Submitted:
06 July 2023
Posted:
10 July 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
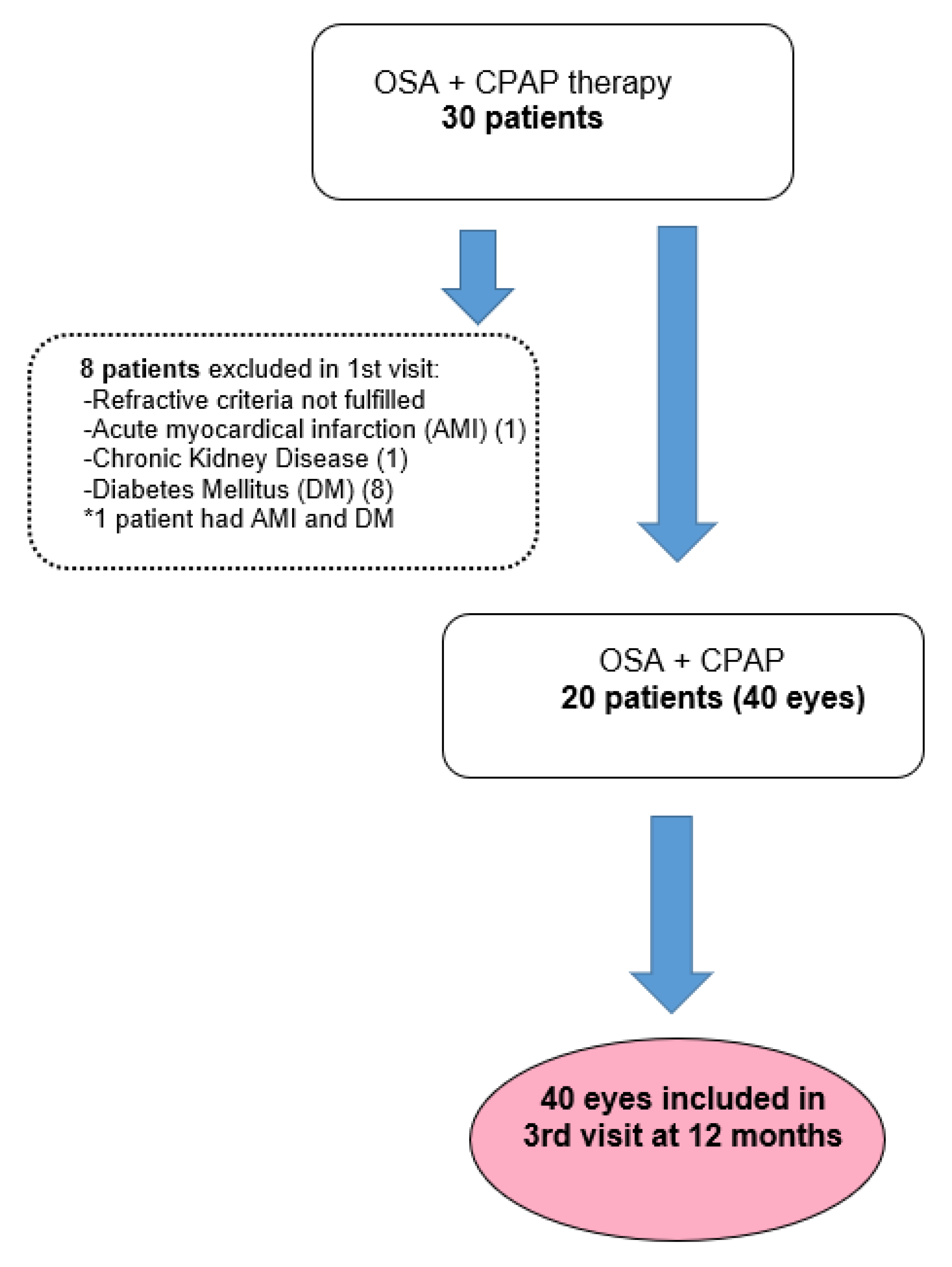
2.1. Study participants
2.2. Overnight polysomnography
2.3. Ophthalmologic examination
2.4. CPAP
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
References
- Benjafield, A.V.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S. M.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pepin, J.L.; Peppard, P.E.; Sinha, S.; Tufik, S.; Valentine, K.; Malhotra, A. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: a literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Fabiani, M.; Fabiani, V.; Ceci, F.; Lillo, R.; Lolli, V.; Brunori, M.; Pannitteri, G.; Cravotto, E.; et al. Severity of OSAS, CPAP and cardiovascular events: A follow-up study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, P.; Kohler, M.; McNicholas, W.T.; Barbe, F.; McEvoy, R.D.; Somers, V.K.; Lavie, L.; Pepin, J.L. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Nat. Reviews. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, S.P.; Al Mansouri, F.A.; Farouk, M.; Al Hashemi, A.A.; Singh, R. Prevalence of glaucoma in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea: ocular morbidity and outcomes in a 3 year follow-up study. Eye 2014, 28, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Riangwiwat, T.; Rattanawong, P.; Nesmith, B.L.W.; Deobhakta, A. ASSOCIATION OF OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA WITH CENTRAL SEROUS CHORIORETINOPATHY AND CHOROIDAL THICKNESS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Retina 2018, 38, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S.; Shapiro, C.M.; Flanagan, J. Sleep-disordered breathing and effects on ocular health. Can J Ophthalmol 2007, 42, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.; Hofmann, R.J. Ocular Manifestations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J Clin Sleep Med 2017, 13, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Gamez, B.; Fernandez-Marin, M.C.; Gomez-Chaparro, J.L.; Munoz-Cabrera, L.; Lopez-Barea, J.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Lopez-Miranda, J. Relationship of oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 2011, 37, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Bonilla, P.; Gimenez-Gomez, R.; Munoz-Villanueva, M.D.C.; Jurado-Gamez, B. Retinal and Choroidal Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure as Treatment for Sleep Apnea: Results at 12 Months. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Bonilla, P.; Munoz-Villanueva, M.C.; Gimenez-Gomez, R.; Jurado-Gamez, B. Retinal and choroidal thickness measurements in obstructive sleep apnea: impacts of continuous positive airway pressure treatment. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2021, 259, 3381–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yo, C.; Ariyasu, R.G. Racial differences in central corneal thickness and refraction among refractive surgery candidates. J Refract Surg 2005, 21, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porwal, A.C.; Shrishrimal, M.; Punamia, R.P.; Mathew, B.C. Assessment of intraocular pressure measurement between Goldman applanation tonometer, rebound tonometer, non-contact tonometer, and its correlation with central corneal thickness. Indian J Ophthalmol 2023, 71, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglior, S.; Albe, E.; Guareschi, M.; Mandelli, G.; Gomarasca, S.; Orzalesi, N. Intraobserver and interobserver reproducibility in the evaluation of ultrasonic pachymetry measurements of central corneal thickness. Br J Ophthalmol 2004, 88, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojarun, A.; Vieversyte, Z.; Jaruseviciene, R.; Galgauskas, S.; Asoklis, R.; Zablockis, R. Effect of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Corneal Morphological Characteristics. Cornea 2019, 38, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalkiadaki, E.; Andreanos, K.; Florou, C.; Droutsas, K.; Maniou, C.; Amfilochiou, A.; Georgalas, I.; Papaconstantinou, D.; Koutsandrea, C. Corneal Endothelial Morphology and Thickness Alterations in Patients With Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome. Cornea 2021, 40, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseoglu, H.I.; Kanbay, A.; Ortak, H.; Karadag, R.; Demir, O.; Demir, S.; Gunes, A.; Doruk, S. Effect of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome on corneal thickness. Int Ophthalmol 2016, 36, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, M.; Huseyinoglu, N.; Cagatay, H.H.; Ceylan, E.; Keles, S.; Gokce, G. Is there a relationship between sleep apnea and central corneal thickness? Curr Eye Res 2013, 38, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmanson, J.P.; Chu, L.W. Corneal response to rigid contact lens wear. Br J Ophthalmol 1982, 66, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkiadaki, E.; Andreanos, K.; Karmiris, E.; Mani, A.; Kastanakis, E.; Amfilochiou, A.; Papaconstantinou, D.; Koutsandrea, C.; Georgalas, I. Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment for Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome on Corneal Morphological Characteristics. Cornea 2021, 40, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloberes, P.; Duran-Cantolla, J.; Martinez-Garcia, M.A.; Marin, J.M.; Ferrer, A.; Corral, J.; Masa, J.F.; Parra, O.; Alonso-Alvarez, M.L.; Teran-Santos, J. Diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery. Arch Bronconeumol 2011, 47, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J Clin Sleep Med 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Ayappa, I.A.; Caples, S.M.; Kimoff, R.J.; Patel, S.R.; Harrod, C.G. Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Positive Airway Pressure: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Sleep Med 2019, 15, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Gamez, B.; Bardwell, W.A.; Cordova-Pacheco, L.J.; Garcia-Amores, M.; Feu-Collado, N.; Buela-Casal, G. A basic intervention improves CPAP adherence in sleep apnoea patients: a controlled trial. Sleep Breath 2015, 19, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, J.H.; Efron, N. Corneal hypoxia and hypercapnia during contact lens wear. Optom Vis Sci 1990, 67, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakucuk, S.; Mujdeci, M.; Baskol, G.; Arda, H.; Gumus, K.; Oner, A. Changes in central corneal thickness, intraocular pressure, and oxidation/antioxidation parameters at high altitude. Aviat Space Environ Med 2012, 83, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.T. Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in hypoxic inflammation. J Physiol 2008, 586, 4055–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lema, I.; Sobrino, T.; Duran, J.A.; Brea, D.; Diez-Feijoo, E. Subclinical keratoconus and inflammatory molecules from tears. Br J Ophthalmol 2009, 93, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlblad, M.S.; Schaefer, D.P. Eyelid laxity, obesity, and obstructive sleep apnea in keratoconus. Cornea 2013, 32, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, F.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, S.; Savini, G.; Lu, W.; Feng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J. Comparison and evaluation of central corneal thickness using 2 new noncontact specular microscopes and conventional pachymetry devices. Cornea 2014, 33, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, N.; Romero-Aroca, P.; Gris, O.; Camps, J.; Fernandez-Ballart, J. Corneal endothelial changes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and corneal vulnerability to cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 2015, 41, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhaas, M.; Boehm, A.G.; Spoerl, E.; Pursten, A.; Grein, H.J.; Pillunat, L.E. Effect of central corneal thickness, corneal curvature, and axial length on applanation tonometry. Arch Ophthalmol 2006, 124, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patients No. (% or ±SD) N = 20 | |
|---|---|
| Sex (men) | 20 (100 %) |
| Age (years) | 56.5 (± 8.3) |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 30.7 (± 6.8) |
| Glaucoma (%) | 2 (5 %) |
| AHI severe (%) | 20 (100 %) |
| AHI (events/h) | 64.6 (± 22.3) |
| CPAP use (h) | 5.23 (± 1.77) |
| ODI | 69.1 (± 21.3) |
| CT90 | 12.4 (± 11.2) |
| SpO2 mean | 91.4 (± 3) |
| SpO2 minimum | 79.5 (± 8.9) |
| Baseline | 3 months | 12 months | p* raw | p** adjusted(1) (2) (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOP (mmHg) | 14.68 (±2.55) | 13.87 (±2.36) | 15.08 (±2.40) | 0.034 | |
| CCT (µm) | 547.30 (±44.64) | 548.80 (±44.40) | 549.70 (±43.22) | 0.298 | NA |
| VFI (%) | 98.29 (±1.61) | 97.66 (±2.72) | 98.53 (±1.61) | 0.456 | NA |
| VF MD (decibels) | -1.96 (±1.01) | -2.05 (±1.34) | -1.94 (±1.00) | 0.723 | NA |
| CCT difference (3 months Vs baseline) | CCT difference (12 months Vs baseline) | |
|---|---|---|
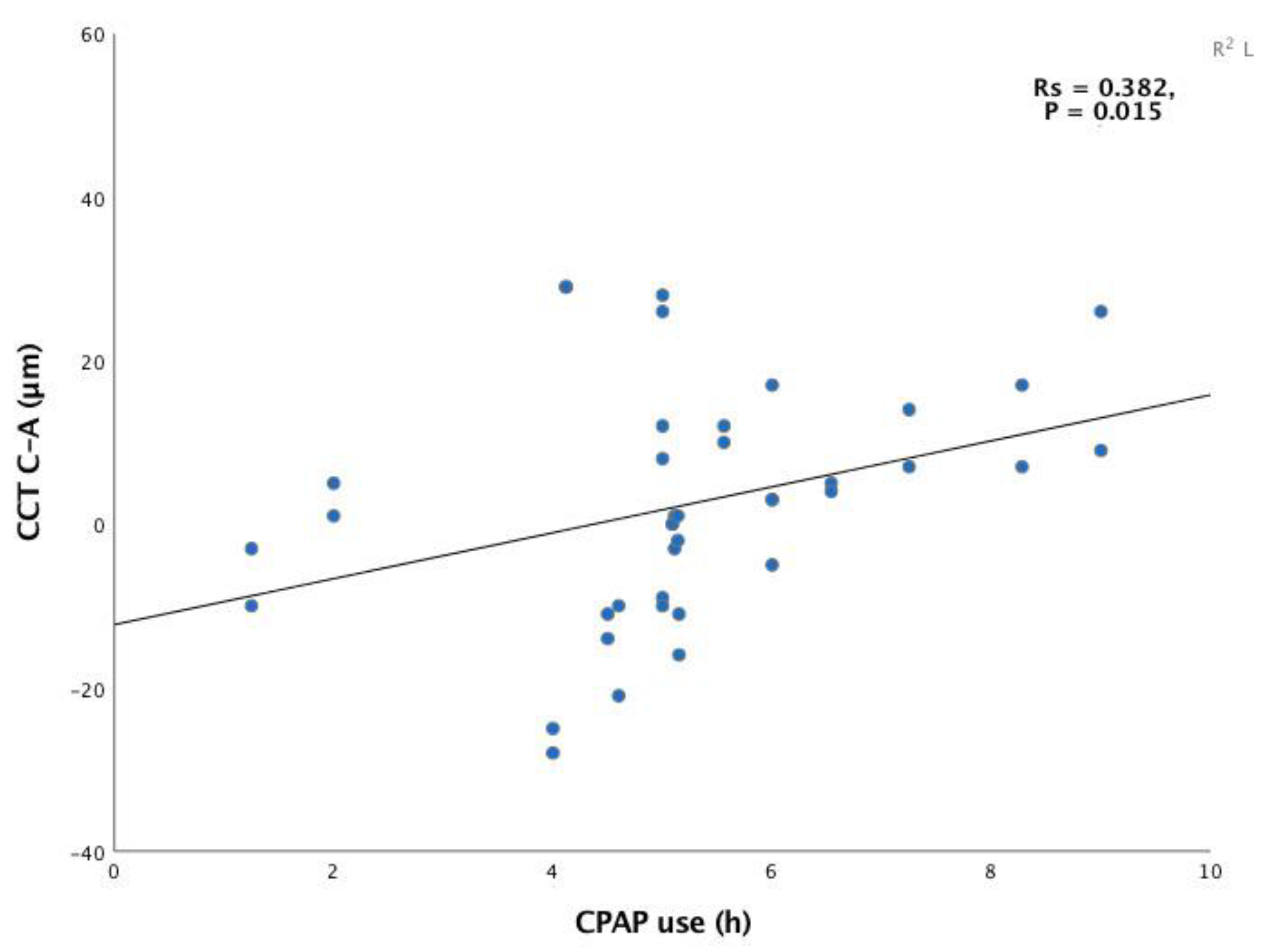
| CPAP use | Rs = 0.294 P = 0.065 |
Rs = 0.382 P = 0.015 |
| AHI | Rs = 0.061 P = 0.71 |
Rs = 0.291 P = 0.069 |
| Minimum SpO2 | Rs = - 0.066 P = 0.684 |
Rs = - 0.197 P = 0.224 |
| ODI | Rs = 0.082 P = 0.615 |
Rs = 0.394 P = 0.012 |
| CT90 | Rs = 0.254 P = 0.113 |
Rs = 0.324 P = 0.041 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




