Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
12 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- The security advantages of integrating AI and edge/fog computing with IIoT are explored.
- The security requirements and challenges encountered in IIoT environments are highlighted.
- Solutions based on AI and edge/fog computing to these security challenges are thoroughly investigated.
2. Research Methodology
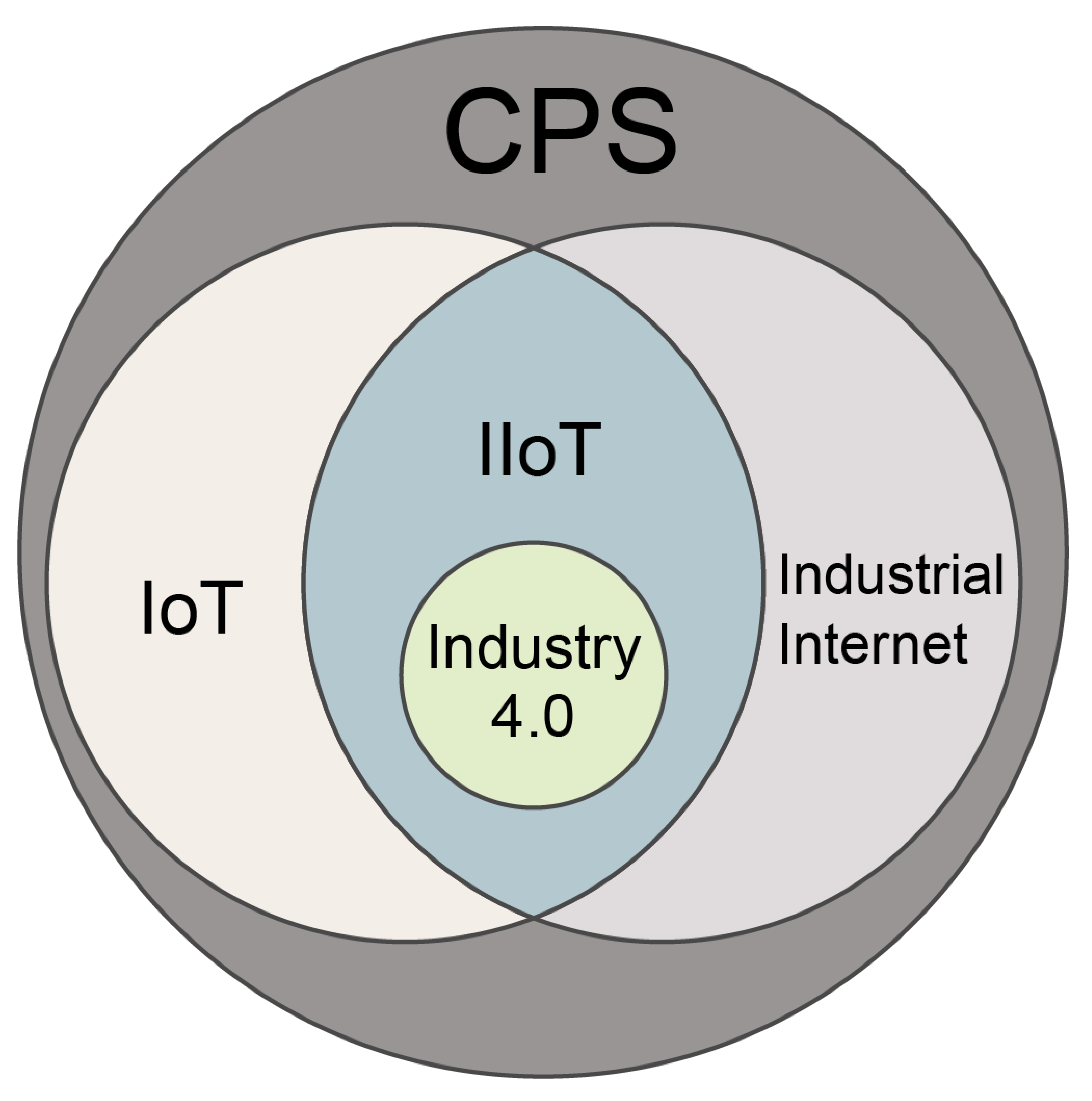
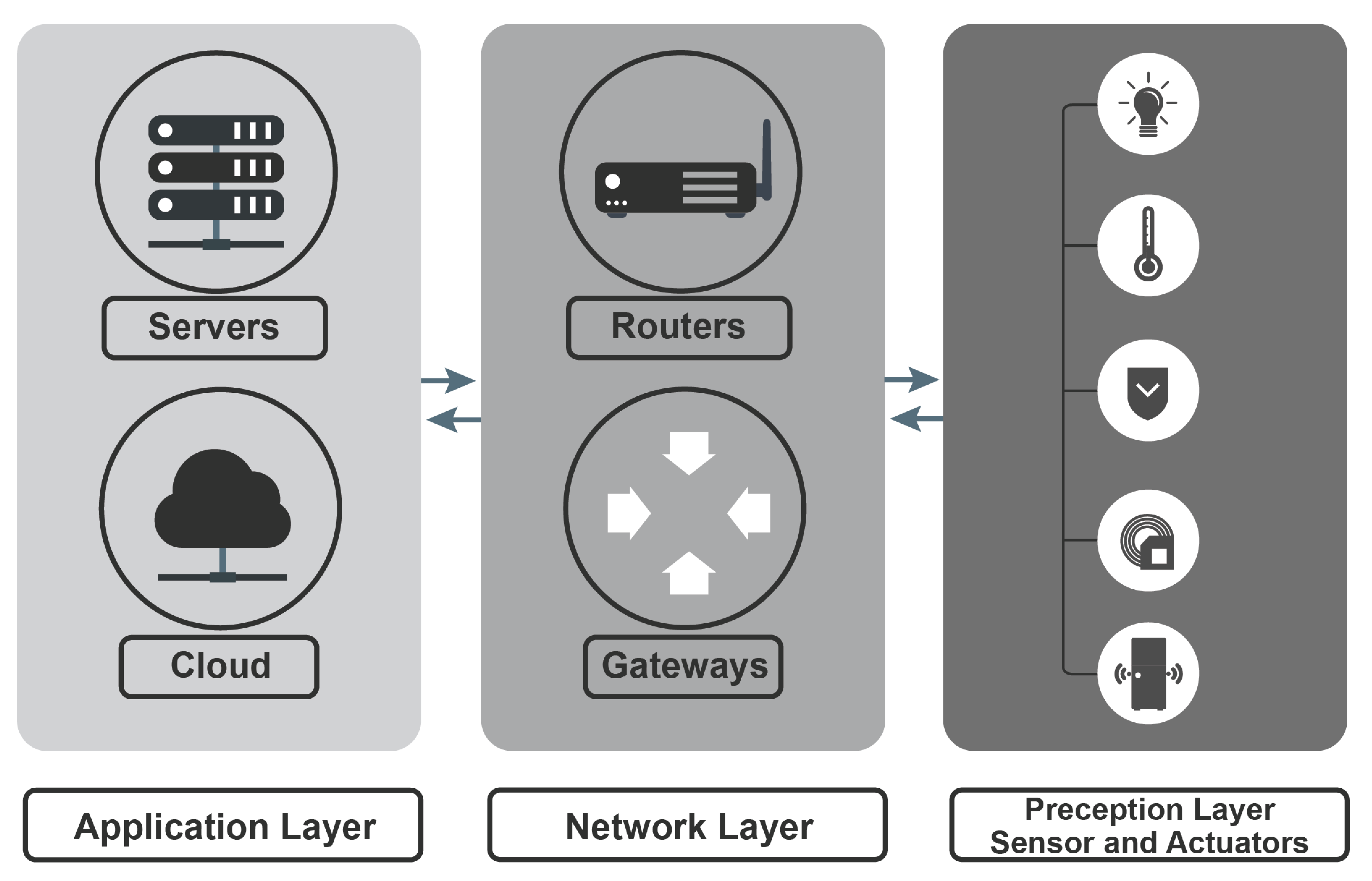
3. IoT/IIoT and Edge/Fog Computing Background
3.1. IoT and IIoT
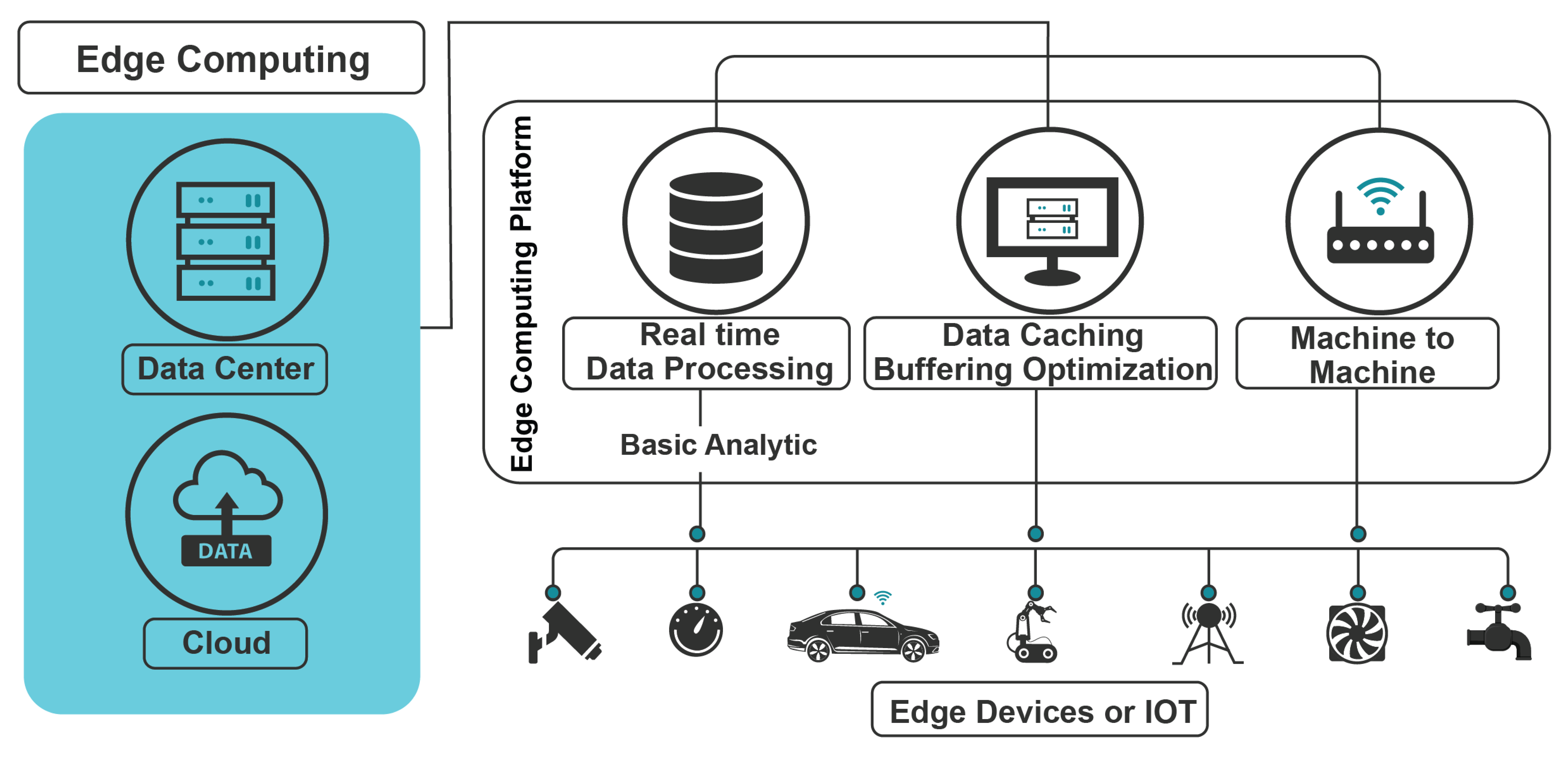
3.2. Edge and Fog Computing
- System performance enhancement: Data processing can be achieved at the network’s edge, improving the system performance of end devices. Edge platforms can accomplish data processing in milliseconds, reducing the latency and communication bandwidth demand, thus enhancing the system’s performance.
- Data security and privacy protection: Edge and fog computing can reduce privacy and security risks, as they transmit and store data in decentralized devices (i.e., near-end devices), as opposed to cloud platforms, which provide centralized data protection solutions. Additionally, data leakage at centralized cloud servers affects many end devices, compared to data leakage at edge/fog devices, involving only a limited number of devices (i.e., the end devices nearby that obtain services from edge/fog platforms).
- Operational cost reduction: When end devices transfer data directly to the cloud, the operational costs related to migrating data, maintaining good bandwidth, and shortening delays are increased. On the other hand, when edge/fog platforms are utilized, the data migration volume, delay, and bandwidth consumption are decreased, leading to reduced operational costs.
4. Related Work
4.1. IoT Security Surveys
4.2. IIoT Security Surveys
4.3. Edge Computing Security Surveys
4.4. Edge Computing in IIoT Surveys
4.5. Secure IIoT-Edge Deployment
5. IIoT Security Requirements
5.1. CIA Triad
- Confidentiality concerns the protection of information in any form. The methods used to satisfy confidentially include access control, encryption, network isolation, and privacy.
- Integrity aims to provide IIoT entities with consistency, authenticity, and accuracy, and allows for building trust with other entities.
- Availability guarantees that the system operates efficiently at all times. Various methods are used to satisfy availability, such as decentralization and redundancy.
5.2. Authentication
5.3. Access Control and Authorization
5.4. Resilience and Maintainability
5.5. Privacy
5.6. Security Monitoring
5.7. Secure Data Sharing
6. IIoT Attack Categories
6.1. Perception Layer Attacks
6.1.1. Node Capture Attacks
6.1.2. Jamming Attacks
6.1.3. Sleep Deprivation Attacks
6.1.4. Replay Attacks
6.2. Network Layer Attacks
6.2.1. Selective-Forwarding Attacks
6.2.2. Eavesdropping Attacks
6.2.3. Sybil and ID Cloning Attacks
6.2.4. Wormhole Attacks
6.2.5. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
6.2.6. Man in the Middle Attacks
6.2.7. Sinkhole Attacks
6.2.8. Blackhole Attacks
6.3. Application Layer Attacks
6.3.1. Malicious Code Injection Attacks
6.3.2. Cross-site or Malicious Scripts Attacks
6.3.3. Malware Injection Attacks
6.3.4. Data Distortion Attacks
6.3.5. SQL Injection Attacks
6.3.6. Ransomware Attacks
6.3.7. Side-channel Attacks
6.3.8. Authorization and Authentication Attacks
7. State-of-the-Art of IIoT Secure Deployment on Edge Computing
7.1. Network Layer Security
7.2. Perception Layer Security
7.3. Application Layer Security
8. Opportunities and Future Directions
8.1. Secure Data Sharing
8.2. Security Monitoring
8.3. Authentication and Access Control
9. Conclusion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things |
| CPS | Cyber-Physical System |
| MCC | Mobile Cloud Computing |
| CC | Cloud Computing |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| DDoS | Distributed Denial of Service |
| IIC | Industrial Internet Consortium |
| GE | General Electric |
| AT&T | American Telephone and Telegraph |
| IBM | International Business Machines |
| CSP | Cloud Service Provider |
| ICV | Intelligent Connected Vehicles |
| CIA | Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability |
| OTA | Over-The-Air |
| DoS | Denial of Service |
| RPL | Routing Protocol for Low-power and lossy networks |
| SQL | Structured Query Language |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition |
| ICS | Industrial Control System |
| WSN | Wireless Sensor Network |
| IDS | Intrusion Detection System |
| SSI | Server-Side Injection |
| XML | eXtensible Markup Language |
| CSRF | Cross-Site Request Forgery |
| XSS | Cross-Site Scripting |
| SSRF | Server-Side Request Forgery |
| DSI | Device-Side Injection |
| RCE | Remote Code Execution |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| SQLI | Structured Query Language Injection |
| VNF | Virtual Network Function |
| AES | Advanced Encryption Standard |
| RSA | Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman |
| SDN | Software-Defined Networking |
| VCC | Vehicular Cloud Computing |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| PKI | Public Key Infrastructure |
| TPM | Trusted Platform Module |
| TEE | Trusted Execution Environment |
| SPOF | Single Point Of Failure |
| RFID | Radio Frequency Identification |
| AP | Access Point |
| Wi-Fi | Wireless Fidelity |
| PEC | Pervasive Edge Computing |
| ABC | Artificial Bee Colony |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| RTT | Round Trip Time |
| IoV | Internet of Vehicles |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| ICS | Industrial Control System |
| FDL | Federated Deep Learning |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| XGBoost | eXtreme Gradient Boosting |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| kNN | k-Nearest Neighbors |
| GDE | Global Detection Enactor |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| HTTP | HyperText Transfer Protocol |
| LAE | Long short-term memory AutoEncoder |
| B-LSTM | Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| GM | Geometric Mean |
| CFBPNN | Cascade Forward Back-Propagation Neural Network |
| CFS | Correlation-based Feature Selection |
| NARX | Non-linear Auto-Regressive network with eXogenous inputs |
| PLC | Program Logic Controller |
| I/O | Input/Output |
| IIRA | Industrial Internet Reference Architecture |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| DTW | Dynamic Time Warping |
| FHSS | Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum |
| DSSS | Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum |
| IPS | Intrusion Prevention System |
| PUF | Physically Unclonable Functions |
| GnuPG | GNU Privacy Guard |
| WAF | Web Application Firewall |
| DNS | Domain Name System |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| AMI | Advanced Metering Infrastructure |
| HAN | Home Area Network |
| MC | Markov Chain |
References
- Chalapathi, G. S. S.; Chamola, V.; Vaish, A.; Buyya, R. Industrial internet of things (iiot) applications of edge and fog computing: A review and future directions. Fog/edge computing for security, privacy, and applications 2021, 293–325. [Google Scholar]
- Alotaibi, B. Utilizing blockchain to overcome cyber security concerns in the internet of things: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal 2019, 19(23), 10953–10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishehgarkhaneh, M. B.; Moehler, R. C.; Moradinia, S. F. Blockchain in the Construction Industry between 2016 and 2022: A Review, Bibliometric, and Network Analysis. Smart Cities 2023, 6(2), 819–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D. Using the internet of things in smart energy systems and networks. Sustainable Cities and Society 2021, 68, 102783. [Google Scholar]
- Tufail, A.; Namoun, A.; Abi Sen, A. A.; Kim, K. H.; Alrehaili, A.; Ali, A. Moisture computing-based internet of vehicles (Iov) architecture for smart cities. Sensors 2021, 21(11), 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisinni, E.; Saifullah, A.; Han, S.; Jennehag, U.; Gidlund, M. Industrial internet of things: Challenges, opportunities, and directions. IEEE transactions on industrial informatics 2018, 14(11), 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, W.; Griffith, D.; Golmie, N. A survey on industrial Internet of Things: A cyber-physical systems perspective. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 78238–78259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basir, R.; Qaisar, S.; Ali, M.; Aldwairi, M.; Ashraf, M. I.; Mahmood, A.; Gidlund, M. Fog computing enabling industrial internet of things: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Sensors 2019, 19(21), 4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanescu, D.; Galán-García, P.; Montalvillo, L.; Unzilla, J.; Urbieta, A. Industrial Data Homogenization and Monitoring Scheme with Blockchain Oracles. Smart Cities 2023, 6(1), 263–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tange, K.; De Donno, M.; Fafoutis, X.; Dragoni, N. A systematic survey of industrial Internet of Things security: Requirements and fog computing opportunities. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2020, 22, 2489–2520. [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty, P.; Berthon, B. Winning with the industrial internet of things: How to accelerate the journey to productivity and growth; Accenture: Dublín, Ireland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani, M. M.; Dushku, E.; Vliegen, J.; Braeken, A.; Dragoni, N.; Mentens, N. (2021, November). Reserve: Remote attestation of intermittent iot devices. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (pp. 578-580).
- Fernández-Carrasco, J. Á.; Echeberria-Barrio, X.; Paredes-García, D.; Zola, F.; Orduna-Urrutia, R. , Zola, F.; Orduna-Urrutia, R. ChronoEOS 2.0: Device Fingerprinting and EOSIO Blockchain Technology for On-Running Forensic Analysis in an IoT Environment. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenofontos, C.; Zografopoulos, I.; Konstantinou, C.; Jolfaei, A.; Khan, M. K.; Choo, K. K. R. Consumer, commercial, and industrial iot (in) security: Attack taxonomy and case studies. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 9, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M. A.; Friha, O.; Hamouda, D.; Maglaras, L.; Janicke, H. Edge-IIoTset: A new comprehensive realistic cyber security dataset of IoT and IIoT applications for centralized and federated learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 40281–40306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, A.; De Donato, W.; Persico, V.; Pescapé, A. Integration of cloud computing and internet of things: a survey. Future generation computer systems 2016, 56, 684–700. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, M.; Martín, C.; Rubio, B. State-of-the-art, challenges, and open issues in the integration of Internet of things and cloud computing. Journal of Network and Computer applications 2016, 67, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadzadeh, G.; Rahmani, A. M. Fog computing applications in smart cities: A systematic survey. Wireless Networks 2020, 26(2), 1433–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M. M.; Beg, M. S. Fog computing for internet of things (IoT)-aided smart grid architectures. Big Data and cognitive computing 2019, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, Y. I.; Osmanaj, V. H.; Jaradat, A.; Al-Ahmad, A. Fog computing security and privacy for the Internet of Thing applications: State-of-the-art. Security and Privacy 2021, 4(2), e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T., Chi; Wu, D. O. Edge computing in industrial internet of things: Architecture, advances and challenges. In IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials; 2020; Volume 22, pp. 2462–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Touqeer, H.; Zaman, S.; Amin, R.; Hussain, M.; Al-Turjman, F.; Bilal, M. Smart home security: challenges, issues and solutions at different IoT layers. The Journal of Supercomputing 2021, 77(12), 14053–14089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, A.; Adhikari, M.; Amgoth, T.; Srirama, S. N. A comprehensive survey on interoperability for IIoT: Taxonomy, standards, and future directions. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 2021, 55(1), 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguliyev, R.; Imamverdiyev, Y.; Sukhostat, L. Cyber-physical systems and their security issues. Computers in Industry 2018, 100, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A. M.; Hussein, D.; Park, S.; Han, S. N.; Crespi, N. The cluster between internet of things and social networks: Review and research challenges. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2014, 1(3), 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivoto, D. G.; de Almeida, L. F.; da Rosa Righi, R.; Rodrigues, J. J.; Lugli, A. B.; Alberti, A. M. Cyber-physical systems architectures for industrial internet of things applications in Industry 4.0: A literature review. Journal of manufacturing systems 2021, 58, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D. S.; Zhang, P.; Silva, J. S. A survey on human-in-the-loop applications towards an internet of all. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2015, 17, 944–965. [Google Scholar]
- Stojmenovic, I. Machine-to-machine communications with in-network data aggregation, processing, and actuation for large-scale cyber-physical systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2014, 1(2), 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Guan, Y. L.; Leung, K. K.; Zhang, Y. Reconfigurable intelligent surface for low-latency edge computing in 6G. IEEE Wireless Communications 2021, 28(6), 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, K.; Dilek, S.; Tosun, S.; Ozdemir, S. A survey on computation offloading and service placement in fog computing-based IoT. The Journal of Supercomputing 2022, 78(2), 1983–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofla, M. S.; Kashani, M. H.; Mahdipour, E.; Mirzaee, R. F. Towards effective offloading mechanisms in fog computing. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2022, 81(2), 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghello, F.; Calore, M.; Zucchetto, D.; Polese, M.; Zanella, A. IoT: Internet of threats? A survey of practical security vulnerabilities in real IoT devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 6(5), 8182–8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshenko, N.; Bou-Harb, E.; Crichigno, J.; Kaddoum, G.; Ghani, N. Demystifying IoT security: An exhaustive survey on IoT vulnerabilities and a first empirical look on Internet-scale IoT exploitations. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2019, 21, 2702–2733. [Google Scholar]
- Kouicem, D. E.; Bouabdallah, A.; Lakhlef, H. Internet of things security: A top-down survey. Computer Networks 2018, 141, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzi, M.; Lazoi, M.; Corallo, A. Cybersecurity for Industry 4.0 in the current literature: A reference framework. Computers in Industry 2018, 103, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, F. Architecture, technologies and challenges for cyber-physical systems in industry 4.0: A systematic mapping study. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement; 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hansch, G.; Schneider, P.; Fischer, K.; Böttinger, K. A unified architecture for industrial IoT security requirements in open platform communications. In Proceedings of the 2019 24th ieee international conference on emerging technologies and factory automation (etfa); IEEE; pp. 325–332.
- Sadeghi, A. R.; Wachsmann, C.; Waidner, M. Security and privacy challenges in industrial internet of things. In Proceedings of the 52nd annual design automation conference, San Fransisco, California, 07–11 June 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sajid, A.; Abbas, H.; Saleem, K. Cloud-assisted IoT-based SCADA systems security: A review of the state of the art and future challenges. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S. F.; Samsudin, A. Recent technologies, security countermeasure and ongoing challenges of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): A survey. Sensors 2021, 21(19), 6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Lin, X.; Shen, X. S. Toward edge-assisted Internet of Things: From security and efficiency perspectives. IEEE Network 2019, 33(2), 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Shao, J.; Wei, G.; Xie, M. Data security and privacy in fog computing. IEEE Network 2018, 32(5), 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Hu, F. Data security and privacy-preserving in edge computing paradigm: Survey and open issues. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 18209–18237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulos, D.; Jayaraman, P. P.; Fazia, M.; Villari, M.; Ranjan, R. Internet of Things and edge cloud computing roadmap for manufacturing. IEEE Cloud Computing 2016, 3(4), 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, A.; Buchinger, D.; Bruegge, B. The conjunction of fog computing and the industrial internet of things-an applied approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops); IEEE, 812; 817. [Google Scholar]
- Sittón-Candanedo, I.; Alonso, R. S.; Rodríguez-González, S.; García Coria, J. A.; De La Prieta, F. Edge computing architectures in industry 4.0: A general survey and comparison. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2019), Seville, Spain, 15, 2019; Springer International Publishing, 13 May 2020; pp. 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, W.; Poledna, S. Fog computing as enabler for the Industrial Internet of Things. Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik 2016, 133(7), 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazam, M.; Zeadally, S.; Harras, K. A. Deploying fog computing in industrial internet of things and industry 4.0. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 14(10), 4674–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, A.; Modi, S.; Mulchandani, S. Towards effective security control assignment in the Industrial Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 2nd World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT); IEEE; pp. 795–800.
- Ferrag, M. A.; Maglaras, L. A.; Janicke, H. , Jiang, J.; Shu, L. Authentication protocols for internet of things: a comprehensive survey. Security and Communication Networks 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.; Barreto, L.; Amaral, A. Network and information security challenges within Industry 4.0 paradigm. Procedia manufacturing 2017, 13, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, A., Khan. Secure-CamFlow: a device-oriented security model to assist information flow control systems in cloud environments for IoTs 2019, 31, e4729.
- Dammak, M.; Boudia, O. R. M.; Messous, M. A.; Senouci, S. M.; Gransart, C. Token-based lightweight authentication to secure IoT networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC); IEEE; pp. 1–4.
- Falco, G.; Caldera, C.; Shrobe, H. IIoT cybersecurity risk modeling for SCADA systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 5(6), 4486–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riad, K.; Hamza, R.; Yan, H. Sensitive and energetic IoT access control for managing cloud electronic health records. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 86384–86393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, S.; Khan, F. I.; Hameed, B. Understanding security requirements and challenges in Internet of Things (IoT): A review. Journal of Computer Networks and Communications 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Tian, Y.; Tian, H. Resilience in Industrial Internet of Things Systems: A Communication Perspective. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2206.00217. [Google Scholar]
- Laszka, A.; Abbas, W.; Vorobeychik, Y.; Koutsoukos, X. Synergistic security for the industrial internet of things: Integrating redundancy, diversity, and hardening. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Internet (ICII); IEEE; pp. 153–158.
- Zhou, L.; Guo, H. (2018, July). Anomaly detection methods for IIoT networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics (SOLI); IEEE; pp. 214–219.
- Bakhshi, Z.; Balador, A.; Mustafa, J. (2018, April). Industrial IoT security threats and concerns by considering Cisco and Microsoft IoT reference models. In 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops (WCNCW) (pp. 173-178). IEEE.
- Solangi, Z. A.; Solangi, Y. A.; Chandio, S.; bin Hamzah, M. S.; Shah, A. (2018, May). The future of data privacy and security concerns in Internet of Things. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Innovative Research and Development (ICIRD) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- Khan, W. Z.; Aalsalem, M. Y.; Khan, M. K. Communal acts of IoT consumers: A potential threat to security and privacy. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 2018, 65(1), 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yeh, K. H.; Hancke, G.; Liu, Z.; Su, C. Security and privacy for the industrial internet of things: An overview of approaches to safeguarding endpoints. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2018, 35(5), 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settanni, G.; Skopik, F.; Karaj, A.; Wurzenberger, M.; Fiedler, R. (2018, May). Protecting cyber physical production systems using anomaly detection to enable self-adaptation. In 2018 IEEE Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS) (pp. 173-180). IEEE.
- Zolanvari, M.; Teixeira, M. A.; Jain, R. (2018, November). Effect of imbalanced datasets on security of industrial IoT using machine learning. In 2018 IEEE international conference on intelligence and security informatics (ISI) (pp. 112-117). IEEE.
- Zugasti, E.; Iturbe, M.; Garitano, I.; Zurutuza, U. (2018, June). Null is not always empty: Monitoring the null space for field-level anomaly detection in industrial IoT environments. In 2018 Global Internet of Things Summit (GIoTS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Elrawy, M. F.; Awad, A. I.; Hamed, H. F. Intrusion detection systems for IoT-based smart environments: a survey. Journal of Cloud Computing 2018, 7(1), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Loyola, J.; Sala, D.; Ali, A. I. (2008, October). Accurate real-time monitoring of bottlenecks and performance of packet trace collection. In 2008 33rd IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN) (pp. 884-891). IEEE.
- Rubio-Loyola, J.; Sala, D.; Ali, A. I. (2008, September). Maximizing packet loss monitoring accuracy for reliable trace collections. In 2008 16th IEEE workshop on local and metropolitan area networks (pp. 61-66). IEEE.
- Ghorbani, A. A.; Lu, W.; Tavallaee, M. Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention, Advances in Information Security 2010. Inf. Syst, 223.
- Anwar, S.; Mohamad Zain, J.; Zolkipli, M. F.; Inayat, Z.; Khan, S.; Anthony, B.; Chang, V. From intrusion detection to an intrusion response system: fundamentals, requirements, and future directions. Algorithms 2017, 10(2), 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bul’ajoul, W.; James, A.; Pannu, M. Improving network intrusion detection system performance through quality of service configuration and parallel technology. Journal of Computer and System Sciences 2015, 81(6), 981–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Li, W.; Kwok, L. F. EFM: enhancing the performance of signature-based network intrusion detection systems using enhanced filter mechanism. computers & security 2014, 43, 189–204. [Google Scholar]
- Abduvaliyev, A.; Pathan, A. S. K.; Zhou, J.; Roman, R.; Wong, W. C. On the vital areas of intrusion detection systems in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 1223. [Google Scholar]
- Nisioti, A.; Mylonas, A.; Yoo, P. D.; Katos, V. From intrusion detection to attacker attribution: A comprehensive survey of unsupervised methods. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 3369. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuyan, M. H.; Bhattacharyya, D. K.; Kalita, J. K. Network anomaly detection: methods, systems and tools. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials.
- Hong, J.; Liu, C. C.; Govindarasu, M. Integrated anomaly detection for cyber security of the substations. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2014, 5(4), 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Pilli, E. S.; Varadharajan, V.; Tupakula, U. Intrusion detection techniques in cloud environment: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2017, 77, 18–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesjak, C.; Ruprechter, T.; Bock, H.; Haid, J.; Brenner, E. (2014, December). ESTADO—Enabling smart services for industrial equipment through a secured, transparent and ad-hoc data transmission online. In The 9th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST-2014) (pp. 171-177). IEEE.
- Autenrieth, P.; Lörcher, C.; Pfeiffer, C.; Winkens, T.; Martin, L. (2018, June). Current significance of IT-infrastructure enabling industry 4.0 in large companies. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
- Jazdi, N. (2014, May). Cyber physical systems in the context of Industry 4.0. In 2014 IEEE international conference on automation, quality and testing, robotics (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- Moyne, J.; Mashiro, S.; Gross, D. (2018, April). Determining a security roadmap for the microelectronics industry. In 2018 29th Annual SEMI Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing Conference (ASMC) (pp. 291-294). IEEE.
- Benias, N.; Markopoulos, A. P. (2017, September). A review on the readiness level and cyber-security challenges in Industry 4.0. In 2017 South Eastern European Design Automation, Computer Engineering, Computer Networks and Social Media Conference (SEEDA-CECNSM) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
- Drias, Z.; Serhrouchni, A.; Vogel, O. (2015, August). Analysis of cyber security for industrial control systems. In 2015 international conference on cyber security of smart cities, industrial control system and communications (ssic) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
- Oztemel, E.; Gursev, S. Literature review of Industry 4.0 and related technologies. Journal of intelligent manufacturing 2020, 31, 127–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, T.; Zhou, L. (2015, August). Industry 4.0: Towards future industrial opportunities and challenges. In 2015 12th International conference on fuzzy systems and knowledge discovery (FSKD) (pp. 2147-2152). IEEE.
- Putra, F. A.; Ramli, K.; Hayati, N.; Gunawan, T. S. PURA-SCIS protocol: A novel solution for cloud-based information sharing protection for sectoral organizations. Symmetry 2021, 13(12), 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.; Castiglione, A.; Martini, B.; Choo, K. K. R. Cloud manufacturing: security, privacy, and forensic concerns. IEEE Cloud Computing 2016, 3(4), 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba Ari, A. A.; Ngangmo, O. K.; Titouna, C.; Thiare, O.; Mohamadou, A.; Gueroui, A. M. Enabling privacy and security in Cloud of Things: Architecture, applications, security & privacy challenges. Applied Computing and Informatics 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Abosata, N.; Al-Rubaye, S.; Inalhan, G.; Emmanouilidis, C. Internet of things for system integrity: A comprehensive survey on security, attacks and countermeasures for industrial applications. Sensors 2021, 21(11), 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S.; Engels, D. W.; Thathapudi, S. (2015, October). Black SDN for the Internet of Things. In 2015 IEEE 12th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (pp. 190-198). IEEE.
- Lakshminarayana, S.; Karachiwala, J. S.; Chang, S. Y.; Revadigar, G.; Kumar, S. L. S.; Yau, D. K.; Hu, Y. C. (2018, June). Signal jamming attacks against communication-based train control: Attack impact and countermeasure. In Proceedings of the 11th ACM Conference on Security & Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks (pp. 160-171).
- Aarika, K.; Bouhlal, M.; Abdelouahid, R. A.; Elfilali, S.; Benlahmar, E. Perception layer security in the internet of things. Procedia Computer Science 2020, 175, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, H. A.; Konstantas, D. A comprehensive study of security and privacy guidelines, threats, and countermeasures: An IoT perspective. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks 2019, 8(2), 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, F.; Ning, H.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Choo, K. K. R. Timestamp scheme to mitigate replay attacks in secure ZigBee networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2020, 21(1), 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikis, P. I. R.; Sarigiannidis, P. G.; Moscholios, I. D. Securing the Internet of Things: Challenges, threats and solutions. Internet of Things 2019, 5, 41–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M. K.; Ghazal, T. M.; Saeed, R. A.; Pandey, B.; Gohel, H.; Eshmawi, A. A. , ... ; Alkhassawneh, H. M. A review on security threats, vulnerabilities, and counter measures of 5G enabled Internet-of-Medical-Things. IET Communications.
- Kaliyar, P.; Jaballah, W. B.; Conti, M.; Lal, C. LiDL: localization with early detection of sybil and wormhole attacks in IoT networks. Computers & Security 2020, 94, 101849. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.; Aggarwal, A.; Chaubey, N. Wormhole attacks and countermeasures in wireless sensor networks: a survey. International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) 2017, ISSN, 0975–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuitcheu, H.; Debes, M.; Aumüller, M.; Seitz, J. (2022, March). Recent review of distributed denial of service attacks in the internet of things. In 2022 5th Conference on Cloud and Internet of Things (CIoT) (pp. 32-39). IEEE.
- Tsiknas, K.; Taketzis, D.; Demertzis, K.; Skianis, C. Cyber threats to industrial IoT: a survey on attacks and countermeasures. IoT 2021, 2(1), 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Bhushan, B.; Khamparia, A. challenges. In Emerging Technologies in Data Mining and Information Security: Proceedings of IEMIS 2020, Volume 1 (pp.; pp. 873–885.
- Sharma, G.; Vidalis, S.; Anand, N.; Menon, C.; Kumar, S. A survey on layer-wise security attacks in IoT: Attacks, countermeasures, and open-issues. Electronics 2021, 10(19), 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butun, I.; Österberg, P.; Song, H. Security of the Internet of Things: Vulnerabilities, attacks, and countermeasures. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials.
- Bagga, M.; Thakral, P.; Bagga, T. (2018, December). A Study on IoT: Model, Communication Protocols, Security Hazards & Countermeasures. In 2018 Fifth International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Grid Computing (PDGC) (pp. 591-598). IEEE.
- Rodríguez, G. E.; Torres, J. G.; Flores, P.; Benavides, D. E. Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks and mitigation: A survey. Computer Networks 2020, 166, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhavathy, M.; Umamaheswari, S. Prevention of Runtime Malware Injection Attack in Cloud Using Unsupervised Learning. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing.
- Xing, K.; Srinivasan, S. S. R.; Rivera, M. J. M.; Li, J.; Cheng, X. Attacks and countermeasures in sensor networks: a survey. Network security 2010, 251–272. [Google Scholar]
- Halfond, W. G.; Viegas, J.; Orso, A. (2006, March). In A classification of SQL-injection attacks and countermeasures. In Proceedings of the IEEE international symposium on secure software engineering (Vol. 1; pp. 13–15.
- Silva, J. A. H.; López, L. I. B.; Caraguay, Á. L. V.; Hernández-Álvarez, M. A survey on situational awareness of ransomware attacks—detection and prevention parameters. Remote Sensing.
- Spreitzer, R.; Moonsamy, V.; Korak, T.; Mangard, S. Systematic classification of side-channel attacks: A case study for mobile devices. IEEE communications surveys & tutorials.
- Jesudoss, A.; Subramaniam, N. A survey on authentication attacks and countermeasures in a distributed environment. Indian Journal of Computer Science and Engineering (IJCSE) 2014, 5(2), 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Deogirikar, J.; Vidhate, A. (2017, February). Security attacks in IoT: A survey. In 2017 International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud)(I-SMAC) (pp. 32-37). IEEE.
- Kumar, S.; Sahoo, S.; Mahapatra, A.; Swain, A. K.; Mahapatra, K. K. (2017, December). Security enhancements to system on chip devices for IoT perception layer. In 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Nanoelectronic and Information Systems (iNIS) (pp. 151-156). IEEE.
- Ingham, M.; Marchang, J.; Bhowmik, D. IoT security vulnerabilities and predictive signal jamming attack analysis in LoRaWAN. IET information security 2020, 14(4), 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Niazy, M. S.; Ziar, R. A.; Khan, S. Survey on IoT: security threats and applications. Journal of Robotics and Control (JRC) 2021, 2(1), 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, E.; Belyakov, D.; Bragin, D.; Konev, A. IoT Security Mechanisms in the Example of BLE. Computers 2021, 10(12), 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, L.; Gupta, D.; Saxena, S.; Tanwar, S. (2021). IoT architectures and its security: a review. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Information Management and Machine Intelligence: ICIMMI 2020 (pp. 87-94). Springer Singapore. [Google Scholar]
- Wallgren, L.; Raza, S.; Voigt, T. Routing attacks and countermeasures in the RPL-based internet of things. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks 2013, 9(8), 794326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z.; Wu, Y. The DPC-based scheme for detecting selective forwarding in clustered wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 20954–20967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Y.; Sengupta, S. (2020, October). A survey on Classification of Cyber-attacks on IoT and IIoT devices. In 2020 11th IEEE Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON) (pp. 0406-0413). IEEE.
- de Oliveira, G. H.; de Souza Batista, A.; Nogueira, M.; dos Santos, A. L. An access control for IoT based on network community perception and social trust against Sybil attacks. International Journal of Network Management 2022, 32(1), e2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Molina, C. D.; Hernandez-Suarez, A.; Sanchez-Perez, G.; Toscano-Medina, L. K.; Perez-Meana, H.; Olivares-Mercado, J. .. Garcia-Villalba, L. J. A dense neural network approach for detecting clone id attacks on the rpl protocol of the iot. Sensors 2021, 21(9), 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongle, P.; Chavan, G. (2015, January). A survey: Attacks on RPL and 6LoWPAN in IoT. In 2015 International conference on pervasive computing (ICPC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Kamaleshwar, T.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Teekaraman, Y.; Kuppusamy, R.; Radhakrishnan, A. Self-adaptive framework for rectification and detection of black hole and wormhole attacks in 6lowpan. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, S. A.; Sonavane, S. S. Wormhole attack detection system for IoT network: A hybrid approach. Wireless Personal Communications 2022, 124(2), 1081–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adefemi Alimi, K. O. , Ouahada, K., Abu-Mahfouz, A. M., Rimer, S., & Alimi, O. A. (2022). Refined LSTM based intrusion detection for denial-of-service attack in Internet of Things. Journal of sensor and actuator networks, 11(3), 32.
- Jazzar, M.; Hamad, M. (2022, January). An Analysis Study of IoT and DoS Attack Perspective. In Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems: ICPS 2021 (pp. 127-142). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, A.; De Sena, A. S.; Gutierrez-Rojas, D.; Melgarejo, D. C.; Hussain, H. M.; Ullah, M. .. ; Nardelli, P. H. Key advances in pervasive edge computing for industrial internet of things in 5g and beyond. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 206734–206754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Miranda, J. C.; Gavrilovska, A. (2018). Towards IoT-DDoS Prevention Using Edge Computing. In USENIX workshop on hot topics in edge computing (HotEdge 18).
- Zhou, L.; Guo, H.; Deng, G. A fog computing based approach to DDoS mitigation in IIoT systems. Computers & Security 2019, 85, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Antonakakis, M.; April, T.; Bailey, M.; Bernhard, M.; Bursztein, E.; Cochran, J. ;... Zhou, Y. (2017). Understanding the mirai botnet. In 26th USENIX security symposium (USENIX Security 17) (pp. 1093-1110).
- Abdul-Ghani, H. A.; Konstantas, D.; Mahyoub, M. A comprehensive IoT attacks survey based on a building-blocked reference model. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2018, 9(3), 355–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannou, C.; Vassiliou, V. Network attack classification in IoT using support vector machines. Journal of sensor and actuator networks 2021, 10(3), 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioulianou, P. P.; Vassilakis, V. G.; Shahandashti, S. F. A trust-based intrusion detection system for RPL networks: Detecting a combination of rank and blackhole attacks. Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy 2022, 2(1), 124–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donta, P. K.; Srirama, S. N.; Amgoth, T.; Annavarapu, C. S. R. Survey on recent advances in IoT application layer protocols and machine learning scope for research directions. Digital Communications and Networks 2022, 8(5), 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Hamad, R.; Abdulrahman, M.; Moala, H.; Elkhediri, S. (2019, May). CyberSecurity: a review of internet of things (IoT) security issues, challenges and techniques. In 2019 2nd International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Acar, G.; Huang, D. Y.; Li, F. , Narayanan, A. ; Feamster, August). Web-based attacks to discover and control local IoT devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 Workshop on IoT Security and Privacy (pp. 29-35)., N. (2018. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, M. R.; Marnerides, A. K.; Mauthe, A.; Hutchison, D. Malware detection in cloud computing infrastructures. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2015, 13(2), 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, C.; Yu, H.; Zhan, J. (2013, July). In Cloud computing security case studies and research. In Proceedings of the world congress on engineering (Vol. 2, No. 2; pp. 1–6.
- Xiao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Liu, C.; Cheng, X.; Yu, J.; Lv, W. Edge computing security: State of the art and challenges. Proceedings of the IEEE 2019, 107(8), 1608–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Malik, A.; Singh, N.; Kumar, S. (2019, March). Recent advances and countermeasures against various attacks in IoT environment. In 2019 2nd international conference on signal processing and communication (ICSPC) (pp. 315-319). IEEE.
- Zolanvari, M.; Teixeira, M. A.; Gupta, L.; Khan, K. M.; Jain, R. Machine learning-based network vulnerability analysis of industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 6(4), 6822–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humayun, M.; Jhanjhi, N. Z.; Alsayat, A.; Ponnusamy, V. Internet of things and ransomware: Evolution, mitigation and prevention. Egyptian Informatics Journal 2021, 22(1), 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, W.; Peinado, M. (2015, May). Controlled-channel attacks: Deterministic side channels for untrusted operating systems. In 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (pp. 640-656). IEEE.
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, R. B. (2016). Cloudradar: A real-time side-channel attack detection system in clouds. In Research in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses: 19th International Symposium, RAID 2016, Paris, France, -21, 2016, Proceedings 19 (pp. 118-140). Springer International Publishing. 19 September.
- Lyu, Y.; Mishra, P. A survey of side-channel attacks on caches and countermeasures. Journal of Hardware and Systems Security 2018, 2, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M. S.; Alsamhi, S. H.; Qiao, Y.; Ye, Y.; Lee, B. (2020). Security of distributed intelligence in edge computing: Threats and countermeasures. The Cloud-to-Thing Continuum: Opportunities and Challenges in Cloud, Fog and Edge Computing, 95-122.
- Alkhwaja, I.; Albugami, M.; Alkhwaja, A.; Alghamdi, M.; Abahussain, H.; Alfawaz, F. .. Min-Allah, N. Password Cracking with Brute Force Algorithm and Dictionary Attack Using Parallel Programming. Applied Sciences 2023, 13(10), 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuin, N. K.; Selvarajah, V. (2021, September). A Case Study: SYN Flood Attack Launched Through Metasploit. In 3rd International Conference on Integrated Intelligent Computing Communication & Security (ICIIC 2021) (pp. 520-525). Atlantis Press.
- Qiu, T.; Liu, J.; Si, W.; Wu, D. O. Robustness optimization scheme with multi-population co-evolution for scale-free wireless sensor networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 1028. [Google Scholar]
- Diro, A.; Chilamkurti, N. Leveraging LSTM networks for attack detection in fog-to-things communications. IEEE Communications Magazine 2018, 56(9), 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekired, D. A.; Khoukhi, L.; Mouftah, H. T. (2019, May). Fog-based distributed intrusion detection system against false metering attacks in smart grid. In ICC 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Huang, H.; Ye, P.; Hu, M.; Wu, J. A multi-point collaborative DDoS defense mechanism for IIoT environment. Digital Communications and Networks 2023, 9(2), 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudassir, M.; Unal, D.; Hammoudeh, M.; Azzedin, F. Detection of botnet attacks against industrial IoT systems by multilayer deep learning approaches. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsogbaatar, E.; Bhuyan, M. H.; Taenaka, Y.; Fall, D.; Gonchigsumlaa, K.; Elmroth, E.; Kadobayashi, Y. DeL-IoT: A deep ensemble learning approach to uncover anomalies in IoT. Internet of Things 2021, 14, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, S. I.; Adebisi, B.; Hammoudeh, M.; Gui, G.; Gacanin, H. Hybrid deep learning for botnet attack detection in the internet-of-things networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 8(6), 4944–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, S. I.; Adebisi, B.; Ande, R.; Hammoudeh, M.; Anoh, K.; Atayero, A. A. smote-drnn: A deep learning algorithm for botnet detection in the internet-of-things networks. Sensors 2021, 21(9), 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalaxmi, P. L. S.; Kumar, G.; Saha, R.; Conti, M.; Kim, T. H.; Thomas, R. DeBot: A deep learning-based model for bot detection in industrial internet-of-things. Computers and Electrical Engineering 2022, 102, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alani, M. M. BotStop: Packet-based efficient and explainable IoT botnet detection using machine learning. Computer Communications 2022, 193, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, S. I.; Ande, R.; Adebisi, B.; Gui, G.; Hammoudeh, M.; Jogunola, O. Federated deep learning for zero-day botnet attack detection in IoT-edge devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 9(5), 3930–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lyu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Lyu, X. FLEAM: A federated learning empowered architecture to mitigate DDoS in industrial IoT. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2021, 18(6), 4059–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazid, M.; Reshma Dsouza, P.; Das, A. K.; Bhat K, V.; Kumar, N.; Rodrigues, J. J. RAD-EI: A routing attack detection scheme for edge-based Internet of Things environment. International Journal of Communication Systems 2019, 32(15), e4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Aksanli, B. (2019, November). Real-time traffic monitoring and SQL injection attack detection for edge networks. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM International Symposium on QoS and Security for Wireless and Mobile Networks (pp. 29-36).
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W.; Luo, X.; Gong, Q.; Yu, F. R. A multi-level DDoS mitigation framework for the industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Communications Magazine 2018, 56(2), 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S. V.; Nagarajan, G. A fuzzy based co-operative blackmailing attack detection scheme for edge computing nodes in MANET-IOT environment. Future Generation Computer Systems 2021, 125, 544–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaminkar, M.; Fotohi, R. SoS-RPL: securing internet of things against sinkhole attack using RPL protocol-based node rating and ranking mechanism. Wireless Personal Communications 2020, 114(2), 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Jan, M. A.; ur Rehman, A.; Mastorakis, S.; Alazab, M.; Watters, P. A secured and intelligent communication scheme for IIoT-enabled pervasive edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2020, 17(7), 5128–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, M. A.; Shaikh, R. A.; Hassan, S. R. An anomaly mitigation framework for iot using fog computing. Electronics 2020, 9(10), 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.; Alosaimi, W.; Alyami, H.; Rauf, H. T.; Damaševičius, R. Botnet attack detection using local global best bat algorithm for industrial internet of things. Electronics 2021, 10(11), 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T. N.; Ngo, Q. D.; Nguyen, H. T.; Nguyen, G. L. An advanced computing approach for IoT-botnet detection in industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2022, 18(11), 8298–8306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, M.; Mathkour, H.; Ben Ismail, M. M. IoT botnet attack detection based on optimized extreme gradient boosting and feature selection. Sensors 2020, 20(21), 6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, J.; Abdellatif, M. M.; Khan, M. M.; Azad, M. A. (2018, April). A novel framework for collaborative intrusion detection for m2m networks. In 2018 9th international conference on information and communication systems (ICICS) (pp. 12-17). IEEE.
- Arshad, J.; Azad, M. A.; Abdeltaif, M. M.; Salah, K. An intrusion detection framework for energy constrained IoT devices. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2020, 136, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, R. H.; Zheng, D.; Li, J.; Wu, P.; Cao, J. Efficient and robust certificateless signature for data crowdsensing in cloud-assisted industrial IoT. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2019, 15(9), 5099–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Lu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, X. Efficient data access control with fine-grained data protection in cloud-assisted IIoT. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 8(4), 2886–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajalli, S. Z.; Mardaneh, M.; Taherian-Fard, E.; Izadian, A.; Kavousi-Fard, A.; Dabbaghjamanesh, M.; Niknam, T. DoS-resilient distributed optimal scheduling in a fog supporting IIoT-based smart microgrid. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2020, 56(3), 2968–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. , Yuan, C., Lai, Y., & Qin, H. (2020). Protection of sensitive data in industrial Internet based on three-layer local/fog/cloud storage. Security and Communication Networks, 2020, 1-16.
- He, S.; Cheng, B.; Wang, H.; Xiao, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J. (2018, April). Data security storage model for fog computing in large-scale IoT application. In IEEE INFOCOM 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS) (pp. 39-44). IEEE.
- Ming, Y.; Yu, X. Efficient privacy-preserving data sharing for fog-assisted vehicular sensor networks. Sensors 2020, 20(2), 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Hong, J.; Ma, Y.; Wei, D. S.; Hong, P.; Yu, N. Fog-aided verifiable privacy preserving access control for latency-sensitive data sharing in vehicular cloud computing. IEEE Network 2018, 32(3), 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. Secure, efficient and revocable data sharing scheme for vehicular fogs. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications 2018, 11, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.; Almaiah, M. A.; Omar Alsayed, A.; Almomani, O. An anonymous channel categorization scheme of edge nodes to detect jamming attacks in wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2020, 20(8), 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bany Salameh, H.; Derbas, R.; Aloqaily, M.; Boukerche, A. (2019, November). In Secure routing in multi-hop iot-based cognitive radio networks under jamming attacks. In Proceedings of the 22nd International ACM Conference on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems (pp. 323-327).
- Abhishek, N. V.; Gurusamy, M. Jade: Low power jamming detection using machine learning in vehicular networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters 2021, 10(10), 2210–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovom, E. M.; Azmoodeh, A.; Dehghantanha, A.; Newton, D. E.; Parizi, R. M.; Karimipour, H. Fuzzy pattern tree for edge malware detection and categorization in IoT. Journal of Systems Architecture 2019, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizani, N.; Ghafoor, A. A network function virtualization system for detecting malware in large IoT based networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2020, 38(6), 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoda, M. E.; Kamruzzaman, J.; Gondal, I.; Imam, T.; Rahman, A. Malware detection in edge devices with fuzzy oversampling and dynamic class weighting. Applied Soft Computing 2021, 112, 107783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, D.; Spreitzenbarth, M.; Hubner, M.; Gascon, H.; Rieck, K.; Siemens, C. E. R. T. (2014, February). Drebin: Effective and explainable detection of android malware in your pocket. In Ndss (Vol. 14, pp. 23-26).
- Allix, K.; Bissyandé, T. F.; Klein, J.; Le Traon, Y. (2016, May). Androzoo: Collecting millions of android apps for the research community. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on mining software repositories (pp. 468-471).
- Alaeiyan, M.; Dehghantanha, A.; Dargahi, T.; Conti, M.; Parsa, S. A multilabel fuzzy relevance clustering system for malware attack attribution in the edge layer of cyber-physical networks. ACM Transactions on Cyber-Physical Systems.
- Shen, S.; Huang, L.; Zhou, H.; Yu, S.; Fan, E.; Cao, Q. Multistage signaling game-based optimal detection strategies for suppressing malware diffusion in fog-cloud-based IoT networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 5(2), 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhawi, O. M.; Baldwin, J.; Dehghantanha, A. Leveraging machine learning techniques for windows ransomware network traffic detection. Cyber threat intelligence 2018, 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Azmoodeh, A.; Dehghantanha, A.; Conti, M.; Choo, K. K. R. Detecting crypto-ransomware in IoT networks based on energy consumption footprint. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 2018, 9, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almashhadani, A. O.; Kaiiali, M.; Sezer, S.; O’Kane, P. A multi-classifier network-based crypto ransomware detection system: A case study of locky ransomware. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47053–47067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorca, D.; Mercaldo, F.; Giacinto, G.; Visaggio, C. A.; Martinelli, F. (2017, April). In Proceedings of the symposium on applied computing (pp. 1718–1723.
- Sgandurra, D.; Muñoz-González, L.; Mohsen, R.; Lupu, E. C. Automated dynamic analysis of ransomware: Benefits, limitations and use for detection. arXiv preprint 2016, arXiv:1609.03020. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, A.; Chen, Y.; Kao, Y.; Lin, T. (2016). Deep learning for ransomware detection. IEICE Technical Report; IEICE Tech. Rep., 116(282), 87-92.
- Ogundokun, R. O.; Awotunde, J. B.; Misra, S.; Abikoye, O. C.; Folarin, O. (2021). Application of machine learning for ransomware detection in IoT devices. In Artificial intelligence for cyber security: methods, issues and possible horizons or opportunities (pp. 393-420). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Al-Hawawreh, M.; Den Hartog, F.; Sitnikova, E. Targeted ransomware: A new cyber threat to edge system of brownfield industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 6(4), 7137–7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Matam, R.; Shu, L.; Maglaras, L.; Ferrag, M. A.; Choudhury, N.; Kumar, V. Security and privacy in fog computing: Challenges. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 19293–19304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jbair, M.; Ahmad, B.; Mus’ ab H, A.; Harrison, R. (2018). Industrial cyber physical systems: A survey for control-engineering tools. 2018 IEEE Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS), 270-276.
- Frey, M.; Gündoğan, C.; Kietzmann, P.; Lenders, M.; Petersen, H.; Schmidt, T. C. ;... Wählisch, M. (2019, April). Security for the industrial IoT: The case for information-centric networking. In 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT) (pp. 424-429). IEEE.
- Fu, J. S.; Liu, Y.; Chao, H. C.; Bhargava, B. K.; Zhang, Z. J. Secure data storage and searching for industrial IoT by integrating fog computing and cloud computing. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 14(10), 4519–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; He, S.; Wang, W.; Susilo, W.; Jin, H. Lightweight searchable public-key encryption for cloud-assisted wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2017, 14(8), 3712–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütte, J.; Brost, G. S. (2018, August). LUCON: Data flow control for message-based IoT systems. In 2018 17th IEEE international conference on trust, security and privacy in computing and communications/12th IEEE international conference on big data science and engineering (TrustCom/BigDataSE) (pp. 289-299). IEEE.
- Moustafa, N.; Adi, E.; Turnbull, B.; Hu, J. A new threat intelligence scheme for safeguarding industry 4.0 systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32910–32924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Donno, M.; Felipe, J. M. D.; Dragoni, N. (2019, June). ANTIBIOTIC 2.0: A fog-based anti-malware for Internet of Things. In 2019 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy Workshops (EuroS&PW) (pp. 11-20). IEEE.
- De Donno, M.; Dragoni, N. (2019, May). Combining AntibIoTic with fog computing: AntibIoTic 2.0. In 2019 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Fog and Edge Computing (ICFEC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- De Donno, M.; Dragoni, N.; Giaretta, A.; Mazzara, M. (2018). AntibIoTic: protecting IoT devices against DDoS attacks. In Proceedings of 5th International Conference in Software Engineering for Defence Applications: SEDA 2016 5 (pp. 59-72). Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawy, M. H.; Pereira, N.; Gidlund, M. Key distribution protocol for industrial Internet of Things without implicit certificates. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 6(1), 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Hong, J.; Omala, A. A. Efficient certificateless access control for industrial Internet of Things. Future Generation Computer Systems 2017, 76, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Deng, R. H.; Liu, J. K.; Yi, X.; Li, Y. Server-aided attribute-based signature with revocation for resource-constrained industrial-internet-of-things devices. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 14(8), 3724–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Bao, Y.; Nie, X.; Asoor, Y. I. Server-aided attribute-based signature supporting expressive access structures for industrial internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2019, 16(2), 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Cheng, X. Efficient and fine-grained signature for IIoT with resistance to key exposure. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8(11), 9189–9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic, F.; Gaertner, M.; Steger, C. (2021, October). Towards trustworthy NFC-based sensor readout for battery packs in battery management systems. In 2021 IEEE International Conference on RFID Technology and Applications (RFID-TA) (pp. 285-288). IEEE.
- Basic, F.; Laube, C. R.; Steger, C.; Kofler, R. (2022, May). A Novel Secure NFC-based Approach for BMS Monitoring and Diagnostic Readout. In 2022 IEEE International Conference on RFID (RFID) (pp. 23-28). IEEE.
- Basic, F.; Gaertner, M.; Steger, C. Secure and Trustworthy NFC-Based Sensor Readout for Battery Packs in Battery Management Systems. IEEE Journal of Radio Frequency Identification 2022, 6, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kalra, S. A lightweight multi-factor secure smart card based remote user authentication scheme for cloud-IoT applications. Journal of information security and applications 2018, 42, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W. I.; Kwak, J. Smart card-based secure authentication protocol in multi-server IoT environment. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2020, 79, 15793–15811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Gan, Q.; Wang, X. Authentication scheme based on smart card in multi-server environment. Wireless Networks 2020, 26, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Xie, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Li, K. C. A mutual security authentication method for RFID-PUF circuit based on deep learning. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology (TOIT) 2021, 22(2), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, S. F.; Mala, H.; Kaliyar, P.; Conti, M. SecLAP: Secure and lightweight RFID authentication protocol for Medical IoT. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 101, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, A.; Gupta, B. B. Secure timestamp-based mutual authentication protocol for IoT devices using RFID tags. International Journal on Semantic Web and Information Systems (IJSWIS) 2020, 16(3), 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izza, S.; Benssalah, M.; Drouiche, K. An enhanced scalable and secure RFID authentication protocol for WBAN within an IoT environment. Journal of Information Security and Applications 2021, 58, 102705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gope, P.; Amin, R.; Islam, S. H.; Kumar, N.; Bhalla, V. K. Lightweight and privacy-preserving RFID authentication scheme for distributed IoT infrastructure with secure localization services for smart city environment. Future Generation Computer Systems 2018, 83, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipps, C.; Herbst, J.; Schotten, H. D. (2021, February). How to Dance Your Passwords: A Biometric MFA-Scheme for Identification and Authentication of Individuals in IIoT Environments. In ICCWS 2021 16th International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security (p. 168). Academic Conferences Limited.
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, P.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, X. Passive user authentication utilizing behavioral biometrics for IIoT systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 9(14), 12783–12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarier, N. D. Efficient biometric-based identity management on the Blockchain for smart industrial applications. Pervasive and Mobile Computing 2021, 71, 101322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, U.; Lee, G. M.; MacDermott, Á.; Rhee, W. S. TrustChain: A privacy preserving blockchain with edge computing. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Cheng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L. (2018, October). Lightweight hardware based secure authentication scheme for fog computing. In 2018 IEEE/ACM Symposium on Edge Computing (SEC) (pp. 433-439). IEEE.
| 1 | A company that offers services to control, coordinate, and optimize online infrastructure. |
| 2 | A daily blog that covers cyberattacks. |
| 3 | A giant European hosting provider. |
| 4 | |
| 5 | Found at https://icsdweb.aegean.gr/awid/
|
| 6 | |
| 7 | These four data sets can be found at https://staff.itee.uq.edu.au/marius/NIDS_datasets/
|
| 8 | This data set can be found at https://research.unsw.edu.au/projects/toniot-datasets
|
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | A representative filter-based technique employed to select important features and ignore insignificant features through minimization of intra-class distances and maximization of inter-class distances. |
| 12 | A mechanism that increases the number of samples of class that has fewer samples; for example, by duplicating the samples of that minority class. |
| 13 | This data set can be found at the following website: https://www.virustotal.com/gui/home/upload
|
| 14 | As indicated by the authors, this data set can be found at http://ransom.mobi/
|
| 15 | |
| 16 | Found at https://gnupg.org/
|
| 17 | An organization responsible for signing, storing, and issuing digital certificates. |
| 18 | An authentication scheme based on a permission-less Blockchain network. |
| 19 | An object that provides a physical component with a trust anchor or an unrivaled fingerprint by exploiting the intrinsic randomness introduced during production. |
| Characteristic | IoT | IIoT |
|---|---|---|
| Application examples | Smart home, health monitoring, | Smart transportation, intelligent logistics, |
| indoor localization | smart manufacturing, remote maintenance | |
| System Framework | Self-reliant | Industrial facility-reliant |
| Delay sensitivity | High | Low |
| Mobility | High | Low |
| Deployment size | Small | Large |
| Deployment preciseness | Low | High |
| Data volume | Medium | High |
| Scope | Ref. | Major contribution | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoT security | [32] | A comprehensive overview of | Attacks perfectly linked to | The role of emerging technologies in |
| IIoT security threats | security requirements | securing IoT networks is not discussed | ||
| [33] | A detailed review of IoT | A distinctive categorization of IoT | Attacks are not completely linked to | |
| threats and vulnerabilities | vulnerabilities and a discussion of | security requirements and the impact | ||
| about 100 research ideas | of integrating emerging technologies | |||
| on IoT security are not discussed | ||||
| [34] | An overview of security requirements | Noteworthy security requirement | The depth of the challenges | |
| for several IoT application domains | prioritization for each application domain | section is minimal | ||
| IIoT security | [35] | A comprehensive review of | Outstanding future directions and potential | Cyberattacks are not linked to security |
| cyberattack classes | applications are discussed | requirements and the impact of | ||
| emerging technologies on IIoT | ||||
| security is not discussed | ||||
| [6] | A survey of challenges faced by | A unique overview of challenges related to | Security requirements and emerging | |
| Industry 4.0 environments | energy adequacy, interoperability, and security | technologies impact are not discussed | ||
| [36] | An overview of IIoT | A unique description of the building and | The depth of the survey | |
| security solutions | linking of IIoT devices with security in mind | is minimal | ||
| [37] | A unified architecture format of | A detailed comparison of security | The authors discuss a limited | |
| security requirements in IIoT | requirements within heterogeneous | number of use cases | ||
| IIoT devices | ||||
| [38,39] | A discussion of IIoT | A comprehensive overview of solutions | The depth of the | |
| security requirements | that deal with security violations | review is minimal | ||
| [40] | An overview of IIoT security, | A distinctive categorization of the IIoT, | Lacks discussion of the role | |
| threats, and counter-measures | exploration of counter-measures taken by | of adopting emerging technologies | ||
| taken by industries | industries utilizing security requirements | to protect the IIoT paradigm | ||
| Edge security | [41] | A overview of edge-IoT | An investigation of opportunities provided by | The depth of the |
| paradigm and applications | edge computing to improve IIoT security | overview is minimal | ||
| [42] | A thorough discussion of | A distinctive observation related to the | The depth of the | |
| fog computing security | unsuitability of methods used to secure CC | discussion is minimal | ||
| and privacy issues | for fog computing is introduced | |||
| [43] | A detailed tutorial of the | Incandescent solutions to privacy | The connection between edge | |
| edge computing paradigm | and security are thoroughly discussed | applications, threats targeting them, | ||
| and security solutions is missing | ||||
| Edge Computing in IIoT | [44] | A roadmap for smart manufacturing to | One of the first surveys | Security requirements and |
| integrate IoT and edge computing | to discuss this area | challenges are inadequately discussed | ||
| [45] | A demonstration of two scenarios of | A unique comparison of cloud and fog | The overview is scenario-specific | |
| how IIoT benefits from fog computing | computing when integrated with IIoT | (i.e., not comprehensive) | ||
| [46] | An overview of edge computing | A comparison of reference | The depth of this | |
| reference architectures in IIoT | architectures is presented | overview is minimal | ||
| [47] | A discussion of the integration | Two enabling technologies that can add value | This survey is | |
| of fog computing and IIoT | to the integration are uniquely discussed | not comprehensive | ||
| [48] | A review of edge computing | A discussion of recently proposed solutions, | The lack of in-depth discussion | |
| and IIoT integration | recent challenges and few use-cases | of security challenges and | ||
| sufficient application examples | ||||
| [8] | Discussion of the industrial revolution | A well-organized and thorough | The discussion part of edge | |
| background and transformation | discussion of communication | computing lacks essential details | ||
| enabling technologies | and network protocols | |||
| [21] | A review of current solutions related | Distinctive technical details of | Security opportunities brought | |
| to adopting edge computing into IIoT | some significant edge services that | when integrating edge computing | ||
| add value to the IIoT paradigm | into IIoT is partially discussed | |||
| Secure IIoT-Edge | [10] | A systematic survey of IIoT security | A thorough discussion of IIoT security | The IIoT attacks are not |
| over the period of 2011–2019 | challenges, requirements, and opportunities | deeply discussed and the | ||
| provided when adopting edge computing that | depth of the opportunities | |||
| could secure IIoT paradigm | part is not sufficient | |||
| Ours | A thorough categorization of IIoT | A distinctive linkage of IIoT attacks and | N/A | |
| attacks, security requirements, and | requirements is introduced and research | |||
| security benefits from integrating | attempts to overcome security challenges | |||
| edge computing and IIoT | (with a focus on the period 2019–2022) | |||
| are comprehensively discussed |
| Layer | Attack | Violated requirements | Common counter-measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perception | Node Capture | Confidentiality, Authentication | Abolishing information related to secure |
| keys after disassociation [91] | |||
| Jamming | Availability | Increasing interference resistance using techniques | |
| such as FHSS [92] and DSSS [93] | |||
| Sleep Deprivation | Availability | Ensuring security policies are not violated | |
| using policy-based IDS [94] | |||
| Replay | Integrity | Utilizing timestamps and nonces [95] | |
| Network | Selective-Forwarding | Availability | Detection and prevention using a combination |
| of IDS and IPS [96] | |||
| Eavesdropping | Confidentiality, Privacy | Employing access control and data | |
| encryption techniques [97] | |||
| Sybil and ID Cloning | Authentication | Applying packet filtering, IDS, and | |
| localization techniques [98] | |||
| Wormhole | Confidentiality, Availability | Deploying secure neighboring discovery techniques and | |
| measuring challenge-response and RTT delay [99] | |||
| Denial of Service | Availability | Utilizing traffic filtering, IDS, and tracking techniques [100] | |
| Man in the Middle | Confidentiality, Authentication | Employing light encryption techniques | |
| and deploying IDS [101] | |||
| Sinkhole | Availability | Employing IDS and IPS to detect and | |
| prevent this threat [102,103] | |||
| Blackhole | Availability | Utilizing various routing paths and deploying IDS | |
| and IPS techniques [104] | |||
| Application | Malicious Code Injection | Confidentiality, Authentication | Employing private-key cryptography, light public-key |
| encryption, and authentication mechanisms [105] | |||
| Cross-site or | Confidentiality, Authentication | Deploying signature-based IDS and content and | |
| Malicious Scripts | pattern analysis techniques [106] | ||
| Malware Injection | Integrity | Deploying IDS, IPS, and malware removal mechanisms [107] | |
| Data Distortion | Integrity and secure | Utilizing access control, encryption, and recovery [108] | |
| data sharing | such as backup mechanisms | ||
| SQL Injection | Confidentiality, integrity | Utilizing parameterized statements, IDS, access control, and | |
| encryption techniques [109] | |||
| Ransomware | Confidentiality, Authentication | Employing traffic filtering, IDS, IPS, | |
| and encryption techniques [110] | |||
| Side-channel | Confidentiality | Protection of cryptography techniques, preventing traffic | |
| analysis, and enforcing strict access control policies [111] | |||
| Authorization and | Authentication and | Using access control and authentication techniques [112] | |
| Authentication | access control |
| Scope | Ref. | Algorithm | Resolved issue | Data set | Performance metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep learning-based IDSs | [152] | LSTM | DoS attacks | ISCX, AWID | 98.22% accuracy on AWID, 99.91% on ISCX |
| [153] | Stochastic MC | false injection | Custom | NA | |
| [154] | LSTM and 1D CNN | DDoS | DoS2019 | 1D-CNN: 99.3% precision, 98.9% recall, 99.1% F1-score | |
| [155] | ANN, RNN-LSTM, RNN-GRU | botnet attacks | BotIoT | ANN: 99% accuracy, RNN: 98% accuracy | |
| [156] | Stacked deep autoencoders | botnet attacks | N-BaIoT | 3% improvement | |
| [157] | LAE and B-LSTM | botnet attacks | BotIoT | 93.17% (binary), 97.29% (multiclass) | |
| [158] | RNN | botnet attacks | BotIoT | 99.75% recall, 99.62% precision and F1-score | |
| [159] | CFBPNN | botnet attacks | 5 datasets | 100% accuracy | |
| [160] | Custom algorithm | botnet attacks | N-BaIoT | 99.76% accuracy, 99.68% F1-score, 0.2250 testing time | |
| [161] | Federated DL | zero-day botnet | Bot-IoT, | Bot-IoT: 99.79% accuracy, 99.51% precision, 96.27% | |
| N-BaIoT | recall, 97.68% F1-score. N-BaIoT: 99.00% accuracy, | ||||
| 96.87% precision, 97.24% recall, 96.88% F1-score | |||||
| [162] | Federated DL | DDoS attacks | UNSW NB-15 | 98% accuracy | |
| Signature-bawed IDSs | |||||
| [163] | Custom algorithm | routing attacks | NS2 | 95.0% detection rate, 1.23% FPRe | |
| [164] | Custom algorithm | SQL injection | Custom | 4.7× improvement | |
| [165] | Custom algorithm | DDoS attacks | Custom | Not reported | |
| [131] | Custom algorithm | DDoS attacks | Custom | Up to 99.84% detection rate, as low as 129 testing time | |
| [166] | Fuzzy logic | Blackhole attacks | Custom | more than 90% accuracy | |
| [167] | Node ranking | sinkhole attacks | NS3 | 96.19% detection rate, 4.16% FPR, 4.04% FNR | |
| [168] | Parallel ABC | Sybil attacks | Simulation | Approximately 97% accuracy, 97% sensitivity | |
| [169] | XGBoost | botnet attacks | BoT-IoT | 99.99% accuracy, 97.5% recall, | |
| 99.5% precision, 98.5% F1-score | |||||
| [170] | Gaussian distribution | Mirai and Gafgyt | N-BaIoT | 90% in multiclass classification | |
| and local search | botnets | ||||
| [171] | Dynamic analysis | botnet attacks | Custom | 98.1% to 91.99% accuracy | |
| [172] | Fisher-score and XGBoost | botnet attacks | N-BaIoT | 99.96% average accuracy |
| Ref. | Method characteristics | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| [178] | Hybrid AES-RSA | It efficiently protects the secrecy of the | It relies on RSA (i.e., an asymmetric |
| data and enables devices to recover | encryption method), which is slow | ||
| the data in a secure manner | |||
| [179] | Hierarchical and distributed | Large-scale and secure method capable | It is not linked to data and |
| of providing IIoT devices with status | infrastructure characteristics | ||
| information of data storage | |||
| [180] | Combining super-increasing sequence | It efficiently provides secure data | It is centralized |
| and modified oblivious transfer | sharing and anonymity | ||
| [181] | Encryption outsourcing and | It achieves encouraging response | The security analysis was not |
| fine-grained access control | latency reduction and overhead | discussed in detail | |
| saving for edge devices | |||
| [182] | Encryption with multi-authority | Data access authorization and secure data sharing | The high scalability of edge |
| cipher-text | are ensured to protect edge devices against | networks might cause other | |
| collusion attacks with low delay | security issues to emerge |
| Ref. | Algorithm | Resolved issue | Data set | Performance metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [186] | Fuzzy pattern tree | malware | Kaggle and Vx-Heaven | 97.0427% and 88.76% accuracies |
| [187] | LSTM | malware | UNSW-NB15 | 70% accuracy |
| [188] | Fuzzy set theory and a | malware | Drebin [189] and AndroZoo[190] | 9% F1-score improvement |
| new loss function | ||||
| [191] | Fuzzy clustering | malware | Custom data sets created from | VirusShare: 94.66%, Kaggle: |
| VirusShare, Kaggle, and | 97.56%, RansomwareTracker: | |||
| RansomwareTracker | 94.26% accuracies | |||
| [192] | Theoretical analysis | malware | NA | NA |
| [193] | J48 | ransomware | VirusTotal | 97.1% detection rate |
| [194] | kNN with DTW capability | ransomware | VirusTotal | Window size 15: 94.27% accuracy, |
| 95.65% recall, 89.19% precision, | ||||
| 92.31% F1-score | ||||
| [195] | Decision tree and naïve Bayes | ransomware | Custom | Packet-based (decision tree): 97.92% |
| accuracy, 97.90 precision, recall, F1-score | ||||
| flow-based (naïve Bayes): 97.08% | ||||
| accuracy, 97.72% precision, 97.71% | ||||
| recall and F1-score | ||||
| [196] | Random forest | ransomware | ransomware and malware-trusted | 97.817% average F1-score of five splits |
| [197] | Logistic regression | ransomware | created from VirusShare website | 96.3% detection rate and 99.5% ROC curve |
| [198] | DNN | ransomware | generated from VirusTotal | 93% accuracy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





