Submitted:
12 July 2023
Posted:
13 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
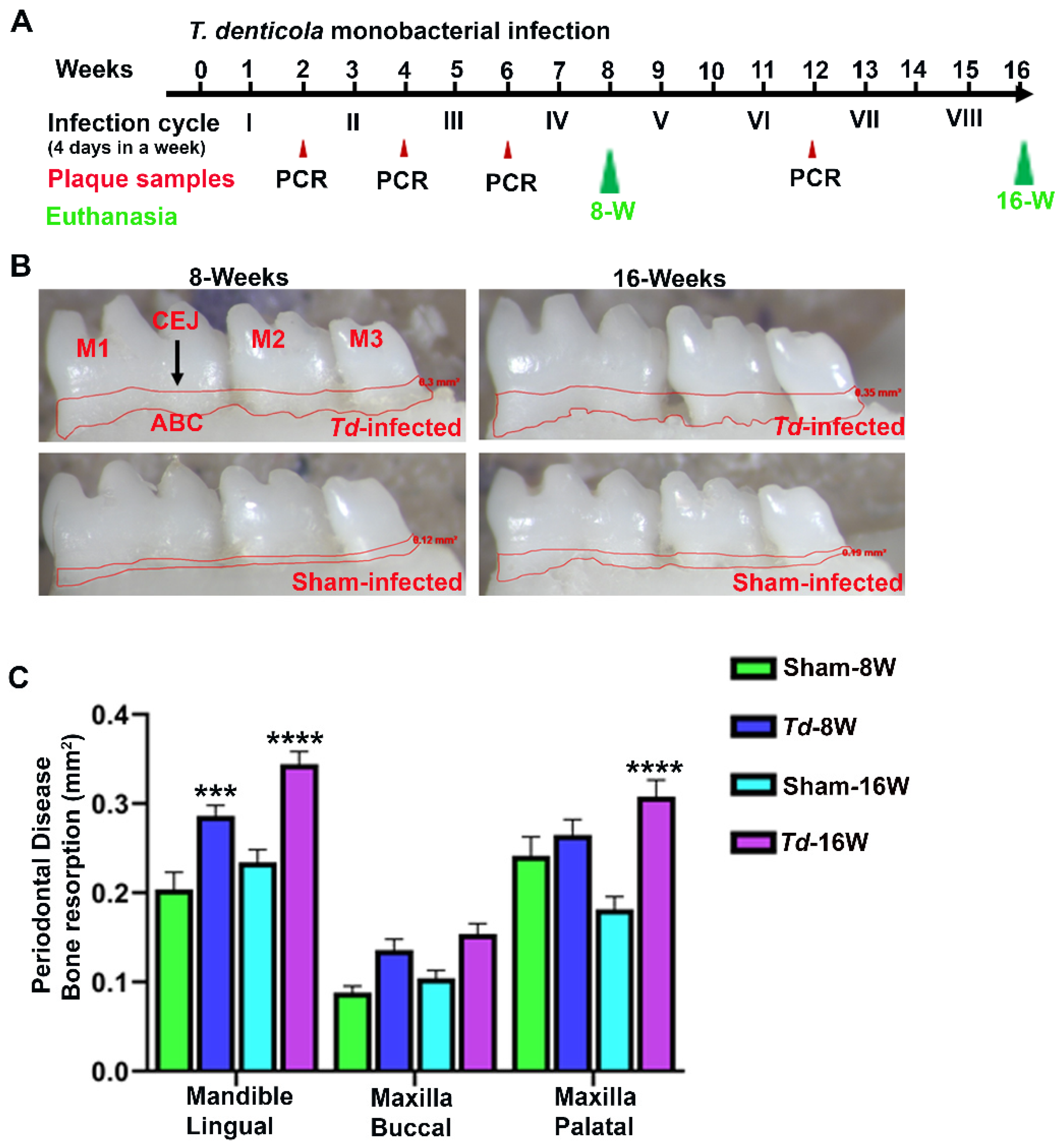
2.1. Effective colonization of T. denticola in mouse gingival tissues
2.2. T. denticola infection increased alveolar bone resorption with minimal dissemination of treponems to distal organs
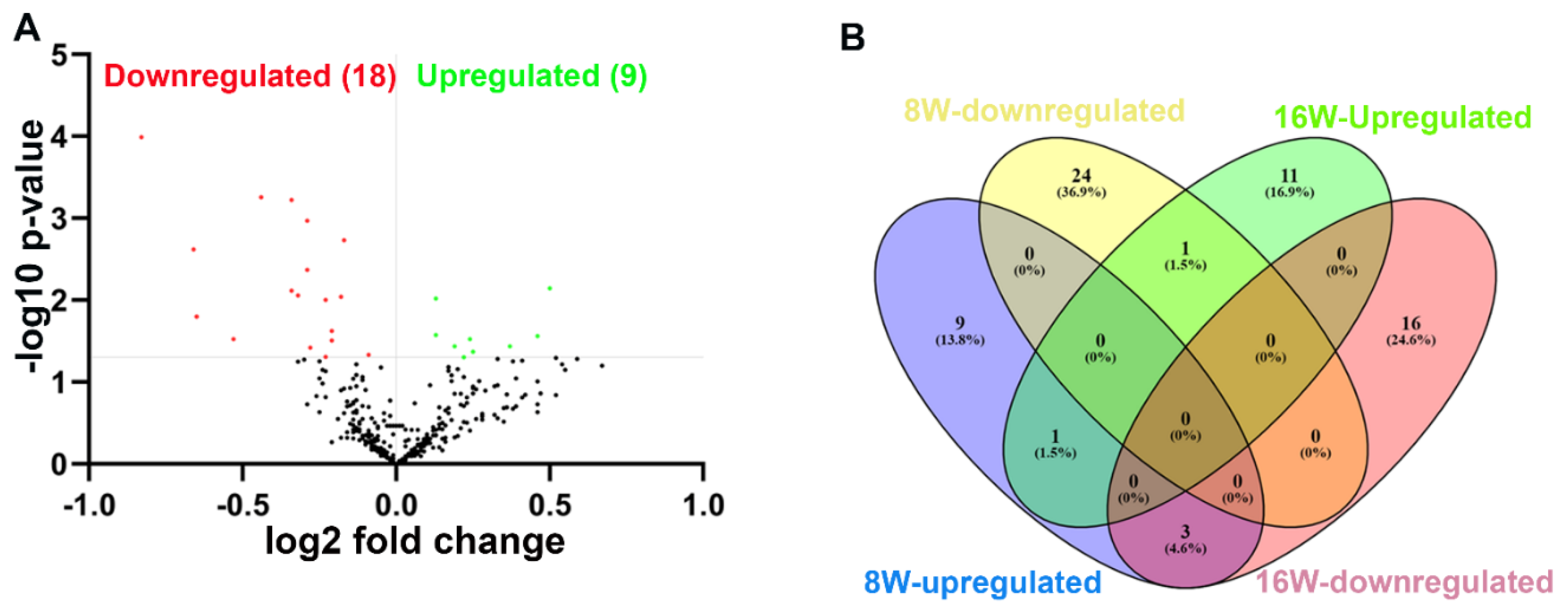
2.3. Nanostring analysis of miRNAs in T. denticola -infected mandibles
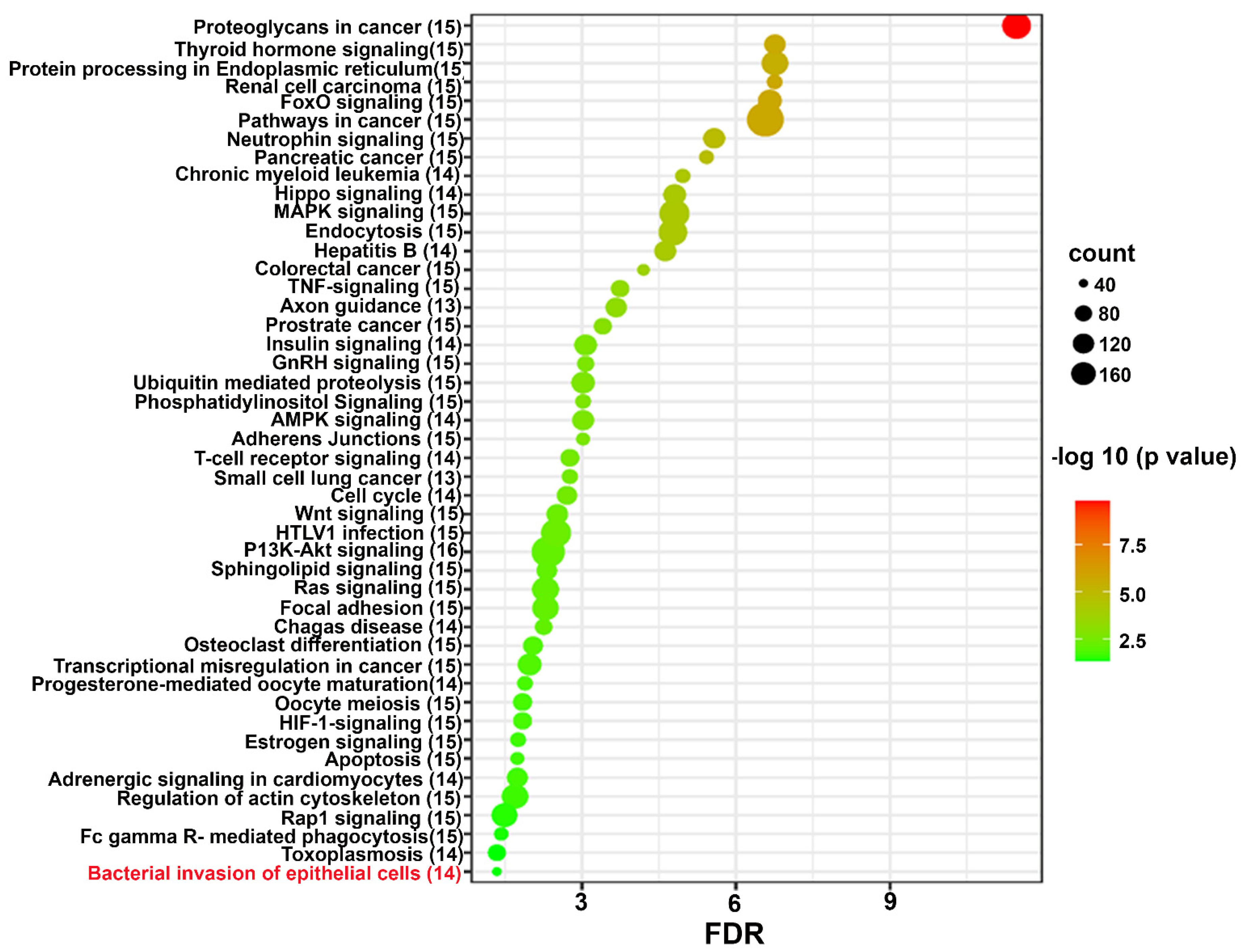
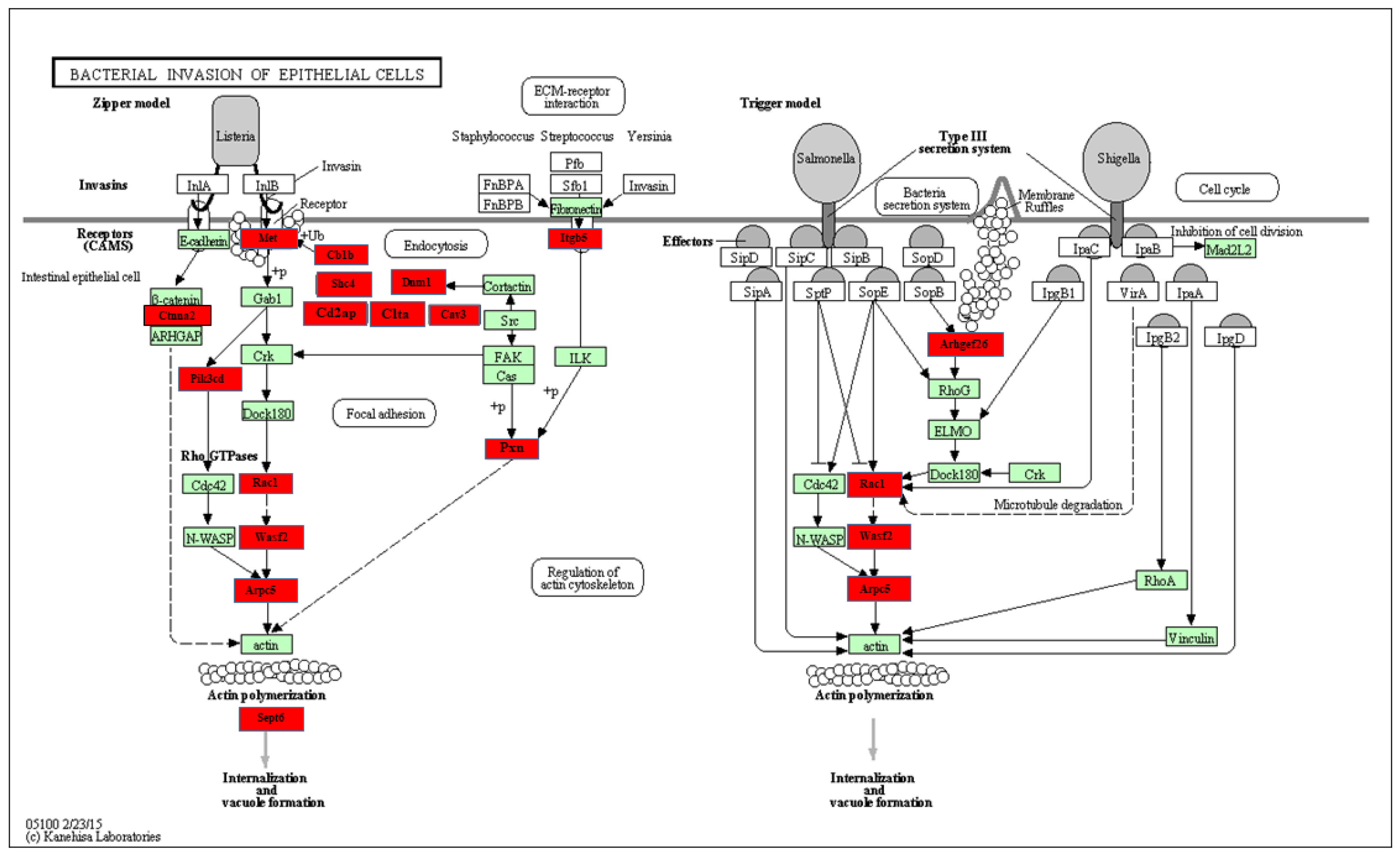
2.4. Functional pathways analysis of Differentially expressed miRNAs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gingival infection of T. denticola to induce periodontitis in C57BL/6J mouse
4.2. T. denticola 16S rRNA gene amplification in oral plaques
4.3. Bacterial systemic dissemination to distal organs
4.4. Horizontal alveolar bone resorption by morphometry
4.5. nCounter® miRNA expression profiling using NanoString analysis
4.6. NanoString data analysis
4.7. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, J.L.; Sullivan, J.C. Circulating cell-free micro-RNA as biomarkers: from myocardial infarction to hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond) 2022, 136, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, S.; de Borja, R.; Tsao, M.S.; McPherson, J.D. Robust global microRNA expression profiling using next-generation sequencing technologies. Lab Invest 2014, 94, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, J.; Ke, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Liao, Y.; Liang, F.; Mei, S.; Li, M.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells associated with syphilis. BMC Infect Dis 2020, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, A.; Min, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, S.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, S.; et al. MiR-1298-5p level downregulation induced by Helicobacter pylori infection inhibits autophagy and promotes gastric cancer development by targeting MAP2K6. Cell Signal 2022, 93, 110286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Tamizu, E.; Uno, S.; Uwamino, Y.; Fujiwara, H.; Nishio, K.; Nakano, Y.; Shiono, H.; Namkoong, H.; Hoshino, Y.; et al. hsa-miR-346 is a potential serum biomarker of Mycobacterium avium complex pulmonary disease activity. J Infect Chemother 2017, 23, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davuluri, K.S.; Chauhan, D.S. microRNAs associated with the pathogenesis and their role in regulating various signaling pathways during. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12, 1009901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.; Cruz, A.R.; Rodrigues Lopes, I.; Maudet, C.; Sunkavalli, U.; Silva, R.J.; Sharan, M.; Lisowski, C.; Zaldívar-López, S.; Garrido, J.J.; et al. Functional screenings reveal different requirements for host microRNAs in Salmonella and Shigella infection. Nat Microbiol 2020, 5, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, B.R.; Zhang, M.; Sonntag, W.E.; Drevets, D.A. Neuroinvasive Listeria monocytogenes infection triggers accumulation of brain CD8. J Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D.; Cugini, M.A.; Smith, C.; Kent, R.L., Jr. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J Clin Periodontol 1998, 25, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Su, L.; Duan, X.; Chen, X.; Hays, A.; Upadhyayula, S.; Shivde, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, D.; et al. MicroRNA-21 down-regulates inflammation and inhibits periodontitis. Mol Immunol 2018, 101, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; Shu, R.; Jiang, S.Y.; Liu, D.L.; Zhang, X.L. Comparison of microRNA profiles of human periodontal diseased and healthy gingival tissues. Int J Oral Sci 2011, 3, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motedayyen, H.; Ghotloo, S.; Saffari, M.; Sattari, M.; Amid, R. Evaluation of MicroRNA-146a and Its Targets in Gingival Tissues of Patients With Chronic Periodontitis. J Periodontol 2015, 86, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Song, D.; Lu, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Tan, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, D. Expression Profiles of Inflammation-associated microRNAs in Periapical Lesions and Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts Inflammation. J Endod 2016, 42, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Constantinides, C.; Kebschull, M.; Papapanou, P.N. MicroRNAs Regulate Cytokine Responses in Gingival Epithelial Cells. Infect Immun 2016, 84, 3282–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, M.A.; Rivera, M.; Lucas, A.; Chan, E.K.; Kesavalu, L. Polymicrobial infection with periodontal pathogens specifically enhances microRNA miR-146a in ApoE-/- mice during experimental periodontal disease. Infect Immun 2011, 79, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravindraja, C.; Kashef, M.R.; Vekariya, K.M.; Ghanta, R.K.; Karanth, S.; Chan, E.K.L.; Kesavalu, L. Global Noncoding microRNA Profiling in Mice Infected with Partial Human Mouth Microbes (PAHMM) Using an Ecological Time-Sequential Polybacterial Periodontal Infection (ETSPPI) Model Reveals Sex-Specific Differential microRNA Expression. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godovikova, V.; Goetting-Minesky, M.P.; Timm, J.C.; Fenno, J.C. Immunotopological Analysis of the Treponema denticola Major Surface Protein (Msp). J Bacteriol 2019, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetting-Minesky, M.P.; Godovikova, V.; Fenno, J.C. Approaches to Understanding Mechanisms of Dentilisin Protease Complex Expression in Treponema denticola. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 668287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Chan, Y.; Gao, W.; Leung, W.K.; Watt, R.M. Diversity of Treponema denticola and Other Oral Treponeme Lineages in Subjects with Periodontitis and Gingivitis. Microbiol Spectr 2021, 9, e0070121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, A.N.; Hawkes, C.G.; Blake, C.S.; Fitzsimonds, Z.R.; Zhu, B.; Buck, G.; Lamont, R.J.; Miller, D.P. Treponema denticola Induces Interleukin-36gamma Expression in Human Oral Gingival Keratinocytes via the Parallel Activation of NF-kappaB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways. Infect Immun 2022, 90, e0024722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, J.; Martin, M.; Passineau, M.J.; Godovikova, V.; Fenno, J.C.; Wu, H. Activation of the Innate Immune System by Treponema denticola Periplasmic Flagella through Toll-Like Receptor 2. Infect Immun 2018, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, G.; Ben-Adi, S.; Genzler, T.; Sela, M.; Rosen, G. Involvement of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in the innate immune response to Treponema denticola and its outer sheath components. Infect Immun 2009, 77, 3939–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, G.; Shapira, L. How has neutrophil research improved our understanding of periodontal pathogenesis? J Clin Periodontol 2011, 38 Suppl 11, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukkapalli, S.S.; Rivera, M.F.; Velsko, I.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, D.; Bhattacharyya, I.; Gangula, P.R.; Lucas, A.R.; Kesavalu, L. Invasion of oral and aortic tissues by oral spirochete Treponema denticola in ApoE(-/-) mice causally links periodontal disease and atherosclerosis. Infect Immun 2014, 82, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, K.; Ishihara, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Hirayama, A.; Inayama, Y.; Okuda, K. Detection of Treponema denticola in atherosclerotic lesions. J Clin Microbiol 2001, 39, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendra, J.; Mahendra, L.; Fageeh, H.N.; Fageeh, H.I.; Ibraheem, W.; Abdulkarim, H.H.; Kanakamedala, A.; Prakash, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Balaji, T.M.; et al. miRNA-146a and miRNA-126 as Potential Biomarkers in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Generalized Periodontitis. Materials (Basel) 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixner, F.; Thomma, A.; Cipollini, G.; Widder, S.; Rattei, T.; Zink, A. Metagenomic analysis reveals presence of Treponema denticola in a tissue biopsy of the Iceman. PLoS One 2014, 9, e99994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Su, X.; Wu, L.; Cai, Q.; Wu, H. Treponema denticola Induces Alzheimer-Like Tau Hyperphosphorylation by Activating Hippocampal Neuroinflammation in Mice. J Dent Res 2022, 101, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Lv, X.; Liu, D.; Guo, H.; Yao, G.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Yang, Y. METTL3-mediated maturation of miR-126-5p promotes ovarian cancer progression via PTEN-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 2021, 28, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, A.; Nazari-Jahantigh, M.; Wei, Y.; Bidzhekov, K.; Gremse, F.; Grommes, J.; Megens, R.T.; Heyll, K.; Noels, H.; Hristov, M.; et al. MicroRNA-126-5p promotes endothelial proliferation and limits atherosclerosis by suppressing Dlk1. Nat Med 2014, 20, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Qu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tian, H.L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.Y. MicroRNA-126-3p/-5p Overexpression Attenuates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in a Mouse Model of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Stroke 2020, 51, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Ren, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, N. microRNA-132 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via GDF5 and the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Pathol Res Pract 2019, 215, 152722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tuazon, J.P.; Borlongan, C.V.; Yu, G. MicroRNA-133a and Myocardial Infarction. Cell Transplant 2019, 28, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Niu, J.; Steer, C.J.; Zheng, G.; Song, G. MicroRNA-378 promotes hepatic inflammation and fibrosis via modulation of the NF-kappaB-TNFalpha pathway. J Hepatol 2019, 70, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ell, B.; Mercatali, L.; Ibrahim, T.; Campbell, N.; Schwarzenbach, H.; Pantel, K.; Amadori, D.; Kang, Y. Tumor-induced osteoclast miRNA changes as regulators and biomarkers of osteolytic bone metastasis. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zhang, P.; Wen, L.; Jia, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, L. miR-22 promotes stem cell traits via activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5799–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, R.; Nares, S.; Zhang, S.; Barros, S.P.; Offenbacher, S. MicroRNA modulation in obesity and periodontitis. J Dent Res 2012, 91, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Gupta, S.; Ciszek, R.; Heiskanen, M.; Lapinlampi, N.; Kukkonen, J.; Leinonen, V.; Puhakka, N.; Pitkanen, A. Plasma miR-9-3p and miR-136-3p as Potential Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Experimental and Human Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.; Richardson, S.; Benyeogor, I.; Omosun, Y.; Dye, K.; Medhavi, F.; Lundy, S.; Adebayo, O.; Igietseme, J.U.; Eko, F.O. Differential miRNA Profiles Correlate With Disparate Immunity Outcomes Associated With Vaccine Immunization and Chlamydial Infection. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 625318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soofiyani, S.R.; Hosseini, K.; Soleimanian, A.; Abkhooei, L.; Hoseini, A.M.; Tarhriz, V.; Ghasemnejad, T. An Overview on the Role of miR-451 in Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Therapy, and Prognosis. Microrna 2021, 10, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecklin-Wasmer, C.; Guarnieri, P.; Celenti, R.; Demmer, R.T.; Kebschull, M.; Papapanou, P.N. MicroRNAs and their target genes in gingival tissues. J Dent Res 2012, 91, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Bai, Q.; Lu, Q. miR-30a-5p inhibits osteogenesis and promotes periodontitis by targeting Runx2. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhou, H.; Hong, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Huang, H. miR-30 family members negatively regulate osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 7503–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, B.; Zhang, P.; Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Yang, F.; Chen, E. MiR-496 promotes migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting RASSF6 in colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol 2020, 235, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.; Pan, J.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Tao, J. The Circular RNA circRNA124534 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Through Modulation of the miR-496/β-Catenin Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krell, J.; Frampton, A.E.; Jacob, J.; Pellegrino, L.; Roca-Alonso, L.; Zeloof, D.; Alifrangis, C.; Lewis, J.S.; Jiao, L.R.; Stebbing, J.; et al. The clinico-pathologic role of microRNAs miR-9 and miR-151-5p in breast cancer metastasis. Mol Diagn Ther 2012, 16, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, D.; Moshaverinia, A.; Liu, D.; Kou, X.; Yu, W.; Yang, R.; Sun, L.; Shi, S. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in tight-skin mice identifies miR-151-5p as a therapeutic target for systemic sclerosis. Cell Res 2017, 27, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Zhi, T.; Xu, X. miR-720 is a key regulator of glioma migration and invasion by controlling TARSL2 expression. Hum Cell 2021, 34, 1504–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhang, W.; Wen, T.; Nie, J.; Ding, L.; Yi, D. MiR-100-5p regulates cardiac hypertrophy through activation of autophagy by targeting mTOR. Hum Cell 2021, 34, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratz, F.; Hohnloser, C.; Bemtgen, X.; Jaenich, C.; Kreuzaler, S.; Hoefer, I.; Pasterkamp, G.; Mastroianni, J.; Zeiser, R.; Smolka, C.; et al. MicroRNA-100 Suppresses Chronic Vascular Inflammation by Stimulation of Endothelial Autophagy. Circ Res 2018, 122, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolka, C.; Schlösser, D.; Koentges, C.; Tarkhnishvili, A.; Gorka, O.; Pfeifer, D.; Bemtgen, X.; Asmussen, A.; Groß, O.; Diehl, P.; et al. Cardiomyocyte-specific miR-100 overexpression preserves heart function under pressure overload in mice and diminishes fatty acid uptake as well as ROS production by direct suppression of Nox4 and CD36. FASEB J 2021, 35, e21956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Lv, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, K.; Ni, C.; Wang, K.; Kong, M.; et al. Small extracellular vesicles containing miR-486-5p promote angiogenesis after myocardial infarction in mice and nonhuman primates. Sci Transl Med 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, Y.; Feng, Z.; Sheng, J.; Dong, A.; Zhang, M.; Cao, L. miR-345-5p regulates adipogenesis via targeting VEGF-B. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 17114–17121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, B.; Horváth, J.; Tar, I.; Kiss, C.; Márton, I.J. Salivary miR-31-5p, miR-345-3p, and miR-424-3p Are Reliable Biomarkers in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathogens 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.A.; Pereira, T.S.F.; Brito, J.A.R.; Cortelli, S.C.; Cortelli, J.R.; Gomez, R.S.; Costa, F.O.; Miranda Cota, L.O. Comparison of miRNA expression profiles in individuals with chronic or aggressive periodontitis. Oral Dis 2019, 25, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik Mohamed Kamal, N.N.S.; Awang, R.A.R.; Mohamad, S.; Shahidan, W.N.S. Plasma- and Saliva Exosome Profile Reveals a Distinct MicroRNA Signature in Chronic Periodontitis. Front Physiol 2020, 11, 587381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, N.; Fadaei, R.; Haqgou, M.; Barez, S.R.; Kargasheh, F.B.; Shanaki, M.; Dilmaghani, N.A. Emerging Role of miR-372 and miR-101a in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin Lab 2020, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.F.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Mao, Q.; Liu, Y.H. Circulating miR-128 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for glioma. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2017, 160, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhai, R.; Hua, B.; Bao, L.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Yao, W.; Fan, H.; Hao, C. miR-let-7d attenuates EMT by targeting HMGA2 in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. RSC Adv 2019, 9, 19355–19364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Gong, Q. miR-423 Promotes Breast Cancer Invasion by Activating NF-kappaB Signaling. Onco Targets Ther 2020, 13, 5467–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Tang, H.; Li, X.Y.; Deng, M.F.; Wei, N.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.F.; Wang, D.Q.; Fu, P.; Wang, J.Z.; et al. Targeting the HDAC2/HNF-4A/miR-101b/AMPK Pathway Rescues Tauopathy and Dendritic Abnormalities in Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Ther 2017, 25, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yue, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, M.; Gao, J.; Wu, B. miR-21 and miR-101 regulate PLAP-1 expression in periodontal ligament cells. Mol Med Rep 2012, 5, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, C. NF-kappaB inducible miR-30b-5p aggravates joint pain and loss of articular cartilage via targeting SIRT1-FoxO3a-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome. Aging (Albany NY) 2021, 13, 20774–20792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.F.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Qian, S.X.; Xu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.P. miR-30b protects nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons from MPP(+)-induced neurotoxicity via SNCA. Brain Behav 2020, 10, e01567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, M.T.; Arbitrio, M.; Caracciolo, D.; Cordua, A.; Cuomo, O.; Grillone, K.; Riillo, C.; Carida, G.; Scionti, F.; Labanca, C.; et al. miR-221/222 as biomarkers and targets for therapeutic intervention on cancer and other diseases: A systematic review. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2022, 27, 1191–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Guo, Q. MiR-26b-5p-modified hUB-MSCs derived exosomes attenuate early brain injury during subarachnoid hemorrhage via MAT2A-mediated the p38 MAPK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull 2021, 175, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravindraja, C.; Sakthivel, R.; Liu, X.; Goodwin, M.; Veena, P.; Godovikova, V.; Fenno, J.C.; Levites, Y.; Golde, T.E.; Kesavalu, L. Intracerebral but Not Peripheral Infection of Live Porphyromonas gingivalis Exacerbates Alzheimer's Disease like Amyloid Pathology in APP-TgCRND8 Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carè, A.; Catalucci, D.; Felicetti, F.; Bonci, D.; Addario, A.; Gallo, P.; Bang, M.L.; Segnalini, P.; Gu, Y.; Dalton, N.D.; et al. MicroRNA-133 controls cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Med 2007, 13, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Xiao, J.; Ren, A.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Xie, B.; Gao, X.G.; Wang, Y.W. Role of miR-1 and miR-133a in myocardial ischemic postconditioning. J Biomed Sci 2011, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.Q.; Jiang, Z.M.; Zhao, Q.P.; Xin, F. MicroRNA-133a improves the cardiac function and fibrosis through inhibiting Akt in heart failure rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2015, 71, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavalu, L.; Falk, C.W.; Davis, K.J.; Steffen, M.J.; Xu, X.; Holt, S.C.; Ebersole, J.L. Biological characterization of lipopolysaccharide from Treponema pectinovorum. Infect Immun 2002, 70, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, J.; Yi, C.; Li, T. MicroRNA-486-5p Promotes Acute Lung Injury via Inducing Inflammation and Apoptosis by Targeting OTUD7B. Inflammation 2020, 43, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Liu, W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, H.L. MicroRNA-486-5p functions as a diagnostic marker for carotid artery stenosis and prevents endothelial dysfunction through inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8667–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Rocha, J.L.; Samblas, M.; Milagro, F.I.; Bressan, J.; Martinez, J.A.; Marti, A. Noncoding RNAs, cytokines, and inflammation-related diseases. FASEB J 2015, 29, 3595–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklossy, J. Historic evidence to support a causal relationship between spirochetal infections and Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2015, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklossy, J. Bacterial Amyloid and DNA are Important Constituents of Senile Plaques: Further Evidence of the Spirochetal and Biofilm Nature of Senile Plaques. J Alzheimers Dis 2016, 53, 1459–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Su, X.; Tang, Z.; Jian, L.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, X.; Wu, H. Treponema denticola Induces Neuronal Apoptosis by Promoting Amyloid-beta Accumulation in Mice. Pathogens 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, F.; Pisani, V.; Arcangeli, F.; Harding, A.; Singhrao, S.K. The Mechanistic Pathways of Periodontal Pathogens Entering the Brain: The Potential Role of Treponema denticola in Tracing Alzheimer's Disease Pathology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Awil, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Hou, D. Cilostazol for Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis 2022, 51, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesavalu, L.; Ebersole, J.L.; Machen, R.L.; Holt, S.C. Porphyromonas gingivalis virulence in mice: induction of immunity to bacterial components. Infect Immun 1992, 60, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesavalu, L.; Holt, S.C.; Ebersole, J.L. In vitro environmental regulation of Porphyromonas gingivalis growth and virulence. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2003, 18, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukkapalli, S.S.; Velsko, I.M.; Rivera-Kweh, M.F.; Zheng, D.; Lucas, A.R.; Kesavalu, L. Polymicrobial Oral Infection with Four Periodontal Bacteria Orchestrates a Distinct Inflammatory Response and Atherosclerosis in ApoE null Mice. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0143291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukkapalli, S.S.; Velsko, I.M.; Rivera-Kweh, M.F.; Larjava, H.; Lucas, A.R.; Kesavalu, L. Global TLR2 and 4 deficiency in mice impacts bone resorption, inflammatory markers and atherosclerosis to polymicrobial infection. Mol Oral Microbiol 2017, 32, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.F.; Lee, J.Y.; Aneja, M.; Goswami, V.; Liu, L.; Velsko, I.M.; Chukkapalli, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, I.; Chen, H.; Lucas, A.R.; et al. Polymicrobial infection with major periodontal pathogens induced periodontal disease and aortic atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic ApoE(null) mice. PLoS One 2013, 8, e57178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velsko, I.M.; Chukkapalli, S.S.; Rivera-Kweh, M.F.; Zheng, D.; Aukhil, I.; Lucas, A.R.; Larjava, H.; Kesavalu, L. Periodontal pathogens invade gingiva and aortic adventitia and elicit inflammasome activation in alphavbeta6 integrin-deficient mice. Infect Immun 2015, 83, 4582–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukkapalli, S.S.; Rivera-Kweh, M.F.; Velsko, I.M.; Chen, H.; Zheng, D.; Bhattacharyya, I.; Gangula, P.R.; Lucas, A.R.; Kesavalu, L. Chronic oral infection with major periodontal bacteria Tannerella forsythia modulates systemic atherosclerosis risk factors and inflammatory markers. Pathog Dis 2015, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravindraja, C.; Vekariya, K.M.; Botello-Escalante, R.; Rahaman, S.O.; Chan, E.K.L.; Kesavalu, L. Specific microRNA Signature Kinetics in Porphyromonas gingivalis-Induced Periodontitis. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioce, M.; Rutigliano, D.; Puglielli, A.; Fazio, V.M. Butein-instigated miR-186-5p-dependent modulation of TWIST1 affects resistance to cisplatin and bioenergetics of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma cells. Cancer Drug Resist 2022, 5, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, W460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Cui, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.; et al. miRTarBase update 2022: an informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group/Bacteria/Weeks | Positive gingival plaque samples (n=10) | |||
| 2 weeks | 4 weeks | 6 weeks | 12 weeks | |
| Group I/ T. denticola ATCC 35405 [8-weeks] | 1/10 | 10/10 | NC | --- |
| Group II/ T. denticola ATCC 35405 [16-weeks] | 1/10 | 10/10 | NC | 10/10 |
| Group III/ Sham-infection [8-weeks] | 0/10 | NC | NC | --- |
| Group IV/ Sham-infection [16-weeks] | 0/10 | NC | NC | 0/10 |
| Positive systemic tissue specimens for T. denticola (16-weeks) (n=5 Males and 5 Females) | ||||||
| Bacterial infection | Sex (M/F) | Heart | Lungs | Kidney | Liver | Spleen |
| T. denticola | M | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| F | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Weeks/Infection/Sex | Upregulated miRNAs (p<0.05) | Downregulated miRNAs (p<0.05) |
| 8 Weeks - T. denticola infected Vs 8 Weeks - Sham infection (n=10) |
13 (miR-133a, miR-126-5p) | 25 (miR-375, miR-34b-5p) |
| 8 Weeks - T. denticola infected Female Vs Male (n=5) |
128 | 14 |
| 16 Weeks - T. denticola infected Vs 16 Weeks - Sham infection (n=10) |
13 (miR-486, miR-126-3p, miR-126-5p) | 19 |
| 16 Weeks - T. denticola infected Female Vs Male (n=5) |
9 | 8 |
| 8 Weeks - T. denticola infected Vs 16 Weeks - T. denticola infected |
9 (miR-126-5p) | 19 |
| Upregulated miRNAs in 8-weeks T. denticola infection | ||||
| miRs | Fold change | p-value | Reported functions | Number of Target Genes |
| mmu-miR-133a | 1.83 | 0.0176 | Abundant in heart and it is shown to be involved in the early pathological cascade of myocardial infarction [34]. | 1426 (e.g., Med13, Rrp8, Cup, Srrm2, Wipi2, Dlc1, Tgfb2, Rsbn1l, Kat6b, Pold2) |
| mmu-miR-378 | 1.57 | 0.0198 | Major role in hepatic inflammation and fibrosis by targeting NFκB-TNFα axis [35]. Major secreted biomarkers for osteolytic bone metastasis [36]. Expressed greater degree in microvesicles of osteoclasts. | -- |
| mmu-miR-22 | 1.55 | 0.0012 | Promotes cell differentiation, tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis by maintaining Wnt/β-catenin signaling and cancer stem cells function [37]. Observed in the inflammatiory mouse lung and brain tissues of Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid treated mice. Upregulated in the periodontal disease and obesity [38]. | 2150 (e.g., Arl8b, Syne1, Mbp, Med13, Srrm2, Tpm3, Inpp1, Bin1, Seam3d, Abcg5) |
| mmu-miR-136 | 1.37 | 0.0066 | Potential miRNA biomarker in both experimental and human mild traumatic brain injury [39]. | 809 (e.g., Arl8b, Syne1, Med13, Mreg, Rsbn1l, Erc2, Akap8, Sf3a1, Akt2, Apob) |
| mmu-miR-2135 | 1.36 | 0.0389 | Upregulated in chlamydial infection in experimental mice [40]. | -- |
| mmu-miR-451 | 1.33 | 0.0191 | Strongly dysregulated in lung cancer and and important miRNA for lung tumor progression [41]. Strongly upregulated in the gingival tissue of Periodontitis [42]. | |
| mmu-miR-30a | 1.28 | 0.0254 | Overexpressed in gingival tissues in periodontitis patients that inhibits osteogenesis and promotes periodontitis [43]. | |
| mmu-miR-30c | 1.25 | 0.0401 | Negative regulator of osteogenic differentiation and bone morphometric protein (BMP)-induced osteogenic differentiation [44]. | |
| mmu-miR-496 | 1.22 | 0.0020 | Tumor metastasis mediated by Wnt signaling pathways in colorectal cancer [45]. Enforced expression of miR-496 reversed the osteogenesis [46]. | |
| mmu-miR-126-5p | 1.21 | 0.0148 | Major role in ovarian cancer by promoting chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cells [30]. Attenuates blood-brain barrier after ischemic stroke [32]. | |
| mmu-miR-151-5p | 1.15 | 0.0088 | Associated with metastasis in breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma [47]. Is a therapeutic target for systemic sclerosis [48]. | |
| mmu-miR-720 | 1.14 | 0.0111 | Promotes glioma growth and upregulates invasion-related genes. Significantly upregulated in glioma tissues and cells [49]. | |
| mmu-miR-100 | 1.11 | 0.0484 | Overexpressed in hypertrophic hearts and promotes pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy through activation of autophagy [50], a potential protective anti-athero-miR [51]. Modulator of cardiac metabolism, ROS production and protective effect in pressure-overload-induced cardiac stress and heart failure [52]. | |
| Upregulated miRNAs in 16-weeks T. denticola infection | ||||
| mmu-miR-486 | 1.29 | 0.0350 | Promotes cardiac angiogenesis through fibroblastic MMP19-VEGFA cleavage signaling pathway [53]. Upregulated in chronic myeloid leukemia. Strongly upregulated in the gingival tissue of Periodontitis [42]. | -- |
| mmu-miR-126-5p | 1.28 | 0.0050 | Major role in ovarian cancer by promoting chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cells [30]. Attenuates blood-brain barrier after ischemic stroke [32]. Promotes the proliferation of endothelial cells and limiting the atherosclerosis [31]. | -- |
| mmu-miR-345-5p | 1.23 | 0.0004 | Overexpression of miR-345 reduce lipid accumulation in adipocytes and their related genes involved in lipogenic transcription, fatty acid synthesis and fatty acid transport [54]. Consistently upregulated salivary biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma [55]. | 124 (e.g., Dlc1, Rarg, Glu1, Dmgdh, Afmid, Acp2, Inpp5b, Eng, Caprin1, Senp2) |
| mmu-miR-132 | 1.21 | 0.0100 | Inhibits differentiation of periodontal ligament cells into osteoblasts [33]. | 482 (e.g., Tthdf3, Wipf, Mapk1, Nek7, Selk, Tspy13, Hus1, Stk35, Arid5b, Plek) |
| mmu-miR-126-3p | 1.2 | 0.0432 | Significantly upregulated in the gingival tissues of chronic and aggressive periodontitis patients [56] and saliva samples of chronic periodontitis [57]. | -- |
| mmu-miR-101a | 1.2 | 0.0460 | Decreased expression observed in serum samples in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) [58]. | |
| mmu-miR-128 | 1.18 | 0.026 | Overexpressed in glioma and a potential noninvasive biomarker to diagnose glioma [59]. | |
| mmu-let-7d | 1.17 | 0.0044 | Attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis [60]. | |
| mmu-miR-423-5p | 1.17 | 0.0199 | Overexpression of miR-423-5p induced breast cancer cell invasion through NFκB signaling pathway [61]. | |
| mmu-miR-101b | 1.17 | 0.0421 | Play a critical mediator of Tauopathy and Dendritic abnormalities in Alzheimer’s Disease progression [62,63]. | |
| mmu-miR-30b | 1.16 | 0.0453 | Overexpressed in osteoarthritis (OA) patients, OA rats and aggravates joint pain and loss of articular cartilage [64,65]. | |
| mmu-miR-221 | 1.14 | 0.0367 | Oncogenic miRNA that is involved in many hematologic and solid malignancies and some non-malignant diseases [66]. | |
| mmu-miR-26b | 1.08 | 0.0442 | Inhibit M1 polarization of microglia by inactivating toll-like receptor pathway [67]. | |
| miRNAs | Fold change | p-value | # of genes | List of genes |
| miR-22* | 1.55 | 0.0011 | 13 | Cbl, Pik3r1, Pik3r3, Ctnna1, Bcar1, Sept8, Dnm1, Wasf2, Rhoa, Actb, Crkl, Rac1, Cav3. |
| miR-30a | 1.28 | 0.0254 | 10 | Cblb, Pik3r1, Ctnna1, Sept8, Sept2, Wasl, Crk, Rac1, Itgb1, Pik3cd. |
| miR-30c | 1.25 | 0.0401 | 10 | Cblb, Pik3r1, Ctnna1, Sept8, Sept2, Wasl, Crk, Rac1, Itgb1, Pik3cd. |
| miR-345-5p* | 1.23 | 0.0004 | 1 | Sept2. |
| miR-132 | 1.21 | 0.0100 | 7 | Cblb, Cltc, Sept2, Actb, Arpc4, Crk, Sept11. |
| miR-101a | 1.2 | 0.0461 | 16 | cbl, Cblb, Sept8, Cltc, Ctnna2, Rhoa, Actb, Sept6, Crk, Cd2ap, Sept11, Itgb1, Elmo1, Met, Cdc42, Cav3. |
| miR-128 | 1.18 | 0.0261 | 9 | Rhog, Pik3r1, Sept8, Dnm1, Wasf2, Sept2, Gab1, Cd2ap, Met. |
| let-7d | 1.17 | 0.0044 | 4 | Rhog, Cltc, Fn1, Met. |
| miR-101b | 1.17 | 0.0421 | 3 | Cltc, Actb, Met. |
| miR-30b | 1.16 | 0.0453 | 9 | Pik3r1, Ctnna1, Cblb, WasI, Sept2, Rac1, Crk, Itgb1, Pik3cd. |
| miR-221 | 1.14 | 0.0367 | 9 | Pik3r1, Pik3r3, DNM2, Ptk2, Cttn, Gab1, Crk, Cd2ap, Itgb1. |
| miR-26b | 1.08 | 0.0442 | 8 | Pik3r3, Cblb, Cltc, Itga5, Sept6, Rac1, Pik3cb, Itgb1. |
| miR-133a | 1.83 | 0.0176 | 6 | Ctnna1, Bcar1, Sept8, WasI, Cd2ap, Arpc5. |
| miR-136 | 1.37 | 0.0066 | 3 | Sept3, Dnma, Crk. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





