Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
11 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Chatbot System Architecture and Applications
2.2. Chatbot Methods
2.2.1. Rule-Based Methods
2.2.2 Corpus-Based and Retrieval-Based Methods
2.2.3. Extractive-Based and Generative-Based Methods
2.3. Discussions and Gap
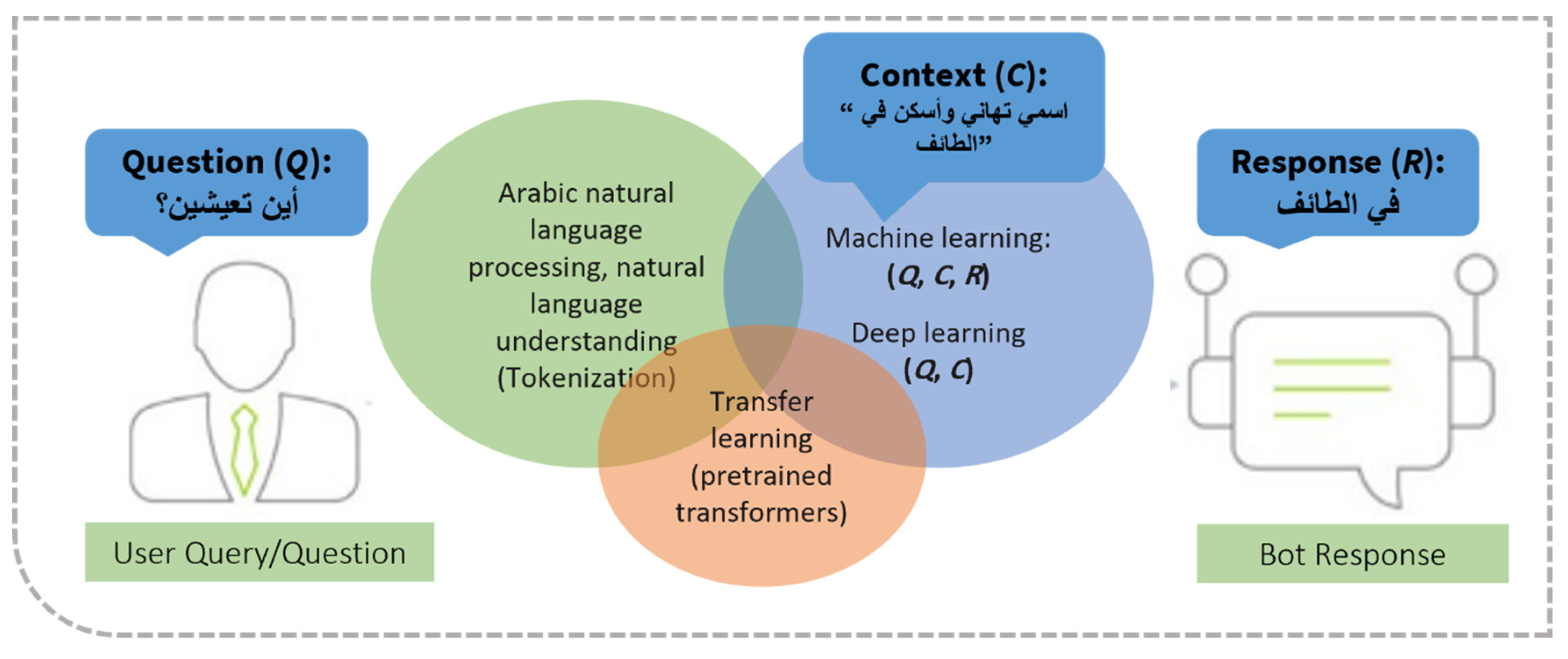
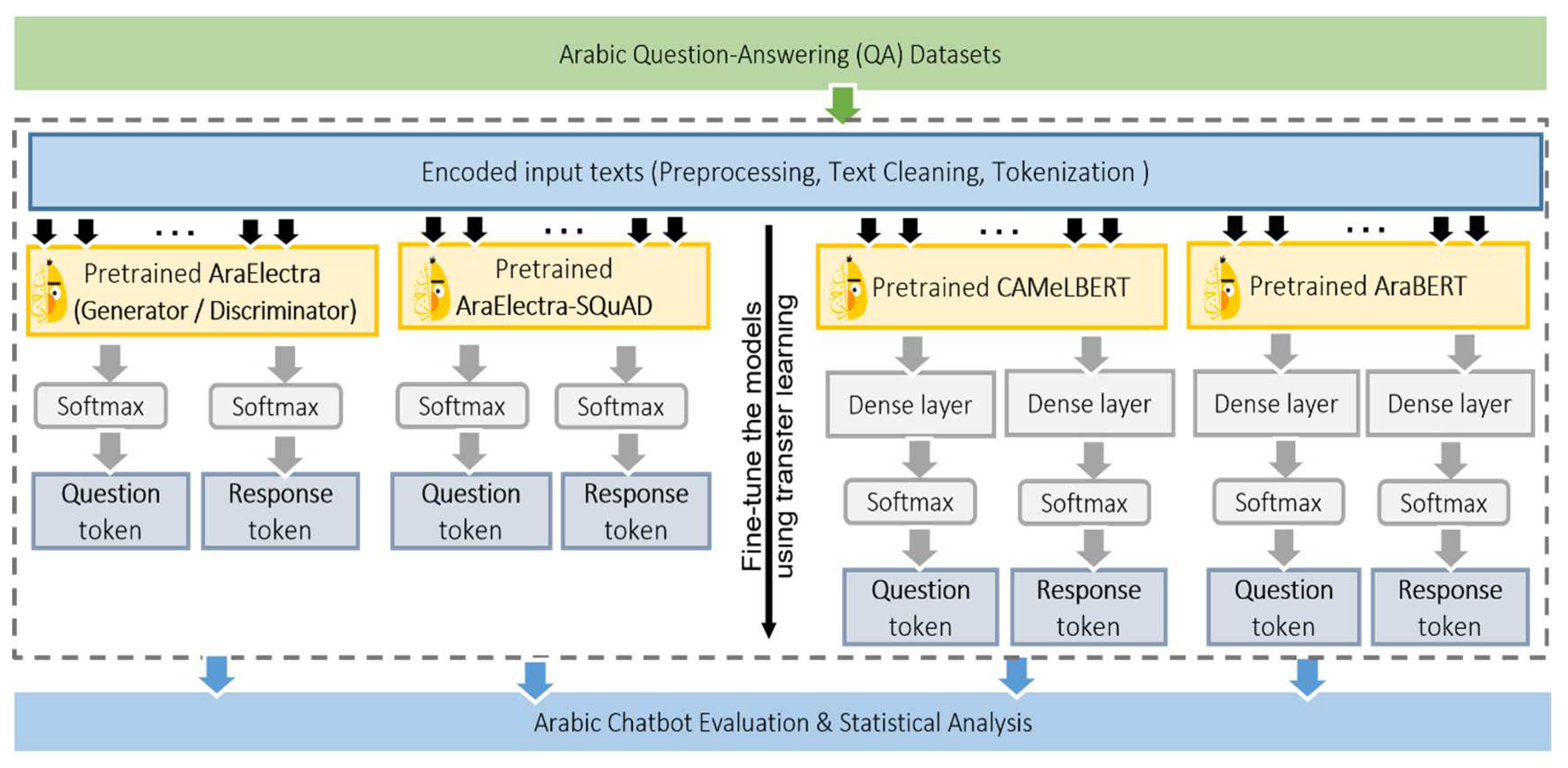
3. Methodology
3.1 General Framework
3.2. Details of Extractive QA and Transfer Learning Method for Arabic Chatbot
- Dataset preprocessing: We utilized large datasets of questions and their corresponding answers, together with a large corpus collection of textual documents which contains the contexts these questions and answers were taken from. In this step, we implemented various pre-reprocessing steps to remove any unwanted elements such as special characters, stop words or noisy words. Further, we cleaned the corpus by removing any irrelevant or misleading information.
- Initialization: In this study, we used several pre-trained transformers. The final fully connected layer(s) of the pre-trained network was removed and replaced with new layer(s) that represent the questions/queries and responses/answers. This process saved a lot of time and computational resources compared to training a network from scratch, as the network can start from a good initial state based on its prior experience. Several parameters were initialized such as the patch size, the number of epochs, the learning rate, wherein we used initialization settings like the state-of-the-art studies in QA tasks in English.
- Fine-tuning: Several BERT-like transformers in Arabic were fine-tuned using large datasets of annotated QA pairs for the task of extractive QA. This step was crucial to achieve the aims of our study whereby the goal of the model was to read a passage of text and extract a concise answer to a given question from the passage. To elaborate, we first provided them with a dataset of questions and their corresponding answers, as well as the passage from which the answer was extracted. The model was then trained to predict the correct answer given a passage and a question. During the fine-tuning process, the transformers' last (i.e., added) layers were trained using a task-specific loss function that aims to optimize the model to generate the correct answer for a given question. The model was trained to select the answer by identifying the start and end positions of the answer in the passage. The fine-tuning process involved adjusting the weights of the pre-trained transformers using backpropagation to optimize the model's output. The loss function was minimized in several epochs to improve the model's accuracy in predicting the correct answer to a given question.
- Testing and evaluation: Once the fine-tuning was complete, our models were used for extractive QA in Arabic chatbot. When a user asks a question, the chatbot can feed the question into the model, which will then provide an answer based on corpus collection with a confidence score. Hence, our proposed models were tested on different datasets and real-world scenarios to check their robustness and accuracy. In order to compute the confidence and similarity scores, several semantic embedding models were used. A semantic embedding model is an NLP method that allows words or phrases to be represented as vectors of numbers in a multi-dimensional space. The idea behind this model is that words that are similar in meaning will be located close to each other in this space, while words that are dissimilar will be located far apart. In this study, variants of distilbert and bert-based models for Arabic were employed to predict the answers or responses based on their surrounding context.
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Datasets
4.2 Resources and Tools
4.3 Evaluation
5. Experimental Results
5.1 Initial Results Using a Sample of Selected Questions from MSA-QA and DA-QA Datasets
5.2 Initial Results Using a Sample of Selected Questions from MSA-QA and ARCD-QA Datasets
5.3 Experimental Results Using All Questions from MSA-QA and ARCD-QA Datasets
6. Conclusion and Future Works
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caldarini, G.; Jaf, S.; McGarry, K.; McGarry, K. A Literature Survey of Recent Advances in Chatbots. 2022, 2022, 41-41. [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.A.; Habash, N. Botta: An Arabic Dialect Chatbot. In Proceedings of the COLING 2016, the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Osaka, Japan, 2016; pp. 208-212.
- Al-Ghadhban, D.; Al-Twairesh, N. Nabiha: An Arabic Dialect Chatbot; 2020.
- Joukhadar, A.; Saghergy, H.; Kweider, L.; Ghneim, N. Arabic dialogue act recognition for textual chatbot systems. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of The First International Workshop on NLP Solutions for Under Resourced Languages (NSURL 2019) co-located with ICNLSP 2019-Short Papers, 2019; pp. 43-49.
- Shi, N.; Zeng, Q.; Lee, R. Language Chatbot-The Design and Implementation of English Language Transfer Learning Agent Apps. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Automation, Electronics and Electrical Engineering, AUTEEE 2020, 2020/11//, 2020; pp. 403-407.
- Vasilev, I.; Slater, D.; Spacagna, G.; Roelants, P.; Zocca, V. Python Deep Learning: Exploring deep learning techniques and neural network architectures with PyTorch, Keras, and TensorFlow, 2nd Edition; Packt Publishing: 2019.
- Alhassan, N.A.; Saad Albarrak, A.; Bhatia, S.; Agarwal, P. A Novel Framework for Arabic Dialect Chatbot Using Machine Learning. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Alruily, M. ArRASA: Channel Optimization for Deep Learning-Based Arabic NLU Chatbot Framework. Electronics (Switzerland) 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Ghaddar, A.; Wu, Y.; Bagga, S.; Rashid, A.; Bibi, K.; Rezagholizadeh, M.; Xing, C.; Wang, Y.; Xinyu, D.; Wang, Z.; et al. Revisiting Pre-trained Language Models and their Evaluation for Arabic Natural Language Understanding. 2022, arXiv:2205.10687. [CrossRef]
- Suta, P.; Lan, X.; Wu, B.; Mongkolnam, P.; Chan, J.H. An overview of machine learning in chatbots. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Robotics Research 2020, 9, 502-510. [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulou, E.; Moussiades, L. Chatbots: History, technology, and applications. Machine Learning with Applications 2020, 2, 100006-100006. [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zain Amin, M. Conversational AI Chatbot Based on Encoder-Decoder Architectures with Attention Mechanism Application of Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) for Data Mining in Healthcare Operations View project Performance Evaluation of Supervised Machine Learning Classifiers for Predicting Healthcare Operational Decisions View project Conversational AI Chatbot Based on Encoder-Decoder Architectures with Attention Mechanism. Artificial Intelligence Festival 2019, 2. [CrossRef]
- Majid, R.; Santoso, H.A. Conversations Sentiment and Intent Categorization Using Context RNN for Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems, ICACCS 2021, 2021/3//, 2021; pp. 46-50.
- Ilievski, V.; Musat, C.; Hossmann, A.; Baeriswyl, M. Goal-Oriented chatbot dialog management bootstrapping with transfer learning. In Proceedings of the IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018; pp. 4115-4121.
- Nguyen, T.T.; Le, A.D.; Hoang, H.T.; Nguyen, T. NEU-chatbot: Chatbot for admission of National Economics University. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence 2021, 2. [CrossRef]
- Moriuchi, E.; Landers, V.M.; Colton, D.; Hair, N. Engagement with chatbots versus augmented reality interactive technology in e-commerce. Journal of Strategic Marketing 2021, 29, 375-389. [CrossRef]
- Siglen, E.; Vetti, H.H.; Lunde, A.B.F.; Hatlebrekke, T.A.; Strømsvik, N.; Hamang, A.; Hovland, S.T.; Rettberg, J.W.; Steen, V.M.; Bjorvatn, C. Ask Rosa – The making of a digital genetic conversation tool, a chatbot, about hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. Patient Education and Counseling 2022, 105, 1488-1494. [CrossRef]
- Khadija, A.; Zahra, F.F.; Naceur, A. AI-Powered Health Chatbots: Toward a general architecture. In Proceedings of the Procedia Computer Science, 2021; pp. 355-360.
- Baha, T.A.I.T.; Hajji, M.E.L.; Es-Saady, Y.; Fadili, H. Towards highly adaptive Edu-Chatbot. In Proceedings of the Procedia Computer Science, 2021; pp. 397-403.
- K., H.K.; Palakurthi, A.K.; Putnala, V.; K., A.K. Smart College Chatbot using ML and Python. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on System, Computation, Automation and Networking (ICSCAN), 3-4 July 2020, 2020; pp. 1-5.
- Vyawahare, S.; Chakradeo, K. Chatbot assistant for english as a second language learners. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Convergence to Digital World - Quo Vadis, ICCDW 2020, 2020/2//, 2020.
- Gowda, M.P.C.; Srivastava, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Ghosh, A.; Raj, H. Development of Information Technology Telecom Chatbot: An Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 2021 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Engineering and Management, ICIEM 2021, 2021/4//, 2021; pp. 216-221.
- Mathew, R.B.; Varghese, S.; Joy, S.E.; Alex, S.S. Chatbot for Disease Prediction and Treatment Recommendation using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), 23-25 April 2019, 2019; pp. 851-856.
- Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Liao, Y.; Wang, J. Supervised machine learning chatbots for perinatal mental healthcare. In Proceedings of the Proceedings - 2020 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Human-Computer Interaction, ICHCI 2020, 2020/12//, 2020; pp. 378-383.
- Rakib, A.B.; Rumky, E.A.; Ashraf, A.J.; Hillas, M.M.; Rahman, M.A. Mental Healthcare Chatbot Using Sequence-to-Sequence Learning and BiLSTM. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 2021; pp. 378-387.
- Chempavathy, B.; Prabhu, S.N.; Varshitha, D.R.; Vinita; Lokeswari, Y. AI based Chatbots using Deep Neural Networks in Education. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Energy, ICAIS 2022, 2022; pp. 124-130.
- Almurayh, A. The Challenges of Using Arabic Chatbot in Saudi Universities. IAENG International Journal of Computer Science 2021, 48.
- Zahour, O.; Benlahmar, E.H.; Eddaoui, A.; Ouchra, H.; Hourrane, O. A system for educational and vocational guidance in Morocco: Chatbot e-orientation. In Proceedings of the Procedia Computer Science, 2020; pp. 554-559.
- Thorat, S.A.; Jadhav, V. A Review on Implementation Issues of Rule-based Chatbot Systems. Social Science Research Network 2020.
- Singh, J.; Joesph, M.H.; Jabbar, K.B.A. Rule-based chabot for student enquiries. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019/6//, 2019.
- Maeng, W.; Lee, J. Designing a Chatbot for Survivors of Sexual Violence: Exploratory Study for Hybrid Approach Combining Rule-based Chatbot and ML-based Chatbot. In Proceedings of the 5th Asian CHI Symposium 2021, 2021/5//, 2021; pp. 160-166.
- Alsheddi, A.S.; Alhenaki, L.S. English and Arabic Chatbots: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2022, 13, 662-675. [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, A.; Md Touhidul Islam, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, L. Acceptance of Chatbot based on Emotional Intelligence through Machine Learning Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Proceedings - 2022 2nd International Conference on Frontiers of Electronics, Information and Computation Technologies, ICFEICT 2022, 2022; pp. 610-616.
- Achuthan, S.; Balaji, S.; Thanush, B.; Reshma, R. An Improved Chatbot for Medical Assistance using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies, ICICT 2022 - Proceedings, 2022; pp. 70-75.
- Goel, R.; Arora, D.K.; Kumar, V.; Mittal, M. A Machine Learning based Medical Chatbot for detecting diseases. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Innovative Practices in Technology and Management, ICIPTM 2022, 2022; pp. 175-181.
- Goel, R.; Goswami, R.P.; Totlani, S.; Arora, P.; Bansal, R.; Vij, D. Machine Learning Based Healthcare Chatbot. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering, ICACITE 2022, 2022; pp. 188-192.
- Mahanan, W.; Thanyaphongphat, J.; Sawadsitang, S.; Sangamuang, S. College Agent: The Machine Learning Chatbot for College Tasks. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology, DAMT 2022 and 5th ECTI Northern Section Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Computer and Telecommunications Engineering, NCON 2022, 2022; pp. 329-332.
- Prasetyo, A.; Santoso, H.A. Intents Categorization for Chatbot Development Using Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems, ICACCS 2021, 2021/3//, 2021; pp. 551-556.
- Dhyani, M.; Kumar, R. An intelligent Chatbot using deep learning with Bidirectional RNN and attention model. In Proceedings of the Materials Today: Proceedings, 2019; pp. 817-824.
- Patil, S.; Mudaliar, V.M.; Kamat, P.; Gite, S. LSTM based Ensemble Network to enhance the learning of long-term dependencies in chatbot. Int. J. Simul. Multidisci. Des. Optim. 2020, 11, 25.
- Pathak, K.; Arya, A. A Metaphorical Study of Variants of Recurrent Neural Network Models for A Context Learning Chatbot. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks, ISCON 2019, 2019/11//, 2019; pp. 768-772.
- Kasthuri, E.; Balaji, S. Natural language processing and deep learning chatbot using long short term memory algorithm. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021. [CrossRef]
- Anki, P.; Bustamam, A.; Al-Ash, H.S.; Sarwinda, D. High Accuracy Conversational AI Chatbot Using Deep Recurrent Neural Networks Based on BiLSTM Model. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Information and Communications Technology, ICOIACT 2020, 2020/11//, 2020; pp. 382-387.
- Jalaja, T.; Adilakshmi, D.T.; Sharat Chandra, M.S.; Imran Mirza, M.; Kumar, M. A Behavioral Chatbot Using Encoder-Decoder Architecture : Humanizing conversations. 2022/11//, 2022; pp. 51-54.
- Boussakssou, M.; Ezzikouri, H.; Erritali, M. Chatbot in Arabic language using seq to seq model. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2022, 81, 2859-2871. [CrossRef]
- Rajamalli Keerthana, R.; Fathima, G.; Florence, L. Evaluating the performance of various deep reinforcement learning algorithms for a conversational chatbot. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference for Emerging Technology, INCET 2021, 2021/5//, 2021.
- Cuayáhuitl, H.; Lee, D.; Ryu, S.; Cho, Y.; Choi, S.; Indurthi, S.; Yu, S.; Choi, H.; Hwang, I.; Kim, J. Ensemble-based deep reinforcement learning for chatbots. Neurocomputing 2019, 366, 118-130. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Shivananda, A.; Kulkarni, A. Building a Chatbot Using Transfer Learning. In Natural Language Processing Projects : Build Next-Generation NLP Applications Using AI Techniques; Apress: Berkeley, CA, 2022; pp. 239-255.
- Aksu, I.T.; Chen, N.F.; D’Haro, L.F.; Banchs, R.E. Reranking of Responses Using Transfer Learning for a Retrieval-Based Chatbot. In Increasing Naturalness and Flexibility in Spoken Dialogue Interaction: 10th International Workshop on Spoken Dialogue Systems, Marchi, E., Siniscalchi, S.M., Cumani, S., Salerno, V.M., Li, H., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; pp. 239-250.
- Vijayaraghavan, V.; Cooper, J.B.; Rian Leevinson, R.L. Algorithm Inspection for Chatbot Performance Evaluation. In Proceedings of the Procedia Computer Science, 2020; pp. 2267-2274.
- Ahmed, A.; Ali, N.; Alzubaidi, M.; Zaghouani, W.; Abd-alrazaq, A.; Househ, M. Arabic chatbot technologies: A scoping review. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Update 2022, 2, 100057-100057. [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C. TransferTransfo: A Transfer Learning Approach for Neural Network Based Conversational Agents. 2019.
- Aljawarneh, E. Arabic Questions Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/EmranAljawarneh/Arabic-questions-dataset (accessed on 9 Feb. 2023).
- Mozannar, H.; Hajal, K.E.; Maamary, E.; Hajj, H. Neural Arabic Question Answering. 2019.
| 1 | https://huggingface.co/aubmindlab/bert-base-arabert |
| 2 | https://huggingface.co/aubmindlab/araelectra-base-generator |
| 3 | https://huggingface.co/aubmindlab/araelectra-base-discriminator |
| 4 | https://huggingface.co/CAMeL-Lab/bert-base-arabic-camelbert-mix |
| 5 | https://huggingface.co/ZeyadAhmed/AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA |
| 6 | https://github.com/EmranAljawarneh/Arabic-questions-dataset |
| 7 | https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/z3rocool/arabic-wikipedia-dump-2021?datasetId=1179369 |
| 8 | https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/thedevastator/unlocking-arabic-language-comprehension-with-the |

| Industry/ Application | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Customer service | Sentiment and intent analysis and emotion recognition in customer service chatbots | [13,14] |
| Goal-oriented conversation management bootstrapping | [14] | |
| e-Commerceand Telecom | Engagement with chatbots versus augmented reality interactive technology in e-commerce | [16] |
| Information technology telecom chatbot | [22] | |
| Healthcare and Medicaldiagnosis | Ask Rosa: digital genetic conversation chatbot about hereditary breast and ovarian cancer | [17] |
| AI-Powered health chatbots general architecture | [18] | |
| Chatbot for disease prediction and treatment recommendation | [23] | |
| Mental healthcare chatbots | [24,25] | |
| Education | Highly adaptive educational chatbot | [19] |
| NEU-chatbot: chatbot for admission of National Economics University | [15] | |
| Educational and smart chatbots for colleges and universities | [20,26,27,28] | |
| Language learning | Chatbot assistant for English as a second language learners | [5,21] |
| Method | Description | dataset | Accuracy | Pros. | Cons. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLP NLU | AI-powered healthcare chatbots Arabic NLU chatbot framework |
- |
- |
utilize NLU, NLG, deep learning | inaccurate data decrease accuracy | [8,18] |
| ML | Acceptance of Chatbot based on Emotional Intelligence through Machine Learning Algorithm | international students with experience in using chatbot | 97% | TAM and EI theory to predict users' intentions | data limited to international students, difficult to interpret | [33] |
| An Improved Chatbot for Medical Assistance using Machine Learning | various sources: medical journals, online forums, and websites | 93 % | streamline medical processes and save time | SVM's accuracy may not be perfect | [34] | |
| Chatbot for Disease Prediction and Treatment Recommendation using Machine Learning | comprised of patient data, medical history, and symptoms | - | alternative to hospital visits-based diagnosis | not as accurate as traditional hospital visits | [23] | |
| Supervised Machine Learning Chatbots for Perinatal Mental Healthcare | pregnant women, newborns, and their families | - | reduce barriers and help clinicians make accurate diagnoses | not accurately detect subtle changes in mental health | [24] | |
| A Novel Framework for Arabic Dialect Chatbot Using Machine Learning | extracted IT problems/ solutions from multiple domains | accuracy, response time | no explanation of how ML was employed | [7] | ||
| RNN | Intents Categorization for Chatbot Development Using Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Learning | university guest book available from its website | 81% | understands variations in sentence expression | requires big data, difficult or expensive to implement | [38] |
| Conversations Sentiment and Intent Categorization Using Context RNN for Emotion Recognition | conversations inside a movie | 79% | successful to recognizing emotions in text-based dialogs | only uses a single dataset for testing the algorithm | [13] | |
| Deep learning with Bidirectional RNN and attention model | Reddit dataset | - | perform English to English translation | No accuracy measured | [39] | |
| LSTM | LSTM Based Ensemble Network to Enhance the Learning of Long-term Dependencies in Chatbot | Cornell Movie Dialog Corpus | 71.59% | retain contextual meaning of conversations | - | [40] |
| A Metaphorical Study of Variants of Recurrent Neural Network Models for Context Learning Chatbot | Facebook bAbi dataset | 96% | help to create chatbots for web applications | only tests RNN models on a single dataset | [41] | |
| Natural language processing and deep learning chatbot using long-short term memory algorithm | conversations with users and assessments | - | understand questions and provide detailed answers | does not address accuracy and reliability | [42] | |
| AI based Chatbots using Deep Neural Networks in Education | set of answer and question pairs | - | provide accurate and useful responses to student queries | incorrect / difficulty handling complex queries | [26] | |
| AI Chatbot Using Deep Recurrent Neural Networks Based on BiLSTM Model | Cornell Movie Dialog Corpus | 99% | outperform other chatbots in accuracy and response time | only compares with a few other systems. | [43] | |
| GRU | A Metaphorical Study of Variants of Recurrent Neural Network Models for A Context Learning Chatbot | Facebook bAbi dataset | 72% | - | - | [41] |
| Encoder-Decoder | AI Chatbot Based on Encoder-Decoder Architectures with Attention | Cornell movie subtitle corpus | - | improve the experience and interaction | lack of review of similar methods | [12] |
| Behavioural Chatbot Using Encoder-Decoder Architecture | - | - | increase replicability | focus on mimics fictional character, | [44] | |
| Seq2seq | Chatbot in Arabic language using seq to seq model. |
~81,659 pairs of conversations | - | use common conversational topics | no detailed description of the dataset, making it difficult to replicate | [45] |
| Mental Healthcare Chatbot Using Seq2Seq Learning and BiLSTM | The Mental Health FAQ | - | assist mental healthcare | - | [25] | |
| Transfer Learning | Goal-Oriented Chatbot Dialog Management Bootstrapping with Transfer Learning | - | - | overcome low in-domain data availability | focuses on technical aspects not chatbot performance | [14] |
| The Design and Implementation of English Language Transfer Learning Agent Apps | English Language Robot |
- | integrate recognition service from Google and GPT-2 | no comparison with existing chatbots for language learning | [5] | |
| Building Chatbot Using Transfer learning: End to end implementation and evaluation | - | show fine tuning and optimizing | no comparison evaluation | [48] | ||
| Reranking of Responses Using Transfer Learning for a Retrieval-Based Chatbot | WOCHAT dataset Ubuntu dialogue dataset |
highest ratings from the human subjects | - | [49] | ||
| Reinforcement Learning | Evaluating the Performance of Various Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for a Conversational Chatbot | Cornell Movie-dialogs corpus and CoQA (A Conversational QA Challenge) | - | comprehensive review of reinforcement learning | difficult to compare to other approaches | [46] |
| Ensemble-based deep reinforcement learning for chatbots | Chitchat data | training ensemble of agents improved chatbot performance | Require more training time | [47] |
| Transformer name (based on Huggingface) | Size | Task | Description | Pre-training datasets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
aubmindlab/bert-base-arabertv02 aubmindlab/bert-base-arabertv2 aubmindlab/bert-base-arabertv01 aubmindlab/bert-base-arabert1 |
base | Text Generation | AraBERT is a pretrained Arabic language model with pre-segmented text, trained and evaluated similar to the original BERT in English. | OSCAR, Arabic Wikipedia, Arabic Books collected from various sources, Arabic News Articles and Arabic text collected from social media platforms, such as Twitter and online forums. |
|
aubmindlab/bert-large-arabertv2 aubmindlab/bert-large-arabertv02 |
large | Text Generation | ||
| aubmindlab/araelectra-base-generator2 | base | Text prediction, QA |
The generator model generates new text based on learned patterns from training data, achieved state-of-the-art performance on Arabic QA datasets. | OSCAR unshuffled and filtered, Arabic Wikipedia dump from 2020/09/01, the 1.5B words Arabic Corpus, the OSIAN Corpus, and Assafir news articles |
| aubmindlab/araelectra-base-discriminator3 | base | Text prediction, QA |
The discriminator model classifies or makes predictions based on input features | |
|
CAMeL-Lab/bert-base-arabic-camelbert-mix4 CAMeL-Lab/bert-base-arabic-camelbert-ca CAMeL-Lab/bert-base-arabic-camelbert-da CAMeL-Lab/bert-base-arabic-camelbert-msa |
base | Text Generation | Pre-trained BERT models for Arabic texts with different dialects and structures, formal and informal Arabic. | MSA : Arabic Gigaword, Abu El-Khair Corpus, OSIAN corpus, Arabic Wikipedia, Arabic OSCAR DA : A collection of dialectal data CA : OpenITI (Version 2020.1.2) |
| ZeyadAhmed/AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA5 | base | QA | AraElectra-based model fine-tuned on QA pairs to predict unanswerable questions. | Arabic-SQuADv2.0 dataset |
| Dataset | Number of Documents | Description | ||
| Questions | Answers | Corpus | ||
| MSA-QA | 398 | 398 | 398 | This repository of Arabic Questions Dataset6 provides an Arabic question for data science and machine learning. |
| ARCD-QA | 1,395 | 1,395 | 365,568 | The corpus contains a comprehensive Arabic Wikipedia dump 20217, including articles, discussions, and textual information from 2021. The questions were created by crowd-workers in ARCD8 |
| DA-QA | 98,422 | 98,422 | 98,422 | Arabic AskFM dataset collection of questions and answers mostly about Islamic topics by various authors in dialectal Arabic (DA) on the AskFM platform. |
| Question | AraBERT | AraElectra-SQuAD | ||||||
| Base | Large | Base | Large | |||||
| Sim. | Conf. | Sim. | Conf. | Sim. | Conf. | Sim. | Conf. | |
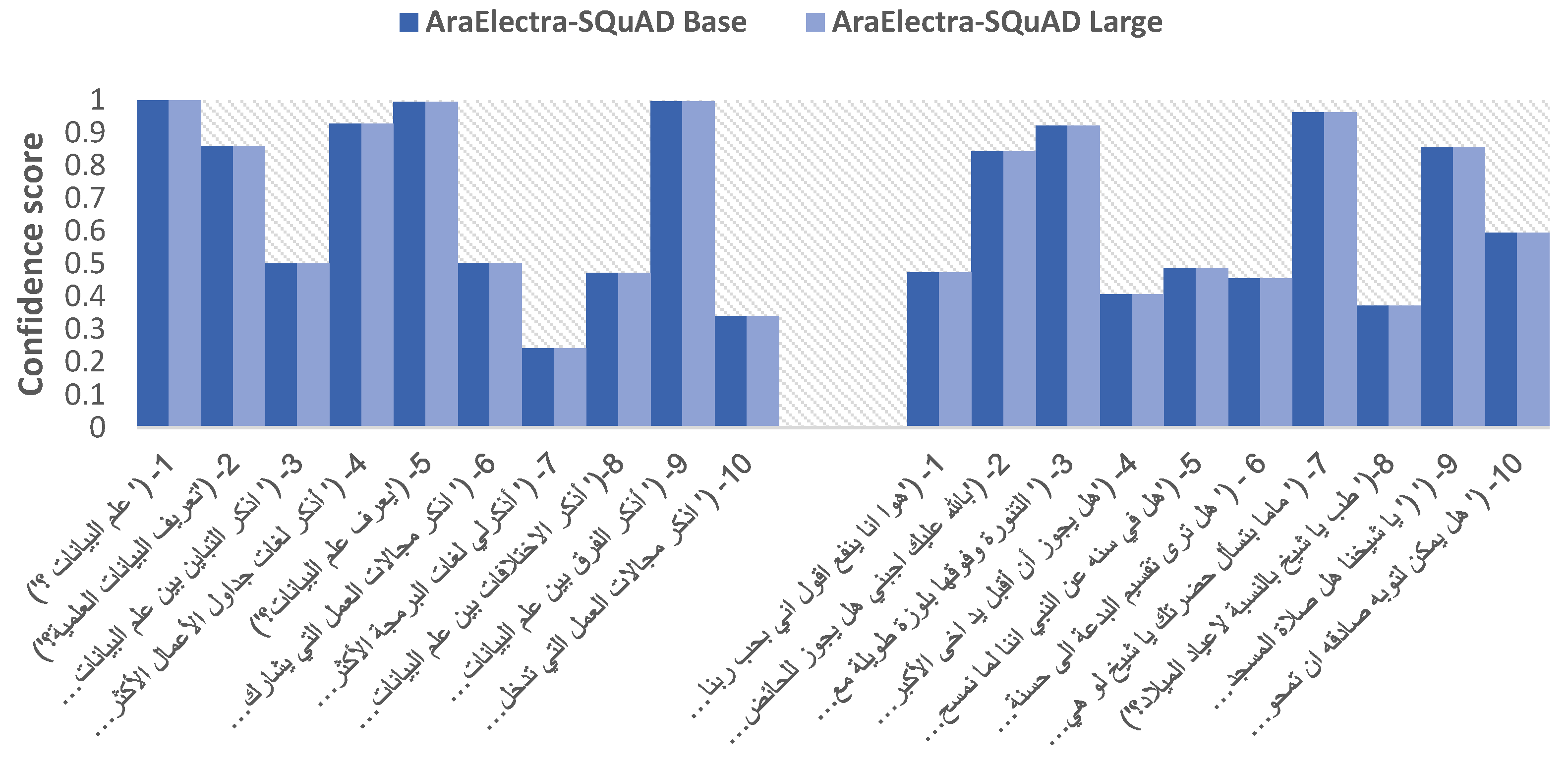
| 1- (' علم البيانات ؟') | 0.8890 | 0.3355 | 0.9284 | 0.1700 | 0.9191 | 0.9993 | 0.6480 | 0.9993 |
| 2- ('تعريف البيانات العلمية؟') | 0.9447 | 0.1249 | 0.9486 | 0.1867 | 0.9652 | 0.8601 | 0.6321 | 0.8601 |
| 3- (' اذكر التباين بين علم البيانات والذكاء الاصطناعي؟') | 0.9980 | 1.0 | 0.9291 | 0.1234 | 0.9801 | 0.5006 | 0.7498 | 0.5006 |
| 4- (' أذكر لغات جداول الأعمال الأكثر شيوعًا في مجال علم البيانات؟') | 0.9905 | 0.5 | 0.9531 | 0.1741 | 0.9778 | 0.9276 | 0.8334 | 0.9276 |
| 5- ('يعرف علم البيانات؟') | 0.9424 | 0.25 | 0.9384 | 0.2627 | 0.9343 | 0.9951 | 0.6901 | 0.9951 |
| 6- (' اذكر مجالات العمل التي يشارك فيها علم البيانات؟') | 0.9585 | 0.1250 | 0.9895 | 0.5 | 0.9747 | 0.5020 | 0.8945 | 0.5020 |
| 7- (' أذكرلي لغات البرمجة الأكثر شيوعًا في مجال علم البيانات؟') | 0.9908 | 0.1702 | 0.9887 | 0.1184 | 0.9847 | 0.2424 | 0.8175 | 0.2424 |
| 8-(' أذكر الاختلافات بين علم البيانات والذكاء الاصطناعي؟') | 0.9670 | 1.0 | 0.9419 | 0.5476 | 0.9817 | 0.4718 | 0.8070 | 0.4718 |
| 9- (' أذكر الفرق بين علم البيانات والمثقفين الاصطناعي؟') | 0.9851 | 0.5102 | 0.9453 | 0.2202 | 0.9831 | 0.9954 | 0.8256 | 0.9954 |
| 10- (' اذكر مجالات العمل التي تدخل فيها البيانات علميا؟') | 0.9470 | 0.5 | 0.9677 | 0.1448 | 0.9686 | 0.3397 | 0.8673 | 0.3397 |
| Question | AraBERT | AraElectra-SQuAD | ||||||
| Base | Large | Base | Large | |||||
| Sim. | Conf. | Sim. | Conf. | Sim. | Conf. | Sim. | Conf. | |
| 1- ('هوا انا ينفع اقول اني بحب ربنا اووي عشان هوا عسل وبيحبنا؟') | 0.9825 | 0.2331 | 0.9366 | 0.1322 | 0.9729 | 0.4737 | 0.8815 | 0.4737 |
| 2- ('بالله عليك اجبني هل يجوز للحائض زيارة المقابر ضروري بالله عليك؟') | 0.9801 | 0.1713 | 0.9848 | 0.1724 | 0.9710 | 0.8436 | 0.7874 | 0.8436 |
| 3- (' التنورة وفوقها بلوزة طويلة مع طرحة تغطي الصدر كده حجاب شرعي؟') | 0.9902 | 0.4014 | 0.9603 | 0.2438 | 0.9767 | 0.9217 | 0.8508 | 0.9217 |
| 4- ('هل يجوز أن أقبل يد اخى الأكبر كشكر وعرفان لفضله عليا منذ صغرى ؟') | 0.9809 | 0.2571 | 0.9936 | 0.3674 | 0.9827 | 0.4069 | 0.9191 | 0.4069 |
| 5- ('هل في سنه عن النبي اننا لما نمسح الارض بالمياه نحط عليها ملح ؟؟') | 0.9858 | 0.1859 | 0.975 | 0.1683 | 0.9762 | 0.4853 | 0.8186 | 0.4853 |
| 6 - (' هل ترى تقسيم البدعة الى حسنة وسيئة؟') | 0.9842 | 0.3012 | 0.9371 | 0.2435 | 0.9675 | 0.4547 | 0.6798 | 0.4547 |
| 7- (' ماما بتسأل حضرتك يا شيخ لو هي شارية ليا حاجات للمستقبل أدوات منزلية وغيره هل عليها زكاة أم لا ؟') | 0.986 | 0.3289 | 0.9763 | 0.1594 | 0.9838 | 0.9624 | 0.8619 | 0.9624 |
| 8-(' طب يا شيخ بالنسبة لاعياد الميلاد؟') | 0.9846 | 0.3816 | 0.946 | 0.1539 | 0.9584 | 0.3724 | 0.7328 | 0.3724 |
| 9- (' (' يا شيخنا هل صلاة المسجد للرجال فرض وتاركه آثم غير مقبول صلاته ؟ | 0.9408 | 0.2420 | 0.9839 | 0.1719 | 0.9764 | 0.8567 | 0.8407 | 0.8567 |
| 10- (' هل يمكن لتوبه صادقه ان تمحو ما قبلها فكأنما ما أذنب المرء قط ؟ا) | 0.9469 | 0.4698 | 0.9851 | 0.1635 | 0.9792 | 0.5950 | 0.8337 | 0.5950 |
| Dataset | Transformer | Semantic Embeddings Model | Avg. Sim. | Avg. Conf. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSA-QA | bert-base-arabertv02 | bert-base-arabertv02 | 0.8457 | 0.3304 |
| bert-large-arabertv02 | bert-large-arabertv02 | 0.6657 | 0.4504 | |
| bert-base-arabertv2 | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.8915 | 0.1695 | |
| bert-large-arabertv2 | bert-large-arabertv2 | 0.7727 | 0.3989 | |
| bert-base-arabertv01 | bert-base-arabertv01 | 0.8183 | 0.2779 | |
| bert-base-arabert | bert-base-arabert | 0.7776 | 0.2452 | |
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-mix | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-mix | 0.47667 | 0.3876 | |
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-ca | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-ca | 0.9625 | 0.1935 | |
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-da | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-da | 0.8168 | 0.4612 | |
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-msa | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-msa | 0.5394 | 0.2493 | |
| ARCD-QA | bert-base-arabertv02 | bert-base-arabertv02 | 0.7599 | 0.3320 |
| bert-large-arabertv02 | bert-large-arabertv02 | 0.6774 | 0.4816 | |
| bert-base-arabertv2 | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.6491 | 0.1822 | |
| bert-large-arabertv2 | bert-large-arabertv2 | 0.6519 | 0.2913 | |
| bert-base-arabertv01 | bert-base-arabertv01 | 0.8635 | 0.2271 | |
| bert-base-arabert | bert-base-arabert | 0.8507 | 0.4800 | |
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-mix | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-mix | 0.9122 | 0.2598 | |
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-ca | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-ca | 0.9352 | 0.2972 | |
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-da | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-da | 0.8664 | 0.2937 | |
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-msa | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-msa | 0.7378 | 0.3381 |
| Dataset | Transformer | Semantic Embeddings Model | Avg. Sim. | Avg. Conf. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
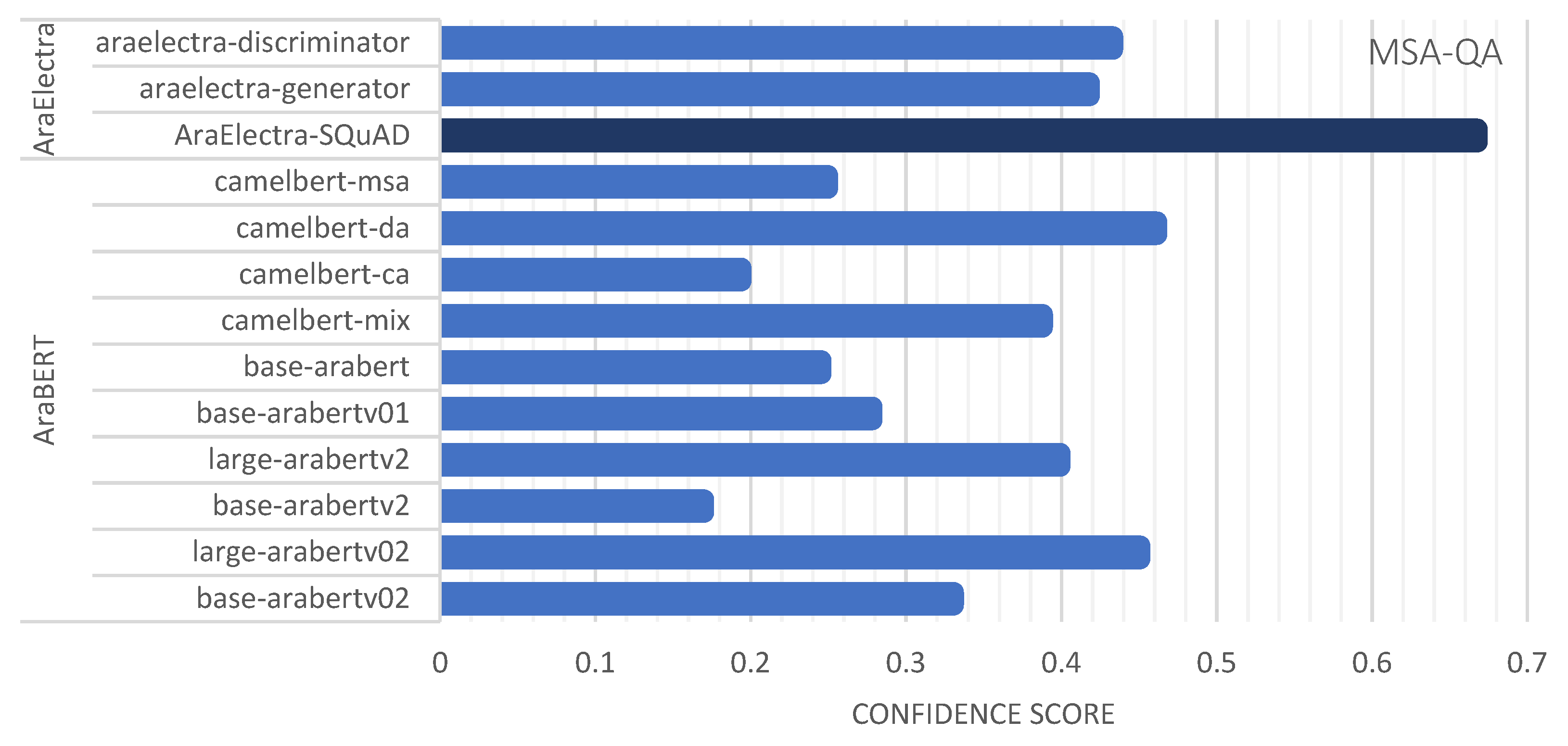
| MSA-QA | AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.8242 | 0.6675 |
| AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.9786 | 0.6675 | |
| araelectra-base-generator | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.6434 | 0.4179 | |
| araelectra-base-discriminator | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.7652 | 0.4329 | |
| araelectra-base-generator | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.9687 | 0.3043 | |
| araelectra-base-discriminator | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.5688 | 0.4286 | |
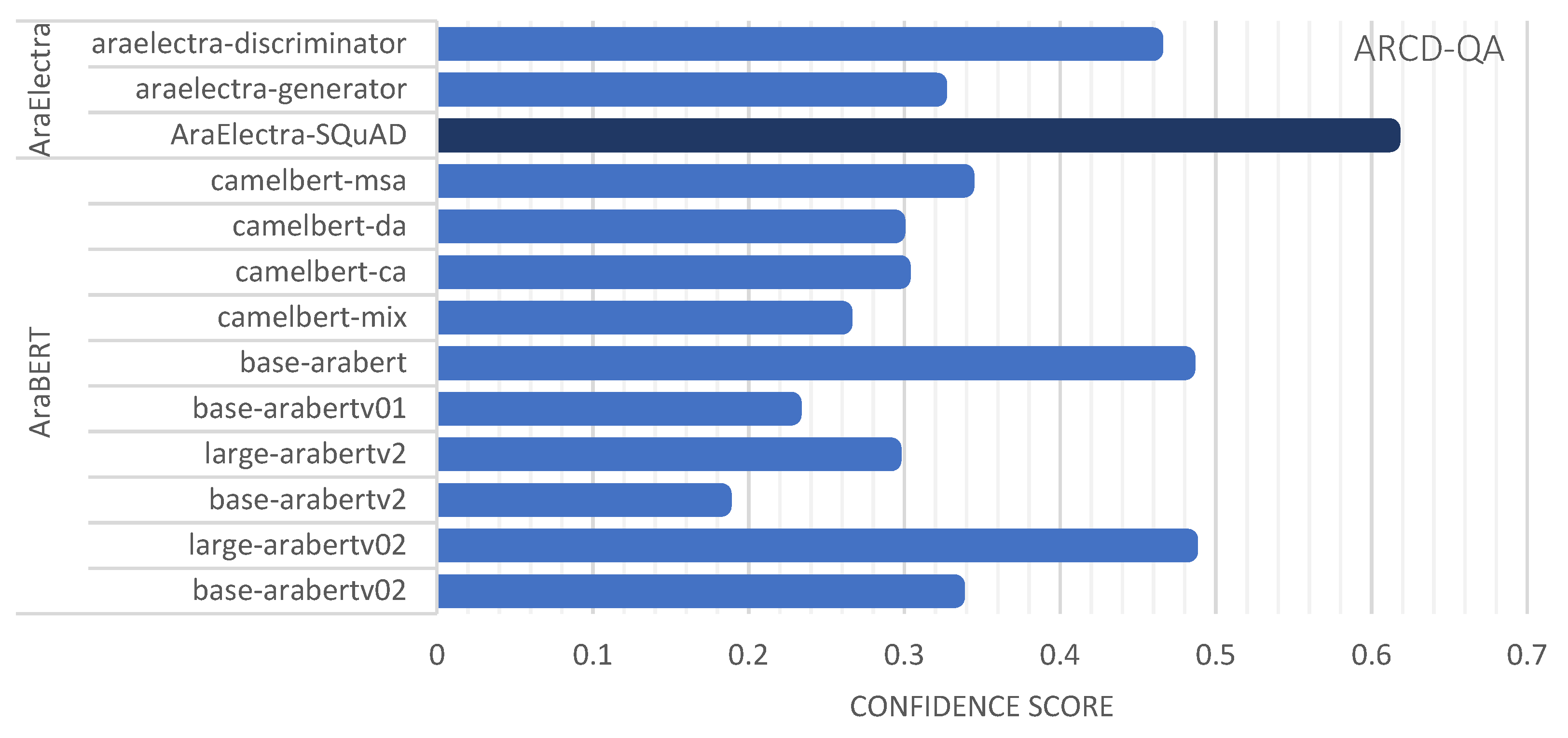
| ARCD-QA | AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.6952 | 0.6116 |
| AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.9806 | 0.6116 | |
| araelectra-base-generator | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.7385 | 0.1957 | |
| araelectra-base-discriminator | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.7388 | 0.2086 | |
| araelectra-base-generator | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.9166 | 0.3206 | |
| araelectra-base-discriminator | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.8962 | 0.4593 |
| Dataset | Transformer | Semantic Embeddings Model | Avg. Sim. | Avg. Conf. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AraBERT-based | MSA-QA | bert-base-arabertv02 | bert-base-arabertv02 | 0.8256 | 0.3897 | |
| bert-large-arabertv02 | bert-large-arabertv02 | 0.8365 | 0.2128 | |||
| bert-large-arabertv2 | bert-large-arabertv2 | 0.7673 | 0.4251 | |||
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-da | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-da | 0.9229 | 0.3634 | |||
| ARCD-QA | bert-base-arabertv02 | bert-base-arabertv02 | 0.6986 | 0.2038 | ||
| bert-large-arabertv02 | bert-large-arabertv02 | 0.6241 | 0.5465 | |||
| bert-base-arabert | bert-base-arabert | 0.9396 | 0.2426 | |||
| bert-base-arabic-camelbert-msa | bert-base-arabic-camelbert-msa | 0.7727 | 0.1901 | |||
| AraElectra-based | MSA-QA | AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.8268 | 0.6422 | |
| AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.9773 | 0.6422 | |||
| araelectra-base-generator | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.7013 | 0.3616 | |||
| araelectra-base-discriminator | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.7218 | 0.3291 | |||
| ARCD-QA | AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA | bert-base-arabertv2 | 0.6852 | 0.6657 | ||
| AraElectra-Arabic-SQuADv2-QA | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.9660 | 0.6658 | |||
| araelectra-base-generator | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.9036 | 0.2908 | |||
| araelectra-base-discriminator | distilbert-base-uncased | 0.8573 | 0.4147 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





