Submitted:
14 July 2023
Posted:
17 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
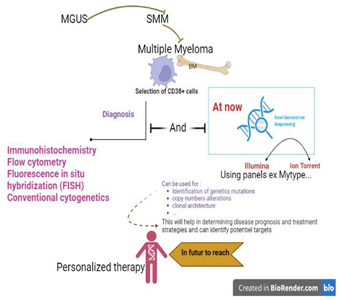
1. Introduction and Etiology of Multiple Myeloma
2. Epidemiology of Multiple Myeloma
2.1. Incidence
2.2. Mortality
2.3. Risk factors
2.3.1. Age
2.3.2. Sex
2.3.3. Race
3. Diagnosis Multiple Myeloma
3.1. Clinical Features
3.2. Laboratory Evaluation in MM
3.3. Imaging Investigation
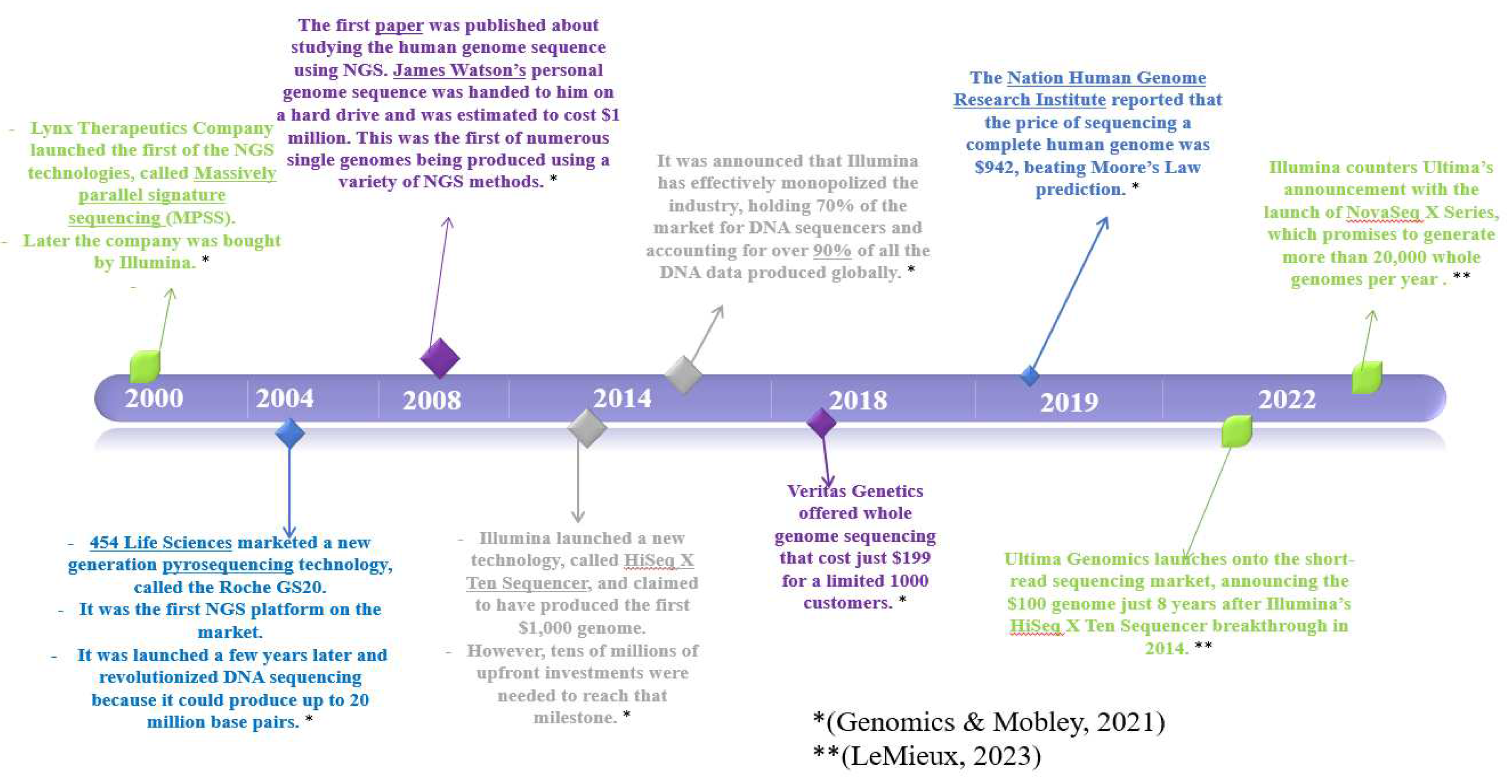
4. NGS
4.1. Definition and Brief History of NGS
4.2. Key Moments in Evolution of NGS Technology
4.3. NGS Platforms and Techniques for MM
4.3.1. Introduction
4.3.2. Illumina Sequencing Platform
4.3.3. Ion Torrent sequencing platform
4.5. Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) in Multiple Myeloma
4.6. Types of MRD Tests
5. Methods
5.1. Search Strategy
5.2. Eligibility Criteria
5.3. Data Extraction
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Platforms Used
6.2. Type of Samples
| Type of samples | Percentage of use |
|---|---|
| Bone Marrow (BM) | 44,55% |
| Unsited | 35,26% |
| Peripheral Blood (PB) | 6,02% |
| BM and PB | 5,46% |
| BM, PB and Plasma Samples | 2,18% |
| Plasma Samples | 2,18% |
| BM and Plasma Samples | 1,09% |
| Serum Samples | 1,09% |
| Plasmacytoid Dendritic cells (PDCs) | 1,09% |
| BM and Biopsies | 0,54% |
| PB, BM and Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded Samples (FFPE) | 0,54% |
6.3. Studies Focusing on the Study of WES in Myeloma Patients by the NGS
| Study | Year of the study | Country | Number of patients used in the study | Type of patients | Type of samples used | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [30] | 2022 | Erbil Iraq | - | - | PB |
| 2 | [31] | 2021 | New delhi India | 62 | - | - |
| 3 | [32] | 2021 | AIIMS, New Delhi | 71 | NDMM | PCs |
| 4 | [33] | 2021 | Helsinki, Finland | 8 | - | BM |
| 5 | [34] | 2021 | New York, NY | 1154 | - | - |
| 6 | [35] | 2020 | Galway, Ireland | 291 | RRMM | BM |
| 7 | [36] | 2020 | Tampa, FL | 196 | - | - |
| 8 | [37] | 2019 | Turin, Italy | 42 | RRMM | - |
| 9 | [38] | 2019 | Milano, Italy | 40 | RRMM | - |
| 10 | [39] | 2018 | Arkansas USA | 1141 | - | |
| 11 | [40] | 2018 | Wurzburg Germany | 1 | - | - |
| 12 | [41] | 2018 | Boston, MA | 629, 1144, 205 | MM, NDMM, NDMM | PB |
| 13 | [42] | 2017 | Boston MA | 186 | - | - |
| 14 | [43] | 2017 | Adelaide Australia | 10 | - | - |
| 15 | [44] | 2017 | New York USA | 19 | - | - |
| 16 | [45] | 2017 | Boston, MA | 151 | MM, SMM, MGUS | PB |
| 17 | [46] | 2017 | Liège, Belgium | 10 | - | BM |
| 18 | [47] | 2016 | Cambridge UK | 14 | - | - |
| 19 | [48] | 2016 | Southampton UK | 25 | - | - |
| 20 | [49] | 2016 | Boston, MA | 63 | NDMM, RRMM, SMM, MGUS | PB |
| 21 | [50] | 2016 | - | 1000 | NDMM | - |
| 22 | [51] | 2016 | Little Rock, AR | 2161 | - | - |
| 23 | [52] | 2016 | Little Rock, AR | 33 | - | - |
| 24 | [53] | 2015 | Boston, MA, USA | 29 | - | - |
| 25 | [54] | 2015 | Little Rock, AR | - | - | BM |
| 26 | [55] | 2014 | Cambridge UK | 23 | - | - |
| 27 | [56] | 2012 | London, United Kingdom | - | - | BM |
| 28 | [57] | 2011 | Boston, MA, USA | - | - | - |
6.4. Studies Involving MRD Assessment by NGS
6.5. The Use of WGS and In-House Panels in the Diagnosis of MM
| Study | Year | Country | Number of cases | Type of patients | Type of samples | Type of NGS investigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [69] | 2021 | New York, NY | 1154 | - | - | WGS and WES |
| [68] | 2020 | Heidelberg, Germany | 15 | RRMM | - | Exploratory biomarker assessments include cytogenetics, genomic analysis (WGS, RNAseq) and phospho-IHC. |
| [70] | 2019 | New York, USA | 154 | - | BM | WGS with myTYPE panel |
| [71] | 2018 | New York, USA | - | - | BM | WGS using myTYPE panel |
| [39] | 2018 | Arkansas USA | 1141 | WGS, WES, and targeted panel sequencing | ||
| [72] | 2018 | Little Rock, AR | 439 | NDMM | - | WGS, WES or targeted panel (TP) modalities. |
| [73] | 2017 | St. Louis MO | 995 | - | - | WGS (were identified using custom Seq-FISH software on long-insert whole genome sequencing data.) |
| [42] | 2017 | Boston MA | 186 | - | - | WES and WGS libraries were constructed with Agilent SureSelect XT2 library prep kit, |
| [51] | 2016 | Little Rock, AR | 2161 | - | - | WGS, WES, targeted panel sequencing, expression data from RNA-Seq and Gene Expression array |
| [74] | 2016 | New York, USA | - | - | - | WGS |
| [59] | 2015 | Boston, MA, USA | 29 | - | - | WGS, (22 patients) WES (17 patients) |
| [75] | 2014 | Phoenix, AZ | - | - | - | WGS |
| [76] | 2012 | London, UK | 13 | MM, SMM | BM | WGS |
| [56] | 2012 | London, UK | - | - | BM | WGS, WES, SNVs |
| Study | Year | Country | Number of cases | type of samples | Type of NGS investigations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [77] | 2022 | Stockholm Sweden | 159 | - | NGS MRD assay with myTYPE panel |
| [78] | 2020 | New York USA | 74 | - | NGS-based assay with myTYPE panel |
| [70] | 2019 | New York, USA | 154 | BM | WGS with myTYPE panel |
| [71] | 2018 | New York, USA | - | BM | WGS using myTYPE panel |
| [79] | 2018 | New York USA | 147 | BM | NGS assay based myTYPE panel |
| [80] | 2018 | Trondheim, Norway | 177 | BM | LymphoTrack® VDJ assay NGS based myTYPE panel assay |
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caulier et al., « Epidemiological landscape of young patients with multiple myeloma diagnosed before 40 years of age: the French experience », Blood, vol. 138, no 25, p. 2686-2695, déc. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Veres et I. A. Cardos, « Multiple myeloma: focus on international epidemiology literature », Acta Medica Transilv., vol. 27, no 1, 2022.
- J. Cowan et al., « Global Burden of Multiple Myeloma: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 », JAMA Oncol., vol. 4, no 9, p. 1221-1227, sept. 2018. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Boyle et al., « Improving prognostic assignment in older adults with multiple myeloma using acquired genetic features, clonal hemopoiesis and telomere length », Leukemia, vol. 36, no 1, Art. no 1, janv. 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Sung et al., « Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries », CA. Cancer J. Clin., vol. 71, no 3, p. 209-249, 2021. [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, S. J. Gibson, A. S. Sperling, P. G. Richardson, I. Ghobrial, et C. C. Mo, « The emerging importance and evolving understanding of clonal hematopoiesis in multiple myeloma », Semin. Oncol., vol. 49, no 1, p. 19-26, févr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Marinac, I. M. Ghobrial, B. M. Birmann, J. Soiffer, et T. R. Rebbeck, « Dissecting racial disparities in multiple myeloma », Blood Cancer J., vol. 10, no 2, p. 19, févr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. H. Schinasi et al., « Multiple myeloma and family history of lymphohaematopoietic cancers: Results from the International Multiple Myeloma Consortium », Br. J. Haematol., vol. 175, no 1, p. 87-101, oct. 2016. [CrossRef]
- K. Brigle et B. Rogers, « Pathobiology and Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma », Semin. Oncol. Nurs., vol. 33, no 3, p. 225-236, août 2017. [CrossRef]
- « Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | Explore the technology ». https://www.illumina.com/science/technology/next-generation-sequencing.html (consulté le 16 janvier 2023).
- LeMieux, « The NGS Race Is On Souped-Up Sequencers Vie for Frontrunner Status », Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. News, vol. 43, no 1, p. 44-48, janv. 2023. [CrossRef]
- F. L. Genomics et I. Mobley, « A brief history of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) », Front Line Genomics, 26 juillet 2021. https://frontlinegenomics.com/a-brief-history-of-next-generation-sequencing-ngs/ (consulté le 16 janvier 2023).
- S. Yohe et B. Thyagarajan, « Review of Clinical Next-Generation Sequencing », Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med., vol. 141, no 11, p. 1544-1557, nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- « NGS Workflow Steps | Illumina sequencing workflow ». https://www.illumina.com/science/technology/next-generation-sequencing/beginners/ngs-workflow.html (consulté le 3 juin 2023).
- R. Pereira, J. Oliveira, et M. Sousa, « Bioinformatics and Computational Tools for Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis in Clinical Genetics », J. Clin. Med., vol. 9, no 1, p. 132, janv. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yin, C. Butler, et Q. Zhang, « Challenges in the application of NGS in the clinical laboratory », Hum. Immunol., vol. 82, no 11, p. 812-819, nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Charalampous et T. Kourelis, « Minimal Residual Disease Assessment in Multiple Myeloma Patients: Minimal Disease With Maximal Implications », Front. Oncol., vol. 11, 2022, Consulté le: 23 février 2023. [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.801851.
- J. Hillengass et al., « Disease Monitoring In Multiple Myeloma », Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk., janv. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Ho et T. Kourelis, « The burden of myeloma: novel approaches to disease assessment », Hematology, vol. 2022, no 1, p. 356-362, déc. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Paiva, J. San-Miguel, et H. Avet-Loiseau, « MRD in multiple myeloma: does CR really matter? », Blood, vol. 140, no 23, p. 2423-2428, déc. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Bal et al., « Impact of autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation on disease burden quantified by next-generation sequencing in multiple myeloma treated with quadruplet therapy », Am. J. Hematol., vol. 97, no 9, p. 1170-1177, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Cho et al., « Real-world data on prognostic value of measurable residual disease assessment by fragment analysis or next-generation sequencing in multiple myeloma », Br. J. Haematol., vol. 198, no 3, p. 503-514, 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Fonseca et al., « Integrated analysis of next generation sequencing minimal residual disease (MRD) and PET scan in transplant eligible myeloma patients », In Review, preprint, sept. 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Kriegsmann et al., « Comparison of bone marrow and peripheral blood aberrant plasma cell assessment by NGF in patients with MM », Blood Adv., vol. 7, no 3, p. 379-383, janv. 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Urushihara et al., « Eight-color multiparameter flow cytometry (EuroFlow-NGF) is as sensitive as next-generation sequencing in detecting minimal/measurable residual disease in autografts of patients with multiple myeloma », eJHaem, vol. 4, no 1, p. 184-191, 2023. [CrossRef]
- T. Yoroidaka et al., « Measurable Residual Disease Assessment Using Next-Generation Flow in Patients With Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma Treated With a Combination of Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone », Anticancer Res., vol. 43, no 1, p. 157-165, janv. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Drandi, S. Ferrero, et M. Ladetto, « Droplet Digital PCR for Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Mature Lymphoproliferative Disorders », in Digital PCR: Methods and Protocols, G. Karlin-Neumann et F. Bizouarn, Éd., in Methods in Molecular Biology. New York, NY: Springer, 2018, p. 229-256. [CrossRef]
- S. Galimberti, S. Balducci, F. Guerrini, M. Del Re, et R. Cacciola, « Digital Droplet PCR in Hematologic Malignancies: A New Useful Molecular Tool », Diagnostics, vol. 12, no 6, Art. no 6, juin 2022. [CrossRef]
- V. V. Subhash et al., « Whole-genome sequencing facilitates patient-specific quantitative PCR-based minimal residual disease monitoring in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, neuroblastoma and Ewing sarcoma », Br. J. Cancer, vol. 126, no 3, Art. no 3, févr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Kakoo, M. Al-Attar, et T. Rasheed, « Exonic variants in multiple myeloma patients associated with relapsed/ refractory and response to bortezomib regimens », Saudi J. Biol. Sci., vol. 29, no 1, p. 610-614, janv. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Farswan et al., « Branching clonal evolution patterns predominate mutational landscape in multiple myeloma », Am. J. Cancer Res., vol. 11, no 11, p. 5659-+, 2021.
- G. Kaur et al., « P-050: Whole Exome Sequencing provides novel insights in synonymous and non-synonymous mutational landscapes of Multiple Myeloma », Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk., vol. 21, p. S65-S66, oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Adhikari, M. Kankainen, et C. A. Heckman, « Comparison of Structural and Short Variants Detected by Linked-Read and Whole-Exome Sequencing in Multiple Myeloma », Cancers, vol. 13, no 6, p. 1212, mars 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Williams et al., « Hispanic or Latin American Ancestry Is Associated with a Similar Genomic Profile and a Trend Toward Inferior Outcomes in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma As Compared to Non-Hispanic White Patients in the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation (MMRF) CoMMpassstudy », Blood, vol. 138, p. 4117, nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. E. O’Dwyer et al., « Integrative Analysis of the Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Patients Treated With Venetoclax in Combination With Bortezomib and Dexamethasone: Biomarker Analyses From the Phase 3 BELLINI Study », Blood, vol. 136, p. 40-41, nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Song et al., « Molecular Insights into Clonal Hematopoiesis and Therapy-Related Myeloid Neoplasm in Patients with Multiple Myeloma and Cytopenia(s) », Blood, vol. 136, p. 6-7, nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ziccheddu et al., « The Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Double-Refractory Multiple Myeloma », Blood, vol. 134, p. 3056, nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Ziccheddu et al., « Analysis of the genomic and transcriptomic landscape of chemoresistant multiple myeloma », Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk., vol. 19, no 10, Supplement, p. e58-e59, oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Ashby et al., « Da », Blood, vol. 132, p. 4441, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. C. Da Via’ et al., « mou », Blood, vol. 132, p. 3181, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. H. Mouhieddine et al., « The Role of Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential (CHIP) in Multiple Myeloma: Immunomodulator Maintenance Post Autologous Stem Cell Transplant (ASCT) Predicts Better Outcome », Blood, vol. 132, p. 749, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Bustoros et al., « Next Generation Sequencing Identifies Smoldering Multiple Myeloma Patients with a High Risk of Disease Progression », Blood, vol. 130, p. 392, déc. 2017.
- K. Dutta, J. P. Grady, D. R. Hewett, L. B. To, L. Fink, et A. C. W. Zannettino, « laga », Blood, vol. 130, p. 391, déc. 2017.
- Lagana et al., « Clonal Evolution in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Patients: A Follow-up Study from the Mmrf Commpass Genomics Project », Blood, vol. 130, p. 325, déc. 2017.
- S. Manier, X. Leleu, et H. Avet-Loiseau, « Rôle pronostique des microARN des exosomes circulants dans le myélome multiple », médecine/sciences, vol. 33, no 11, p. 939-941, nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Wenric et al., « Exome copy number variation detection: Use of a pool of unrelated healthy tissue as reference sample », Genet. Epidemiol., vol. 41, no 1, p. 35-40, janv. 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. Bolli et al., « A DNA target-enrichment approach to detect mutations, copy number changes and immunoglobulin translocations in multiple myeloma », Blood Cancer J., vol. 6, no 9, p. e467, sept. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Bryant et al., « Single Cell Whole Exome Sequencing in an Index Case of Amp1q21 Multiple Myeloma to Define Intraclonal Variation », Blood, vol. 128, no 22, p. 5651, janv. 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Manier, K. Salem, S. V. Glavey, A. M. Roccaro, et I. M. Ghobrial, « Genomic Aberrations in Multiple Myeloma », Cancer Treat. Res., vol. 169, p. 23-34, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Miller et al., « Correlation Between Somatic Mutation Burden, Neoantigen Load and Progression Free Survival in Multiple Myeloma: Analysis of MMRF CoMMpass Study », Blood, vol. 128, no 22, p. 193, janv. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Walker et al., « The Multiple Myeloma Genome Project: Development of a Molecular Segmentation Strategy for the Clinical Classification of Multiple Myeloma », Blood, vol. 128, no 22, p. 196, janv. 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. Weinhold et al., « Clonal selection and double-hit events involving tumor suppressor genes underlie relapse in myeloma », Blood, vol. 128, no 13, p. 1735-1744, sept. 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. C. Munshi et al., « Next Generation Sequencing in Multiple Myeloma », Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk., vol. 15, p. e2-e3, sept. 2015. [CrossRef]
- K. Zielinska, K. Leigh, H. Gomez, et R. K. Van Laar, « Validation of the Nextseq 500 and Development of a High-Throughput NGS Pipeline for Identifying Clinically-Relevant Gene Variants in Multiple Myeloma Specimens », Blood, vol. 126, no 23, déc. 2015, Consulté le: 7 juin 2022. [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/summary/8e9f0957-98a2-4fc0-b446-ccf7a6255ce7-3ca6fb9a/relevance/1.
- N. Bolli et al., « A Next Generation Sequencing-Based Approach to Detect Gene Mutations, Copy Number Changes and IGH Translocations in Multiple Myeloma », Blood, vol. 124, no 21, p. 3364, déc. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Walker et al., « mun », Blood, vol. 120, no 5, p. 1077-1086, août 2012. [CrossRef]
- N. C. Munshi et al., « Whole Genome Sequencing Defines the Clonal Architecture and Genomic Evolution in Myeloma: Tumor Heterogeneity with Continued Acquisition of New Mutational Change », Blood, vol. 118, no 21, p. 297, nov. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Kakoo, M. Al-Attar, et T. Rasheed, « Exonic variants in multiple myeloma patients associated with relapsed/ refractory and response to bortezomib regimens », Saudi J. Biol. Sci., vol. 29, no 1, p. 610-614, janv. 2022. [CrossRef]
- N. C. Munshi et al., « Next Generation Sequencing in Multiple Myeloma », Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk., vol. 15, p. e2-e3, sept. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. D. Khoury et al., « The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms », Leukemia, vol. 36, no 7, Art. no 7, juill. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Medina et al., « Comparison of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and next-generation flow (NGF) for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment in multiple myeloma », Blood Cancer J., vol. 10, no 10, p. 108, oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Ha et al., « Ig Gene Clonality Analysis Using Next-Generation Sequencing for Improved Minimal Residual Disease Detection with Significant Prognostic Value in Multiple Myeloma Patients », J. Mol. Diagn., vol. 24, no 1, p. 48-56, janv. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ho et al., « Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Assay Shows High Clonal Characterization Success Rate for Plasma Cell Neoplasms, and Concordance with Flow Cytometry in Minimal Residual Disease Detection », Blood, vol. 132, p. 4475, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Kim, H. J. Kim, et Y. K. Lee, « IGH and IGK Rearrangement and IGH Somatic Hypermutation Analysis Using Next-generation Sequencing for the Detection of Clonality in High-risk Korean Multiple Myeloma Patients », Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk., vol. 19, no 10, Supplement, p. e68-e69, oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yao, Y. Bai, S. Kumar, E. Au, A. Orfao, et C. S. Chim, « Minimal Residual Disease Detection by Next-Generation Sequencing in Multiple Myeloma: A Comparison With Real-Time Quantitative PCR », Front. Oncol., vol. 10, p. 611021, janv. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yao, Y. Bai, A. Orfao, et C. S. Chim, « Standardized Minimal Residual Disease Detection by Next-Generation Sequencing in Multiple Myeloma », Front. Oncol., vol. 9, 2019, Consulté le: 17 mai 2022. [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fonc.2019.00449.
- Q. Yao, Y. Bai, S. Kumar, E. Au, A. Orfao, et C. S. Chim, « Minimal Residual Disease Detection by Next-Generation Sequencing in Multiple Myeloma: A Comparison With Real-Time Quantitative PCR », Front. Oncol., vol. 10, p. 611021, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Raab et al., « Safety and Preliminary Efficacy Results from a Phase II Study Evaluating Combined BRAF and MEK Inhibition in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (rrMM) Patients with Activating BRAF V600E Mutations: The GMMG-Birma Trial », Blood, vol. 136, p. 44-45, nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Williams et al., « Hispanic or Latin American Ancestry Is Associated with a Similar Genomic Profile and a Trend Toward Inferior Outcomes in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma As Compared to Non-Hispanic White Patients in the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation (MMRF) CoMMpassstudy », Blood, vol. 138, p. 4117, nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- V. Yellapantula et al., « Comprehensive detection of recurring genomic abnormalities: a targeted sequencing approach for multiple myeloma », Blood Cancer J., vol. 9, p. 101, déc. 2019. [CrossRef]
- V. Yellapantula et al., « Mytype: A Capture Based Sequencing Approach to Detect Somatic Mutations, Copy Number Changes and IGH Translocations in Multiple Myeloma », Blood, vol. 132, p. 5588, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Wardell et al., « Extracting Prognostic Molecular Information from PET-CT Imaging of Multiple Myeloma Using Radiomic Approaches », Blood, vol. 132, p. 1906, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Fiala et al., « Next Generation Sequencing Based Revised International Staging System (R-ISS) for Multiple Myeloma », Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk., vol. 17, no 1, Supplement, p. e18, févr. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Perumal et al., « Network Modeling Reveals CDC42BPA and CLEC11A As Novel Driver Genes of t(4; 14) Multiple Myeloma », Blood, vol. 128, no 22, p. 802, janv. 2016. [CrossRef]
- K. Stephenson, B. Benard, M. Klug, A. Christofferson, et J. J. Keats, « Clonal Diversity of a Myeloma Tumor: From Generations of Cells to Treatment Implications », Blood, vol. 124, no 21, p. 3424, déc. 2014. [CrossRef]
- L. Melchor et al., « Intra-Clonal Heterogeneity Is a Critical Early Event in the Preclinical Stages of Multiple Myeloma and Is Subject to Darwinian Fluctuation throughout the Disease », Blood, vol. 120, no 21, p. 3941, nov. 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. Hultcrantz et al., « Capture Rate of V(D)J Sequencing for Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Multiple Myeloma », Clin. Cancer Res., vol. 28, no 10, p. 2160-2166, mai 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Hultcrantz et al., « Baseline VDJ clonotype detection using a targeted sequencing NGS assay: allowing for subsequent MRD assessment », Blood Cancer J., vol. 10, no 7, p. 76, juill. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Hultcrantz et al., « Capture Rate of the Adaptive Next Generation Sequencing VDJ Assay in Multiple Myeloma », Blood, vol. 132, p. 3184, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Rustad et al., « V(D)J Sequence Capture for DNA-Based Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Multiple Myeloma », Blood, vol. 132, p. 4444, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).