1. Introduction
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a condition that delays the repolarization of the heart, predisposing individuals to arrhythmias which can result in syncope, seizures, or sudden death (1, 2). LQTS affects an estimated 1 in 2,000-7,000 people and is defined by a prolonged corrected QT interval (QTc) reading on a surface electrocardiogram (ECG) (3). The QT interval is a surrogate measure of the ventricular action potential duration (APD). Causes of LQTS include both congenital and acquired alterations in certain cardiac ion channels. These alterations can cause abnormal ion currents within the heart and thus increase the QT interval and the APD. We here tested whether zebrafish hearts would be a good model to study LQTS and for development of pharmacological treatments of LQTS.
Zebrafish have been suggested as a model organism for studying LQTS (4). Despite distinct differences from mammalian hearts, such as the presence of two rather than four cardiac chambers, the zebrafish heart is remarkably similar to mammalian hearts in numerous ways, which makes it suitable as a simple model system. The electrophysiology of the zebrafish heart has been thoroughly studied, demonstrating pace-making activity and a ventricular APD resembling that of the human heart (5, 6). Furthermore, larval and adult zebrafish ECG recordings demonstrate a similar sequence of electrical activation and relaxation as those seen in human hearts (7). Moreover, zebrafish ECG recordings display comparable resting heart rates and conduction intervals to human ECG recordings, and the QT interval has a nearly linear relationship with the RR interval (8, 9). This allows for the development of zebrafish models that can be used to examine delayed ventricular repolarization and prolongations of the APD and QTc interval (i.e., LQTS) and to develop pharmacological interventions to reverse these disorders.
There are two major delayed rectifier currents in the ventricles of the human heart, IKr and IKs (10). IKr is generated by the Kv11.1 channel and is the rapid delayed rectifier current (11). The slow delayed rectifier current, IKs, is generated by channels consisting of tetramers of the Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) α-subunit associated with ancillary KCNE1 β-subunits. At resting heart rates, most of the repolarizing potassium current in human ventricles is generated by Kv11.1 channels while Kv7.1/KCNE1 channels act as a reserve when additional repolarizing current is needed, typically during high sympathetic tone (8, 12). The repolarization reserve capabilities of K+ currents are utilized as a mechanism to protect against cardiac arrhythmias in both physiological and pathological states (13). There have been multiple genes identified which encode components of such ion channels and mutations of these genes result in specific subtypes of LQTS. For instance, LQT1 involves a mutation in the KCNQ1 gene, LQT2 involves a mutation of the KCNH2 gene (which encodes the Kv11.1 channel), and LQT5 involves a mutation of the KCNE1 gene (14).
Given the roles of IKr and IKs in the pathophysiology of LQTS in humans, quantifying the prevalence of potassium channels such as Kv7.1 and Kv11.1 in zebrafish hearts is of paramount importance for assessing their use in cardiac models. Previous studies utilizing E4031, a selective Kv11.1 channel blocker, have consistently demonstrated a prolongation of the APD in both the ventricle and atrium of zebrafish hearts, indicating that IKr plays a significant role in the action potential plateau duration of the zebrafish heart (6, 15). On the contrary, previous studies utilizing chromanol 293B, a Kv7.1 and Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel blocker, did not demonstrate a significant effect on the ventricular APD in 48-hour-old zebrafish embryos (16). Additionally, immunohistochemistry staining of the embryonic heart of zebrafish revealed no Kv7.1 (16). These findings suggest that embryonic zebrafish hearts do not possess IKs. However, transcripts of the KCNQ1 α-subunit have been detected in the adult zebrafish heart and chromanol 293B was reported to prolong the QT interval and ventricular APD in adult zebrafish (17-19).
The difficulty of functionally identifying IKs within zebrafish cardiomyocytes may be because IKs is masked under a larger IKr, and only becomes apparent under conditions which minimize IKr or when additional K+ currents are needed. This is similar to how IKs act as a repolarization reserve in some mammalian hearts. Therefore, one of the purposes of the work presented here is to examine the role of IKs in zebrafish hearts under rest and stress (drug-induced LQT2). These were assessed by measuring changes in APD after applying the IKs blocker chromanol 293B alone and after applying chromanol 293B for further APD prolongation following IKr block with E4031, respectively. In addition, the same approach was performed with different IKs activators.
This work also evaluated the zebrafish heart as a model for the study of the effects of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) analogues on the APD. As of late, PUFAs are being studied as a potential medical therapy for treating diseases such as LQTS. Treatment of LQTS currently relies primarily on beta-blockers, flecainide (NaV channel inhibitor), implanted cardioverter defibrillators, and sympathetic denervation (20-25). None of these treatments address the pathological process of LQTS and thus do not restore the QT interval, but rather prevent or stop dangerous cardiac arrhythmias (26). Furthermore, some patients are unable to tolerate certain treatments due to side effects. A recent simulation study suggested that enhancement of IKs, which can be achieved by certain PUFAs and PUFA analogues, is a potential safe and effective LQTS treatment with antiarrhythmic effects (27, 28).
The chemical structure of PUFAs consist of a long hydrocarbon tail with two or more double bonds attached to a charged, hydrophilic head group (29) (
Figure 1A). The mechanism by which PUFAs enhance ion currents is referred to as the lipoelectric hypothesis, in which the PUFAs incorporate into the cell membrane adjacent to an ion channel (30). From there, the PUFA’s headgroup interacts with positively charges in the voltage sensing domain, to negative shift the V
50 of activation, and in the pore domain, to increasing the conductance of the Kv7.1/KCNE1 (31) (
Figure 1A,B). While PUFAs can affect cardiac NaV, CaV, and Kv channels, their selectively and effect depends on the specific PUFA analogues (32). Some PUFA analogues, such as docosahexaenoyl glycine (DHA-Gly), have demonstrated QT-interval shortening effects with a pronounced increased activity of Kv7.1/KCNE1 within
ex-vivo and
in-vivo guinea pig hearts as well as shortening the APD of human-induced pluripotent stem-cell derived cardiomyocytes (32, 33). The work presented here will also analyse the effect of DHA-Gly and Linoleoyl glycine (LIN-Gly), two PUFA analogues that were previously found to be more selective for human
IKs channels compared to other PUFA analogues (2), on zebrafish hearts
ex-vivo. Our hypothesis was that the zebrafish heart ex-vivo might be a good model for the early screening of Kv7.1 and
IKs activators on their effect on the cardiac action potential related to its effects previously described on Kv7.1 and
IKs.
We found that the PUFA analogues tested only slightly affected the zebrafish APD. However, a stronger Kv7.1 activator (ML-277) shortened the zebrafish APD, which shows that zebrafish is a possible model for testing anti-arrhythmic drugs related to Kv7.1 and Kv7.1/KCNE1 when using activators with larger effects and great affinity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Heart Isolation Procedure
All studies in animals were conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
One-year-old male adult TAB wild-type zebrafish (n = 60) were purchased from the COX Science Centre of the University of Miami and kept at controlled conditions of temperature (between 26-28°C) and pH (between pH 6.8-7.5). Ex-vivo whole hearts were used to quantify the ventricular action potential (AP) using optical recordings. Zebrafish were euthanized by placement in an ice bath, followed by transection of the spinal cord. Subsequently, the zebrafish were placed into a 60-mm Petri dish pre-coated with a layer of SYLGARD184 (Dow Corning, Midland MI, USA) previously filled with chilled external solution. The external solution contains (in mM): 140 NaCl, 4 KCl, 1.8 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, 10 glucose, and 10 HEPES. pH adjusted to 7.4. Then, the zebrafish were fixated by pins over the head and the caudal fin. Lifting from the top of the operculum, the pectoral fin was removed with gentle tensile force, and the surrounding dermal area was peeled off, exposing the heart to the external solution. To excise the heart from the body, the surrounding tissue was removed, and the zebrafish heart was separated from the bulbus arteriosus. Once the heart was excised, it was incubated in pre-warmed external solution with the myosin II inhibitor (-)-blebbistatin (20 µM; Cayman Chemical, RRID:SCR_008945, Ann Arbor MI, USA) for 10 min to prevent contractions of the heart.
2.2. Action Potential Optical Recordings and Analysis
AP parameters were analysed by measuring the voltage across the plasma membrane on the ventricular surface of the zebrafish heart using the voltage-sensing dye CytoVolt1. The zebrafish heart was incubated with CytoVolt1 (also known as Di-4-ANBDQBS, 20 µM; Potentiometric Probes, Connecticut CT, USA) for 60 min. The voltage sensing dye was diluted in pre-warmed external solution plus 20 µM of (-)-blebbistatin (to avoid movement artifacts). Optical APs were recorded with external solution plus 20 µM of (-)-blebbistatin at a controlled temperature (28 °C). AP optical recordings were made using a MacroFluo Leica Microscope coupled with a Leica APOZ6 zoom and a 5x/0.5 LWD objective. The data acquisition was performed by a photodiode (UDT sensors Inc. Hawthorne, CA) connected to an Axopatch 200B amplifier and an Axon Digidata 1550B digitizer (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA). The zebrafish hearts were paced at 1 Hz (30 Volt) with a two-electrode system and a Grass S 9 stimulator. Stocks of DHA-Gly (100 mM) and LIN-Gly (100 mM) were prepared in ethanol. The respective channel blocker and activator, E4031 (Alomone Labs, RRID:SCR_013570, Jerusalem, Israel), (-)-[3R,4S]-Chromanol 293B and, JNJ303 (Tocris Bioscience, RRID:SCR_003689, Bristol, UK), ML-277 (Sigma-Aldrich, RRID:SCR_008988, St. Louis, MO, USA), or PUFA analogues (DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly, Cayman Chemical, RRID:SCR_008945, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) were added accordingly and measurements were taken every 10 minutes (min).
Recordings were performed on control conditions (saline solution) and at three different times (after 10 min, 20 min, and 30 min) after applying each drug. From each recording, 10 AP were averaged. APD was measured at 25, 50, 80, and 90 percent of repolarization, to obtain APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90, respectively (
Figure 1C). APD25 and APD50 demonstrate the effect of the drugs on the early phases of the AP repolarization. APD80 reflects the entire repolarization process (phases 1, 2, and 3). APD90 captures the end of repolarization. The absolute change of APD (ΔAPD) between the drug and the control was analysed in ΔAPD in percentage of change (
Figure 1C). To analyse phase 3 of repolarization, the subtraction APD80-APD25 was compared between control and drug/PUFA analogue conditions.
Moreover, we included the APD25/APD80 ratio as a quantitative measurement of the AP morphology, a smaller ratio reflects AP triangulation and a larger APD25/APD80 ratio represents a more squared AP shape.
2.3. Molecular Biology
In vitro zebrafish KCNQ1 (ZDB-GENE-061214-5) and KCNE1 (ZDB-GENE-141104-1) cRNA were transcribed using mMessage mMachine T7 RNA Transcription Kit (RRID:SCR_004098, Ambion, Austin, TX). A total of 50 ng cRNA was injected into defolliculated Xenopus laevis oocytes (EcoCyte Bioscience, RRID:SCR_014773, Austin, TX). Oocytes were injected with KCNQ1 cRNA and co-injected with KCNQ1 cRNA and KCNE1 cRNA at a ratio of 3:1, weight:weight, resulting in an excess of KCNE1 subunits compared to KCNQ1 subunits. After cRNA injection, oocytes were incubated in ND96 solution (96 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 5 mM HEPES; pH = 7.5) for 2 to 3 days before electrophysiological experiments.
2.4. Two-Electrode Voltage Clamp
Oocytes were recorded in a two-electrode voltage clamp configuration at room temperature. Recording pipettes were filled with 3 M KCl. The chamber was filled with ND96 solution. JNJ303 and chromanol 293B with different concentrations (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 and 100 µM) in ND96 were perfused onto oocytes. PUFA analogues with different concentrations (0.2, 0.7, 2, 7 and 20 µM) in ND96 were perfused onto oocytes. From a holding potential of -80 mV followed by a hyperpolarizing prepulse to -140 mV, steps from -100 mV to +60 mV (in +20 mV increments) were applied to activate the channel followed by a tail voltage of -40 mV to obtain the tail current.
A concentration-response relationship was analysed with the Hill equation: I ⁄ I0 , where I is the current amplitude at 0 mV for each concentration, A is the relative increase in current (ΔI/I0) caused by the drug, Km (IC50) is the apparent affinity of the drug, and x is the concentration and n is the Hill coefficient.
A conductance versus voltage (GV) curve was obtained by plotting the normalized tail currents versus different test pulses to determine the steady-state voltage dependence of current activation. Tail currents were measured at -40 mV following the test pulses. Then the GV curve was fit with a single Boltzmann equation: G(V)=Amin+(Amax-Amin)/(1+exp((V-V1⁄2)/K)), where Amax and Amin are the maximum and minimum conductance, respectively, V1⁄2 is the voltage where 50% of the maximal conductance level is reached and K is the slope factor. Data were normalized between the Amax and Amin values of the fit.
2.5. Statistics
Shapiro-Wilk tests were performed in all collected data to test for normal distribution. Then, statistical data significance was determined by a paired t-test, where p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Each time for each drug was compared with its control (same experiment without drug). Also, the average of the drug effect at different times was compared with its control (same experiment without drug). Data were represented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) and the number of experiments (n), for each set of experiments
3. Results
3.1. AP Optical Recordings Are Stable in Control Conditions
The APD of the zebrafish ventricle was measured optically in control conditions at different percentages of repolarization (APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90) (
Figure 1C, left) and the change ΔAPD (in percentage) was calculated between the control condition and the drug or the PUFA analogues conditions (
Figure 1C, right). The APD80 average (in ms) for control conditions was 211.8 ± 8.3 ms (n = 54). The APD80 (in ms) for control conditions was also analysed at different recording times as time matched controls (
Figure 1D). No significant differences were found in APD80 in control conditions at 10, 20, or 30 min after the first control condition recording, nor when the average of the APD80 measured at the three times was compared with the first control (
Figure 1D, n = 4, NS, p > 0.05,
Table 4).
Table 4.
Average of APD80 at different times.
Table 4.
Average of APD80 at different times.
| |
APD80 (ms) |
|
APD80 (ms) |
(n, p) |
| CTRL |
174.9 ± 15.7 |
Long CTRL |
185.2 ± 13.5 |
n = 6, NS, p > 0.05 |
| E4031 |
332.2 ± 19.2 |
Long E4031
|
338.6 ± 17.8 |
n = 3, NS, p > 0.05 |
| E4031 CTRL |
217.6 ± 7.1 |
E4031 |
350.5 ± 11.4 |
n = 22, p < 0.001 |
| C293B CTRL |
225.9 ± 33.5 |
C293B |
243.0 ± 39.8 |
n = 3, NS, p > 0.05 |
| E4031 |
392.8 ± 14.0 |
E4031/C293B |
463.5 ± 16.2 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
| JNJ303 CTRL |
180.2 ± 17.3 |
JNJ303 |
204.7 ± 13.5 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
| E4031 |
325.6 ± 14.3 |
E4031/JNJ303 |
369.8 ± 28.7 |
n = 4, NS, p > 0.05 |
| DHA-Gly CTRL |
212.3 ± 9.1 |
DHA-Gly |
206.1 ± 6.7 |
n = 7, NS, p > 0.05 |
| LIN-Gly CTRL |
210.8 ± 14.9 |
LIN-Gly |
204.8 ± 15.1 |
n = 5, p < 0.05 |
| E4031 |
325.3 ± 36.3 |
E4031/DHA-Gly |
438.6 ± 54.7 |
n = 4, NS, p > 0.05 |
| E4031 |
397.9 ± 14.6 |
E4031/LIN-Gly |
433.0 ± 19.7 |
n = 3, NS, p > 0.05 |
| ML-277 CTRL |
236.4 ± 26.6 |
ML-277 CTRL |
211.1 ± 22.3 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
| E4031 |
301.5 ± 13.1 |
E4031/ ML-277 |
272.2 ± 8.4 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
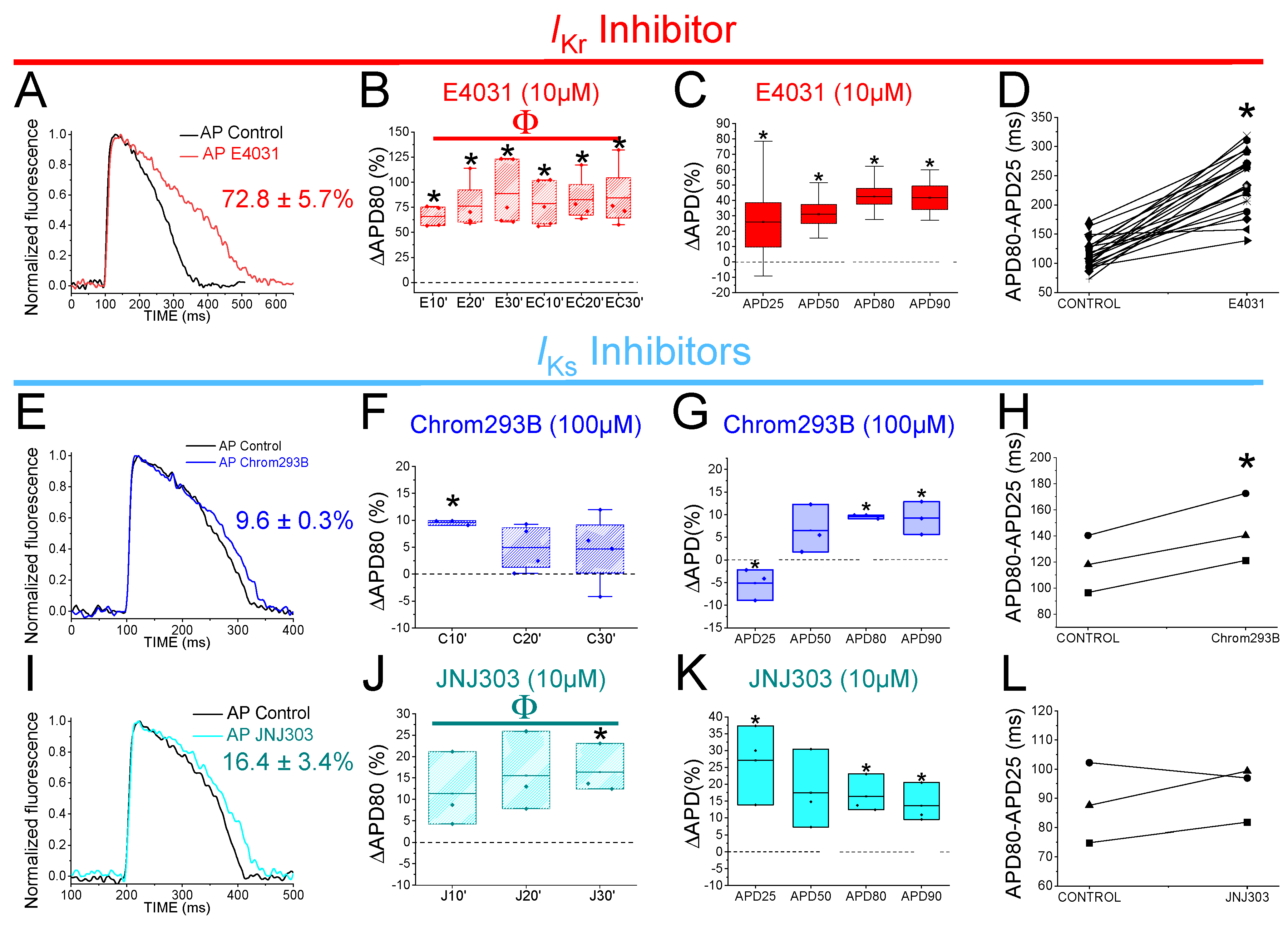
3.2. The IKr Inhibitor E4031 Prolongs Zebrafish APD
We started by analysing the effects of E4031, an
IKr inhibitor. 1 µM E4031 was previously reported to prolong the zebrafish ventricle APD90 by ≈ 24% (6). We used E4031 as a control and to generate drug-induced LQT2 zebrafish hearts.
Figure 2A shows representative traces of AP before (black) and after (red) 30 min of exposure to E4031 (10 µM). E4031 (10 µM) prolonged APD80 by 72.8 ± 5.7% (n = 26, p < 0.001). The drug effect on the APD80 (ΔAPD80%) was measured at 10, 20, 30 min after applying the drug (
Figure 2B). E4031 (10 µM) significantly increased the APD80 at all times recorded (
vs. control condition APD80), and no significant differences were observed among the different times recorded after applying the drug. Because E4031 was used for drug-induced LQT2 condition, a control with this drug was also measured after an additional 10, 20, 30 min after being applied for a second time to analyse whether the effect of E4031 was stable after the first 30 min (
Figure 2B,
Table 4). 30 min after applying E4031, the APD prolongation remained stable, and no increase of the APD80 was observed (
Table 4). To further analyse the effect of E4031, we examined the drug effect at different percentages of AP repolarization at time 30 min. We measured the ΔAPD(%) for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 (
Figure 2C). E4031 (10 µM) increased the APD at every percentage (
Table 1). However, the most significant change observed was at APD80 and APD90, as expected for a Kv11.1 channel blocker (
Table 1). We also analysed AP repolarization during phase 3, specifically, because it is the AP phase where
IKr and
IKs are mainly involved in the AP. Therefore, to analyse phase 3, we calculated the difference between the APD80 and APD25 (in ms) and compared the drug condition
vs. control condition values. Phase 3 was significantly affected by 10 µM E4031 (233.7 ± 10.0 ms vs. 113.4 ± 4.3 ms for APD80-APD25 in E4031 and control conditions, respectively, n = 26, p < 0.001) (
Figure 2D). E4031 prolonged the zebrafish AP under all conditions tested, demonstrating that
IKr contributes to the repolarization of the ventricular AP in zebrafish, which is consistent with previous studies in the literature (6).
3.3. Two Different human IKs Inhibitors Have Different Effects on Zebrafish AP
Chromanol 293B is a human Kv7.1/KCNE1 selective channel blocker with an IC50 of ≈ 7 µM (34). Chromanol 293B (100 µM) significantly prolonged the zebrafish APD80 by 9.6 ± 0.3% at time 10 min (n = 3, p < 0.05) (
Figure 2E,F). This small but significant effect in APD80 was not found at 20 or 30 min after applying chromanol 293B, nor when the average of APD80 values at different times was compared with the control condition values (
Figure 2F,
Table 4). However, this small but significant effect at 10 min was similar to the one observed by Abramochlin et al. in isolated zebrafish cardiomyocytes (19). When we examined the ΔAPD at different percentages of repolarization (at T = 10 min), we observed that chromanol 293B significantly prolonged the APD80 and APD90 (
Figure 2G,
Table 1). Furthermore, chromanol 293B modified phase 3 of the AP (144.6 ± 15.0 ms vs. 118.3 ± 12.6 ms for APD80-APD25 in chromanol 293B and control conditions, respectively, n = 3, p < 0.05) (
Figure 2H), as expected for an
IKs inhibitor.
Because the effects of chromanol 293B effects were small, we studied another potent human Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel blocker, JNJ303. The IC50 for JNJ303 was previously found to be 78 nM for human Kv7.1/KCNE1 (35). After 30 min, JNJ303 (10 µM) prolonged APD80 by 16.4 ± 3.4% (n = 3, p < 0.01,
Figure 2J). Surprisingly, JNJ303 showed a greater effect on APD25 than on APD80 or APD90 (
Figure 2K,
Table 1), suggesting that JNJ303 might be affecting other ion channels involved in the zebrafish AP. Moreover, JNJ303 did not significantly affect phase 3 of the zebrafish AP (
Figure 2L, 92.7 ± 5.5 ms vs. 88.2 ± 7.9 ms for APD80-APD25 in JNJ303 and control conditions, respectively, n = 3, NS, p > 0.05), as would have been expected if JNJ303 inhibited
IKs channels.
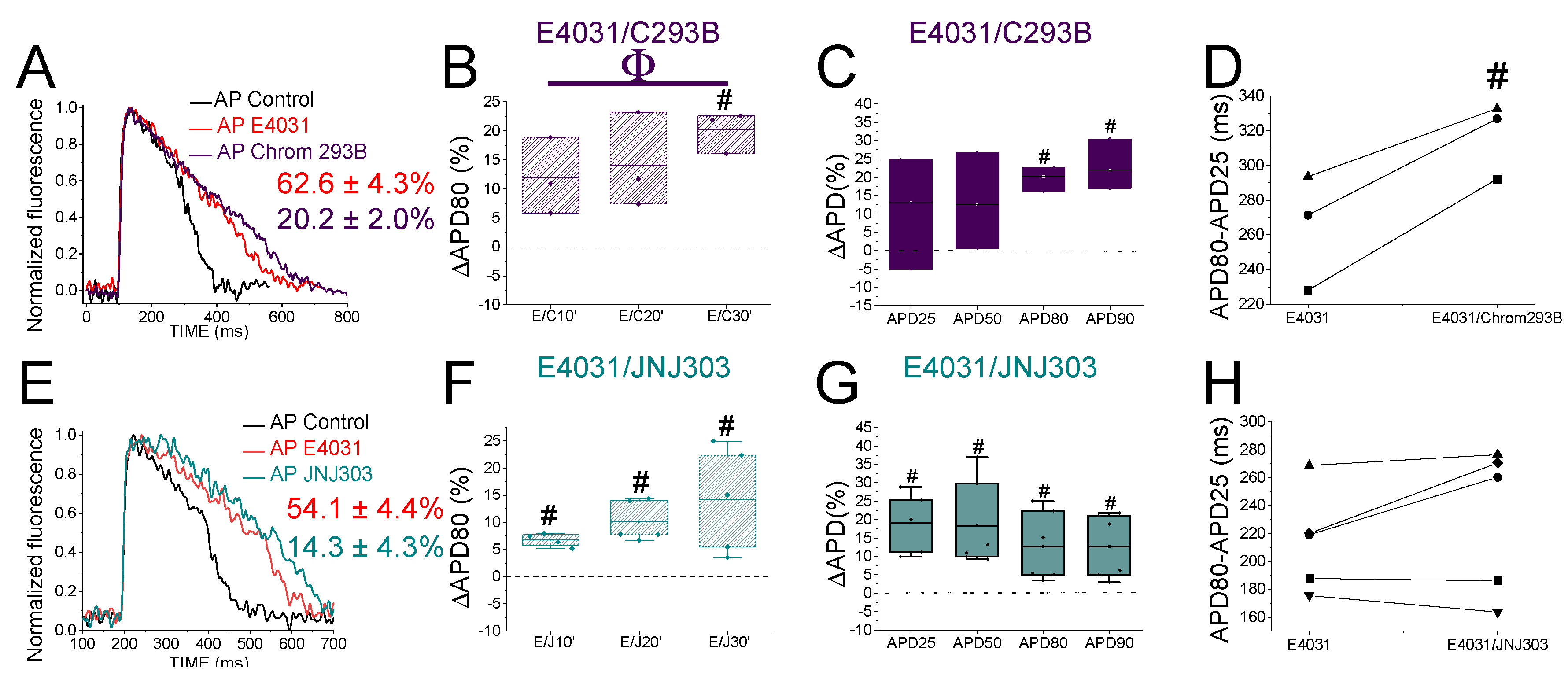
3.4. The IKs Blocker Chromanol 293B Prolongs the APD More after IKr Inhibition
In humans, the IKr is the primary contributor current for AP repolarization. However, mutations in the Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel, which generates the IKs, can cause fatal cardiac arrhythmia. This suggests that the IKs is also crucial for repolarization, but its importance depends on the underlying conditions. For instance, Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel activation is essential for the Fight-or-Flight response of the sympathetic nervous system. Also, Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel activation has been described as crucial in stressful situations and in any exercise activity where the heart rate is increased. Therefore, we examined the contribution of IKs when IKr was compromised to know if IKs is more significant in the zebrafish heart under this condition.
To evaluate
IKs contribution when
IKr is compromised, we first recorded zebrafish AP in the absence and the presence of E4031. We then waited 30 min after the application of E4031 before we applied a combination of E4031 plus chromanol 293B.
Figure 3A shows representative traces before applying E4031 (black), after applying E4031 (10 µM, red), and after applying E4031/chromanol 293B (10 µM/100 µM, dark purple). In the presence of E4031/chromanol 293B (10 µM/100 µM) the APD80 was significantly prolonged by 20.2 ± 2.0% compared to the recording before the application of the combination of drugs (n = 3, p < 0.01). In the control condition with only E4031, the APD80 reached a steady-state 30 min after applying the drug and the APD80 did not prolong after that (
Figure 2B,
Table 4). After applying E4031/chromanol 293B (10 µM/100 µM), we observed a significant APD80 prolongation after 30 min (
Figure 3B) , and when APD80 values measured at different times (10, 20, 30) were averaged and compared with E4031 APD80 values (
Table 4). Moreover, when we analysed the APD at different repolarization percentages, we observed that E4031/chromanol 293B generated a significant APD prolongation at APD80 and APD90 compared with its control E4031 alone (
Figure 3C,
Table 1). We observed that chromanol 293B prolongation affected AP phase 3 (
Figure 3D), as expected for an Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel blocker (264.3 ± 19.24 ms vs. 317.2 ± 12.7 ms for APD80-APD25 in E4031 conditions and E4031/chromanol 293B, respectively, n = 3, p <0.05).
Our results showed that chromanol 293B has a larger effect on the APD when IKr is blocked, suggesting that IKs is more important for the repolarization in zebrafish hearts when IKr is compromised.
3.5. The Human IKs Inhibitor JNJ303 Does Not Prolong the APD More after IKr Inhibition
To test further whether JNJ303 affects Kv7.1/KCNE1 in the zebrafish heart, we combined E4031 and JNJ303. In the presence of E4031/JNJ303 (10 µM/10 µM) the APD80 was significantly prolonged, by 14.3 ± 4.3%, compared to the recording before the application of the combination of drugs (n = 5, p < 0.05) (
Figure 3E). We observed additional APD80 prolongation at all times tested after applying E4031/JNJ303 (
Figure 3F). Surprisingly, when we analysed the E4031/JNJ303 combination at different percentages of repolarization (
Figure 3G), we observed that the longest AP prolongation occurred at APD25 and APD50 instead of at APD80 or APD90 (
Table 1) as would be expected for a compound that affects Kv7.1/KCNE1. Moreover, the combination of E4031/JNJ303 did not significantly affect phase 3 of the zebrafish AP (
Figure 3H, 231.5 ± 23.5 ms vs. 214.3 ± 16.2 ms for APD80-APD25 in E4031/JNJ303 and E4031 conditions, respectively, n = 5, NS, p > 0.05). These results are similar to what we observed for JNJ303 alone and suggest that JNJ303 does not inhibit zebrafish
IKs to a large extent.
3.6. JNJ303 is Not an Effective IKs Inhibitor of Zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 Currents
To test directly the effect of JNJ303 on zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1, we expressed zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 in
Xenopus laevis oocytes and applied JNJ303 and chromanol 293B (
Figure S1 and S2, respectively). Only the application of very high concentrations of JNJ303 inhibited zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 currents (
Figure S1A). The IC50 value estimated for JNJ303 for zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 was >100 µM (n = 3) (
Figure S1B), much higher than what was described for the human Kv7.1/KCNE1 (IC50 ≈78 nM) (35). Together with our results on
ex-vivo hearts for JNJ303, the results suggest that JNJ303 might be affecting different cardiac ion channels involved in the zebrafish AP than Kv7.1/KCNE1.
To confirm that chromanol 293B directly affects zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1, we used the same approach for zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes with chromanol 293B (
Figure S2). We also tested chromanol 293B in zebrafish Kv7.1. 10 µM chromanol 293B inhibited zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 currents (
Figure S2) by 43.7 ± 0.04% (n = 5, p < 0.01,
Table S1). At the concentration tested, chromanol 293B shifted the voltage dependence of the activation of zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 slightly towards positive potentials (n = 5, p < 0.05). Moreover, 10 µM chromanol 293B inhibited zebrafish Kv7.1 current (
Figure S2) by 76.0% ± 0.04 % (n = 5, p < 0.001,
Table S2). In human Kv7.1/KCNE1, the chromanol 293B IC50 (≈ 7 µM) was described by Lerche et al. in 2007. The inhibition induced in human Kv7.1/KCNE1 was more potent than in human Kv7.1 homomeric channel (IC50 ≈ 27 µM) (34). Our results suggest that the inhibition of zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 was similar to that observed in human Kv7.1/KCNE1. However, the chromanol 293B effect observed on zebrafish Kv7.1 was greater than in zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1.
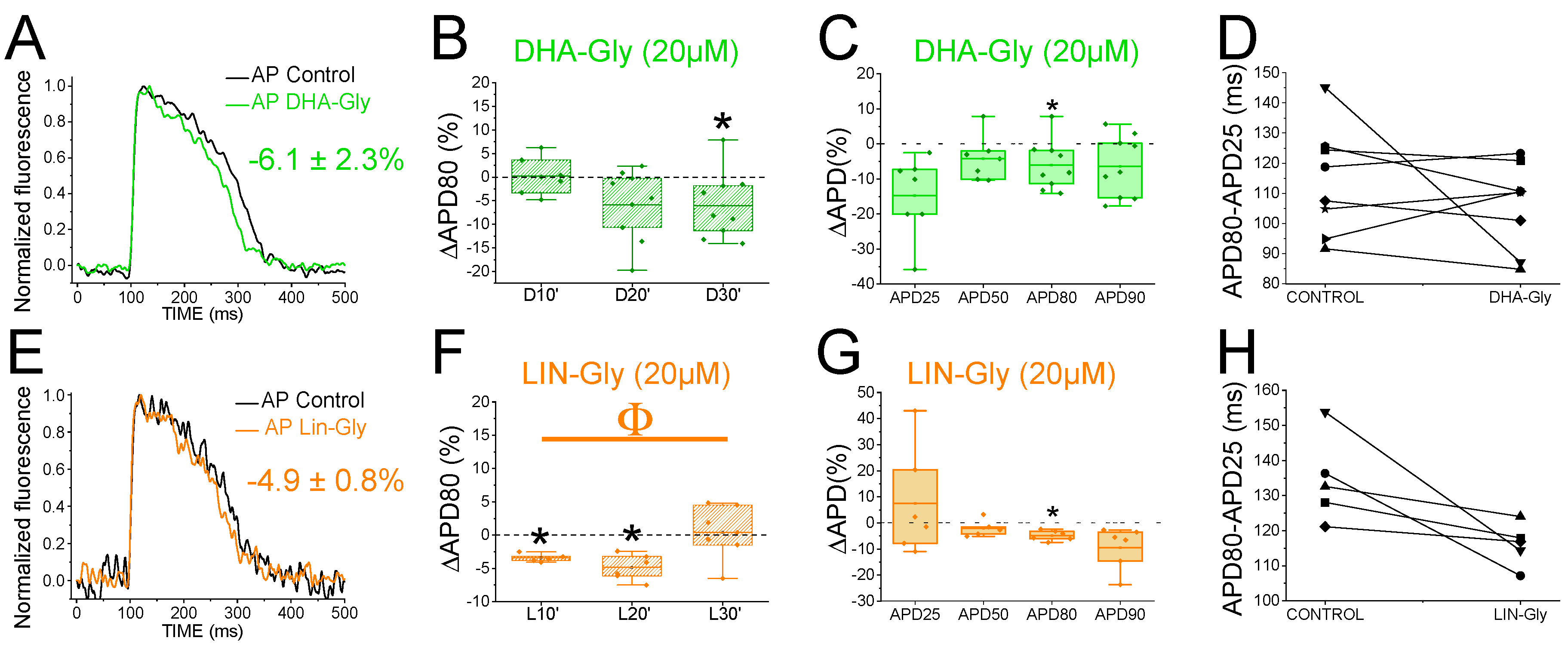
3.7. PUFA Analogues Have Modest Effects on Zebrafish AP
To determine whether the zebrafish heart is an appropriate model for early-screening of human antiarrhythmic drugs affecting
IKs channels, we examined the effects of PUFA analogues on the optical recordings of zebrafish AP. DHA-Gly (20 µM) shortened the APD80 by 6.1 ± 2.3 % (n = 9, p < 0.05) at 30 min (
Figure 4A). However, DHA-Gly did not significantly shorten the APD80 when averaging the APD80 values at different times (10, 20, and 30 min) and comparing to the control condition (
Table 4). We also analysed the DHA-Gly effect at different percentages of repolarization (
Table 2). DHA-Gly only shortened the APD80 (
Figure 4C,
Table 2). However, when we analysed phase 3 of the AP (
Figure 4D), we did not find any significant difference between control condition conditions and after applying the PUFA analogue (108.1 ± 4.9 ms vs. 118.0 ± 6.8 ms for APD80-APD25 in DHA-Gly and control conditions, respectively, n = 9, NS, p > 0.05).
LIN-Gly (20 µM) shortened the AP by 4.9 ± 0.8 % (n = 6, p < 0.01) 20 min after application (
Figure 4E,F). LIN-Gly shortened the APD80 at both 10 min (by 3.4 ± 0.3 %, n = 5, p < 0.001) and at 20 min after applying LIN-Gly (by -4.9 ± 0.8 %, n = 6, p < 0.01). However, this small effect was not maintained over time and no AP shortening was seen after 30 min of exposure to the LIN-Gly (
Figure 4F). However, LIN-Gly shortened APD80 when the average of APD80 values at the different times was compared with control conditions APD80 values (
Table 4).
Figure 4G shows the ΔAPD measured at different percentages of repolarization. LIN-Gly significantly shortened the APD80 as expected for a compound that might be activating Kv7.1/KCNE1 (
Table 2). We did not observe any significant change in phase 3 between control conditions and the PUFA analogue conditions (
Figure 4H, 112.4 ± 4.3 ms vs. 127.2 ± 1.7 ms for APD80-APD25 in LIN-Gly and control conditions, respectively, n = 6, NS, p > 0.05). These results indicate that PUFA analogues only slightly, or not significantly, shortened the zebrafish AP.
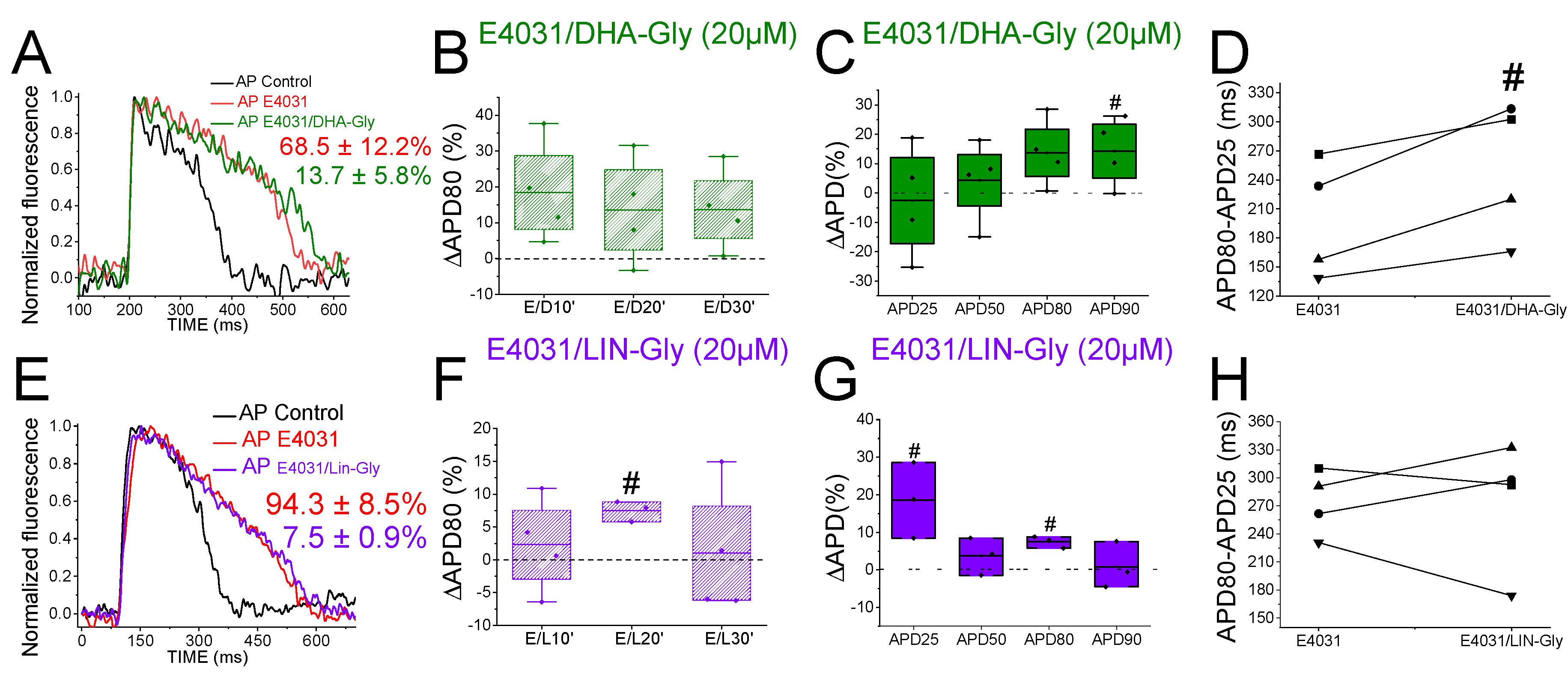
3.8. PUFA Analogues do Not Reverse APD in Drug-Induced LQTS Zebrafish Hearts
Because the
IKs contribution to the repolarization seems more prominent when
IKr is compromised (
Figure 3), we used the
IKr channel blocker, E4031, i) to elucidate whether the PUFA analogues effects observed were due to targeting
IKs (i.e. we would expect a greater PUFA-induced shortening of zebrafish AP in the presence of E4031) and, ii) to examine the ability of PUFA analogues to reverse the prolonged AP when LQT2 is drug-mimicked. To that end, we first applied E4031 and waited 30 min. We then recorded the zebrafish AP after applying E4031 combined with the PUFA analogues DHA-Gly or LIN-Gly.
Figure 5A shows the zebrafish AP representative traces before the application of E4031 (black), after the application of E4031 (red), and after E4031/DHA-Gly (dark green). No significant effects were observed after applying E4031/DHA-Gly at any time tested when analysed at APD80 (
Figure 5B, n = 4, NS, p > 0.05). Moreover, no significant effects were observed when analysing the average of APD80 values at different times (10, 20, 30) compared with E4031 APD80 values (
Table 4). However, when we analysed the APD at different percentages of repolarization, surprisingly, we observed a significant prolongation of APD90 (
Figure 5C,
Table 2). Moreover, when we analysed phase 3, we observed a significant prolongation of phase 3 when comparing the combined compounds vs. its control conditions, E4031 alone (250.4 ± 35.1 ms vs. 199.2 ± 30.4 ms APD80-APD25 for E4031/DHA-Gly and E4031, respectively, n = 4, p < 0.05.
Figure 5D). These results show that DHA-Gly did not shorten the APD when LQT2 was drug-induced. On the contrary, these results suggest that the combination of E4031 and DHA-Gly affects the zebrafish AP by increasing the APD.
We used the same approach with the other PUFA analogue, LIN-Gly.
Figure 5E shows representative traces before (black) and after applying E4031 (red) and then after applying E4031/LIN-Gly (purple). The combination of E4031/LIN-Gly (10 µM/20 µM) prolonged the APD80 compared to its control E4031 (10 µM) when recorded at 20 min. However, it did not promote any effect at 30 min after applying (
Figure 5F). No significant effects were observed when analysing the average of E4031/LIN-Gly APD80 values at different times (10, 20, 30) compared with E4031 APD80 values (
Table 4). The combination of E4031/LIN-Gly (10 µM/20 µM) also prolonged APD25 (
Figure 5G,
Table 2). This result agrees with what was observed when analysed in phase 3 of the AP (
Figure 5H, 274.2 ± 34.6 ms vs. 273.4 ± 17.4 ms APD80-APD25 for E4031/LIN-Gly and E4031, respectively, n = 4, NS, p > 0.05). These results show that DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly did not shorten the APD in drug-induced LQT2 zebrafish hearts.
3.9. DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly Have only Modest Effects on Zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 Channels
Because LIN-Gly or DHA-Gly did not shorten the APD in drug-induced LQT2 zebrafish hearts we wanted to directly analyse the effects of DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly on zebrafish Kv7.1 and Kv7.1/KCNE1. Thus, the PUFA analogues were tested on the zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes (
Figure S3 and S4). Application of 20 µM DHA-Gly did not modify the current amplitude nor the voltage dependence of zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 (
Figure S3, Table S1). However, 20 µM LIN-Gly promoted the activation of the Kv7.1/KCNE1 by left-shifting the voltage-dependence of activation (ΔV
0.5), and increased the magnitude of the current (I/I0) of the zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 (
Figure S4, Table S1) at a voltage (V = 0 mV) that mimics the voltage at the action potential plateau in zebrafish ventricles. Moreover, PUFA analogues were tested on the zebrafish Kv7.1 expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes (
Figure S3 and S4). Application of 20 µM of DHA-Gly left-shifted the V0.5 by 12.2 ± 2.7 mV (n = 4, p < 0.05) and increased the maximal conductance of zebrafish Kv7.1 (n = 4, p < 0.01). DHA-Gly increased the magnitude of the current (I/I0) of the zebrafish Kv7.1 (n = 4, p < 0.001) (
Figure S3, Table S2). LIN-Gly showed similar effects as DHA-Gly in zebrafish Kv7.1 (
Figure S4, Table S2). Moreover, LIN-Gly showed similar effects in zebrafish Kv7.1 and zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1. These results show that DHA-Gly and Lin-Gly only modestly (around 2 fold), or not at all, increase the currents in Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1.
3.10. DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly Did Not Reverse the Triangulation Effect of Drug-Induced LQT2
Triangulation is an outcome of some drugs that cause LQTS (36). For example, when APD25 or APD50 do not change by the drug, but APD80 or APD90 is prolonged, the shape of the AP changes and it appears more similar to a triangle. This change in the AP shape can be quantified by analysing and comparing the APD25/APD80 ratio between control conditions and drug conditions.
Figure 6A shows AP traces in control conditions (black), and after applying the
IKr inhibitor (red), the
IKs inhibitor (blue and light blue), and the combination of
IKr and
IKs inhibitors (dark purple and dark turquoise). The control condition showed a more squared AP, whereas E4031, Chromanol 293B, and the combination of E4031/Chromanol 293B AP shapes were more triangular. However, the AP shape in JNJ303 and the combination E4031/JNJ303 were more similar to that observed in the control condition, i.e., squared AP shape. E4031, Chromanol 293B, and the combination of E4031/Chromanol 293 significantly decreased the APD25/APD80 ratio (
Figure 6B), corroborating what we observed in the qualitative analysis (
Table 3). However, JNJ303 and the combination of E4031/JNJ303 did not change the AP shape nor reduce the APD25/APD80 ratio compared to control conditions (
Table 3). For PUFA analogues and their combination with E4031 (
Figure 6C,D), we expected a more squared AP shape, even more so than control conditions (
Figure 6A), and an increase in APD25/APD80 ratio due to the expected increase in
IKs. However, there was no change between the control conditions and the PUFA analogues conditions neither qualitative or quantitative (
Figure 6C,D,
Table 3). Moreover, when we analysed the E4031/PUFA analogues combination, we found that PUFA analogues did not reverse the triangulation promoted by E4031 (
Figure 6C,D).
3.11. The IKs Activator ML-277 Partially restored the APD in Drug-Induced LQT2 Zebrafish Hearts
PUFA analogues caused only a small shortening on the zebrafish APD. Hence, we wanted to test whether stronger Kv7.1 activator would shorten the zebrafish APD more. We therefore examined ML-277 (IC50 = 270 nM for human Kv7.1) effects on zebrafish APD. ML-277 was first tested on zebrafish Kv7.1 expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes, where it increased the current substantially more (>8 fold) than the PUFA analogues (
Figure S5,
Table S2). ML-277 (10 µM) shortened the APD80 after 10, 20 and 30 min of application (
Figure 7A,B). Moreover, significant APD Shortening was observed when the average of APD80 values at the different times (10, 20, 30) was compared with APD80 values in control conditions (
Table 4). Moreover, ML-277 shortened the APD at different percentages of repolarization, APD50 and APD80 (
Figure 7C,
Table 1). However, ML-277 did not show any effect on Phase 3 of repolarization (
Figure 7D). To determine whether, as for chromanol 293B, the effect of ML-277 might be increased when
IKr channels were compromised, we examined ML-277 effect on the zebrafish APD in drug-induced LQT2. We therefore applied E4031(10µM) and E4031/ML-277(10µM/10µM) sequentially. ML-277 shortened the APD80 by 13.6 ± 2.6% compared with its control E4031 alone (
Figure 7E, n = 5, p < 0.01). After applying E4031/ML-277, the APD80 showed significant shortened, at all times tested (
Figure 7F), when we compared it with its control with E4031 suggesting that ML-277 partly restored the APD80 when drug-induced LQT2 (
Figure 7F). Moreover, ML-277 significantly shortened the APD when the average of APD80 values of the different times (10, 20, 30) was compared with APD80 values in control conditions (
Table 4). Moreover, ML-277 significantly shortened the APD50, APD80 and APD90 (
Figure 7G,
Table 1). ML-277 also significantly shortened Phase 3 of repolarization in drug-induce LQT2 (
Figure 7H, 164.4 ± 21.4 vs. 208.7 ± 16.7 APD80-APD25 for E4031/ML-277 and E4031, respectively, n = 5 p < 0.05). Although there is not a considerable increase in the ML-277 change at APD80 (%) in the presence of E4031 compared to the absence of E4031, these results still suggest that the ML-277 effect on the APD is greater when
IKr is compromised because now ML-277 also significantly affected APD90 and Phase 3 of repolarization, while these ML-277 effects were not observed in the absence of E4031.
4. Discussion
This study evaluated the zebrafish heart as a model for early screening of IKs activators as potential human antiarrhythmic drugs. We drug-induced LQTS in zebrafish hearts with the application of chromanol 293B (IKs blocker) and E4031 (IKr blocker) to simulate LQT1/5 and LQT2, respectively. E4031 was found to significantly prolong the zebrafish heart APD as has been previously described (6). A significant effect of chromanol 293B was observed at APD80 and APD90 (promoting triangulation of the AP shape) and these effects were greater when chromanol 293B was applied after E4031. Moreover, ML-277 shortened the APD50, APD80, and APD90, and partly restored the APD after applying E4031. These results show that IKs is present in adult zebrafish cardiomyocytes and that the contribution of IKs to the repolarization is greater when IKr is compromised, suggesting that IKs serves as a repolarization reserve in zebrafish as in humans.
4.1. IKr and IKs Contribution to Zebrafish AP Repolarization
The small effect of chromanol 293B in prolonging the zebrafish heart APD shown here was previously described by Abramochlin et al., in 2018, who found that 100 µM chromanol 293B inhibited
IKs by only 36% in isolated zebrafish cardiomyocytes. The critical residues (T312, I337, F340) for the chromanol 293B binding site in human Kv7.1 are conserved in zebrafish Kv7.1 (19, 34). They found strong transcript expression of the KCNQ1 gene encoding for the α-subunit of the Kv7.1 channel in the adult zebrafish atrium and ventricle. However,
KCNE1, encoding for the KCNE1 β-subunit, was expressed at 21- and 17-times lower levels in the ventricle and atrium, respectively, when compared to
KCNQ1 (19). Moreover, for those currents not inhibited by E4031 in zebrafish cardiomyocytes (assumed to be mainly
IKs), the activation kinetics resembled more the kinetics of Kv7.1 alone (19). Abramochlin et al. therefore proposed that the low affinity of chromanol 293B they found in zebrafish cardiomyocytes might be due to the low expression of KCNE1 in zebrafish cardiomyocytes relative to human cardiomyocytes because chromanol 293B is more potent in inhibiting human Kv7.1/KCNE1 than human Kv7.1. However, we found that the effect of chromanol 293B was greater on the zebrafish Kv7.1 than on the zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 when recorded in
Xenopus laevis oocytes: 10 µM chromanol 293B inhibited zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes by around 50%, and the same concentration almost inhibited 80% of the zebrafish Kv7.1 current. The inhibitory effects observed in zebrafish cardiomyocytes are similar compared to chromanol 293B’s effect on human (IC50 ≈ 7 µM) and zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes. In our study, the small effect observed in the zebrafish APD80 when 100 µM chromanol 293B and 10 µM ML-277 were applied compared with the results observed for zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 (10 µM chromanol 293B and 1 µM ML-277) in
Xenopus laevis oocytes suggests that the Kv7.1 or the Kv7.1/KCNE1 contribution to the zebrafish action potential under resting conditions is small. Moreover, all zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 inhibitory and activating effects analysed (
Figure S6) in
Xenopus laevis oocytes suggest that the contribution of Kv7.1 is higher than Kv7.1/KCNE1. Our results are consistent with the earlier study showing limited expression of KCNE1 in zebrafish cardiomyocytes (19). For example, we see a bigger effect in zebrafish heart of ML-277 than the two PUFA compounds, just as ML-277 has bigger effects than the two PUFAs on Kv7.1 channels expressed in oocytes.
Understanding the role of IKs and IKr is critical given the importance of these currents for the repolarization in the human heart. It should be noted that there are significant differences even among mammalian hearts when it comes to the activity of each ion channel. For instance, IKr inhibition in humans results in a significantly larger APD90 prolongation (80%) when compared to dogs (30%) and guinea pigs (20%), whereas IKs inhibition has almost no effect on human and dog APDs, but severely prolongs the guinea pig APD (37, 38). Sympathetic activity of β-adrenergic receptors on guinea pig ventricular cells and human atrial and ventricular cells potentiates IKs (37, 39, 40). Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that although IKs does not play a large role in the basal state of the human heart, it plays an important role in preventing APD prolongation when human ventricular repolarization reserve is attenuated and sympathetic tone is increased (38, 41). Here, we show that the addition of chromanol 293B after IKr inhibition by E4031 produced a further increase in APD80 and APD90 (also observed in the triangulation analysis) in zebrafish hearts. Moreover, the effect of ML-277 (presumably through IKs channels) on the APD90 was increased after applying E4031. These results suggest that IKs may serve primarily as a reserve current for periods of stressed activity, and while under resting conditions, repolarization of the zebrafish heart is mostly determined by IKr. Zebrafish hearts therefore share a similar response to Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv11.1 inhibition as the human heart (38).
Our results demonstrated that when IKr is compromised, the relevance of IKs is significantly higher, suggesting a repolarization reserve mechanism for IKs in zebrafish hearts.
4.2. Small Effects of Other Human IKs Inhibitors
The human
IKs inhibitor JNJ303 did not prolong phase 3 and prolonged APD25 and APD50 more than APD80 and APD90 in the zebrafish optical AP recordings, suggesting that JNJ303 is not a good zebrafish
IKs inhibitor. JNJ303 inhibition of human Kv7.1/KCNE1 has only been observed in the presence of the KCNE1 subunit. The JNJ303 binding site is described as in a fenestration in the pore domain formed at the interface of these two subunits, suggesting that JNJ303 is a gating modifier instead of a pore blocker (35). We showed that JNJ303 has a very low affinity for zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes (
Figure S1). This suggests that there might be structural differences between human and zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and that the presence of the zebrafish KCNE1 is not enough to recapitulate the JNJ303 effect observed in human Kv7.1/KCNE1. The mechanism underlying the significant APD25 prolongation observed with JNJ303 on the zebrafish APD remains unclear.
4.3. PUFA Analogues Slightly Shorten Zebrafish AP
Activators of Kv7.1/KCNE1 have been proposed as a suitable treatment for LQTS (42). PUFA analogues have been shown as activators of human Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 by exerting dual effects to increase
IKs by 1) shifting the voltage dependence of activation towards negative potentials and 2) increasing the channel maximum conductance (31) (
Figure 1B). However, PUFA analogues can also broadly modulate other cardiac voltage-gated ion channels. DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly (
Figure 1A) were selected for this study due to their relatively high selectivity for human Kv7.1/KCNE1 and smaller effects on human NaV and CaV channels (2). DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly have been shown to shorten the QT interval and the APD in
ex-vivo drug-induced LQT2 guinea pig hearts (42, 43). DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly showed a moderate shortening effect of the zebrafish APD, consistent with a limited
IKs or Kv7.1 contribution to repolarization under resting conditions. However, although DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly slightly shortened the zebrafish APD under rest conditions, they did not produce any shortening effect when LQTS was drug-induced with E4031 in zebrafish heart. This could be explained by that DHA-Gly and LIN-Gly exerted only modest effects on the zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 expressed in
Xenopus laevis oocytes.
In contrast to our results on PUFA analogues DHA-Gly and Lin-Gly, we showed that the stronger Kv7.1 activator (and, most likely, more specific compound) ML-277 partly reversed the prolongation produced by E4031 in zebrafish hearts, suggesting that the PUFA analogues are not modulating Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 strongly enough in the zebrafish hearts to cause large effects on the APD. Similarly, PUFAs have been shown to have no or only small effects on cardiac arrhythmia in human clinical trial. Here we shown that a strong IKs activator, such as ML-277, has a significant effect on APD in zebrafish hearts, suggesting that strong IKs activators might be good candidates for developing novel anti-arrhythmic compounds.
To conclude, our results show that zebrafish hearts share similarities with the human heart regarding the activation and contribution of the delayed rectifiers potassium currents IKs and IKr involved in the cardiac AP repolarization (38). We also demonstrate that effective IKs activators restore the APD in drug-induced LQT2 zebrafish heart, which suggests that zebrafish heart might be a good animal model to test the anti-arrhythmic activity of IKs activators. Although there are some differences in the pharmacology of zebrafish IKs compared to human IKs that has to be taken into account in future drug development.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Figure S1: JNJ303 does not inhibit zebrafish IKs recorded in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Figure S2: Chromanol 293B inhibits zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 currents recorded in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Figure S3: DHA-Gly does not increase zebrafish IKs recorded in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Figure S4: LIN-Gly increases zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 currents recorded in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Figure S5: ML-277 effects on zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 currents recorded in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Figure S6: Summary of zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 and Kv7.1 blockers and activators effects recorded in Xenopus laevis oocytes. SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 1. Zebrafish
IKs measurements in
Xenopus laevis oocytes for IKs inhibitors, and IKs activator and PUFA analogues. SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 2. Zebrafish Kv7.1 measurements in Xenopus laevis oocytes for Kv7.1 inhibitors, and Kv7.1 activator and PUFA analogues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: AdlC, HPL, Supervision: AdlC, Project administration: HPL, Investigation: AdlC. XW, QCR, IHI, IE, MEP, SIL, Formal analysis: AdlC. XW, QCR, IHI, IE, SIL, Funding acquisition: SIL, HPL, Writing—original draft: AdlC, Writing—review & editing: AdlC, QCR, HPL.
Funding
This work was supported by the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (grant agreement No. 850622 to S.I.L), and the National Institutes of Health (R01HL131461, to H.P.L.).
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Mark A. Skarsfeldt, Bo Hjort-Bentzen, and Pia Rengtved Lundegaard (University of Copenhagen) for helping with setting up the zebrafish model for this study.
Disclosures
A patent application (#62/032,739) including a description of the interaction of charged lipophilic compounds with the KCNQ1 channel has been submitted by the University of Miami with H.P.L and S.I.L. identified as inventors. Dr. Hans Peter Larsson is the equity owner of VentricPharm, a company that operates in the same field of research as the study.
References
- Levine, E.; Rosero, S.Z.; Budzikowski, A.S.; Moss, A.J.; Zareba, W.; Daubert, J.P. Congenital long QT syndrome: Considerations for primary care physicians. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2008, 75, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, B.M.; de la Cruz, A.; Wu, X.; Jowais, J.J.; Perez, M.E.; Liin, S.I.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid analogues differentially affect cardiac NaV, CaV, and KV channels through unique mechanisms. elife 2020, 9, e51453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, P.J.; Stramba-Badiale, M.; Crotti, L.; Pedrazzini, M.; Besana, A.; Bosi, G.; et al. Prevalence of the Congenital Long-QT Syndrome. Circulation 2009, 120, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, K.E.; Venkateshappa, R.; Pang, Z.K.; Faizi, S.; Tibbits, G.F.; Claydon, T.W. Utility of Zebrafish Models of Acquired and Inherited Long QT Syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 624129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, N.C.; Shaw, R.M.; Jungblut, B.; Huisken, J.; Ferrer, T.; Arnaout, R.; et al. Genetic and physiologic dissection of the vertebrate cardiac conduction system. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemtsas, P.; Wettwer, E.; Christ, T.; Weidinger, G.; Ravens, U. Adult zebrafish heart as a model for human heart? An electrophysiological study. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2010, 48, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, D.J.; Jones, I.L.; Ellinor, P.T.; MacRae, C.A. In vivo recording of adult zebrafish electrocardiogram and assessment of drug-induced QT prolongation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H269–H273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; James, N.A.; Beshay, A.R.; Chang, E.E.; Lin, A.; Bashar, F.; et al. Adult zebrafish ventricular electrical gradients as tissue mechanisms of ECG patterns under baseline vs. oxidative stress. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1891–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vornanen, M.; Hassinen, M. Zebrafish heart as a model for human cardiac electrophysiology. Channels 2016, 10, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristani-Firouzi, M.; Chen, J.; Mitcheson, J.S.; Sanguinetti, M.C. Molecular biology of K(+) channels and their role in cardiac arrhythmias. Am. J. Med. 2001, 110, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, M.C.; Warmke, J.W.; Ganetzky, B.; Robertson, G.A. HERG, a human inward rectifier in the voltage-gated potassium channel family. Science 1995, 269, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banyasz, T.; Jian, Z.; Horvath, B.; Khabbaz, S.; Izu, L.T.; Chen-Izu, Y. Beta-adrenergic stimulation reverses the I Kr-I Ks dominant pattern during cardiac action potential. Pflugers Arch. 2014, 466, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S. IKs protects from ventricular arrhythmia during cardiac ischemia and reperfusion in rabbits by preserving the repolarization reserve. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudicessi, J.R.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Ackerman, M.J. The genetic architecture of long QT syndrome: A critical reappraisal. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 28, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravens, U. Ionic basis of cardiac electrophysiology in zebrafish compared to human hearts. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018, 138, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alday, A.; Alonso, H.; Gallego, M.; Urrutia, J.; Letamendia, A.; Callol, C.; et al. Ionic channels underlying the ventricular action potential in zebrafish embryo. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 84, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Sharma, K.; Laster, K.; Hersi, M.; Torres, C.; Lukas, T.J.; et al. Kcnq1-5 (Kv7.1-5) potassium channel expression in the adult zebrafish. BMC Physiol. 2014, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.T.; Wu, C.K.; Chiang, F.T.; Tseng, C.D.; Lee, J.K.; Yu, C.C.; et al. In-vitro recording of adult zebrafish heart electrocardiogram—A platform for pharmacological testing. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramochkin, D.V.; Hassinen, M.; Vornanen, M. Transcripts of Kv7.1 and MinK channels and slow delayed rectifier K(+) current (I(Ks)) are expressed in zebrafish (Danio rerio) heart. Pflugers Arch. 2018, 470, 1753–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J.; Windle, J.R.; Hall, W.J.; Zareba, W.; Robinson, J.L.; McNitt, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of flecainide in subjects with Long QT-3 syndrome (DeltaKPQ mutation): A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005, 10 (Suppl. 4), 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, W.J.; Silka, M.J.; Oliver, R.P.; Halperin, B.D.; McAnulty, J.H.; Kron, J. Use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in the congenital long QT syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 78, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, Q.F.; Du, R.; Xu, Q.M.; Ke, Q.M.; Wang, B.; et al. Congenital long QT syndrome caused by the F275S KCNQ1 mutation: Mechanism of impaired channel function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 380, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, A.J.; McDonald, J. Unilateral cervicothoracic sympathetic ganglionectomy for the treatment of long QT interval syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 903–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgro, A.; Drake, T.M.; Lopez-Ayala, P.; Phan, K. Left cardiac sympathetic denervation in the management of long QT syndrome and catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: A meta-regression. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2019, 14, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.J., Jr.; Stump, G.L.; Wallace, A.A.; Gilberto, D.B.; Jahansouz, H.; et al. Antiarrhythmic efficacy of selective blockade of the cardiac slowly activating delayed rectifier current, I(Ks), in canine models of malignant ischemic ventricular arrhythmia. Circulation 1999, 100, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, P.J.; Crotti, L.; Insolia, R. Long-QT syndrome: From genetics to management. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshneya, M.; Devenyi, R.A.; Sobie, E.A. Slow Delayed Rectifier Current Protects Ventricular Myocytes From Arrhythmic Dynamics Across Multiple Species: A Computational Study. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e006558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Larsson, H.P. Insights into Cardiac IKs (KCNQ1/KCNE1) Channels Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatti, P.; Peluso, G.; Nicolai, R.; Calvani, M. Polyunsaturated fatty acids: Biochemical, nutritional and epigenetic properties. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjesson, S.I.; Hammarstrom, S.; Elinder, F. Lipoelectric modification of ion channel voltage gating by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 2242–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liin, S.I.; Yazdi, S.; Ramentol, R.; Barro-Soria, R.; Larsson, H.P. Mechanisms Underlying the Dual Effect of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Analogs on Kv7.1. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 2908–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, B.M.; de la Cruz, A.; Wu, X.; Jowais, J.J.; Perez, M.E.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid analogues differentially affect cardiac NaV, CaV, and KV channels through unique mechanisms. eLife 2020, 9, e51453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarsfeldt, M.A.; Liin, S.I.; Larsson, H.P.; Bentzen, B.H. Polyunsaturated fatty acid-derived IKs channel activators shorten the QT interval ex-vivo and in-vivo. Acta Physiol. 2020, 229, e13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerche, C.; Bruhova, I.; Lerche, H.; Steinmeyer, K.; Wei, A.D.; Strutz-Seebohm, N.; et al. Chromanol 293B binding in KCNQ1 (Kv7.1) channels involves electrostatic interactions with a potassium ion in the selectivity filter. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, E.; Rothenberg, I.; Krisp, C.; Hundt, F.; Fraenzel, B.; Eckey, K.; et al. KCNE1 induces fenestration in the Kv7.1/KCNE1 channel complex that allows for highly specific pharmacological targeting. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannankeril, P.; Roden, D.M.; Darbar, D. Drug-induced long QT syndrome. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 760–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, T.; Rudy, Y. Quantitative comparison of cardiac ventricular myocyte electrophysiology and response to drugs in human and nonhuman species. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H1023–H1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, N.; Virág, L.; Bitay, M.; Takács, J.; Lengyel, C.; Biliczki, P.; et al. Restricting excessive cardiac action potential and QT prolongation: A vital role for IKs in human ventricular muscle. Circulation 2005, 112, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, M.C.; Jurkiewicz, N.K.; Scott, A.; Siegl, P.K. Isoproterenol antagonizes prolongation of refractory period by the class III antiarrhythmic agent E-4031 in guinea pig myocytes. Mechanism of action. Circ. Res. 1991, 68, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fermini, B.; Nattel, S. Rapid and slow components of delayed rectifier current in human atrial myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 1994, 28, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliczki, P.; Virág, L.; Iost, N.; Papp, J.G.; Varró; A. Interaction of different potassium channels in cardiac repolarization in dog ventricular preparations: Role of repolarization reserve. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 137, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liin, S.I.; Silvera Ejneby, M.; Barro-Soria, R.; Skarsfeldt, M.A.; Larsson, J.E.; Starck Harlin, F.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid analogs act antiarrhythmically on the cardiac IKs channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5714–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarsfeldt, M.A.; Liin, S.I.; Larsson, H.P.; Bentzen, B.H. Polyunsaturated fatty acid-derived I(Ks) channel activators shorten the QT interval ex-vivo and in-vivo. Acta Physiol. 2020, 229, e13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
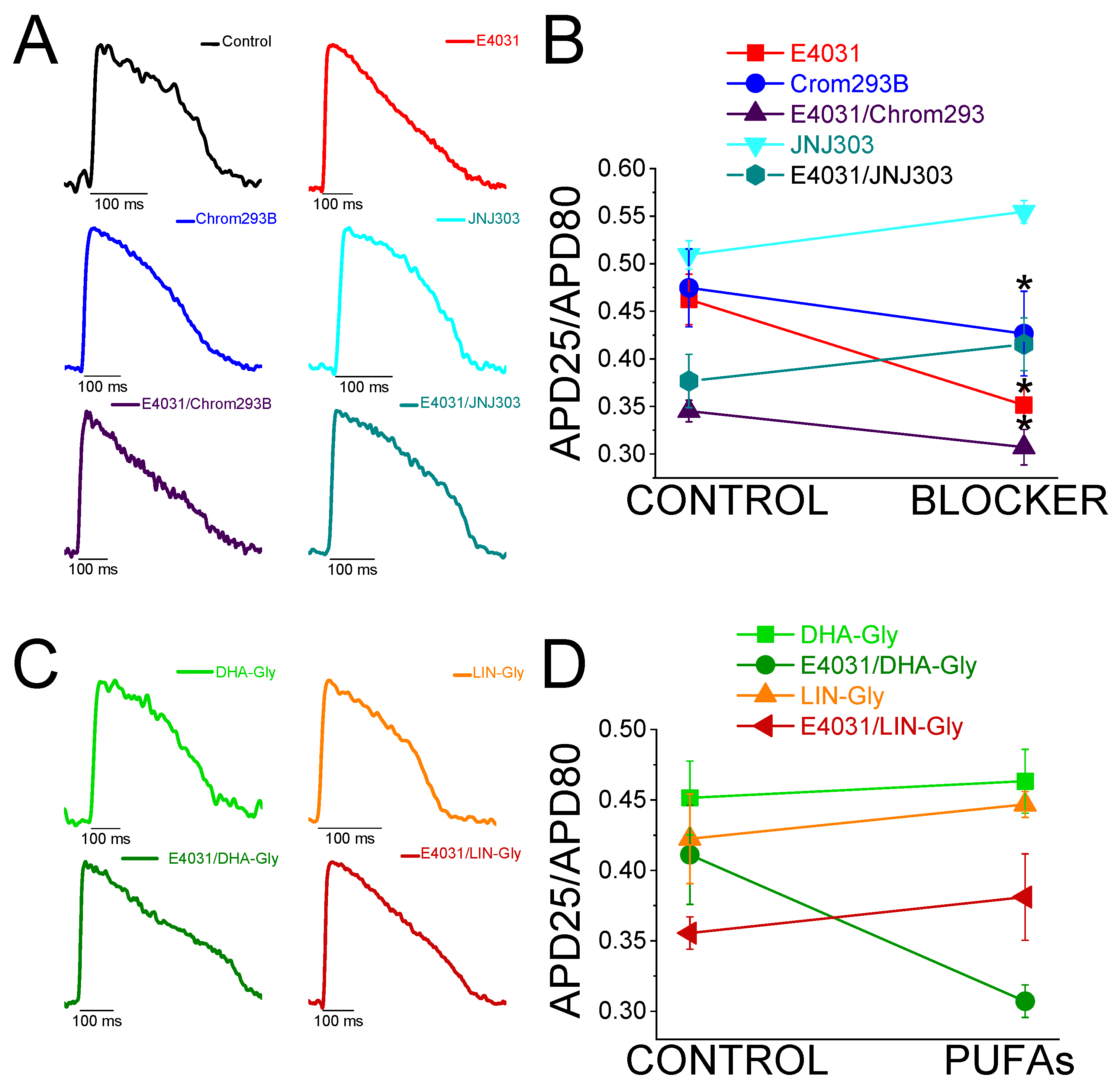
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the topology of Kv7.1/KCNE1, the lipoelectric hypothesis and zebrafish optical AP analysis diagram A) PUFA analogues molecular structure B) The lipoelectric hypothesis (previously shown in (42) but adapted to zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 stoichiometry) Top, schematic illustration showing how the negatively-charged head group of the PUFA analogue attracts the positively charged voltage sensor of the channel and activates the channel. Bottom, a second electrostatic effect of the negatively-charged head group of the PUFA analogue with a positively-charged residue located in the pore domain of the channels promotes the conductance increase of the channel. C) Schematic of the optical AP analysis methodology. The left panel shows how APD at different repolarization percentages was measured. The right panel shows how change, ΔAPD (%), between control conditions and the drug was measured at different percentages of repolarization (APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90). D) APD80 (in ms) measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after first control recording). Black bars show the control condition measured over time (C10’, C20’, and C30’) (mean ± SEM; NS: not significant).
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the topology of Kv7.1/KCNE1, the lipoelectric hypothesis and zebrafish optical AP analysis diagram A) PUFA analogues molecular structure B) The lipoelectric hypothesis (previously shown in (42) but adapted to zebrafish Kv7.1/KCNE1 stoichiometry) Top, schematic illustration showing how the negatively-charged head group of the PUFA analogue attracts the positively charged voltage sensor of the channel and activates the channel. Bottom, a second electrostatic effect of the negatively-charged head group of the PUFA analogue with a positively-charged residue located in the pore domain of the channels promotes the conductance increase of the channel. C) Schematic of the optical AP analysis methodology. The left panel shows how APD at different repolarization percentages was measured. The right panel shows how change, ΔAPD (%), between control conditions and the drug was measured at different percentages of repolarization (APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90). D) APD80 (in ms) measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after first control recording). Black bars show the control condition measured over time (C10’, C20’, and C30’) (mean ± SEM; NS: not significant).
Figure 2.
IKrandIKsinhibitors prolong zebrafish AP. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after (red) applying E4031 (10 µM). B) ΔAPD80 (%) after (red) applying E4031 (10 µM), measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of the drug) C) ΔAPD(%) produced by the drug measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of the drug on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in control conditions and after E4031 application. E-H) The same as in A-D but for the IKs inhibitor chromanol 293B (100 µM). I-L) The same as in A-D but for the IKs inhibitor JNJ303 (10 µM) (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs. control condition).
Figure 2.
IKrandIKsinhibitors prolong zebrafish AP. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after (red) applying E4031 (10 µM). B) ΔAPD80 (%) after (red) applying E4031 (10 µM), measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of the drug) C) ΔAPD(%) produced by the drug measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of the drug on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in control conditions and after E4031 application. E-H) The same as in A-D but for the IKs inhibitor chromanol 293B (100 µM). I-L) The same as in A-D but for the IKs inhibitor JNJ303 (10 µM) (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs. control condition).
Figure 3.
IKsinhibitors prolong more zebrafish AP after drug-induced LQT2. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after applying E4031 (red, 10 µM), and E4031/chromanol 293B (10 µM/100 µM, dark purple). B) ΔAPD80 (%)measured at different recording times vs. E4031 control condition (10, 20, and 30 min after application of E4031/chromanol 293B). C) ΔAPD(%) produced by the combination of drugs measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of the combination of drugs on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in E4031 (control conditions) and after E4031/chromanol 293B application. E-H) The same as in A-D but for the combination E4031/JNJ303 (10 µM/10 µM) (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, # p <0.05 vs. E4031 condition, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs E4031 condition).
Figure 3.
IKsinhibitors prolong more zebrafish AP after drug-induced LQT2. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after applying E4031 (red, 10 µM), and E4031/chromanol 293B (10 µM/100 µM, dark purple). B) ΔAPD80 (%)measured at different recording times vs. E4031 control condition (10, 20, and 30 min after application of E4031/chromanol 293B). C) ΔAPD(%) produced by the combination of drugs measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of the combination of drugs on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in E4031 (control conditions) and after E4031/chromanol 293B application. E-H) The same as in A-D but for the combination E4031/JNJ303 (10 µM/10 µM) (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, # p <0.05 vs. E4031 condition, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs E4031 condition).
Figure 4.
PUFA analogues have modest effects on zebrafish AP. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after (light green) applying DHA-Gly (20 µM). B) ΔAPD80 (%) after (light green) applying DHA-Gly (20 µM), measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of the PUFA-analogue) C) ΔAPD(%) produced by the PUFA-analogue measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of the PUFA-analogue on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in control conditions and after DHA-Gly application. E-H) The same as in A-D but for the PUFA-analogue LIN-Gly (20 µM) (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs. control condition).
Figure 4.
PUFA analogues have modest effects on zebrafish AP. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after (light green) applying DHA-Gly (20 µM). B) ΔAPD80 (%) after (light green) applying DHA-Gly (20 µM), measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of the PUFA-analogue) C) ΔAPD(%) produced by the PUFA-analogue measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of the PUFA-analogue on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in control conditions and after DHA-Gly application. E-H) The same as in A-D but for the PUFA-analogue LIN-Gly (20 µM) (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs. control condition).
Figure 5.
PUFA analogues do not shorten the zebrafish AP in LQT2 drug-induced conditions. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after sequentially applying E4031 (10 µM, red) and E4031/ DHA-Gly (10 µM/20 µM, dark green). B) ΔAPD80 (%) measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of the combination drug/PUFA analogue). E4031 recording, measured at 30 min, was used as control condition. C) ΔAPD(%) produced by the combination of drug/PUFA analogue measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of the combination of drug/PUFA analogue on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in E4031 (control conditions) and after E4031/DHA-Gly application. E-H) The same as A-D but for the combination E4031/LIN-Gly (10 µM/20 µM) (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, # p <0.05 vs. E4031 condition, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs. its control condition; control condition or E4031 condition).
Figure 5.
PUFA analogues do not shorten the zebrafish AP in LQT2 drug-induced conditions. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after sequentially applying E4031 (10 µM, red) and E4031/ DHA-Gly (10 µM/20 µM, dark green). B) ΔAPD80 (%) measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of the combination drug/PUFA analogue). E4031 recording, measured at 30 min, was used as control condition. C) ΔAPD(%) produced by the combination of drug/PUFA analogue measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of the combination of drug/PUFA analogue on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in E4031 (control conditions) and after E4031/DHA-Gly application. E-H) The same as A-D but for the combination E4031/LIN-Gly (10 µM/20 µM) (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, # p <0.05 vs. E4031 condition, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs. its control condition; control condition or E4031 condition).
Figure 6.
IKr and IKs inhibitors promote triangulation while IKs activators do not square the zebrafish AP shape. A) Representative traces of control conditions (black), and in the presence of IKr and IKs inhibitors and the combination of inhibitors to show the qualitative effect of triangulation of the different drug and drugs combination. B) APD25/APD80 ratio in the control condition and after applying the drug for each drug or combination of drugs. C) Representative traces in the presence of PUFA analogues and the combination of E4031/ PUFA analogues to show the qualitative effect of triangulation. D) APD25/APD80 ratio in the control condition and after applying the PUFA analogues or E4031/ PUFA analogues, for each condition examined. For drug combination conditions, CONTROL refers to the drug condition previously applied to the combination of drugs (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05).
Figure 6.
IKr and IKs inhibitors promote triangulation while IKs activators do not square the zebrafish AP shape. A) Representative traces of control conditions (black), and in the presence of IKr and IKs inhibitors and the combination of inhibitors to show the qualitative effect of triangulation of the different drug and drugs combination. B) APD25/APD80 ratio in the control condition and after applying the drug for each drug or combination of drugs. C) Representative traces in the presence of PUFA analogues and the combination of E4031/ PUFA analogues to show the qualitative effect of triangulation. D) APD25/APD80 ratio in the control condition and after applying the PUFA analogues or E4031/ PUFA analogues, for each condition examined. For drug combination conditions, CONTROL refers to the drug condition previously applied to the combination of drugs (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05).
Figure 7.
ML-277 shortens zebrafish AP before and after drug-induced LQT2. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after (pink) applying ML-277 (10 µM). B) ΔAPD80 (%)after applying ML-277 (10 µM), measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of ML-277) C) ΔAPD(%) produced by ML-277 measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of ML-277 on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in control conditions and after ML-277 application E) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after sequentially applying E4031 (10 µM, red) and E4031/ML-277 (10 µM/10 µM, grey). F) ΔAPD80 (%)measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of the combination drug/ML-277). E4031 recording, measured at 30 min, was used as control condition. G) ΔAPD(%) produced by the combination of drug/ML-277 measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 H) Effect of the combination of drug/ML-277on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in E4031 (control conditions) and after E4031/ML-277 application. (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, # p <0.05 vs. E4031 condition, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs. its control condition; control condition or E4031 condition).
Figure 7.
ML-277 shortens zebrafish AP before and after drug-induced LQT2. A) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after (pink) applying ML-277 (10 µM). B) ΔAPD80 (%)after applying ML-277 (10 µM), measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of ML-277) C) ΔAPD(%) produced by ML-277 measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 D) Effect of ML-277 on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in control conditions and after ML-277 application E) Representative zebrafish AP traces before (black) and after sequentially applying E4031 (10 µM, red) and E4031/ML-277 (10 µM/10 µM, grey). F) ΔAPD80 (%)measured at different recording times (10, 20, and 30 min after application of the combination drug/ML-277). E4031 recording, measured at 30 min, was used as control condition. G) ΔAPD(%) produced by the combination of drug/ML-277 measured for APD25, APD50, APD80, and APD90 H) Effect of the combination of drug/ML-277on phase 3 of the AP. APD80-APD25 in E4031 (control conditions) and after E4031/ML-277 application. (mean ± SEM; * p <0.05 vs. control conditions, # p <0.05 vs. E4031 condition, Фp < 0.05 APD80 time data average vs. its control condition; control condition or E4031 condition).
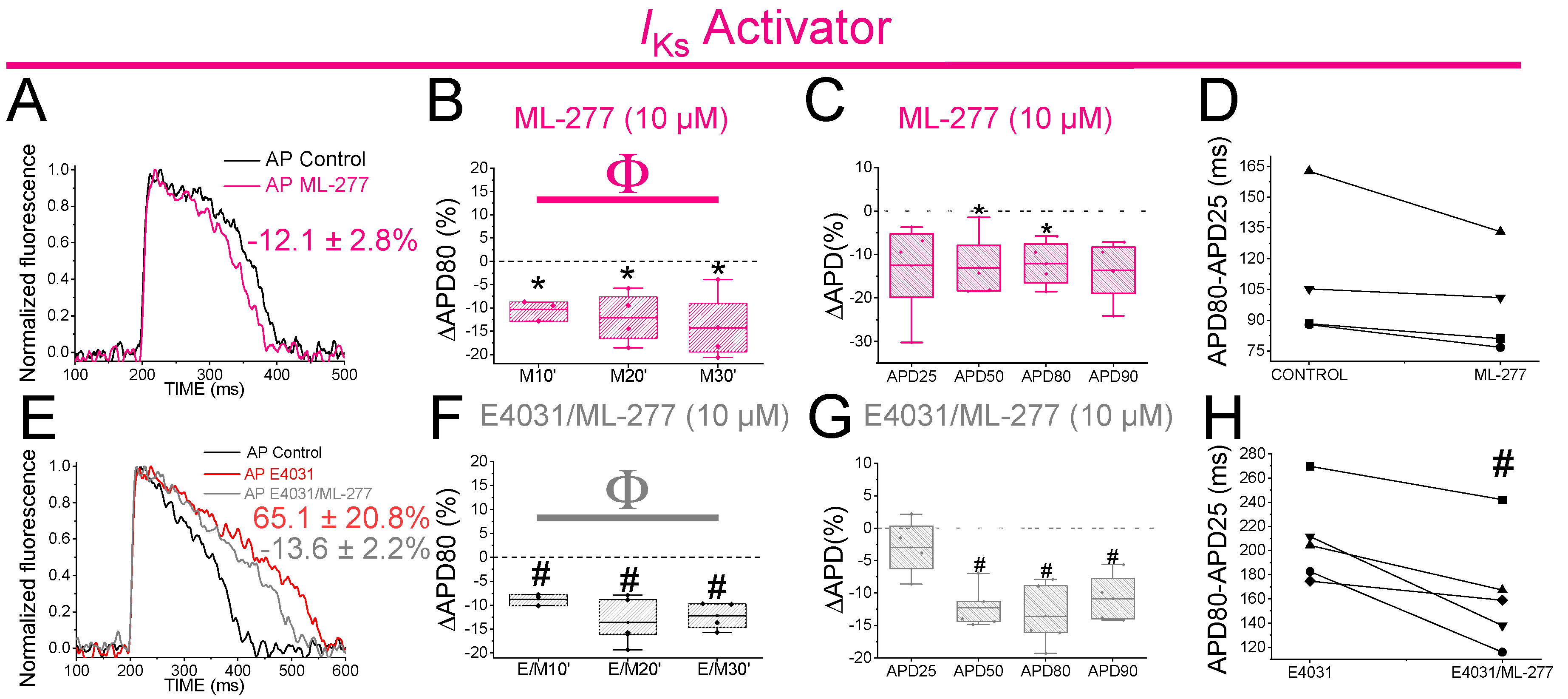
Table 1.
Zebrafish APD measurements at different percentages of repolarization for IKr and IKs inhibitors, and IKs activator.
Table 1.
Zebrafish APD measurements at different percentages of repolarization for IKr and IKs inhibitors, and IKs activator.
| |
ΔAPD25 (%) |
(n, p) |
ΔAPD50 (%) |
(n, p) |
ΔAPD80 (%) |
(n, p) |
ΔAPD90 (%) |
(n, p) |
| E4031 |
48.3 ± 14.6 |
n = 26,
p < 0.001 |
49.6 ± 4.8 |
n = 26,
p < 0.001 |
72.8 ± 5.7 |
n = 26,
p < 0.001 |
71.6 ± 5.8 |
n = 26, p <0.001 |
| C293B |
-5.1 ± 2.0 |
n = 3,
p < 0.05 |
6.5 ± 3.1 |
n = 3, NS,
p > 0.05 |
9.6 ± 0.3 |
n = 3,
p < 0.05 |
9.2 ± 2.1 |
n = 3, p < 0.01 |
| JNJ303 |
27.1 ± 7.0 |
n = 3,
p < 0.05 |
17.5 ± 6.8 |
n = 3, NS,
p > 0.05 |
16.4 ± 3.4 |
n = 3,
p < 0.01 |
13.6 ± 3.5 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
| E4031/C293B |
13.2 ± 9.2 |
n = 3, NS,
p > 0.05 |
12.5 ± 7.6 |
n = 3, NS,
p > 0.05 |
20.2 ± 2.0 |
n = 3,
p < 0.01 |
22.0 ± 4.3 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
| E4031/JNJ303 |
27.5 ± 10.5 |
n = 5,
p < 0.05 |
20.2 ± 5.5 |
n = 5,
p < 0.05 |
14.3 ± 4.3 |
n = 5,
p < 0.05 |
14.0 ± 4.1 |
n = 5,
p < 0.05 |
| ML-277 |
-12.5 ± 6.0 |
n = 4, NS,
p > 0.05 |
-13.1 ± 4.0 |
n = 4,
p < 0.05 |
12.1 ± 2.3 |
n = 4,
p < 0.05 |
-13.6 ± 3.8 |
n = 3, NS,
p > 0.05 |
| E4031/ ML-277 |
3.9 ± 7.1 |
n = 5, NS,
p > 0.05 |
-12.3 ± 1.5 |
n = 5,
p < 0.01 |
-13.6 ± 2.2 |
n = 5,
p < 0.01 |
-14.0 ± 3.5 |
n = 5,
p < 0.05 |
Table 2.
Zebrafish APD measurements at different percentages of repolarization for PUFA analogues.
Table 2.
Zebrafish APD measurements at different percentages of repolarization for PUFA analogues.
| |
ΔAPD25 (%) |
(n, p) |
ΔAPD50(%)
|
(n, p) |
ΔAPD80(%)
|
(n, p) |
ΔAPD90(%)
|
(n, p) |
| DHA-Gly |
-0.7 ± 10.5 |
n = 9, NS, p > 0.05 |
-4.5 ± 3.4 |
n = 9, NS, p > 0.05 |
-6.1 ± 2.3 |
n = 9, p < 0.05 |
-6.4 ± 3.0 |
n = 9, NS, p > 0.05 |
| LIN-Gly |
7.6 ± 8.4 |
n = 6, NS, p > 0.05 |
-6.4 ± 4.5 |
n = 6, NS, p > 0.05 |
-4.9 ± 0.8 |
n = 6, p < 0.01 |
-9.4 ± 3.3 |
n = 6, NS,p > 0.05 |
| E4031/DHA-Gly |
-2.6 ± 9.5 |
n = 4, NS, p > 0.05 |
4.4 ± 6.9 |
n = 4, NS, p > 0.05 |
13.7 ± 5.8 |
n = 4, NS, p > 0.05 |
14.2 ± 5.8 |
n = 4,p < 0.05 |
| E4031/LIN-Gly |
18.6 ± 5.8 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
3.7 ± 2.9 |
n = 3, NS, p > 0.05 |
7.5 ± 0.9 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
0.8 ± 3.6 |
n = 3, NS, p > 0.05 |
Table 3.
Triangulation (APD25/APD80 values).
Table 3.
Triangulation (APD25/APD80 values).
| |
APD25/APD80 |
|
APD25/APD80 |
(n, p) |
| E4031 CTRL |
0.48 ± 0.03 |
E4031 |
0.36 ± 0.02 |
n = 24, p < 0.001 |
| C293B CTRL |
0.47 ± 0.14 |
C293B |
0.41 ± 0.06 |
n = 3, p < 0.01 |
| E4031 |
0.35 ± 0.01 |
E4031/C293B |
0.31 ± 0.02 |
n = 3, p < 0.05 |
| JNJ303 CTRL |
0.51 ± 0.02 |
JNJ303 |
0.55 ± 0.01 |
n = 3, NS, p > 0.05 |
| E4031 |
0.38 ± 0.03 |
E4031/JNJ303 |
0.42 ± 0.03 |
n = 5, NS, p > 0.05 |
| DHA-Gly CTRL |
0.45 ± 0.02 |
DHA-Gly |
0.46 ± 0.02 |
n = 9, NS, p > 0.05 |
| LIN-Gly CTRL |
0.41 ± 0.04 |
LIN-Gly |
0.46 ± 0.01 |
n = 5, NS, p > 0.05 |
| E4031 |
0.38 ± 0.11 |
E4031/DHA-Gly |
0.33 ± 0.1 |
n = 3, NS, p > 0.05 |
| E4031 |
0.34 ± 0.02 |
E4031/LIN-Gly |
0.36 ± 0.04 |
n = 5, NS, p > 0.05 |
| ML-277 CTRL |
0.51 ± 0.03 |
ML-277 CTRL |
0.51 ± 0.03 |
n = 4, NS, p > 0.05 |
| E4031 |
0.37 ± 0.03 |
E4031/ ML-277 |
0.44 ± 0.03 |
n = 5, NS, p > 0.05 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).