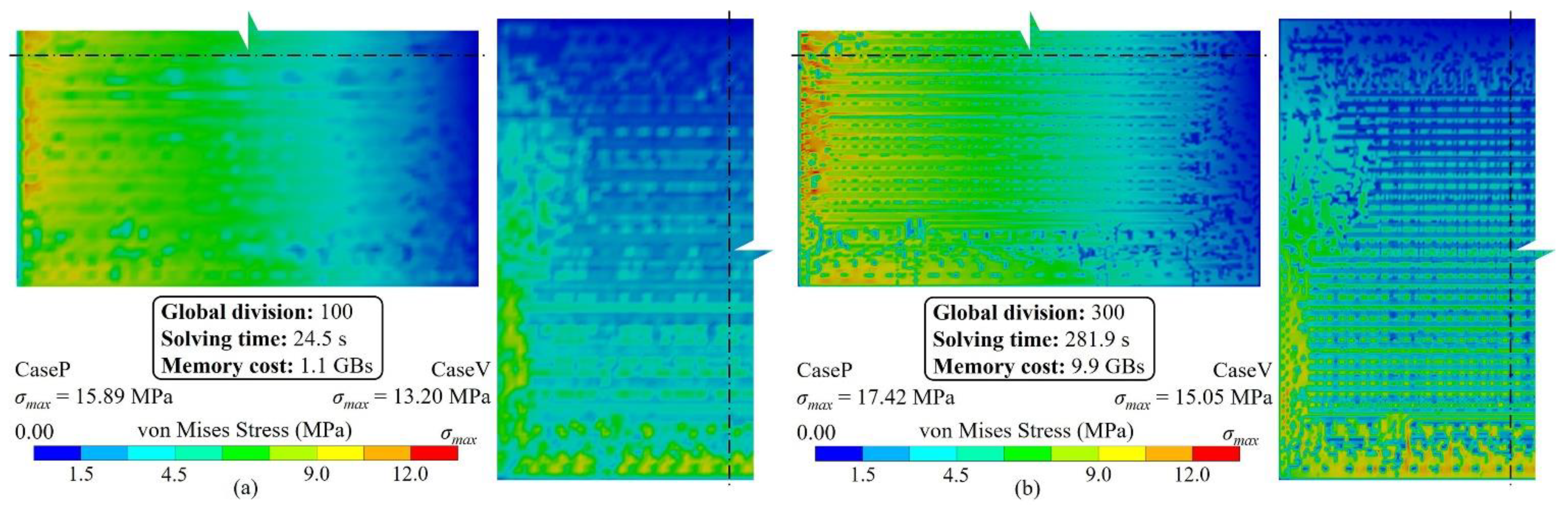
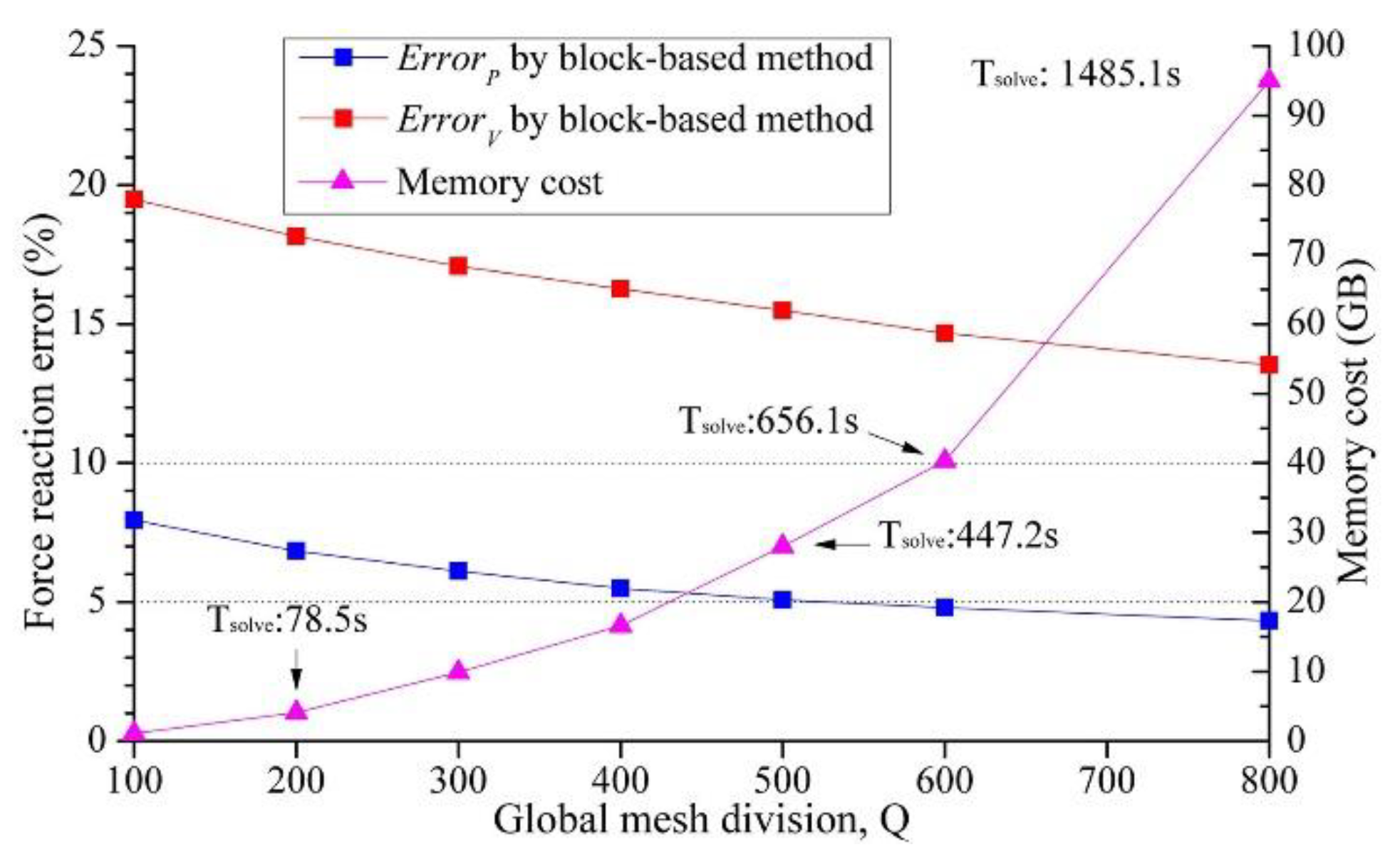
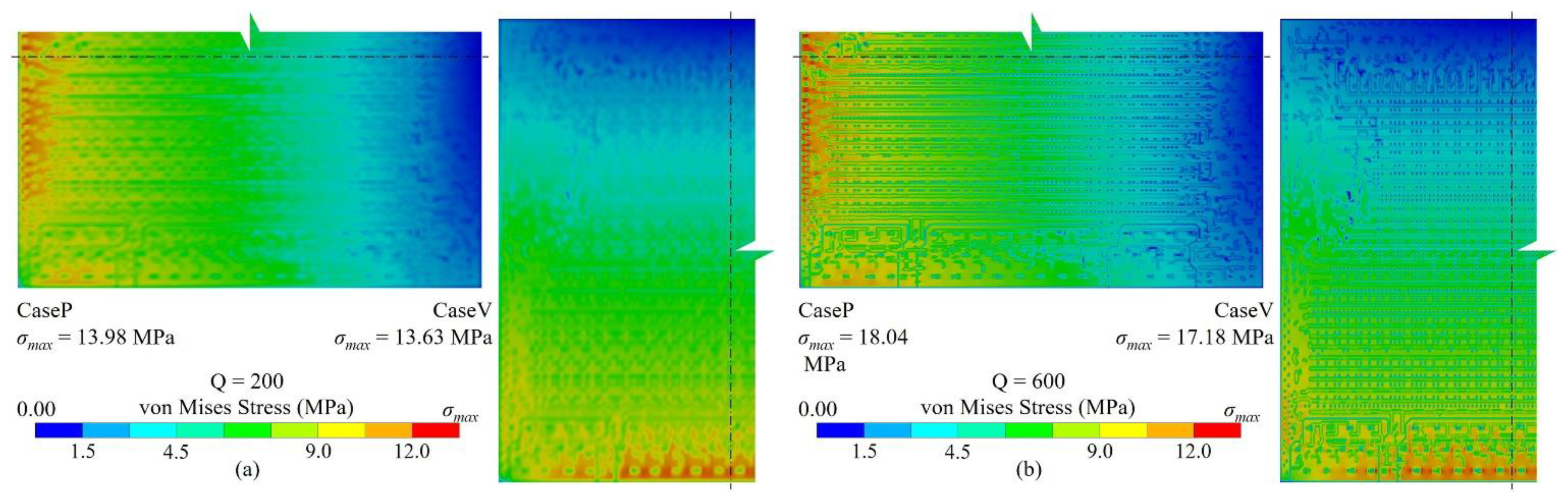
3.1. Method validation
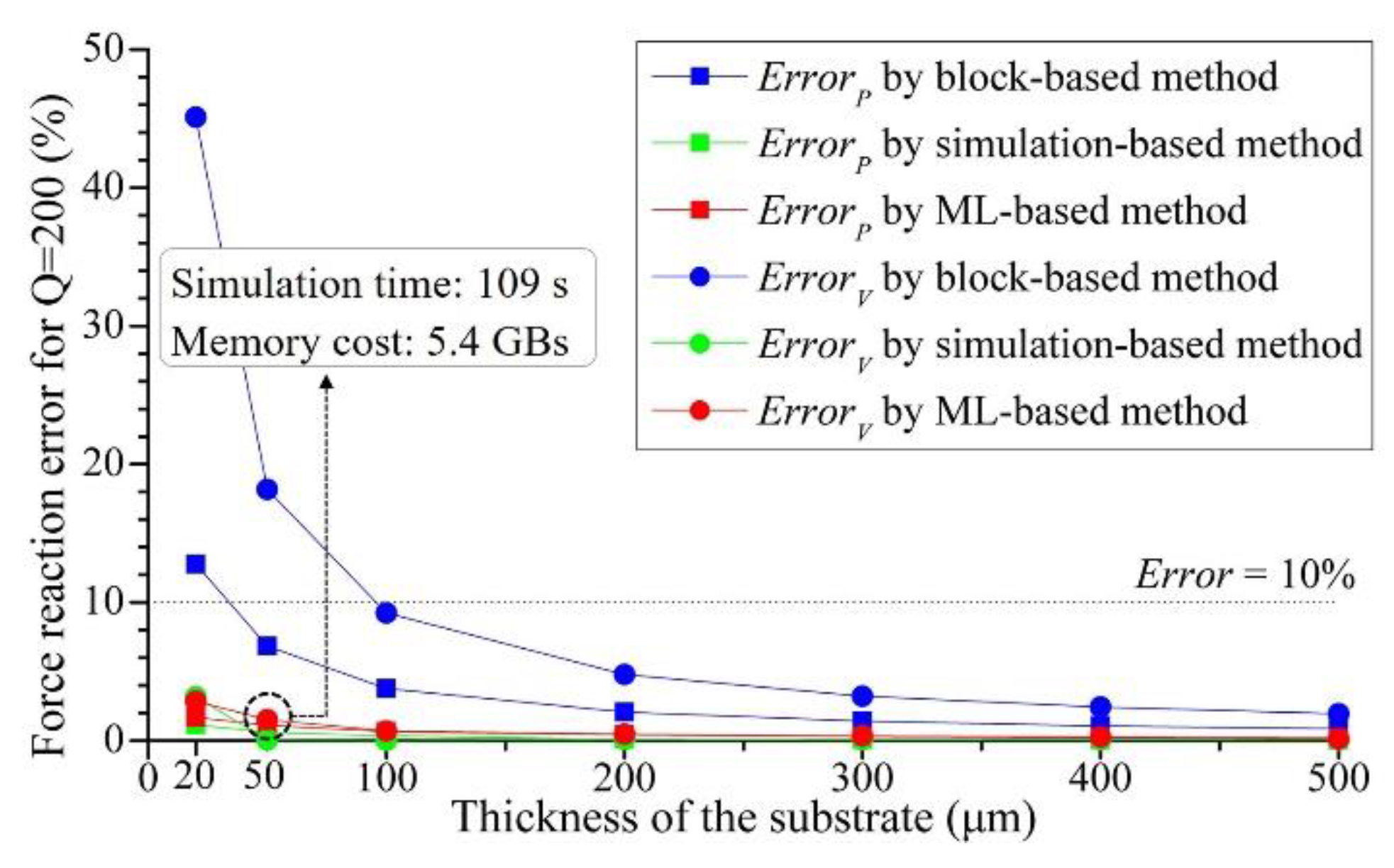
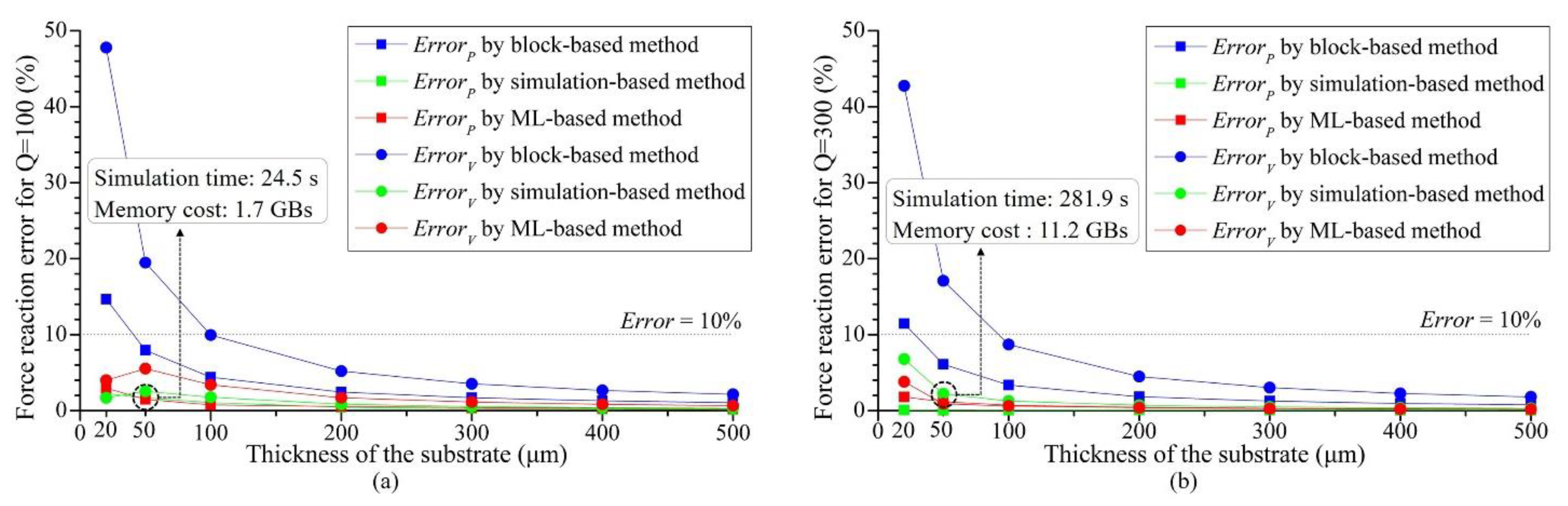
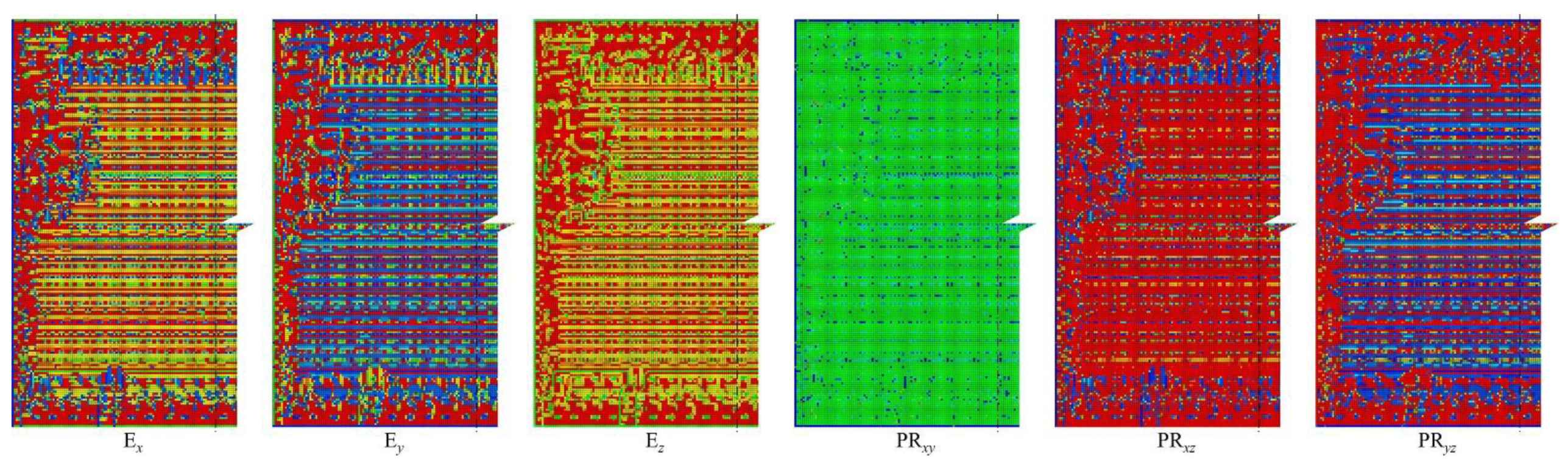
3.2. Key factors influence
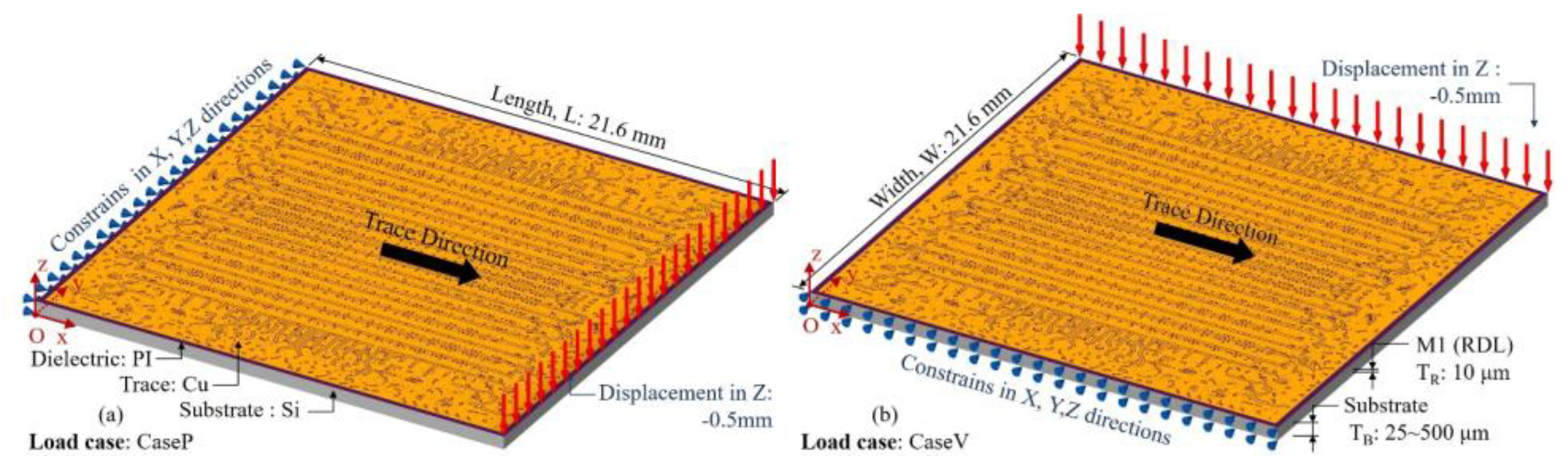
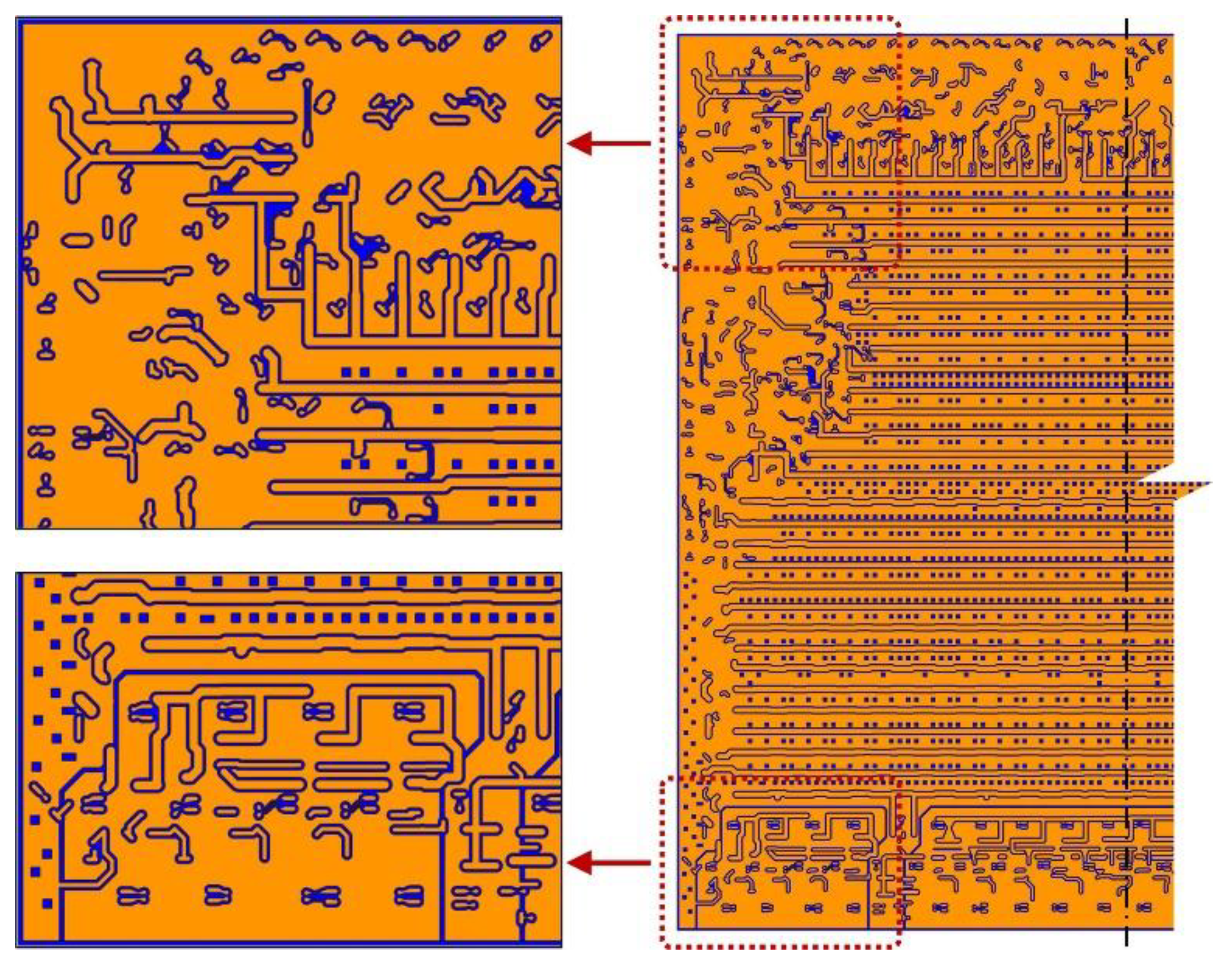
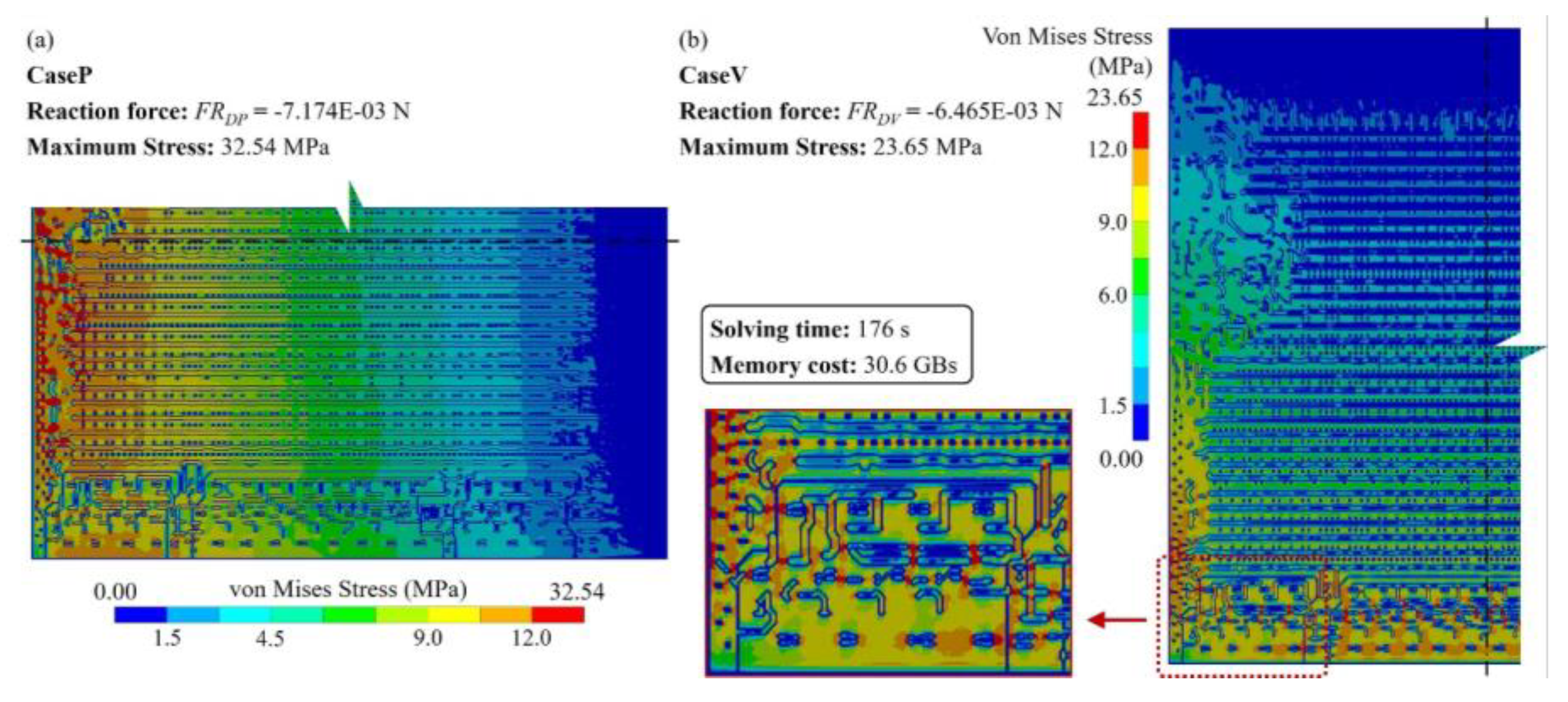
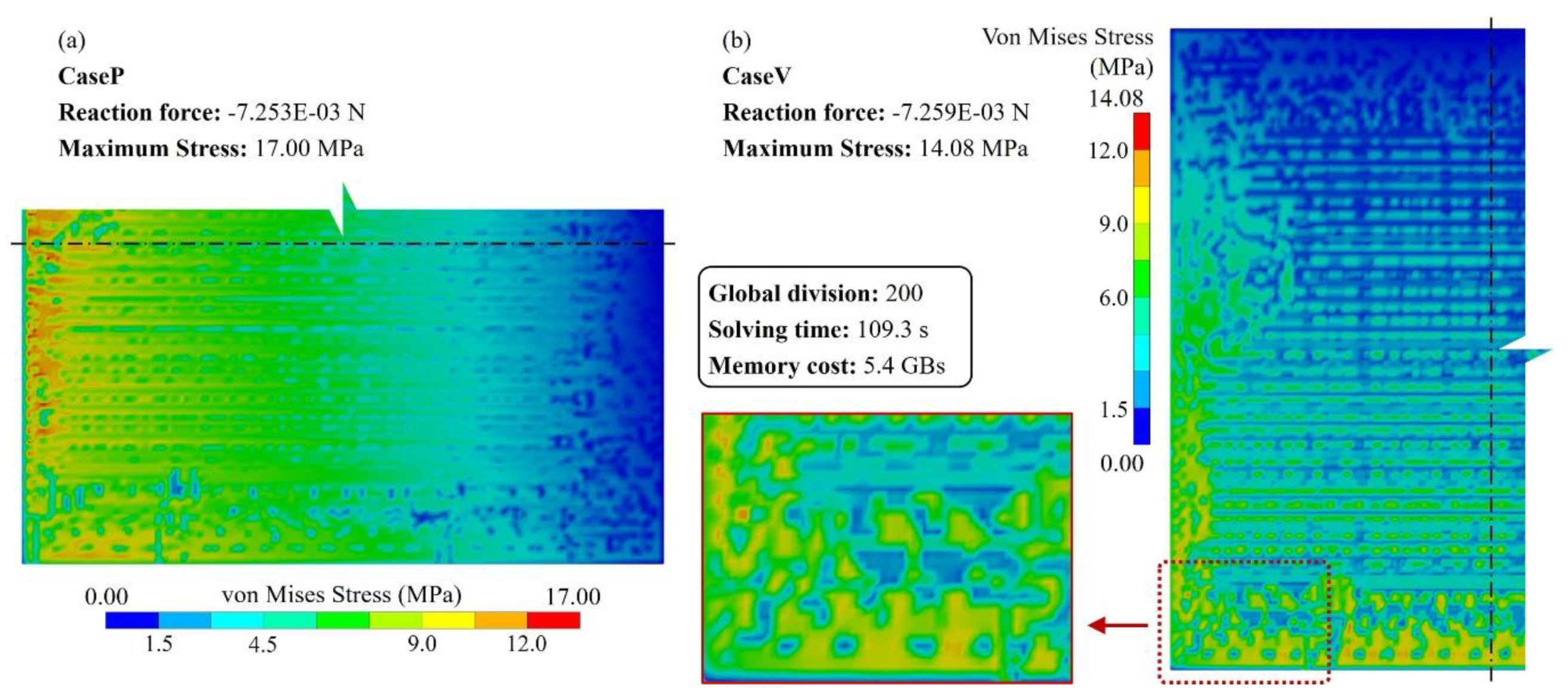
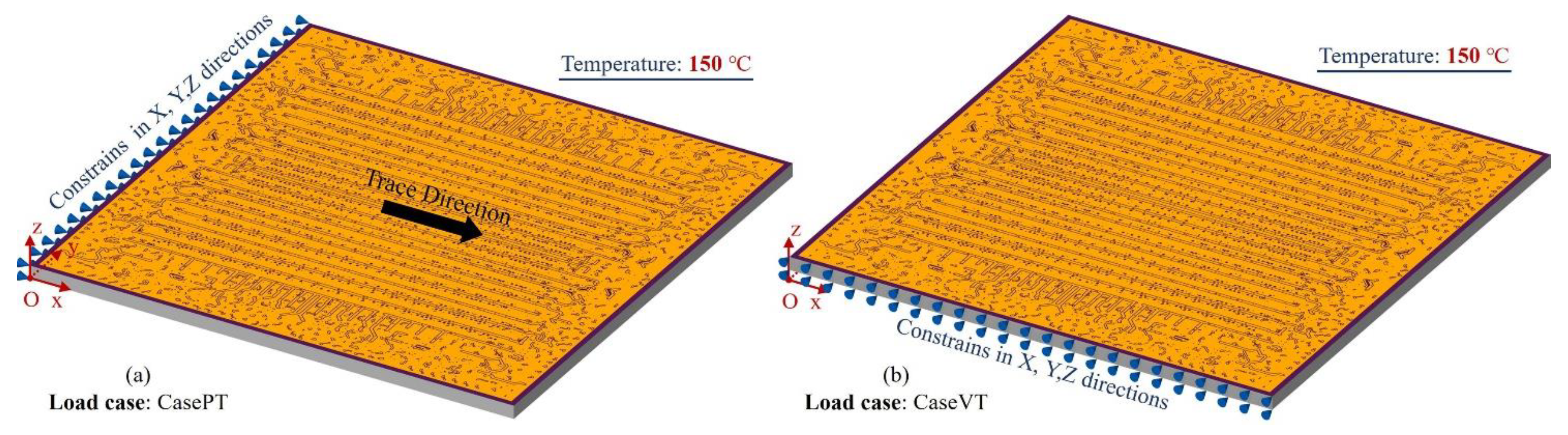
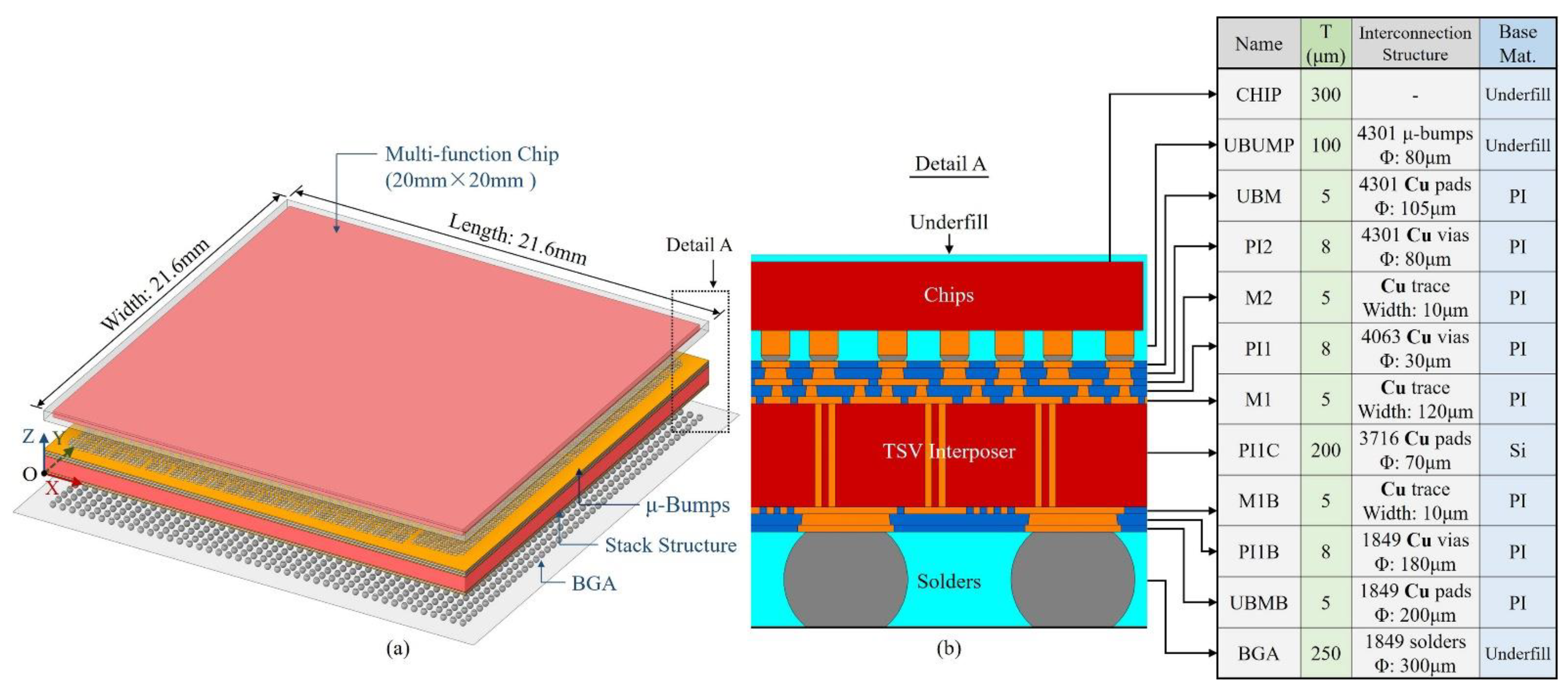
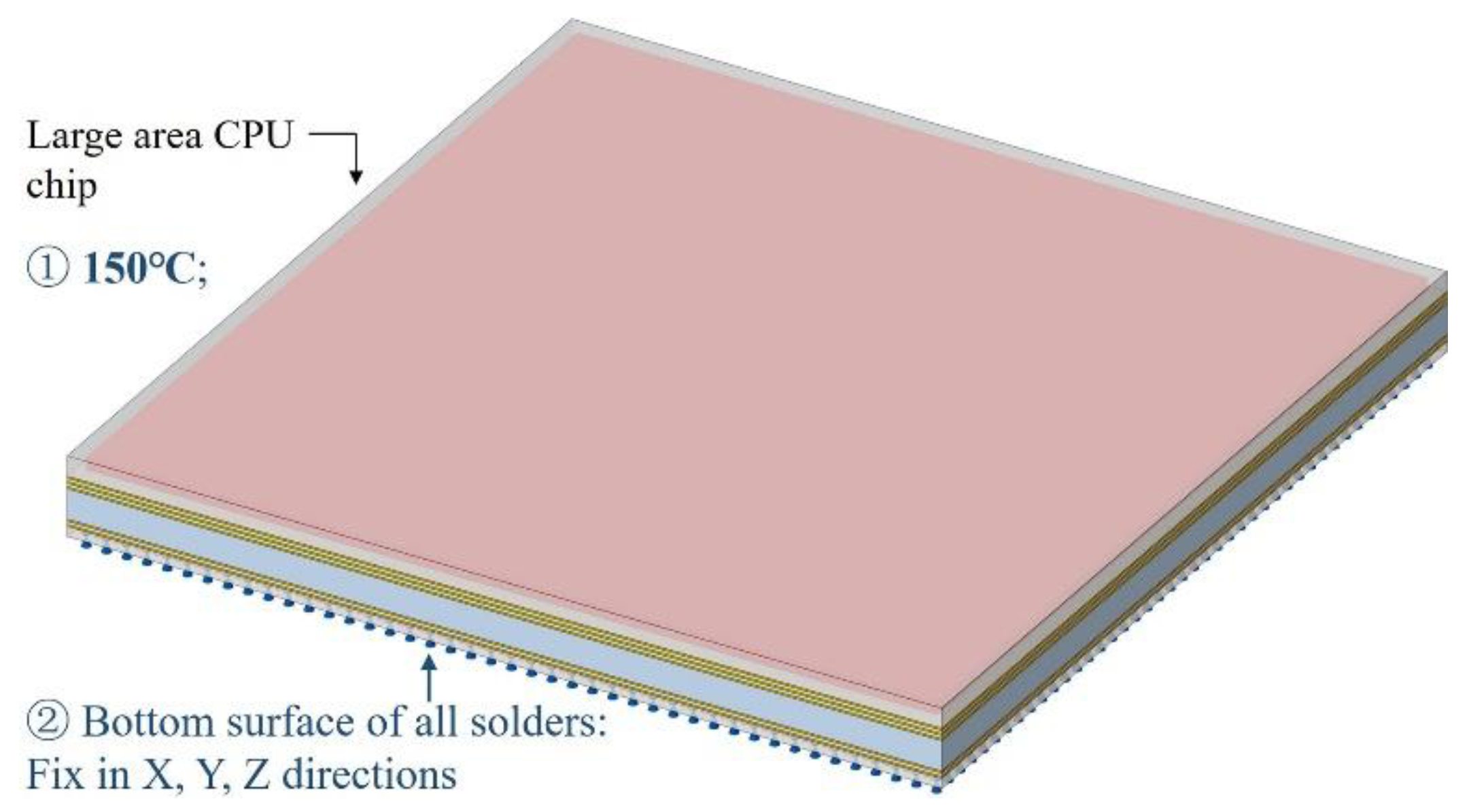
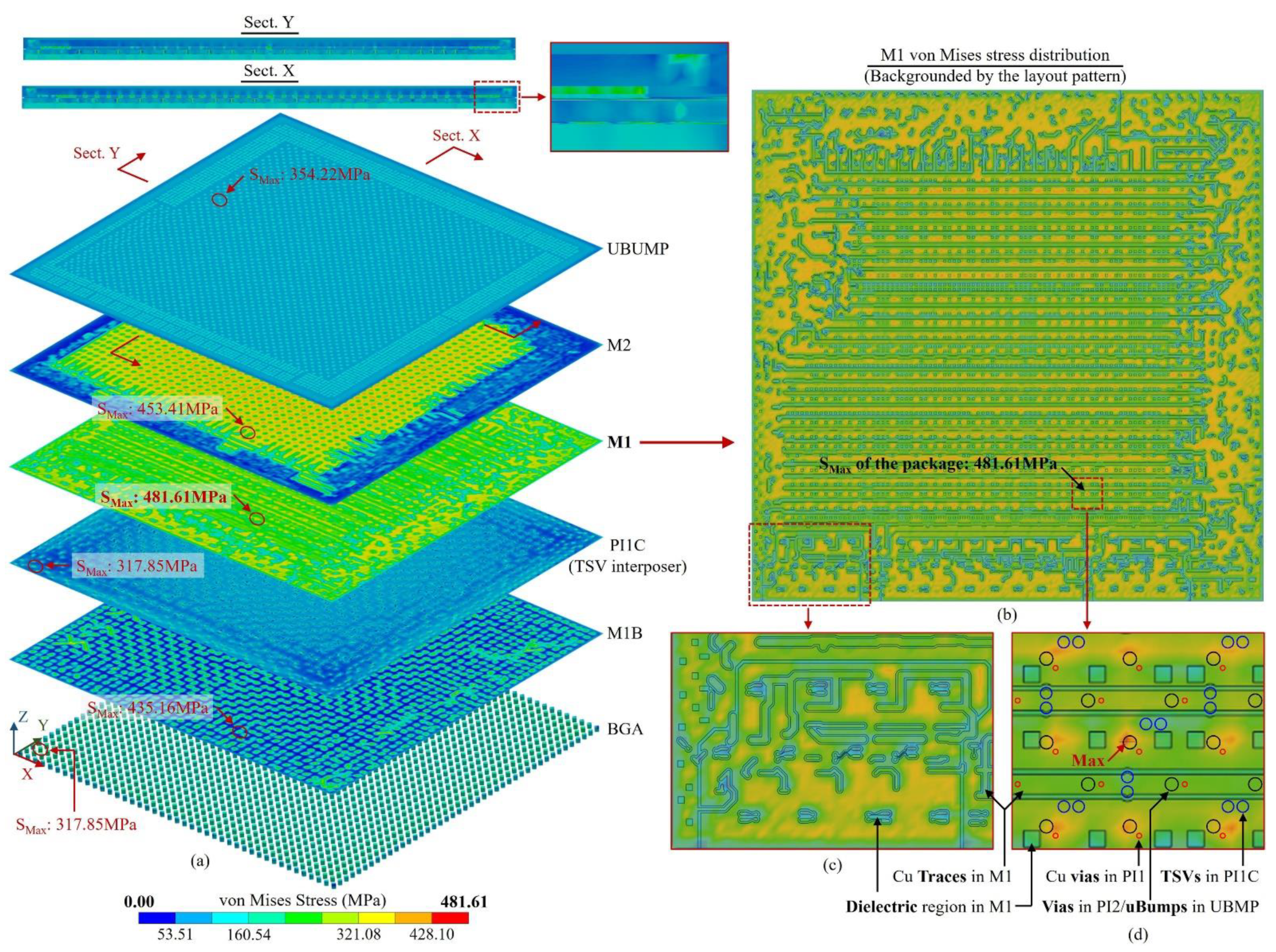
3.3. Large area 2.5D integrated CPU chip thermo-mechanical simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, P.K.; Lu, C.Y.; Wei, W.H.; Chiu, C.; Ting, K.C.; Hu, C.; Tsai, C.H.; Hou, S.Y.; Chiou, W.C.; Wang, C.T.; et al. Wafer Level System Integration of the Fifth Generation CoWoS®-S with High Performance Si Interposer at 2500 Mm2. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 71st Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, San Diego, CA, USA, June 2021; pp. 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ingerly, D.B.; Enamul, K.; Gomes, W.; Jones, D.; Kolluru, K.C.; Kandas, A.; Kim, G.-S.; Ma, H.; Pantuso, D.; Petersburg, C.F.; et al. Foveros: 3D Integration and the Use of Face-to-Face Chip Stacking for Logic Devices. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM); IEEE, San Francisco, CA, USA, December 2019; pp. 19.6.1–19.6.4. [Google Scholar]
- SAMSUNG, X-Cube technology. Available online: https://semiconductor.samsung.com/us/foundry/advanced-package/ (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Yu, D.C.H.; Wang, C.-T.; Lin, C.-C.; Lu, C.-H.; Wu, G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-T.; Ku, T.; Yee, K.-C.; Tsai, C.-H. SoIC_H Technology for Heterogeneous System Integration. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2022, 69, 7167–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSMC-SoIC. Available online: https://3dfabric.tsmc.com/english/dedicatedFoundry/technology/SoIC.htm#SoIC_CoW (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Lin, M.L.; Liu, M.S.; Chen, H.W.; Chen, S.M.; Yew, M.C.; Chen, C.S.; Jeng, S.-P. Organic Interposer CoWoS-R + (plus) Technology. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 72nd Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, San Diego, CA, USA, May 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Co, S.E. Advanced Fan-Out Panel Level Package (FO-PLP) Development for High-End Mobile Application.
- Ahmad, M.; DeLaCruz, J.; Ramamurthy, A. Heterogeneous Integration of Chiplets: Cost and Yield Tradeoff Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 23rd International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems (EuroSimE); IEEE, St Julian, Malta, 25 April 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Suggs, D.; Subramony, M.; Bouvier, D. The AMD “Zen 2” Processor. IEEE Micro 2020, 40, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High Bandwidth memory (HBM) DRAM. Available online: https://www.jedec.org/standards-documents/docs/jesd235a (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Kudo, H.; Takano, T.; Tanaka, M.; Mawatari, H.; Kitayama, D.; Tai, T.; Tsunoda, T.; Kuramochi, S. Panel-Based Large-Scale RDL Interposer Fabricated Using 2-Μm-Pitch Semi-Additive Process for Chiplet-Based Integration. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 72nd Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, San Diego, CA, USA, May 2022; pp. 836–844. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Jin, J.; Kang, G.; Hwang, H.; Kim, B.; Yun, H.; Park, J.; Lee, C.; Kang, U.-B.; Lee, J. Novel Approach to Highly Robust Fine Pitch RDL Process. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 71st Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, San Diego, CA, USA, June 2021; pp. 2246–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Nimbalkar, P.; Bhaskar, P.; Blancher, C.; Kathaperumal, M.; Swaminathan, M.; Tummala, R. Novel Zero Side-Etch Process for <1μm Package Redistribution Layers. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 72nd Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, San Diego, CA, USA, May 2022; pp. 2168–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, T.; Kudo, H.; Tanaka, M.; Akazawa, M. Submicron-Scale Cu RDL Pattering Based on Semi-Additive Process for Heterogeneous Integration. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 69th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, Las Vegas, NV, USA, May 2019; pp. 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Hu, C.; Chiu, C.; Ting, K.C.; Lin, T.S.; Wei, W.H.; Chiou, W.C.; Lin, V.J.C.; Chang, V.C.Y.; et al. Wafer-Level Integration of an Advanced Logic-Memory System Through the Second-Generation CoWoS Technology. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 4071–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, A.; Schleicher, F.; De Vos, J.; Stucchi, M.; Chery, E.; Miller, A.; Beyer, G.; Van der Plas, G.; Walsby, E.; Roberts, K.; et al. Extreme Wafer Thinning and Nano-TSV Processing for 3D Heterogeneous Integration. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 70th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, Orlando, FL, USA, June 2020; pp. 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Serbulova, K.; Chen, S.-H.; Hellings, G.; Hiblot, G.; Veloso, A.; Jourdain, A.; De Boeck, J.; Groeseneken, G.; Horiguchi, N. Impact of Sub-Μm Wafer Thinning on Latch-up Risk in STCO Scaling Era. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual EOS/ESD Symposium (EOS/ESD); IEEE, Tucson, AZ, USA, 26 September 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, V.-L.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Park, S.; Singh, C. A Study of Substrate Models and Its Effect On Package Warpage Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 69th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, Las Vegas, NV, USA, May 2019; pp. 1130–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Temperature Cycling, JEDEC Standard JESD22-A104C 2005.
- Lee, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-M.; Liu, H.-C.; Syu, J.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chang, T.-C. Reliability Evaluation of Ultra Thin 3D-IC Package under the Coupling Load Effects of the Manufacturing Process and Temperature Cycling Test. Microelectronic Engineering 2021, 244–246, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, F.X.; Lin, J.-K.; Au, K.Y.; Hsiao, H.-Y.; Zhang, X. Stress Analysis and Design Optimization for Low-k Chip With Cu Pillar Interconnection. IEEE Trans. Compon., Packag. Manufact. Technol. 2015, 5, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machani, K.V.; Kuechenmeister, F.; Breuer, D.; Klewer, C.; Cho, J.K.; Young-Fisher, K. Chip Package Interaction (CPI) Risk Assessment of 22FDX ® Wafer Level Chip Scale Package (WLCSP) Using 2D Finite Element Analysis Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 70th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, Orlando, FL, USA, June 2020; pp. 1100–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-C.; Kao, K.-S.; Liu, H.-C.; Hsieh, C.-P.; Chang, T.-C. Micro Solder Joint Reliability and Warpage Investigations of Extremely Thin Double-Layered Stacked-Chip Packaging. Journal of Electronic Packaging 2022, 144, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, F.X.; Pang, J.H.L. Fatigue Reliability Analysis of Sn–Ag–Cu Solder Joints Subject to Thermal Cycling. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Relib. 2013, 13, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wells, B. Substrate Trace Modeling for Package Warpage Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 66th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC); IEEE, Las Vegas, NV, USA, May 2016; pp. 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- McCaslin, L.O.; Yoon, S.; Kim, H.; Sitaraman, S.K. Methodology for Modeling Substrate Warpage Using Copper Trace Pattern Implementation. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2009, 32, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdevit, L.; Khanna, V.; Sharma, A.; Sri-Jayantha, S.; Questad, D.; Sikka, K. Organic Substrates for Flip-Chip Design: A Thermo-Mechanical Model That Accounts for Heterogeneity and Anisotropy. Microelectronics Reliability 2008, 48, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Yao, Y.; Charn, E.; Chen, E. Block-Based Finite Element Modeling, Simulation, and Optimization of the Warpage of Embedded Trace Substrate. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC); IEEE, Singapore, December 2018; pp. 802–806. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-C.; Wang, C.-W.; Chen, C.-Y. Comparison of Mechanical Modeling to Warpage Estimation of RDL-First Fan-Out Panel-Level Packaging. IEEE Trans. Compon., Packag. Manufact. Technol. 2022, 12, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.F.; Ganapathy, V.; Jardine, A.K.S.; Tsang, A.H.C.; Thulukkanam, K.; Karnopp, D. Principles of Composite Material Mechanics, 4th ed.; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yaddanapudi, V.K.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Rath, R.; Gandhi, R. Validation of New Approach of Modelling Traces by Mapping Mechanical Properties for a Printed Circuit Board Mechanical Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 17th Electronics Packaging and Technology Conference (EPTC); IEEE, Singapore, December 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Nam, S.; Ji, H.; Choi, J.; Jin, J.-E.; Kim, Y.; Na, J.; Ryu, M.-Y.; Cho, Y.-H.; Lee, H.; et al. Multiple Machine Learning Approach to Characterize Two-Dimensional Nanoelectronic Devices via Featurization of Charge Fluctuation. npj 2D Mater Appl 2021, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Demirel, M.F.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J.-M. Graph Neural Networks for an Accurate and Interpretable Prediction of the Properties of Polycrystalline Materials. npj Comput Mater 2021, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Xu, B. Transferable, Deep-Learning-Driven Fast Prediction and Design of Thermal Transport in Mechanically Stretched Graphene Flakes. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16597–16606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Huang, W.-Z.; Li, M.; Feng, X.-Q. Deep Learning Method for Determining the Surface Elastic Moduli of Microstructured Solids. Extreme Mechanics Letters 2021, 44, 101226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Xu, Z.; Hu, J.; Yan, B.; Ding, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, P.; Deng, J. Thermal Conductivity Prediction of UO2-BeO Composite Fuels and Related Decisive Features Discovery via Convolutional Neural Network. Acta Materialia 2022, 240, 118352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvanayagam, C.; Duong, P.L.T.; Raghavan, N. AI-Assisted Package Design for Improved Warpage Control of Ultra-Thin Packages. In Proceedings of the 2020 21st International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems (EuroSimE); IEEE, Cracow, Poland, July 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Selvanayagam, C.; Duong, P.L.T.; Wilkerson, B.; Raghavan, N. Global Optimization of Surface Warpage for Inverse Design of Ultra-Thin Electronic Packages Using Tensor Train Decomposition. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 48589–48602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silicon-Si. Available online: https://www.matweb.com/search/DataSheet.aspx?MatGUID=7d1b56e9e0c54ac5bb9cd433a0991e27&ckck=1 (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Material: Copper – PVD or Electroplated. Available online: https://www.mit.edu/~6.777/matprops/copper.htm (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- McKeen, L.W. Film Properties of Plastics and Elastomers, 4th ed.; Elsevier, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-813292-0. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





