Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
12 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate composition
2.2. Vase vegetation experiment
2.3. Laboratory analysis
2.4. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. pH i EC
3.2. Sorption properties
3.3. TOC, TN, C/N
3.4. Contents of available forms of P, K, and Mg
3.5. Yield of plants grown on the evaluated substrates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahuja, D.; Tatsutani, M.; Schaffer, D. Sustainable energy for developing countries. Surveys and Perspectives Integrating Environment and Society. 2009, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, H.; Sciubba, J.D. The Effect of Population Growth on the Environment: Evidence from European Regions. Eur J Popul. 2018, 35, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosbellet, C.; Vidal-Beaudet, L.; Caubel, V.; Charpentier, S. Improvement of soil structure formation by degradation of coarse organic matter. Geoderma. 2011, 162, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OESD, 209. Bisiness Models fos the Circular Economy. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/environment/ business-models -for-the-circular-economy-g2g9dd62-en.htm (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- Bourguignon, D. Circular economy 1.0 and 2.0: a comparison [WWW Document]. Available online: http://www.europarl.europa.eu/EPRS/EPRS-AaG-573937-Circular-economy-1-0-and-2-0-comparison-FINAL.pdf 2016 (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- Montanarella, L.; Panagos, P. The relevance of sustainable soil management within the European Green Deal. Land Use Policy. 2021, 100, 104950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, D.; Pizzol, R.; Calza, P.; Malandrino, M.; Gaggero, E.; Padoan, E.; Ajmone-Marsan, F. Constructed technosols: A strategy toward a circular economy. Applied Sciences. 2021, 11, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring soil quality to mitigate soil degradation. Sustainability. 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabętowicz, J.; Stępień, W. Fertilizers from waste as a source of nutrients in fertilization of crops. Agricultural use of waste and by-products as a link in the circular economy. Publisher: SSW i Fundacja „Pro Civis”, Country: Warszawa-Kielce. 2020.
- Weiler, J.; Firpo, B.A.; Schneider, I.A.H. Technosol as an integrated management tool for turning urban and coal mining waste into a resource. Minerals Engineering. 2020, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, B.; Mao, Y.; Robinson, D. Three pillars of sustainability: in serch of conceptual origins. Sunstain. Sci. 2019, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.G.; Bullock, S.E.T.; H€albich, T.F.J.; Lindsay, P. Environmental impacts associated with an abandoned mine in the Witbank Coalfield, South Africa. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2001, 45, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifovic, R.; Fatys, K.; Chen, J.M.; Praszczak, J. Assessing land cover change resulting from large Surface mining development. Int. J. of Applied Earth Observation and geoinformation. 2005, 7, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, N.; Hudson-Edwards, K.; Faroogi, A. True cost of coal: coal mining industry and its associated environmental impacts on water resource development. Journal of Sustainable Mining. 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.; Shao, Y.; Song, W.; Yang, F.; Luo, Y. A performance evaluation of China's coal-fired power generation with pollutant mitigation options. J. Clean. Prod. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Cherubin, M.R.; Ferreira, T.O. Soil quality assessment of constructed Technosols: Towards the validation of a promising strategy for land reclamation, waste management and the recovery of soil functions. Journal of Environmental Management. 2020, 276, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, K.; Hartemink, A. Linking soil to ecosystem services – a global review. Geoderma. 2016, 262, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J. Wounding Earth's fragile skin. Science. 2004, 304, 1616–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a waste 2.0: a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050. World Bank Publications. Urban Development;. Washington, DC: World Bank. © World Bank. 2018. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/30317 License: CC BY 3.0 IGO (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- Basu, A.J.; Van Zyl, D.J.A. Industrial ecology framework for achieving cleaner production in the mining and minerals industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, D.M.; Boger, D.V.; Côte, C.M.; Mulligan, D.R. Sustainable development principles for the disposal of mining and mineral processing wastes. Resour. Pol. 2011, 36, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, C.R.; do Amaral Filho, J.R.; Tubino, R.M.C.; Schneider, I.A.H. Use of coal waste as fine aggregates in concrete paving blocks. Geomaterials. 2013, 3, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolboushkin, A.Y.; Ivanov, A.I.; Fomina, O.A. Use of coal-mining and processing wastes in production of bricks and fuel for their burning. Procedia Eng. 2016, 150, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, S.; Modarres, A.; Soltaninejad, M.; Madani, H. Mechanical properties of roller compacted concrete pavement containing coal waste and limestone powder as parcial replacements cement. Construct. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firpo, B.A.; do Amaral Filho, J.R.; Schneider, I.A.H. A brief procedure to fabricate soils from coal mine wastes based on mineral processing, agricultural, and environmental concepts. Minerals Engineering. 2015, 76, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.F.; Delaqua, G.C.G.; Nicolite, M.; Marvila, M.T.; de Azevedo, A.R.; Alexandre, J.; Monteiro, S.N. Eco-friendly mortars with addition of ornamental stone waste-A mathematical model approach for granulometric optimization. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2020, 248, 119283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R. Reclamation and revegetation of fly ash disposal sites–challenges and research needs. J Environ Manag. 2009, 90, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah-Antwi, C.; Kwiatkowska-Malina, J.; Thornton, S.F.; Fenton, O.; Malina, G.; Szara, E. Restoration of soil quality using biochar and brown coal waste: a review. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Bhattarai, R.; Li, Y.; Si, B.; Dong, X.; Wang, T.; Yao, Z. Towards sustainable coal industry: turning coal bottom ash into wealth. Sci Total Environ. 2021, 804, 149985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, M.; Edraki, M.; Faezeh, F.; Ahn, J. Opportunities for mineral carbonation in Australia’s mining industry. Sustainability. 2019, 11, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Kirkham, M.B.; Ok, Y.S. Spoil to soil: mine site rehabilitation and revegetation. CRC Press, 2017.
- Darmody, R.G.; Daniels, W.L.; Marlin, J.C.; Cremeens, D.L. Topsoil: What is it and who cares. Annual meetings of the american society of mining and reclamation. 2009, 26, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Lal, R. Quality change of mine soils from different sources in response to amendments-A laboratory study. Environment and Natural Resources Research. 2014, 4, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.D.; Lock, A.S.; Beckett, P.J.; Spiers, G. Developing manufactured soils from industrial by-products for use as growth substrates in mine reclamation. Restor. Ecol. 2017, 25, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Barriga, F.; Díaz, V.; Acosta, J.A.; Muñoz, M.A.; Faz, A.R.; Zornoza, R. Organic matter dynamics, soil aggregation and microbial biomass and activity in Technosols created with metalliferous mine residues, biochar and marble waste. Geoderma. 2017, 301, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, S.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A.; Żukowska, G.; Bik, M.; Szewczuk, Cz.; Zawadzki, K. The role of mineral wool and sewage sludge in shaping the nitrogen content in the reclaimed soilless formation. Przemysł Chemiczny. 2012, 91, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Żukowska, G.; Baran, S.; Pawłowski, A.; Myszura, M.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A.; Wesołowska, S.; Pawłowska, M. Reclamation of drill cuttings landfill. Rocznik Ochrona Środowiska. 2016, 18, 988–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Kołodziej, B.; Bryk, M.; Otremba, K. Effect of rockwool and lignite dust on physical state of rehabilitated post-mining soil. Soil and Tillage Research. 2020, 199, 104603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. Soil Quality. In Determination of pH; ISO, 10390; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Laboratory Methods Manual. Soil Survey Investigation Report; United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, National Soil Survey Center: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN 15936:2013:02. Available online: https://sklep.pkn.pl/pn-en-15936-2013-02p.html (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- International Organization for Standardization. Soil Quality. In Determination of Total Nitrogen Content by Dry Combustion; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Laboratory Methods Manual. Soil Survey Investigation Report; United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, National Soil Survey Center: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN 16170:2017-02 - Sewage sludge, treated bio-waste and soil - Determination of elements by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). Available online: https://sklep.pkn.pl/pn-en-16170-2017-02e.html (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- Malina, A. Multidimensional Analysis of the Spatial Differentiation of the Structure of the Polish Economy by Voivodship; Publishing House of the Cracow University of Economics (Wydawnictwo Akademii Ekonomicznej): Kraków, Poland, 2004; p. 162. [Google Scholar]
- Moghimian, N.; Hosseini, S.M.; Kooch, Y.; Darki, B.Z. Impacts of changes in land use/cover on soil microbial and enzyme activity. Catena. 2017, 157, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatka, S.; Malec, M.; Kru, E.; Ryczek, M. Evaluation of possibility of natural utilisation of coal mine waste used for surface levelling. Acta Agrophysica. 2017, 24, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Czop, M.; Kościelan, A.; Żydek, K. Testing physicochemical properties and fitotoxicity of selected extractive waste in light of a Circular Economy. Scientific Journals of the Institute of Mineral Resources and Energy Management of the Polish Academy of Sciences. 2019, 109, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Firpo, B.A.; Weiler, J.; Schneider, I.A. Technosol made from coal waste as a strategy to plant growth and environmental control. Energy Geoscience. 2021, 2, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, J.; Firpo, B.A.; Schneider, I.A.H. Coal waste derived soil-like substrate: An opportunity for coal waste in a sustainable mineral scenario. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2018, 174, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompała-Bąba, A.; Bierza, W.; Błońska, A.; Sierka, E.; Magurno, F.; Chmura, D.; Besenyei, L.; Radosz, Ł.; Woźniak, G. Vegetation diversity on coal mine spoil heaps – how important is the texture of the soil substrate? Biologia. 2019, 74, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, S.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A.; Żukowska, G. Assessment of the suitability of sewage sludge and Grodan mineral wool for the reclamation of soilless soil based on the content of assimilable forms of phosphorus, potassium and magnesium. Soil Science Annual. 2006, 57, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, S.; Pranagal, J.; Bik, M. Possibilities of using Grodan mineral wool and sewage sludge to shape water properties in soils devastated in the Frash sulfur extraction process. Mineral Resources Management. 2008, 24, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, S.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A.; Żukowska, G.; Bik, M. Sorption properties of a soilless formation reclaimed with sewage sludge and mineral wool. Problem Books of Progress in Agricultural Sciences. 2008, 533, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, S.; Wójcikowska – Kapusta, A.; Żukowska, G.; Bik-Małodzińska, M.; Wesołowska-Dobruk, S. Influence of sludge-ash composts on some properties of reclaimed land. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2015, 41, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żukowska, G.; Baran, S.; Wójcikowska – Kapusta, A. Organic carbon content and fractional composition of organic matter in soil reclaimed with sewage sludge. Przemysł Chemiczny. 2012, 91, 1267–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Żukowska, G.; Baran, S.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A.; Wesołowska-Dobruk, S. Kopiy, L.; Bik-Małodzińska, M. Sewage sludge and mineral wool for reclamation of devastated soils and in forest management. Nauk. Visn. NLTU Ukr. 2014, 24, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawska, J.; Pawłowska, M. Effect of drill cuttings addition on physicochemical and chemical properties of soil and red clover (Trifolium pretense L. ) growth. PLOS ONE. 2020, 15, e0242081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrzałek, A.; Nowińska, K. Development of plant communities on mining waste tips subjected to various methods of reclamation. W: Dzieje Górnictwa – element europejskiego dziedzictwa kultury, Wrocław. 2013, 297-306.
- FAO. World reference base for soil resources. A framework for international classification, correlation and communication. World Soil Resources Reports. 2006, 103.
- Kacprzak, M.; Kupich, I.; Jasinska, A.; Fijałkowski, K. Bio-Based Waste’ Substrates for Degraded Soil Improvement—Advantages and Challenges in European Context. Energies. 2022, 15, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, G.; Kaiser, K.; Guggenberger, G.; Haumaier, L. Differences in the chemical composition of dissolved organic matter from waste material of different sources. Biology and Fertility of Soils. 2002, 36, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, W.L.; Stewart, B. Reclamation of Coal Refuse Disposal Areas. VCE publication. 2010.
- Filho, A.J.R.; Firpo, B.A.; Broadhurst, J.L.; Harrison, S.T. On the feasibility of South African coal waste for production of ‘FabSoil’, a Technosol. Minerals Engineering. 2020, 146, 106059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, Y. Phosphorus: a limiting factor for restoration of soil fertility in a newly reclaimed coal mined site in Xuzhou, China. Land Degradation & Development. 1998, 9, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Doley, D.; Audet, P. What part of mining are ecosystems? Defining success for the “restoration” of highly disturbed landscapes. In: V.R. Squires (Ed.), Ecological Restoration: Global Challenges, Social Aspects and Environmental Benefits (Chapter 4), 978-1-63484-611-0, Nova Science Publishers, New York. 2016.
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Chen, L.; Cui, Y.; Tan, T. Nitrogen conversion in relation to NH3 and HCN during microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge. Environmental science & technology. 2013, 47, 3498–3505. [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse, B.R.; Boyer, S.; Adair, K.L.; Wratten, S.D. Using municipal biosolids in ecological restoration: What is good for plants and soil may not be good for endemic. [CrossRef]
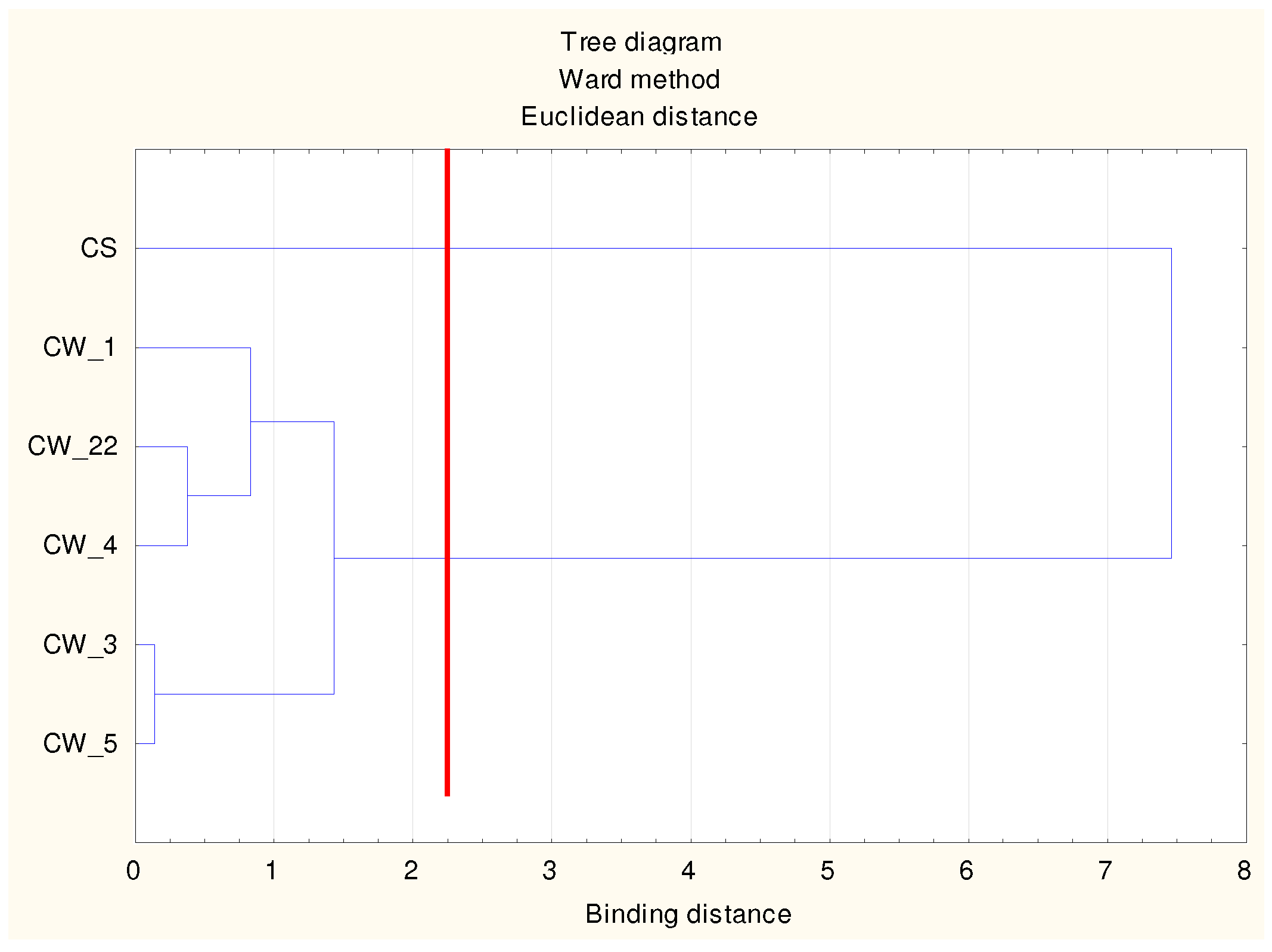
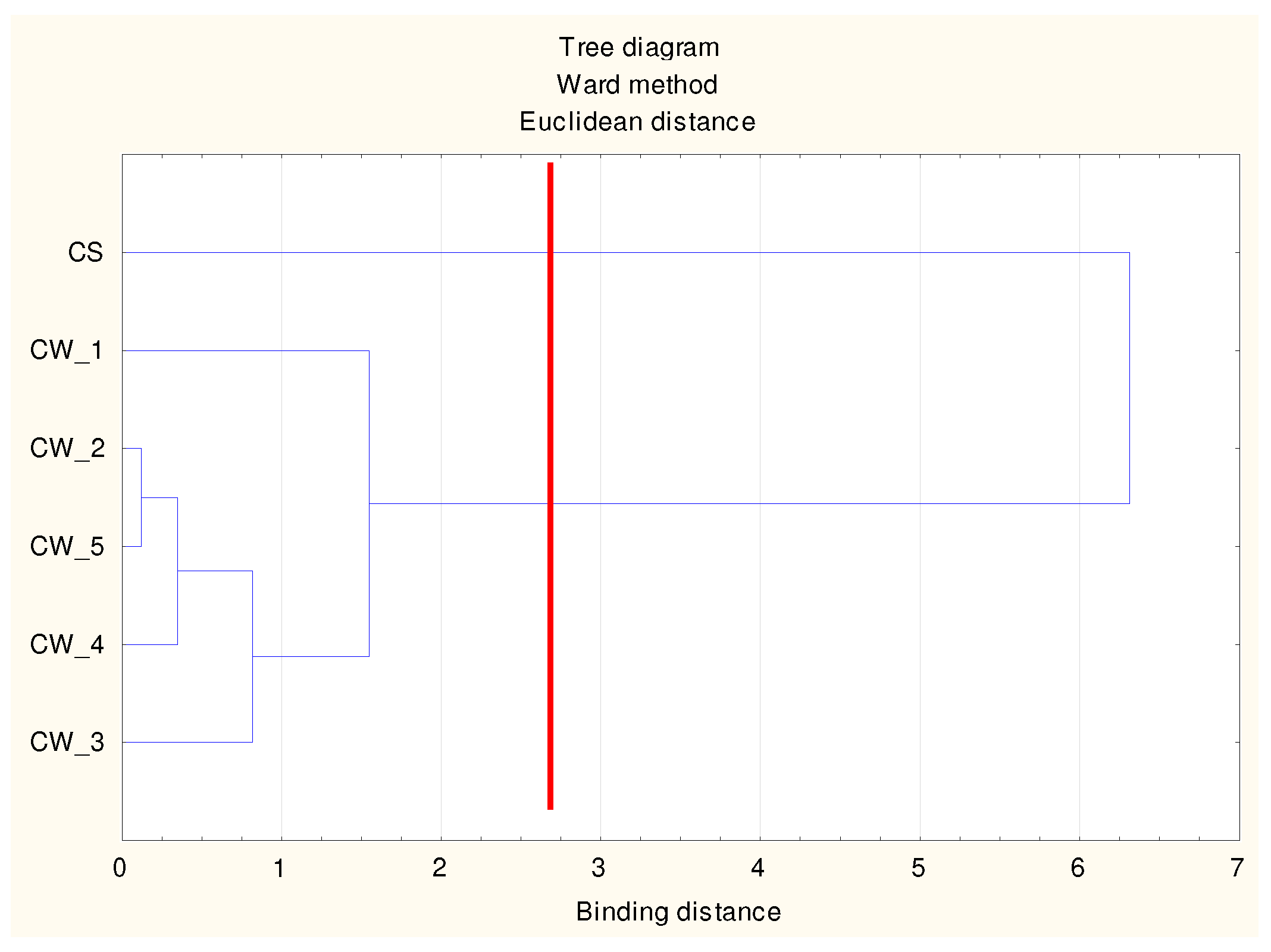
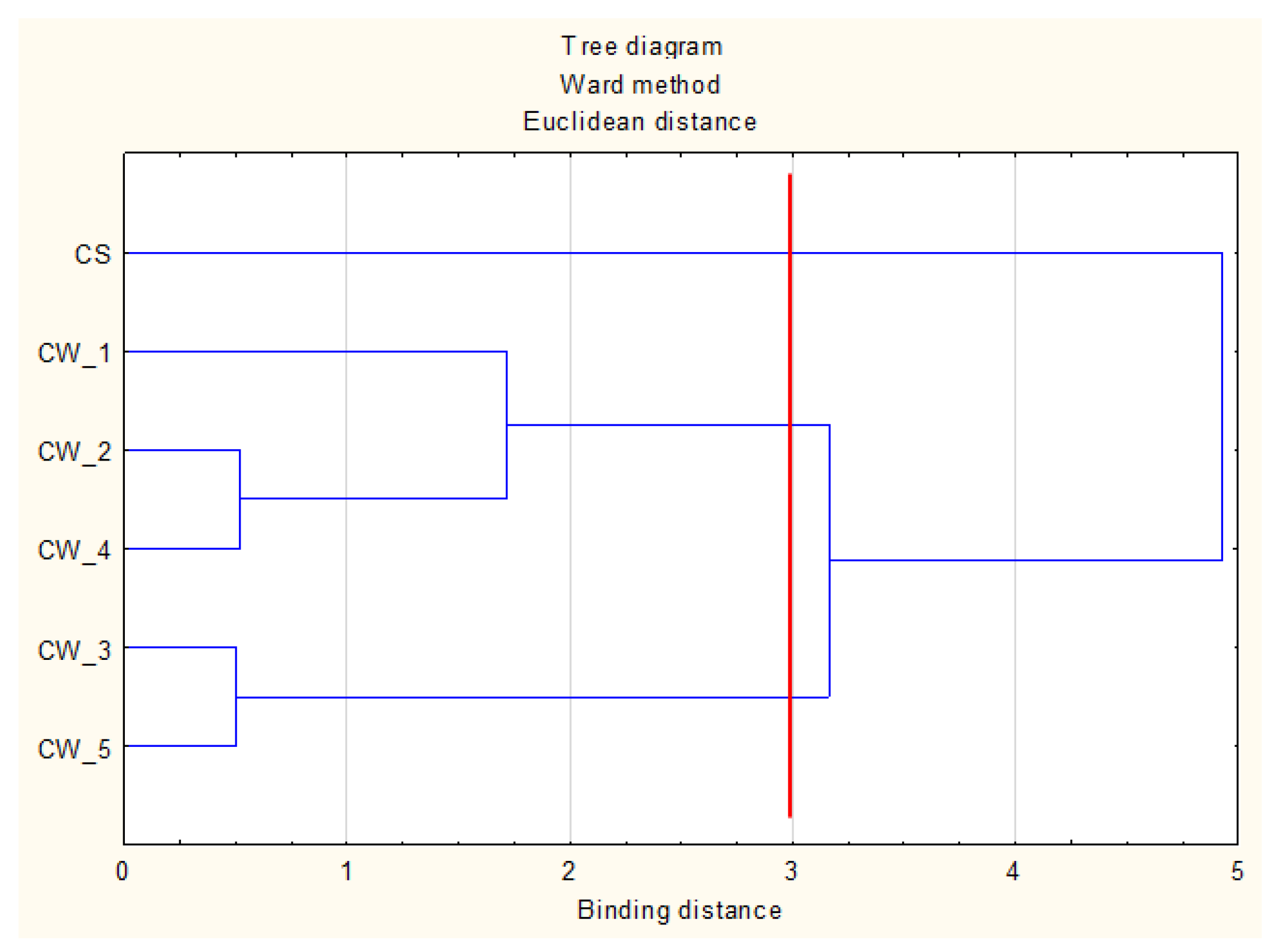
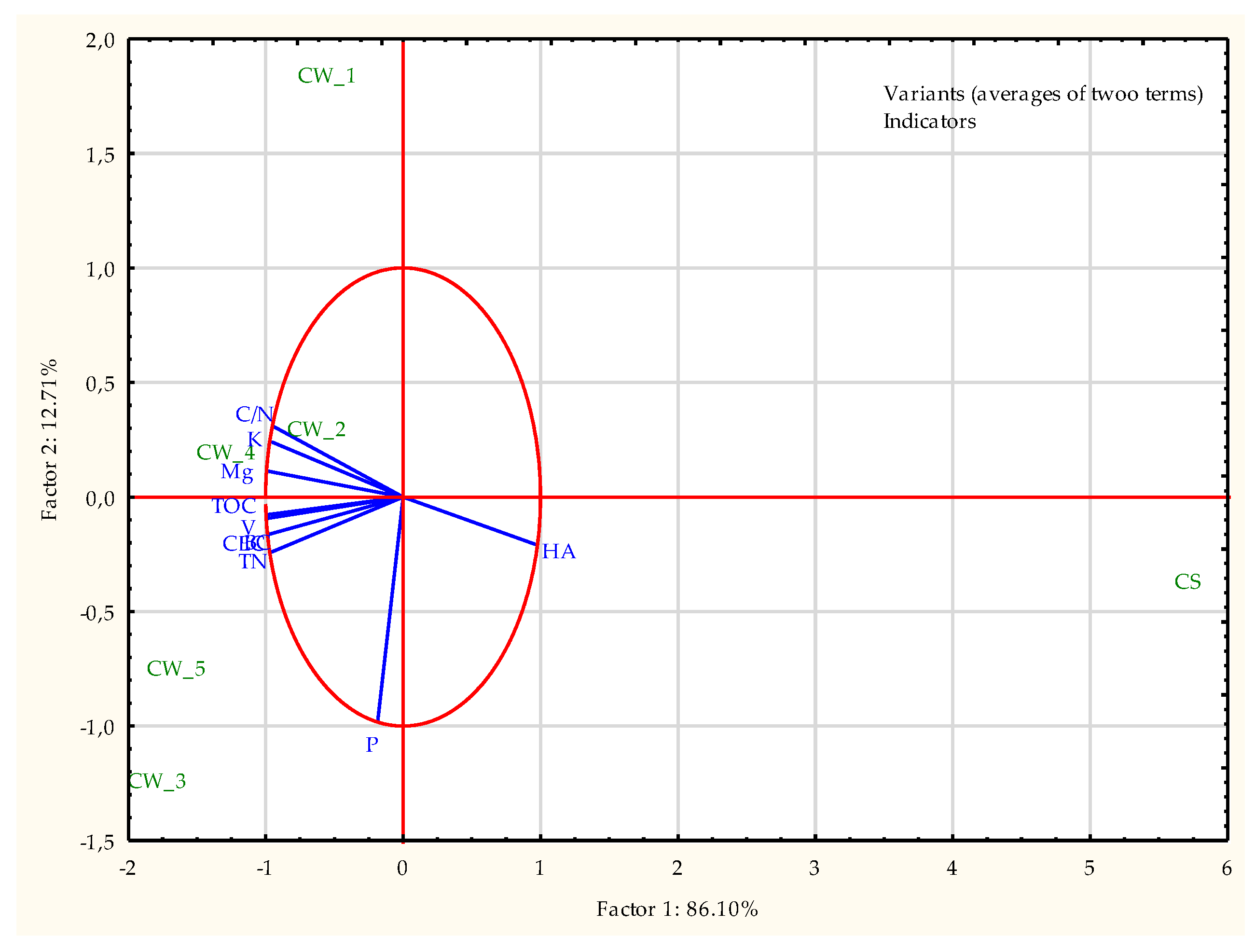
| Property | Unit | Coal Waste (CW) | Sewage Sludge (SS) | Mineral Wool (MW) |
Control Soil (CS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction | pH w H2O | 7.30 | 6.45 | 6.72 | 4.48 |
| pH 1 mol·dm −3 KCl |
7.10 | 6.15 | 652 | 4.08 | |
| Hydrolytic acidity (HA) | cmol(+)·kg-1 | 0.61 | 4.74 | 0.23 | 2.70 |
| Exchangeable base cations (BC) | 11.47 | 29.15 | 23.22 | 3.38 | |
| Cation exchange capacity of the soil (CEC) | 12.08 | 33.89 | 23.45 | 6.08 | |
| Degree of saturation of the sorption complex with basic cations (V) | % | 94.9 | 86.1 | 99.0 | 55.6 |
| TOC | g·kg-1 | 6850 | 207.50 | n.o. | 7.50 |
| TN | 2.36 | 38.10 | n.o. | 0.88 | |
| C/N | - | 29.0 | 5.6 | n.o. | 8.5 |
| Salinity | gNaCl·kg-1 | 1.80 | 286 | 0.06 | 0.11 |
| P available | mg·kg-1 | 1.6 | 742.5 | 632.2 | 18.2 |
| K available | 208.4 | 13.68 | 1249.2 | 3.,0 | |
| Mg available | 180.0 | 135.0 | 54.,2 | 17.1 | |
| Pb | 47.5 | 39.8 | 38.3 | 27.5 | |
| Zn | 45.8 | 874.5 | 44.9 | 24.8 | |
| Cu | 45.5 | 301.5 | 26.5 | 20.1 | |
| Cd | 1.04 | 3.54 | 1.05 | 0.36 | |
| Cr | 33.9 | 89.3 | 11.4 | 19.6 | |
| Ni | 35.9 | 37.6 | 22.6 | 5.8 | |
| Hg | 0.029 | 0.984 | 0.006 | 0.035 | |
| Ba | 308.0 | 110.5 | 27.5 | 41.5 |
| Variant | Substrate characteristics | Control Soil (CS) |
Coal Waste (CW) |
Sewage Sludge (SS) |
Mineral Wool (MW) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % w/w s.m | kg s.m. | % w/w s.m | kg s.m. | % w/w s.m | kg s.m. | % w/w s.m | kg s.m. | ||
| CS | Control Soil | 100 | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CW_1 | Coal Waste – 100% | - | - | 100 | 10 | - | - | - | - |
| CW_2 | Coal Waste 97.5% + Sewage Sludge 2.5% | - | - | 97.5 | 9.75 | 2.5 | 0.25 | - | - |
| CW_3 | Coal Waste 95% + Sewage Sludge 5% | - | - | 95 | 9.50 | 5 | 0.50 | - | - |
| CW_4 | Coal Waste 96.5% + Sewage Sludge 2.5% + Mineral Wool 1% | - | - | 96.5 | 9.65 | 2.5 | 0.25 | 1 | 1 |
| CW_5 | Coal Waste 94% + Sewage Sludge 5% + Mineral Wool 1% | - | - | 94 | 9.4 | 5 | 0.50 | 1 | 1 |
| Variant | Term | pH | Electrical conductivity (EC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mol KCl·dm-3 | mS·cm-1 | ||
| CS | I | 3.90 ± 0.01a | 0.11 ± 0.02a |
| II | 4.29 ± 0.01b | 0.10 ± 0.02a | |
| III | 4.90 ± 0.02c | 0.09 ± 0.01a | |
| CW_1 | I | 7.20 ± 0.01k | 0.65 ± 0.02bc |
| II | 7.00 ± 0.01ij | 0.60 ± 0.00b | |
| III | 6.80 ± 0.01g | 0.57 ± 0,01b | |
| CW_2 | I | 6.00 ± 0.02i | 0.79 ± 0.05fg |
| II | 6.82 ± 0.02g | 0.77 ± 0.03def | |
| III | 5.68 ± 0.02e | 0.69 ± 0.07cd | |
| CW_3 | I | 6.80 ± 0.02g | 1.14 ± 0.02i |
| II | 6.50 ± 0.01d | 0.95 ± 0.02h | |
| III | 6.50 ± 0.01d | 0.76 ± 0.01de | |
| CW_4 | I | 7.07 ± 0.07j | 0.84 ± 0.02fg |
| II | 6.90 ± 0.01h | 0.79 ± 0.01fg | |
| III | 6.71 ± 0.01f | 0.70 ± 0.02cd | |
| CW_5 | I | 7.03 ± 0.06ij | 1,12 ± 0.04i |
| II | 6.59 ± 0.01e | 0.95 ± 0.03h | |
| III | 6.60 ± 0.01e | 0.85 ± 0.01g |
| Variant | Term | HA | BC | CEC | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cmol(+) kg-1 | % | ||||
| CS | I | 2.69 ± 0.18 cd | 3.37 ± 0.15a | 6.06 ± 0.31a | 3.37 ± 0.15a |
| II | 2 78 ± 0.24 d | 3.80 ± 0 10a | 6 58 ± 0.21a | 3.80 ± 0.10a | |
| III | 2.48 ± 0.10 c | 4.67 ± 0.06b | 7.15 ± 0.14b | 4.67 ± 0.06b | |
| CW_1 | I | 0.62 ± 0.03 ab | 11.48 ± 0.26c | 12.10 ± 0.28c | 11.48 ± 0.26c |
| II | 0.59 ± 0.03 ab | 12.22 ± 0.12d | 12.81 ± 0.15d | 12.22 ± 0.12d | |
| III | 0.57 ± 0.03 a | 12.56 ± 0.28de | 13.13 ± 0.25d | 12.56 ± 0.28de | |
| CW_2 | I | 0.84 ± 0.07 b | 13.20 ± 0.09f | 14.04 ± 0.10ef | 13.20 ± 0.09f |
| II | 0.78 ± 0.01 ab | 13.13 ± 0.16f | 13.91 ± 0.17e | 13.13 ± 0.16f | |
| III | 0.76 ± 0.07 ab | 13.03 ± 0.08ef | 13.79 ± 0.15e | 13.03 ± 0.08ef | |
| CW_3 | I | 0.79 ± 0.05 ab | 15.10 ± 0.10kl | 15.89 ± 0.15l | 15.10 ± 0.10jk |
| II | 0.77 ± 0.04 ab | 14.81 ± 0.10ijk | 15.57 ± 0.08jkl | 14.81 ± 0.10ijk | |
| III | 0.74 ± 0.01 ab | 14.37 ± 0.18hi | 15.11 ± 0.17hij | 14.37 ± 0.18hi | |
| CW_4 | I | 0.74 ± 0.02 ab | 13.91 ± 0.15gh | 14.65 ± 0.13gh | 13.91 ± 0.15gh |
| II | 0.71 ± 0.05 ab | 14.12 ± 0.19gh | 14.83 ± 0.15ghi | 14.12 ± 0.19gh | |
| III | 0.63 ± 0.07 ab | 13.83 ± 0.16g | 14.46 ± 0.11fg | 13.83 ± 0.16g | |
| CW_5 | I | 0.72 ± 0.03 ab | 15.21 ± 0.04l | 15.93 ± 0.02l | 15.21 ± 0.04k |
| II | 0.69 ± 0.04 ab | 15.11 ± 0.16kl | 15.81 ± 0.14kl | 15.11 ± 0.16jk | |
| III | 0.63 ± 0.07 ab | 14.67 ± 0.23ij | 15.29 ± 0.24ijk | 14.67 ± 0.23ij | |
| Variable | Mean Values of the Output Variables in the Clusters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clusters 1 (CS) |
Clusters 2 (CW_1, CW_2) |
Clusters 3 (CW_3, CW_4, CW_5) |
|
| BC | 3.94 | 13.60 | 14.57 |
| HA | 2.65 | 0.69 | 0.71 |
| CEC | 6.59 | 13.30 | 15.28 |
| V | 3.94 | 12.60 | 14.57 |
| Variant | Term | TOC | TN | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g·kg-1 | ||||
| CS | I | 7.51 ± 0.22a | 0.84 ± 0.02a | 8.94 |
| II | 7.61 ± 0.17a | 0.89 ± 0.03a | 8.55 | |
| III | 8.21 ± 0.34a | 0.93 ± 0.03a | 8.23 | |
| CW_1 | I | 68.54 ± 0.79e | 2.36 ± 0.09bcd | 29.04 |
| II | 64.44 ± 0.54d | 2.27 ± 0.13bc | 28.39 | |
| III | 51.77 ± 0.25b | 2.15 ± 0.13b | 24.08 | |
| CW_2 | I | 82.40 ± 1.06g | 3.22 ± 0.03hi | 25.60 |
| II | 75.50 ± 0.45f | 3.14 ± 0.04gh | 78.64 | |
| III | 52.82 ± 0.64b | 2.63 ± 0.04de | 20.08 | |
| CW_3 | I | 95.49 ± 0.59j | 3.37 ± 0.14hi | 28.34 |
| II | 91.52 ± 0.93i | 3.44 ± 0.12i | 26.60 | |
| III | 57.60 ± 0.98c | 3.22 ± 0.02hi | 17.89 | |
| CW_4 | I | 85.30 ± 1.05h | 3.18 ± 0.07ghi | 26.82 |
| II | 62.30 ± 1.15d | 2.77 ± 0.06ef | 22.50 | |
| III | 56.49 ± 0.10c | 2.47 ± 0.07cd | 22.87 | |
| CW_5 | I | 95.21 ± 0.93j | 3.33 ± 0.10hi | 28.59 |
| II | 64.58 ± 0.41d | 2.94 ± 0.16fg | 21.97 | |
| III | 58.10 ± 1.24c | 2.86 ± 0.10ef | 20.31 | |
| Variable | Mean Values of the Output Variables in the Clusters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clusters 1 (CS) |
Clusters 2 (CW_1) |
Clusters 3 (CW_2, CW_3, CW_4, CW_5) |
|
| TOC | 7.77 | 61.58 | 73.11 |
| TN | 0.89 | 2.26 | 3.05 |
| C/N | 8.78 | 27.23 | 23.80 |
| Variant | Term | P | K | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg-1 | ||||
| I | 18.23 ± 0.21de | 33.00 ± 2.00b | 17.10 ± 0.30a | |
| CS | II | 17.37 ± 0.21d | 38.80 ± 1.40c | 20.00 ± 1.20a |
| III | 12.47 ± 0.15bc | 25.13 ± 0.50s | 20.20 ± 1.00a | |
| I | 1.77 ± 0.35a | 208.40 ± 2.00k | 180.00 ± 1.32c | |
| CW_1 | II | 1.43 ± 0.15a | 217.20 ± 1.73l | 203.00 ± 1.80g |
| III | 1.23 ± 0.25a | 116.60 ± 1.00f | 201.80 ± 0.53g | |
| I | 14 04 ± 0.44c | 198.50 ± 2.00j | 187.20 ± 1.80d | |
| CW_2 | II | 12.50 ± 0.17bc | 132.20 ± 1.00g | 235.00 ± 2.11j |
| III | 10.90 ± 1.67b | 83.40 ± 1.00d | 190.77 ± 0.32e | |
| I | 33.50 ± 1.00i | 242.27 ± 0.70m | 198.13 ± 0.95f | |
| CW_3 | II | 27.50 ± 1.10 gh | 148.10 ± 2.10h | 241.13 ± 0.68k |
| III | 26.37 ± 1.85g | 81.97 ± 1.15d | 179.97 ± 0.45c | |
| I | 21.00 ± 0.30f | 236.40 ± 0.40ł | 196.80 ± 0.92f | |
| CW_4 | II | 13.80 ± 0.10c | 162.67 ± 0.45i | 219.20 ± 1.20i |
| III | 10.80 ± 0.20b | 85.80 ± 0.40d | 184.47 ± 0.50d | |
| I | 29.40 ± 0.30h | 273.10 ± 2.80n | 218.40 ± 0.60i | |
| CW_5 | II | 25.50 ± 0.70g | 144.20 ± 2.40h | 209.80 ± 0.60h |
| III | 19.87 ± 0.45ef | 95.73 ± 0.50e | 170.87 ± 0.12b | |
| Zmienne | Mean Values of the Output Variables in the Clusters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clusters 1 (CS) |
Clusters 2 (CW_3, CW_5) |
Clusters 3 (CW_1, CW_2, CW_4) |
|
| K | 32.31 | 164.23 | 160.13 |
| Mg | 19.10 | 203.05 | 199.80 |
| Variants | White mustard | Maize |
|---|---|---|
| CS | 76.17 ± 0.85b | 112.70 ± 1.14b |
| CW_1 | 26.47 ± 0.64a | 52.23 ± 0.35a |
| CW_2 | 212.93 ± 0.91c | 351.53 ± 0.61d |
| CW_3 | 251.43 ± 0.55e | 402.23 ± 0.64e |
| CW_4 | 223.57 ± 0.40d | 328.93 ± 0.38c |
| CW_4 | 350.90 ± 1.15f | 453.60 ± 10.13f |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





