1. Introduction
Water, besides its importance in life on planet, confronts intense harvesting, impoundments, pollution and contamination among others, making the future of this resource insecure and uncertain, especially when looking at it from the prism of climate change [
1]. Freshwater ecosystems are threatened by a various widespread stressors as eutrophication and contamination aggravated by the climate crisis and practices as water harvesting and impoundments [
2]. Wetlands, lakes, and temporal waterbodies are rapidly disappearing demanding essential and meaningful coordination in water management towards precise goals. So, the water managers must act proactively to avoid further losses and cooperate/mobilize more stakeholders and end users.
Water resources management (WRM) is not simply an optimization problem. The process of water resources management requires a systemic approach. This implies the involvement of interacting entities, intricate dynamics, and multifaceted elements. Typically, water resources management approach frequently involves many criteria, multi -purposes, many stakeholders, structural or not measures among many others [
3]. Furthermore, Tsakiris [
4] proposed three general sets functioning as management poles for water systems: the water availability sources, water consumption centers and the environment. So, the WRM was introduced as an approach where all of the system “poles” are harmonically addressed for providing immediate solutions but sustainably to safeguard the future [
4].
Originally, WRM approach had a typical sub-sectoral approach, dealing mostly with water supply, sanitation, irrigation and hydropower generation [
5] hence, the problem could be concluded to a monocriterion optimization problem based on the axiomatic consideration that the “needs” must be covered. There was often a lack of coordination between sectors, and the environmental requirements either were ignored, or some simple constraints were added within the mathematical formulation. In the 70s, the Environmental Impact Assessment was introduced whilst the sustainability concept was introduced in the 90s [
4].
From a more environmental perspective, the three major pillars of Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM) is the equitable access to water resources while enhancing environmental sustainability and promoting economic efficiency of the resource (including allocations). The notion of IWRM entails an endeavor to comprehensively address and harmonize various technical and social aspects of water utilization and governance. Inevitably, it entails the involvement of stakeholders in some capacity [
6]. Stakeholder engagement is receiving more and more research attention for solutions design and implementation to tackle water challenges during the last two decades. The importance of “hearing the local voices” is reflected in organizations resolutions like the World Bank, the UN and the OECD, or the European Commission (aligned with Europe 2020 strategy). Good water governance and IWRM are intertwined with stakeholder engagement [
7].
The IWRM, has introduced stakeholder engagement and adaptivity (among other associated practices) as a scheme for novel paradigm management. Nonetheless, the successful implementation of such practices remains a formidable challenge [
8]. The participatory approaches, aiming to engage (in an institutionalized approach) the stakeholders, aims in fostering a sense of ownership from the design until the measures implementation has not yet (theoretically) yielded the expected reforms in water management [
9].
Nowadays new concepts and challenges are incorporated in the IWRM as the adaptation to Water-Energy-Food-Environment (WEFE) nexus, the extreme phenomena, public participation, and globalization among others. The largest water-related policy that exists at this time in Europe is the revised 20+ version of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) (2000/60/EC) introducing a framework for a “basin approach” which also embeds the concept of IWRM paradigm. But, even the WFD has raised skepticism due to several issues in reaching good status in EU waterbodies, since stakeholder engagement is low and, in most countries, there is a top-down procedure in decision making, usually adopting horizontal measures.
Multicriteria decision making (MCDM) is a valuable tool in water resources management problems since it can incorporate complex and often conflicting goals and objectives and multiple-stakeholders. The MCDM techniques can help decision makers to systematically evaluate and rank different options based on multiple criteria, such as cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, social acceptability, and technical feasibility. By considering multiple criteria, MCDM can help decision makers to make more informed and transparent decisions since the weights and the score of some criteria can be assessed by using the participation of the stakeholders. However, there are problematics and challenges which must be addressed as the qualitative evaluation of the criteria, the existence of multi-stakeholders, the different nature of criteria and the inherent uncertainty of the multicriteria problem among others. There are several “schools” of multicriteria analyses, of which, the distance methods are used to a great extent since these methods can be understandable to the analyst and they have a medium degree of difficulty. These approaches identify ideal and anti-ideal points which are fictitious alternatives in the edges of the decision spaces. They then distinguish the alternatives that are nearest to the ideal and furthest from the anti-ideal [
10].
Due to the fact that, by using the fuzziness, the uncertainty can be incorporated in the models and furthermore, since the fuzzy logic simulates the human reasoning, the fuzziness is widely used in mutlicriteria analysis. In brief, fuzzy set theory [
11] generalizes the classical or crisp sense according to Zimmerman [
12], Kafas [
13] into fuzziness sense involved in human language, that is, in human judgment, evaluation, decisions, within a non-exclusive list of linguistic social terms. Fuzziness can express the linguistic variables which are variables whose values are words or sentences in a natural or artificial language [
14]. Apart from these, the fuzziness can enable us to express the grey zone of the decision and furthermore can provide understandable ways to aggregate different information. Fuzziness, based on the ability to imitate the way of thinking, can generate understandable solutions without ambiguous considerations like the weights’ choice or the aggregation method of objective functions among others [
15], [
16] [
17].
After the invention of intuitionistic fuzzy (IF) set and IF numbers [
18] [
19], the expression to describe the fuzzy sets are totally changed. The fuzzy set uses only a membership function to indicate the degree of belongingness of a member into the set under consideration. The degree of non-belongingness is just automatically the complement by using the widely used fuzzy complement [
20]. The intuitionistic fuzzy sets overcome this restriction.
The inherent uncertainty of many real problems can be robustly incorporated by using an intuitionistic fuzzy set (IFS) [
18] which is an extension of an ordinary fuzzy set (FS) [
11]. The main difference between IFS and FS is the representation of hesitancy. More specifically, by using fuzzy sets, the decision can be obtained based on the satisfaction (or dissatisfaction) degree to an alternative using the membership function and its compliment. Whereas, in the case that the decision maker (DM) uses the IFS can further provide the hesitation degree to an alternative that is equal to the difference between the unit and the sum of the membership degree and the non-membership degree. Consequently, the opinion of the DM’s can be reflected more comprehensively [
21]. Nowadays the use of Intuitionistic fuzzy set has a great importance since enable us to use the stakeholder’s opinion and after that to quantify this information. In recent years, the field of intuitionistic fuzzy multicriteria methods has exhibited significant potential, as evidenced by its growing prominence, particularly since the year 2009 [
22].
Linking the above, meaning stakeholder participation within IWRM with the aid of IFS, we focus on the spatial scale of the application. Remote areas are generally characterized by low income (Thrace region is one of the poorest regions in EU), lack of river stewardship, Non-Government Organization (NGO) and environmental awareness, factors that are crucial for stakeholder engagement in decision making. This made our effort larger but more valuable. The eye4water project [
23] has invested in seminars/workshops, living labs, newsletters, data and findings open publications and citizens to researchers’ interactions in a “cluster” type, to foster regional water governance, to enhance the sustainability of monitoring networks and to create stronger bonds with the society. Holding just a consulting role, eye4water wishes to support decision making and strategic planning by taking into account the stakeholders’ opinion on pressures and possible solutions, assisting ultimately in two remote rural river basins (Laspias and Lissos) resilience and risk mitigation. By activating many forms of two-way communication among participants and utilizing institutional support in the form of facilitation and coordination we aim at good water governance processes.
The aims of this study are to incorporate stakeholders’ opinions to assist operationalization and decision making for participatory integrated water resources management in the remote rural Laspias river basin. Stakeholder groups were pinpointed for collaboration in the form of co-management-based governance arrangement. To this aim, semi-structured interviews were held in key areas within the basin. Intuitionistic fuzzy set was used to translate the opinion of the stakeholders concerning the weights and the evaluation of criteria. Next, an Intuitionistic distance-based method was applied in order to rank several alternatives under multiple criteria. The catchment of the Laspias is characterized by plains and natural areas with low vegetation and intense agricultural activity, all leading to the appearance of important water quality problems. [
24]
3. The proposed methodology
3.1. Stakeholders involvement/opinion research
Motivational drivers from the scientific part were the participatory of local population representatives, spatial extent in reaching villages that are in close range with the river (within the basin) and the addressing stakeholder groups that (in our opinion) contribute to the rivers. To manage it we had to meet them in their workplaces, their fields and local cafes and actually persuade them that their opinion matters. The project enablers as the social pages and the website contributed much. From the volunteer’s part, their major motivations were that they were heard and the will to co-shape solutions that fit them, to state their discomfort towards the managing authorities and to provide a contribution to science.
The campaign for stakeholders’ opinions on management practices had a duration of 5 days in May 2022. In-situ research was held in the form of semi structured interviews based on a questionnaire where an open discussion between the researchers and stakeholders was taking place based on a set of questions with qualitative in nature answers. In total 41 stakeholders were interviewed of which 29 were farmers and citizens working occasionally in agriculture and 12 were experts. The experts include both practitioners (workers in competent services/bodies, water corporations, and local authorities), as well as academia and research members of the D.U.Th. The primary objective was to ensure that the questions posed were uncomplicated and easily comprehensible, thus enabling individuals lacking rudimentary education to provide their valuable insights. The intention was to inclusively incorporate the opinions of diverse respondents. The primary method employed for data collection was through oral interviews, with an average interview duration of 40 minutes allocated per participant, meticulously gauging the perceptions of individuals pertaining to the judicious administration of the river.
The quota of the participant groups was selected in order to counterbalance the linguistic terms for assessing the weightiness of stakeholders and to guarantee for the proper inclusion of people with different experience. In other words, the questionnaire-based of interviews were chosen to contribute to the development of the multicriteria model taking into account the experience and expertise of the stakeholders of the case study. Personal data concerning age, educational level, basic employment/occupation, and experience were initially recorded. Then, a set of 10 questions was formed dealing with problems within the basin, provision services by the river, activities posing pressure, need for intervention (surface water and aquifers), cultivation practices, crop selection, criteria, applicable measures’ importance, and ways to attract young people (growth and decentralization). However, it should be noted that the main question of this process, apart from the recognition of the problems, from a mathematical point of view is the assessment of the weights of the criteria.
3.2. Combining the aspects of the participants by using intuitionistic fuzzy operator
As described below in more details, in order to quantify the information and to combine the aspects of the stakeholders regarding either the scores of the criteria or the weights of the criteria, an operator based on the principles of intuitionistic fuzzy sets is used. This is the intuitionistic fuzzy weighted averaging (IFWA) operator [
33].
Indeed, several researchers have recently concentrated on the topic of aggregation techniques pertaining to intuitionistic fuzzy information [
34], [
35] and [
36]. They put emphasis to define the concept of IFN’s and to develop a method that these IFN’s can be ranked on the basis of the functions of their score and accuracy. Apart from the definition of IFN’s they have settled an operational system of laws and have imported a series of operators in order to aggregate intuitionistic fuzzy information. The intuitionistic fuzzy weighted averaging operator (IFWA) presented in this study is one of these operators [
33].
Let
}be an intuitionistic fuzzy number assigned to criterion
by k-th DM. Then the weights of the criteria are computed using the IFWA operator.
where
The above equation is based on Eq (4), Eq (6) and this operation produced also an intuitionistic fuzzy value. Where
is the corresponding weight of k-th stakeholders or more general the people who participate in the research and it can be obtained by using the following equation proposed by [37]:
the values μ
κ, ν
κ, π
κ can be taken from
Table 1.
Since there are weights, the symmetry property in Εq. 14 does not hold. However, regarding the membership function μ this aggregator is near to the fuzzy union, since, if at least, one stakeholder proposes This fact remember to us the boundary condition of the fuzzy union.
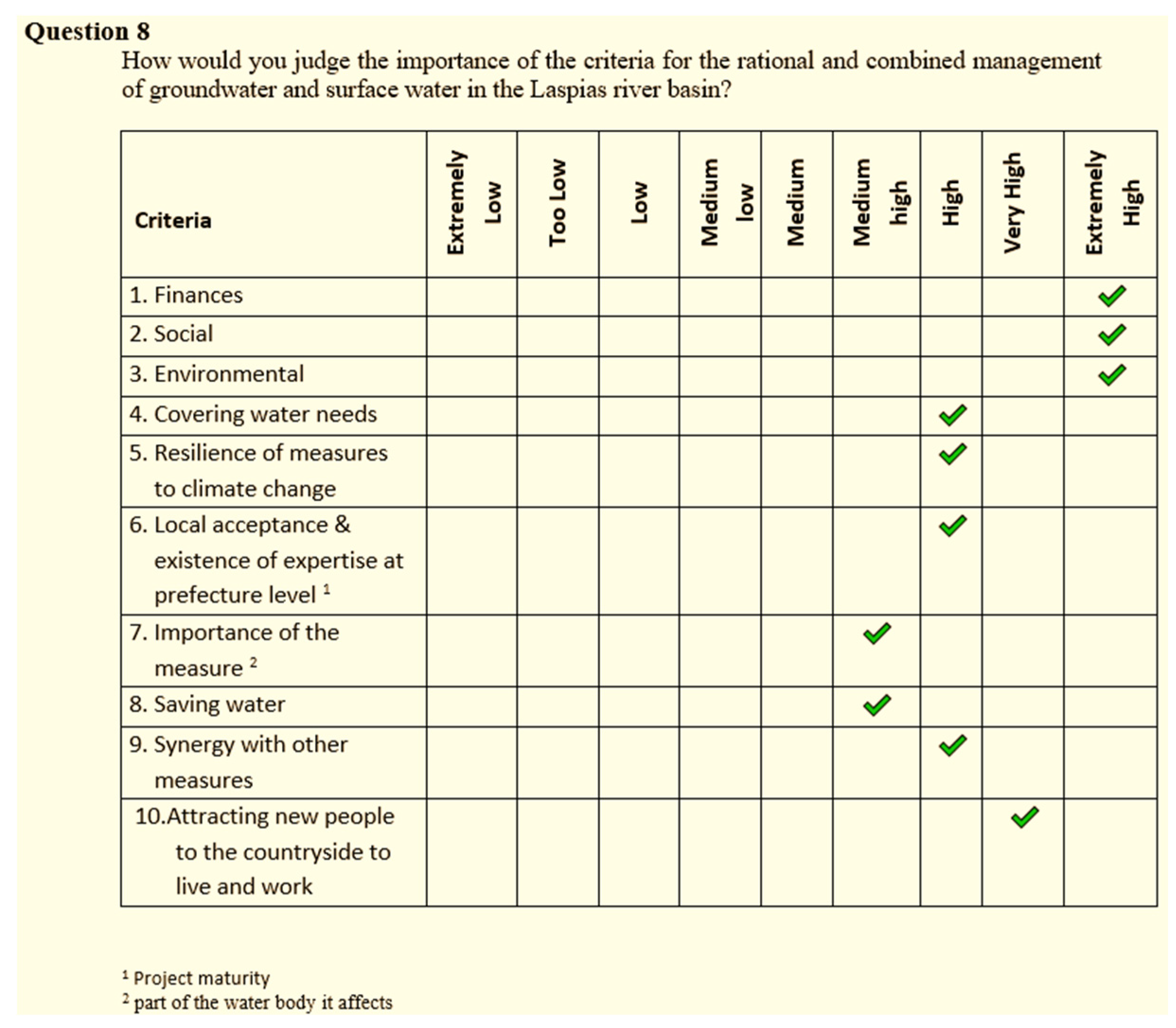
To take this information, the fulfill of questionnaires and interviews are primary required, where the education, the training and the experience of the respondents themselves have been denoted. The questionnaires were filled with qualitative terms which were converted into intuitionistic fuzzy values according to the following tables.
In the second step, we invited the participants in the same questionnaire to answer how they would judge the importance of the criteria for the rational use of the Laspias river. Which again was done in verbal terms and turned into intuitionistic fuzzy values via
Table 2. By the same way the participants can evaluate some kind of criteria.
Table 1 and
Table 2 show the conversion into intuitionistic fuzzy values. For instance, if the linguistic term expressing the importance of stakeholders is either beginner or expert the degree of hesitancy π is equal to zero.
3.3. Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS using Similarity measure.
TOPSIS, which was developed by [
39], is based on the idea that the chosen alternative should have the shortest distance from the positive ideal solution and simultaneously the longest distance from the negative ideal solution. Let A = {A
1, A
2, ..., A
m} be a set of alternatives and X = {X
1, X
2, ..., X
n} be a set of criteria, the procedure for Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS method has been given as follows:
Step 1. Determine the weights of each participant. Assume that participants contributed in the investigation. The importance of each participant was calculated with respect to
Table 1, that is, by considering the educational level and the experience. Then the weight of each participant can be obtained as a crisp value by using Eq. 15.
Step 2. Aggregate all the information based on the participants by using the IFWA operator (Eq.14). In this application these steps concern mainly the weights of the criteria. W denoted a set of grades of importance. The weights of the criteria are also computed using the (Eq.14).
Step 3. Construct intuitionistic fuzzy decision matrix for each criterion and alternative Aj by transforming the opinions of experts into Intuitionistic Fuzzy Values.
Step 4. Construct aggregated weighted intuitionistic fuzzy decision matrix for each criterion (Ci) and alternative Aj using (Eq.4), where W represents a set of grades of importance. It is obvious that the first term expresses a fuzzy intersection and the second term expresses a fuzzy union.
Hence, the aggregated weighted intuitionistic fuzzy decision matrix can be defined as follows:
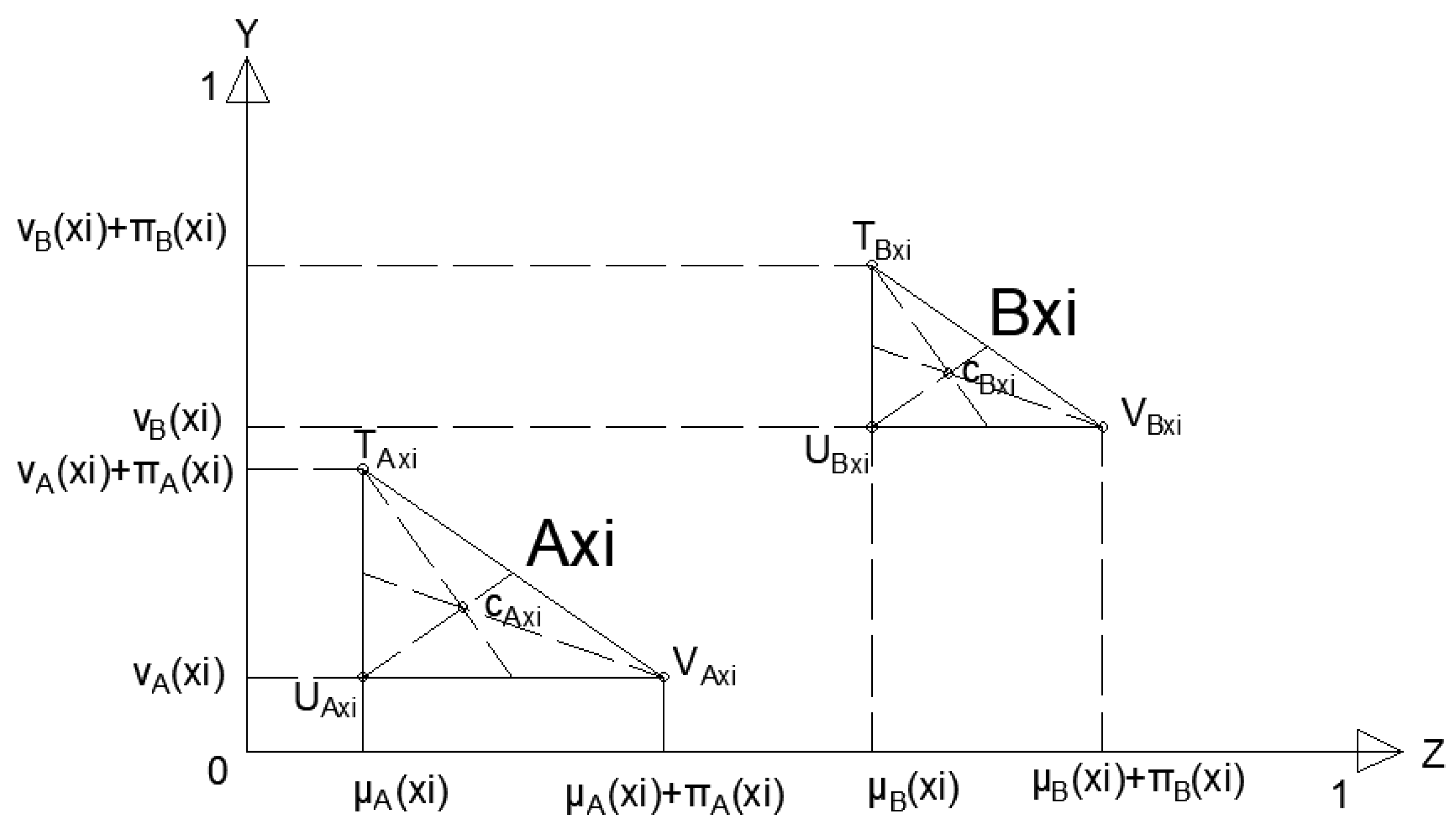
Step 5. Determine intuitionistic fuzzy positive ideal and intuitionistic fuzzy negative ideal solutions. And let they exist only benefit criteria. A* is the intuitionistic fuzzy positive ideal solution and A- is the intuitionistic fuzzy negative ideal solution.
Then A* and A
- [
40]:
where
Step 6. Calculate for each alternative the similarity from both the ideal and anti-ideal solutions: The similarity measures,
and
of each alternative from intuitionistic fuzzy positive ideal and negative fuzzy ideal solutions are calculated with respect to criterion C
j [28]:
Finally, a simple weighted model is used to assess the similarity measures over all criteria:
Step 7. Calculate the relative closeness coefficient to the intuitionistic fuzzy ideal solution. The relative closeness coefficient of an alternative A
i with respect to the intuitionistic fuzzy ideal solution A
* is defined as follows [29]:
Step 8. Rank the alternatives.
After the relative closeness coefficient is determined, alternatives are ranked according to descending order of Ci*.
4. Case Study
4.1. Description of the study area
Laspias River watershed (code EL12-07) occupies an area of 221.8 km
2, and it is part of the Nestos River basin belonging to the River Basin District of Thrace (
Figure 2a). To the west of the Laspias River stretches the plain of the Nestos River, while to the east of Laspias toward the Vistonida lagoon stretches the plain of Xanthi. The largest part of the area is agricultural land without the presence of an irrigation network that can cover water needs. Thus, irrigation is based on the water of river and groundwater. The Mediterranean climate has great seasonality resulting in contrasting hydrological conditions, that, when combined with the actual water (mostly agricultural) needs, typically threaten freshwater habitats due to the high flow variability (often intermittent during summer).
A few parts of the Laspias watershed have been characterized as protected areas, while habitat fragmentation, nitrate pollution, recipient of organic load and heavy metals (landfill, WWTP, industries) are observed [
41] [
42] [
43]. The lowland of Laspias watershed overlies the groundwater systems of Delta Nestos (EL1200060) and Xanthi-Komotini (EL1200050) (
Figure 2c) which have quality problems in the coastal zone due to sea intrusion as a consequence of over-pumping [
44], [
45]. The groundwater system in the study area consists of two aquifers, an upper phreatic to semi-confined aquifer and a lower confined aquifer. Rainfall naturally feeds the upper aquifer through the mechanism of infiltration whilst the recharge through the stream bed percolation of the north hilly area is considerably less. The lower aquifer largely recharges both from River Nestos percolation through buried old stream beds and from the lateral groundwater inflows coming from the neighboring Vistonida Lagoon hydrogeological basin [
44].
The Laspias river basin can be distinguished in the areas affected by the river and groundwater, and those that are affected only by the groundwater systems. More specifically, the areas of influence of the river and groundwater are delimited from the west by the imaginary line that starts from the settlement of Dekarcho, passes between the settlements of Neo Erasmio and Maggana, and ends at the western part of Maggana beach. The eastern limit of the area of influence of river Laspias is the imaginary line that joins the settlements of Melissa and Myrodato and ends at Myrodato beach. In the north, the Laspias river is influential up to the settlements of Kypseli, Exohi and Magiko. In fact, the farmers are not aware of the river and their crops are irrigated exclusively with groundwater (
Figure 2a and 2b).
As abovementioned, quality problems of groundwater are observed in the southern part of the investigated area demarcated between the coastline and the settlement of Maggana where a significant number both of small diameter shallow wells and larger diameter deep wells are observed. As concerned the area which is not affected by the river, the problems are related to the groundwater quantity. In particular, in the settlement of Kypseli, almost all of the shallow wells show very little supply as a result of which farmers group together to dig deep wells, since both the construction cost and the energy cost are very high per person. Deep wells may show a greater supply, but their collective use cannot fully cover the irrigation needs of each individual.
It should be mentioned that the water of the Laspias river is recharged with water of better quality from the Nestos river through a network of canals. The central canal passes through the area of the settlement of Olvio. The injection point is located E-SE of the settlement of Dekarcho. In the area between the settlements of Dekarcho and Maggana, an informal small irrigation network has been developed due to the presence of ditches. The use of these ditches is multiple as they are not only used as irrigation canals but also as a network of artificial recharge of groundwater thus contributing indirectly and directly to the qualitative and quantitative upgrading of groundwater.
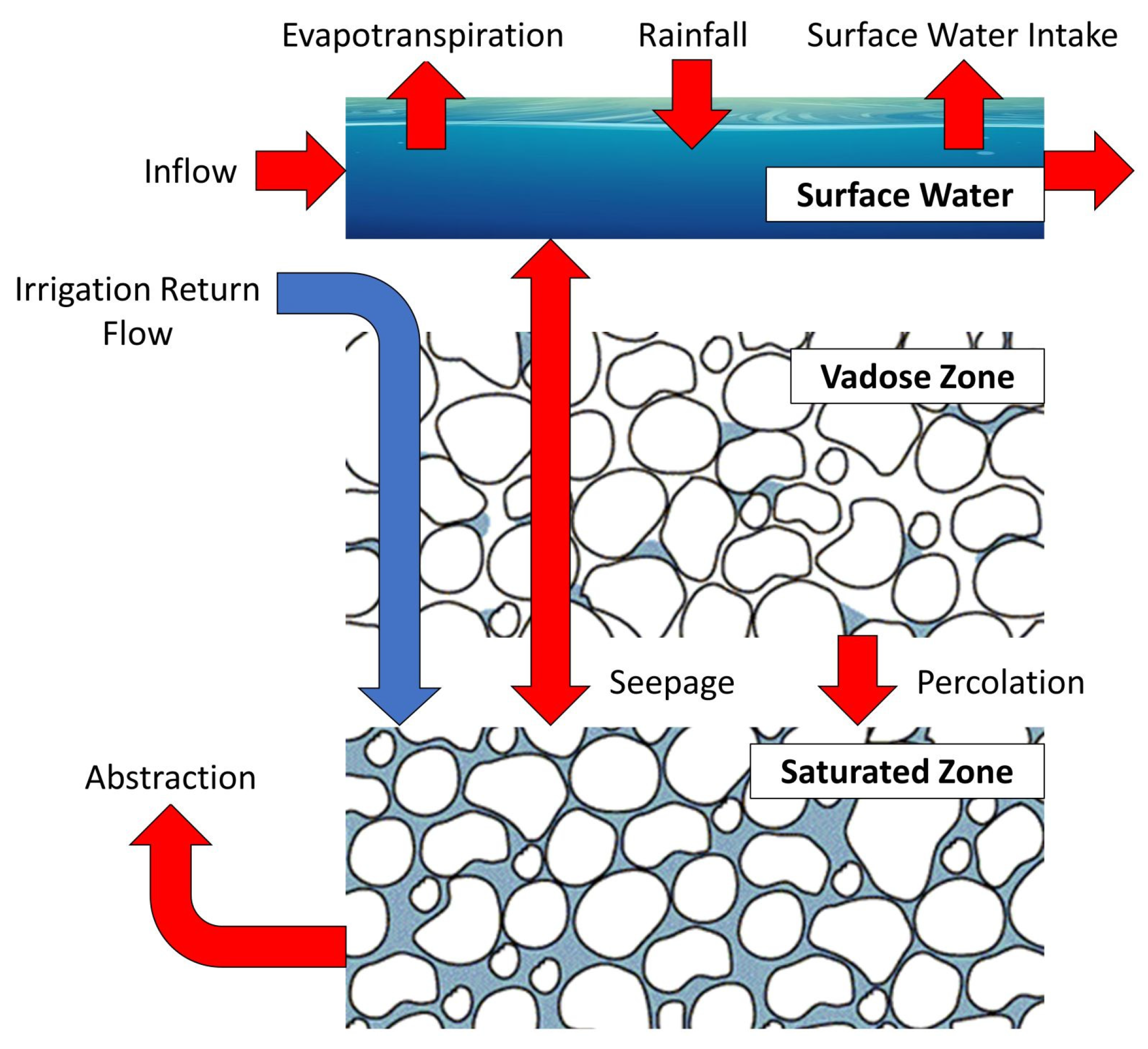
The simulation of the Laspias watershed should not be based on a water balance model which considers the groundwater system as a single reservoir. The relevant procedure is governed by high uncertainty for the following reasons: a) the boundaries of the Laspias watershed are not identical with the boundaries of the groundwater systems, b) apart from rainfall , the Laspias watershed receives significant surface water amount from Nestos River, and c) the different lateral hydraulic interconnections of the groundwater system and the great inflows from Nestos River to the groundwater system through deep percolation are not taken into account (
Figure 3).
4.2. Criteria Identification
The selection of appropriate criteria is one of the most important steps in water resources management and depends on the physical, natural, and socio-financial characteristics of the study area and data availability. However, it is also desired their number be minimal in order to reduce complexity. Ten criteria encompassing the properties of the given watershed were identified. These are financial, social, environmental, covering water needs, resilience to climate change, local acceptance and the existence of know-how at the prefecture level, the importance of measures, water saving, synergy with other measures, and attracting young people to the countryside to live and work criteria.
Financial criterion: It is one of the three general criteria and refers to the cost of construction, operation and more generally to the cost of implementation and maintenance of a proposed measure (alternative).
Social criterion: It is the second general criterion and refers to the development and welfare of local society caused by a measure suggested.
Environmental criterion: The last general criterion refers to the environmental degradation / upgrading of the local conditions due to the implementation of a proposed measure.
Covering water needs criterion: It focuses on satisfying the water needs of all stakeholders mainly in quantitative terms.
Resilience to climate change: Every proposed measure is assessed regarding its resilience to climate change, for instance, an increase in the frequency of extreme hydrological events should be taken into account.
Local acceptance and existence of know-how criterion: This criterion ensures the sustainability of the measure over time. Obviously, a measure proposed should be initially acceptable from the local societies and it should be sufficient know-how by local authorities for its subsequent operation and maintenance.
Importance of measure criterion: This criterion refers to the part of the water body affected by the proposed measure.
Water saving criterion: It refers to measures that could save water by collection and reuse, such as reuse of biological treatment effluents.
Synergy with other measures: to be combined with other measures. For instance, a water quantity of an irrigation network can be used to fill in basins/ditches for artificial recharge of groundwater.
Attracting young people to the countryside to live and work criterion: This measure was included to assess stakeholder opinion regarding the employment of young people in the primary sector.
4.3. Proposed alternatives
As aforementioned, the output of this research is the ranking of the alternatives (i.e. the measures proposed) in terms of their effectiveness in the rational management of the water resources of the Laspias watershed. The preparation of the alternatives was based on the experience of the local conditions and each alternative is evaluated based on the above ten criteria: i) reuse waste water (A1), ii) inflow of Laspias river from a surplus water of the canals (A2), iii) changing crops to less water-bearing types (A3), iv) establishment of a centralized irrigation network(A4), v) grant/use of automation in the irrigation activities (A5), vi) artificial recharge of groundwater utilizing excess water a) based on flood basin (A6), b) based on ditch network (A7), vii) intensification of irrigation (A8), viii) no change to the existing situation (A9), viii) redesign of production lines and internal recycling of water flows (A10), ix) removal/deactivation of pollutants (A11), x) strict implementation of the pricing policy on water use (A12), xi) strict implementation of the pollution pricing policy (A13), xii) monitoring of system pollutants (A14).
5. Results and Discussion
Farmers recognize the problem of river quantity and quality and are interested in finding solutions that will allow them to maintain their business operations.
The biggest concern of the most stakeholders seem to be related to the quality of the water of the Laspias river, especially in drought periods. However, in the region of Dekarcho the farmers put also emphasis on the water irrigation quantities. A significant percentage (≈78%) of the respondents consider that the Laspias river needs any intervention, approximately 19% consider that maybe some intervention is needed, while only one respondent (≈2.5%) considers that no intervention is necessary. Regarding groundwater, the corresponding percentages are ≈66% (27/41), ≈22% (9/41) and 5/41 (≈12%). The development of an irrigation network that will be based on the drilling of new municipal/public wells is advanced by the stakeholders (mainly farmers) as one of the best alternatives to deal with the water shortage regarding the area which is not affected by the Laspias River. It is also worth mentioned that approximately 53% of the respondents believe that irrigation can contribute to the economic development of the region in the future, while a significant percentage (≈34%) does not know what such an ecosystem service of the Laspias river could be.
Also of interest are the answers to the question based on which criteria farmers choose the type of crop. As mentioned above, the sample size in this question is n=29 (crowd of farmers). According to the responses, economic efficiency is the most popular answer, followed by human productivity as ratio between the production divided to the human work (in hours). Dryland or thirsty crops are not a selection criterion, except in the area around the settlement of Abdira where most of the crops are dryland cotton due to the presence of the Abdira swell. Resistant crops, perennial, annual or seasonal crops, as well as traditional crops are also not a selection criterion if the criteria of economic efficiency and less employment are not met. Furthermore, the cultivators placed greater emphasis on the economic criterion, but also placed great importance on the environment (
Figure 4).
As aforementioned the following steps are used in order to achieve the multicriteria ranking under multiple stakeholders:
Step 1. Determine the weights of each participant. The importance of each participant was calculated with respect to
Table 1, that is, by considering the educational level and the experience. Then the weight of each participant can be obtained as a crisp value by using Eq. 15 [
37].
For instance, based on the answers the 1st stakeholder was a Proficient (Pt) with μ=0.5 v=0.45 and π=0.05 and therefore his weight:
The denominator of this equation is estimated by summing all 43 numerators of the participants.
We got completed 43 questionnaires, 29 of them were farmers and the rest were experts or administrative officers.
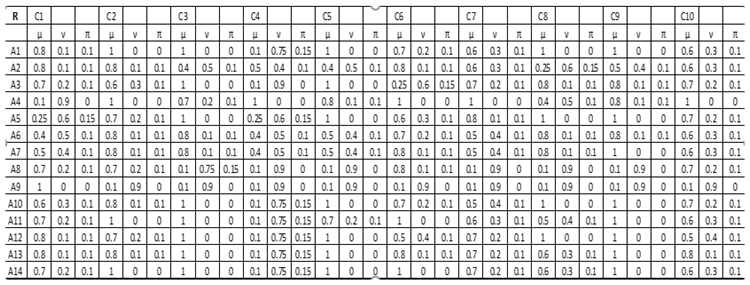
Step 2. Aggregation of all the information based on the participants by using the IFWA operator (Eq.14). In this application these steps concern mainly the weights of the criteria. As aforementioned in this application participants took place with a different level of practice and education, so the value λ takes different values. The final criteria’s weights derived as fuzzy intuitionistic information are presented in
Table 3.
From the results it is produced that stakeholders put great importance to the environmental criterion and less to criteria involving various technical projects. However, the economical aspect seems as the most important criterion.
There might be some threads to validity for the faultless and reproducible methodology in acquiring stakeholders’ opinion and for the methodology used for translating qualitative and quantitative information, though, the societal needs, values, and aspirations were expressed and could be integrated into planning. The findings could be dependent on prior training and knowledge, but also reflect their social, political and cultural individual backgrounds. The stakeholder’s opinion might not be the most solid from a scientific point of view, but what is needed for operationalization of the basin, is exactly the balancing of priorities and competing demands in an assimilable way by policy makers.
Step 3. Construct intuitionistic fuzzy decision matrix for each criterion (Ci) and alternative Aj by transforming the opinions of experts into Intuitionistic Fuzzy Values using (Eq.16).
Step 4. Construct aggregated weighted intuitionistic fuzzy decision matrix for each criterion based on the alternative Aj and the corresponding weight using Eq (4).
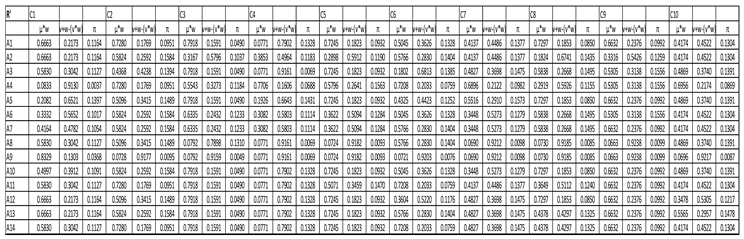
Hence, the aggregated weighted intuitionistic fuzzy decision matrix is presented in
Table 5 using (Eq.17).
Step 5. Determine intuitionistic fuzzy positive ideal (A*) and intuitionistic fuzzy negative ideal (A-) solutions. And let they exist only benefit criteria.
Step 6. Calculate for each alternative the similarity from both the ideal and anti-ideal solutions:
The similarity measures, and , of each alternative from intuitionistic fuzzy positive ideal and intuitionistic fuzzy negative ideal solutions are calculated with respect to criterion Ci using Equations 18 and 19. Finally, a simple weighted model is used to assess the similarity measures over all criteria.
Step 7. Calculate the relative closeness coefficient to the intuitionistic fuzzy positive ideal solution.
The relative closeness coefficient of an alternative Aj with respect to the intuitionistic fuzzy ideal solution A* is defined as follows:
where 0 ≤≤ 1 (i=0, 1, 2, ….m)
Step 8. Rank the alternatives with descending order. The final results are presented in
Table 7.
In addition, two main methods are examined. The first one is based on the concept of entropy (Appendix). It differs to the proposed method since the concept of entropy is used instead of the IFWA operator in order to assess the weights of criteria. In this case a main disadvantage is produced, that is that the questionnaires regarding the weight’s importance will not be considered. The method put emphasis on the criteria with low hesitancy and finally, the A4 alternative is finally selected.
The second examined method is the method of [
37]. The main difference between the proposed method and the method of [
37] is that the Euclidean distance is used during the implementation of the TOPSIS method. The results are presented in
Table 8.
Regarding the two TOPSIS methods, they have little deviation in the results. Hence, the reuse waste water (A1), strict implementation of the pollution pricing policy (A13) and the monitoring of system pollutants (A14) are firstly selected. In addition, by using the widely used TOPSIS the alternative A4 has a lower rank.
The main difference is that the similarity based TOPSIS puts emphasis on the alternative of creation of a central irrigation network (4th choice). In fact, this choice restores the water regime situation before the great river infrastructure. It is very encouraging that the alternative of doing nothing is last in preference among all the methods we worked on. It should be noted that these three first alternatives (strict implementation of the pollution pricing policy(A13), monitoring of system pollutants(A14) and waste water reuse (A1) can be characterized as eco-friendly. The final ranking could be characterized rather as rational and balanced. Therefore, the similarity measures which is used has a theoretical sound foundation and leads to balanced solutions.
Consequently, the use of the IFWA operator to combine the aspects about the weight and the intuitionistic fuzzy similarity based TOPSIS method is selected because of its balanced outcomes.
It is worth mentioning that the alternative A
4, (which is ranked first at entropy method) in a previous study [
46] it has been substantiated that it is possible to transfer water from Nestos River and create a large and organized irrigation network that will meet the water needs of the wider area and simultaneously has environmental benefits. According to the same study, the annual volume of the Nestos River is approximately estimated at 788 x 10
6 m
3, exceeding the beneficial volume of the main (from a reservoir system) reservoir of Thesauros which is 570 x 10
6 m
3. It should be pointed out that only 3,000 ha located between the Nestos River and the Laspias River are irrigated from the water of the Nestos River, while 16,000 ha are irrigated to the west of Nestos River in the prefecture of Kavala. Irrigation of the hectares of the area under consideration is mainly carried out with a system of open canals. Thus, in a way, the natural recharge of the aquifers, which was contributed by the Nestos Delta covering the area until water training of Nestos River in 1955 with a lot of structures, is artificially compensated.