Submitted:
14 July 2023
Posted:
17 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
0. Introduction
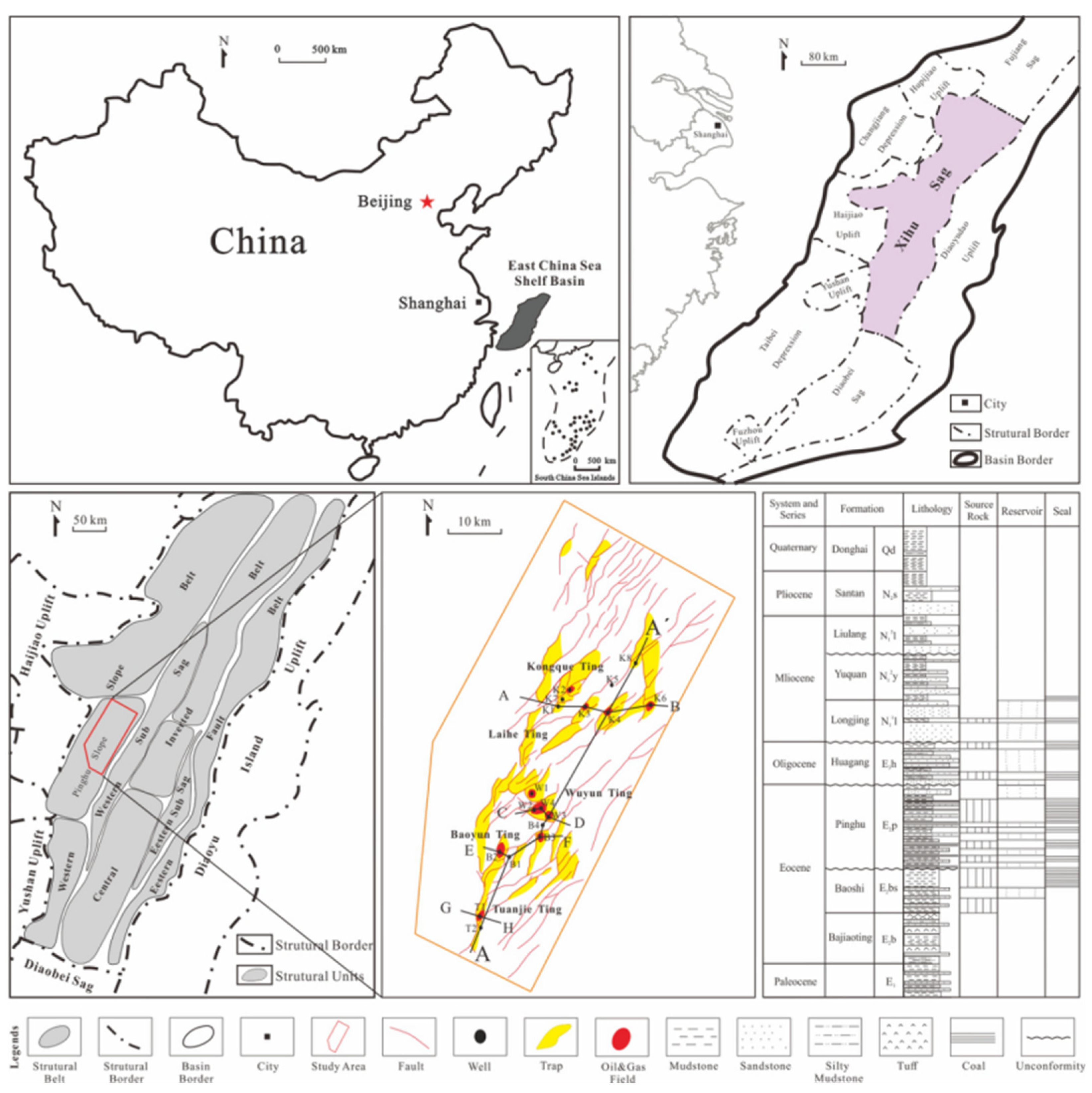
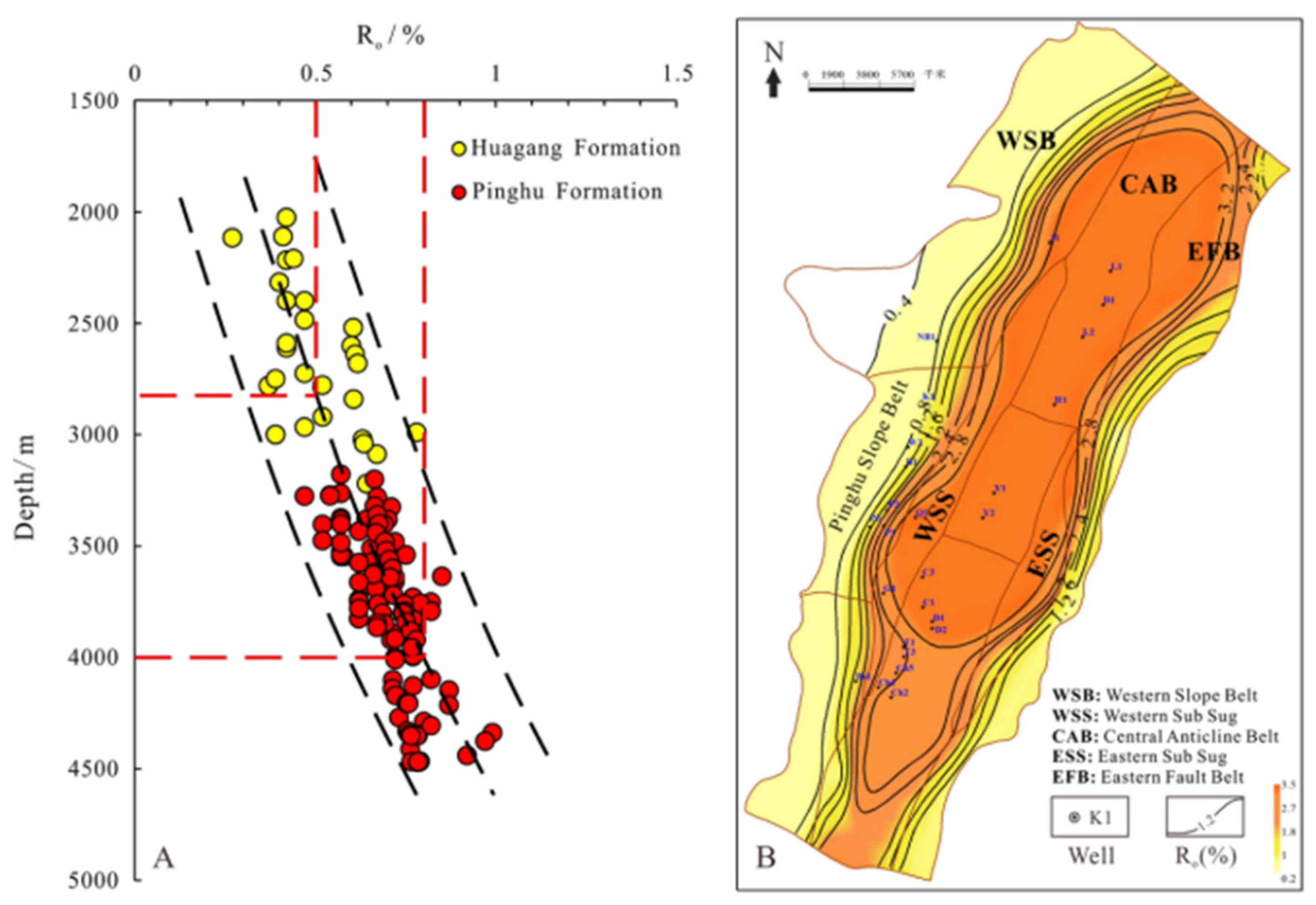
1. Geological background
2. Sampling and methodology
2.1. Sampling locations and data collection
2.2. Experimental methods
3. Results
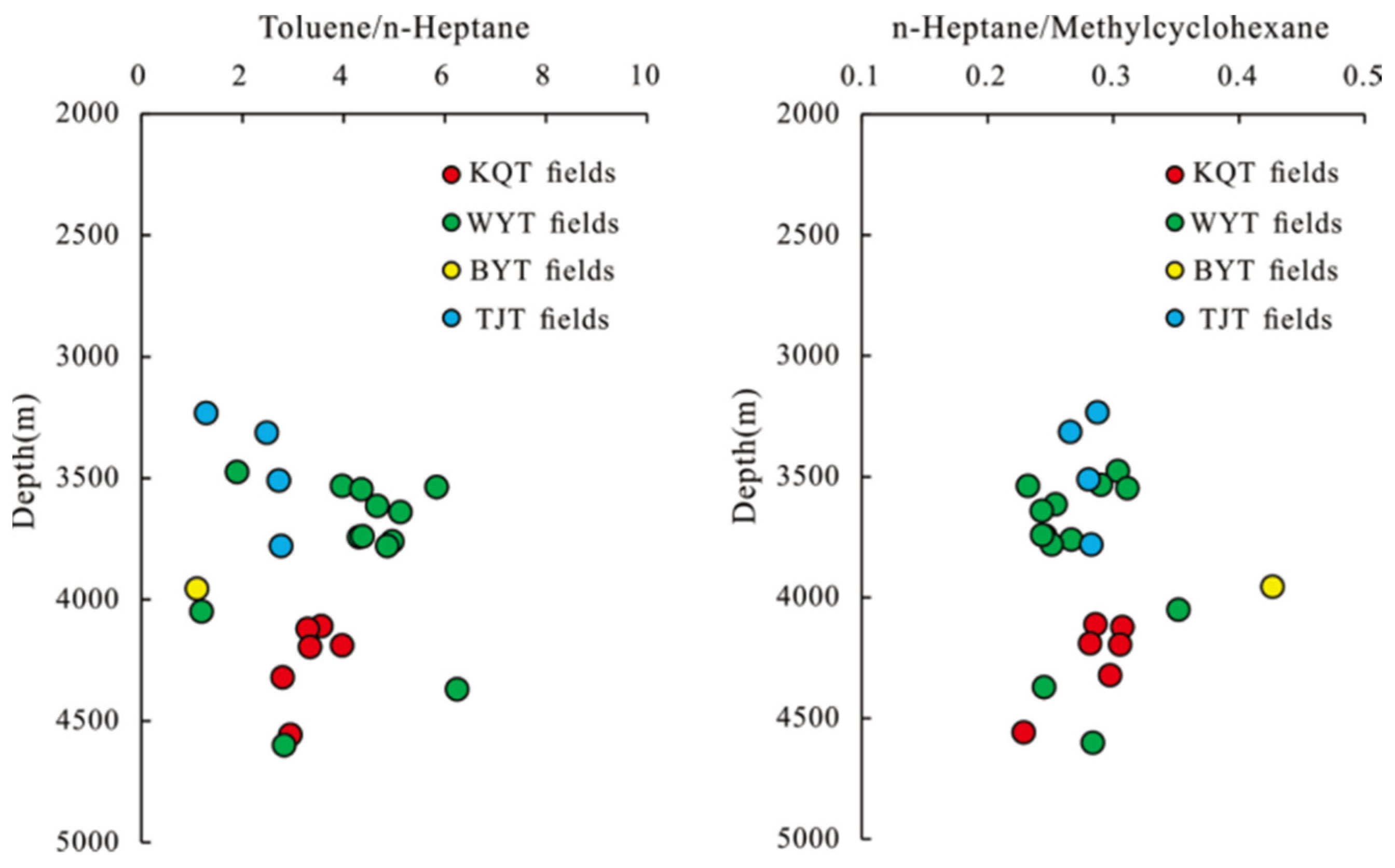
3.1. Chemical compositions of the oil and gas
| Well | Depth/m | Formation | δ13C1 | δ13C2 | δ13C3 | δ13iC4 | δ13nC4 | δ13CO2 | Rog/% |
| K2* | 4160 | E2p | -37.1 | -22.7 | -20.8 | -19.8 | -21.7 | / | 0.9 |
| K3* | 4116 | E2p | -37.8 | -27.2 | -25.4 | -26.1 | -24.6 | / | 0.8 |
| K4 | 4190 | E2p | -35.4 | -25.7 | -24.4 | -25.4 | -24.8 | / | 0.9 |
| 4557 | E2p | -37.6 | -27.5 | -26.1 | -27.4 | -25.9 | / | 0.8 | |
| K6* | 4238 | E3h | -33.5 | -26.3 | -24.0 | -23.7 | -23.0 | -5.2 | 1.0 |
| 4818 | E2p | -33.6 | -28.4 | -27.1 | -22.7 | -22.7 | -5.6 | 1.0 | |
| K7 | 4121 | E2p | -34.6 | -25.3 | -24.5 | -26.8 | -25.4 | -10.6 | 1.0 |
| W3 | 4371 | E2p | -33.9 | -25.3 | -24.2 | -25.8 | -24.8 | -5.9 | 1.0 |
| 4600 | E2p | -41.0 | -28.6 | -26.1 | / | / | -4.8 | 0.7 | |
| W4* | 3532 | E2p | -35.2 | -26.7 | -24.5 | -25.1 | -23.7 | -6.6 | 1.0 |
| 3537 | E2p | -35.4 | -26.9 | -24.7 | -25.3 | -24.2 | -7.1 | 0.9 | |
| 3614 | E2p | -35.6 | -26.7 | -24.6 | -25.4 | -23.8 | -8.8 | 0.9 | |
| 3641 | E2p | -36.2 | -26.0 | -23.7 | -24.8 | -23.0 | -9.4 | 0.9 | |
| 3740 | E2p | -36.6 | -28.5 | -25.9 | -27.0 | -24.7 | -9.8 | 0.9 | |
| 3744 | E2p | -37.1 | -26.3 | -23.7 | -24.8 | -23.0 | -7.3 | 0.9 | |
| 3760 | E2p | -36.4 | -25.9 | -23.3 | -24.3 | -22.6 | -9.4 | 0.9 | |
| 3780 | E2p | -37.1 | / | / | / | / | / | 0.9 | |
| 4050 | E2p | -39.9 | -29.5 | -27.3 | -28.7 | -26.2 | -10.6 | 0.8 | |
| 4056 | E2p | -39.9 | -29.5 | -27.4 | -28.9 | -26.1 | -10.6 | 0.8 | |
| B1 | 3774 | E2p | -34.3 | -27.4 | -27.4 | / | -27.1 | -18.9 | 1.0 |
| 3955 | E2p | -35.0 | -30.9 | -27.8 | / | -26.3 | -19.8 | 1.0 | |
| B2 | 3455 | E2p | -33.7 | -26.7 | -22.1 | / | -30.1 | -15.6 | 1.0 |
| 3773 | E2p | -34.7 | -27.1 | -25.7 | / | -24.9 | -17.3 | 1.0 | |
| T1* | 2848 | E3h | -42.5 | -27.4 | -25.8 | -26.9 | -25.3 | -6.7 | 0.7 |
| 3233 | E2p | -37.2 | -27.4 | -26.2 | -27.5 | -25.3 | -7.0 | 0.9 | |
| 3314 | E2p | -35.5 | -27.3 | -26.2 | -27.3 | -25.2 | -7.7 | 0.9 | |
| T2 | 3510 | E2p | -36.0 | -27.4 | -26.3 | -27.6 | -25.7 | / | 0.9 |
| 3780 | E2p | -36.2 | -27.5 | -26.2 | -27.4 | -25.4 | / | 0.9 |
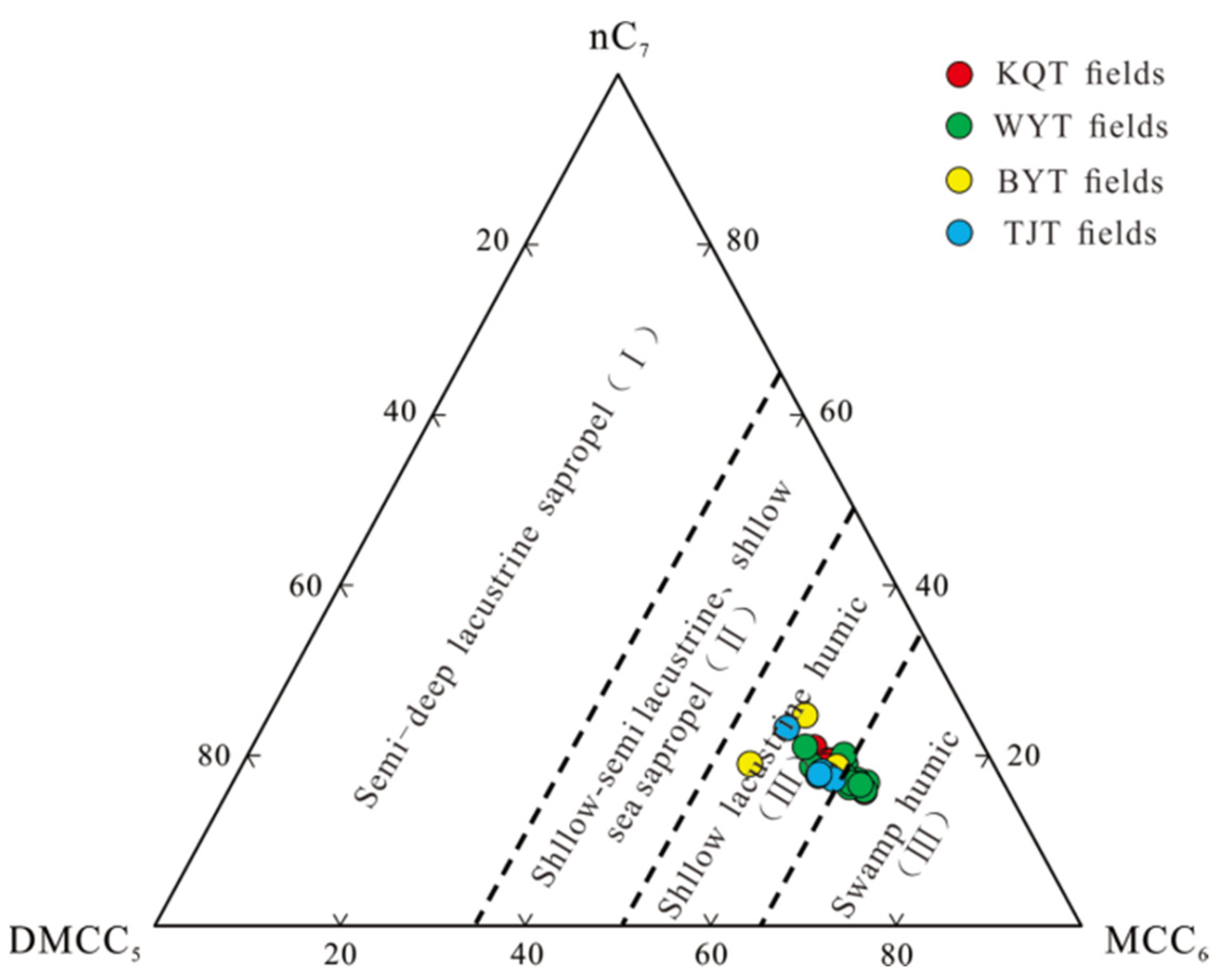
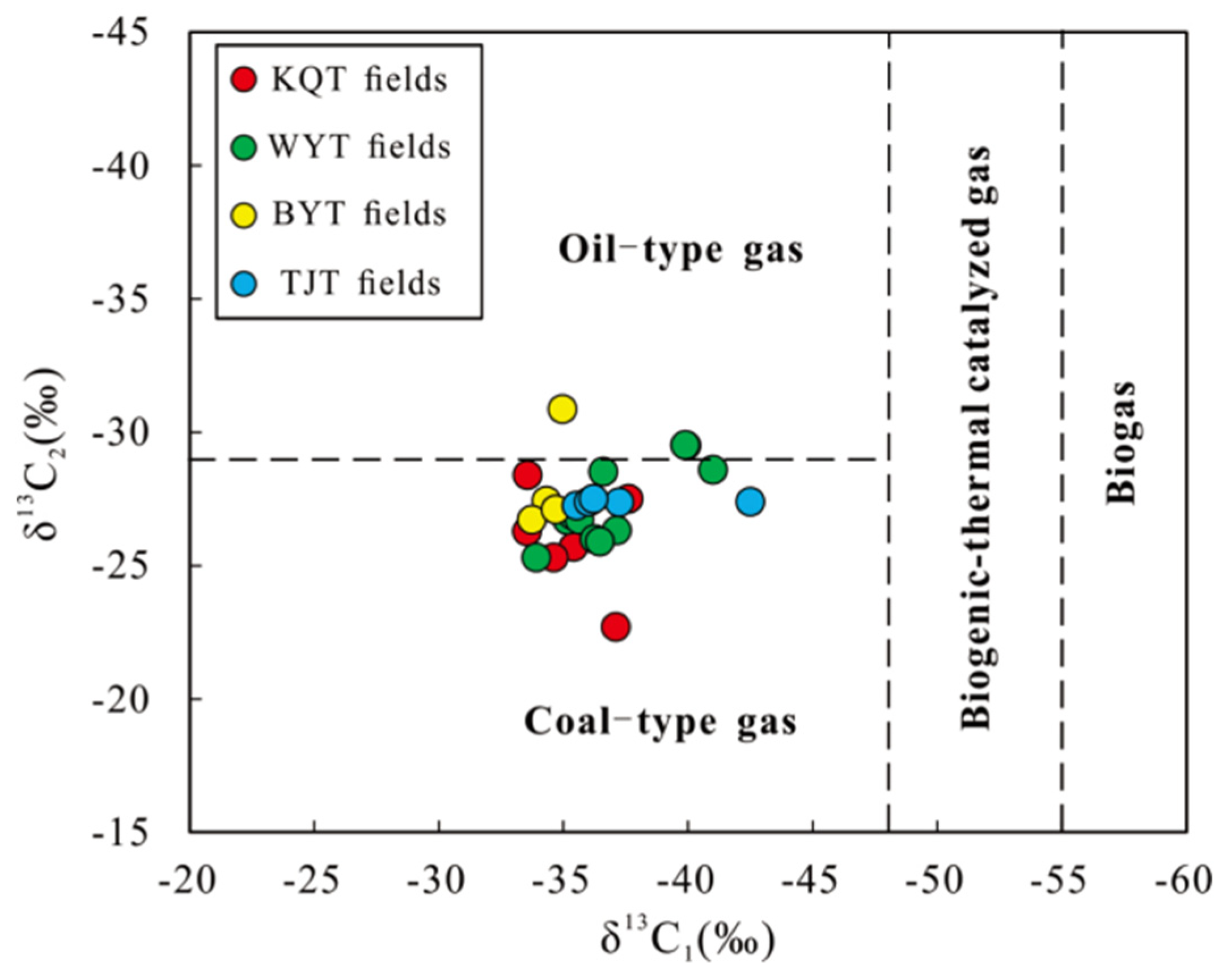
3.2. Genesis of oil and gas
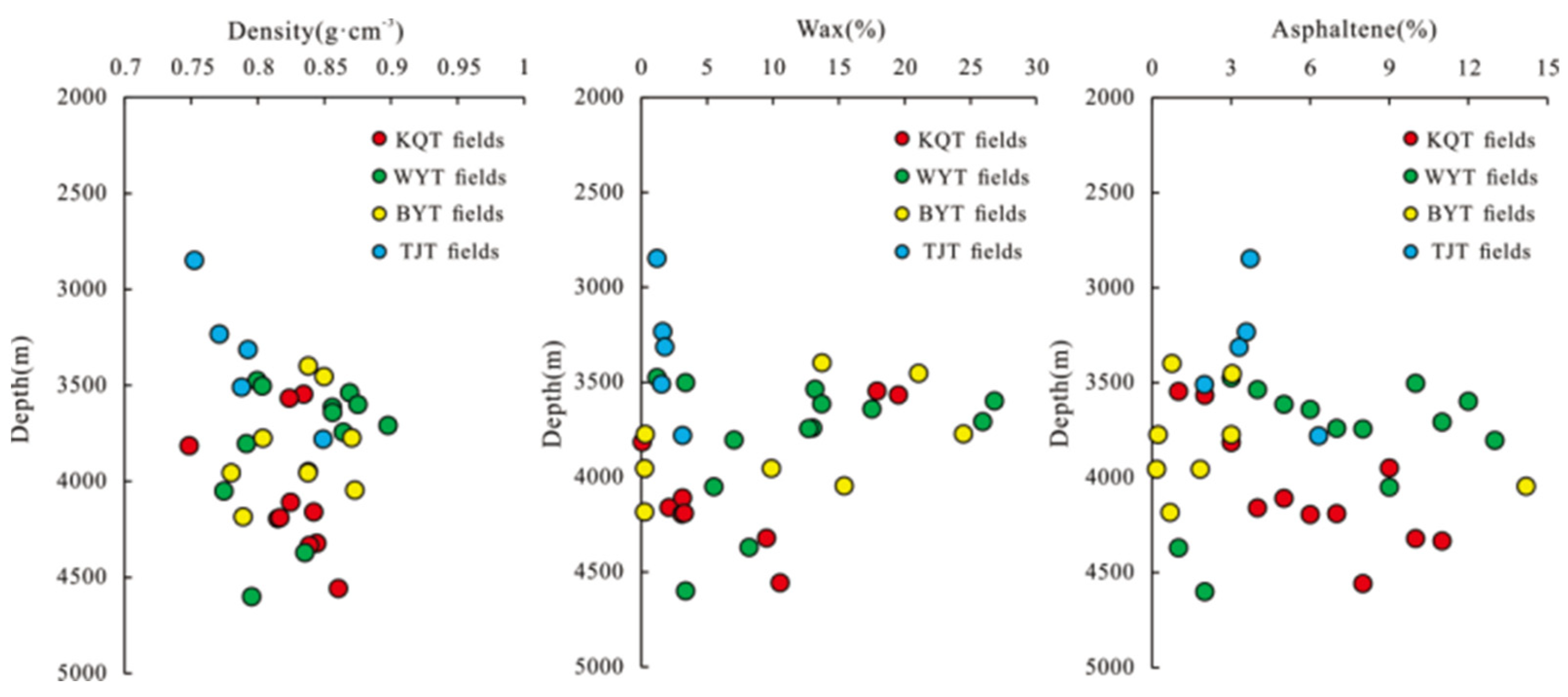
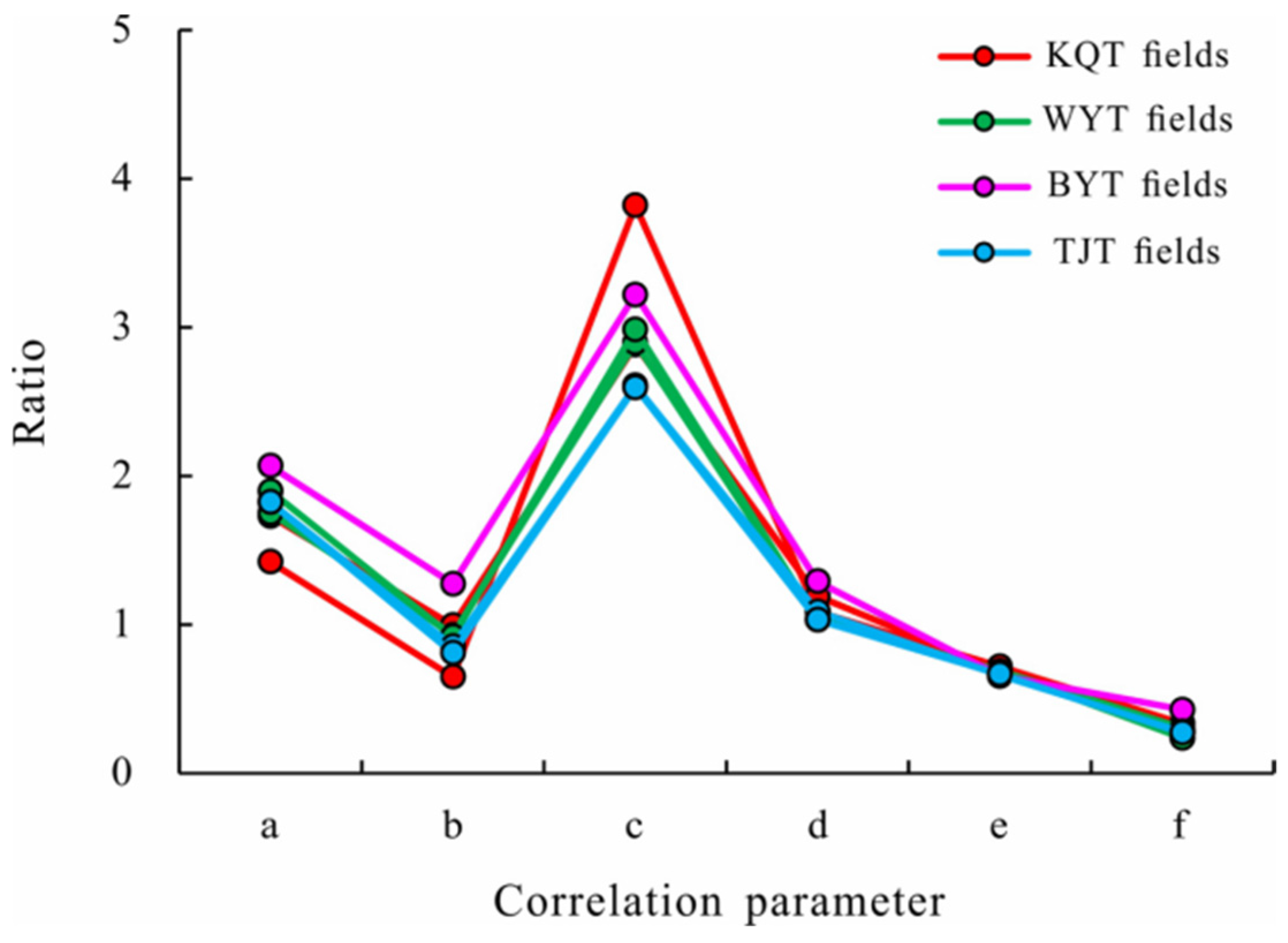
3.3. Maturity of oil and gas
| Well | Depth/m | Formation | K1 | T/℃ | RoK/% | MPI1 | RoP/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2* | 4160 | E2p | 1.20 | 123.14 | 0.8 | 0.84 | 0.9 |
| K3* | 4116 | E2p | 1.18 | 130.24 | 0.9 | 1.02 | 1.0 |
| 4195 | E2p | 1.17 | 130.91 | 0.9 | 1.01 | 1.0 | |
| K4* | 4190 | E2p | 1.18 | 130.69 | 0.9 | 0.97 | 1.0 |
| 4557 | E2p | 1.23 | 126.22 | 0.9 | 0.71 | 0.8 | |
| K5 | 4321 | E2p | 1.18 | 130.97 | 0.9 | 1.04 | 1.0 |
| W3 | 4371 | E2p | 1.19 | 131.08 | 0.9 | 1.15 | 1.1 |
| 4600 | E2p | 1.17 | 132.39 | 1.0 | 1.00 | 1.0 | |
| W4* | 3475 | E2p | 1.20 | 130.62 | 0.9 | 0.98 | 1.0 |
| 3532 | E2p | 1.19 | 131.22 | 0.9 | 1.09 | 1.1 | |
| 3537 | E2p | 1.18 | 130.13 | 0.9 | 1.09 | 1.1 | |
| 3546 | E2p | 1.17 | 130.66 | 0.9 | 1.03 | 1.0 | |
| 3614 | E2p | 1.19 | 129.18 | 0.9 | 1.10 | 1.1 | |
| 3641 | E2p | 1.19 | 129.72 | 0.9 | 0.97 | 1.0 | |
| 3744 | E2p | 1.20 | 129.97 | 0.9 | 1.03 | 1.0 | |
| 3760 | E2p | 1.18 | 131.22 | 0.9 | 1.09 | 1.1 | |
| 3780 | E2p | 1.01 | 135.03 | 1.0 | 1.25 | 1.1 | |
| B1 | 3955 | E2p | 1.13 | 133.57 | 1.0 | 1.02 | 1.0 |
| T1* | 2848 | E3h | 1.19 | 130.81 | 0.9 | 0.74 | 0.8 |
| 3233 | E2p | 1.19 | 130.34 | 0.9 | 0.82 | 0.9 | |
| T2* | 3314 | E2p | 1.19 | 128.16 | 0.9 | 0.66 | 0.8 |
| 3510 | E2p | 1.18 | 130.81 | 0.9 | 1.26 | 1.2 | |
| 3780 | E2p | 1.18 | 130.63 | 0.9 | 1.00 | 1.0 |
4. Discussion
4.1. Origin of oil and gas
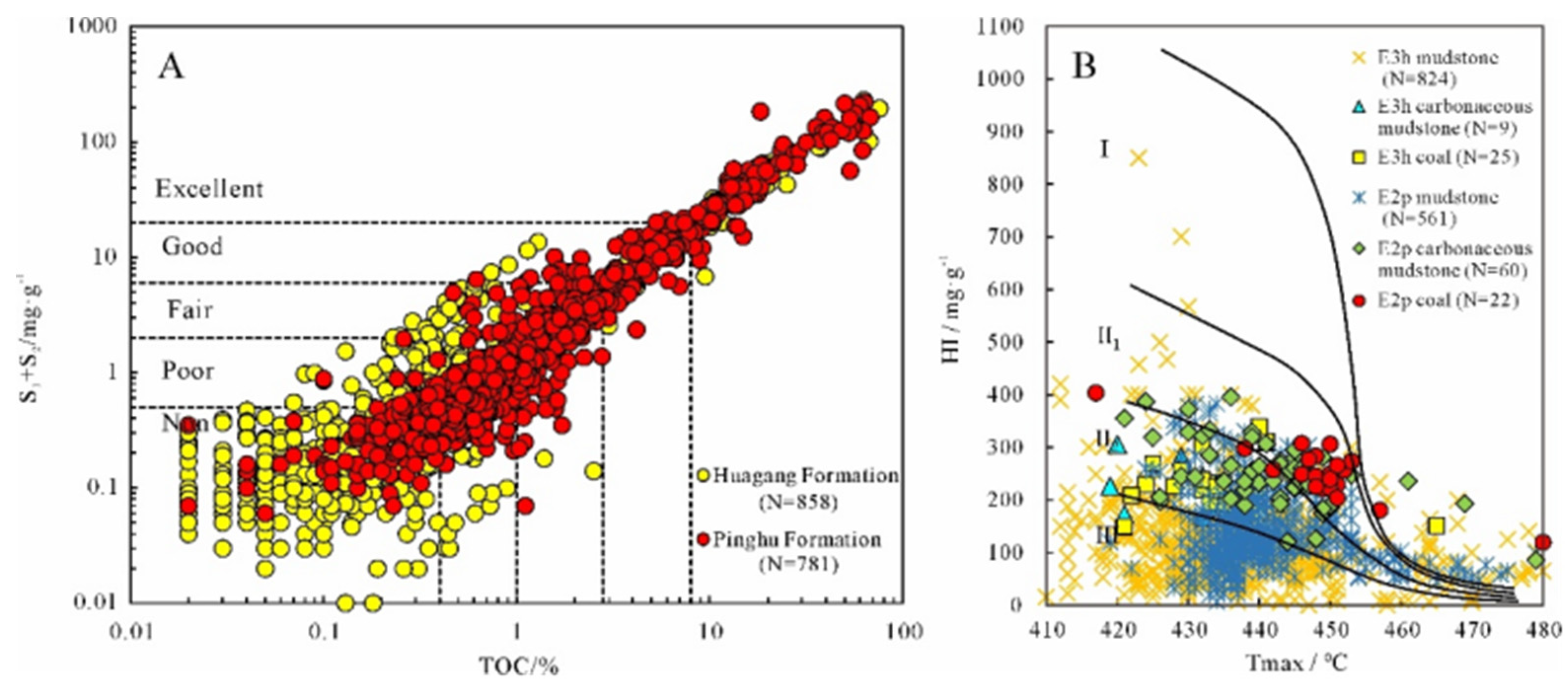
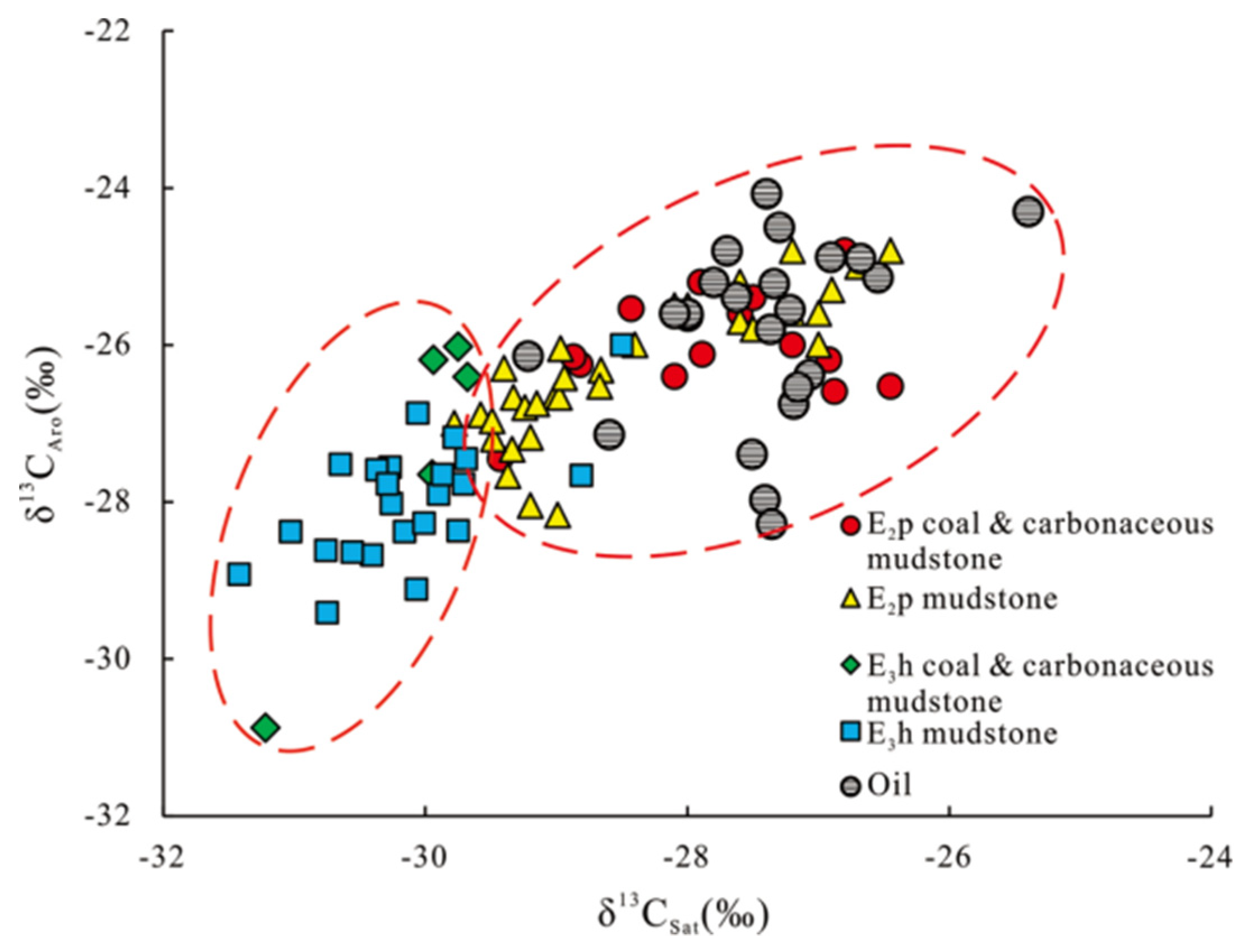
4.1.1. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks
4.1.2. Oil and gas source correlations
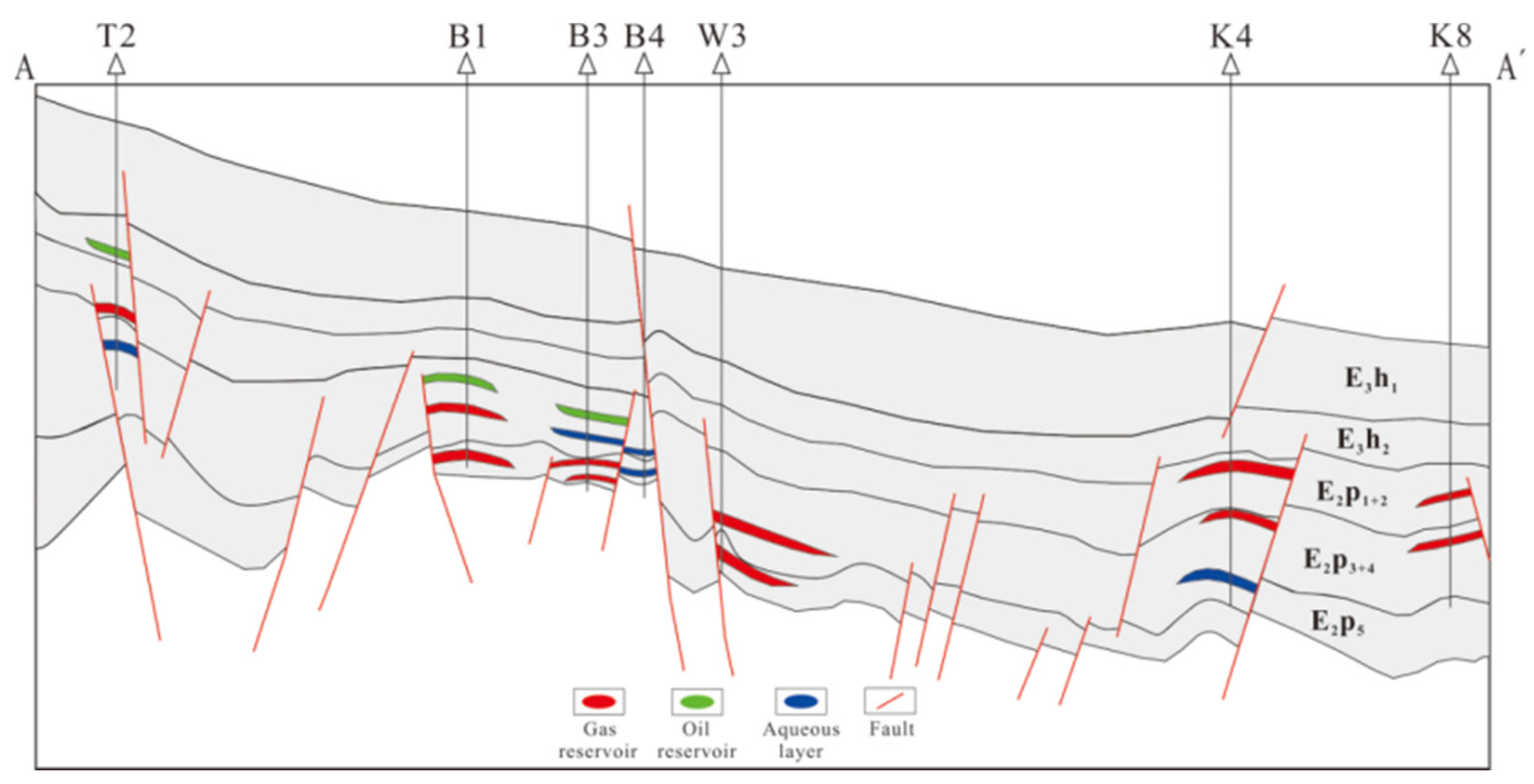
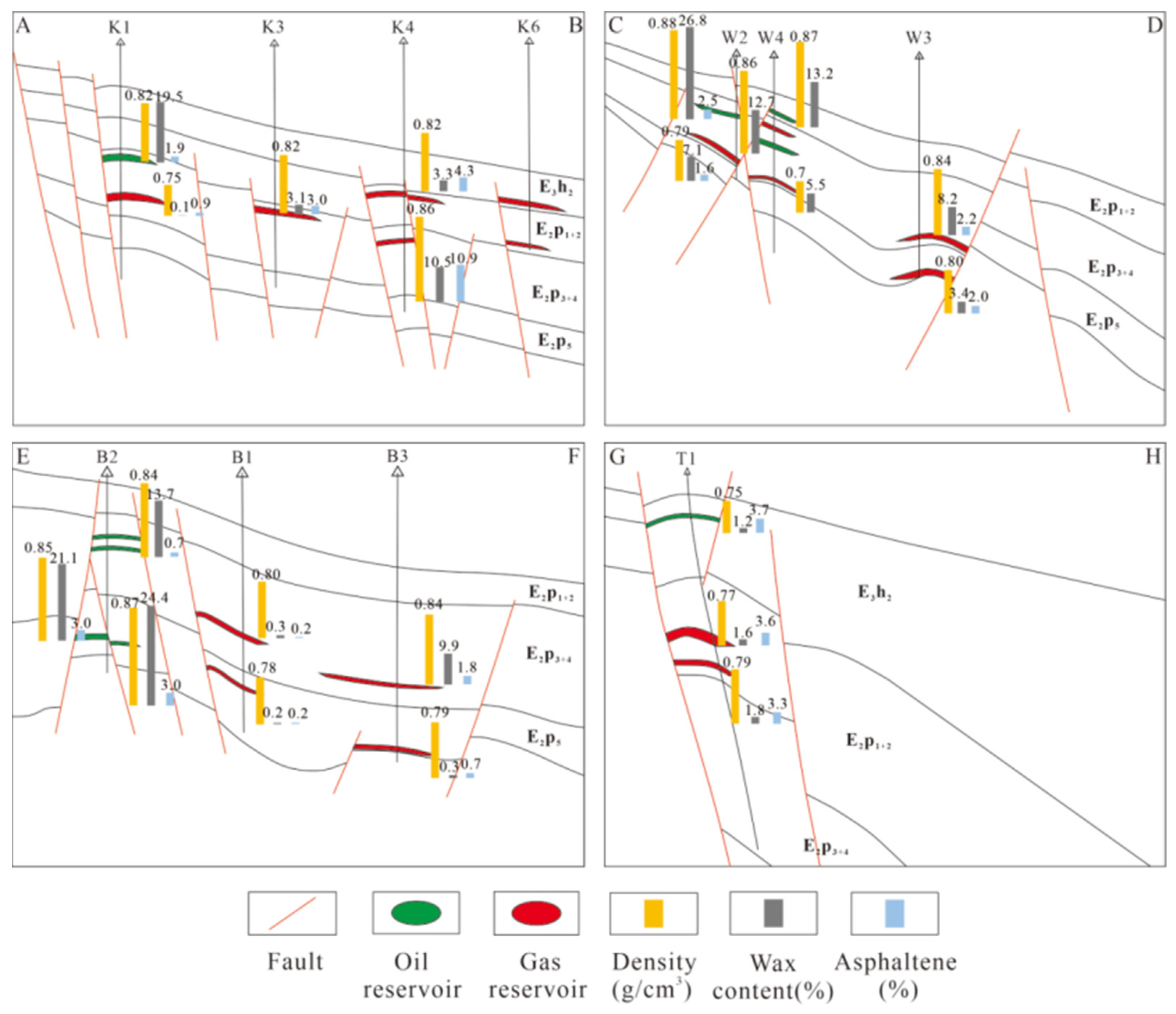
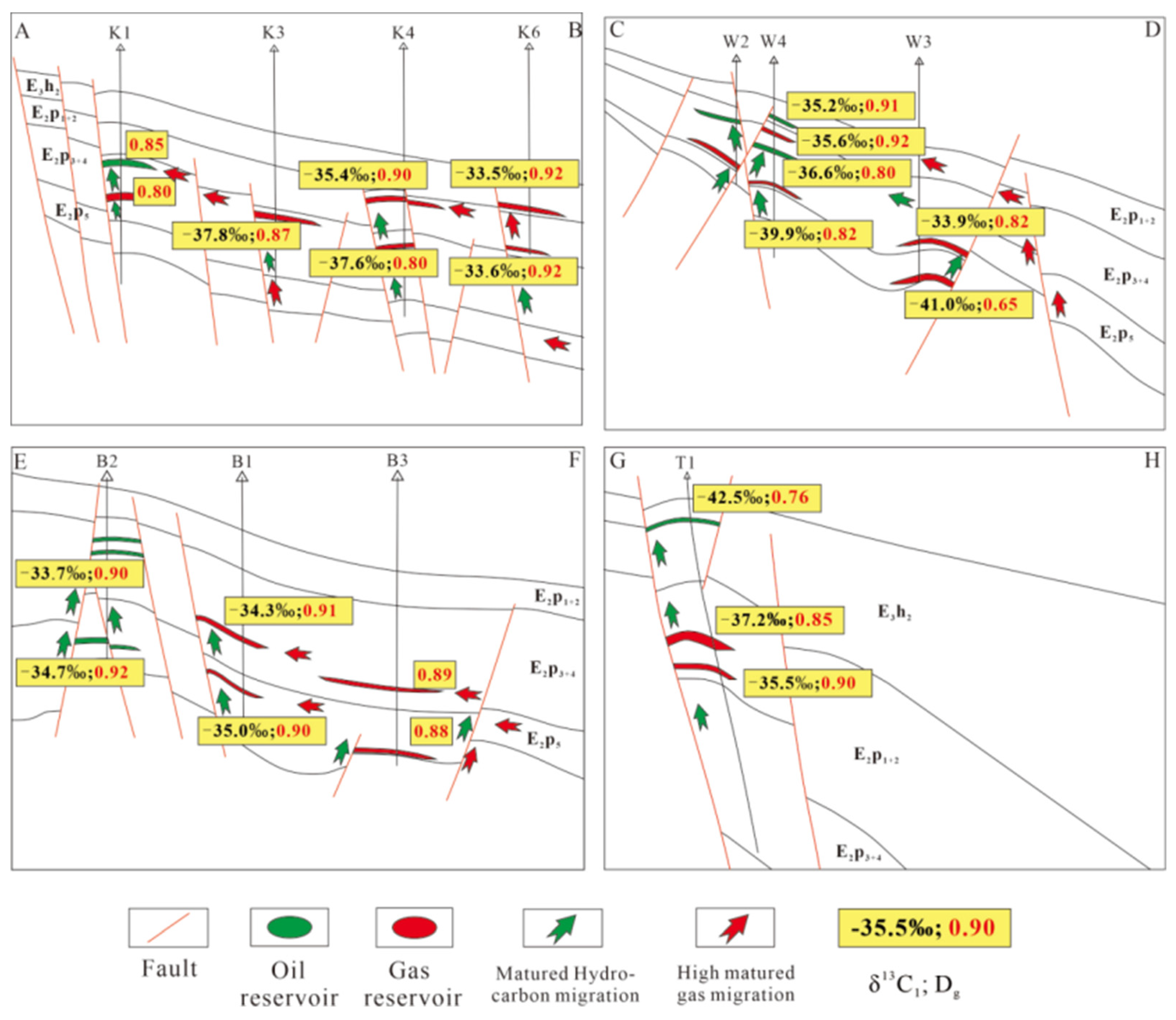
4.2. Analysis of oil and gas migration and accumulation
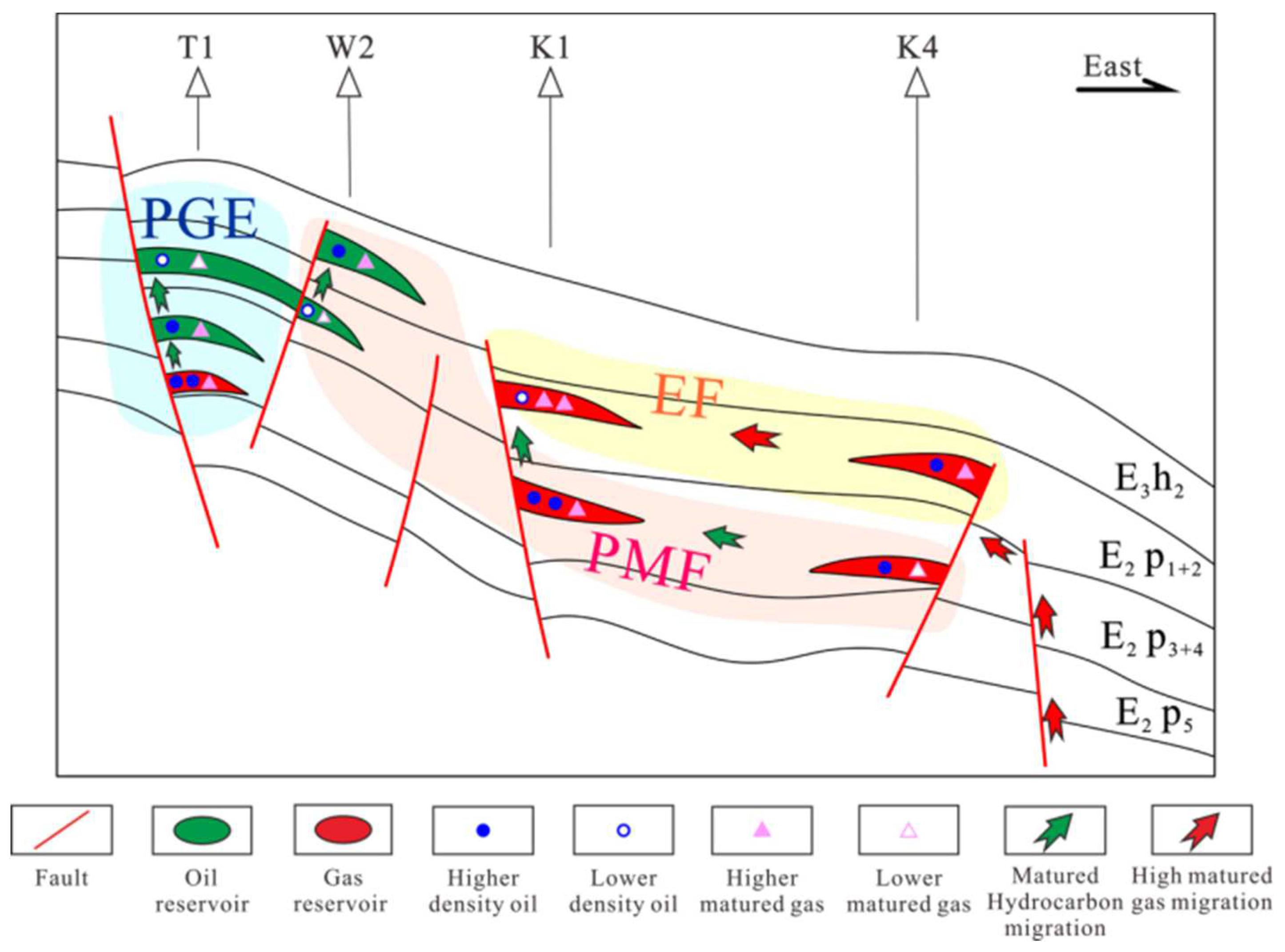
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, S.; Ye, J.; Lei, C.; Shan, C.; Tian, Y.; Liu, F. Geochemical characteristics of Pinghu crude oils in Pingbei area of Xihu Sag. Xin. Petrol. Geol. 2014, 35, 542–546. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, S.; Gao, W.; Li, N. Formation and distribution of marine-continental transitional lithologic reservoirs in Pingbei slope belt, Xihu sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. China Petrol. Exp. 2019, 24, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, W.; Lei, M. Genesis and maturity identification of oil and gas in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Petrol. Exp. Dev. 2013, 40, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, H.; Gao, M. Detection of diamantane hydrocarbons in the oil of Pinghu slope belt and its geochemical significance. J. Oil Gas Tech. 2014, 36, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Hou, D.; Cao, B. Study of precursors for condensates and light oils in Xihu Sag of East China Sea Basin. Geochim. 2015, 44, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Song, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liang, S.; Wang, L. Geochemical characteristics and source of crude oil in Xihu sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Petrol. Geol. Exp. 2019, 41, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Li, P.; Ma, L.; Liu, H. Source of natural gas in Xihu Sag of the East China Sea Basin. Geol. Sci. Tech Inform. 2014, 33, 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Cao, B.; Xu, Z.; Qin, L.; Xu, F.; Tang, J. Sedimentary facies and the characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs of Huagang Formation in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. J. CUT. 2012, 39, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Xu, X.; Sun, B. Oil/gas geochemical character in the Xihu Trough of the East China Sea. Offsho. Oil. 2000, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, M.; Gao, W.; Zhang, H. Pooling mechanisms of “evaporating fractionation” of oil and gas in Xihu Sag, East China Sea. Petrol. Exp. Dev. 2003, 30, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Miao, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Yang, S. Distribution of gas enrichment regions controlled by source rocks and geothermal heat in China Offshore Basin. Nat. Gas Industry. 2013, 33, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Pang, X. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion of tertiary coaly source rocks and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Xihu Sag of the East China Sea Shelf Basin, China. J. Asian earth sci. 2022, 22, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Gong, D.; Ni, Y. Stable carbon isotopes of coal-derived gases sourced from the Mesozoic coal measures in China[J]. Org. Geochem. 2014, 74, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X. The geochemical characteristics, genetic types and sources analysis of natural gas in Pingbei area, Xihu Sag. China Offshore Oil. Gas. 2019, 31, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Ge, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B. The development and application fingerprint parameters for hydrocarbons absorbed by source rocks and light hydrocarbons in natural gas. Petrol. Geol. Exp. 1990, 12, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J. Identification and distinction of various alkane gases. Sci. China B. 1992, 2, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, W. A new genetic type of natural gas: biogenic-thermal catalyzed gas. Sci. China B. 1992, 20, 975–980. [Google Scholar]
- Mango, F. An invariance in the isoheptanes of petroleum. Science, 1987, 237, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, F. The light hydrocarbons in petroleum: a critical review. Org. Geochem. 1997, 26, 417–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Huang, G. Compositions and geochemical characteristics of light hydrocarbons in typical marine oils and typical coal-formed oils. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2008, 19, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, M. Application of aromatic compounds as maturity indicators in source rocks and crude oils. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 1988, 5, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, W.; Lei, M. Genesis and maturity identification of oil and gas in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Petrol. Exp. Dev. 2013, 40, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J. Geochemical characteristics and sources of natural gas in the northern Xihu Sag. Nat. Gas Industry, 2019, 39, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Y. A two-stage model of carbon isotopic fractionation in coal-gas. Geochim. 1999, 28, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Z.G. Tong, Z.; He, Q.; He, S.; Yang, S.; Xiong, B.; Hao, J. Geothermal field and its effect on source rock in the Xihu Sag, the East China Sea Basin. Petrol. Geol. Exp. 2009, 31, 466–471. [CrossRef]
- Erdman, J.; Morris, D. Geochemical correlation of petroleum. AAPG Bull. 1974, 58, 2326–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, W.J. Source rock-crude oil correlation by isotopic type-curves. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 1978, 42, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Xu, Y. Study on carbon and hydrogen isotopes composition of crude oils. Ac. Sedim. Sin. 1998, 16, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, K. Fractionated aromatic petroleums and the generation of gas-condensates. Organic Geochemistry 1987, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Hu, S.; Wang, H.; Wen, Y. Study on carbon and hydrogen isotopes composition of crude oils. J. Oil Gas Tech. 2014, 36, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Li, C.; Zhang, D. Geochemistry of petroleum migration during the formation of Karamay Oilfield. Sci. China, Seb.B. 1989, 02, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, S. Genetic analysis of waxy hydrocarbons in lower paleozoic source oil of manjiaer oil and gas system in Tarim Basin. Acta Sedim. Sin., 1997, 02, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, S.; Su, A. Geochemistry in the process of petroleum migration and accumulation. Petrol. Geo. & Exp., 2001, 23, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, S. Genetic analysis of the origin of the Lower Paleozoic waxy hydrocarbon from the Manjiar oil-gas system, Tarim Basin. Ac. Sedim. Sin. 1997, 15, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Larter, S.; Mills, N. phase-controlled transport fractionations in migrating. In: England W A, eds. Petroleum Migration. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1991, 59, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Gu, H. Fluid history analysis in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea. Nat. Gas Industry. 2006, 26, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Xiang, Y. Play evolution analysis of Xihu Sag. Offsho. Oil. 2009, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Ye, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, J. Characteristics and hydrocarbon generation-expulsion histories of source rocks of Pingbei area in Xihu Sag. Offsho. Oil. 2009, 29, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, H. The key factor controlling hydrocarbon accumulation in Xihu Sag. Offsho. Oil. 2008, 23, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.; Lei, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, H. Application of PVTx simulation of fluid inclusions to estimate petroleum charge stages and restore pressure: using Pinghu structural belt in Xihu Sag as an example. Geol. Sci. Tech. Inf. 2014, 33, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.H.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, P. Coupling relationship between diagenetic evolution and oil and gas accumulation of tight sandstone reservoir in Pinghu structural belt in Xihu Sag, Eastern Sea Basin. J. CSU Sci. 2015, 46, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Petroleum Geology. Beijing, Petrol. Industry Pre. 1990, 1, 152–167. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Pei, X.; Qi, H. Natural Gas Geology in China. Beijing, Petrol. Industry Pre. 1992, 1, 225–284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Tian, C. Fractures in the Pingbei area and their control on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Xihu Sag of the East China Sea. Sh. Lan. Re. 2014, 35, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
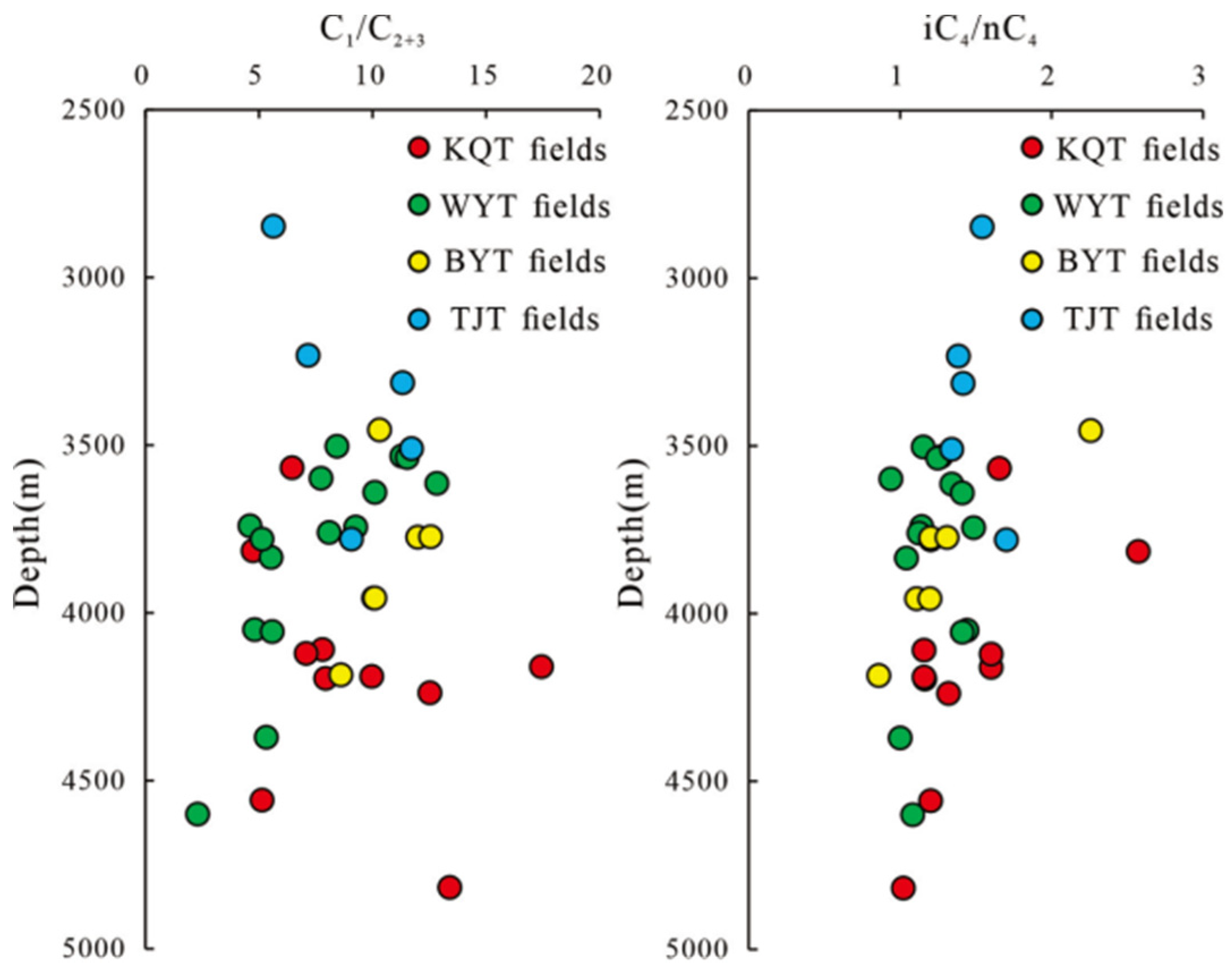
| Well | Depth/m | Formation | C1/% | C2/% | C3/% | iC4/% | nC4/% | iC5/% | nC5/% | N2/% | CO2/% | Dg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 3567 | E2p | 79.03 | 8.68 | 3.54 | 0.96 | 0.58 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 4.19 | 2.72 | 0.85 |
| 3815 | E2p | 75.96 | 10.33 | 5.70 | 1.80 | 0.70 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 1.70 | 3.40 | 0.80 | |
| K2* | 4160 | E2p | 89.10 | 4.48 | 0.63 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.36 | 5.00 | 0.94 |
| K3* | 4116 | E2p | 81.02 | 7.35 | 3.03 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 6.19 | 0.87 |
| 4195 | E2p | 81.42 | 7.29 | 2.97 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 6.19 | 0.87 | |
| K4 | 4190 | E2p | 85.51 | 6.28 | 2.30 | 0.59 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 4.11 | 0.90 |
| 4557 | E2p | 73.20 | 8.43 | 5.83 | 1.68 | 1.40 | 0.49 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 7.79 | 0.80 | |
| K6* | 4238 | E3h | 89.82 | 5.51 | 1.66 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 1.99 | 0.92 |
| 4818 | E2p | 91.61 | 5.33 | 1.50 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.92 | |
| K7 | 4121 | E2p | 79.43 | 8.38 | 2.84 | 1.04 | 0.65 | 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.59 | 6.29 | 0.86 |
| W1* | 3503 | E2p | 86.70 | 7.19 | 3.08 | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 1.29 | 0.88 |
| W2* | 3599 | E2p | 84.89 | 7.80 | 3.17 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 1.79 | 0.87 |
| 3834 | E2p | 80.82 | 9.84 | 4.79 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.34 | 1.70 | 0.83 | |
| W3 | 4371 | E2p | 77.24 | 10.11 | 4.37 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 1.28 | 4.38 | 0.82 |
| 4600 | E2p | 59.47 | 14.97 | 10.95 | 2.81 | 2.60 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 7.87 | 0.00 | 0.65 | |
| W4* | 3532 | E2p | 87.88 | 5.76 | 2.02 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.61 | 2.94 | 0.91 |
| 3537 | E2p | 88.22 | 5.76 | 1.89 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 3.43 | 0.91 | |
| 3614 | E2p | 89.56 | 5.18 | 1.80 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.81 | 1.84 | 0.92 | |
| 3641 | E2p | 87.73 | 6.28 | 2.41 | 0.53 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.57 | 1.92 | 0.90 | |
| 3740 | E2p | 76.73 | 10.98 | 5.71 | 1.21 | 1.06 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 3.60 | 0.80 | |
| 3744 | E2p | 83.44 | 6.70 | 2.30 | 0.40 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 4.16 | 2.64 | 0.90 | |
| 3760 | E2p | 84.18 | 7.53 | 2.88 | 0.59 | 0.53 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.90 | 3.12 | 0.88 | |
| 3780 | E2p | 77.37 | 10.35 | 4.72 | 0.94 | 0.79 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 1.66 | 4.02 | 0.82 | |
| 4050 | E2p | 76.30 | 9.74 | 6.14 | 1.83 | 1.27 | 0.44 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 3.53 | 0.80 | |
| 4056 | E2p | 79.05 | 8.97 | 5.17 | 1.58 | 1.12 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.00 | 3.29 | 0.82 | |
| B1 | 3774 | E2p | 88.16 | 4.84 | 2.51 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.60 | 2.52 | 0.91 |
| 3955 | E2p | 86.47 | 5.58 | 3.02 | 0.62 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 1.56 | 1.96 | 0.90 | |
| B2 | 3455 | E2p | 89.21 | 5.98 | 2.67 | 0.88 | 0.39 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.08 | 0.90 |
| 3773 | E2p | 88.59 | 5.43 | 1.62 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 2.00 | 1.61 | 0.92 | |
| B3* | 3955 | E2p | 86.82 | 5.42 | 3.18 | 0.80 | 0.67 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.44 | 2.41 | 0.89 |
| 4184 | E2p | 86.92 | 6.94 | 3.16 | 0.60 | 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 1.01 | 0.88 | |
| T1* | 2848 | E3h | 73.08 | 7.06 | 5.89 | 4.36 | 2.83 | 1.77 | 0.89 | 1.89 | 1.55 | 0.76 |
| 3233 | E2p | 81.80 | 6.97 | 4.46 | 1.44 | 1.04 | 0.36 | 0.19 | 1.31 | 2.26 | 0.85 | |
| 3314 | E2p | 87.58 | 5.22 | 2.51 | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.85 | 2.03 | 0.90 | |
| T2 | 3510 | E2p | 87.51 | 5.07 | 2.40 | 0.63 | 0.47 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.54 | 2.94 | 0.91 |
| 3780 | E2p | 87.06 | 5.57 | 4.02 | 1.31 | 0.77 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 0.88 |
| Well | Depth/m | Formation | δ13C/‰, PDB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil | Sat | Aro | Nso | Asp | |||
| K2 | 4160 | E2p | -24.8 | -25.4 | -24.3 | / | / |
| K5 | 4321 | E2p | -26.9 | -27.2 | -25.6 | -26.7 | -27.3 |
| W3 | 4371 | E2p | -25.9 | -27.3 | -24.5 | / | / |
| 4600 | E2p | -26.2 | -27.7 | -24.8 | / | / | |
| W4 | 3475 | E2p | -27.3 | -27.5 | -27.4 | -28.9 | -28.3 |
| 3532 | E2p | -27.3 | -27.4 | -28.0 | -29.7 | -28.1 | |
| 3537 | E2p | -27.2 | -28.0 | -25.6 | -26.4 | -27.5 | |
| 3546 | E2p | -27.0 | -27.1 | -26.4 | -27.7 | -27.5 | |
| 3614 | E2p | -26.6 | -27.6 | -25.4 | -26.1 | -27.0 | |
| 3641 | E2p | -26.8 | -27.3 | -25.2 | -26.0 | -26.9 | |
| 3744 | E2p | -26.9 | -27.4 | -25.8 | -26.2 | -27.3 | |
| 3760 | E2p | -27.2 | -27.2 | -26.8 | -29.0 | -28.0 | |
| 3780 | E2p | -26.9 | -27.2 | -26.5 | -27.9 | -28.1 | |
| B1 | 3955 | E2p | / | -27.8 | -25.2 | -26.5 | -26.2 |
| 3774 | E2p | / | -27.4 | -24.1 | -26.8 | -27.0 | |
| B2 | 3398 | E2p | / | -28.6 | -27.1 | / | / |
| 3453 | E2p | / | -27.4 | -28.3 | -27.1 | / | |
| 3773 | E2p | / | -29.2 | -26.1 | / | / | |
| T1 | 2848 | E3h | -26.3 | -26.6 | -25.1 | / | / |
| 3233 | E2p | -26.2 | -26.9 | -24.9 | / | / | |
| 3314 | E2p | -26.1 | -26.7 | -24.9 | / | / | |
| T2 | 3510 | E2p | -26.4 | -28.0 | -25.6 | / | / |
| 3780 | E2p | -26.9 | -28.1 | -25.6 | / | / | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




