1. Introduction
Sarcopenia is a geriatric syndrome characterized by progressive and generalized loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, and function and it is correlated with physical disability, poor quality of life, and death [
1]. Sarcopenia is also officially recognized as a disease in 2016 (International Diagnostic Code of Diseases M62.84). According to the Health ABC Generation Study, elderly people with diabetes show decreased muscle mass and strength in the lower extremity than healthy people of the same age [
2]. Therefore, the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS) has specifically suggested that patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) must be screened for sarcopenia [
1].
Sarcopenia in patients with T2DM is associated with reduced quality of life, a lower physical activity level, and poor nutrition [
3]. A previous study has also found that a lower serum vitamin D
3 level is associated with lower muscle mass, lower muscle strength, poorer physical performance, and a higher risk of sarcopenia [
4]. Elderly people may have a decreased serum vitamin D
3 level because of factors such as reduced dietary intake, insufficient sun exposure, thinner skin, and decreased intestinal absorption. Therefore, elderly people with diabetes and vitamin D deficiency
may be more susceptible to sarcopenia.
Despite growing interest in diabetes combined with sarcopenia in Taiwan, a limited number of studies have investigated the risk factors of T2DM “combined” with possible sarcopenia or sarcopenia. Moreover, most of these epidemiological studies did not observe the effects of nutritional intake, serum vitamin D
3 level, or physical activity on the risk of sarcopenia. Furthermore, differs from the diagnostic criteria used by other studies, the present study used the latest 2019 AWGS guidelines [
5] as diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia. This study aimed (i) to understand the prevalence of possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia, (ii) to compare the differences in blood biochemical values, nutritional intake, physical performance, and physical activity between patients with and without sarcopenia, and (iii) to determine the risk factors of possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia among patients with T2DM in Taiwan.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
This was a primary care clinic-based study in southern Taiwan, participants were recruited from August 2020 to October 2020. The participants were patients aged 50–80 years who had received the diagnosis of T2DM more than 1 year before the study’s initiation. Patients with musculoskeletal injury (such as sprain, contusion, bruise, and fracture) or a major medical condition [such as chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetic nephropathy and history of cancer, heart disease, and stroke, those with known risks for sarcopenia], undergoing dialysis, have a coronary stent (to avoid any electromagnetic interference), unable to stand/ walk alone or with accessories, cognitive impairment, and involved in a weight loss program in the preceding 3 months (such as consuming a calorie-restricted diet, taking weight loss-related medications, or losing >5% of body weight) were excluded.
Participants were asked to complete the basic information and physical activity questionnaires, which included questions related to sex, age, diabetes onset period, lifestyle habits (smoking, alcohol drinking, and betel nut consumption), medications used in the treatment of chronic diseases (such as oral hypoglycemic agents, insulin injection, blood-pressure-lowering agents, and hypolipidemic agents), use of nutritional supplements and vitamin D3 supplement, daily sun exposure (frequency and time) and sun protection, and daily leisure-time physical activity. Then, 5 mL of routine venous blood sample was drawn for biochemical analysis. Body composition and physical performance were measured for the diagnosis of sarcopenia, and each participant’s dietary patterns were assessed by a registered dietitian.
This study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Review Committee of Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital (IRB: KSVGH20-CT8-12). Before the experiment was begun, all participants were informed of the research purpose, process, and precautions in detail, and participants were enrolled only after their consent was obtained. The study was conducted according to the principles presented in the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
Participants were asked to empty their bladders before the anthropometric measurements. The participant’s height was determined using an automatic measuring machine height weight scale (Super-View HW-3050, Fubio Medical Systems Co., Ltd., Taoyuan, Taiwan), their waist and hip circumferences were evaluated using a measuring tape, and body weight, BF%, and BMI were obtained using bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) method by Inbody 270 body composition analyzer (Biospace Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea). Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were measured using an electronic blood pressure monitor (HBP-9020, Omron Healthcare Co. Ltd., Kyoto, Japan).
2.3. Screening for Sarcopenia
As suggested in the AWGS 2019 guideline, calf circumference measurement [
6] and sarcopenia self-assessment scales (e.g., the SARC-F scale [
7] and SARC-CalF scale [
8]) are practical tools for sarcopenia risk assessment. In our primary care clinics, calf circumference measurement and the SARC-F scale were used for sarcopenia risk assessment.
Calf circumference was measured with the participant in a sitting posture. The participant was asked to remove clothing covering the calf and to place both feet on the ground naturally, with the calf and thigh at a 90° angle. The tape measure was kept horizontal as it was passed around the widest part of the calf, and the circumference was measured without squeezing the skin.
The SARC-F scale was completed by the participants; this scale comprises five assessment items: strength, assistance in walking, rising from a chair, climbing stairs, and falls. Each item has a score of 0–2 points, and the total score is 0–10 points. A total score of ≥4 points indicates that the individual is at risk of sarcopenia; higher scores indicate higher sarcopenia risk.
2.4. Diagnosis of Sarcopenia
Following the latest 2019 AWGS diagnostic consensus on sarcopenia [
5], BIA (Inbody 270) was used as a quick and reliable tool in community settings [
9] for the assessment of skeletal muscle mass index (SMI), which was calculated by appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM)/height
2 and ASM/BMI ratio [
5,
10,
11].
Handgrip strength test with a digital handheld dynamometer (Camry Scale, CA, USA) was used for the assessment of muscle strength. The participant was asked to adopt a standing position with their elbows completely relaxed and straight. Their hands were tested twice each, and the maximum grip strength value was considered to be the muscle strength test value. Sarcopenia was defined as a handgrip strength of <28 kg for males and <18 kg for females [
12].
The physical performance test included a Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), which comprises a 4-m gait speed test, a five times sit-to-stand test, and a balance test. The total score was 0 (worst performance) to 12 (best performance) points. A score
< 9 was indicative of poor physical performance [
13]. In the balance test, the participant was asked to stand with their feet side by side, one foot against the side of the big toe of the other foot, and feet in a straight line. Whether the participant could maintain each position for 10 s was evaluated. In the 4-m gait speed test, the participant was asked to walk in a straight line for 4 m. The time required to complete this walk was recorded, and the walking speed was then calculated. Slow gait speed was defined using AWGS 2019 reference value of < 1.0 m/s. In the five times sit-to-stand test, the participant was asked to sit on a chair, stand up, and sit back again five times. The time taken to complete this task was recorded in seconds. The longer time (≥12 seconds) was indicative of poor physical performance [
14].
2.5. Biochemical Analyses
Routine blood tests for T2DM—including fasting blood sugar, serum HbA1c, triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), serum creatinine (S-Cr), and serum vitamin D3 concentration were analyzed. The blood samples were entrusted to the Zhongshan Medical Laboratory of Pingtung City, Taiwan, which conducted a unified blood biochemical test.
The simplified Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula (=186 × S-Cr − 1.154 × Age − 0.203 × 0.742 [if female patient]) was used to calculate the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), which was used as the renal function index.
The Roche Immunoassay Total Vitamin D Assay Reagent (Elecsys Vitamin D total, Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) and electrochemiluminescence immunoassay were used to quantify the serum 25-(OH)D3 concentration.
2.6. Nutritional Intake
Nutritional intake was assessed using 24-h dietary recall and Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ). A professional dietitian conducted a one-to-one inquiry for the 24-h dietary recall, and the FFQ was administered to collect information regarding the intake of vitamin-D-containing foods in the preceding month.
2.6.1. 24-H dietary Recall
Dietary intake data were converted into total daily calorie intake (kcal) and macronutrients (proteins, fats, and carbohydrates) were expressed in grams (g) and grams per kilogram (g/kg) of body weight (BW).
2.6.2. Food Frequency Questionnaire
The food sources of FFQ were developed by the Nutrients Database of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Food and Drug Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare in Taiwan. This questionnaire contains questions about the frequency and portion size of consumption of particular items to calculate the daily intake of vitamin D. In this study, Cronbach’s coefficient α was used to calculate the internal consistency coefficients of the items included in the questionnaire. The result of the reliability measure was good: α=0.715 in our study which means all items in our questionnaire were internally consistent and reliable to assess the daily intake of vitamin D.
2.7. Leisure-time Physical Activity Measurement
The Godin Leisure-Time Exercise Questionnaire, developed by Godin and Shephard in 1985 [
15], was assessed the “daily leisure-time physical activity” of the participants. The 4-item questionnaire with the first three questions seeking information on the number of times one engages in different intensities (high, moderate, and light) of leisure-time physical activity for at least 15 min duration in 7 days. The number of times a participant engaged in physical activities of different intensities was included in the formula to calculate the total score (total score = [high-intensity activity × 9] + [moderate-intensity activity × 5] + light activity × 3]).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS Version 22.0 statistic software package (IBM SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Data were expressed as mean ±standard deviation (SD) or percentage (%). The participants’ basic information, body composition, blood biochemical parameters, nutritional intakes, physical performance, and total score of leisure-time physical activity were determined by using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a post-hoc Scheffé analysis. The univariate logistic regression analysis was performed to explore the factors associated with the presence of possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia. Significant variables were entered into the multivariate logistic regression checked on multicollinearity and Hosmer-Lemeshow test to determine the factors associated with possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia in the participants with T2DM. The risk association is expressed as the odds ratio (OR). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
The sample size was calculated using G*Power version 3.1.9.7, with F test set α error at 0.05, power level at 90% and theoretical large effect size of 0.4 was used. Since the main objective was to compare the difference in parameters between the three groups, one-way ANOVA was set to calculate the sample size. The results showed that the minimum number of participants for this study was 84. With additional compensation for a possible dropout rate of 30%, the sample size was set to 110 participants.
3. Results
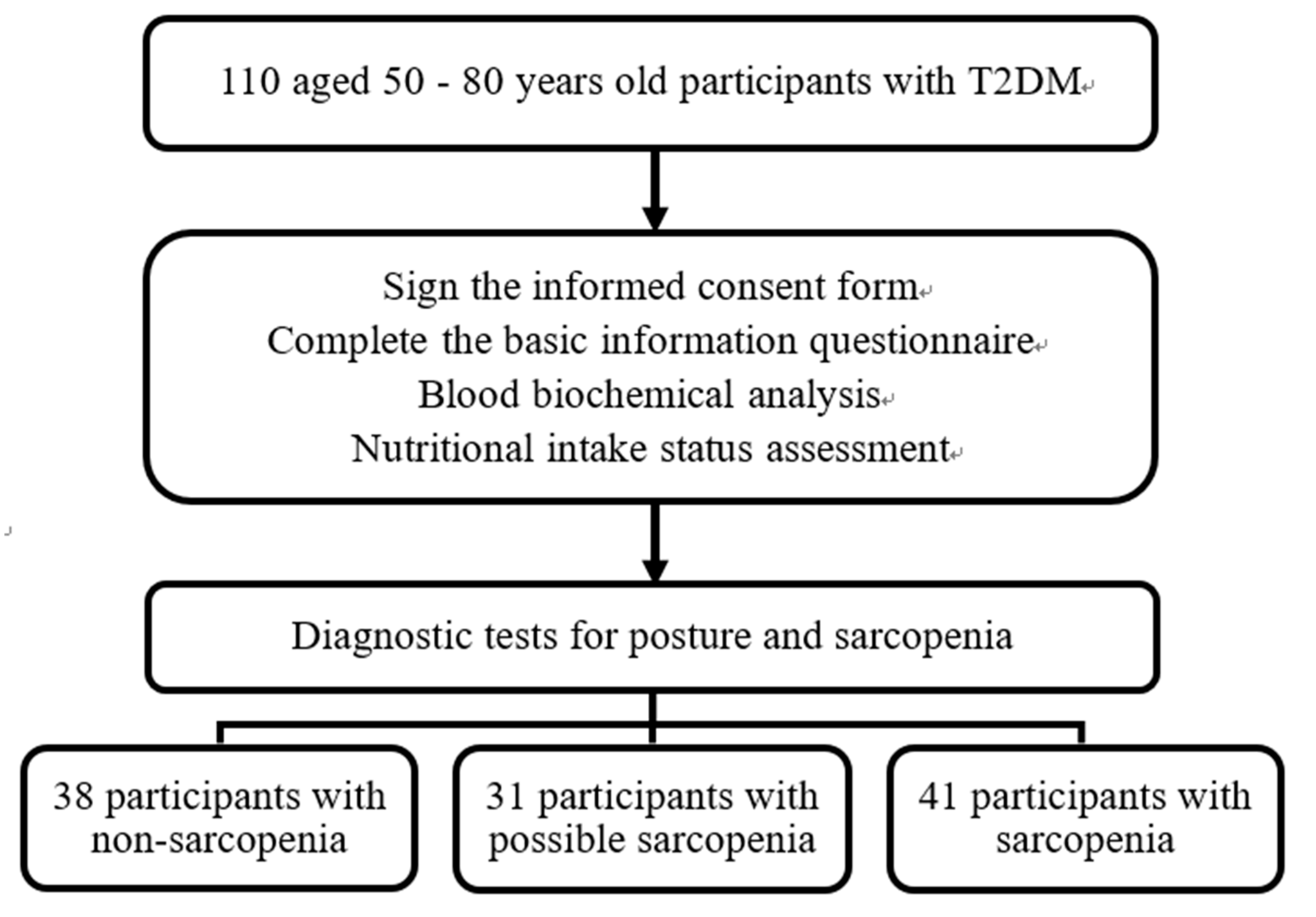
The study enrolled 110 participants (46 male and 64 female), including 38 without sarcopenia, 31 with possible sarcopenia (28.2%), and 41 with sarcopenia (37.3%) (
Figure 1); their mean ages were 64.4 ± 7.3, 67.1 ± 7.2, and 70.2 ± 6.0 years, respectively. The mean age of the participants in the Sarcopenia group (70.2 ± 6.0 years) was significantly higher than that in the Non-sarcopenia group (64.4 ± 7.3 years), and differences were noted in gender, diabetes onset period, and smoking. No significant differences were discovered in the use of chronic disease medications, alcohol and betel nut consumption, or chronic diseases (diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia;
Table 1).
The main source of vitamin D in humans is diet and sunlight exposure; therefore, this study also assessed daily sun exposure and sun protection. A comparison of the daily sun exposure and sun protection status showed no significant difference between the groups (
Table 2). However, the results found that 67.3% of the patients had daily sun exposure for more than 20 min (26 [68.4%] in the Non-sarcopenia group, 22 [71.0%] in the Possible sarcopenia group, and 26 [63.4%] in the Sarcopenia group).
There were significantly higher cholesterol levels in the Sarcopenia group than in the Possible sarcopenia group and higher HDL-C levels than in the Non-sarcopenia group. The Sarcopenia and Possible sarcopenia group had significantly lower serum vitamin D
3 levels than the Non-sarcopenia group (
Table 3).
The total consumption of calories and macronutrients (carbohydrate, protein, and fat) differed significantly among the three groups. The calorie intake per kilogram of BW was significantly lower in the Possible sarcopenia group (25.1 ± 4.2 kcal/kg BW) than in the Non-sarcopenia group (27.9 ± 4.6 kcal/kg BW). The protein intake per kilogram of BW was significantly lowest in the Sarcopenia group (0.89 ± 0.19 g/kg) than in the Possible sarcopenia (0.92 ± 0.20 g/kg BW) and Non-sarcopenia groups (1.04 ± 0.25 g/kg BW), and carbohydrate and lipid intake were also significantly lower in the Sarcopenia group. In addition, the FFQ results revealed that the Sarcopenia group had the lowest daily intake of vitamin-D-rich foods than the other two groups, but no significant difference between the groups was discovered (
Table 4).
Regarding physical performance, the body composition (body weight, BMI, BF%, and waist and hip circumference), diagnostic indicators of sarcopenia (muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical performance), and sarcopenia risk assessment (calf circumference and SARC-F scale) were significantly worse in the Sarcopenia group than the other two groups. In addition, although no significant difference in daily leisure-time physical activity was discovered among three groups, the score of leisure-time physical activity of the Possible sarcopenia and Sarcopenia groups was lower than that of the Non-sarcopenia group (
p = 0.052) (
Table 5).
Univariate logistic regression analyses showed that age, serum vitamin D levels, dietary protein intake, and BF% were associated with possible sarcopenia; as well as age, LDL-C levels, dietary energy and protein intake, BMI, and BF% were associated with sarcopenia.
Table 6 and
Table 7 showed the risk factors associated with possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia using multivariate logistic regression analysis. Compared with the Non-sarcopenia group, only serum vitamin D
3 concentration was associated with lower risk of possible sarcopenia (OR = 0.916; 95% CI, 0.846–0.991;
p = 0.028). Similarly, compared with the Possible sarcopenia group, BMI (OR = 0.339; 95% CI, 0.187–0.613;
p < 0.001) and dietary protein intake (OR = <0.001, 95% CI: <0.001–0.974;
p = 0.013) were significantly associated with lower risk of sarcopenia. Furthermore, dietary energy intake (OR = 1.573, 95% CI: 1.016-2.435;
p = 0.042), BF% (OR = 1.221; 95% CI, 1.025–1.454;
p = 0.025), and age (OR = 1.271; 95% CI, 1.067–1.514;
p = 0.007) were significantly associated with a higher risk of sarcopenia.
4. Discussion
We established the prevalence and risk factors of possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia among patients with T2DM in Taiwan. The current prevalence of T2DM with sarcopenia in Asian countries other than Taiwan is approximately 14.8%–28.8% [
16,
17,
18,
19], whereas the prevalence in the present study was higher at 37.3%. This difference may be related to the present study’s small number of participants and use of the 2019 AWGS diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia, which are stricter diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia.
T2DM was independently associated with an increased risk of sarcopenia and suggested that patients with T2DM should be considered in screening for sarcopenia [
20]. HbA1c can reflect the long-term glycemic control from the last
3 months, the present study found no significant difference in HbA1c level among the three groups with T2DM. which is inconsistent with previous studies [
17,
21]. The difference between those studies and the present study may be due to our study design, only a single HbA1c data point was collected, and the participants regularly used hypoglycemic drugs to control their blood glucose levels. Therefore, the results may not truly reflect their glycemic status. According to the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study and other epidemiological studies, people with dyslipidemia are more prone to cardiovascular diseases than those without dyslipidemia, regardless of whether they have diabetes [
22]. Clinically, patients with T2DM should pay attention to whether their lipid panel blood tests are abnormal and use lipid-lowering drugs to prevent cardiovascular diseases. In this study, although the TC concentration was significantly higher in the Sarcopenia group than in the Possible sarcopenia group, most patients were routinely taking lipid-lowering drugs; therefore, the values of the lipid panel were within the normal range.
A study found that regardless of age and gender, serum vitamin D
3 concentration was strongly correlated with muscle mass and physical performance [
23]. However, the mean serum vitamin D
3 concentrations in the three groups indicated that our participants achieved vitamin D sufficiency levels (defined as ≥30 ng/mL) [
24] and the findings were consistent with a previous study showing that vitamin D sufficiency may be associated with prolonged sun exposure in elderly men also living in southern Taiwan [
25]. The experimental period of this study was August to October, and 67.3% of the participants reported long exposure (≥20 min) to the sun.
Our study indicated that higher BMI and lower body fat percentage (BF%) have protective effects on sarcopenia, which is consistent with previous studies in elderly Koreans or elderly Japanese diabetes patients [
26,
27]. Furthermore, a previous study indicated that obesity was a risk factor for sarcopenia when defined by BF% instead of BMI [
28]. Sarcopenic obesity (SO) is a category of obesity and a high-risk geriatric syndrome in the elderly. Sedentary behavior and an unhealthy diet are independently associated with SO [
29,
30]. Although no significant difference in daily leisure-time physical activity between the three groups in the present study, T2DM patients with possible sarcopenia or sarcopenia were less physically active than those without sarcopenia, which is consistent with the previous study [
3]. The present study also found that lower protein intake (g/kg BW) is a risk factor for T2DM complicated with sarcopenia, consistent with previous studies [
31,
32]. More large-scale local studies are required to further explore the recommended daily protein intake for preventing sarcopenia in this population. Therefore, the management of nutrition and exercise strategies to reduce excess energy intake and BF% can accurately help old-aged T2DM patients to prevent both sarcopenia and obesity.
The strengths of this study are that this is one of the very few studies in Taiwan to examine the prevalence of possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia among T2DM and its association with multiple factors. We investigated as comprehensively as possible the association between blood biochemical parameters (especially serum vitamin D3 concentration), nutritional intake (especially vitamin D intake and supplements), physical function, and physical activity (Godin Leisure-Time Exercise Questionnaire) in these patients. In addition, a professional dietitian used the 24-h dietary recall and FFQ to assess the actual daily intake of vitamin D.
This study also has some limitations. First, we could not fully clarify the causal relationship between sarcopenia and its associated factors due to the cross-sectional study design. Second, because we set strict inclusion criteria, the sample size was relatively small. T2DM in the elderly had a higher prevalence of many comorbidities such as CKD, which is one of the major causes and exacerbating factors for sarcopenia [
33]. Third, our primary care clinic has limited space and funding, so the Dual-energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) and 6-m gait speed tests cannot be conducted. Fourth, we cannot rule out the potential recall bias, because reliability and accuracy cannot be objectively ascertained in the self-reported variables. Fifth, we only recorded the use of oral medications and insulin treatment of participants, the correlation between specific drugs and sarcopenia was not fully explored. Finally, the data from a local study site (from one city in Taiwan) would not reflect the nationwide prevalence of sarcopenia.
5. Conclusions
This is one of the few studies in Taiwan to use the latest 2019 AWGS diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia and to compare the nutritional intake (including assessment of dietary vitamin D intake and sun exposure), blood biochemical parameters (especially serum vitamin D3 concentration), body composition, leisure-time physical activity, and other related factors of patients with T2DM and with possible sarcopenia or sarcopenia. The study found that adequate protein consumption, a higher BMI, and a lower body fat percentage can prevent sarcopenia. Particularly, adequate serum vitamin D3 concentration can prevent possible sarcopenia. Thus, the findings can be a reference for future public health education and lifestyle intervention to decrease the prevalence of sarcopenia among the elderly in Taiwan.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.T.H., J.Y.L., and W.H.C.; methodology, Y.T.H. and J.Y.L.; software, Y.T.H. and W.H.C.; validation, Y.T.H. and W.H.C.; formal analysis, Y.T.H., C.J.L., and W.H.C.; investigation, Y.T.H. and J.Y.L.; resources, Y.T.H. and Y.J.L.; data curation, Y.T.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.T.H. and W.H.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.T.H., C.J.L., Y.J.L., and W.H.C.; visualization, Y.T.H.; supervision, Y.T.H. and W.H.C.; project administration, Y.T.H., Y.J.L., and W.H.C.; funding acquisition, Y.T.H. and J.Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan [grant number: VGHKS110-036].
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study received ethical approval from the Human Research Ethics Review Committee of Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital (approval No.: KSVGH20-CT8-12).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital Research Program (Project number: KSVGH110-036). The authors especially thank Jing-Min Liang for his guidance on the statistical analysis of our study. We also would like to thank Wallace Academic Editing for providing editorial assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, L.K.; Liu, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Hsu, P.S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Mandel, R.; Fain, M.J. Frailty: An emerging geriatric syndrome. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals-Vázquez, C.; Suárez-Cadenas, E.; Estébanez Carvajal, F.M.; Aguilar Trujillo, M.P.; Jiménez Arcos, M.M.; Vázquez Sáchez, M.Á. Relationship between quality of life, physical activity, nutrition, glycemic control and sarcopenia in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Dietrich, T.; Orav, E.J.; Hu, F.B.; Zhang, Y.; Karlson, E.W.; Dawson-Hughes, B. Higher 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with better lower-extremity function in both active and inactive persons aged > or =60 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, A.C.; Liu, L.K.; Lee, W.J.; Peng, L.N.; Chen, L.K. Calf circumference as a screening instrument for appendicular muscle mass measurement. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, S.; Kaneko, R.; Murata, K. SARC-F for screening of sarcopenia among older adults: A meta-analysis of screening test accuracy. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Hu, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, D.; et al. Screening sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults: SARC-F vs SARC-F combined with calf circumference (SARC-CalF). J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 277–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.Y.; Chow, S.K.; Hung, V.W.; Wong, C.H.; Wong, R.M.; Tsang, C.S.; Kwok, T.; Cheung, W.H. Diagnosis of sarcopenia by evaluating skeletal muscle mass by adjusted bioimpedance analysis validated with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M.; et al. The FNIH sarcopenia project: Rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.C.; Hwang, A.C.; Liu, L.K.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, L.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Hung, C.H.; Wang, C.J.; Lin, M.H.; et al. FNIH-defined sarcopenia predicts adverse outcomes among community-dwelling older People in Taiwan: Results from I-Lan longitudinal aging study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auyeung, T.W.; Arai, H.; Chen, L.K.; Woo, J. Letter to the editor: normative data of handgrip strength in 26344 older adults - a pooled dataset from eight cohorts in Asia. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makiura, D.; Ono, R.; Inoue, J.; Kashiwa, M.; Oshikiri, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kakeji, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Miura, Y. Preoperative sarcopenia is a predictor of postoperative pulmonary complications in esophageal cancer following esophagectomy: A retrospective cohort study. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2016, 7, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Arima, K.; Okabe, T.; Mizukami, S.; Tomita, Y.; Kanagae, M.; Goto, H.; Horiguchi, I.; Abe, Y.; Aoyagi, K. Usefulness of chair stand time as a surrogate of gait speed in diagnosing sarcopenia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin, G.; Shephard, R.J. A simple method to assess exercise behavior in the community. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 1985, 10, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murata, Y.; Kadoya, Y.; Yamada, S.; Sanke, T. Sarcopenia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Prevalence and related clinical factors. Diabetol. Int. 2018, 9, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, F.Y.; Koh, Y.L.E.; Malhotra, R.; Ostbye, T.; Lee, P.Y.; Shariff Ghazali, S.; Tan, N.C. Prevalence of and factors associated with sarcopenia among multi-ethnic ambulatory older Asians with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a primary care setting. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Gang, X.; Wang, G.; Xiao, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, G. A cross-sectional study: Associations between sarcopenia and clinical characteristics of patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020, 99, e18708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazlina, S.G.; Lee, P.Y.; Chan, Y.M.; A Hamid, M.S.; Tan, N.C. The prevalence and factors associated with sarcopenia among community living elderly with type 2 diabetes mellitus in primary care clinics in Malaysia. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0233299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.N.; Park, M.S.; Yang, S.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Kang, H.J.; Song, W.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, N.H.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, D.S.; et al. Prevalence and determinant factors of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1497–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechmann, L.M.; Jonasson, T.H.; Canossa, V.S.; Trierweiler, H.; Kisielewicz, G.; Petterle, R.R.; Moreira, C.A.; Borba, V.Z.C. Sarcopenia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional observational study. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 7841390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, P.; Peacock, I.; Donnelly, R. The UK prospective diabetes study (UKPDS): Clinical and therapeutic implications for type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.C.; Chen, H.L.; Tseng, W.T.; Wu, I.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.I.; Lee, M.M.; Liu, K.; Hsiung, C.A. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and physical performance in older adults: A nationwide study in Taiwan. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.C.; Wu, M.Y.; Vhin, W.L.; Chang, Y.F.; Chang, C.S.; Wu, S.J.; Lin, C.W.; Wu, C.H. Prevalence and associated factors of serum vitamin D inadequacy in older men living in Southern Taiwan. Taiwan Assoc. Fam. Med. 2017, 27, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, Y.; Narita, T.; Fujita, H.; Morii, T.; Sato, T.; Sassa, M.H.; Yamada, Y. Importance of physical evaluation using skeletal muscle mass index and body fat percentage to prevent sarcopenia in elderly Japanese diabetes patients. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.C.; Won, C.W.; Soh, Y. Association of high body mass index, waist circumference, and body fat percentage with sarcopenia in older women. BMC geriatrics. 2022, 22, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cheng, K.Y.; Tong, X.; Cheung, W.H.; Chow, S.K.; Law, S.W.; Wong, R.M.Y. The role of obesity in sarcopenia and the optimal body composition to prevent against sarcopenia and obesity. Front Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1077255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A. & Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Li, Y.; Ma, L. Sarcopenic Obesity: An Emerging Public Health Problem. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, A.A.; Hayhoe, R.P.G.; Cameron, D. The relationships between sarcopenic skeletal muscle loss during ageing and macronutrient metabolism, obesity and onset of diabetes. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.D.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.P.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, J.B.; Hong, F.Y.; Chen, W.X. Relationship between chronic kidney disease and sarcopenia. Scientific reports. 2021, 11, 20523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).