1. Introduction
Kidneys play an important role in many vital tasks such as maintaining water and electrolyte balance in our body, regulating acid-base balance, regulating blood pressure with the renin they secrete, regulating the body's production of erythropoietin with erythrocyte, activating vitamin D3, and removing drugs and toxins from the body [
1]. Kidneys are the target organs for many drugs and toxic substances, especially due to their high metabolic activity, removal of harmful substances from the body and active transport functions. [
2]. Nephrotoxicity is the condition in which the structure of the kidney is damaged by chemicals and decreases by affecting the kidney function negatively. In the case of drug-induced nephrotoxicity, acute kidney injury occurs with cell death due to apoptosis and necrosis, and may lead to death due to kidney failure. Therefore, drug-induced nephrotoxicity may be the primary cause of morbidity and mortality [
3]. Today, the use of chemotherapeutic agents has increased considerably due to the increase in cancer cases. MTX, a chemotherapeutic agent, is widely used in leukemia, osteosarcoma, lymphoma, head and neck tumors, breast cancer, lung cancer, and some other cancer types [
4]. MTX and its metabolites are largely eliminated by the kidney and enter cells by active transport. In the mechanism of MTX-induced kidney toxicity; The direct toxic effect of MTX, inhibition of enzymes related to DNA synthesis and increasing the production of free oxygen radicals (ROS) are seen. ROS are directly or indirectly involved in a wide variety of clinical disorders such as atherosclerosis, viral infection, reperfusion injury, macular degeneration, pulmonary toxicity, cataractogenesis, diabetes, cancer, and toxic cell damage [
5,
6]. Clinical and toxicological assessment of kidney function routinely relies on measurement of blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine, but their relatively low sensitivity often precludes early detection of kidney injury. Therefore, it is important to identify new sensitive and reliable biomarkers of renal nephrotoxicity. In addition, the development of new biomarkers that can accurately detect drug-induced kidney damage is needed both for drug development studies and for clarification and treatment of the mechanism of this type of kidney damage [
7]. One way to discover potential biomarkers is to use omics data [
8]. Recently, genomic data has been used a lot in the determination of diseases, and these data have had a very important effect on the creation of personal profiles by examining the diseases on the basis of genes, and in the regulation of personal treatment and side effects. Detection of drug-induced gene changes is of critical importance for the detection of drug-induced kidney damage [
9]. With the increasing use of both experimental and computational methods in RNA-seq technologies, the number of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) has increased greatly in the last few years [
10,
11]. It has been reported that lncRNAs are associated with kidney diseases such as acute kidney disease, chronic kidney disease and kidney transplantation [
12,
13].However, although there are genomic studies for drug-related nephrotoxicity, studies related to lncRNA are not frequently encountered. For this reason, there is a need for such studies in the literature in order to eliminate the deficiencies in this area.
Machine learning (ML) methods, which have been to a large extent used in the health field recently, help researchers in the early prediction, diagnosis, prognosis and individual patient care decision making of various diseases and other medical disorders [
14,
15]. In addition, in recent years, ML has contributed to the literature in identifying possible biomarkers for many disease states such as cancer [
16]. Some methods were needed in order to make the results obtained as a result of modeling of ML methods more interpretable and explainable. Based on these requirements, the concept of explicable artificial intelligence (XAI) was introduced. The use of classification models to diagnose disease in the field of health largely depends on the ability of the models to be interpreted and explained by the researcher [
17,
18]. The XAI methods used for this purpose provide a patient-specific explanation for a particular classification, thus allowing for a more understandable explanation of any complex classifier in the clinical [
19].
This study aims to model the lncRNA data of kidney tissues taken from rats without pathology and treated with methotrexate with ML methods and to determine possible biomarkers for early diagnosis of nephrotoxicity by providing the interpretability of the model with XAI methods as a result of the modeling.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
In order to discover probable biomarkers underlying drug-induced nephrotoxicity and classify nephrotoxicity at the clinical level, 20 female Wistar Albino rats (weight: 250 ± 20g; age: 3 months;) were acquired from the Inonu University Experimental Animal Production and Research Center.
Control group (MK): This group was injected intraperitoneally with physiological saline as a carrier solvent on the first day of the experiment.
Nephrotoxicity group (M): This group was given a single dose of 20 mg/kg MTX intraperitoneal on the first day of the experiment.
On the 4th day of the experiment, xylazine (24 mg/kg intraperitoneal) and ketamine (225 mg/kg intraperitoneal) were given to the rats under high-dose anesthesia, and kidney tissue samples of the rats were taken and genomic, histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses were performed.
2.2. Random Forest Method
The RF technique, put up by Breiman in 2001, is a machine learning algorithm with several decision trees that combines the Bagging and Random Subspaces methodologies. In RF algorithm, it is a supervised machine learning algorithm in which calculations of multiple decision trees are combined to produce a final result. Thanks to its ease of use and flexibility, it has accelerated its adoption as it addresses both classification and regression problems [
20]. In the RF algorithm, the dataset is first randomly divided into two sections in the RF algorithm: the training data for learning and the validation data for assessing the learning level. Following this, multiple decision trees are randomly generated from the dataset using the "boostrap method". The branching of each tree is determined by randomly picked determinants at node positions. The RF outcome estimate is the mean of all the tree's outcomes. As a result, each tree effects the RF estimation for certain weights. The RF method outperforms other machine learning algorithms because of its capacity to accept training data from subsets at random and generate trees using random approaches. Furthermore, because training is performed on numerous randomly selected sub-datasets via boostrap sampling, the RF technique minimizes overfitting. [
21,
22].
2.3. Data Analysis and Modeling Tasks
The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to assess the conformance of quantitative data to normal distribution. Non-normal distribution data were presented using the median (minimum-maximum), whereas normal distribution data were summarized using the mean±standard deviation. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare non-normally distributed data, while the independent sample t-test was used to examine normal distributed data. All analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0 for Windows (New York, USA). The TMM (Trimmed mean of M values) normalization method was employed for the relevant data. In bioinformatics analysis, the False Discovery Rate (FDR) was utilized to make evaluations.
Within the scope of the investigation, the Boruta technique was applied as the variable selection method. Python programming language will be used for the application of tree-based model planned to be used within the scope of the study and for explainable artificial intelligence modeling afterwards. In this study, the model performance was evaluated using Se, Sp, B-Acc, Npv, Acc, Ppv, and F1-score metrics. Furthermore, the images used in the visualizations were developed using the R programming language and Excel software.
2.4. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Analyses
2.4.1. Histopathological analyses
Rat kidney tissues were divided into tiny fragments of 3–4 mm for histological analysis. Following that, plastic tissue was put in follow-up cassettes and preserved for 24 hours in 10% formaldehyde. The tissues were rinsed in running tap water for 24 hours after fixation. They were rendered transparent in xylene, dehydrated in various grades of alcohol, and then imbedded in paraffin. A Leica RM2145 microtome was used to cut sections from paraffin blocks that were 5 microns thick. To study the overall histological structure, the slices were stained using the hematoxylin-eosin procedure. Renal damage was evaluated in terms of peritubular infiltration, vacuolization of tubular epithelial cells, shedding and necrosis. Ten areas were examined at X20 magnification from each section, and histopathological scoring was determined according to the degree and extent of renal damage. According to the severity of the damage; It was rated as 0 (no change), 1 (mild), 2 (moderate), and 3 (severe) [
23]. The preparations were examined with the Leica DFC280 light microscope and the Leica Q (Leica Micros Imaging solution Ltd, Cambridge, UK) image analysis system, scored and photographed.
2.4.2. Immunohistochemical analyses
Immunohistochemical staining with Cystatin C antibody was used to observe tubule damage in kidney sections. For immunohistochemistry analyses, sections that were deparaffinized and rehydrated were placed in a 2100 Antigen Retriever incubator and boiled in 0.01 M citrate (pH 6.0) for 15 to 20 minutes. The sections were exposed to 3% hydrogen peroxide for 12 minutes in order to inhibit the endogenous peroxidase enzyme activity. After washing the sections with Phosphate Buf-fered Saline (PBS), protein block (ultra V block) was applied for 5 minutes. After that, the sections were exposed to primary antibody for 60 minutes at 37°C. The tissues were treated with biotin-based secondary antibodies for 10 minutes at 37 °C after being rinsed with PBS. Following this process, the slices were treated with streptavidin peroxidase for 10 minutes at 37°C. Following hematoxylin staining, slices with chromogen applied were covered with water-based concealer. Semi-quantitative scoring was used to determine the staining immunoreactivity prevalence (0: 0-25%, 1: 26-50%, 2: 51-75%, and 3: 76-100%) and severity (0: none, +1: mild, +2: moderate, +3: severe) [
24].
2.5. Genomic analyses
2.5.1. Total Rna Isolation and Quality Control from Harvested Tissues
Total RNA was isolated from kidney tissue samples using kits that allow for high-efficiency isolation even with low-volume samples. The miRNeasy Serum/Plasma Kit (Qiagen, Cat. No./ID: 217184) is developed to purification cell-free total RNA, namely miRNA and other small RNA, from very tiny amounts of serum and plasma. Qubit (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, California, USA) was used to fluorometrically quantify the amount of RNAs collected. The RNAs were verified for quality using a Bioanalyzer before sequencing. RNA integrity number (RIN) ≥7 samples were sequenced with the control.
2.5.2. Preparing and sequencing NGS libraries for lncRNA sequences
The "TruSeq Stran-ded Total RNA Library Prep Kit" from the Illumina corporation was used to create the sequencing library for lncRNA sequences under the following circumstances:
Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) were isolated from the total RNA, and the remaining RNAs were purified and fragmented. The Bioanalyzer was used to verify the elimination of rRNA. First strand cDNA was created by reverse transcription of the remaining RNA fragments using random hexamer sequences. The RNA template was then removed, and the second strand of cDNA (blunt ds cDNA) was synthesized [
25]. To prevent the fragments from attaching to one other during the adaptor ligation procedure, a single 'A' nucleotide was inserted to the 3' ends of the blunt ds cDNAs. To hybridize the ds cDNA fragments to the flow cell surface, indexing adapters were introduced. Finally, DNA fragments were enriched, and sample libraries were standardized and pooled. The samples were read using the paired-end (PE) 2x150 llumina NovaSeq 6000 platform with 50M reads as the baseline [
26].
3. Results
3.1. Histopathological Results
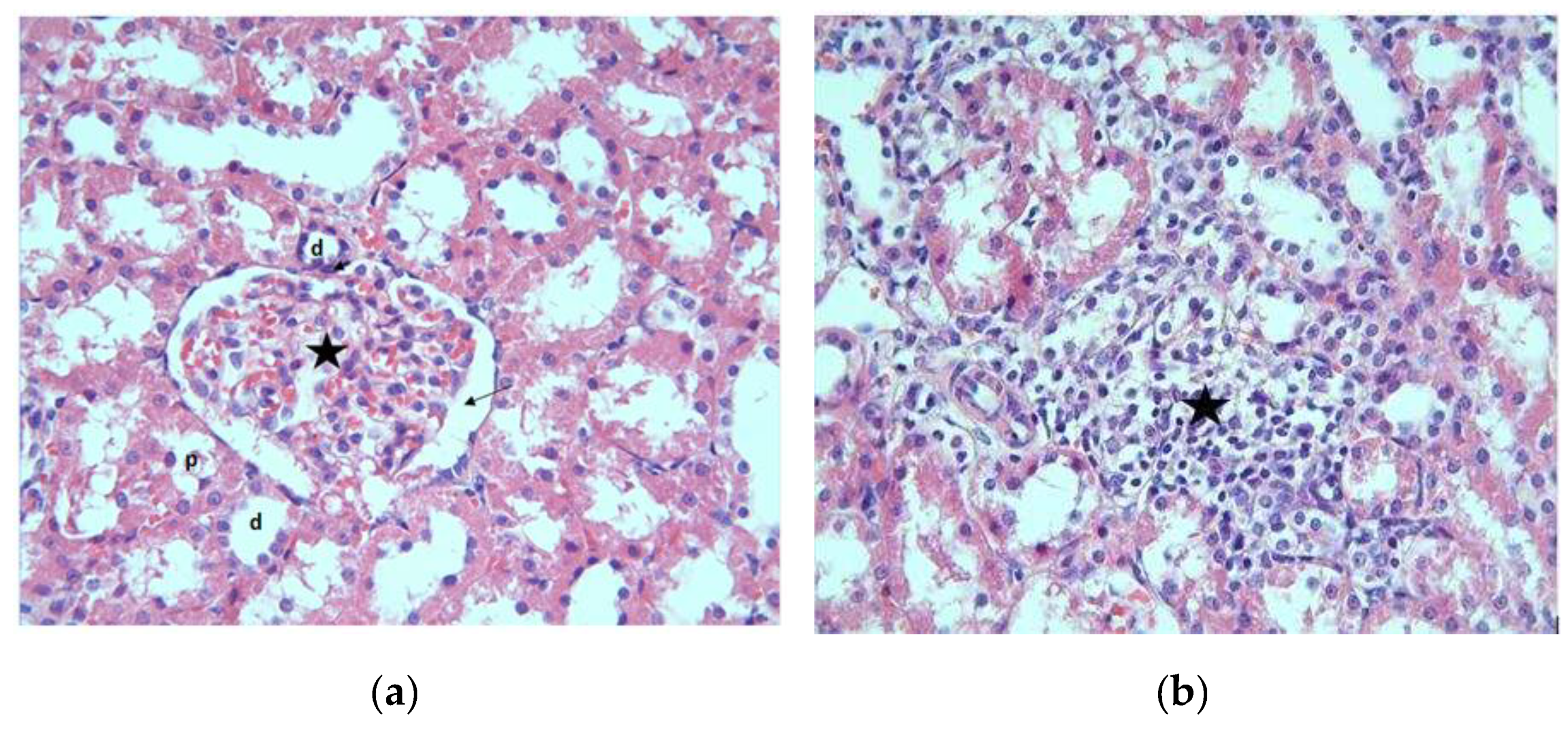
In the kidney sections of the control group stained with the hematoxylin-eosin staining method, the outer leaf of the Bowman capsule in the renal corpuscle and the glomerular tuft within it had a normal appearance. The macula densa formed by changing the morphology of the distal tubule cells approaching the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle was observed as normal. The Bowman distance between the outer leaf of the Bowman's capsule and the inner leaf surrounding the glomerular tuft was of normal width.
The epithelial cells surrounding the lumen of the proximal tubule around the renal corpuscles in the cortex were normal in appearance with round and central nuclei and acidophilic cytoplasm. The inner lumen borders were not very clear due to the microvilli located at the apical part of the cells. Distal tubular epithelial cells were easily distinguished from proximal tubules by their paler staining and wider lumens (
Figure 1a). In the MTX group, in the preparations examined by the hematoxylin-eosin staining method, prominent areas of inflammation were observed in the intertubular regions of the cortex (
Figure 1b).
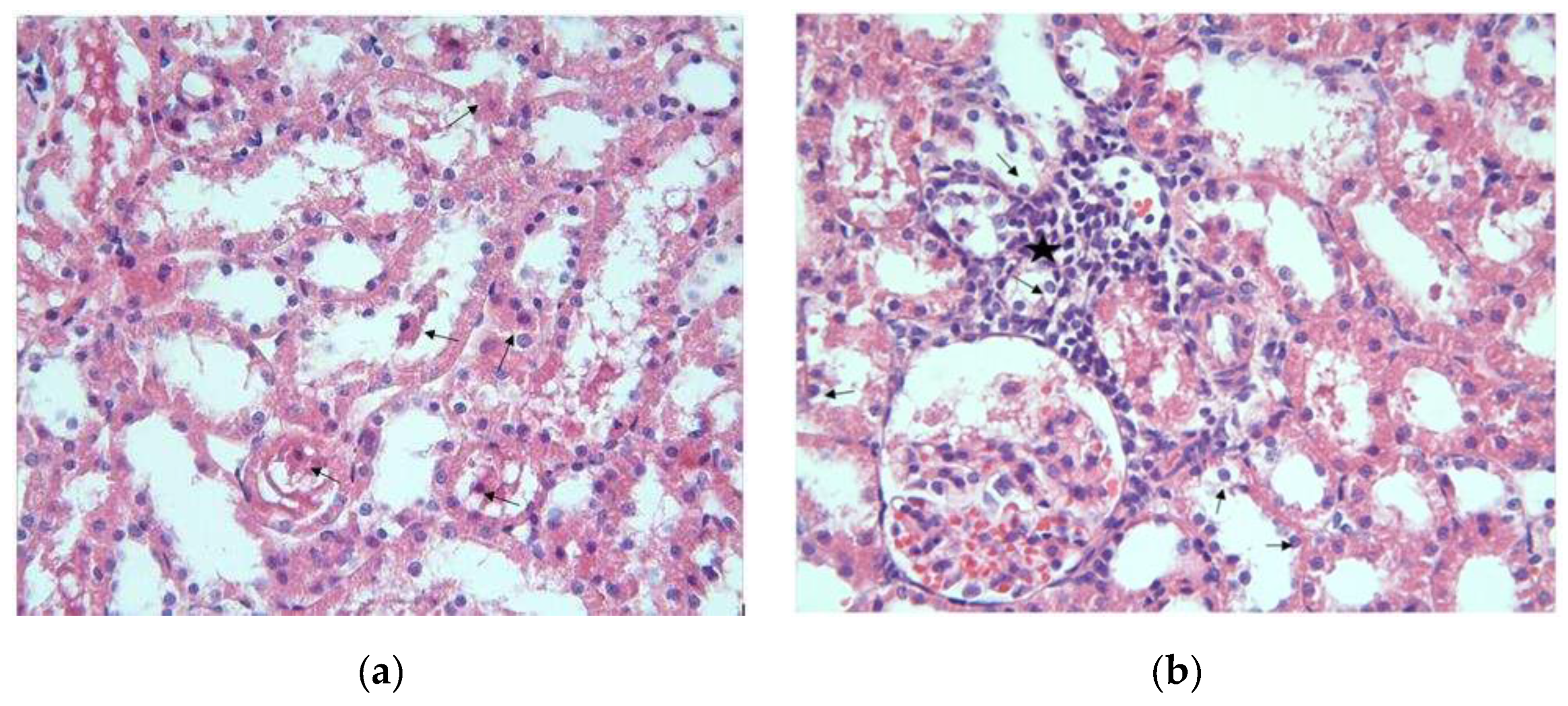
In the sections, epithelial cells of some tubules were observed to spill into the lumen (
Figure 2a). In this group, vacuolization was also detected in the cytoplasm of some tubule cells (
Figure 2b).
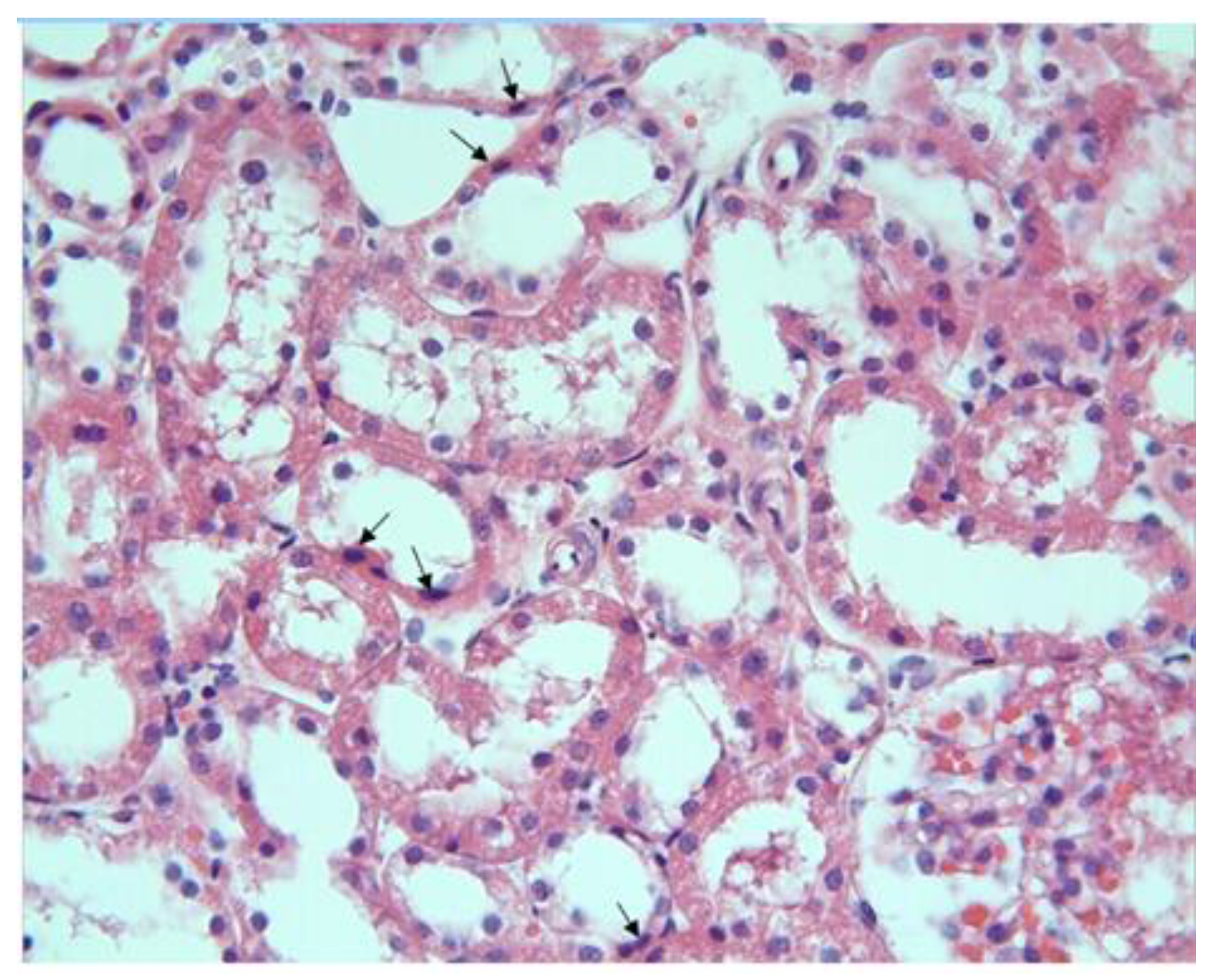
Another remarkable finding was the presence of necrotic cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and dark nuclei in some tubules (
Figure 3).
3.2. Immunohistochemical Results
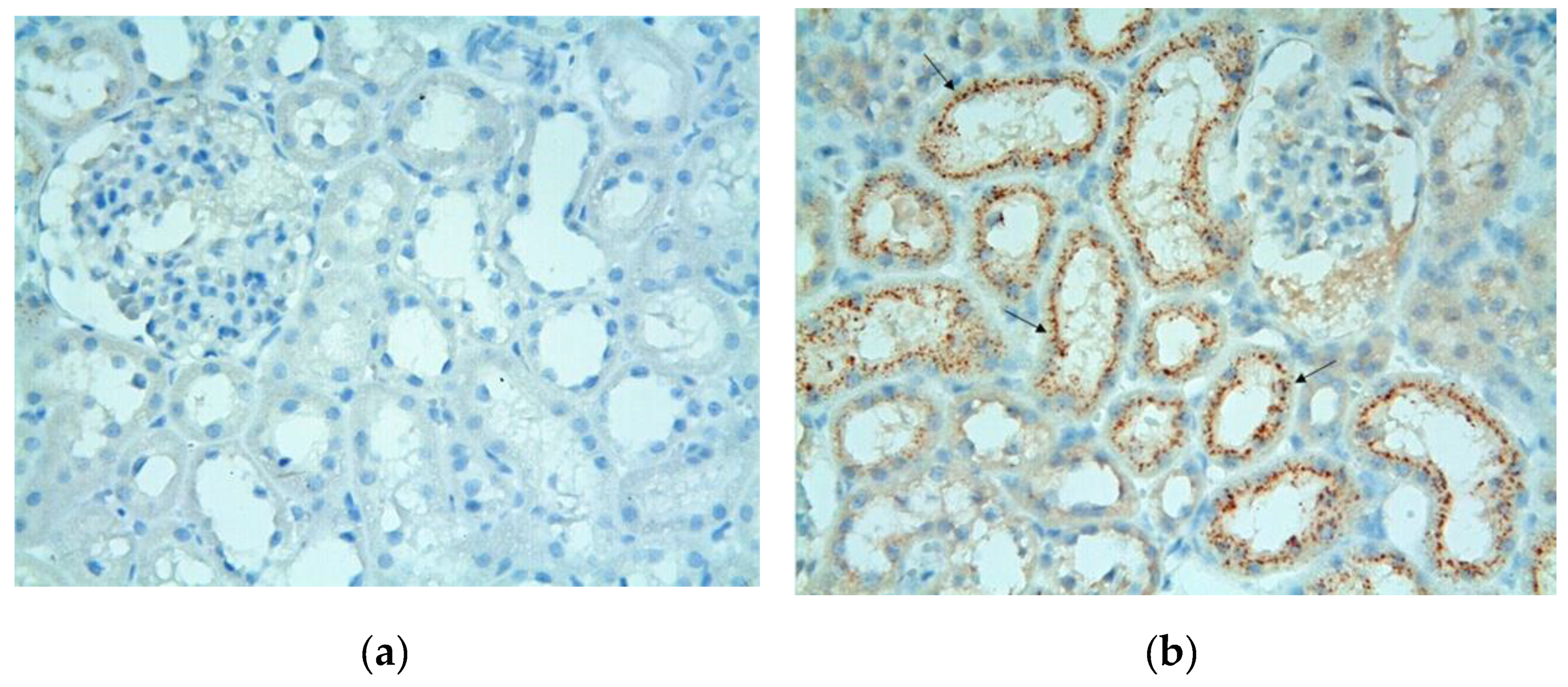
In the control group, positive tubule cells were not found in the sections where the Cystatin C immunohistochemical staining method was applied (
Figure 4a). In the MTX group, the density of positively stained tubules in the sections using the Cystatin C immunohistochemical staining method was observed to increase in this group compared to the control group (
Figure 4b).
The descriptive statistics for the rats used in the experiment are shown in
Table 1.
Table 2 provides descriptive statistics by the nephrotoxicity and control groups.
3.3. Differential Expression Results
There are 16.386 expressions in the dataset that was used for the investigation. The bioinformatics study found that 52 lncRNAs expressed differently in the groups (FDR < 0.05). A total of 35 of them displayed up-expression (logFC > 1), while 17 displayed down-expression (logFC < - 1). A presentation of the dataset can be found in the supporting materials.
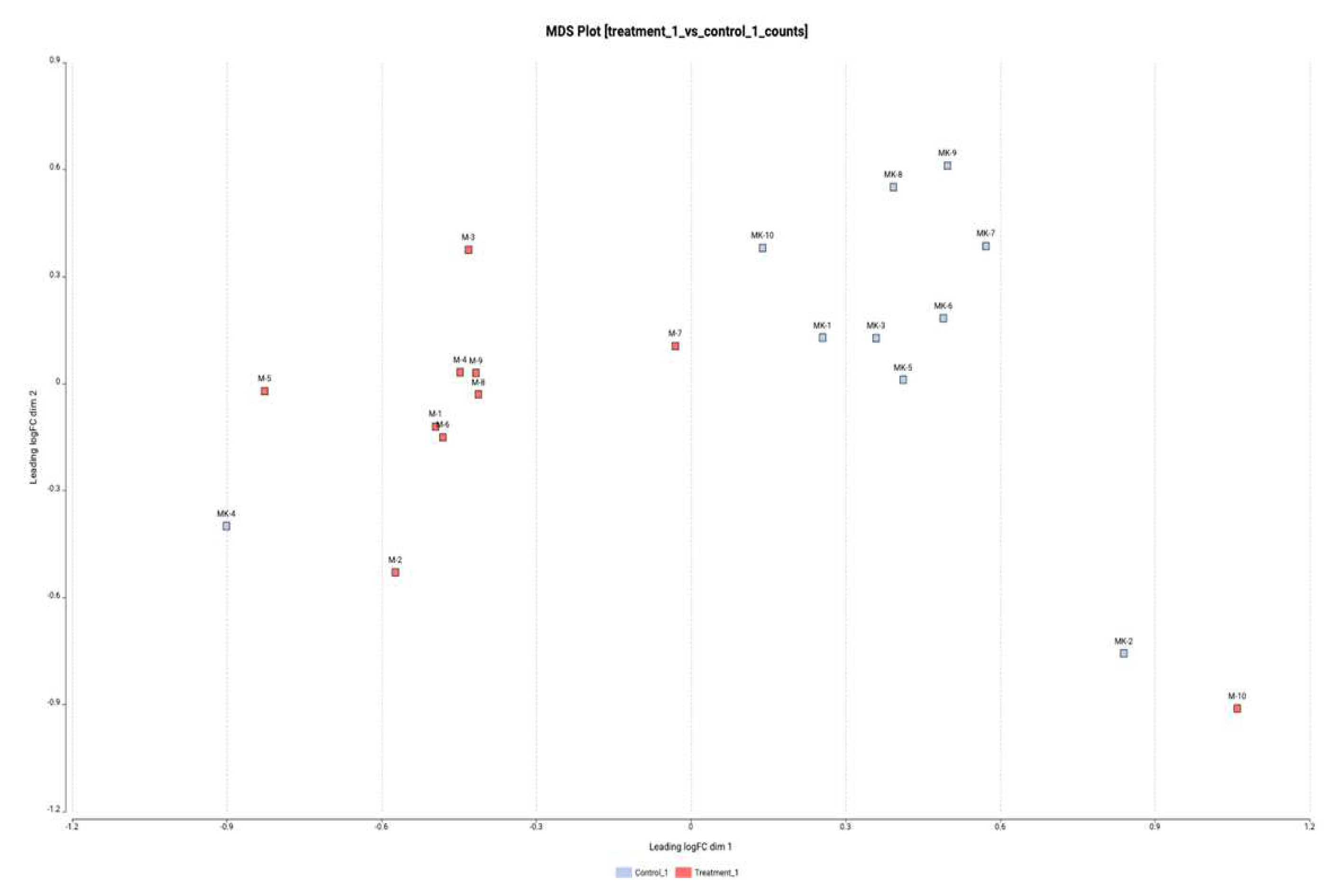
The distribution of the samples was found to be consistent in terms of lncRNA expression levels in the comparison of the nephrotoxicity group (M) and the control group (MK) based on the principal components (PCO) analysis. Controls and application examples show some unity among themselves. However, although this distinction is not sharp, a distinction has emerged due to the lower number of lncRNAs showing total expression changes. When the nephrotoxicity group and control group samples were compared individually with each other, it was determined that more lncRNAs were exposed to expression level changes in M2 and MK2 samples.
Figure 5 depicts a graphic representation of PCO analysis.
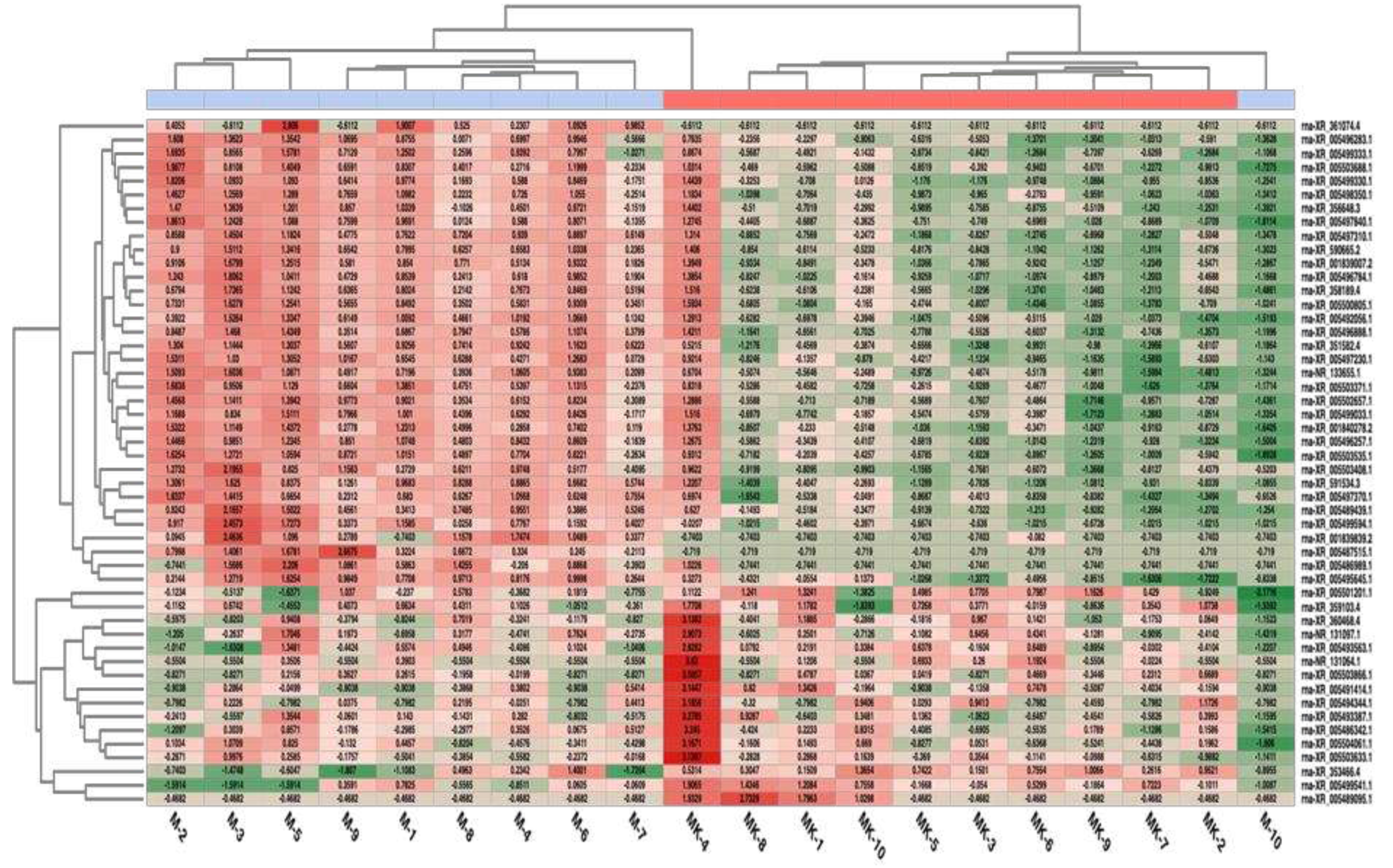
Figure 6 shows a heatmap representation of the 50 lncRNA expressions with the highest variation in expression levels comparison.
Overexpressed lncRNAs are indicated in red and suppressed lncRNAs are shown in green for the 50 lncRNAs that exhibited the highest variation in the M versus MK comparison. When compared to the control, the application samples had different expression patterns. However, it was determined that some samples (such as M-10, MK-4 and MK-2) deviated from the application and control groups.
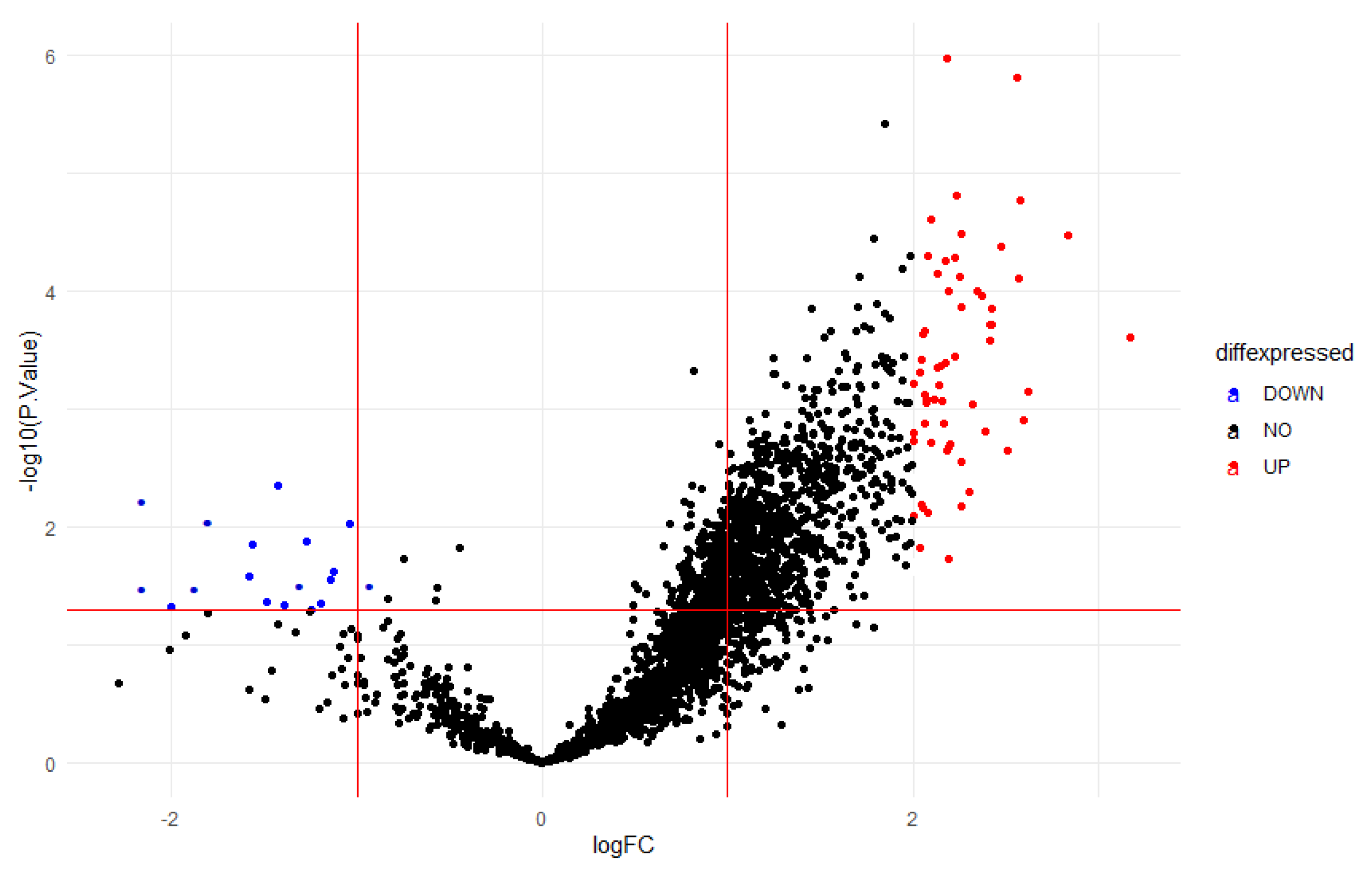
Figure 7 shows the volcano plot used to visualize differentially expressed genes.
Figure 7 shows that the red and blue lncRNAs represent up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively, lncRNAs. The lncRNAs in black are those that do not differ in expression between the two groups.
3.4. Biostatistics Analysis and Modeling Results
The TMM (Trimmed mean of M values) normalization approach was used to extract data from 16.386 lncRNAs in the data set. In the study, 31 lncRNAs that may be associated with the disease state were selected using the Boruta variable selection method, one of the variable selection methods from lncRNAs that show different regulations (up and down) in order to reveal lncRNAs that may be associated with the disease state.
Table 3 contains the selected expressions and data set descriptions, the descriptors of the expressions chosen for the target variable under consideration, their statistical significance, the log fold change (LogFC) per gene for the target variable, and the data analysis results of these selected expressions.
Table 3 shows that statistically significant differences in lncRNA expression were identified between the rat group with nephrotoxicity and the control group for all lncRNA expressions except rna-XR_005493563.1 (LOC120096731) (p<0.05).
The findings of performance metrics achieved as a result of the tree-based RF model using selected lncRNAs are shown in
Table 4.
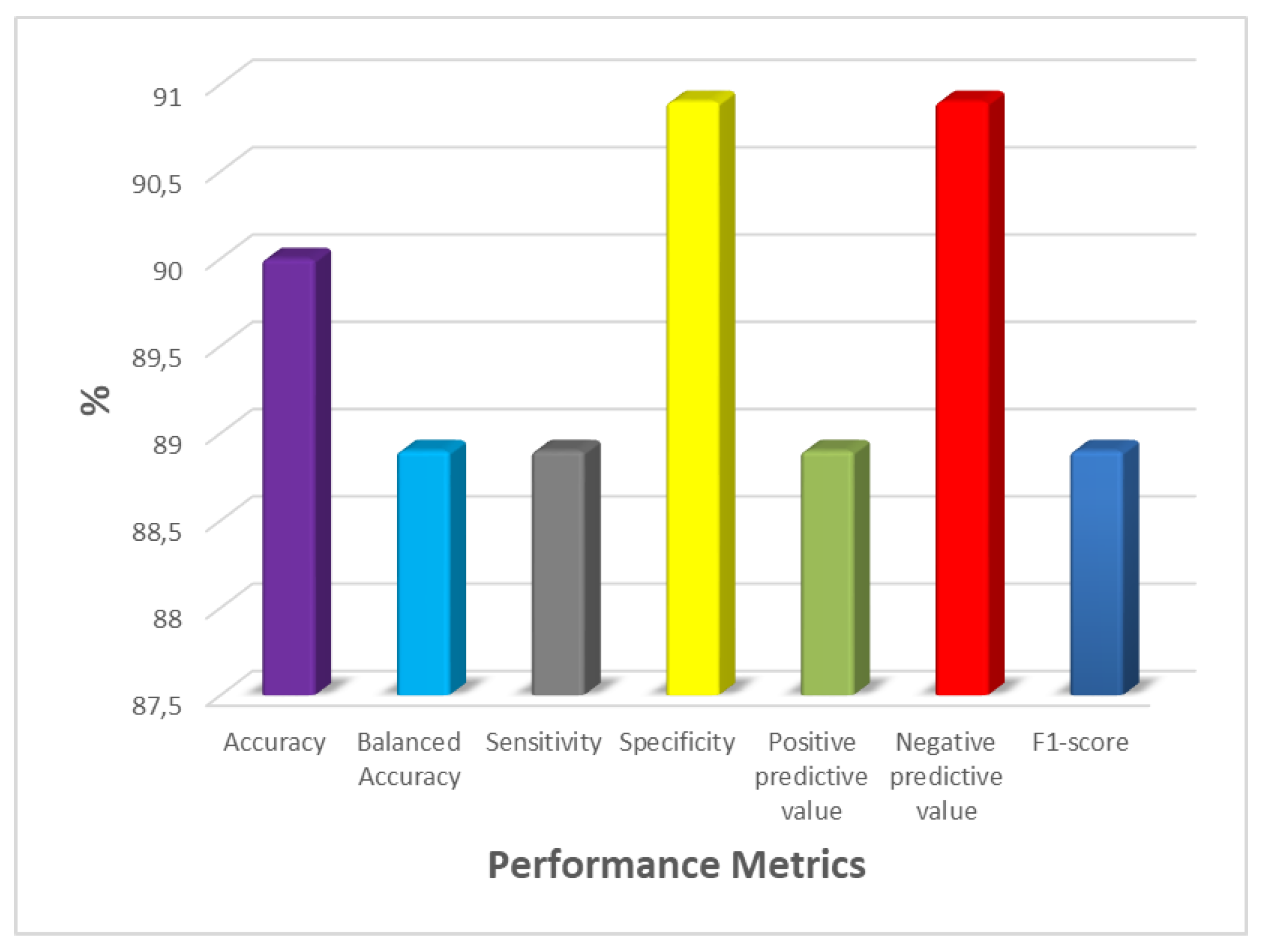
According to the classification performance of the RF model’s B-Acc was 88.9%, Acc was 90%, Sp was 90.9%, Se was 88.9%, NPV was 90.9%, PPV was 88.9%, and F1-score was 88.9%.
A graph of the RF model's performance metrics is shown in
Figure 8.
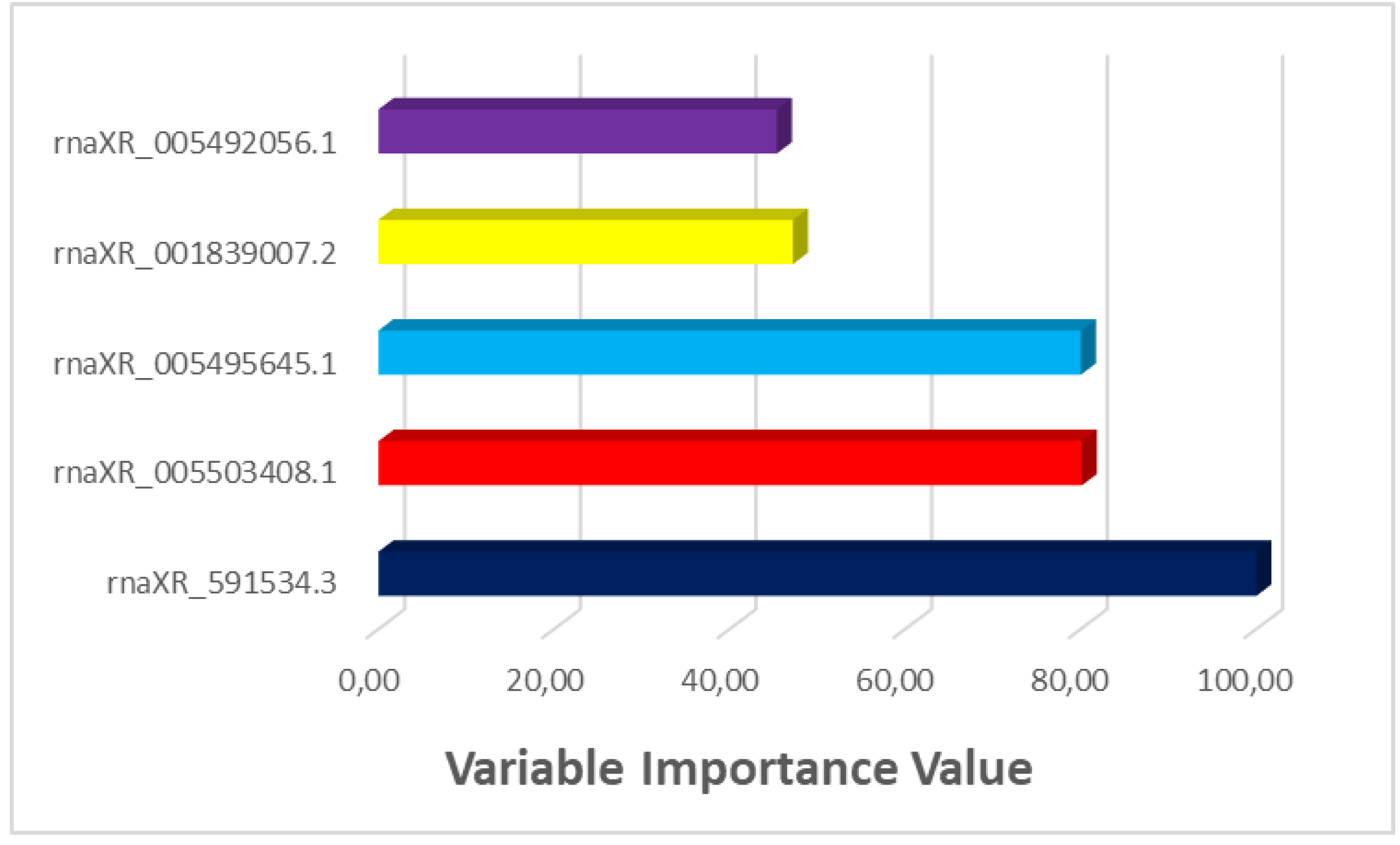
Variable importance values of expressions for the genes selected to explain the target variable (nephrotoxicity) are shown in
Table 5.
Figure 9 shows the variable importance levels of the top five expressions with the highest variable significance for the genes selected to explain the output variable.
LIME, one of the local explainable artificial intelligence methods, was applied to the tree-based Random Forest model.
Figure 10,
Figure 11 and
Figure 12 show the results for the first three rats as a result of the LIME method. Green bars show features that are positively correlated with the target variable, while red bars show features that are negatively correlated with the target variable.
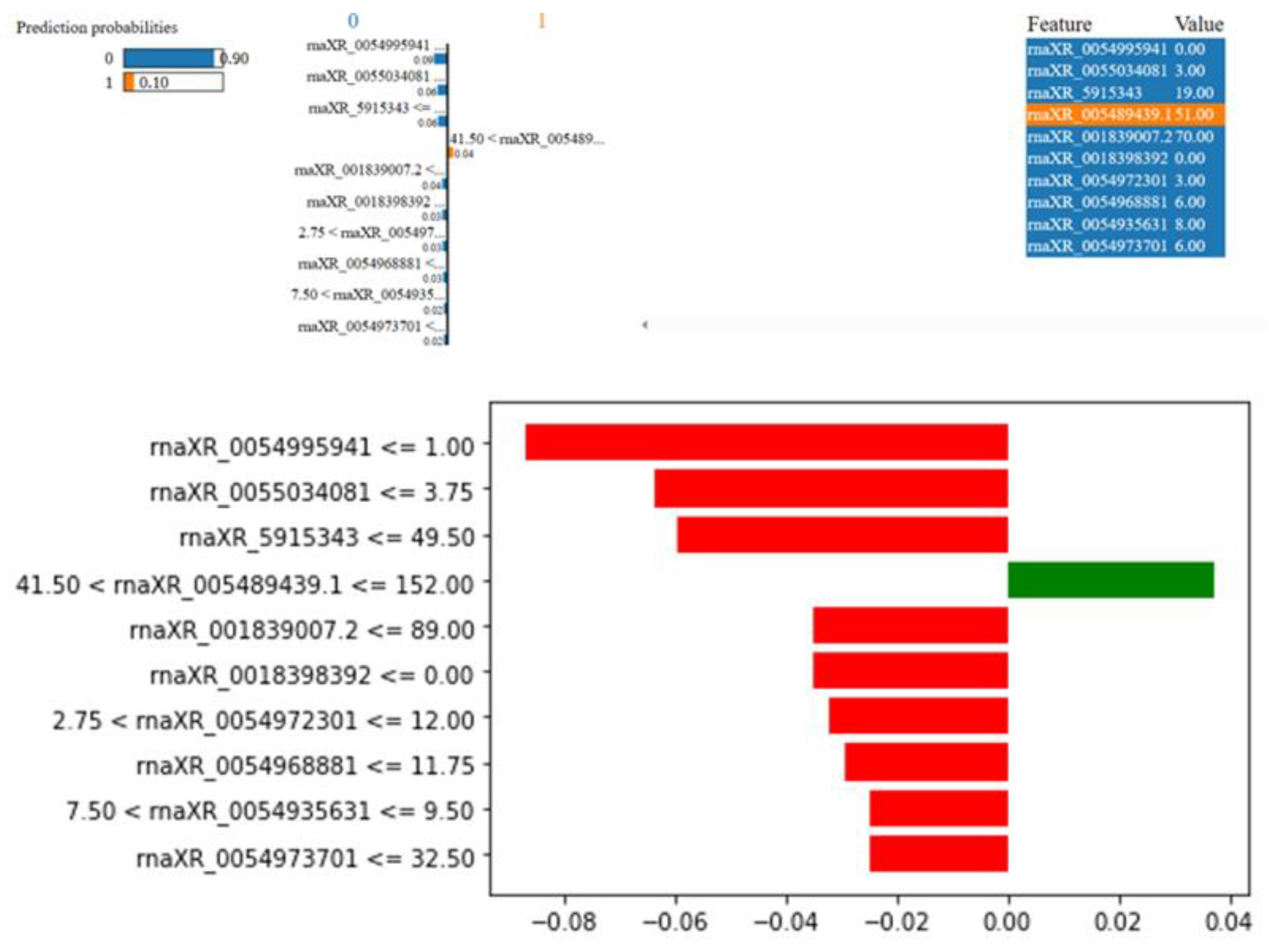
It was estimated that the rat in
Figure 10 did not have Nephrotoxicity with 90% probability. This rat has rna-XR_005499594.1 value less than 1.0, rna-XR_005503408.1 value less than 3.75, rna-XR_591534.3 value less than 49.50, rnaXR_001839007.2 value less than 89.00, rna-XR_001839839.2 value less than 0.00, rna-XR_005497230.1 value between 2.75 and 12.00, rna-XR_005496888.1 value less than 11.75, rna-XR_005493563.1 value between 7.5 and 9.5 rna-XR_005497370.1 less than 32.5 reduced the likelihood of nephrotoxicity. On the other hand, rnaXR_005489439.1 value between 41.50 and 152.00 increased the probability of nephrotoxicity.
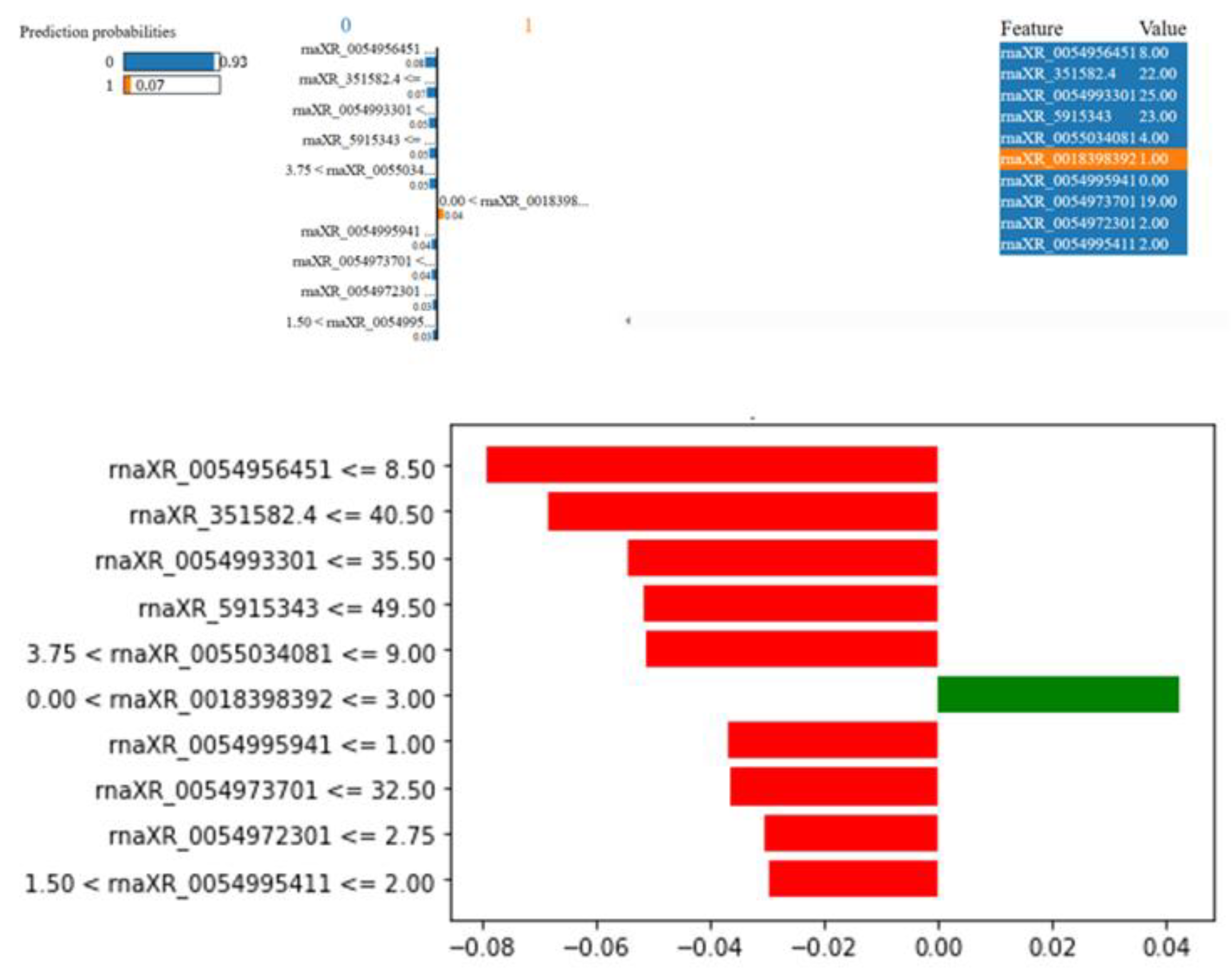
It was estimated that the rat in
Figure 11 did not have Nephrotoxicity with a probability of 93%. This rat has rnaXR_005495645.1 value less than 8.50, rnaXR_351582.4 value less than 40.50, rnaXR_351582.4 value less than 35.50, rnaXR_591534.3 value less than 49.50, rnaXR_005503408.1 values between 3.75 and 9.00, rna-XR_005499594.1 value less than 1.00, rna-XR_005497370.1 value less than 32.50, rna-XR_005497230.1 value less than 2.75 and rnaXR_005499541.1 values between 1.50 and 2.00 reduced the possibility of nephrotoxicity. On the other hand, rna-XR_001839839.2 value between 0.0 and 3.00 increased the probability of nephrotoxicity.
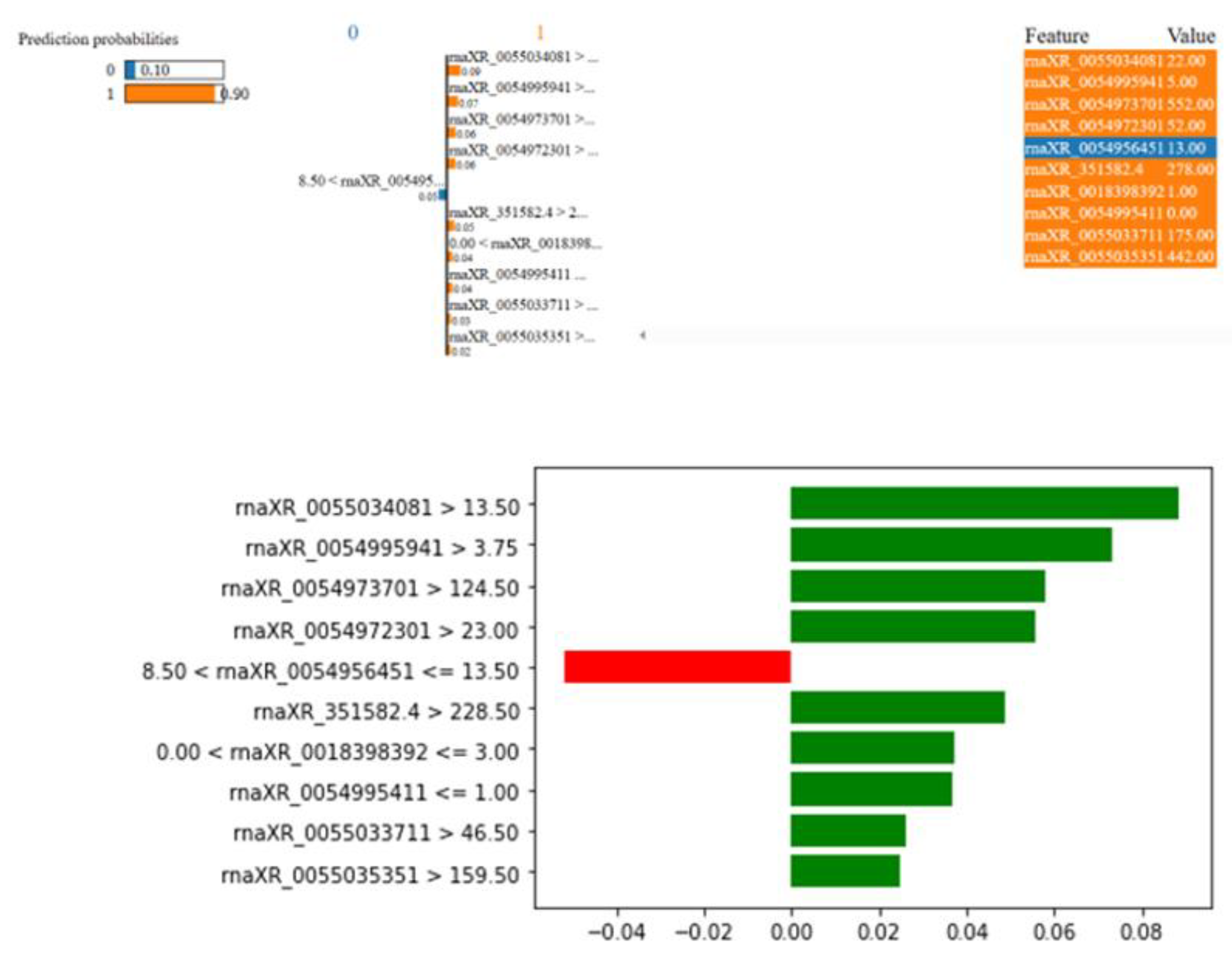
The rat in
Figure 12 was estimated to have 90% probability of Nephrotoxicity. This rat has rnaXR_005503408.1 value greater than 13.50, rna-XR_005499594.1 value greater than 3.75, rna-XR_005497370.1 value greater than 124.5, rna-XR_005497230.1 value greater than 23.00, rnaXR_351582. 4 value greater than 228.50, rna-XR_001839839.2 value between 0.0 and 3.00, rnaXR_005499541.1 value less than 1.00, rnaXR_005503371.1 value greater than 46.50, and rnaXR_005503535.1 value greater than 159.50 increased the possibility of nephrotoxicity. On the other hand rnaXR_005495645.1 value between 8.50 and 13.50 decreased the possibility of nephrotoxicity.
4. Discussion
Antineoplastic drugs not only kill pathologically growing cancer cells in the body, but also destroy rapidly proliferating normal cells. Therefore, many cancer drugs also have side effects on tissues including bone marrow, blood cells, and other rapidly proliferating cells. Although kidney cells do not divide fast, their high blood flow, ability to concentrate poisons in the medullary interstitium, and particular transporters in the tubular epithelium make them highly susceptible to toxic injury [
27,
28]. Tubulopathies, acute renal failure, and glomerulopathies as prevalent clinical manifestations and nephrotoxicity, defined as any kidney injury directly or indirectly caused by drugs; it occurs when kidney-specific detoxification and excretion does not work properly due to damage or destruction of kidney function by exogenous or endogenous toxic substances [
3].
Drug toxicity frequently occurs in the kidney, which is the principal control mechanism that maintains the body's homeostasis and is hence highly vulnerable to xenobiotics [
29]. Understanding the harmful mechanisms of nephrotoxicity can help in the creation of medications with fewer side effects and more therapeutic advantages. Mechanisms of drug-induced nephrotoxicity include tubular cell toxicity, inflammation, changes in glomerular hemodynamics, crystal nephropathy, thrombotic microangiopathy, and rhabdomyolysis. New biomarkers that can detect kidney damage early and more precisely must be discovered and developed in order to effectively prevent drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Biomarker candidates for nephrotoxicity assessment have been identified. Although some fail to provide specificity and sensitivity, studies are promising [30-32]. The most effective technique for preventing or limiting nephrotoxicity is to have sensitive and specific biomarkers available early in the drug development process, well before clinical trials begin. In preclinical models and clinical settings, these biomarkers should be able to accurately anticipate toxicity, enabling drug developers to successfully counsel patients to modify or abandon potential medicines and switch to alternatives that affect the same target without toxicity [
32].
In this study, genomic, histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses were performed with samples taken from rats with nephrotoxicity induced by an antineoplastic drug, methotrexate, and from rats in the control group, in order to determine biomarkers for drug-induced nephrotoxicity. lncRNA sequence analyses, which are known to be involved in many regulatory mechanisms in the case of transcription and subsequent gene expression, and fulfill primary functions for quite different biological processes, were performed from tissue samples taken within the scope of genomic analyses.
According to the histopathological analyses performed in this study, the outer leaf of the Bowman capsule in the renal corpuscle and the glomerular tuft in the cortex were normal in the kidney sections stained with the hematoxylin-eosin staining method in the control group. In the MTX group, significant areas of inflammation were observed in the intertubular areas of the cortex in the preparations examined by the hematoxylin-eosin staining method. In the control group, the macula densa formed by changing the morphology of the distal tubule cells approaching the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle was observed to be normal, and the Bowman distance between the outer leaf of the Bowman's capsule and the inner leaf surrounding the glomerular tuft was also of normal width. In the MTX group, it was observed that epithelial cells of some tubules spilled into the lumen in some stained sections. Another observed condition was the presence of necrotic cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and dark nuclei in some tubules. With all these results, it is said that the general structure of the kidney went beyond what is known and the formation of necrotic cells was observed in the experimental group using MTX. This produces symptoms of kidney damage caused by the drug.
According to the results of the immunohistochemical analysis, positive tubule cells were not found in the control group in the sections where the Cystatin C immunohistochemical staining method was applied, while the density of the positively stained tubules in the MTX group was increased in this group when compared to the control group. It is said that these differences are based on drug use and liver damage occurs in the drug-administered group compared to the control group. These analyses reveal that histopathologically and immunohistochemically, MTX causes damage to the kidney.
In this study, a genomic dataset containing 16,386 lncRNAs obtained from kidney tissues of rats with nephrotoxicity and control group rats was used. According to the findings of the bioinformatic analysis, rna-XR_005487515.1 id lncRNA showed significantly higher gene expression in the hepatotoxicity group than in the control group. Similarly rna-XR_361074.4, rna-XR_001839839.2, rna-XR_005486989.1, rna-NR_133655.1, rna-XR_005499594.1, rna-XR_005499333.1, rna-XR_005497370.1, rna-XR_005497370.1, rna-XR_005499594.1_ lncRNAs with rna-XR_351582.4 id have higher gene expression in the group with nephrotoxicity than in the control group. rna-XR_005489095.1, rna-NR_131064.1, rna-XR_005494344.1, rna-XR_005503866.1, rna-XR_005491414.1, rna-XR_360468.4, rna-XR_005501201.1, rna-XR_7.1, 00549338 XR_005499541.1, rna-XR_005493563.1 lncRNAs with id have very low gene expression in the group with nephrotoxicity compared to the control group.
According to the results of the biostatistical analysis, all genes except rna-XR_005493563.1 (LOC120096731) lncRNA out of 31 lncRNA obtained by Boruta variable selection showed statistically significant differences for the two groups. It shows that it can correctly classify nephrotoxicity according to the performance criteria obtained as a result of the tree-based RF machine learning modeling made by taking the target (nephrotoxicity) variable with 31 lncRNA selected by Boruta variable selection method used in the study. In addition, as a result of RF modeling, lncRNAs with the id rnaXR_591534.3, rnaXR_005503408.1, rnaXR_005495645.1, rnaXR_001839007.2, rnaXR_005492056.1 and rna_XR_005492522.1 have the highest five variable significance values. Therefore, these lncRNAs can be used as biomarker candidates for nephroxicity. When the LIME results are considered, it has been observed that the high level of lncRNAs with id rnaXR_591534.3 and rnaXR_005503408.1 increases the possibility of nephrotoxicity.
This study has some limitations. This study was carried out with the data obtained from the mouse experiment and lays the groundwork for future studies. However, human studies are needed to confirm the results so that the results of the study can be generalized and used in potential drug development studies.
5. Conclusions
In order for the possible biomarkers obtained within the scope of this study to be used in the presence of drug-induced nephrotoxicity, the results obtained from various studies should be supported. In addition, after the possible biomarker candidates discovered with the results of high-performance tree-based modeling and LIME method are supported by other studies, results for the personalization of diagnosis and treatment can be provided.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C., I.B.C., H.P., A.K. and O.O.; methodology, A.K., S.Y., E.T., I.B.C., H.P., S.A. and Z.K..; formal analysis, I.B.C., Z.K. and E.T.; resources, C.C. and I.B.C.; data curation, O.O., A.K. and E.T.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C. and I.B.C.; writing—review and editing, C.C., I.B.C., N.D. and S.A.; visualization, I.B.C. and N.D.; supervision, C.C. and I.B.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: The study was supported and funded by the Inonu University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (Project ID: TOA-2021-2593).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was performed in line with the principles of the ARRIVE guidelines. Ethics committee approval was obtained from Inonu University Faculty of Medicine Animal Experiments Local Ethics Committee (Approval no: 2021/8-7, approval date 12 April 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We thank the Inonu University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit for supporting our project (Project ID: TOA-2021-2593).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maurya, H.; Kumar, T.; Kumar, S. Anatomical and physiological similarities of kidney in different experimental animals used for basic studies. J Clin Exp Nephrol 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, E.; Domański, L.; Dziedziejko, V.; Kajdy, A.; Stefańska, K.; Kwiatkowski, S. The Mechanism of Drug Nephrotoxicity and the Methods for Preventing Kidney Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, G.T.M.; Foresto, R.D. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira 2020, 66, s82–s90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannoodee, M.; Mittal, M. Methotrexate. In StatPearls [internet]; StatPearls Publishing: 2022.
- Bhattacharya, S. Reactive Oxygen Species and Cellular Defense System. In Free Radicals in Human Health and Disease; Rani, V., Yadav, U.C.S., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Florea, A.-M.; Büsselberg, D. Cisplatin as an Anti-Tumor Drug: Cellular Mechanisms of Activity, Drug Resistance and Induced Side Effects. Cancers 2011, 3, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, K.D.; Dougherty, B.V.; Vinnakota, K.C.; Pannala, V.R.; Wallqvist, A.; Kolling, G.L.; Papin, J.A. Predicting changes in renal metabolism after compound exposure with a genome-scale metabolic model. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 412, 115390–115390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, L.; Smolinska, A.; Attali, A.; Stoop, M.P.; Ampt, K.A.; van Aken, H.; Suidgeest, E.; Tuinstra, T.; Wijmenga, S.S.; Luider, T.; et al. Fusion of metabolomics and proteomics data for biomarkers discovery: case study on the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 254–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirbasli, D.; Isil Ulman, F. Coronary artery disease from a perspective of genomic risk score, ethical approaches and suggestions. Anadolu kardiyoloji dergisi-the anatolian journal of cardiology 2012, 12.
- Nguyen, Q.; Carninci, P. Expression Specificity of Disease-Associated lncRNAs: Toward Personalized Medicine. Poxviruses 2015, 394, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, A.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Lei, J.; Xu, H.; Leng, Z.; Li, T.; et al. LncTarD: a manually-curated database of experimentally-supported functional lncRNA–target regulations in human diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D118–D126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyan, H.M.; Dogan, S.; Terzi, M.Y.; Begen, M.A.; Turgut, F.H. Association of serum lncRNA H19 expression with inflammatory and oxidative stress markers and routine biochemical parameters in chronic kidney disease. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2021, 25, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Jia, H.; Ji, P.; He, Y.; Chen, L. Identification of the candidate lncRNA biomarkers for acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battineni, G.; Sagaro, G.G.; Chinatalapudi, N.; Amenta, F. Applications of Machine Learning Predictive Models in the Chronic Disease Diagnosis. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Das, N.N.; Gupta, D.; Gupta, K.; Bindra, J. Efficient Automated Disease Diagnosis Using Machine Learning Models. J. Heal. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Lane, H.-Y. Machine Learning and Novel Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjoa, E.; Guan, C. A Survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Toward Medical XAI. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4793–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, W.; Müller, K.-R. Towards explainable artificial intelligence. Explainable AI: interpreting, explaining and visualizing deep learning 2019, 5-22.
- Shi, S.; Zhang, X.; Fan, W. A modified perturbed sampling method for local interpretable model-agnostic explanation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.07434 2020. arXiv:2002.07434 2020.
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Machine learning 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.M.; Iverson, L.R.; Liaw, A. Newer Classification and Regression Tree Techniques: Bagging and Random Forests for Ecological Prediction. Ecosystems 2006, 9, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, P.; Džeroski, S. Combining bagging and random subspaces to create better ensembles. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis; 2007; pp. 118–129. [Google Scholar]
- Taslidere, E.; Dogan, Z.; Elbe, H.; Vardi, N.; Cetin, A.; Turkoz, Y. Quercetin protection against ciprofloxacin induced liver damage in rats. Biotech. Histochem. 2015, 91, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlakpinar, H.; Ozhan, O.; Ermis, N.; Vardi, N.; Cigremis, Y.; Tanriverdi, L.H.; Colak, C.; Acet, A. Acute and Subacute Effects of Low Versus High Doses of Standardized Panax ginseng Extract on the Heart: An Experimental Study. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2019, 19, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, M.; Comegna, M.; Succoio, M.; Leggiero, E.; Pastore, L.; Faraonio, R.; Cimino, F.; Passaro, F. Comparative Analysis of Gene Expression Data Reveals Novel Targets of Senescence-Associated microRNAs. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e98669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigoni, A.; Ranzani, V.; Rossetti, G.; Panzeri, I.; Abrignani, S.; Bonnal, R.J.; Pagani, M. Analysis RNA-seq and Noncoding RNA. Polycomb Group Proteins: Methods and Protocols 2016, 125-135.
- Eren, E.; Alper, A.; Arıcan, A. Kanser tedavisinde kullanılan ilaçlar ve nefrotoksisite. Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi 2012, 26, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Petejova, N.; Martinek, A.; Zadrazil, J.; Teplan, V. Acute toxic kidney injury. Ren. Fail. 2019, 41, 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Naimi, M.S.; Rasheed, H.; Hussien, N.R.; Al-Gareeb, A. Nephrotoxicity: Role and significance of renal biomarkers in the early detection of acute renal injury. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2019, 10, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Moon, A.-R. Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Its Biomarkers. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.A.; Vaidya, V.S.; Bonventre, J.V. Biomarkers of nephrotoxic acute kidney injury. Toxicology 2008, 245, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Vaidya, V.S.; Schmouder, R.; Feig, P.; Dieterle, F. Next-generation biomarkers for detecting kidney toxicity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
(a) Normal-looking glomeruli (star), macula densa (arrowhead), Bowman's space (arrow), proximal (p) and distal tubules (d) in the renal tissue section of the control group. H-E X400; (b) MTX group, areas of inflammation (asterisk) monitored. H-E X400.
Figure 1.
(a) Normal-looking glomeruli (star), macula densa (arrowhead), Bowman's space (arrow), proximal (p) and distal tubules (d) in the renal tissue section of the control group. H-E X400; (b) MTX group, areas of inflammation (asterisk) monitored. H-E X400.
Figure 2.
(a) MTX group, epithelial cells shed into the lumen; (b) MTX group, areas of inflammation (star) and cells with vacuolization in their cytoplasm (arrows) are observed H-E; X400.
Figure 2.
(a) MTX group, epithelial cells shed into the lumen; (b) MTX group, areas of inflammation (star) and cells with vacuolization in their cytoplasm (arrows) are observed H-E; X400.
Figure 3.
MTX group, necrotic cells (arrows) are observed in the tubule epithelium H-E; X200.
Figure 3.
MTX group, necrotic cells (arrows) are observed in the tubule epithelium H-E; X200.
Figure 4.
(a) Control group. Tubule cells stained positive with Cystatin C were not detected. Cystatin CX400; (b) Cystatin C positive stained tubule cells of MTX group (arrows) are observed. Cystatin CX400.
Figure 4.
(a) Control group. Tubule cells stained positive with Cystatin C were not detected. Cystatin CX400; (b) Cystatin C positive stained tubule cells of MTX group (arrows) are observed. Cystatin CX400.
Figure 5.
Nephrotoxicity group vs control group comparison based on PCO analysis.
Figure 5.
Nephrotoxicity group vs control group comparison based on PCO analysis.
Figure 6.
Heatmap for the 50 lncRNAs with the most variation for the two groups.
Figure 6.
Heatmap for the 50 lncRNAs with the most variation for the two groups.
Figure 7.
Volcana plot for differentially expressed genes.
Figure 7.
Volcana plot for differentially expressed genes.
Figure 8.
Graph of Performance Metrics Values for the RF Model.
Figure 8.
Graph of Performance Metrics Values for the RF Model.
Figure 9.
Variable importance values graph for RF model
Figure 9.
Variable importance values graph for RF model
Figure 10.
LIME results for the first rat in the nephrotoxicity group.
Figure 10.
LIME results for the first rat in the nephrotoxicity group.
Figure 11.
LIME results for the second rat in the nephrotoxicity group .
Figure 11.
LIME results for the second rat in the nephrotoxicity group .
Figure 12.
LIME results for the third rat in the nephrotoxicity group.
Figure 12.
LIME results for the third rat in the nephrotoxicity group.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics for the rats utilized in the investigation.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics for the rats utilized in the investigation.
| Variables |
Mean ± Standard Deviation |
| Rat weight starting (g) |
249.15±22.32 |
| Rat weight end (g) |
252.1±24.05 |
| Kidney weight (g) |
0.968±0.1 |
Table 2.
Descriptive statistics for the nephrotoxicity and control groups.
Table 2.
Descriptive statistics for the nephrotoxicity and control groups.
| Variables |
Control |
Nephrotoxicity |
| Rat weight starting (g) |
245.3±24.02 |
253±21.01 |
| Rat weight end (g) |
252±24.03 |
252.2±25.37 |
| Kidney weight (g) |
0.97±0.08 |
0.96±0.12 |
Table 3.
Detailed information about the data analysis results.
Table 3.
Detailed information about the data analysis results.
| Gene Name |
Chromosome |
ID |
Group |
|
|
| M |
MK |
LogFC |
p |
| Mean ± SD |
Median (Min-Max) |
Mean ± SD |
Median (Min-Max) |
| LOC102555118 |
NC_051337.1 |
rna-XR_351582.4 |
226.4±116.41 |
248(42-447) |
35.6±16.85 |
34(17-66) |
1.616 |
0.001* |
| LOC106736471 |
NC_051345.1 |
rna-NR_133655.1 |
102.4±76.73 |
88(5-257) |
11.9±9.48 |
10.5(1-34) |
2.198 |
0.005* |
| LOC103691349 |
NC_051336.1 |
rna-XR_590665.2 |
281.2±123.78 |
294(49-470) |
68.4±78.82 |
46(26-290) |
1.247 |
0.001** |
| LOC108351528 |
NC_051342.1 |
rna-XR_001839007.2 |
454.2±191.95 |
486.5(96-661) |
117.1±118.09 |
80.5(55-449) |
1.118 |
0.001** |
| LOC120098801 |
NC_051336.1 |
rna-XR_005497310.1 |
166±92.76 |
164.5(29-370) |
38.6±36.34 |
26.5(13-139) |
1.187 |
0.001** |
| LOC120094778 |
NC_051344.1 |
rna-XR_005489439.1 |
140±90.62 |
125(28-296) |
28.9±14.03 |
30(9-51) |
1.248 |
0.004* |
| LOC120099280 |
NC_051336.1 |
rna-XR_005498350.1 |
109.6±68.4 |
96(13-206) |
21.6±21.84 |
15.5(7-82) |
1.488 |
0.002** |
| LOC120096007 |
NC_051347.1 |
rna-XR_005492056.1 |
134.4±91.26 |
123.5(17-332) |
32.6±28.96 |
25.5(6-111) |
1.087 |
0.004** |
| LOC120098788 |
NC_051336.1 |
rna-XR_005497230.1 |
27.3±13.61 |
29.5(3-52) |
4.6±4.62 |
2.5(0-15) |
1.751 |
<0.001** |
| LOC120098190 |
NC_051353.1 |
rna-XR_005496257.1 |
85.5±54.7 |
70(9-172) |
19.5±18.58 |
16(4-70) |
1.277 |
0.004** |
| LOC108348888 |
NC_051354.1 |
rna-XR_005496888.1 |
71.2±32.64 |
75.5(12-112) |
17.1±20.59 |
11.5(3-74) |
1.250 |
0.002** |
| LOC103691816 |
NC_051338.1 |
rna-XR_591534.3 |
210.4±116.14 |
230.5(54-421) |
49.2±36.54 |
40.5(19-147) |
1.171 |
0.001** |
| LOC120098816 |
NC_051355.1 |
rna-XR_005497370.1 |
220.6±173.89 |
186(48-552) |
31.3±22.35 |
30(6-73) |
1.992 |
0.007* |
| LOC120096731 |
NC_051349.1 |
rna-XR_005493563.1 |
6.6±6.64 |
3.5(0-18) |
13.2±14.34 |
8(3-51) |
-1.862 |
0.093** |
| LOC120098521 |
NC_051354.1 |
rna-XR_005496784.1 |
362.1±181.28 |
349.5(74-587) |
88.8±100.42 |
58(33-369) |
1.249 |
0.001** |
| LOC120102202 |
NC_051339.1 |
rna-XR_005503371.1 |
84.1±63.57 |
73(13-208) |
15.6±11.47 |
13.5(3-37) |
1.559 |
0.008* |
| LOC102549457 |
NC_051346.1 |
rna-XR_358189.4 |
77.7±42.9 |
75.5(8-154) |
21.1±26.93 |
12.5(4-96) |
1.078 |
0.007** |
| LOC120102261 |
NC_051339.1 |
rna-XR_005503535.1 |
215.2±138.84 |
176.5(16-442) |
47±27.2 |
38.5(26-116) |
1.205 |
0.003** |
| LOC120100781 |
NC_051337.1 |
rna-XR_005500805.1 |
51.1±23.38 |
49(11-82) |
14.4±20.5 |
8(2-71) |
1.114 |
0.002** |
| LOC108348808 |
NC_051353.1 |
rna-XR_005496283.1 |
42.2±26.1 |
37.5(5-84) |
9.1±5.61 |
9(2-19) |
1.287 |
0.003* |
| LOC103691306 |
NC_051336.1 |
rna-XR_005499594.1 |
6.2±4.47 |
5.5(0-12) |
0.6±0.52 |
1(0-1) |
2.178 |
0.001** |
| LOC102552040 |
NC_051344.1 |
rna-XR_001839839.2 |
3.8±4.49 |
3(0-15) |
0.1±0.32 |
0(0-1) |
3.296 |
0.002** |
| LOC120099889 |
|
rna-XR_005499330.1 |
282.2±232.78 |
197(41-831) |
68.2±86.7 |
35(24-308) |
1.431 |
0.002** |
| NC_051336.1 |
| LOC120099800 |
NC_051336.1 |
rna-XR_005499033.1 |
53.7±33.95 |
45(5-102) |
14.2±19.85 |
9.5(1-69) |
1.176 |
0.004** |
| LOC120097836 |
NC_051352.1 |
rna-XR_005495645.1 |
32.8±16.73 |
28.5(13-62) |
7.7±4.32 |
8.5(1-14) |
1.089 |
0.001* |
| LOC120102212 |
NC_051339.1 |
rna-XR_005503408.1 |
18.5±10.54 |
14.5(8-42) |
4±2.31 |
3.5(2-10) |
1.313 |
<0.001** |
| LOC102555751 |
NC_051355.1 |
rna-XR_005497840.1 |
54.9±45.9 |
41(1-162) |
12.1±12.54 |
8.5(3-47) |
1.431 |
0.008** |
| LOC120102327 |
NC_051339.1 |
rna-XR_005503688.1 |
50.7±46.08 |
41.5(1-165) |
9.8±8.04 |
7.5(3-30) |
1.612 |
0.005** |
| LOC120099962 |
NC_051336.1 |
rna-XR_005499541.1 |
1±0.94 |
1(0-3) |
2.3±0.82 |
2(1-4) |
2.047 |
0.005** |
| LOC108352129 |
NC_051345.1 |
rna-XR_001840278.2 |
26±18.34 |
21(0-59) |
5.8±6.94 |
3(2-25) |
1.282 |
0.008** |
| LOC102554372 |
NC_051339.1 |
rna-XR_353438.4 |
48.4±27.61 |
49.5(3-84) |
12.1±6.05 |
11.5(4-21) |
1.037 |
0.002* |
Table 4.
The findings of performance metrics achieved as a result of the tree-based RF model.
Table 4.
The findings of performance metrics achieved as a result of the tree-based RF model.
| Metric |
Value (%) (95% CI) |
| B-Acc |
88.9 (76.7-100) |
| Acc |
90 (76.9-100) |
| Sp |
90.9 (58.7-99.8) |
| Se |
88.9 (51.8-99.7) |
| Npv |
90.9 (58.7-99.8) |
| Ppv |
88.9 (51.8-99.7) |
| F1-score |
88.9 (75.1-100) |
Table 5.
Depicts the variable importance values of chosen lncRNAs used to explain the target variable.
Table 5.
Depicts the variable importance values of chosen lncRNAs used to explain the target variable.
| Gene Name |
Variable Importance Value |
| rnaXR_591534.3 |
100 |
| rnaXR_005503408.1 |
80.127 |
| rnaXR_005495645.1 |
80.02 |
| rnaXR_001839007.2 |
47.205 |
| rnaXR_005492056.1 |
45.374 |
| rnaXR_351582.4 |
42.972 |
| rnaXR_001840278.2 |
42.9 |
| rnaXR_005496784.1 |
41.422 |
| rnaXR_005498350.1 |
39.116 |
| rnaXR_005503371.1 |
38.433 |
| rnanr_133655.1 |
38.301 |
| rnaXR_005497370.1 |
35.986 |
| rnaXR_005500805.1 |
33.445 |
| rnaXR_005496283.1 |
31.788 |
| rnaXR_353438.4 |
30.313 |
| rnaXR_005499330.1 |
29.65 |
| rnaXR_005497310.1 |
29.435 |
| rnaXR_005503535.1 |
29.232 |
| rnaXR_358189.4 |
27.716 |
| rnaXR_005499033.1 |
24.311 |
| rnaXR_005496888.1 |
24.018 |
| rnaXR_590665.2 |
23.715 |
| rnaXR_005497840.1 |
23.365 |
| rnaXR_005503688.1 |
19.988 |
| rnaXR_005499541.1 |
18.123 |
| rnaXR_005496257.1 |
17.68 |
| rnaXR_005499594.1 |
17.632 |
| rnaXR_005497230.1 |
15.566 |
| rnaXR_005493563.1 |
8.101 |
| rnaXR_001839839.2 |
5.695 |
| rnaXR_005489439.1 |
0 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).