Submitted:
06 July 2023
Posted:
07 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
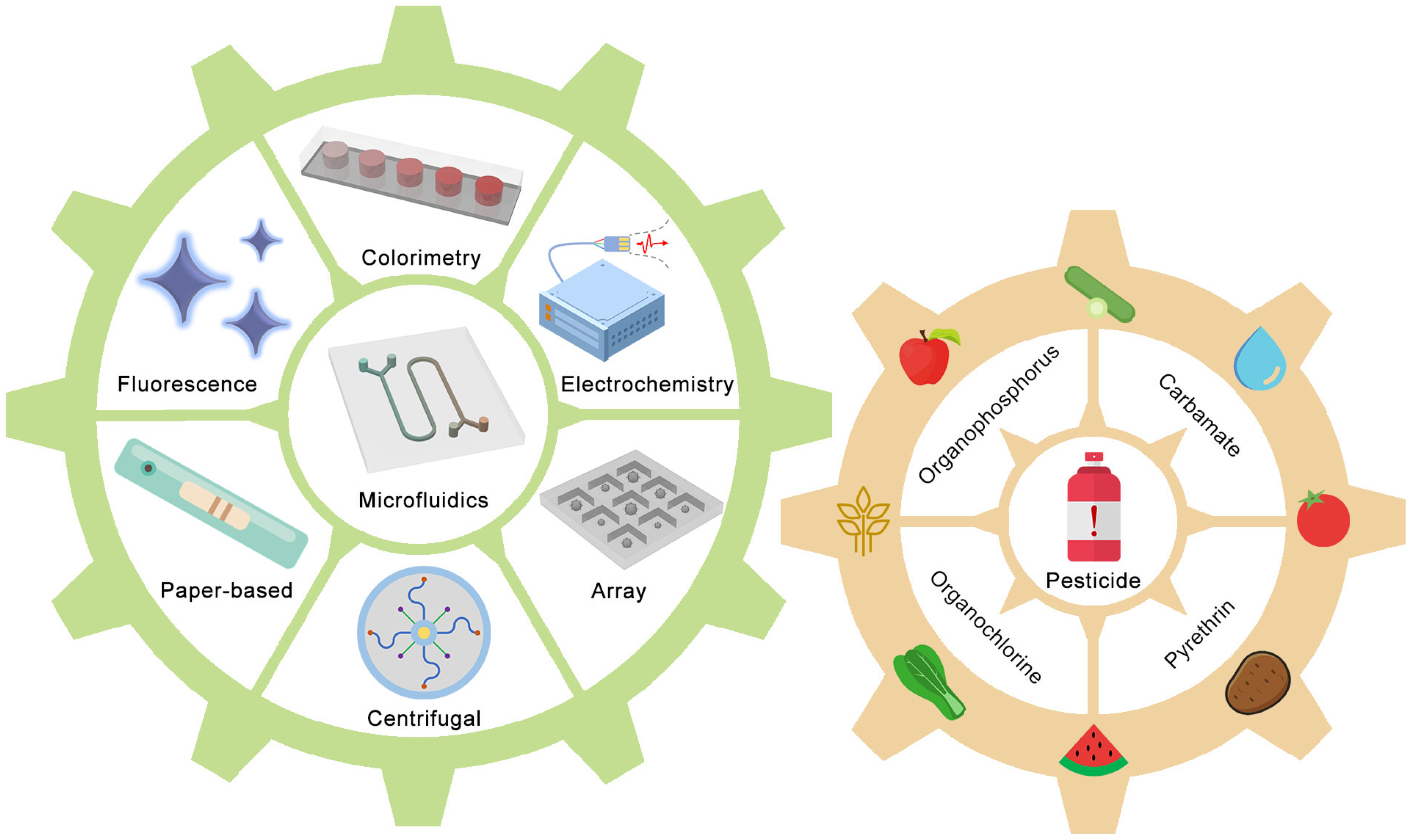
1. Introduction
2. Microfluidic devices for pesticide detection
2.1. Organophosphorus
2.2. Carbamate
2.3. Other pesticides
2.4. Commercialized products
3. Conclusion and future perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weng, X.; Neethirajan, S. Ensuring food safety: Quality monitoring using microfluidics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 10–22. [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.R.; McGuire, M.K.; Stokes, M.; Vicini, J.L. Assessing the Safety of Pesticides in Food: How Current Regulations Protect Human Health. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2019, 10, 80–88. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, M.; Peng, T.; Zhang, P.; Shen, R.; Jia, Y. Detection and discrimination of pathogenic bacteria with nanomaterials-based optical biosensors: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136578. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ibarlucea, B.; Peng, T.; Shen, R.; Li, P.; Zhang, P. Two birds with one stone: A multifunctional nanoplatform for photothermal sensitive detection and real-time inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus with NIR responsive Cu2−XSe@Van NPs. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2023, 381, 133475. [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Parks, C.G.; Goldner, W.S.; Kamel, F.; Umbach, D.M.; Ward, M.H.; Lerro, C.C.; Koutros, S.; Hofmann, J.N.; Freeman, L.E.B.; et al. Pesticide Use and Incident Hypothyroidism in Pesticide Applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2018, 126, 97008. [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 525–535. [CrossRef]
- Raanan, R. Exposure to pesticides and chronic respiratory health effects: what is the link? Thorax 2021, 76, 748-749.
- Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Ji, X.; Hao, Z.; Tao, Z. Smartphone-based enzyme-free fluorescence sensing of organophosphate DDVP. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 419. [CrossRef]
- Rani, L.; Thapa, K.; Kanojia, N.; Sharma, N.; Singh, S.; Grewal, A.S.; Srivastav, A.L.; Kaushal, J. An extensive review on the consequences of chemical pesticides on human health and environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 283, 124657. [CrossRef]
- Parks, C.; Costenbader, K.; Long, S.; Hofmann, J.; Beane, F.L.; Sandler, D. Pesticide use and risk of systemic autoimmune diseases in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112862–112862. [CrossRef]
- Bonner, M.R.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Hoppin, J.A.; Koutros, S.; Sandler, D.P.; Lynch, C.F.; Hines, C.J.; Thomas, K.; Blair, A.; Alavanja, M.C. Occupational Exposure to Pesticides and the Incidence of Lung Cancer in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2017, 125, 544–551. [CrossRef]
- Eskenazi, B.; Bradman, A.; Castorina, R. Exposures of children to organophosphate pesticides and their potential adverse health effects.. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 1999, 107, 409–419. [CrossRef]
- Lozowicka, B. Health risk for children and adults consuming apples with pesticide residue. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 502, 184–198. [CrossRef]
- Umapathi, R.; Park, B.; Sonwal, S.; Rani, G.M.; Cho, Y.; Huh, Y.S. Advances in optical-sensing strategies for the on-site detection of pesticides in agricultural foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 119, 69–89. [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Yang, T.; He, L. Review of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) detection of synthetic chemical pesticides. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 73–82. [CrossRef]
- Umapathi, R.; Sonwal, S.; Lee, M.J.; Rani, G.M.; Lee, E.-S.; Jeon, T.-J.; Kang, S.-M.; Oh, M.-H.; Huh, Y.S. Colorimetric based on-site sensing strategies for the rapid detection of pesticides in agricultural foods: New horizons, perspectives, and challenges. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 446, 214061. [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, I.d.S.; Pizzolato, T.M.; Gama, M.R. Quaternary ammonium pesticides: A review of chromatography and non-chromatography methods for determination of pesticide residues in water samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 35, e00171. [CrossRef]
- Varela-Martinez, D.A.; Gonzalez-Curbelo, M.A.; Gonzalez-Salamo, J.; Hernandez-Borges, J. Analysis of multiclass pesticides in dried fruits using QuEChERS-gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124961.
- Pang, X.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Xing, J.; Su, X.; Liu, G.; Yu, C.; Weng, R. Wide-Scope Multi-residue analysis of pesticides in beef by gas chromatography coupled with quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135171. [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, M.; Cao, J.; She, Y.; Cao, Z.; Hao, Z.; Jin, F.; Wang, J.; El-Aty, A.A. A method for the rapid determination of pesticides coupling thin-layer chromatography and enzyme inhibition principles. Food Chem. 2023, 416, 135822. [CrossRef]
- Tahirbegi, I.B.; Ehgartner, J.; Sulzer, P.; Zieger, S.; Kasjanow, A.; Paradiso, M.; Strobl, M.; Bouwes, D.; Mayr, T. Fast pesticide detection inside microfluidic device with integrated optical pH, oxygen sensors and algal fluorescence. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 188–195. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, J.; Lei, J.; Huo, D.; Huang, Q.; Tan, J.; Li, Y.; Hou, C.; Tian, F. A portable and automatic dual-readout detector integrated with 3D-printed microfluidic nanosensors for rapid carbamate pesticides detection. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2021, 346, 130454. [CrossRef]
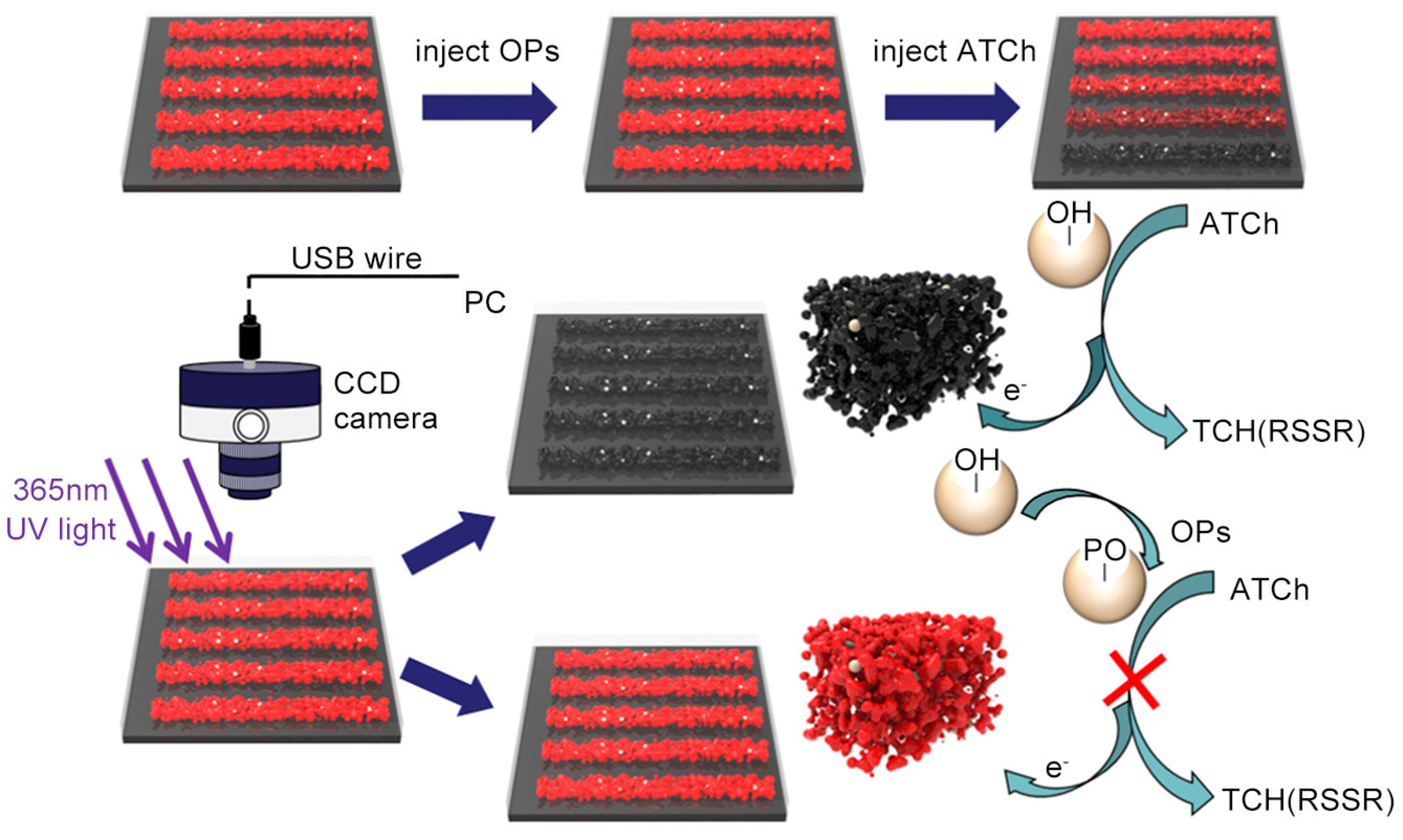
- Hu, T.; Xu, J.; Ye, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ni, Z. Visual detection of mixed organophosphorous pesticide using QD-AChE aerogel based microfluidic arrays sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 112–117. [CrossRef]
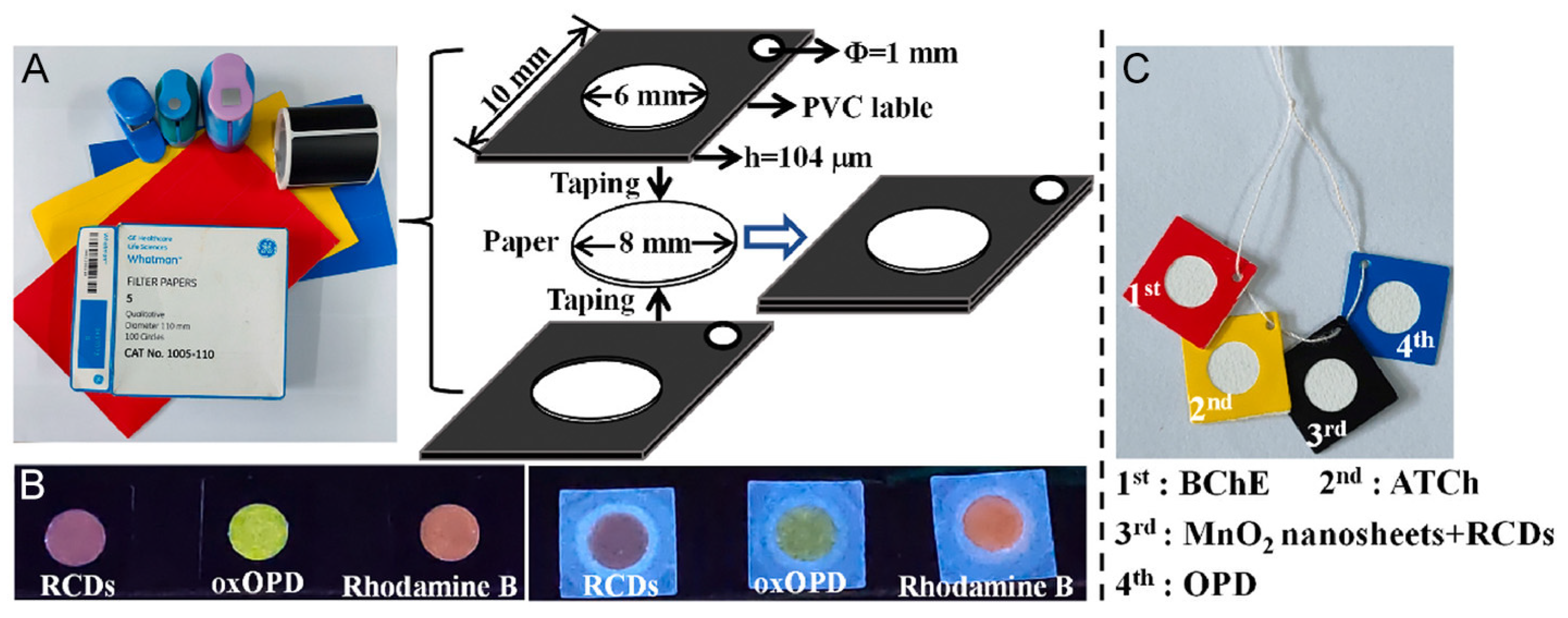
- Tong, X.; Cai, G.H.; Xie, L.W.; Wang, T.T.; Zhu, Y.F.; Peng, Y.Q.; Tong, C.Y.; Shi, S.Y.; Guo, Y. Threaded 3D microfluidic paper analytical device-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for background-free and visual detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 7.
- Kung, C.-T.; Hou, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-N.; Fu, L.-M. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for environmental analysis of soil, air, ecology and river water. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2019, 301, 126855. [CrossRef]
- Vicente, F.A.; Plazl, I.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Žnidaršič-Plazl, P. Separation and purification of biomacromolecules based on microfluidics. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4391–4410. [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Karadaghi, L.R.; Brutchey, R.L.; Malmstadt, N. Purification of Ionic Liquid Solvents in a Self-Optimizing, Continuous Microfluidic Process via Extraction of Metal Ions and Phase Separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 228–237. [CrossRef]
- Salva, M.L.; Rocca, M.; Hu, Y.; Delamarche, E.; Niemeyer, C.M. Complex Nucleic Acid Hybridization Reactions inside Capillary-Driven Microfluidic Chips. Small 2020, 16, e2005476. [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Meng, J.; Li, T.; Cheng, J.; Li, J. A droplet-based multivolume microfluidic device for digital polymerase chain reaction. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2022, 371, 132473. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J. Microfluidic methods for cell separation and subsequent analysis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1180–1192. [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, P.F.; Karimi-Sabet, J.; Amini, Y.; Fadaei, H. Pressure-driven liquid-liquid separation in Y-shaped microfluidic junctions. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 1075–1086. [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Yin, J.; Yue, M.; Mu, Y. Microfluidic devices for multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogens. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110246. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Yang, C.-E.; Ko, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-N.; Liu, C.-C.; Fu, L.-M. Microfluidic detection platform with integrated micro-spectrometer system. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124700. [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Liu, Y.; Mou, L.; Deng, J.; Jiang, X. Microfluidics-Based Biomaterials and Biodevices. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1805033. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, H.; Zong, N.; Jiang, X. Microfluidics for Biomedical Analysis. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900451. [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Emerging Droplet Microfluidics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7964–8040. [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Jiang, X. Materials for Microfluidic Immunoassays: A Review. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601403. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Yue, W.; Sohan, A.; Wan, X.; Zhou, T.; Shi, L.; Qian, C.; Lin, X. Construction of a desirable hyperbolic microfluidic chip for ultrasensitive determination of PCT based on chemiluminescence. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 1978–1986. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, H.; Zeng, S.; Peng, T.; Zhang, P.; Wan, X.; Lang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Jia, Y.; Shen, R.; et al. A self-designed device integrated with a Fermat spiral microfluidic chip for ratiometric and automated point-of-care testing of anthrax biomarker in real samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 230, 115283. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.-F.; Wan, X.-H.; Yang, M.-Z.; Qian, C.-C.; Sohan, A.S.M.M.F. Wave-shaped microfluidic chip assisted point-of-care testing for accurate and rapid diagnosis of infections. Mil. Med Res. 2022, 9, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Nilghaz, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Li, M.; Tian, J.; Cao, R.; Wang, X. Paper-based microfluidics for food safety and quality analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 273–284. [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Feng, X.; He, G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, T.; Yu, X. Recent advances in digital microfluidic chips for food safety analysis: Preparation, mechanism and application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 136–148. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mugahiry, B.; Al-Lawati, H.A.J. Recent analytical advancements in microfluidics using chemiluminescence detection systems for food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115802. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Sun, J.; Liang, R.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, X. Application progress of microfluidics-integrated biosensing platforms in the detection of foodborne pathogens. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 115–129. [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Ai, J.; Wang, N.; Pu, Q. Recent progress of smartphone-assisted microfluidic sensors for point of care testing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116792. [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Shen, H.; Deng, K.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C. Microfluidic devices with simplified signal readout. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2021, 339, 129730. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Pu, H.; Sun, D. Computer simulation of submicron fluid flows in microfluidic chips and their applications in food analysis. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3818–3837. [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, R.; Lee, N.Y. Recent progress in smartphone-based techniques for food safety and the detection of heavy metal ions in environmental water. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130096. [CrossRef]
- Kudr, J.; Zitka, O.; Klimanek, M.; Vrba, R.; Adam, V. Microfluidic electrochemical devices for pollution analysis–A review. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2017, 246, 578–590. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Zheng, W.; Dong, M.; Yu, W.; Chen, Y.; Joo, S.W.; Jiang, X. An enzyme-mediated competitive colorimetric sensor based on Au@Ag bimetallic nanoparticles for highly sensitive detection of disease biomarkers. Anal. 2017, 142, 2954–2960. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Wu, J.; Ran, B.; Xie, M.; Joo, S.W.; Chen, Y. One-step multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogens: Combining a quantum dot-mediated reverse assaying strategy and magnetic separation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 996–1002. [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Cai, G.H.; Xie, L.W.; Wang, T.T.; Zhu, Y.F.; Peng, Y.Q.; Tong, C.Y.; Shi, S.Y.; Guo, Y. Threaded 3D microfluidic paper analytical device-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for background-free and visual detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 114981.
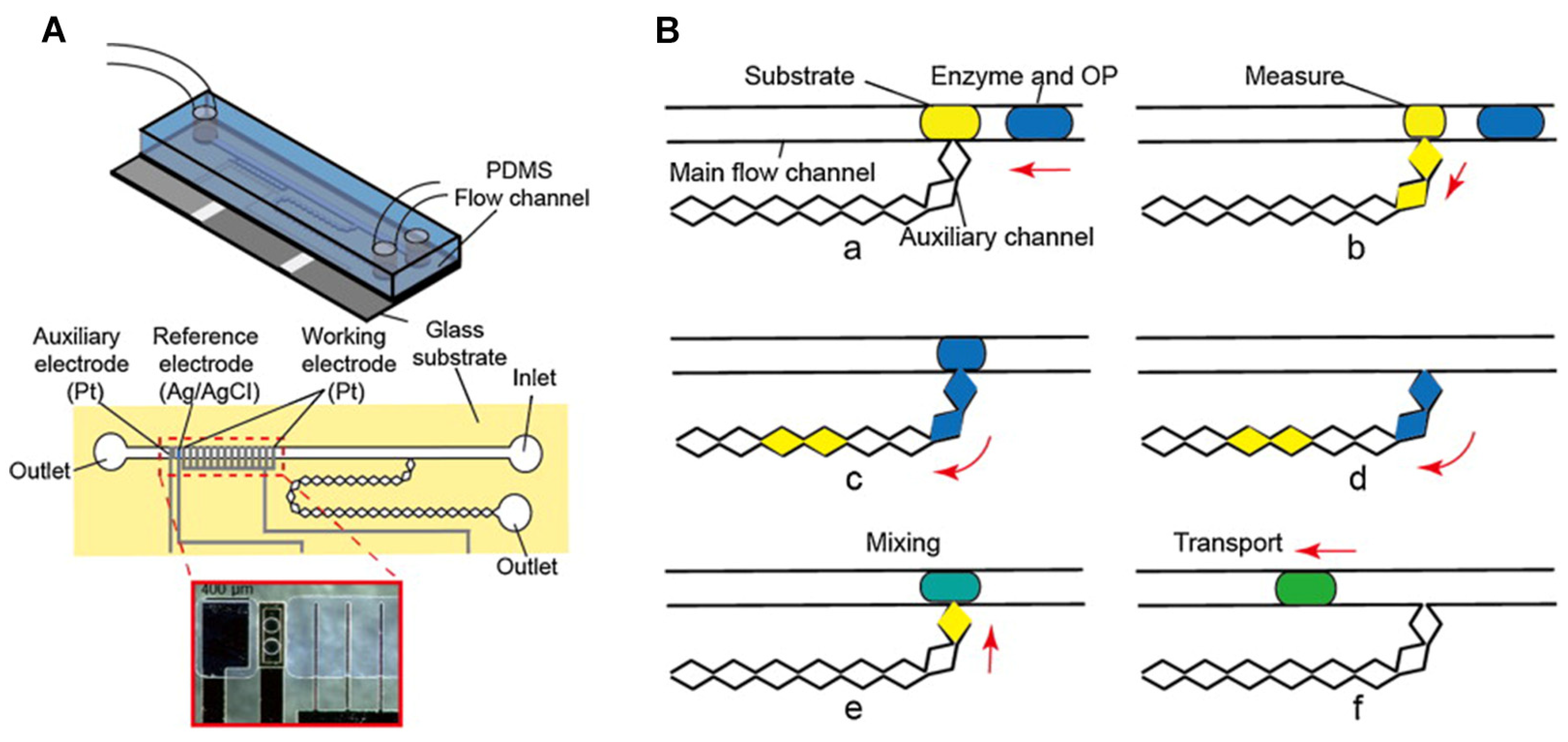
- Wang, J.; Suzuki, H.; Satake, T. Coulometric microdevice for organophosphate pesticide detection. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2014, 204, 297–301. [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.; Ogunneye, A.; Barbarinde, N.; Erenas, M.; Capitán-Vallvey, L. Bioactive microfluidic paper device for pesticide determination in waters. Talanta 2020, 218, 121108. [CrossRef]
- Della Pelle, F.; Del Carlo, M.; Sergi, M.; Compagnone, D.; Escarpa, A. Press-transferred carbon black nanoparticles on board of microfluidic chips for rapid and sensitive amperometric determination of phenyl carbamate pesticides in environmental samples. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 3143–3149. [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Lu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Q. Droplet-based microfluidics for dose–response assay of enzyme inhibitors by electrochemical method. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 796, 68–74. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Huangfu, C.; Zhu, M.; Li, C.; Feng, L. The BODIPY-based chemosensor for the fluorometric determination of organochlorine pesticide dicofol. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131033. [CrossRef]
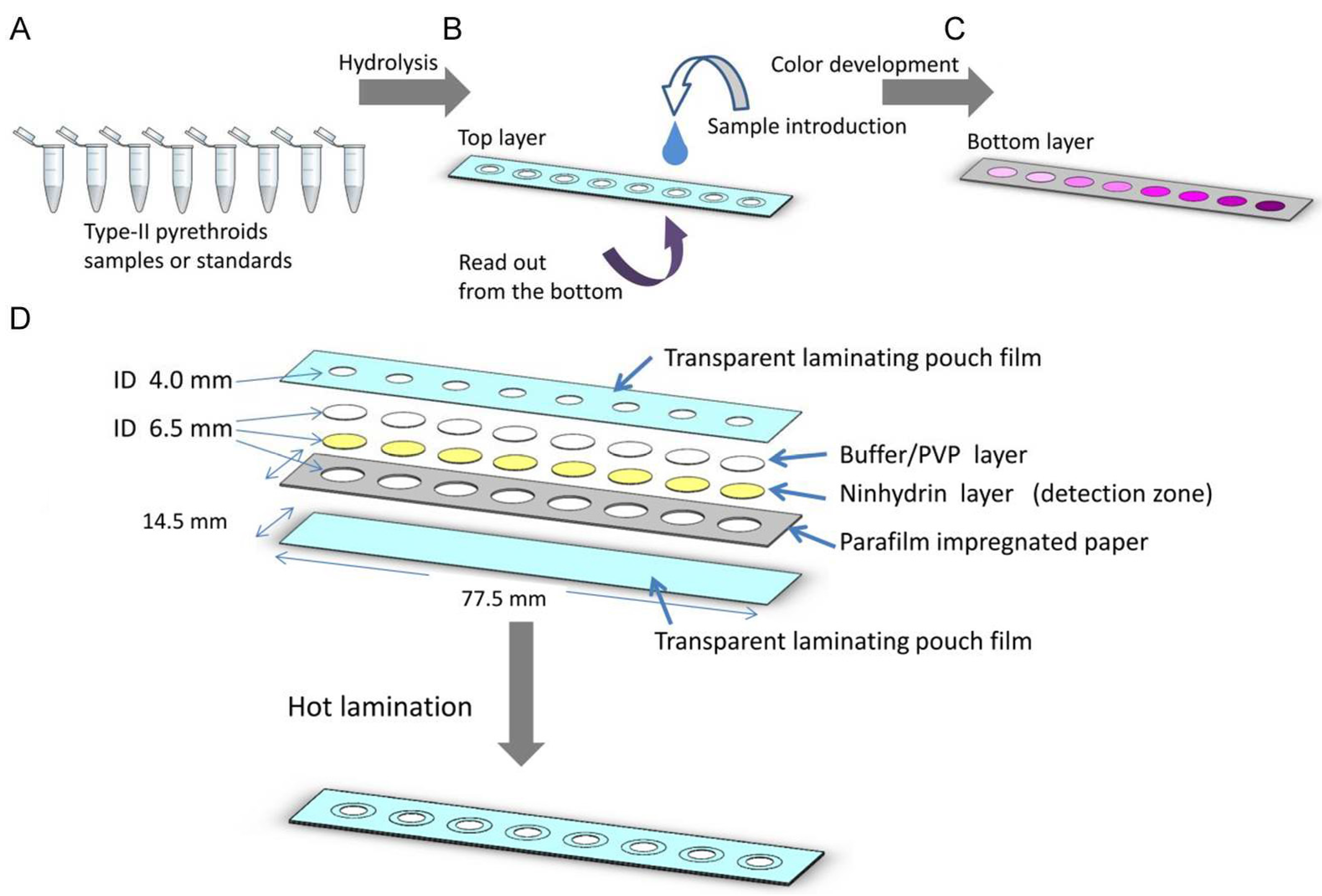
- Pengpumkiat, S.; Nammoonnoy, J.; Wongsakoonkan, W.; Konthonbut, P.; Kongtip, P. A Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device for Type-II Pyrethroid Targets in an Environmental Water Sample. Sensors 2020, 20, 4107. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; You, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X. Determination of residual organophosphorus thioester pesticides in agricultural products by chemical isotope-labelling liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with in-syringe dispersive solid phase clean-up and in situ cleavage. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1055, 44–55. [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, V.K.; Buncel, E.; Vanloon, G.W. Micellar Catalyzed Degradation of Fenitrothion, an Organophosphorus Pesticide, in Solution and Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5824–5830. [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Liu, H.; Ge, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tan, P.; Bai, J.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Chitosan oligosaccharide alleviates and removes the toxicological effects of organophosphorus pesticide chlorpyrifos residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130669. [CrossRef]
- Pawar, K.S.; Bhoite, R.R.; Pillay, C.P.; Chavan, S.C.; Malshikare, D.S.; Garad, S.G. Continuous pralidoxime infusion versus repeated bolus injection to treat organophosphorus pesticide poisoning: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 2136–2141. [CrossRef]
- Engel, S.M.; Bradman, A.; Wolff, M.S.; Rauh, V.A.; Harley, K.G.; Yang, J.H.; Hoepner, L.A.; Barr, D.B.; Yolton, K.; Vedar, M.G.; et al. Prenatal Organophosphorus Pesticide Exposure and Child Neurodevelopment at 24 Months: An Analysis of Four Birth Cohorts. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2016, 124, 822–830. [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Xue, N.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Majdi, H.S.; Darvishmoghaddam, E.; Assilzadeh, H.; Khadimallah, M.A.; Ali, H.E. Risk assessment of organophosphorus pesticide residues in drinking water resources: Statistical and Monte-Carlo approach. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135632. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, S.; Sun, X.; Yi, W.; Pan, R.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Su, H. Association between organophosphorus pesticide exposure and depression risk in adults: A cross-sectional study with NHANES data. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120445. [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhan, J.; Liu, D.; Luo, M.; Han, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, P. Organophosphorus pesticide chlorpyrifos intake promotes obesity and insulin resistance through impacting gut and gut microbiota. Microbiome 2019, 7, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, G.W.; Park, T.J. A facile and sensitive detection of organophosphorus chemicals by rapid aggregation of gold nanoparticles using organic compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 408–412. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Rong, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Z. MnO2 switch-bridged DNA walker for ultrasensitive sensing of cholinesterase activity and organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112605. [CrossRef]
- Cancar, H.D.; Soylemez, S.; Akpinar, Y.; Kesik, M.; Göker, S.; Gunbas, G.; Volkan, M.; Toppare, L. A Novel Acetylcholinesterase Biosensor: Core–Shell Magnetic Nanoparticles Incorporating a Conjugated Polymer for the Detection of Organophosphorus Pesticides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8058–8067. [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Tian, T.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, H. Smartphone-assisted sensor array constructed by copper-based laccase-like nanozymes for specific identification and discrimination of organophosphorus pesticides. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136477. [CrossRef]
- Schütze, A.; Morales-Agudelo, P.; Vidal, M.; Calafat, A.M.; Ospina, M. Quantification of glyphosate and other organophosphorus compounds in human urine via ion chromatography isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129427–129427. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Yu, L.; Hou, T.; Hu, R.; Li, F. Direct and Specific Detection of Glyphosate Using a Phosphatase-like Nanozyme-Mediated Chemiluminescence Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 4479–4485. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Pan, X.; Gan, J.; Zheng, Y. Simultaneous determination of organophosphorus pesticides in fruits and vegetables using atmospheric pressure gas chromatography quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 365–373. [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Zou, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, G.; Guo, M.; Ai, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Z. Development of a sensitive phage-mimotope and horseradish peroxidase based electrochemical immunosensor for detection of O,O-dimethyl organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 218, 127419. [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Jiao, B.; He, Y. CRISPR-Cas12a based fluorescence assay for organophosphorus pesticides in agricultural products. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132919. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, H.; Wei, Y.; Yang, H.; Gu, Y. Ultrathin C3N4 nanosheets-based oxidase-like 2D fluorescence nanozyme for dual-mode detection of organophosphorus pesticides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131171. [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. Upconversion nanoparticle-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay for organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 168–174. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Tian, X.Y.; Fan, Y.S.; Sun, Z.B.; Zheng, K.Y.; Zou, X.B.; Zhang, W. TPB-DMTP@S-CDs/MnO2 Fluorescence Composite on a Dual- Emission-Capture Sensor Module for Fingerprint Recognition of Organophosphorus Pesticides. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 2741–2749.
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Tu, Z.; Sun, X.; He, Q.; Lei, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Organophosphorus pesticides detection using broad-specific single-stranded DNA based fluorescence polarization aptamer assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 216–219. [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wei, J.; Ren, X.; Ren, J.; Tang, F. A simple and sensitive fluorescence biosensor for detection of organophosphorus pesticides using H2O2-sensitive quantum dots/bi-enzyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 402–407. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, Z.; Tong, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, L.; Liu, K.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Two birds with one stone: An enzyme-regulated ratiometric fluorescent and photothermal dual-mode probe for organophosphorus pesticide detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 224, 115074. [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, V.; Palanisamy, S.; Chen, S.-W.; Balu, S.; Yang, T.C.; Banks, C.E. Novel electrochemical synthesis of cellulose microfiber entrapped reduced graphene oxide: A sensitive electrochemical assay for detection of fenitrothion organophosphorus pesticide. Talanta 2019, 192, 471–477. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fan, K.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y. Exploring pralidoxime chloride as a universal electrochemical probe for organophosphorus pesticides detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 982, 78–83. [CrossRef]
- Gopi, P.K.; Ngo, D.B.; Chen, S.-M.; Ravikumar, C.H.; Surareungchai, W. High-performance electrochemical sensing of hazardous pesticide Paraoxon using BiVO4 nano dendrites equipped catalytic strips. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132511. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. Portable electrochemical biosensor based on laser-induced graphene and MnO2 switch-bridged DNA signal amplification for sensitive detection of pesticide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 199, 113906. [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhou, X.; Yu, D.; Jiao, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, S.; Yin, H.; Mao, H. Pesticide residues identification by impedance time-sequence spectrum of enzyme inhibition on multilayer paper-based microfluidic chip. J. Food Process. Eng. 2020, 43, 127419. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Su, H.; Qu, X.; Ju, P.; Cui, L.; Ai, S. Acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on 3-carboxyphenylboronic acid/reduced graphene oxide–gold nanocomposites modified electrode for amperometric detection of organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2011, 160, 1255–1261. [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.; Dooley, K.; Cropek, D.M.; West, A.C.; Banta, S. A dual enzyme electrochemical assay for the detection of organophosphorus compounds using organophosphorus hydrolase and horseradish peroxidase. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2011, 158, 353–360. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z. Determination of some organophosphorus pesticides in water and watermelon samples by microextraction prior to high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 3231–3239. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Preparation, characterization of Fe3O4 at TiO2 magnetic nanoparticles and their application for immunoassay of biomarker of exposure to organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 669–674. [CrossRef]
- Jarrard, H.; Delaney, K.; Kennedy, C. Impacts of carbamate pesticides on olfactory neurophysiology and cholinesterase activity in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 69, 133–148. [CrossRef]
- Pulgarín, J.A.M.; Bermejo, L.F.G.; Durán, A.C. Determination of carbamates in soils by liquid chromatography coupled with on-line postcolumn UV irradiation and chemiluminescence detection. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 13, 2778–2784. [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Concentrations of organophosphorus pesticides in fresh vegetables and related human health risk assessment in Changchun, Northeast China. Food Control. 2016, 60, 353–360. [CrossRef]
- Beland, F.A.; Benson, R.W.; Mellick, P.W.; Kovatch, R.M.; Roberts, D.W.; Fang, J.-L.; Doerge, D.R. Effect of ethanol on the tumorigenicity of urethane (ethyl carbamate) in B6C3F1 mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.; Qi, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y. Quantification ethyl carbamate in wines using reaction-assisted-extraction with 9-xanthydrol and detection by heart-cutting multidimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1001, 86–92. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Z.; Pang, S.; Huang, Y.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Carbofuran toxicity and its microbial degradation in contaminated environments. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127419. [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.-B.; Mani, S.; Parvathinathan, G.; Kanth, R.S. Pesticide Impact Assessment via Using Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Technique in the Lower Rio Grande River Basin, Texas. Water Qual. Expo. Heal. 2009, 1, 145–158. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, J.-M.; Choi, G.-H.; Kim, Y.-W. Development of easy and efficient methods for quantitative analysis of ethyl carbamate using GC-MS in various fermented foods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 599–603. [CrossRef]
- Silva, .A.S.; Lopez-Avila, V.; Pawliszyn, J. Fast and robust direct immersion solid phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry method employing a matrix compatible fiber for determination of triazole fungicides in fruits. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1313, 139–146. [CrossRef]
- Valente, I.M.; Ramos, R.M.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Rodrigues, J.A. Determination of ethyl carbamate in spirits using salting-out assisted liquid–liquid extraction and high performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9136–9141. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; She, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; El-Aty, A.M.A. Acetylcholinesterase Immobilized on Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Coupled with Fluorescence Analysis for Rapid Detection of Carbamate Pesticides. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 1327–1338. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Sun, X.; Wan, X.; Qian, C.; Yue, W.; Sohan, A.S.M.M.F.; Lin, X.; Yin, B. A cascade Fermat spiral microfluidic mixer chip for accurate detection and logic discrimination of cancer cells. Anal. 2022, 147, 3424–3433. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.F.; Wan, X.H.; Sohan, A.; Lin, X.D. Microfluidics-Based POCT for SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostics. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1238.
- Yin, B.; Qian, C.; Wan, X.; Sohan, A.M.F.; Lin, X. Tape integrated self-designed microfluidic chip for point-of-care immunoassays simultaneous detection of disease biomarkers with tunable detection range. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 212, 114429. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, O.; Fan, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Lan, W.; Hu, Y.; Xie, X.; Ma, L.; She, Y.; et al. Fluorescence paper-based sensor for visual detection of carbamate pesticides in food based on CdTe quantum dot and nano ZnTPyP. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127075. [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Kong, D.; Jin, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Liu, F.; Lin, Y.; Lu, G. Fluorometric and colorimetric analysis of carbamate pesticide via enzyme-triggered decomposition of Gold nanoclusters-anchored MnO2 nanocomposite. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2019, 290, 640–647. [CrossRef]
- Bacchin, P.; Snisarenko, D.; Stamatialis, D.; Aimar, P.; Causserand, C. Combining fluorescence and permeability measurements in a membrane microfluidic device to study protein sorption mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118485. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ye, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, H.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H. Simultaneous detection of multiple foodborne bacteria by loop-mediated isothermal amplification on a microfluidic chip through colorimetric and fluorescent assay. Food Control. 2021, 134, 118485. [CrossRef]
- Habibey, R. Incubator-independent perfusion system integrated with microfluidic device for continuous electrophysiology and microscopy readouts. Biofabrication 2023, 15, 118485. [CrossRef]
- Muluneh, M.; Kim, B.; Buchsbaum, G.; Issadore, D. Miniaturized, multiplexed readout of droplet-based microfluidic assays using time-domain modulation. Lab a Chip 2014, 14, 4638–4646. [CrossRef]
- Peric, O.; Hannebelle, M.; Adams, J.D.; Fantner, G.E. Microfluidic bacterial traps for simultaneous fluorescence and atomic force microscopy. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3896–3908. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Yue, W.; Sohan, A.S.M.M.F.; Zhou, T.; Qian, C.; Wan, X. Micromixer with Fine-Tuned Mathematical Spiral Structures. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30779–30789. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Wan, X.; Qian, C.; Sohan, A.S.M.M.F.; Zhou, T.; Yue, W. Enzyme Method-Based Microfluidic Chip for the Rapid Detection of Copper Ions. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1380. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Wan, X.; Qian, C.; Sohan, A.S.M.M.F.; Wang, S.; Zhou, T. Point-of-Care Testing for Multiple Cardiac Markers Based on a Snail-Shaped Microfluidic Chip. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 741058. [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Gao, L.; Zhu, S.; Qiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Ai, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Lu, M.; Zheng, M. Target and non-target analysis of organochlorine pesticides and their transformation products in an agrochemical-contaminated area. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138314. [CrossRef]
- Potapowicz, J.; Lambropoulou, D.; Nannou, C.; Kozioł, K.; Polkowska, Z. Occurrences, sources, and transport of organochlorine pesticides in the aquatic environment of Antarctica. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 735, 139475. [CrossRef]
- Kafaei, R.; Arfaeinia, H.; Savari, A.; Mahmoodi, M.; Rezaei, M.; Rayani, M.; Sorial, G.A.; Fattahi, N.; Ramavandi, B. Organochlorine pesticides contamination in agricultural soils of southern Iran. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124983. [CrossRef]
- Tsygankov, V.Y. Organochlorine pesticides in marine ecosystems of the Far Eastern Seas of Russia (2000–2017). Water Res. 2019, 161, 43–53. [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, A.M. A review of environmental and health effects of organochlorine pesticide residues in Africa. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 1126–1140. [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Miao, J.; Chen, Y.; Yin, D.; Hu, S.; Sheng, G.D. The long-term environmental risks from the aging of organochlorine pesticide lindane. Environ. Int. 2020, 141, 105778. [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wong, M.; Xu, S.; Cai, Z. Association of prenatal exposure to organochlorine pesticides and birth size. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 654, 678–683. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Toms, L.-M.L.; Harden, F.A.; Hobson, P.; White, N.M.; Mengersen, K.L.; Mueller, J.F. Concentrations of organochlorine pesticides in pooled human serum by age and gender. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 10–18. [CrossRef]
- Heys, K.A.; Shore, R.F.; Pereira, M.G.; Martin, F.L. Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides Are Associated with Amyloid Aggregation in Apex Avian Brains. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8672–8681. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, .G.P.; López, M.I.R.; Casillas, T..D.; León, J.A.A.; Mahjoub, O.; Prusty, A.K. Monitoring of organochlorine pesticides in blood of women with uterine cervix cancer. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 853–862. [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.N.; Rauf, S.; Mohammad, A.; Eqani, S.-A.S.; Ahad, K. Organochlorine residual concentrations in cattle egret from the Punjab Province, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 325–341. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Fakhruddin, A.; Islam, N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Gan, S.H.; Alam, K. Detection of the residues of nineteen pesticides in fresh vegetable samples using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Control. 2013, 34, 457–465. [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, M.; Xu, S.; Yan, D. Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: An overview. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 990–1007. [CrossRef]
- Bajunirwe, F. Pyrethroid resistance in sub-Saharan Africa. Lancet 2020, 395, 1236–1237. [CrossRef]
- Stellman, S.D.; Stellman, J.M. Pyrethroid Insecticides—Time for a Closer Look. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 374-375. [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.A. Exposure to Pyrethroids and Health Risk. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1027-1028. [CrossRef]
- (Halcomb), S.E.D.; Cole, M.; Sheets, L. Exposure to Pyrethroids and Health Risk. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1028. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Li, Z.; Zuberi, A.; Arifeen, M.Z.U.; Baig, M.M.F.A. Biomarkers of pyrethroid toxicity in fish. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 945–973. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, N.; Wang, C. Toxicity of the pyrethroid bifenthrin insecticide. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1377–1391. [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Qian, C.; Wang, S.; Wan, X.; Zhou, T. A Microfluidic Chip-Based MRS Immunosensor for Biomarker Detection via Enzyme-Mediated Nanoparticle Assembly. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 688442. [CrossRef]
- MycoLab™ Afla-Quick™. Available online: https://www.envirologix.com/mycolab-afla-quick (accessed on 30th June).
- Raptor™ Integrated Analysis Platform. Available online: https://advancedanimaldiagnostics.com/products/raptor-platform (accessed on 25th June).
- Página no encontrada - Certest Biotec - Raw Materials | Diagnostics | Pharma. Available online: https://www.certest.es/en/products/pesticide-detect (accessed on 30th June).
- ToxiQuant™ Pesticide Microarray Kit. Available online: https://www.biosensingusa.com/products/pesticide-microarray (accessed on 27th June).
- SERS-based Portable Microfluidic Sensor. Available online: https://www.gbctechtraining.com/product_list/sensors.aspx (accessed on 27th June).
- iTube. Available online: https://ayanda-biosystems.com/itube-technology/ (accessed on 30th June).
- RapidChek® SELECT™ Salmonella. Available online: https://www.romerlabs.com/foodsafety/rapidchek-select-salmonella/ (accessed on 26th June).
- BioFlash Biological Identifier - Mobile, high sensitivity biothreat detector | Smiths Detection. Available online: https://www.smithsdetection.com/products/bioflash-biological-identifier/ (accessed on 30th June).
- MELISA-45 System. Available online: https://www.ibistech.net/products/melisa-45/ (accessed on 25th June).
- ATHENA Integrated System. Available online: https://www.cabn.manchester.ac.uk/research/focus-areas/nanotechnology/ (accessed on 27th June).
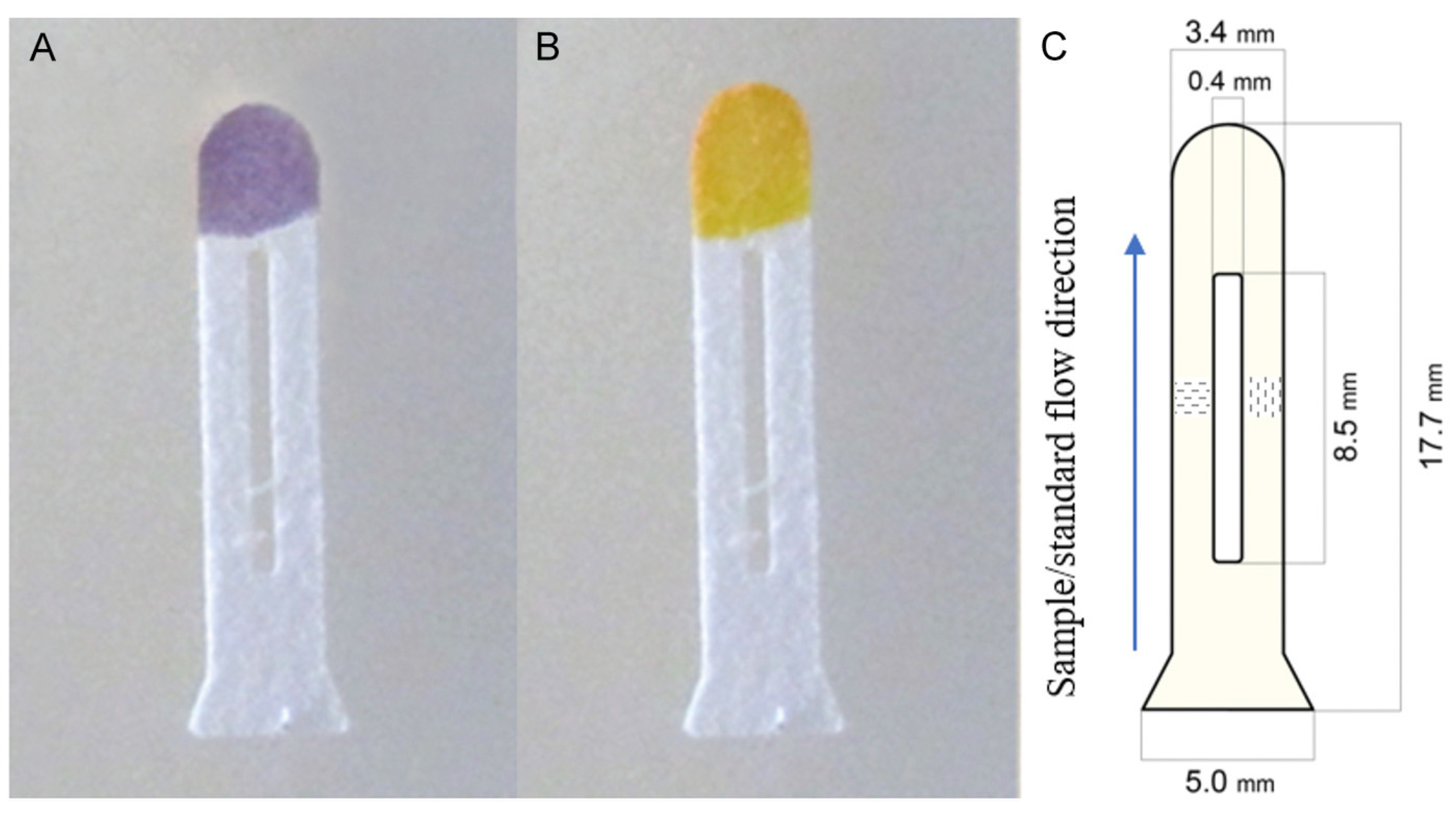
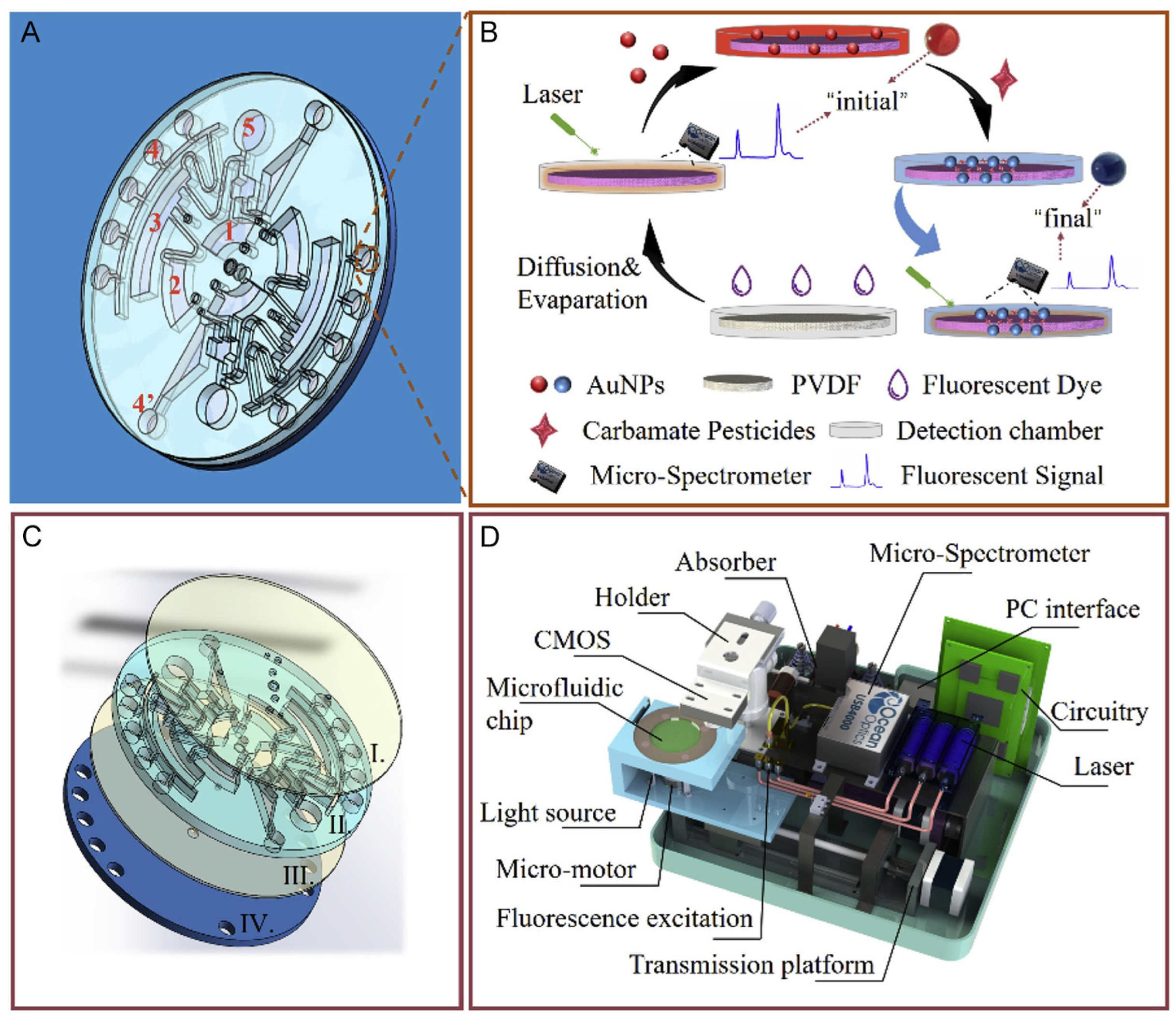
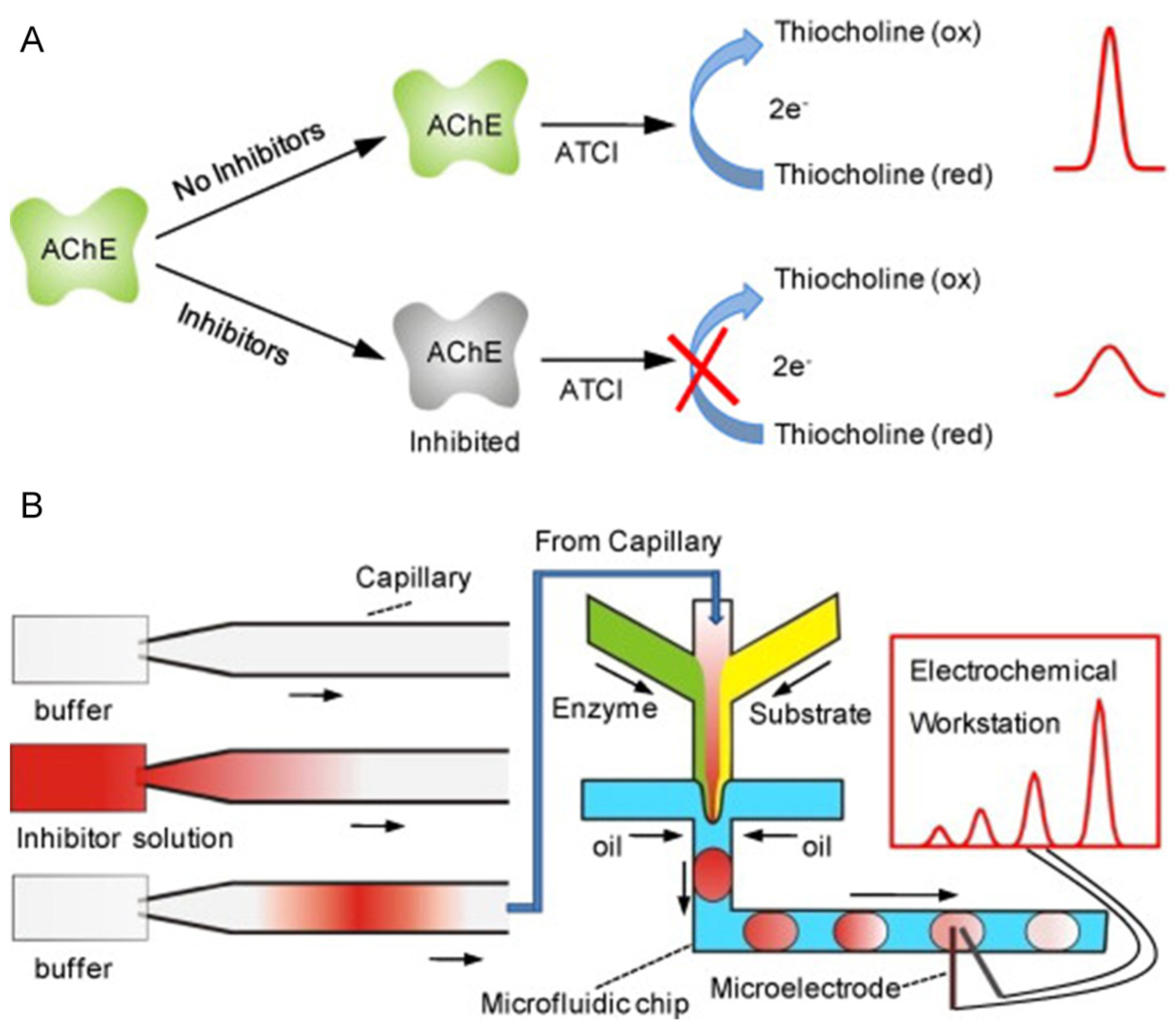
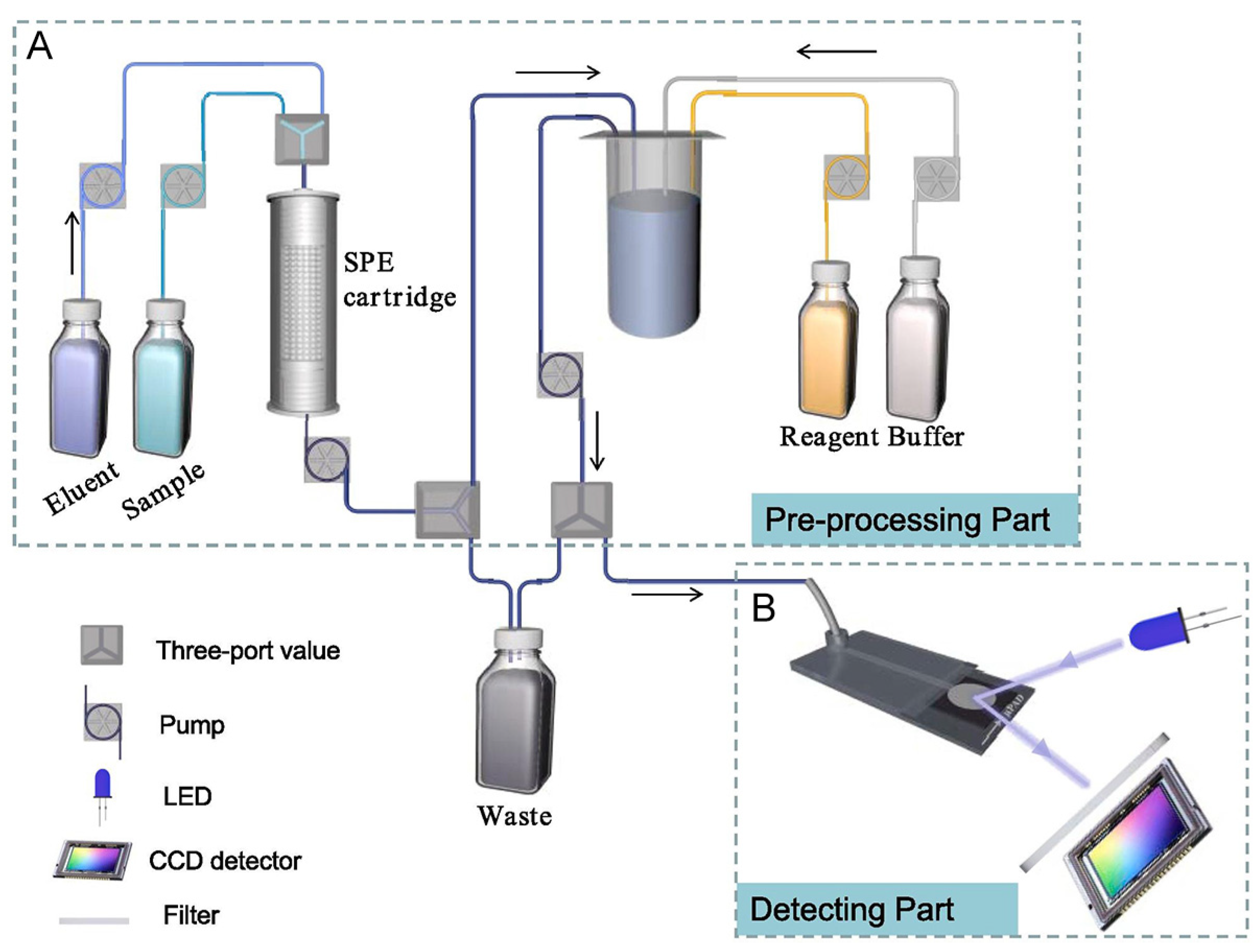
| Pesticide type | Detected pesticides |
Characteristic of the microflfluidic device and the analysis |
Real sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organophosphorus | Paraoxon | LOD: 0.38 pM Assay time: 5 min QD-AChEaerogel based microfluidic arrays sensor Linear range: 10-12-10-5 M |
Apple | [23] |
| DDVP | LOD: 1.0 μg L-1 Assay time: 30 min Threaded 3D microfluidic paper analytical device-based sensor Linear range:2.5-120 μg L-1 |
Spinach Tomato |
[52] | |
| Malathion | LOD:33 nM Assay time:7 min A coulometric microdevice based on plug-based microfluidics Linear range: 10−10-10−2 M |
Waters | [53] | |
| Carbamate | Chlorpyrifos | LOD: 2.0 μg L-1 Assay time:35 min Bioactive microfluidic paper device Linear range:2.0-45 μg L-1 |
Waters | [54] |
| Carbendazim | LOD: 3.102 ppb Assay time:12 min 3D-printed microfluidic nanosensors Linear range: 0.01-10 ppm |
Cabbage | [22] | |
| Carbofuran | LOD: 0.9 μM Assay time:6min Electrochemical microfluidics based on carbon black nanoparticles Linear range: 25-125 μM |
Waters | [55] | |
| Carbaryl | LOD: 15.6 μM Assay time:6 min A simple but robust droplet-based microfluidic system Linear range: 15.6-21.8 μM |
Waters | [56] | |
| Organochlorine | Dicofol | LOD: 200 pbb Assay time:20 min A paper based microfluidic device modified by PTES Linear range: 0-10 ppm |
Tea | [57] |
| Pyrethroid | Cypermethrin | LOD:2.5 µg/mL Assay time:6min A Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device Linear range: 2-15 µg/mL |
Waters | [58] |
| Product Name | Manufacturer | Detected pesticides | Types of Microfluidics technology | Time | Target | Sensitivity | Storage and Stability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MycoLab™ Afla-Quick™ | EnviroLogix Inc | Aflatoxins | Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) | 10 min | Aflatoxins in various food samples | Detects aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, G2 at low ppb levels | Stable at room temperature, shelf life of 12 months | [135] |
| Raptor™ Integrated Analysis Platform | Advanced Animal Diagnostics (AAD) | Various pesticides (customizable) | Microfluidic Immunoassay | 30 min | Pesticides in food and feed samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at room temperature, shelf life of 18 months | [136] |
| Pesticide Detect™ | CerTest Biotec | Various pesticides (customizable) | Microfluidic Immunochromatography | 10 min | Pesticides in food and water samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at room temperature, shelf life of 12 months | [137] |
| ToxiQuant™ Pesticide Microarray Kit | Biosensing Instrument Inc. | Various pesticides (customizable) | Microarray-based detection | 2-3 hours | Pesticides in food and environmental samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at refrigeration temperature, shelf life of 6 months | [138] |
| SERS-based Portable Microfluidic Sensor | GBC Scientific Equipment | Various pesticides (customizable) | Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) | minutes | Pesticides in food and water samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at room temperature, dependent on the instrument | [139] |
| iTube | Ayanda Biosystems | Various pesticides (customizable) | Smartphone-based colorimetric assay | minutes | Pesticides in food samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at room temperature, dependent on the smartphone | [140] |
| RapidChek® SELECT™ Salmonella | Romer Labs | Various pesticides (customizable) | Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) | 15 min | Pesticides in food samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at room temperature, shelf life of 12 months | [141] |
| BioFlash Biological Identifier | Smiths Detection | Various pesticides (customizable) | Immunomagnetic Separation (IMS) | minutes | Pesticides in food and environmental samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at room temperature, dependent on the instrument | [142] |
| MELISA-45 System | IBIS Technologies | Various pesticides (customizable) | Mass Spectrometry | minutes | Pesticides in food and environmental samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at room temperature, dependent on the instrument | [143] |
| ATHENA Integrated System | Centre for Advanced BioNano Systems (Australia) | Various pesticides (customizable) | Lab-on-a-chip | minutes | Pesticides in food samples | Customizable to different pesticide targets | Stable at room temperature, dependent on the instrument | [144] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




