Submitted:
15 July 2023
Posted:
17 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of chitosan from giant snail shell (Achatina marginata):
2.1.1. Deproteinization:
2.1.2. Demineralization:
2.1.3. Decolourization:
2.1.4. Deacetylation:
2.2. Experimentals:
2.3. Purification of chitosan
2.4. The degree of deacetylation [17]
2.5. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticle:
2.6. Synthesis of Fe(III) chitosan:
2.7. Characterisation:
2.8. Evaluation of antimicrobial activities:
2.8.1. Preparation of materials / samples concentration:
2.8.2. Antibiotic Sensitivity Test:
2.8.3. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of the Materials:
3. Results and discussion:
3.1. Degree of deacetylation of chitosan:
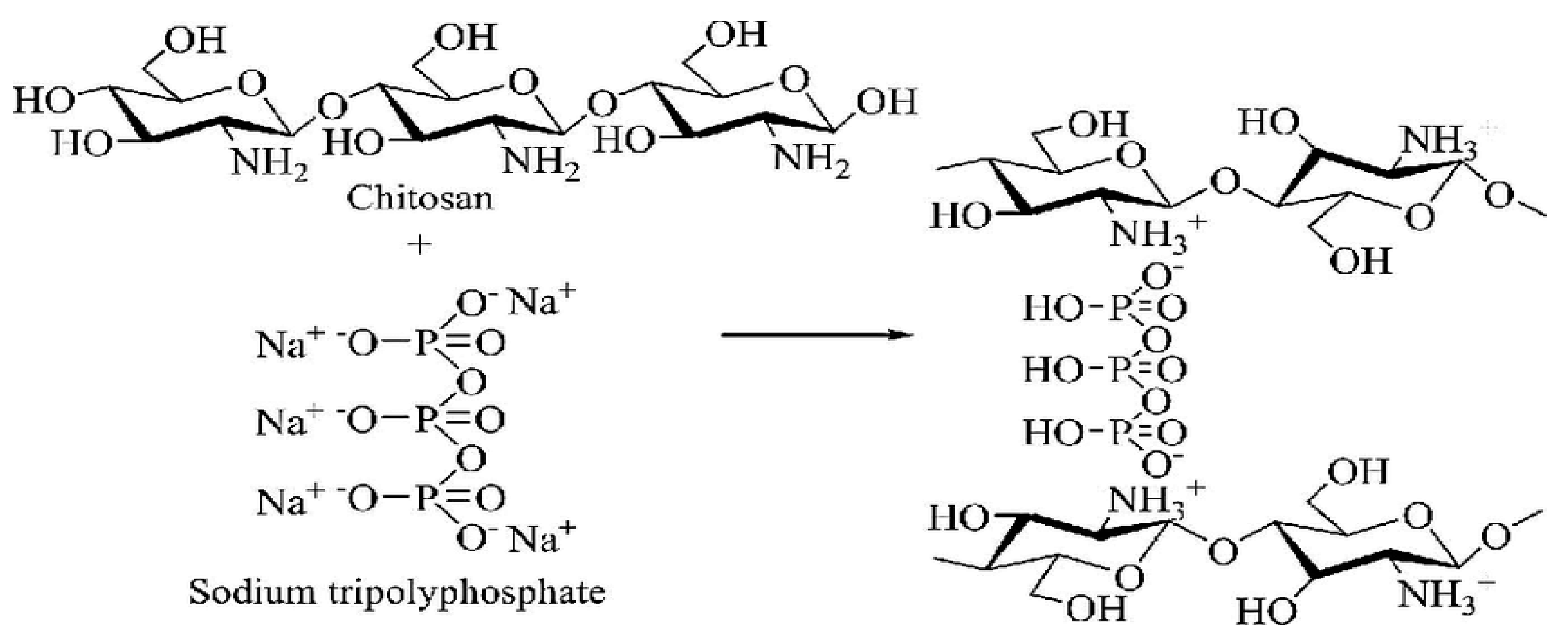
3.2. Ionic interaction between Chitosan and Tripolyphosphate (TPP):
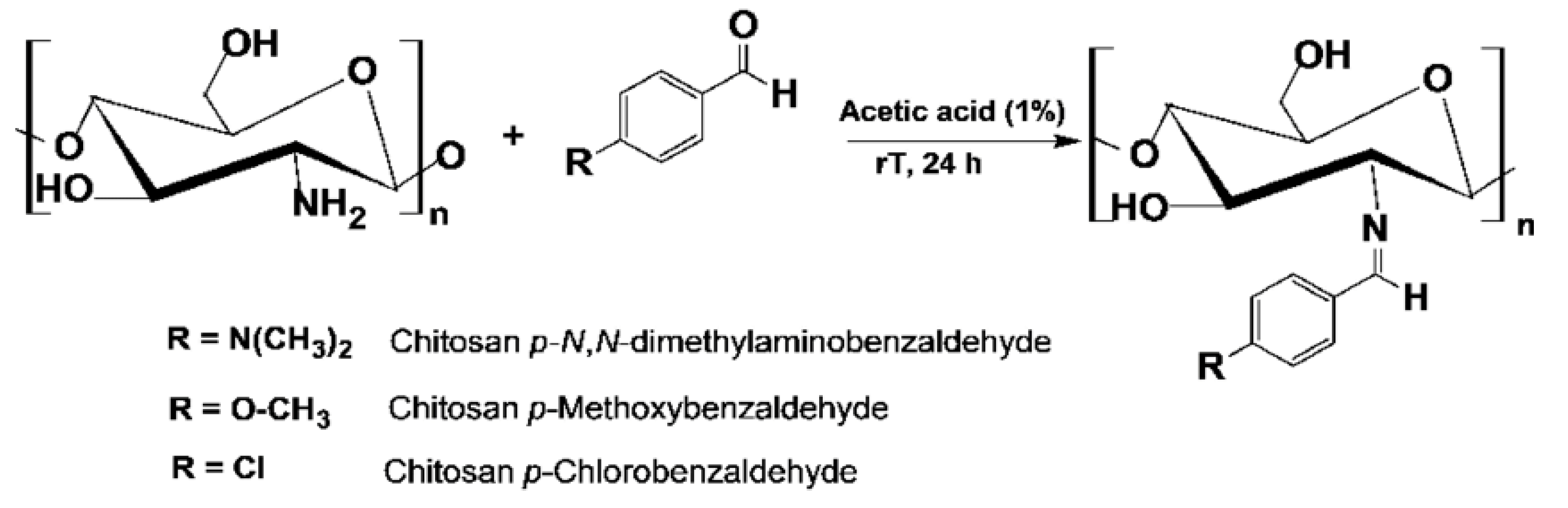
3.3. Complexation of chitosan n-benzaldehyde Schiff base with metal ion:
3.4. Physical appearances of the synthesized materials:
3.5. Data Analysis:
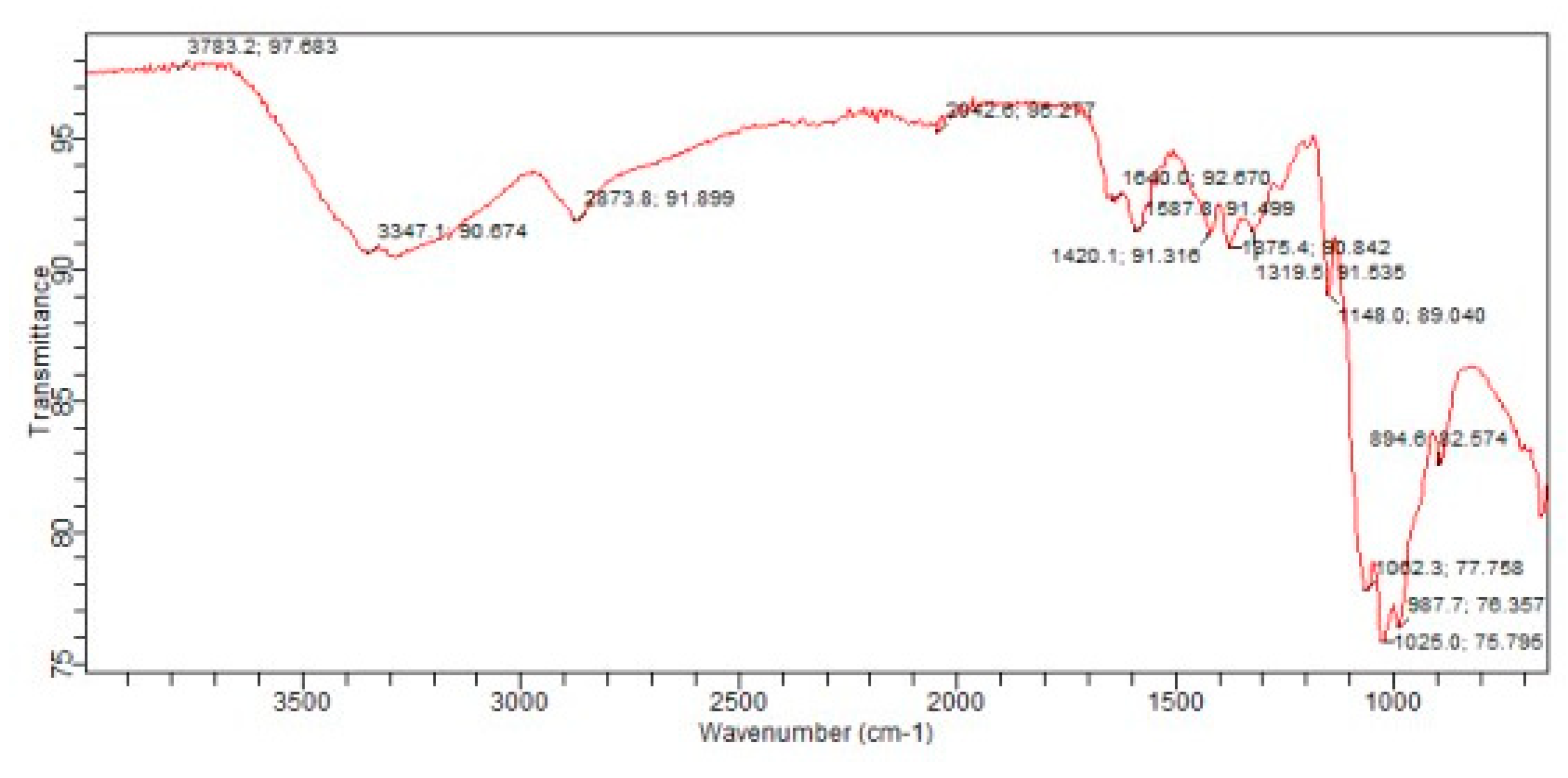
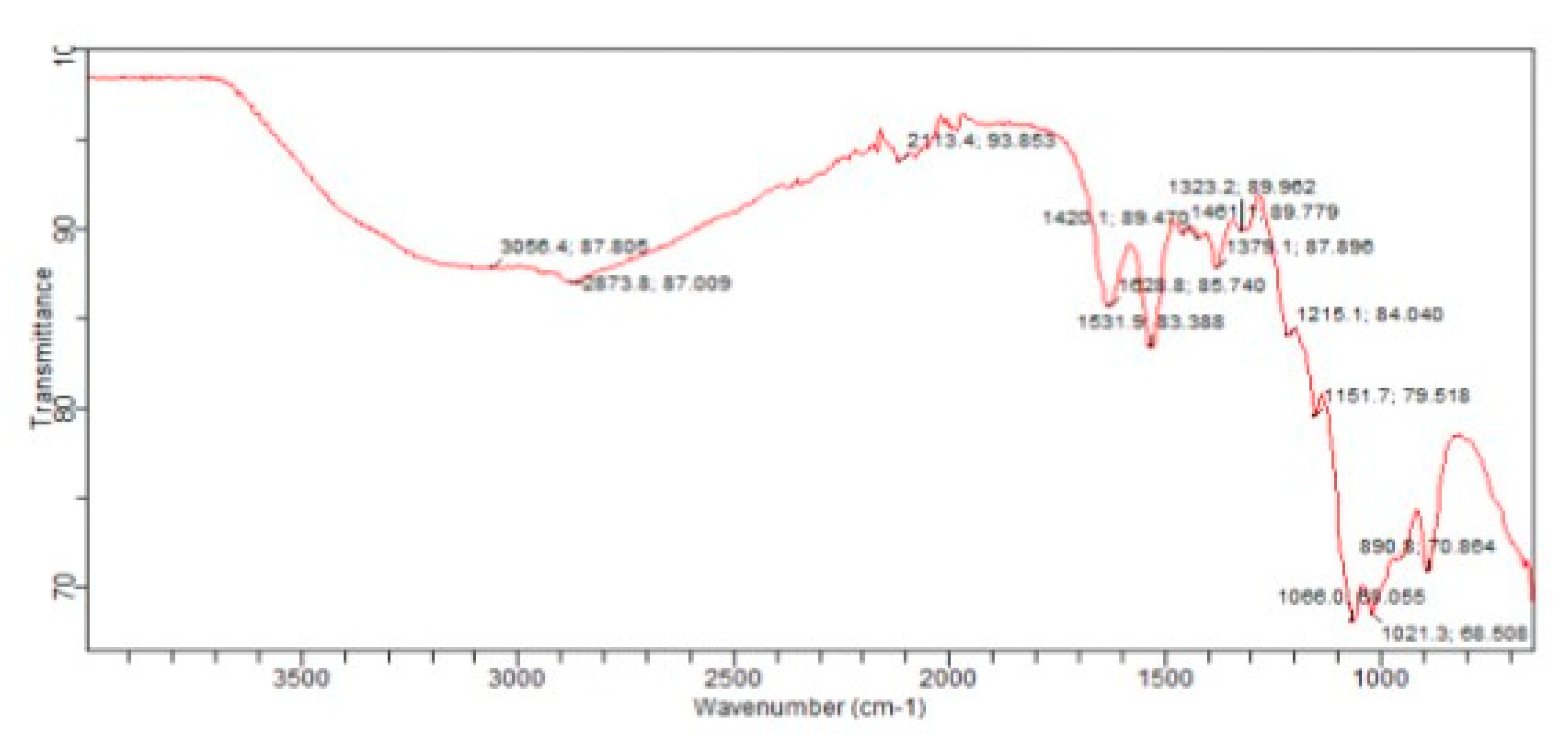
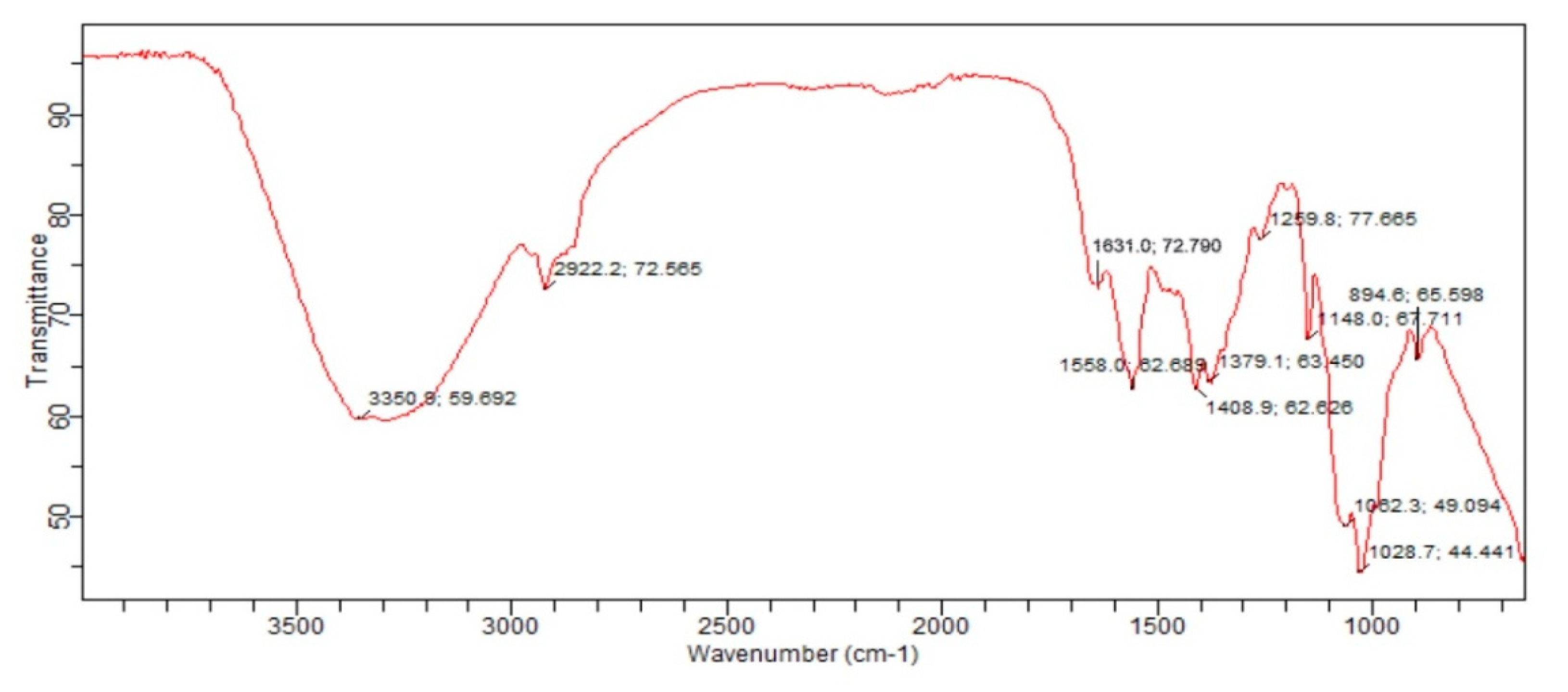
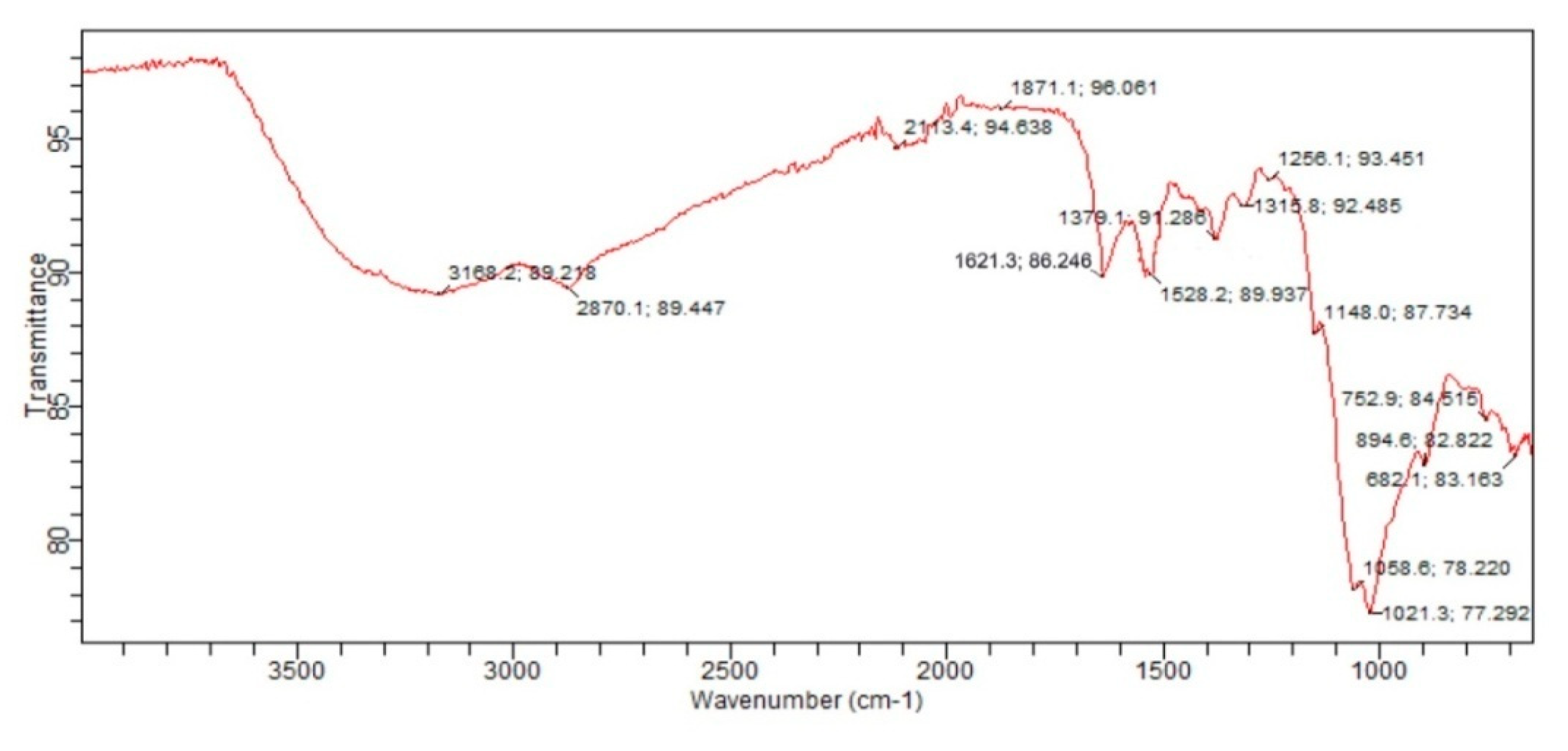
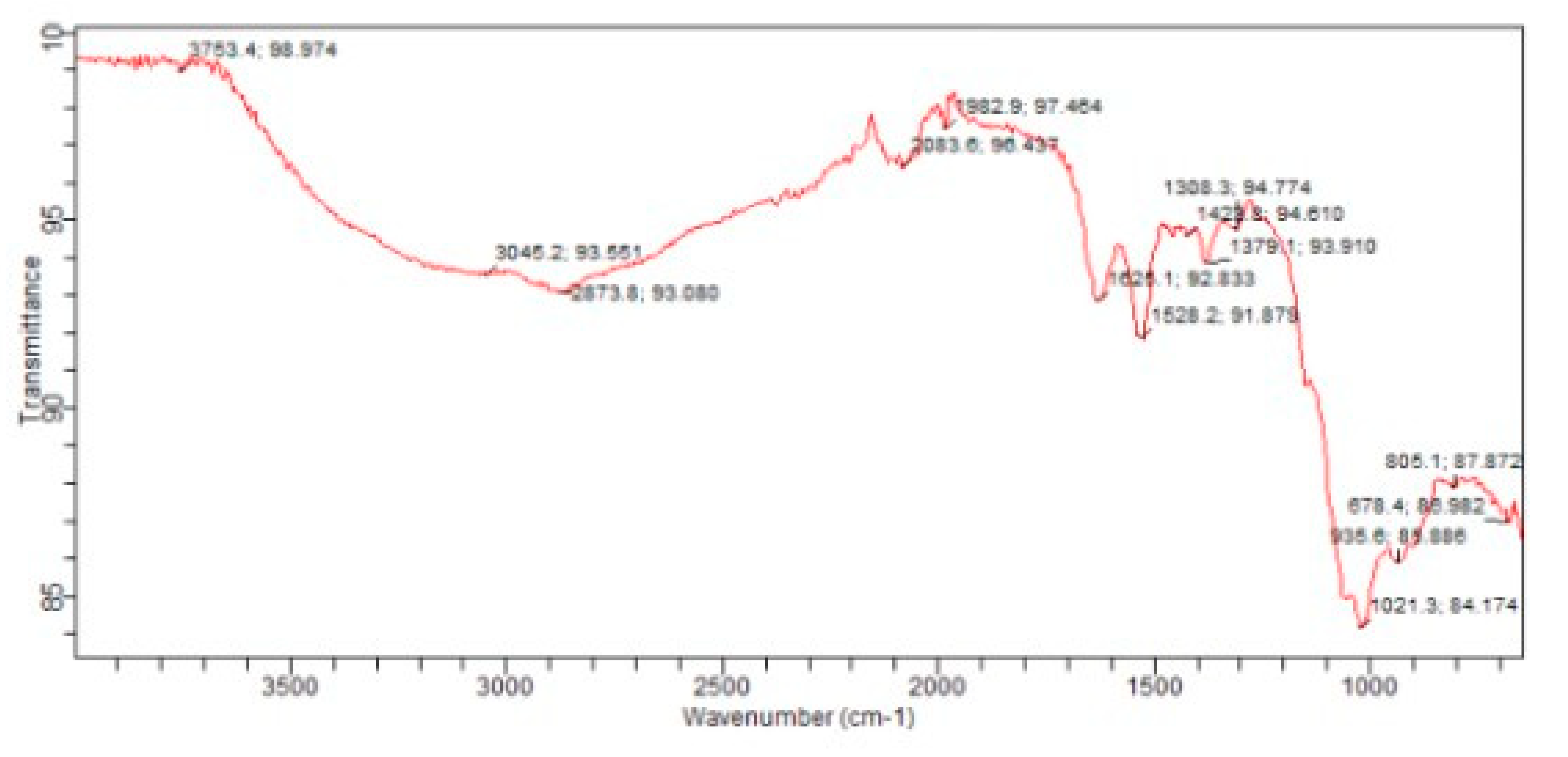
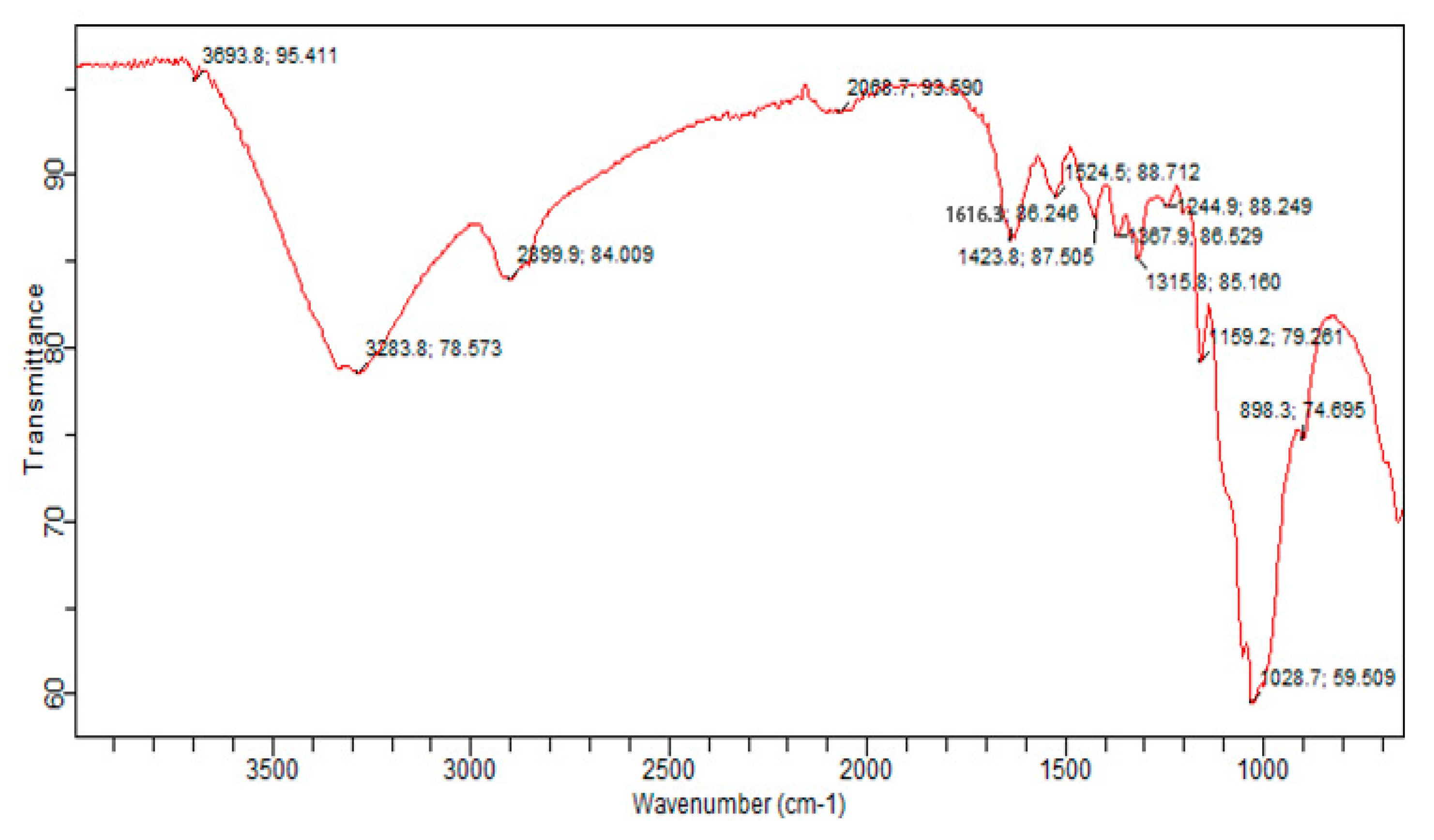
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared(FTIR)Spectroscopy:
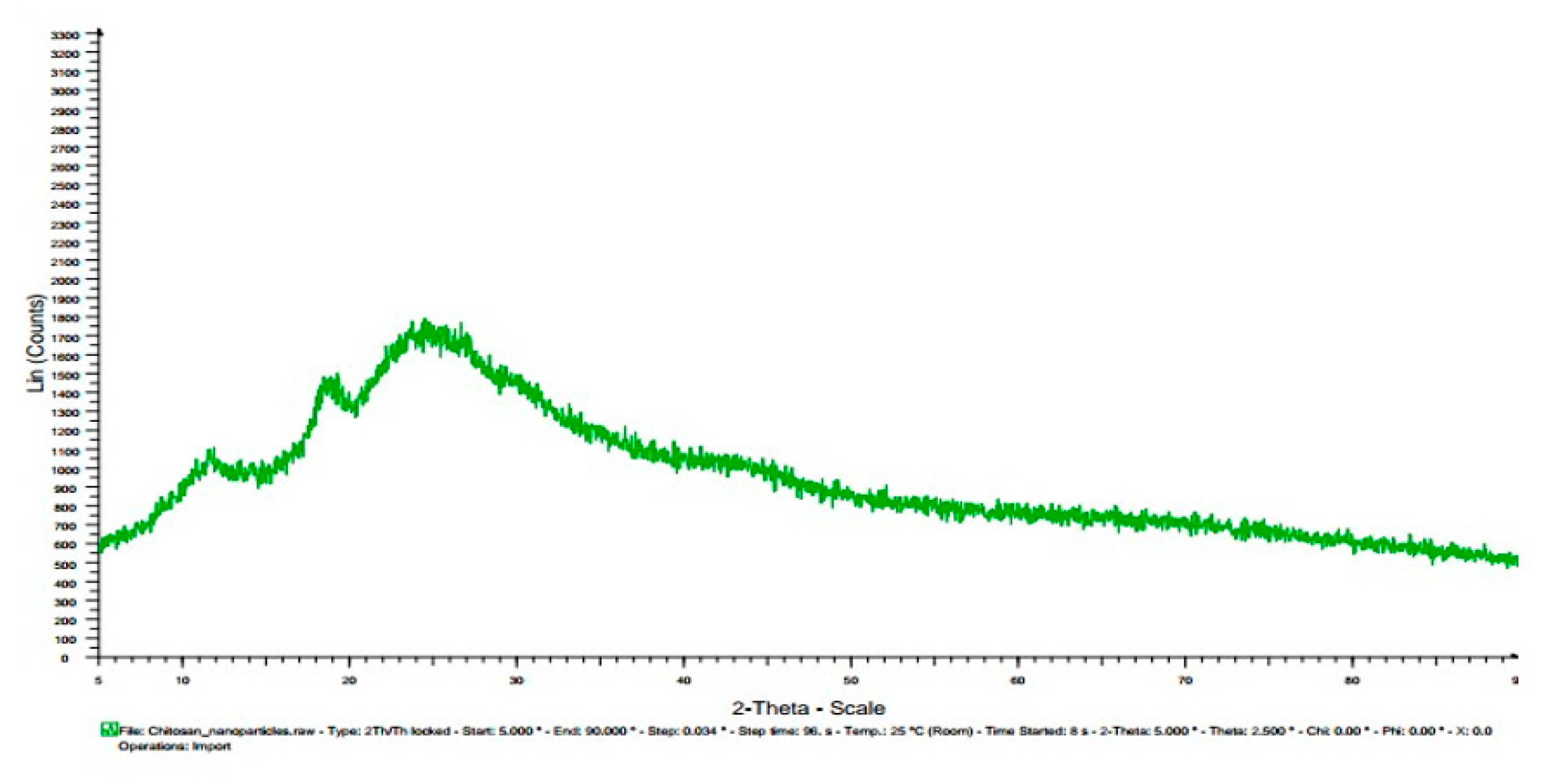
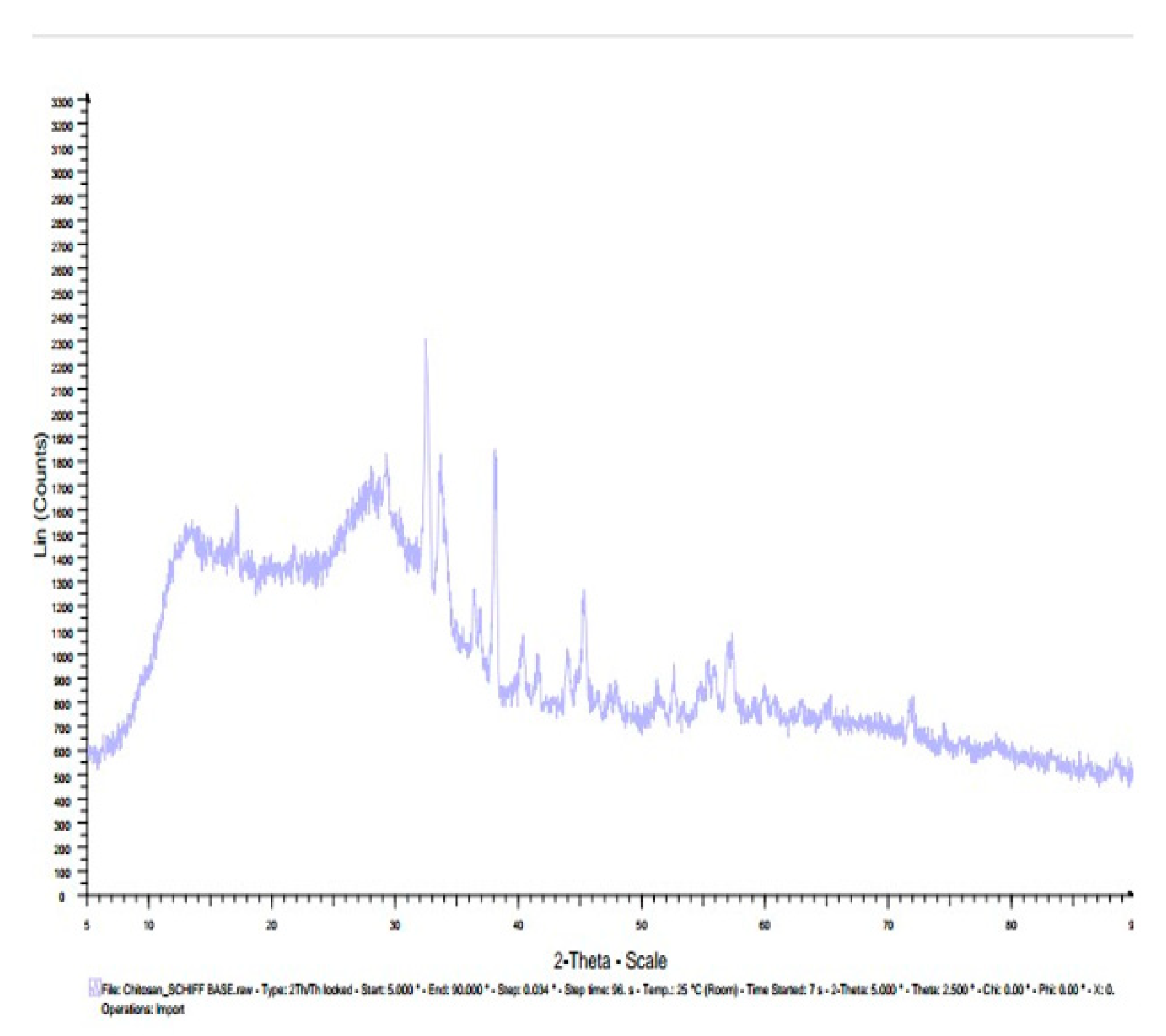
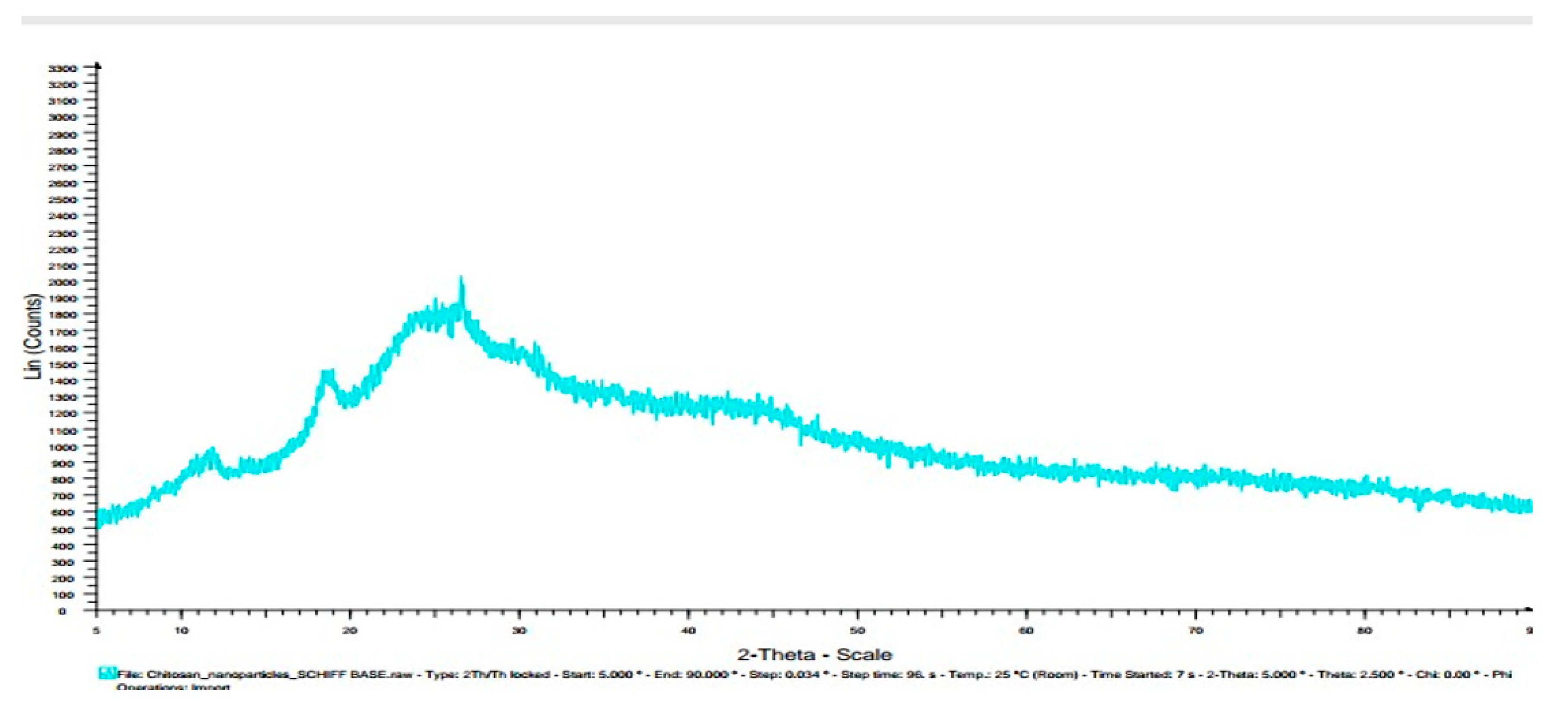
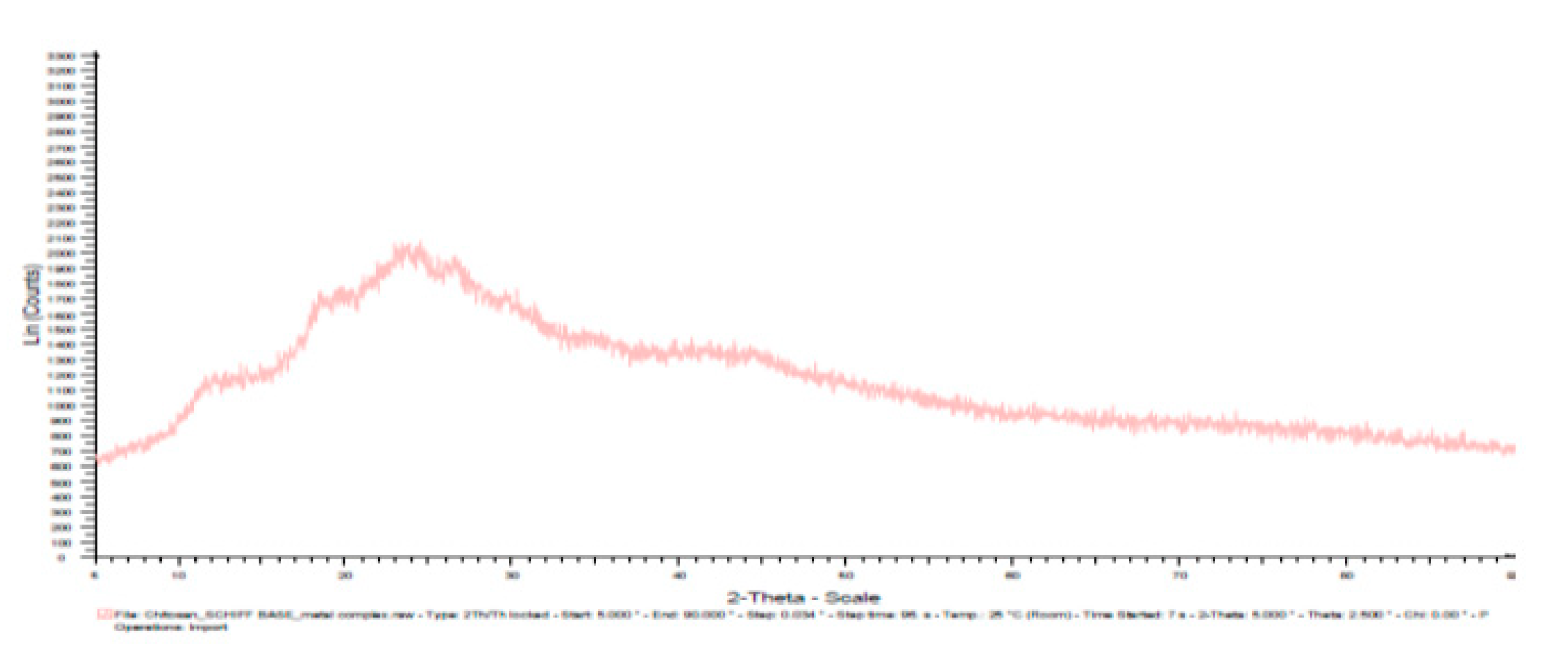
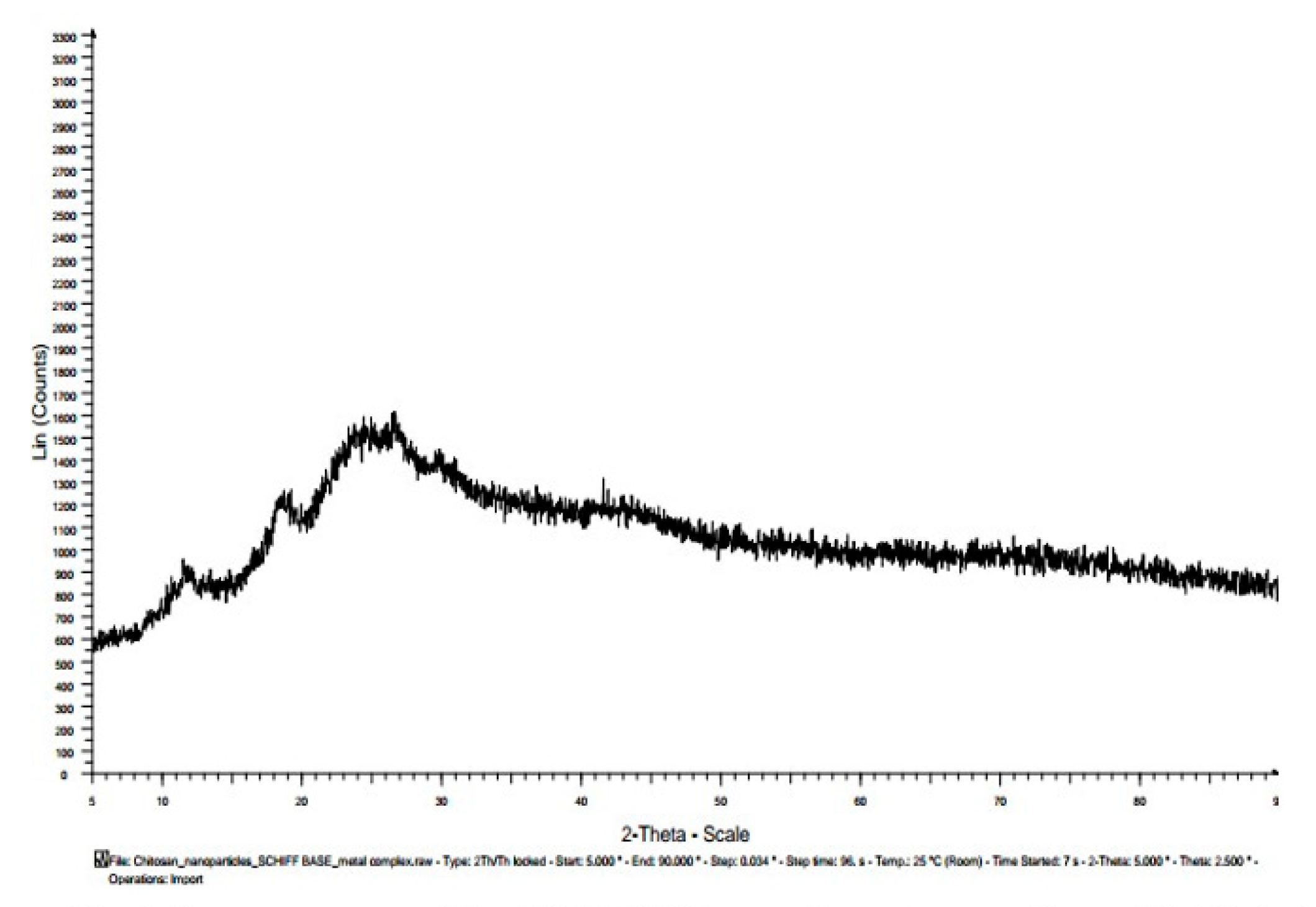
3.7. X-ray diffractogram (XRD):
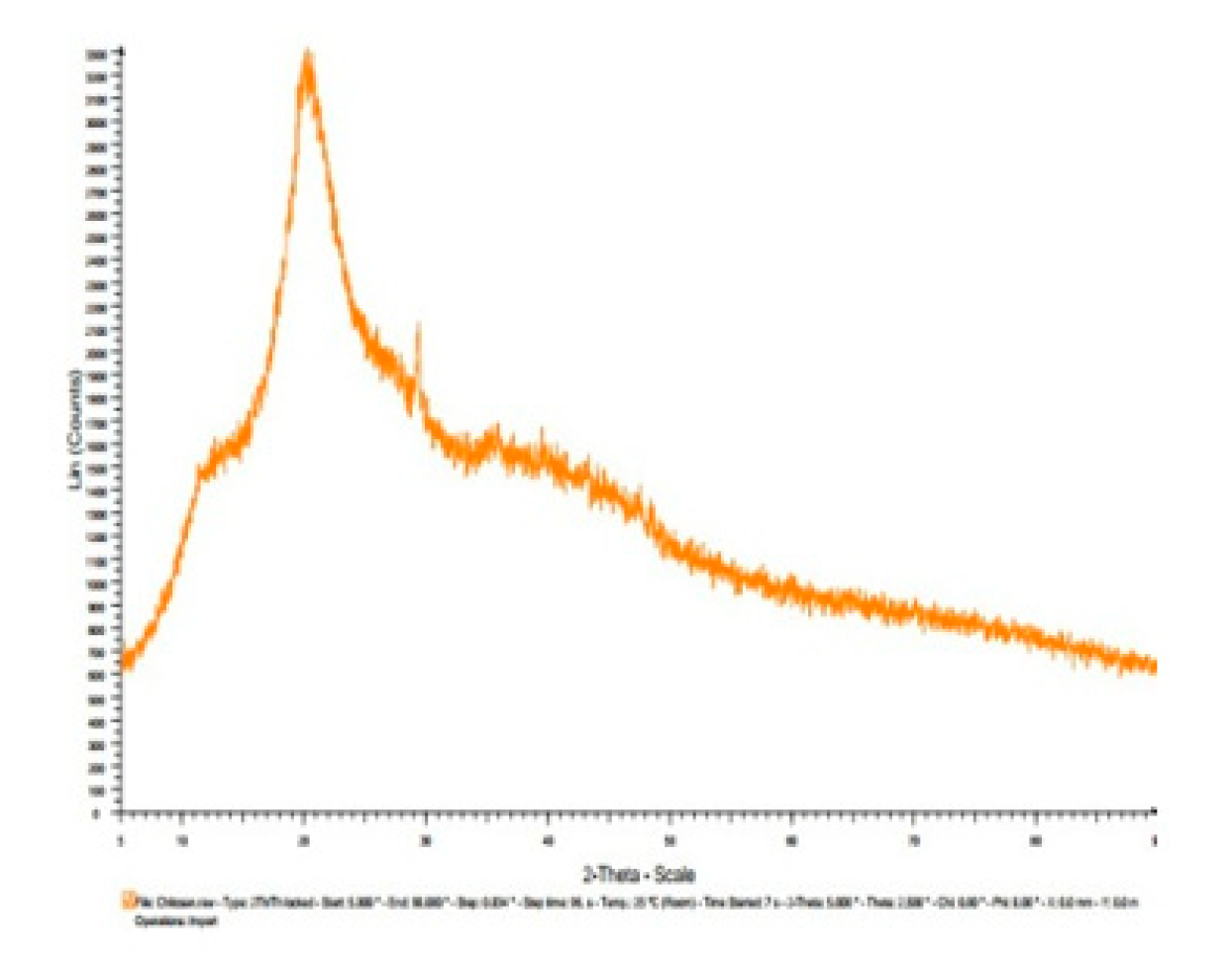
| Materials | Diffracted Peaks at 2θ (Degree) | |
|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 11.5, 20 | |
| Chitosannanoparticle | 12, 19,26,30 | |
| Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 14, 28 | |
| Chitosannanoparticle n – benzaldehydeSchiff base | 12, 19, 25, 27,30 | |
| Fe(III) Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 11.5,18.5, 22.5, 27, 34 | |
| Fe(III) Chitosannanoparticlen – benzaldehydeSchiff base | 12, 18.5, 24, 27, 42 |
3.8. Antibacterial assessment of all the synthesized materials:
3.9. The experimental results of antimicrobial activity of all the materials using the inhibition zone method:
| Materials | 100% | 50% | 25% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 10 | 08 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle | 12 | 10 | 00 |
| Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 14 | 10 | 00 |
| Fe(III) chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 16 | 12 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 16 | 14 | 00 |
| Fe(III) chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehydeSchiff base | 18 | 16 | 10 |
| Materials | 100% | 50% | 25% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 14 | 10 | 08 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle | 16 | 12 | 10 |
| Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 22 | 20 | 18 |
| Fe(III) chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 24 | 22 | 10 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 24 | 22 | 20 |
| Fe(III) chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 26 | 24 | 20 |
| Materials | 100% | 50% | 25% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 16 | 00 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle | 16 | 14 | 00 |
| Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 18 | 16 | 14 |
| Fe(III) chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 20 | 18 | 16 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 20 | 18 | 14 |
| Fe(III) chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 24 | 20 | 18 |
| Materials | 100% | 50% | 25% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 00 | 00 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle | 00 | 00 | 00 |
| Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 00 | 00 | 00 |
| Fe(III) chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 16 | 12 | 10 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehydeSchiff base | 16 | 12 | 10 |
| Fe(III) chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 18 | 14 | 12 |
| Materials | 100% | 50% | 25% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 14 | 12 | 10 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle | 16 | 14 | 12 |
| Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 08 | 00 | 00 |
| Fe (III) chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 10 | 00 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 10 | 08 | 00 |
| Fe (III) chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehydeSchiff base | 12 | 10 | 00 |
| Materials | 100% | 50% | 25% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 08 | 00 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle | 10 | 00 | 00 |
| Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 08 | 08 | 00 |
| Fe(III) chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 10 | 08 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 10 | 08 | 08 |
| Fe(III) chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 12 | 10 | 08 |
| Materials | 100% | 50% | 25% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | 00 | 00 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle | 00 | 00 | 00 |
| Chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 08 | 00 | 00 |
| Fe(III) chitosan n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 10 | 08 | 00 |
| Chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 14 | 12 | 00 |
| Fe(III) chitosan nanoparticle n – benzaldehyde Schiff base | 16 | 14 | 08 |
3.10. Total evaluation of the antimicrobial activities of the produced materials against the various bacteria and fungi:
| Bacteria | Standard Drugs Inhibition Zone (mm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIP | RL | MEM | CN | VA | AMC | CAZ | E | |
| Bacillus subtilis (+) | 26 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 |
| Bacillus cereus (+) | 28 | 00 | 24 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 14 | 00 |
| Samolena(-) | 28 | 12 | 34 | 00 | 08 | 22 | 08 | 12 |
| Pseudomonas (-) | 36 | 20 | 30 | 24 | 00 | 00 | 28 | 00 |
| Staphylococcus aureus (+) | 24 | - | 24 | 24 | 18 | 14 | 10 | 24 |
| Fungi | Fluconazole Inhibition Zone (mm) |
|---|---|
| Candida albicans | 24 |
| Aspergillus niger | 18 |
3.11. Comparison of the antimicrobial activities of the Gram-positive bacteria against Gram negative bacteria:
3.12. Comparison of the antimicrobial activities of the nanoparticle materials against microparticle materials:
3.13. Comparison of the antimicrobial activities of the synthesized materials against standard drugs:
3.13.1. The experimental results of antimicrobial activity of all the standard drugs using the inhibition zone method:
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Disclosure of conflict of interest
References
- Otuokere, I.E.; Anyanwu, J.C.; Igwe, K.K. Ni(II) Complex of a Novel Schiff Base Derived from Benzaldehyde and Sulphathiazole: Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Studies. Commun. Phys. Sci. 2020, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Ayodele, T.O. Ease to Challenges in Achieving Successful Synthesized Schiff base, Chirality, and Application as Antibacterial Agent. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 1626488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warra, A.A. Transition metal complexes and their application in drugs and cosmetics: A Review. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 951–958. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Hernandez, M.A.; McKee, M.L.; Keizer, T.S.; Yearwood, B.C.; Atwood, D.A. Six – coordinate Aluminium cations: characterization, catalysis and theory. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton. Trans. 2002, 3, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhikuan, Y.; Yuting, W.; Yurong, T. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Metal Ions of Crosslinked Chitosan Azacrown Ethers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 3053–3058. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzerelli, R.A.A.; Peter, M.G. Some modified chitosans and their niche applications. In Chitin Handbook; European Chitin Society: Italy, 1997; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, T.M.; Ika, O.W.; Rizky, A.S.; Dionysius, J.D.H.S.; Akhmad, S. In – situ synthesis and characterization of chitosan – Fe3O4 nanoparticles using tripolyphosphate/citrate as cross – linker. Sci. Study Res. 2016, 17, 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Nadia, A.M.; Magdy, W.S.; Ahmed, H.H.; El-ghandour, M.M.; Abel-aziz, O.; Abdel-gawad, F. Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of carboxymethyl Chitosan Schiff base with different benzaldehyde derivatives. J. Am. Sci. 2013, 9, 247–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sashikala, S.; Syed, S.S. Synthesis and characterisation of chitosan Schiff base derivatives. Sch. Res. Libr. 2014, 6, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Knorr, D. Functional properties of chitin and chitosan. J. Food Sci. 1982, 47, 1365–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sagheer, F.; Al-Sughayer, M.; Muslim, S.; Elsabee, M. Extraction and characterization of chitin and chitosan from marine sources in Arabian Gulf. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, H.; Yaghobi, N.; Amanpour, S.; Ahmadi, H.; Mohagheni, M.A.; Hormoni, F. Preparation of Chitosan derived from Shrimp shell, Persian Gulf as blood Hemostasis agent. Iran. Polym. J. 2002, 11, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.M.; Masun, S.M.; Molla, M.A.I.; Rahman, M.M.; Shaikh, A.A.; Roy, S.K. Preparation of Chitosan from shrimp shell and investigation of its properties. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 116–130. [Google Scholar]
- Pradip, K.D.; Joydeep, D.; Tripathy, V.S. Chitin and Chitosan: Chemistry, properties and applications. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2004, 63, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Signini, R.; Campana Filho, S.P. On the preparation and characterization of chitosan hydrochloride Polym. Bull. 1999, 42, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Rajalakshmi, R. , Indira, M., Y., Aruna, U., Vinesha, V., Rupangada, V., Krishna M and S.B. Chitosan Nanoparticles – An emerging trend in nanotechnology. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 2014, 6, 204–229. [Google Scholar]
- Morteza, H.K.; Mohammad, K.; Mobina, K.; Sahar, K. Reinforcement of Chitosan nanoparticles obtained by an Ionic Cross-linking process. Iran. Polym. J. 2011, 20, 455–456. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, T.F.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J.; Gao, L.; Xing, Y.; Li, X. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan-based Schiff Base Compounds with Aromatic Substituent Groups. Iran. Polym. J. 2011, 20, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Eldin, M.M.; Hashem, A.I.; Omer, A.M.; Tamer, T.M. Preparation, Characterisation and antimicrobial evaluation of novel cinnamyl chitosan Schiff base. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 3, 741–755. [Google Scholar]
- Kucukkolbasi, S.; Erdoğan, Z.Ö.; Barek, J.; Sahin, M.; Kocak, N. A Novel Chitosan Nanoparticle-Schiff Base Modified Carbon Paste Electrode as a Sensor for the Determination of Pb(II) in Waste Water. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 2164–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Fan, L.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Chitosan- metal complex as antimicrobial agent: Synthesis, Characterization and Structure–activity study. Polym. Bulletin. 2005, 55, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, ES. Characterization and properties of chitosan in Elnashar PM (ed). Biotechnology of Biopolymers 2011, 90–109. [Google Scholar]
- Tran DL, Vu Dinh H, Le Ngoc, Lien, Nguyen NT and Pham GD (2004). Synthesis and Chacterisation of Chitosan nanoparticles Used as Drug Carrier.1-6. Available online: https.//Www. Research Gate. Net.
- Sashikala, S.; Syed, S.S. Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial activity of chitosan 4-chlorobenzaldehye Schiff base. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2015, 5, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Antony, R.; David, S.T.; Karuppasamy, K.; Saravanan, K.; Thanikaikarasan, S.; Balakumar, S. Structural, Surface, Thermal and Catalytic Properties of Chitosan Supported Cu(II) Mixed Ligand Complex Materials. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 2, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. Biological activities of chitosan and chitooligosaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enaroseha, O.O.; Akpojotor, G.E. Superconductivity Driven by Magnetic Instability in CeCu2Si2. Adv. Phys. Theor. Appl. 2013, 18, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Enaroseha, O.O.; Oyibo, O.; Okpara, N. Analysis of Ground State Properties of Interacting Electrons in the Anderson Model. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2021, 8, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Enaroseha, O.O.; Oyibo, O.; Osiga–Aibangbee, D.; Odia, E.M. Magnetic Phase Diagram in the Periodic Anderson Model (PAM): An Exact Diagonalization Approach. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2021, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Enaroseha, O.; Omamoke, E.; Omehe, N.N. Heat Transfer in Circular Tubes with Supercritical Fluid Using the STAR CCM + CFD Code. Afr. J. Res. Phys. Sci. 2020, 10, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Enaroseha, O.O.; Osuhor, P.O.; Oyibo, O.; Ojegu, E.O. Theoretical Study of Phonon Spectra in Aluminium (Al) and Copper (Cu): Application of Density Functional Theory and Inter– Atomic Force Constant. Solid State Technol. 2021, 64, 1984–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Enaroseha, O.O.; Oyibo, O.; Osuhor, P.O.; Oghenerhoro, O. Lattice Dynamics in Some FCC Metals: Application of Phonon Dispersions in Nickel (Ni) and Platinium (Pt). Solid State Technol. 2021, 64, 4640–4655. [Google Scholar]
- Enaroseha, O.; Omamoke, E. Ab Initio Investigation of AgGa2 and AgGaSe2. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Enaroseha, O.O.; Oyibo, O.; Osiga–Aibangbee, D.; Odia, E.M. Magnetic Phase Transition in the Periodic Anderson Model (PAM): An Exact – Diagonalization Approach. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2021, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
| Materials | Colour |
|---|---|
| Chitosan | Off-white |
| Chitosan nanoparticle | White |
| Chitosan n-benzaldehyde Schiff base | Deep yellow |
| Chitosannanoparticlen-benzaldehydeSchiff base | Deep yellow |
| Fe (III) Chitosan n-benzaldehyde Schiff base | Brown |
| Fe (III) Chitosannanoparticlen-benzaldehydeSchiff base | Brown |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





