Submitted:
17 July 2023
Posted:
18 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
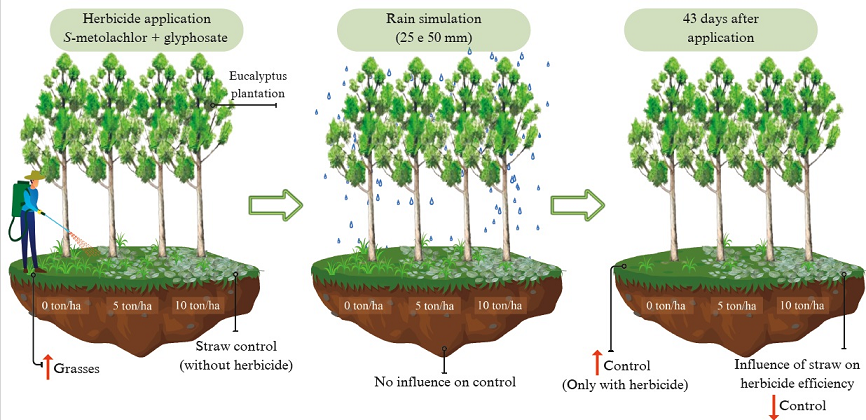
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Location and Soil
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Conducting the Experiment
2.4. Evaluated Parameters
2.5. Statistical Analysis
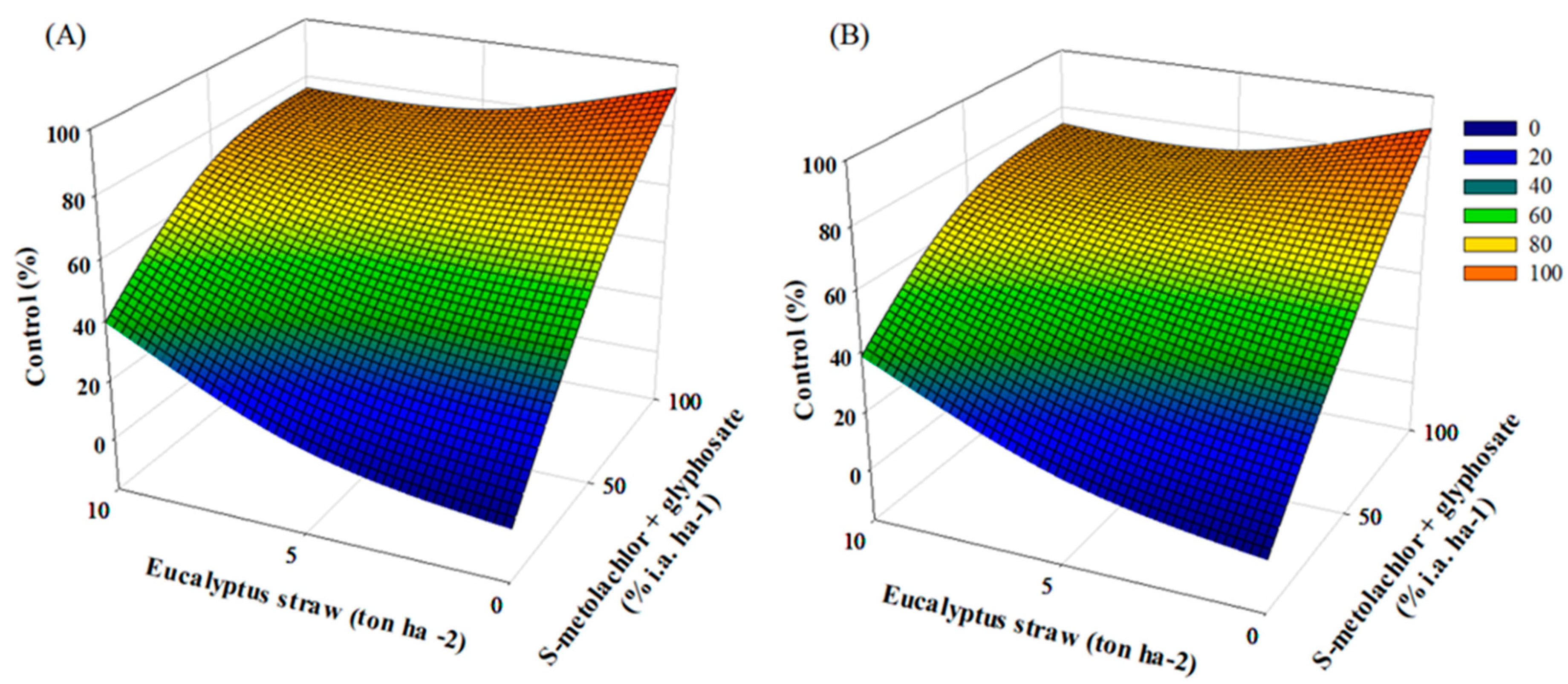
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Flores, T. B.; Alvares, C. A.; Souza, V. C.; Stape, J. L. Eucalyptus no Brasil: zoneamento climático e guia para identificação, Piracicaba: IPEF, 2016; pp. 447.
- Teixeira, C. M. Redução do volume de irrigação de plantio de eucalipto para ganhos operacionais, sociais e ambientais, 2023.
- Indústria Brasileira De Árvores (IBÁ). Relatório Anual 2022. São Paulo: IBÁ, 2022. URL https://www.iba.org/datafiles/publsicacoes/relatorios/relatorio-anual iba2022compactado.pdf. (Accessed on May 24, 2023).
- Indústria Brasileira De Árvores (IBÁ). Relatório Anual 2017. São Paulo: IBÁ, 2017.
- Wilcken, C. F. As pragas exóticas que estão chegando. Revista Opiniões, 2017, 46(14), 2627. URL https://florestal.revistaopinioes.com.br/revista/detalhes/9-pragas-exoticas-que-estao-chegando/. (Accessed on May 24, 2023).
- Brasil. Instrução normativa Nº 112 de 15 de Outubro de 2018. Diário Oficial da União (1): 42018. 2018. URL https://www.jusbrasil.com.br/diarios/212979560/dou-secao-1-15-10-2018-pg-4 (Accessed on May 24, 2023).
- Adams, P. R.; Beadle, C. L.; Mendham, N. J.; Smethurst, P. J. The impact of time and duration of grass control on the growth of a young Eucalyptus globulus Labill. plantation. New Forests, 2003, 26, 147-165. [CrossRef]
- Maciel, J. C.; Duque, T. S.; Ferreira, E. A.; Zanuncio, J. C.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Silva, V. P.; Dos Santos, J. B. Growth, Nutrient Accumulation, and Nutritional Efficiency of a Clonal Eucalyptus Hybrid in Competition with Grasses. Forests, 2022, 13, 1157. [CrossRef]
- Junior, W. R. C.; da Costa, Y. K. S.; Carbonari, C. A.; Duke, S. O.; Alves, P. L. D. C. A.; De Carvalho, L. B. Growth, morphological, metabolic and photosynthetic responses of clones of eucalyptus to glyphosate. Forest ecology and management, 2020, 470, 118218. [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, L. B.; Duke, S. O.; Alves, P. D. C. Physiological responses of Eucalyptus urograndis to glyphosate are dependent on the genotype. Scientia Forestalis, 2018, 118, 177-187. [CrossRef]
- Agrofit, Ministério da agricultura pecuária e desenvolvimento. URL. http://agrofit.agricultura.gov.br/agrofit_cons/principal_agrofit_cons. (Accessed on May 18, 2023).
- Milesi, M.M., Lorenz, V., Durando, M., Rossetti, M.F., Varayoud, J. Glyphosate herbicide: reproductive outcomes and multigenerational effects. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 12, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Gianessi, L.P. The increasing importance of herbicides in worldwide crop production. Pest management science 69(10): 1099–1105, 2013. [CrossRef]
- CTNBio, 2021. Comissão Técnica Nacional De Biossegurança: Parecer Técnico Nº 1638/2021/SEI-CTNBio. URL http://ctnbio.mctic.gov.br/documents/566529/2292301/Parecer+T%C3%A9cnico+7788-2021/eff8fe21-1a5d-49dd-9268-394d99f4f0df?version=1.0. (Accessed on July 13, 2023).
- Bain, C., Selfa, T., Dandachi, T., Velardi, S. ‘Superweeds’ or ‘survivors’? Framing the problem of glyphosate resistant weeds and genetically engineered crops. Journal of Rural Studies, 51(1), 211–221, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, V.H., Oliveira, M.C., Smith, D.H., Santos, J.B., Werle, R. Evaluating efficacy of preemergence soybean herbicides using field treated soil in greenhouse bioassays. Weed Technology, 35(5), 830–837, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Carbonari, C. A.; Gomes, G. L. G. C.; Krenchinski, F. H.; Simões, P. S.; Batista de Castro, E.; Velini, E. D. Dynamics and efficacy of sulfentrazone, flumioxazin, and isoxaflutole herbicides applied on eucalyptus harvest residues. New Forests, 2020, 51, 723-737. [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, A. C. P. R.; da Costa, N. V.; Pereira, M. R. R.; Martins, D. Simulated drift effect of glyphosate in different parts of Eucalyptus grandis plants. Semina: Ciências Agrárias (Londrina), 2012, 33, 1663-1672. [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, D. J.; Fleming, M. B.; Patterson, E. L.; Sebastian, J. R.; Nissen, S. J. Indaziflam: a new cellulose-biosynthesis-inhibiting herbicide provides long-term control of invasive winter annual grasses. Pest management science, 2017, 73, 2149-2162. [CrossRef]
- Minogue, P. J.; Osiecka, A. Selective herbicides for cultivation of Eucalyptus urograndis clones. International Journal of Forestry Research, 2015, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ivantsova, E.; Souders II, C. L.; Martyniuk, C. J. The agrochemical S-metolachlor disrupts molecular mediators and morphology of the swim bladder: Implications for locomotor activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208, 111641. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zuo, L.; Li, W.; Guo, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Greenhouse and field evaluation of isoxaflutole for weed control in maize in China. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7, 1-9. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-12696-7.
- Susha, V. S.; Das, T. K.; Nath, C. P.; Pandey, R.; Paul, S.; Ghosh, S. Impacts of tillage and herbicide mixture on weed interference, agronomic productivity and profitability of a maize–Wheat system in the North-western Indo-Gangetic Plains. Field Crops Research, 2018, 219, 180-191. [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, S. Z.; Pavlovic, P.; Osipitan, O. A.; Barnes, E. R.; Beiermann, C.; Oliveira, M. C.; Jhala, A. Critical time for weed removal in glyphosate-resistant soybean as influenced by preemergence herbicides. Weed Technology, 2019, 33, 393-399. [CrossRef]
- Vinther, F. P.; Brinch, U. C.; Elsgaard, L.; Fredslund, L.; Iversen, B. V.; Torp, S.; Jacobsen, C. S. Field-scale variation in microbial activity and soil properties in relation to mineralization and sorption of pesticides in a sandy soil. Journal of environmental quality, 2008, 37, 1710-1718. [CrossRef]
- Fast, B. J.; Ferrell, J. A.; MacDonald, G. E.; Krutz, L. J.; Kline, W. N. Picloram and aminopyralid sorption to soil and clay minerals. Weed science, 2010, 58, 484-489. [CrossRef]
- Rigi, M. R.; Farahbakhsh, M.; Rezaei, K. Adsorption and desorption behavior of herbicide metribuzin in different soils of Iran. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17, 777-787. http://dorl.net/dor/20.1001.1.16807073.2015.17.3.16.1.
- Schneider, J. G.; Haguewood, J. B.; Song, E.; Pan, X.; Rutledge, J. M.; Monke, B. J.; Xiong, X. Indaziflam effect on bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon L. Pers.) shoot growth and root initiation as influenced by soil texture and organic matter. Crop Science, 2015, 55, 429-436. [CrossRef]
- Mendes, K. F.; Ionoue, M. H.; Tornisielo, V. L. Herbicidas no ambiente: Comportamento e destino. Editora UFV, 2022.
- Monquero, P. A.; Amaral, L. R.; Binha, D. P.; Silva, P. V.; Silva, A. C.; Martins, F. R. A. Mapas de infestação de plantas daninhas em diferentes sistemas de colheita da cana-de-açúcar. Planta Daninha, 2005, 26, 47-55. [CrossRef]
- Osipitan, O. A.; Dille, J. A.; Assefa, Y.; Radicetti, E.; Ayeni, A.; Knezevic, S. Z. Impact of cover crop management on level of weed suppression: a meta-analysis. Crop Science, 2019, 59, 833-842. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Neto, H. F.; de Pauli, F. A.; Júnior, L. C. T.; Marques, M. O. Quantificação da palhada de cana-de-açúcar e potencial controle de plantas daninhas, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Pitelli, R. A.; Durigan, J. C.; Rossello, R. D. Ecologia das plantas daninhas no sistema de plantio direto. In: Siembra directa en el cono sur. Montevideo: PROCISUR, 2001, 203-210.
- Correia, N. M.; Gomes, L. P.; Perussi, F. J. Control of Brachiaria decumbens and Panicum maximum by S-metolachlor as influenced by the occurrence of rain and amount of sugarcane straw on the soil. Acta Scientiarum. Agronomy, 2012, 34, 379-387. [CrossRef]
- Maciel, C. D. G.; Velini, E. D. Simulação do caminhamento da água da chuva e herbicidas em palhadas utilizadas em sistemas de plantio direto. Planta daninha, 2005, 23, 471-481. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, P. V.; Tronquini, S. M.; Barbosa, G. C.; de Carvalho Dias, R.; Veiga, J. P. S.; Inácio, E. M. Eficácia do herbicida flumioxazin no controle de Euphorbia heterophylla, na aplicação sobre diferentes tipos de palha e simulações de chuva: Controle de Euphorbia heterophylla com flumioxazin. Revista de Ciências Agrárias, 2020, 43, 324-332. [CrossRef]
- Clark, S. L.; da Silva, P. V.; Dayan, F. E.; Nissen, S. J.; Sebastian, D. J. The influence of winter annual grass litter on herbicide availability. Weed Science, 2019, 67, 702-709. [CrossRef]
- Barros, N. F.; Novais, R. F. Eucalipto. In: Recomendação para o uso de corretivos e fertilizantes em Minas Gerais: 5º Aproximação. Ribeiro, A.C.; Guimaraes, P.T.G.; Alvarez, V.H. Minas Gerais, Viçosa, MG, 1999, pp. 303–305.
- Bhullar, M. S.; Kaur, S.; Kaur, T.; Jhala, A. J. Integrated weed management in potato using straw mulch and atrazine. HortTechnology, 2015, 25, 335-339. [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, D.; Sobrero, M. T.; Pece, M.; Chaila, S. Effect of environmental factors on the germination of Megathyrsus maximus: an invasive weed in sugarcane in Argentina. Planta Daninha, 2020, 38. [CrossRef]
- Ustarroz, D.; Kruk, B. C.; Satorre, E. H.; Ghersa, C. M. Dormancy, germination and emergence of Urochloa panicoides regulated by temperature. Weed Research, 2016, 56, 59-68. [CrossRef]
- Nakao, E. A.; Cardoso, V. J. M. Priming and temperature limits for germination of dispersal units of Urochloa brizantha (Stapf) Webster cv. basilisk. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 2015, 75, 234-241. [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, J. R.; Mohler, C. L. Light transmittance, soil temperature, and soil moisture under residue of hairy vetch and rye. Agronomy Journal, 1993, 85, 673-680. [CrossRef]
- Nichols, V.; Verhulst, N.; Cox, R.; Govaerts, B. Weed dynamics and conservation agriculture principles: A review. Field Crops Research, 2015, 183, 56-68. O'Connell, P. J.; Harms, C. T.; Allen, J. R. Metolachlor, S-metolachlor and their role within sustainable weed-management. Crop protection, 1998, 17, 207-212.
- Kouame, K. B. J.; Bertucci, M. B.; Savin, M. C.; Bararpour, T.; Steckel, L. E.; Butts, T. R.; Roma-Burgos, N. Resistance of Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) to S-metolachlor in the midsouthern United States. Weed Science, 2022, 70, 380-389. [CrossRef]
- Marchi, G.; Marchi, E. C. S.; Guimarães, T. G. Herbicidas: mecanismos de ação e uso. 2008.
- Negrisoli, R. M.; Negrisoli, M. M.; Cesco, V. J.; Bianchi, L.; Gomes, D. M.; Carbonari, C. A.; Velini, E. D. Glyphosate effect on Merremia aegyptia water transpiration and water use efficiency. Crop Protection, 2023, 169, 106237. [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kukal, M. S.; Irmak, S.; Jhala, A. J. Water use characteristics of weeds: a global review, best practices, and future directions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 12, 794090. [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Marble, S. C.; Pearson, B.; Pérez, H.; MacDonald, G.; Odero, D. C. Short-term preemergence herbicide adsorption by mulch materials and impacts on weed control. HortTechnology, 2019, 29, 889-897. [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Garnier, P.; Rumpel, C.; Parent, S. E.; Benoit, P. Adsorption and desorption behavior of selected pesticides as influenced by decomposition of maize mulch. Chemosphere, 2013, 91, 1447-1455. [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A. L.; Vidal, R. A. Persistência do herbicida S-metolachlor associado ao glyphosate ou paraquat em plantio direto. Planta Daninha, 2008, 26, 385-393. [CrossRef]
- Westra, E. P. Adsorption, leaching, and dissipation of pyroxasulfone and two chloroacetamide herbicides. Doctoral dissertation, Colorado State University, 2012.
- Westra, E. P.; Shaner, D. L.; Barbarick, K. A.; Khosla, R. Evaluation of sorption coefficients for pyroxasulfone, S-metolachlor, and dimethenamid-p. Air, Soil and Water Research, 2015, 8, ASWR-S19682. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C. V. S.; Velini, E. D.; Luchini, L. C.; Negrisoli, E.; Correa, M. R.; Pivetta, J. P.; Silva, F. M. L. Dinâmica do herbicida metribuzin aplicado sobre palha de cana-de-açúcar (Saccarum officinarum). Planta daninha, 2013, 31, 223-230. [CrossRef]
- Carbonari, C. A.; Gomes, G. L.; Trindade, M. L.; Silva, J. R.; Velini, E. D. Dynamics of sulfentrazone applied to sugarcane crop residues. Weed Science, 2016, 64, 201-206. [CrossRef]
- Watts, D. W.; Hall, J. K. Tillage and application effects on herbicide leaching and runoff. Soil and Tillage Research, 1996, 39, 241-257. [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C. O.; Silva, C. M.; Fay, E. F.; Abakerli, R. B.; Maia, A. H.; Durrant, L. R. Microbial degradation of sulfentrazone in a Brazilian rhodic hapludox soil. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 2010, 41, 209-217. [CrossRef]
|
pH (H20) |
P | K | Ca | Mg | Al | H+Al | SB | (t) | T | V | m |
MO dag kg-1 |
| mg dm-3 | ----------------cmolc dm-3------------------ | ---%--- | ||||||||||
| 5,5 | 2,3 | 88 | 1,24 | 0,44 | 0,1 | 2,97 | 1,91 | 2,01 | 4,88 | 39,1 | 5,0 | 1,9 |
| P-rem | Zn | Fe | Mn | Cu | B | Sand | % | 6 | ||||
| mg L-1 | -----------mg dm-3----------- | Clay | 69 | |||||||||
| 20,1 | 2,0 | 37,8 | 148, | 0,8 | 0,1 | Silt | 25 | |||||
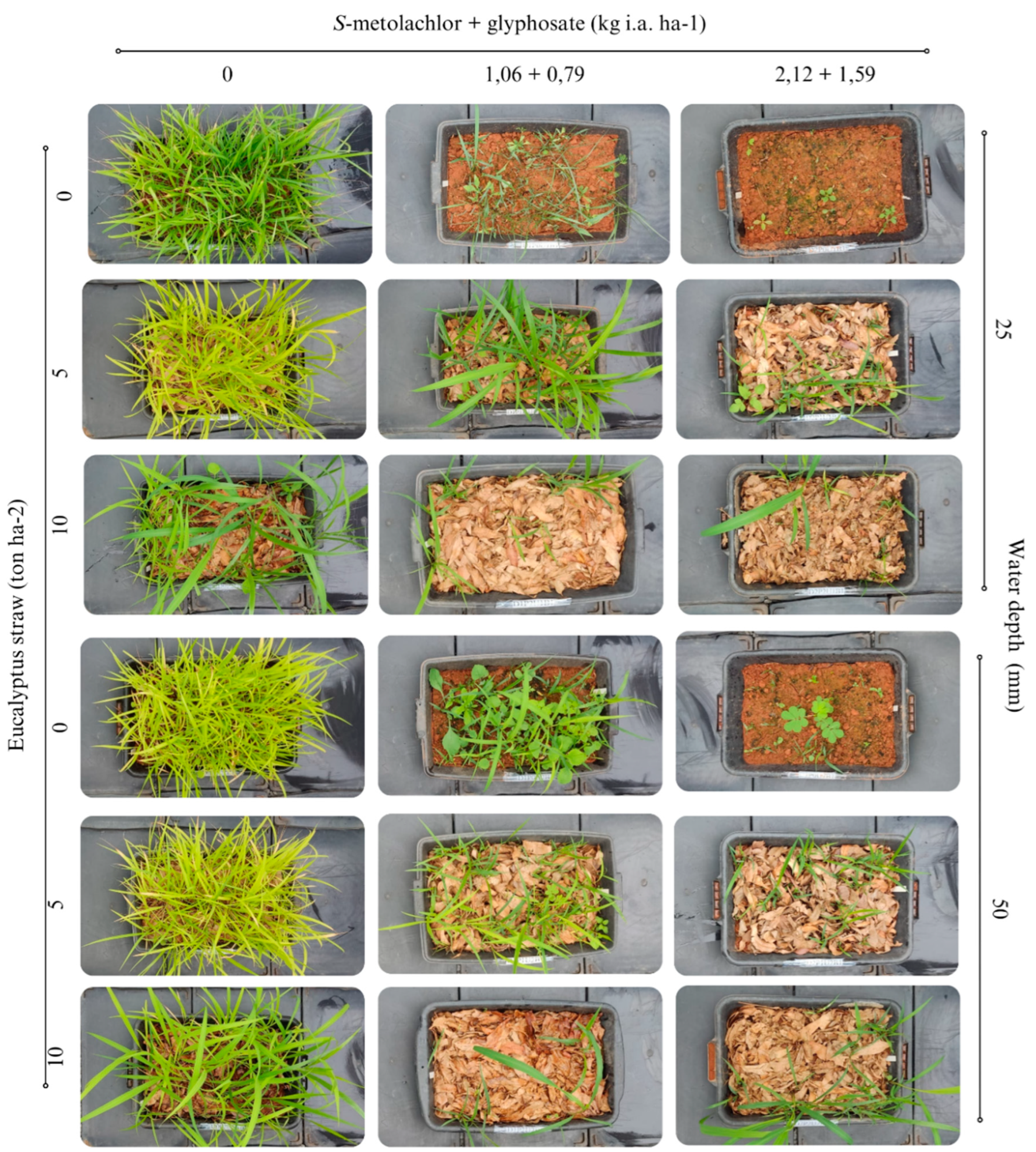
| Variable | Straw (ton ha-2) | S-metolachlor + glyphosate (kg i.a. ha-¹) | CV% | ||
| 0 | 1,06 + 0,79 | 2,12 + 1,59 | |||
| Fresh mass (g) | 0 | 155,31 Aa | 54,79 Ab | 12,34 NSc | 21,1 |
| 5 | 127,33 Aa | 44,08 Ab | 12,92 NSc | ||
| 10 | 82,71 Ba | 27,13 Bb | 21,63 NSc | ||
|
Dry mass (g) |
0 | 43,10 Aa | 8,92 Ab | 1,32 Cc | 26,1 |
| 5 | 32,86 Ba | 7,82 Ab | 1,73 ABc | ||
| 10 | 19,15 Ca | 3,90 Bb | 2,92 Ab | ||
| Dry mass/water ratio | 0 | 0,397 Aa | 0,216 NSb | 0,105 NSc | 20,3 |
| 5 | 0,348 ABa | 0,217 NSb | 0,156 NSc | ||
| 10 | 0,299 Ba | 0,175 NSb | 0,150 NSb | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





