Submitted:
12 July 2023
Posted:
13 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
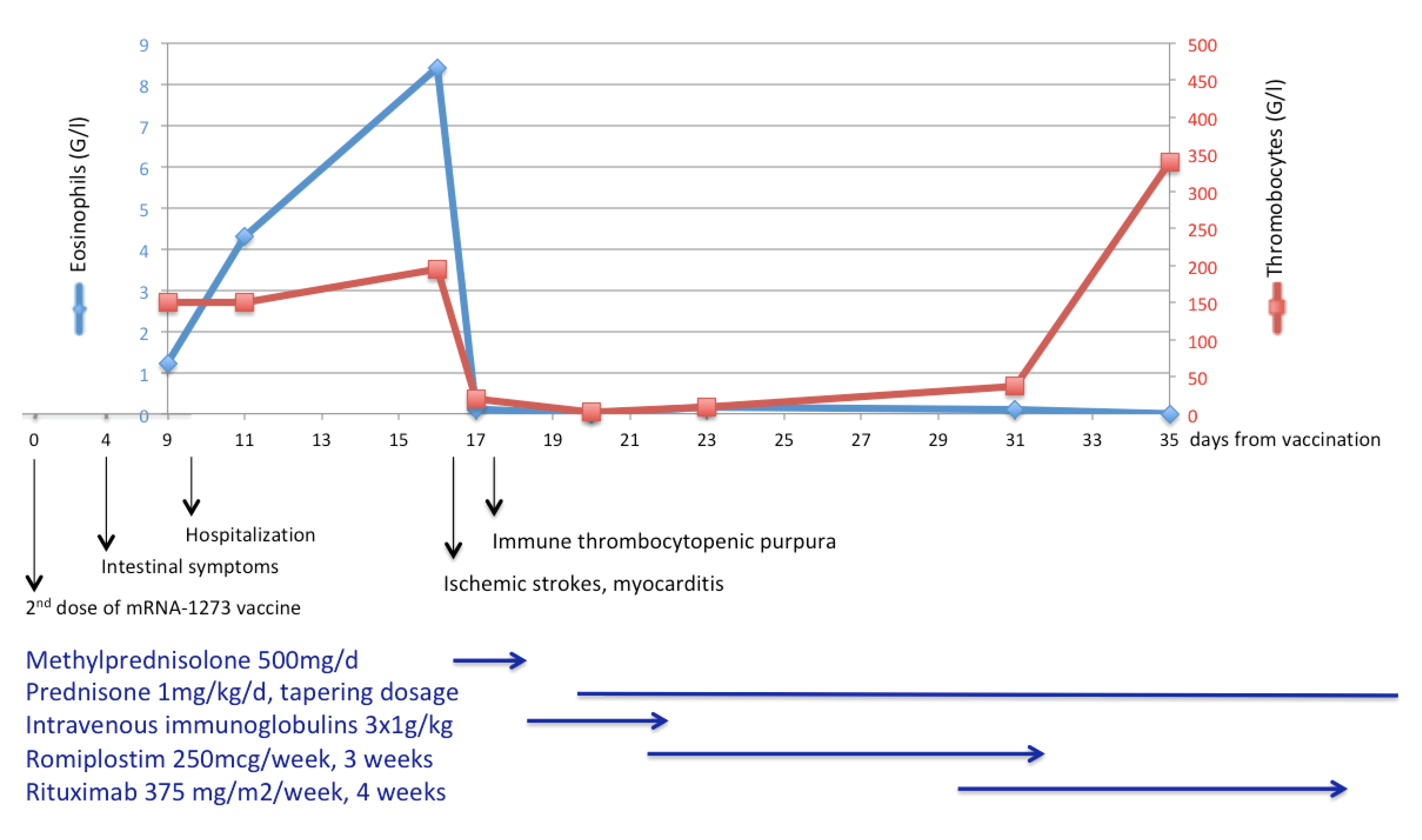
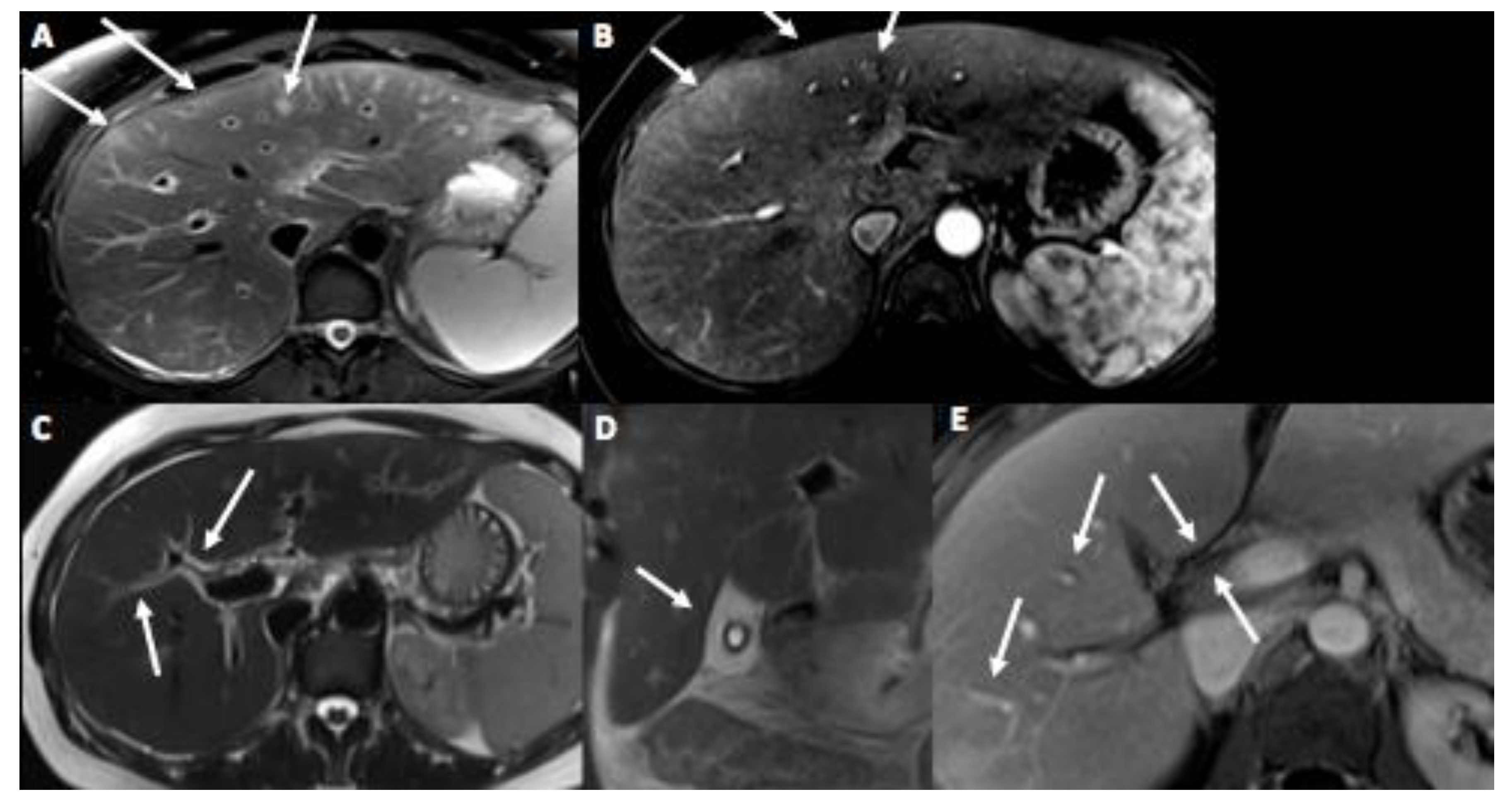
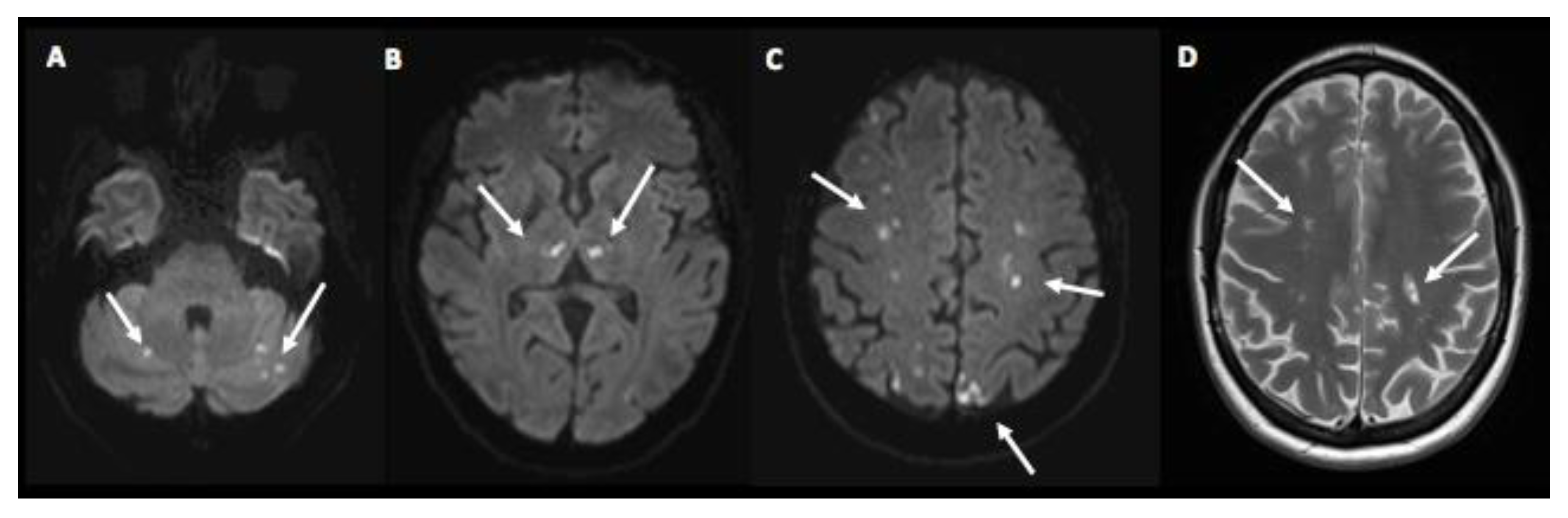
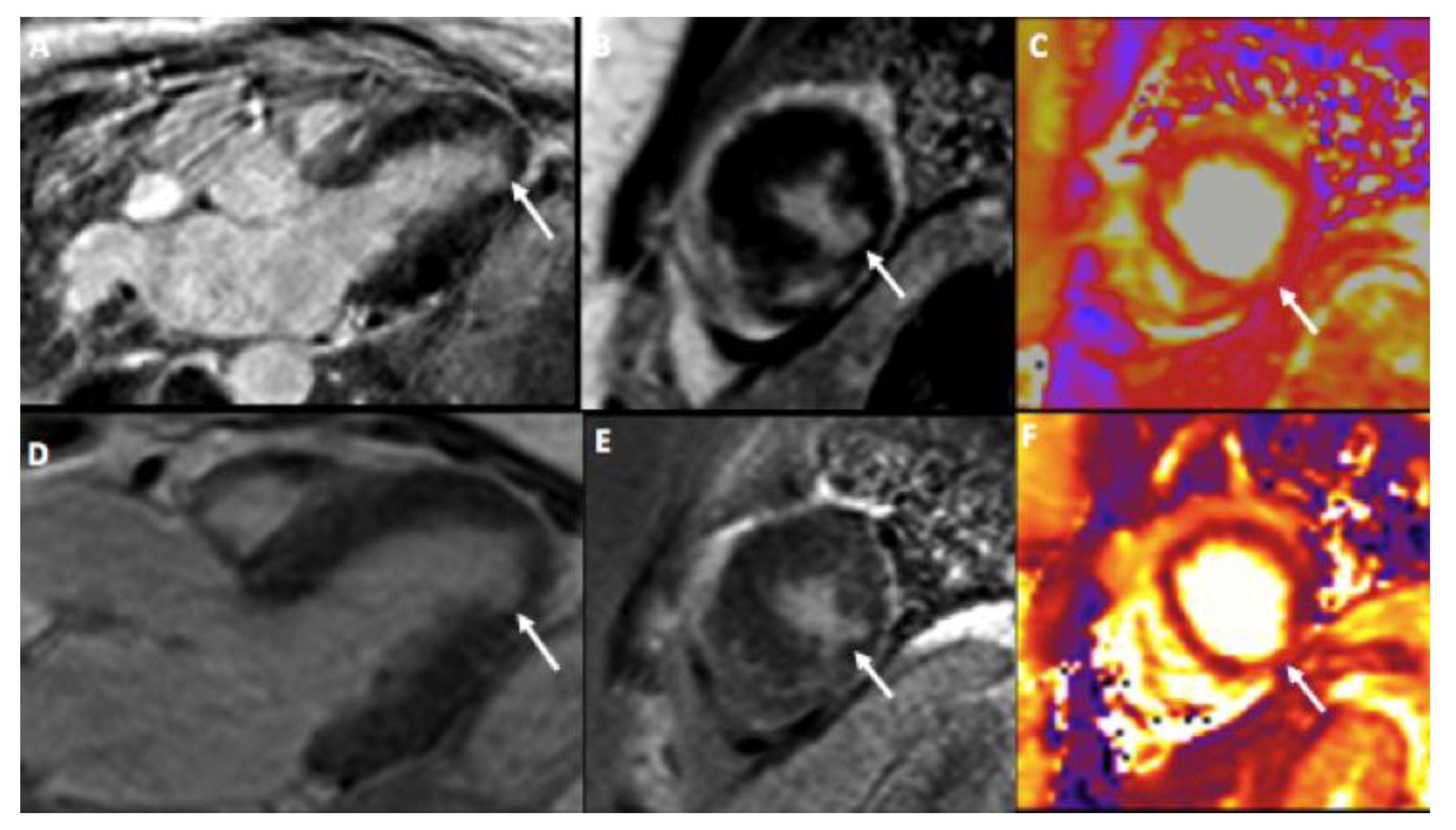
3. Case Presentation
4. Discussion
Funding
Disclosure statement
Authors Contributions
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Swissmedic 2019, © Copyright Reports of Suspected Adverse Reactions to COVID-19 Vaccines in Switzerland Update 23 Available online: https://www.swissmedic.ch/swissmedic/en/home/news/coronavirus-covid-19/covid-19-vaccines-safety-update-13.html (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Yan, M.Z.; Yang, M.; Lai, C.-L. Review of Clinical Trials of COVID-19 Vaccination Booster in SARS-CoV-2 Variants Era: To Take It or Not To Take It. Frontiers in Drug Discovery 2022, 2.
- Watad, A.; De Marco, G.; Mahajna, H.; Druyan, A.; Eltity, M.; Hijazi, N.; Haddad, A.; Elias, M.; Zisman, D.; Naffaa, M.E.; et al. Immune-Mediated Disease Flares or New-Onset Disease in 27 Subjects Following MRNA/DNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination. Vaccines 2021, 9, 435. [CrossRef]
- Chan-Chung, C.; Ong, C.-S.; Chan, L.-L.; Tan, E.-K. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis after COVID-19 Vaccination. QJM 2021, hcab273. [CrossRef]
- Nappi, E.; De Santis, M.; Paoletti, G.; Pelaia, C.; Terenghi, F.; Pini, D.; Ciccarelli, M.; Selmi, C.F.; Puggioni, F.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. New Onset of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Following MRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10, 716. [CrossRef]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, B. Case Report: ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Presenting With Rhabdomyolysis and Pauci-Immune Crescentic Glomerulonephritis After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 MRNA Vaccination. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 762006. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Alkhatib, A.; Meysami, A. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis Diagnosed in an Elderly Female After the Second Dose of MRNA Vaccine Against COVID-19. Cureus 2022, 14, e21176. [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.W.; Chua, C.G.; Lim, X.R.; Francis, P.J.; Xu, C.; Howe, H.S. Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease Flares with Myocarditis Following COVID-19 MRNA Vaccination: A Case-Based Review. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10, 1772. [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Pai, M.; Huisman, M.V.; Makris, M. Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia. Lancet Haematol 2022, 9, e73–e80. [CrossRef]
- Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Suppiah, R.; Robson, J.C.; Craven, A.; Judge, A.; Khalid, S.; Hutchings, A.; Luqmani, R.A.; Watts, R.A.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Ann Rheum Dis 2022, annrheumdis-2021-221794. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.K.; Aeddula, N.R. Churg Strauss Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2021.
- Barbind, K.L.; Boddu, R.; Shijith, K.P.; Mishra, K. Hypereosinophilia: A Rare Cause of Stroke and Multiorgan Dysfunction. BMJ Case Rep 2021, 14, e242619. [CrossRef]
- Badiola, J.; Navarrete-Navarrete, N.; Sabio, J.M. Thrombotic Microangiopathy in a Patient with Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: Case-Based Review. Rheumatol Int 2019, 39, 359–365. [CrossRef]
- Groh, M.; Pagnoux, C.; Baldini, C.; Bel, E.; Bottero, P.; Cottin, V.; Dalhoff, K.; Dunogué, B.; Gross, W.; Holle, J.; et al. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss) (EGPA) Consensus Task Force Recommendations for Evaluation and Management. Eur J Intern Med 2015, 26, 545–553. [CrossRef]
- Ghanima, W.; Khelif, A.; Waage, A.; Michel, M.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Romdhan, N.B.; Kahrs, J.; Darne, B.; Holme, P.A.; RITP study group Rituximab as Second-Line Treatment for Adult Immune Thrombocytopenia (the RITP Trial): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1653–1661. [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.; Mohammad, A.J.; Jones, R.B.; Smith, R.; Jayne, D. Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in the Treatment of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000905. [CrossRef]
- Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris Evaluation of Rituximab-Based Regimen Compared to Conventional Therapeutic Strategy For Remission Induction In Patients With Newly-Diagnosed or Relapsing Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis. Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind Study; clinicaltrials.gov, 2021;
- Gioffredi, A.; Maritati, F.; Oliva, E.; Buzio, C. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: An Overview. Frontiers in Immunology 2014, 5.
- Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Widge, A.T.; Jackson, L.A.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 MRNA-1273 Vaccine in Older Adults. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 2427–2438. [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.; Rizvi, M.; Sadiq, M.S.; Feldman, M. Recrudescence of Severe Polyneuropathy after Receiving Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine in a Patient with a History of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. BMJ Case Rep 2022, 15, e245749. [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, G.; Ledda, A.G.; Ghisu, A.; Vacca, M.; Firinu, D.; Del Giacco, S. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Relapse after COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report. Vaccines 2022, 10, 13. [CrossRef]
| Case | Age, gender | Pre-existing respiratory disease | Pre-existing EGPA (treatment) | mRNA vaccine type | Time between immunization and EGPA symptom onset in days (vaccine dose) | Clinical presentation | Complications | Peak blood eosinophil count (G/l) | ANCA positivity (type) |
FFS | Treatment received |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4] | 62, F | Asthma | No | BNT161b2 | Few days (2nddose) | Fever, numbness in feet and palms, walking disability, purpura, peri-orbital oedema |
Polyneuropathy, optic nerves inflammation, myocarditis, vasculitis at cutaneous biopsy |
13.4 | Yes (anti-MPO) | 1 | MP, RTX |
| [5] | 63, M | Allergic rhino-sinusitis and asthma | No | mRNA-1273 | 1 (1st dose) | Diplopia, headache, dry cough |
3rd cranial nerve palsy, myopericarditis | 12.4 | No | 2 | MP, P, CYC |
| [6] | 79, F | No | No | BNT162b2 | 14 (2nd dose) | Myalgia, Weakness | Rhabdomyolysis, acute kidney injury, pauci-immune crescentic glomerulonephritis and interstitial nephritis with prominent eosinophilia | 5.3 | Yes (p-ANCA, anti-MPO) | 1 | MP, P, CYC |
| [7] | 79, F | Asthma | No | mRNA-1273 | 14 (2nd dose) | Progressive paraesthesia of hands and feet, myalgia, walking disability | DVT, vasculitic neuropathy with eosinophil infiltration | 12.4 | Yes (p-ANCA, anti-MPO) | 0 | P, AZA |
| [20] | N/A, M | Rhino-sinusitis and asthma | Yes (untreated for 7 years) | BNT162b2 | 5 (1st dose) | Weakness, neuropathic pain, blurry vision | Polyneuropathy, mild left foot drop | 0.94 | No | 0 | P |
| [21] | 71, F | Rhino-sinusitis and asthma | Yes (MEP, ICS) | BNT162b2 | 10 (1st dose) | Myalgia, arthralgia, dyspnoea, cough, chest pain, paraesthesia | Mononeuritis multiplex | 4.3 | Yes (p-ANCA) | 0 | MP, P, BEN |
| [8] | 63, F | Allergic rhinitis and asthma | Yes (AZA) | mRNA-1273 | 14 (1st dose) | Dyspnoea, chest pain | Myocarditis | 0.88 | No | 1 | MP. P. CYC |
| [8] | 64, M | Asthma and rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps | No (but constitutional symptoms for 3 months) | BNT162b2 | 2 (1st dose) | Numbness thigh, purpura, chest pain | Endomyocarditis, cutaneous vasculitis, mononeuritis multiplex, possible glomerulonephritis | 5.39 | No | 1 | MP, P, CYC |
| Present case |
46, F | Allergic rhino-sinusitis and asthma | No | mRNA-1273 | 4 (2nd dose) | Enteritis, fever, fatigue, myalgia | Myocarditis, multiple strokes, immune thrombocytopenia | 8.4 | No | 2 | MP, P, IVIG, RPL, RTX, BEN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





