Submitted:
06 July 2023
Posted:
06 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rheological parameters analysis
2.2. The rheological model
2.3. The properties and characteristics of materials
2.3.1. Aeolian sand
2.3.2. Coal gangue
2.3.3. Fly ash
2.3.4. Cement
2.3.5. Chemical admixture
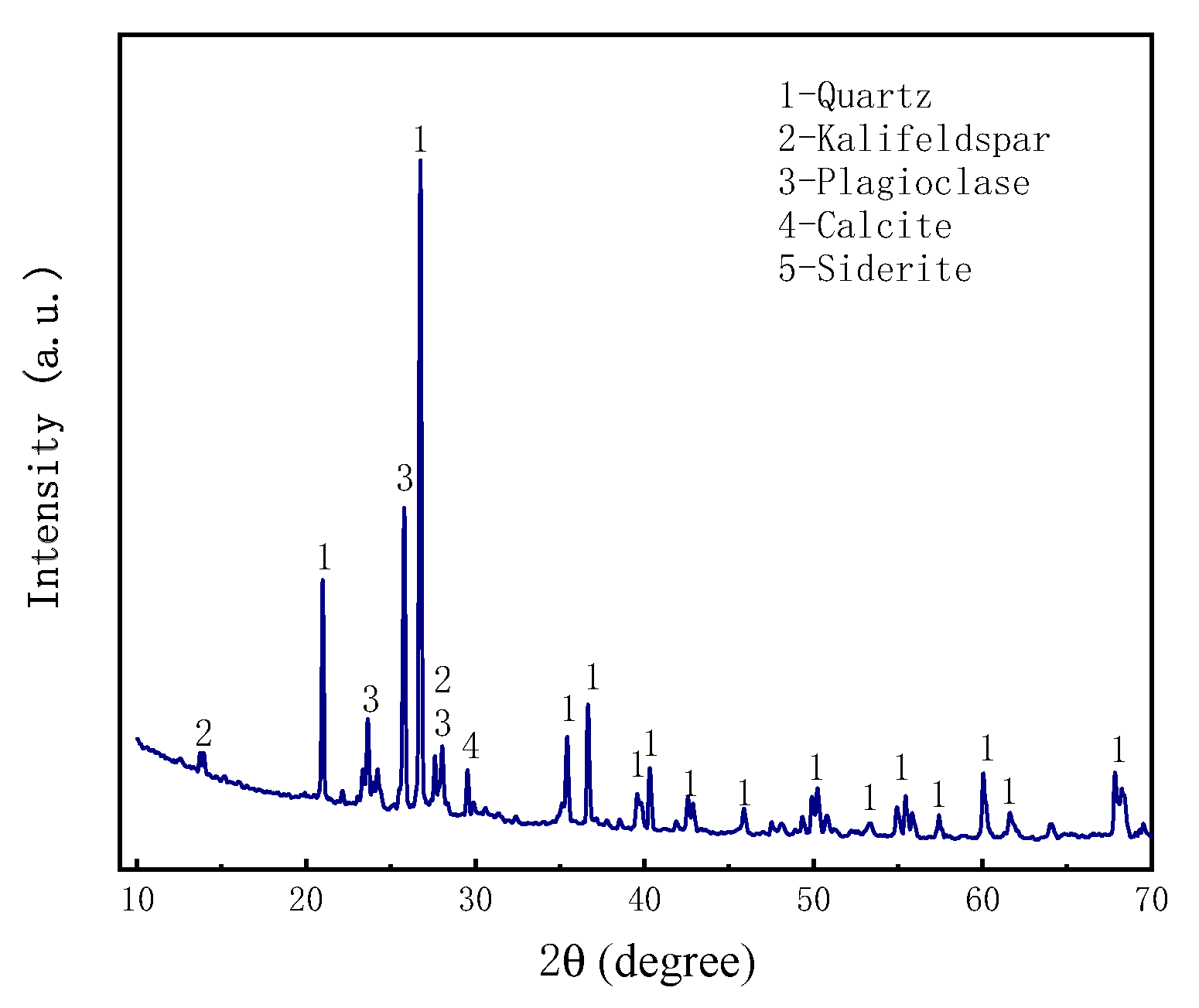
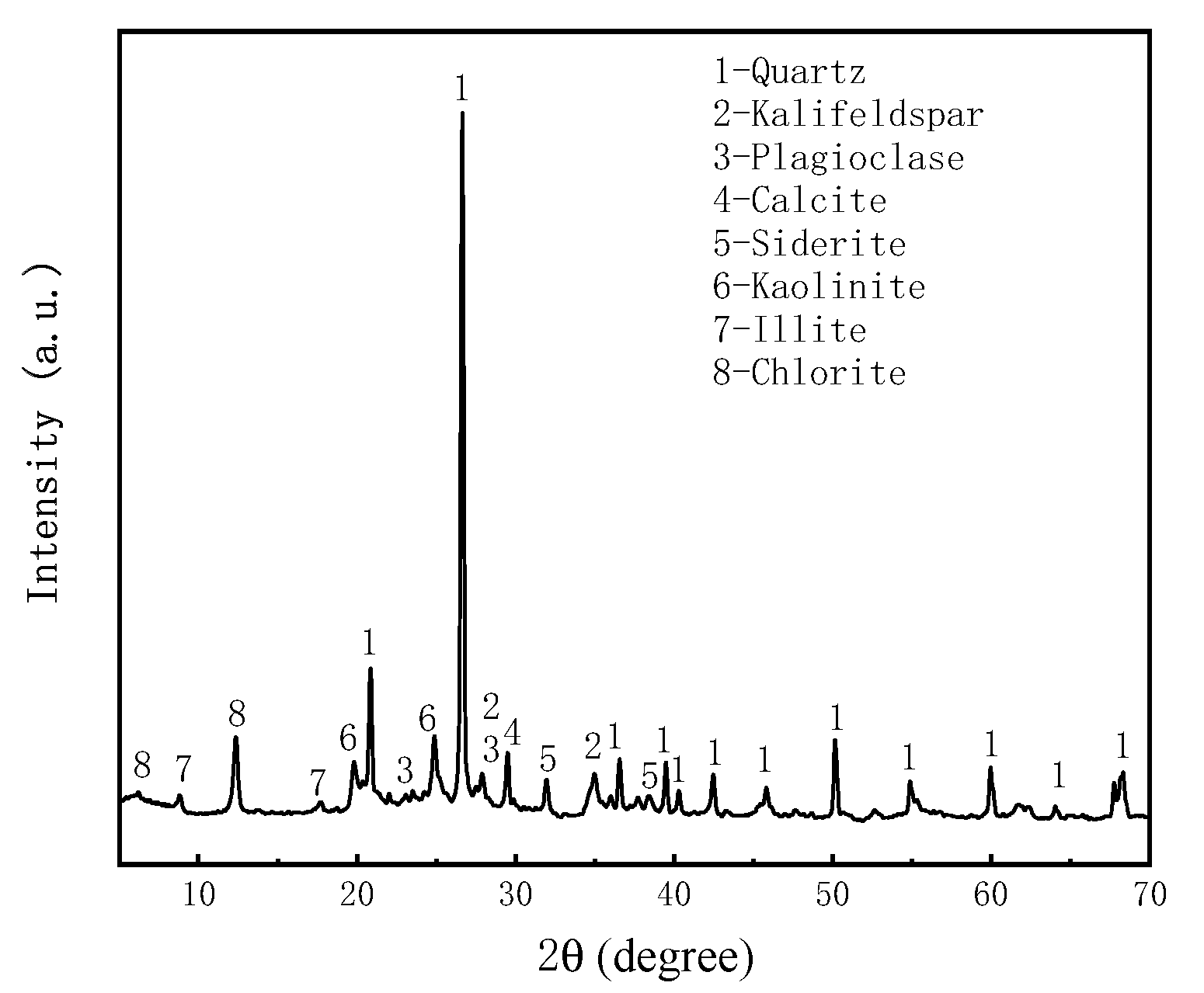
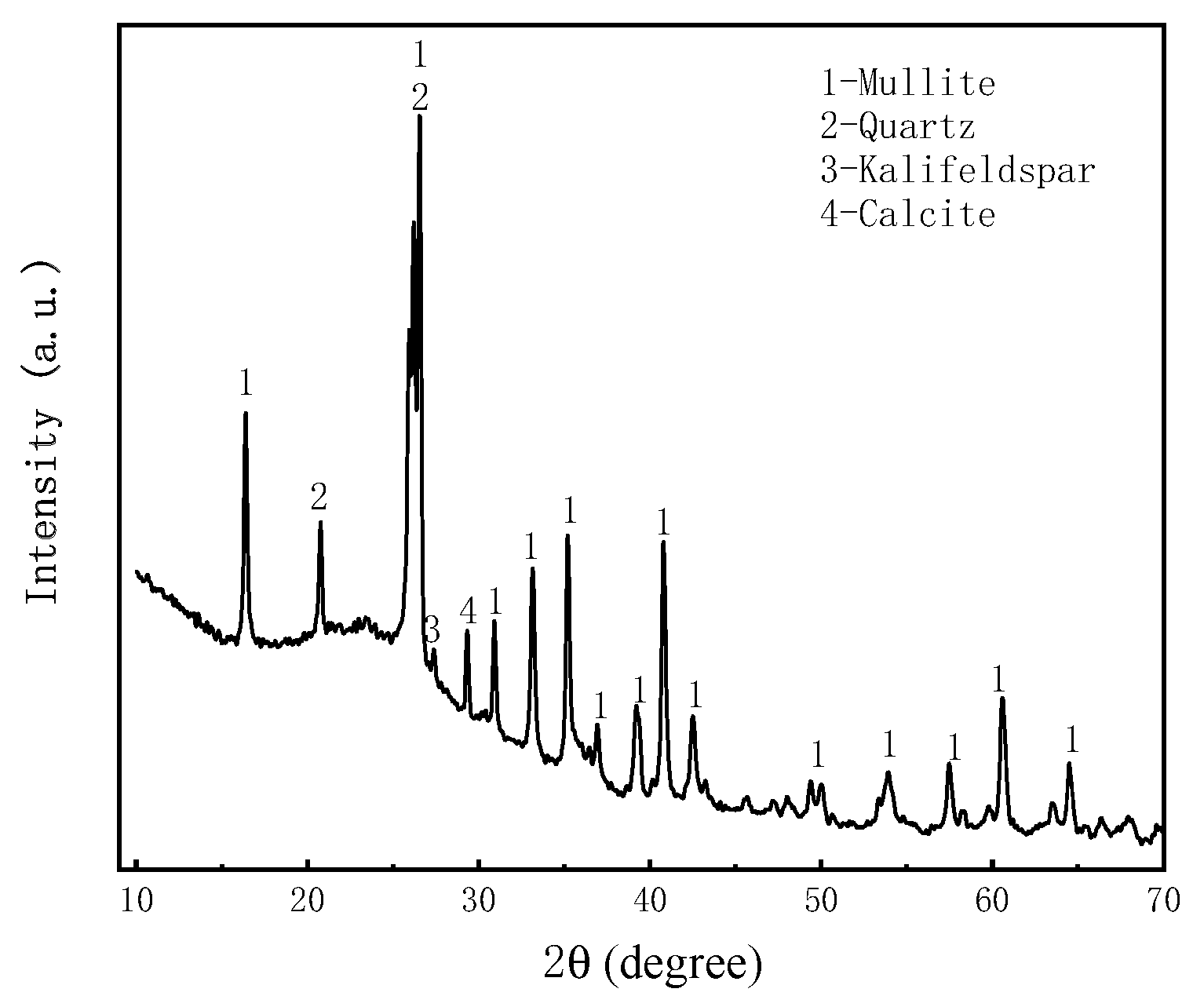
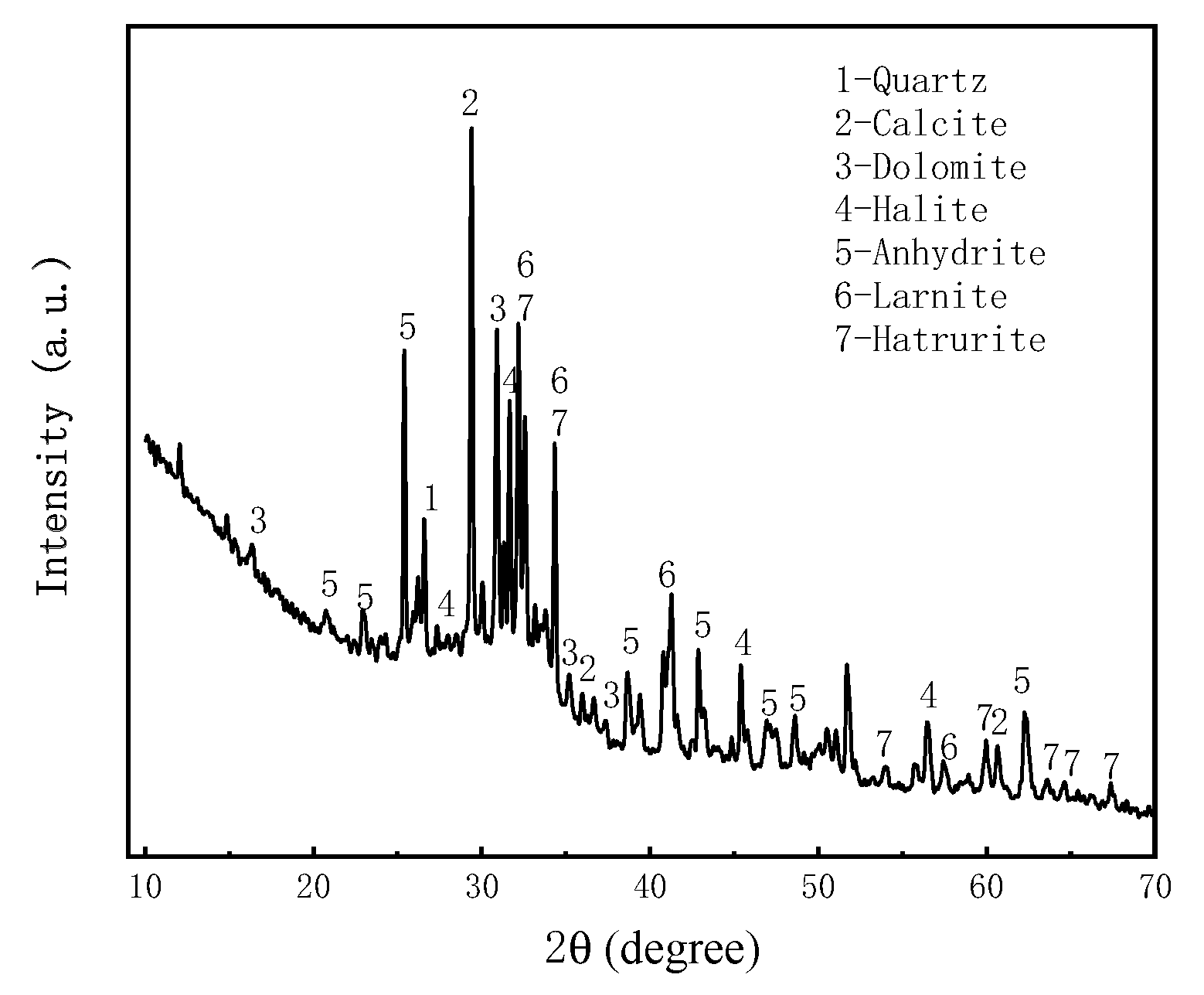
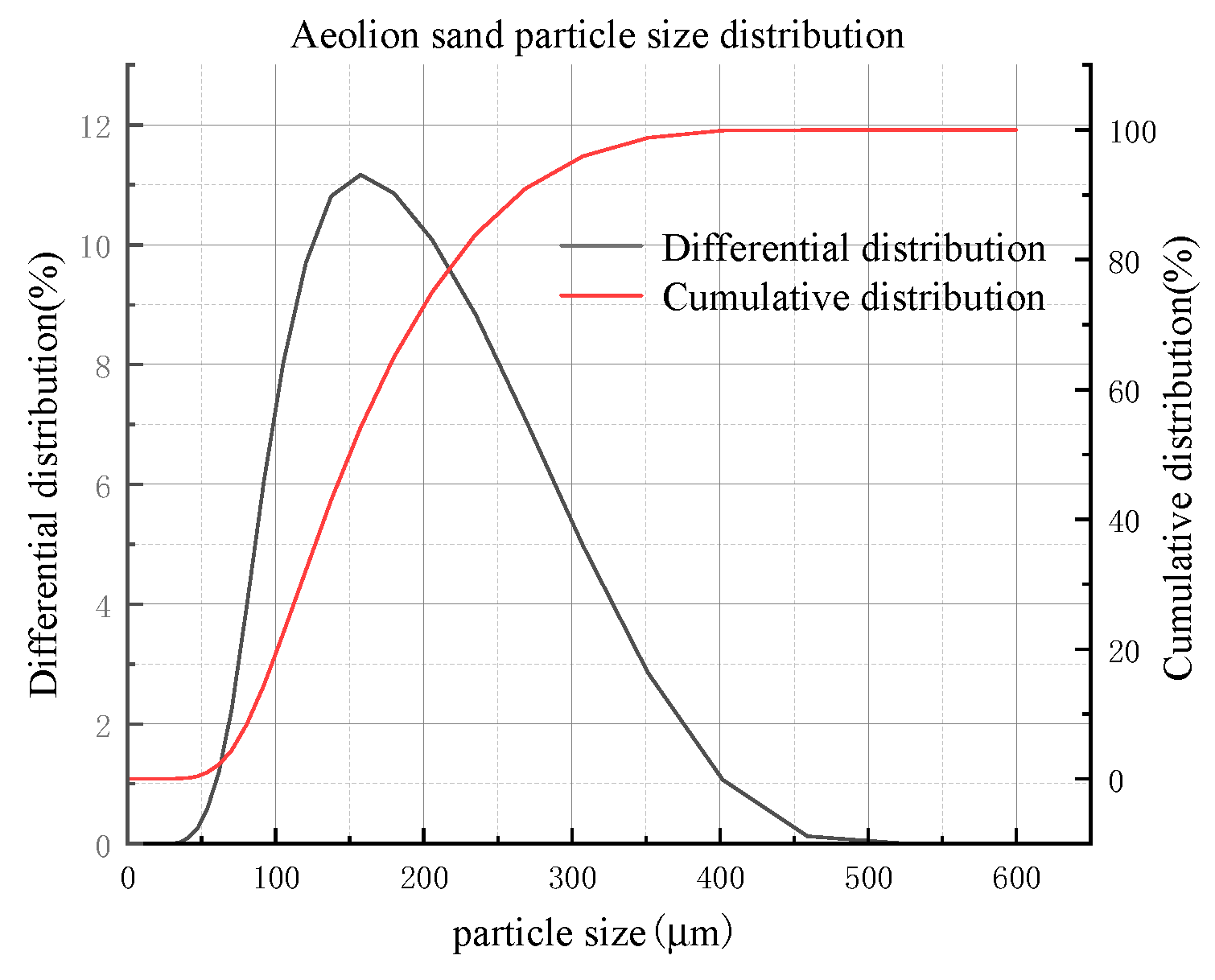
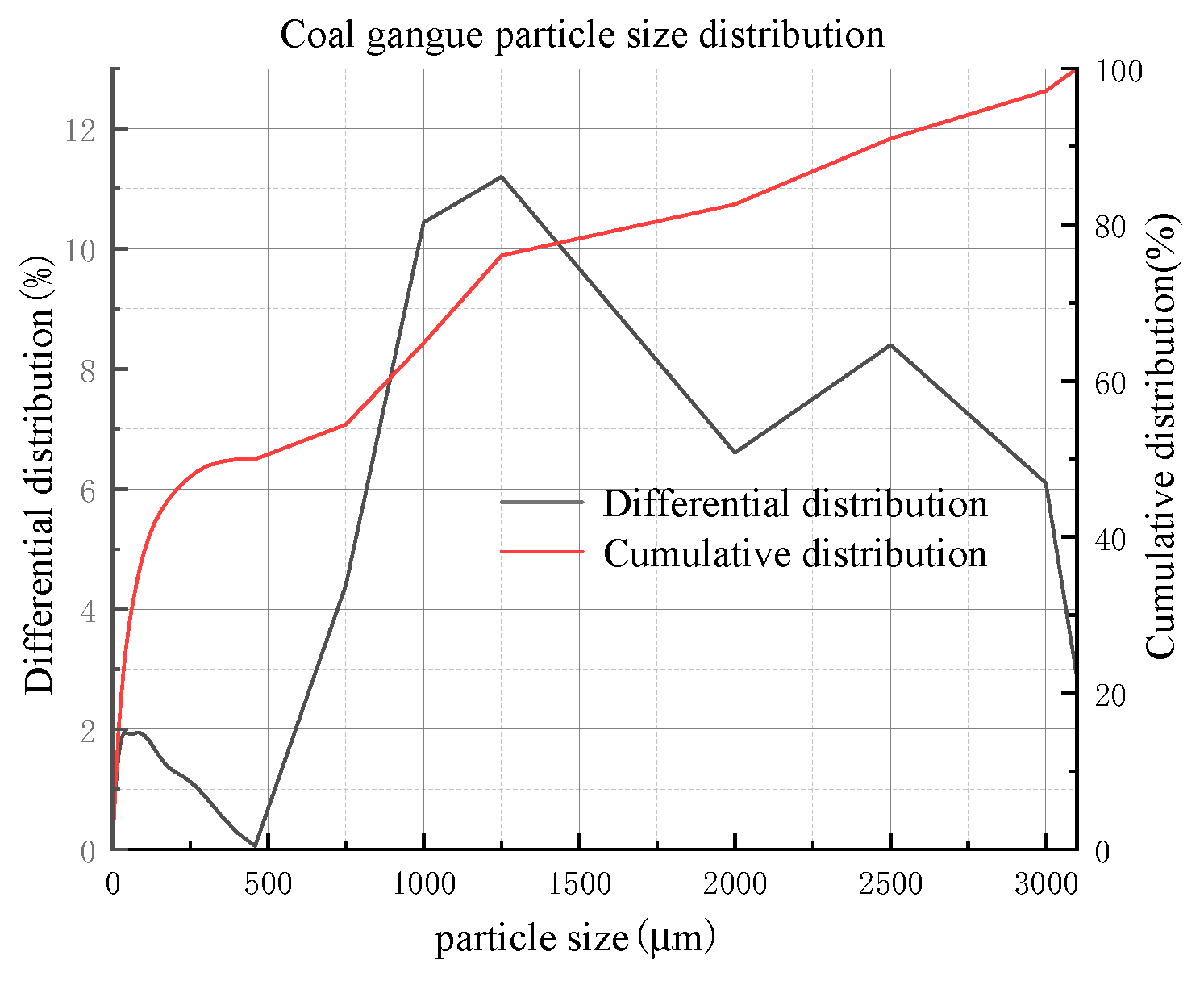
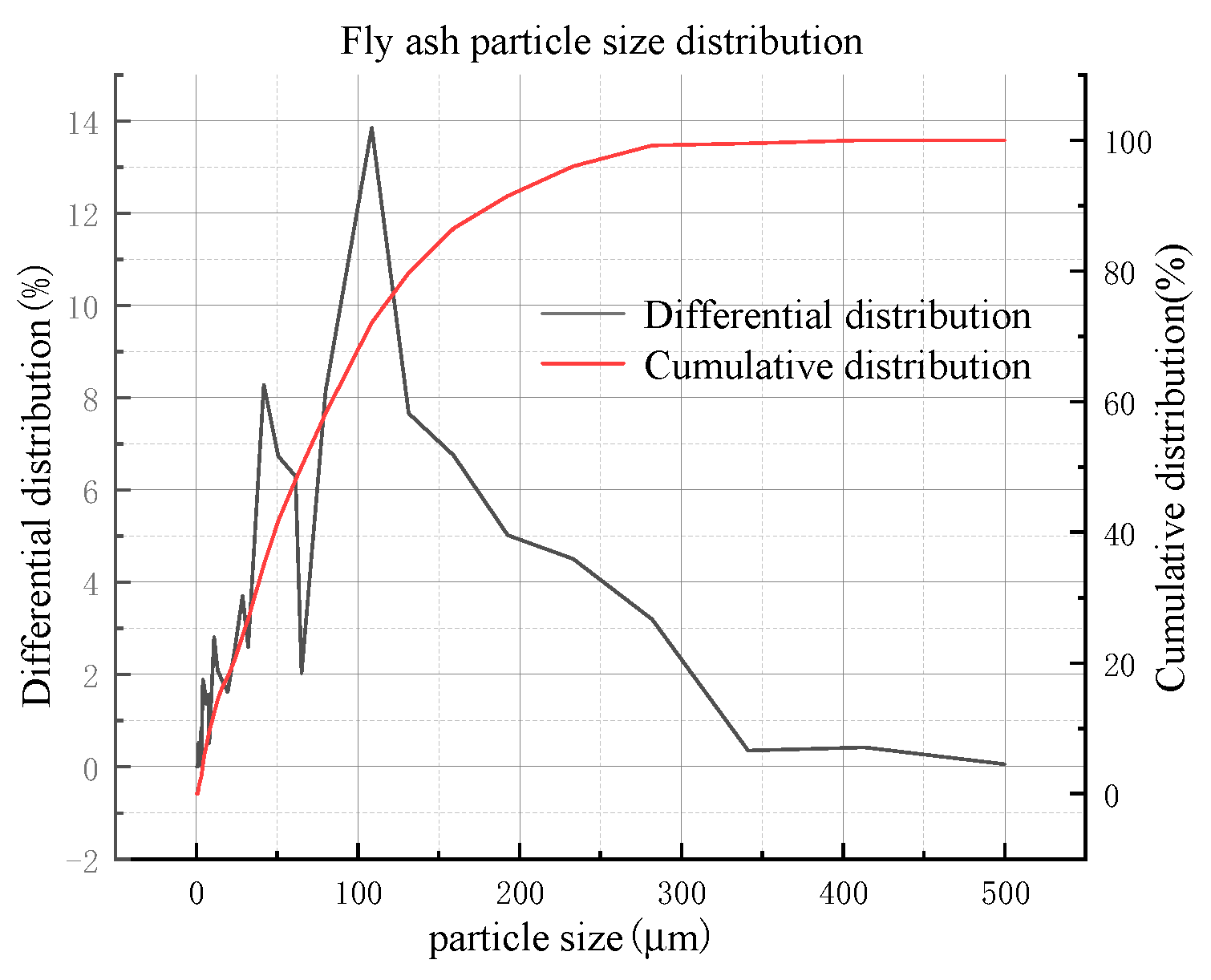
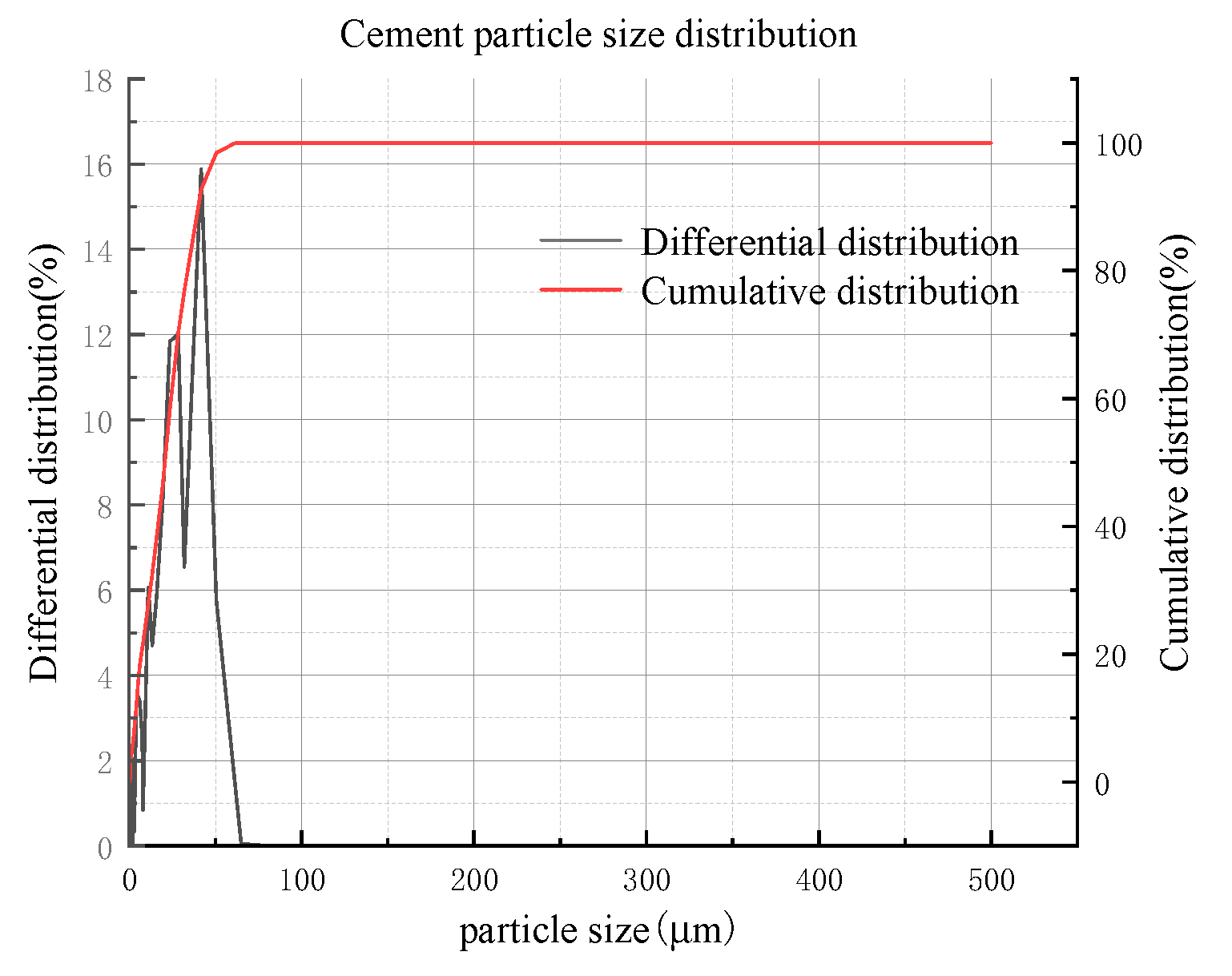
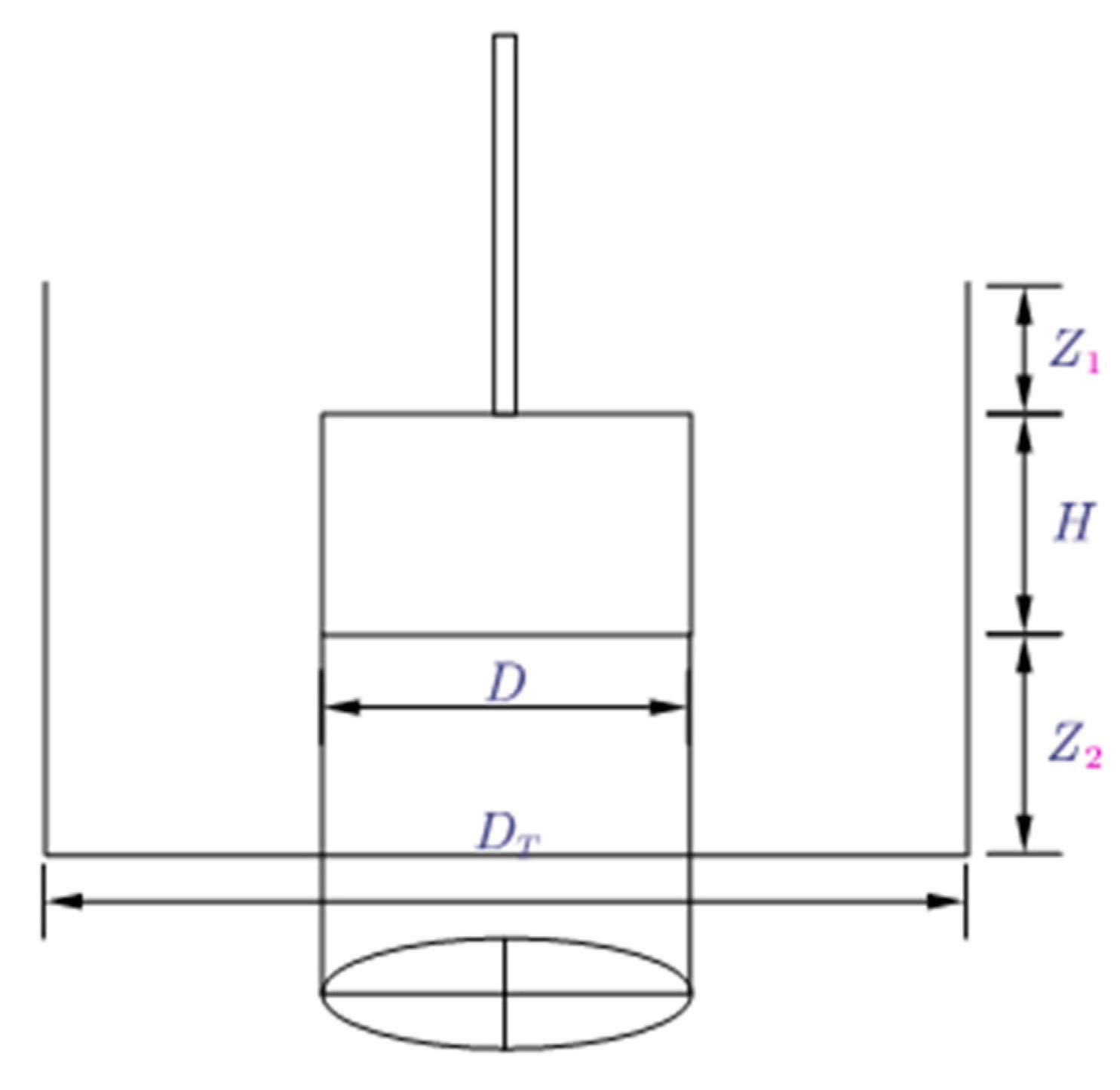
2.4. Instructions for rheometer and vane spindle
2.5. Specimen preparation and experimental methods
| CAFB code | 1# | 2# | 3# | 4# | 5# | 6# | 7# |
| 77.5 | 77.5 | 77.5 | 77.5 | 77.5 | 77.5 | 77.5 | |
| 46 | 43 | 40 | 37 | 34 | 40 | 40 | |
| 5 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 17 | 11 | 11 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.1 | |
| 17.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 | |
| 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | |
| 22.5 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 22.5 |
| CAFB code | d10/μm | d30/μm | d60/μm | d90/μm | d50/μm |
| 1# | 53.771 | 80.586 | 179.465 | 361.146 | 138.018 |
| 2# | 51.263 | 78.586 | 207.453 | 449.321 | 151.538 |
| 3# | 48.755 | 76.587 | 235.442 | 533.496 | 165.059 |
| 4# | 46.247 | 74.587 | 263.43 | 617.671 | 178.579 |
| 5# | 43.74 | 72.594 | 291.507 | 702.089 | 192.149 |
2.5.1. Vane test to determine yield stress and viscosity
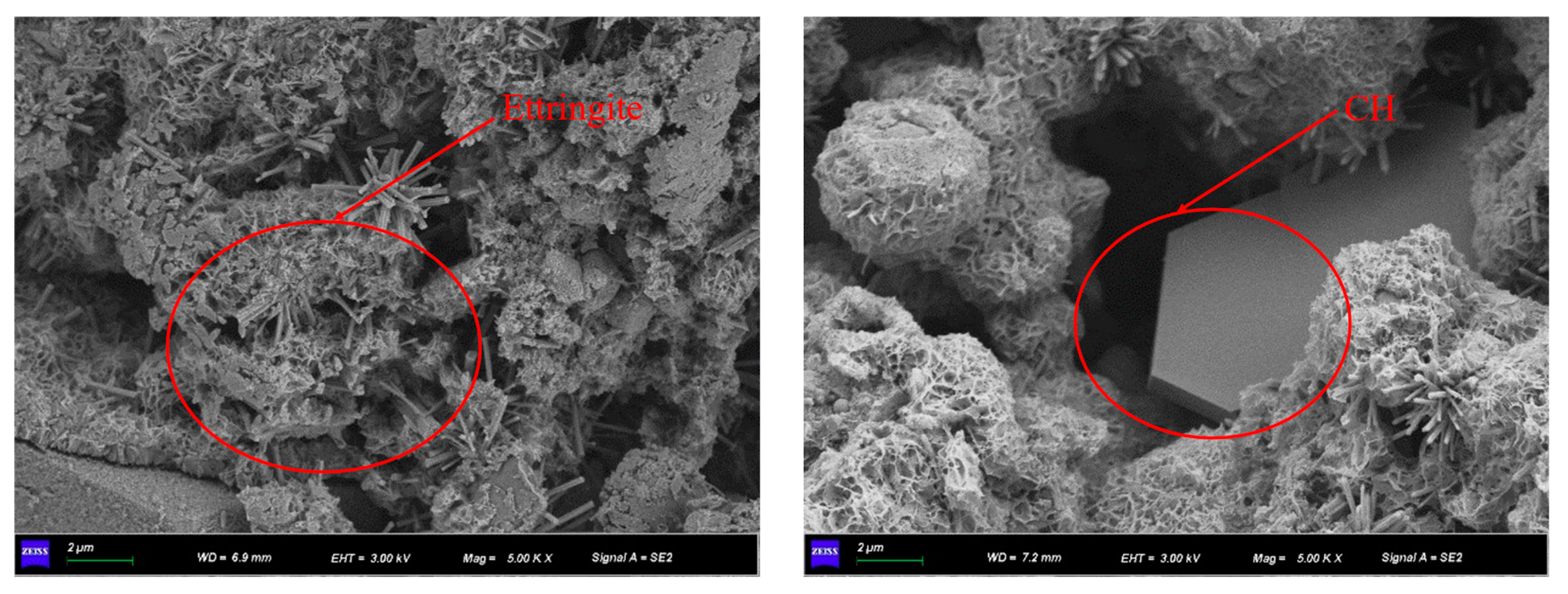
2.5.2. Microstructural analysis
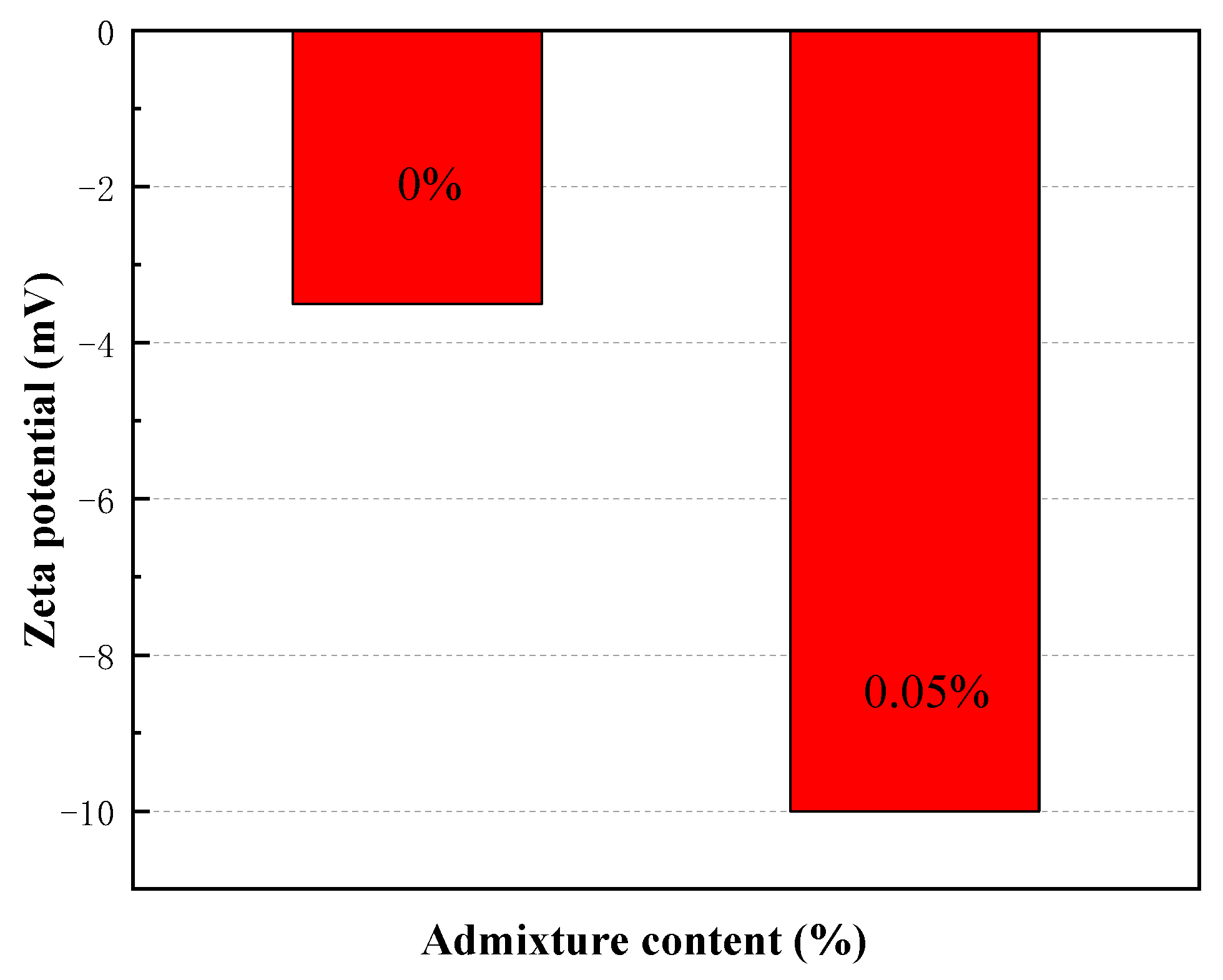
2.5.3. Zeta potential test
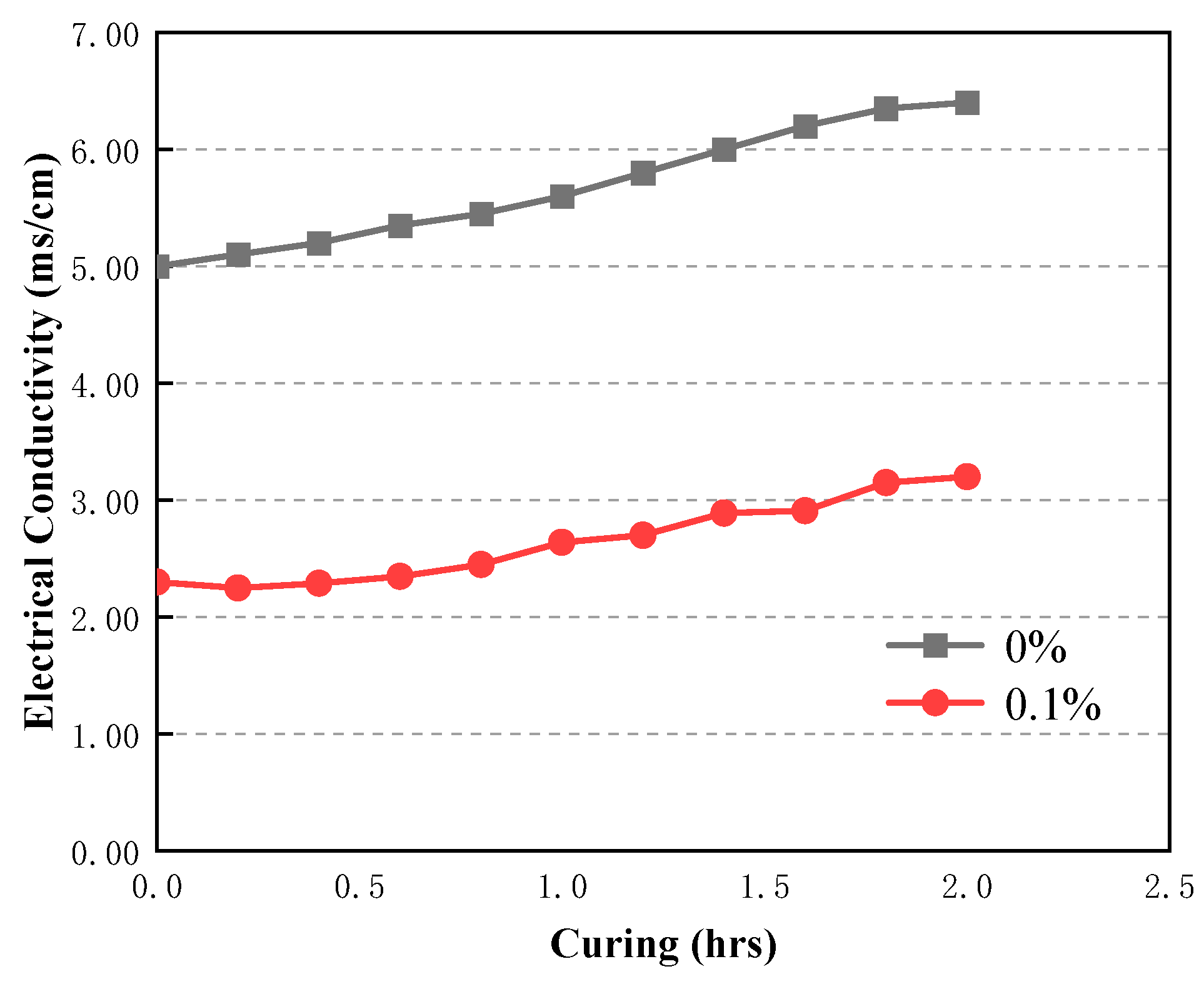
2.5.4. Monitoring program
2.5.5. Scanning electron microscopy tests
3. Results
3.1. Fitting and analysis of rheological parameters
3.2. The influence of the amount of coal gangue added on the rheological properties of the slurry
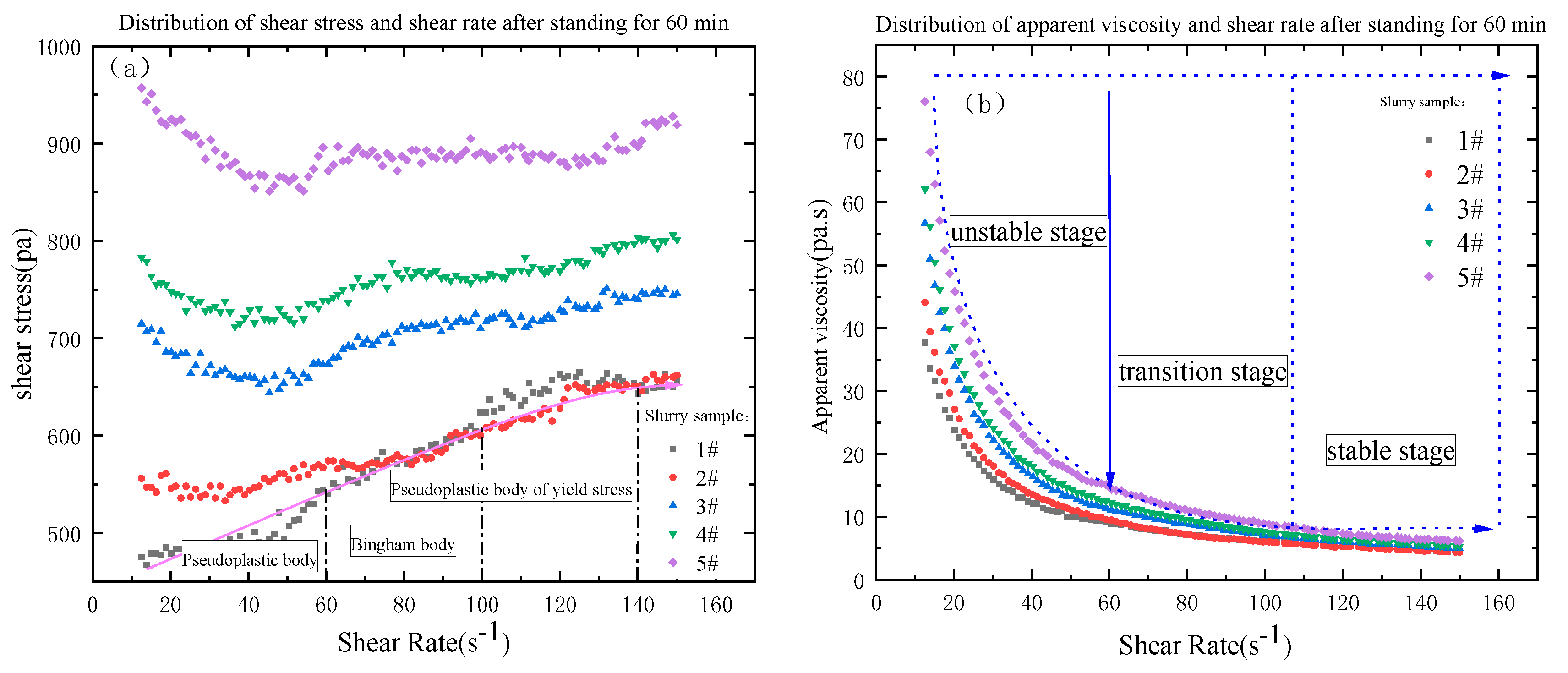
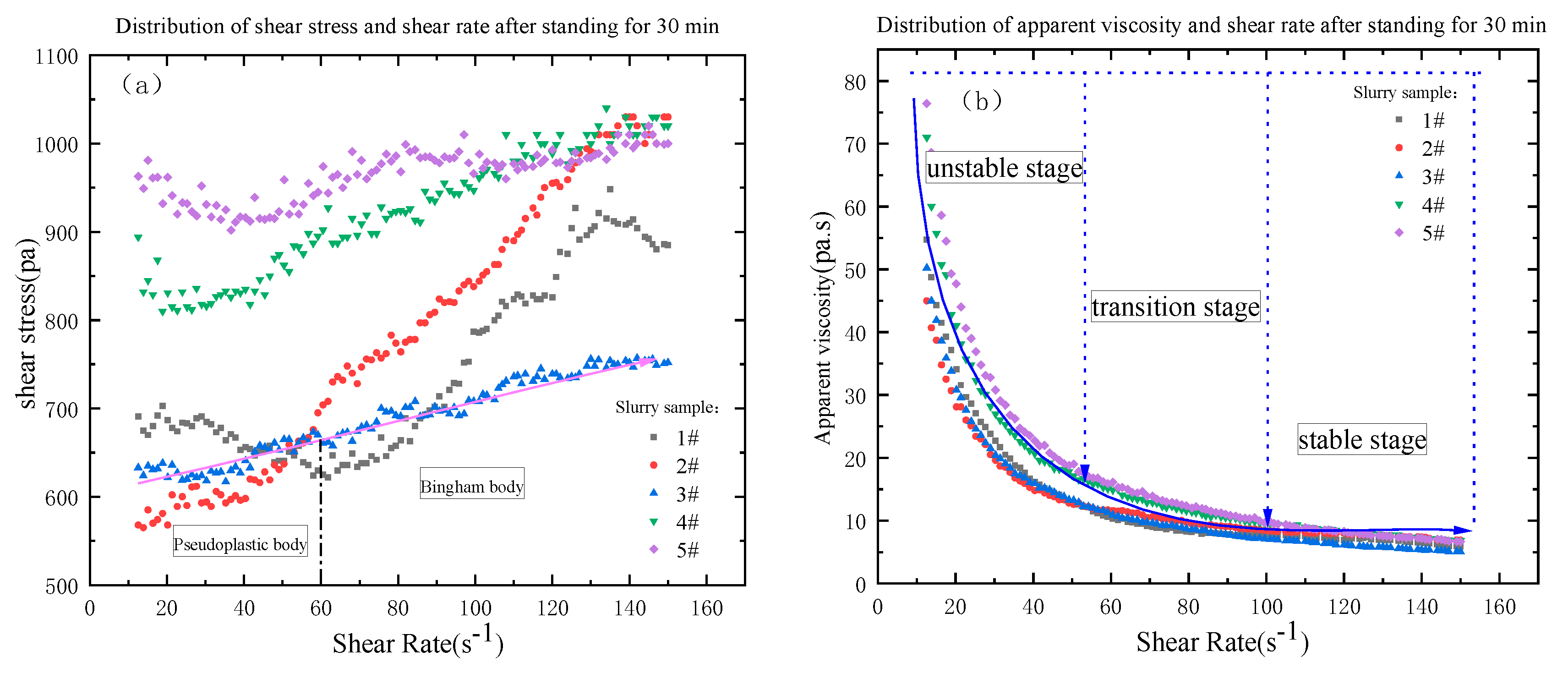

3.3. Correlation between rheological parameters and gradation
3.4. Time-dependent evolution of the rheological properties of CAFB with the ratio of aeolian sand / coal gangue
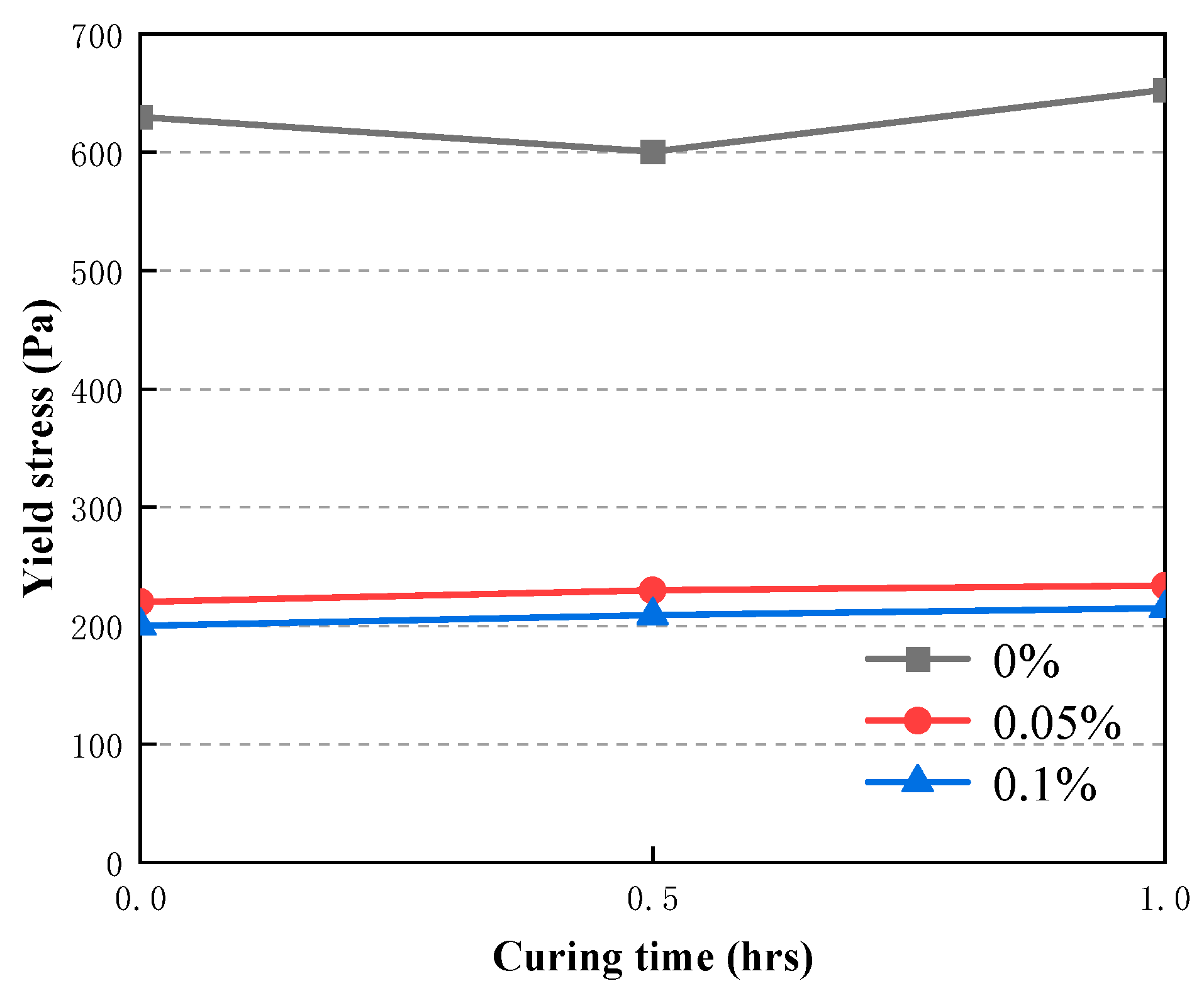
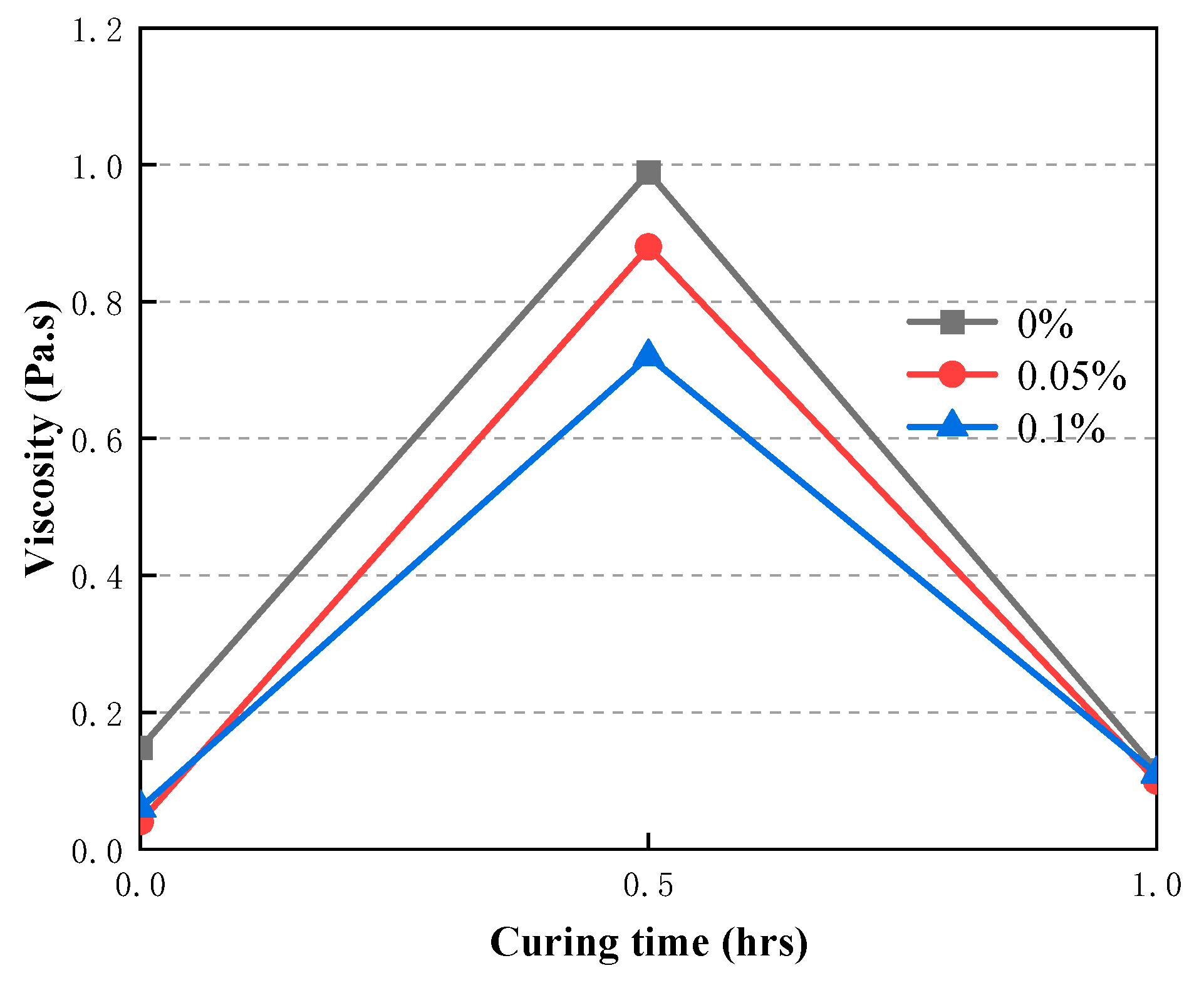
3.5. Time-dependent evolution of the rheological properties of CAFB with plasticizer
5. Conclusions
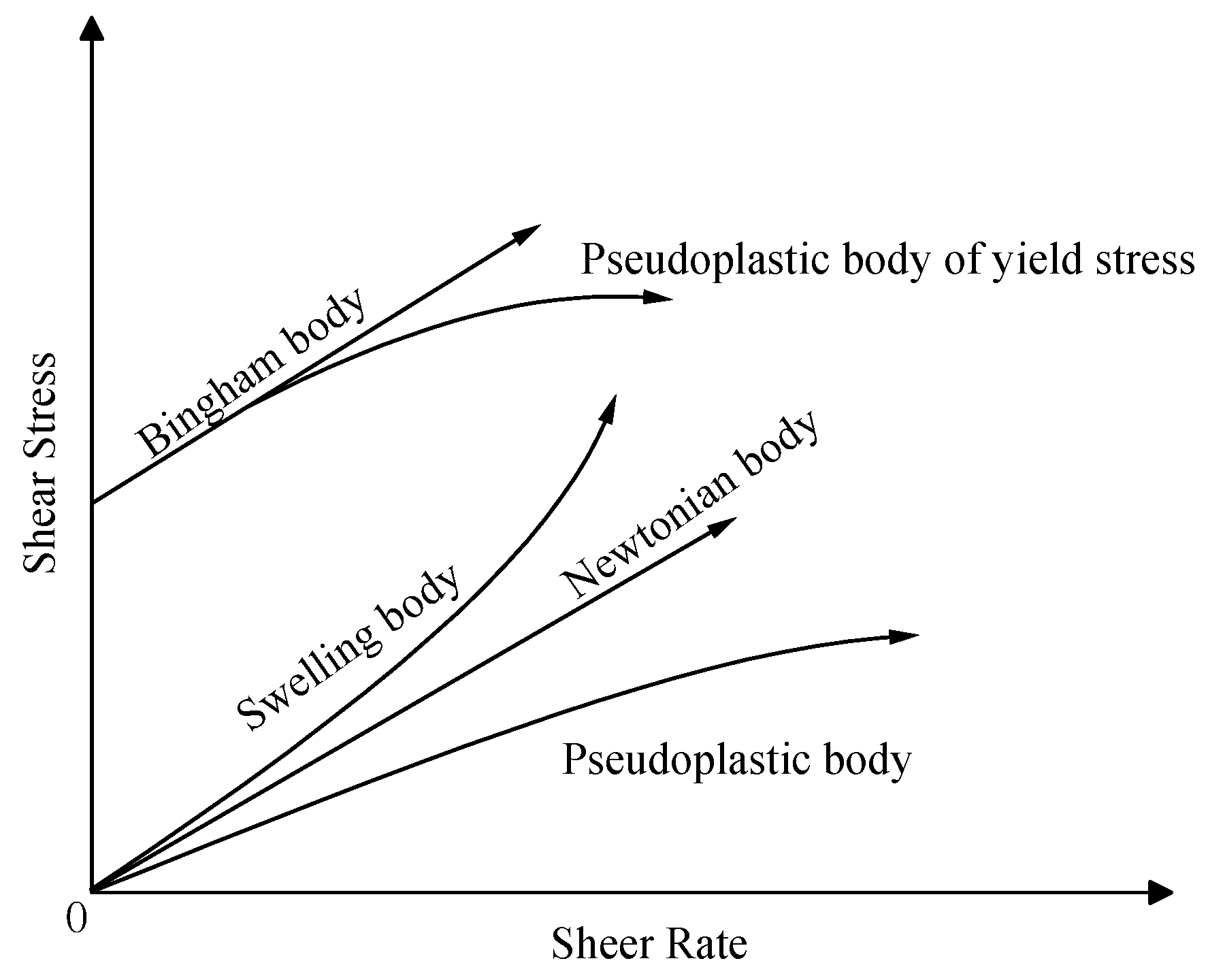
- 3#, 4# and 5# slurry flow index change pattern is basically the same, the index n which characterizes the flow property is greater than 1 after 3 min resting, belongs to swelling body; n is close to 1 after 30min resting, belongs to Bingham body; n is less than 1 after 60 min resting, belongs to pseudoplastic body; 1# and 2# slurry in 3-30min flow index is greater than 1, belongs to swelling body, After 60min of resting, the flow pattern of slurry changes n is less than 1, which belongs to pseudoplastic body.
- With the increase of shear rate and shear time, the viscosity first gradually decreases and then stabilizes, i.e., the rheological properties of the slurry have the characteristic of “shear thinning”; the rheological properties of the slurry process is the comprehensive embodiment of a variety of model composite properties, with the increase of shear rate, the rheological curve of the slurry shows an upward convex shape, showing a pseudoplastic body-Bingham body-Pseudoplastic body(swelling body).
- According to 2# and 3# mixed material, it will be grading configuration aeolian sand, coal gangue, fly ash filling slurry, to ensure long-distance pipeline conveying process slurry flow stability, to ensure smooth pipeline transport.
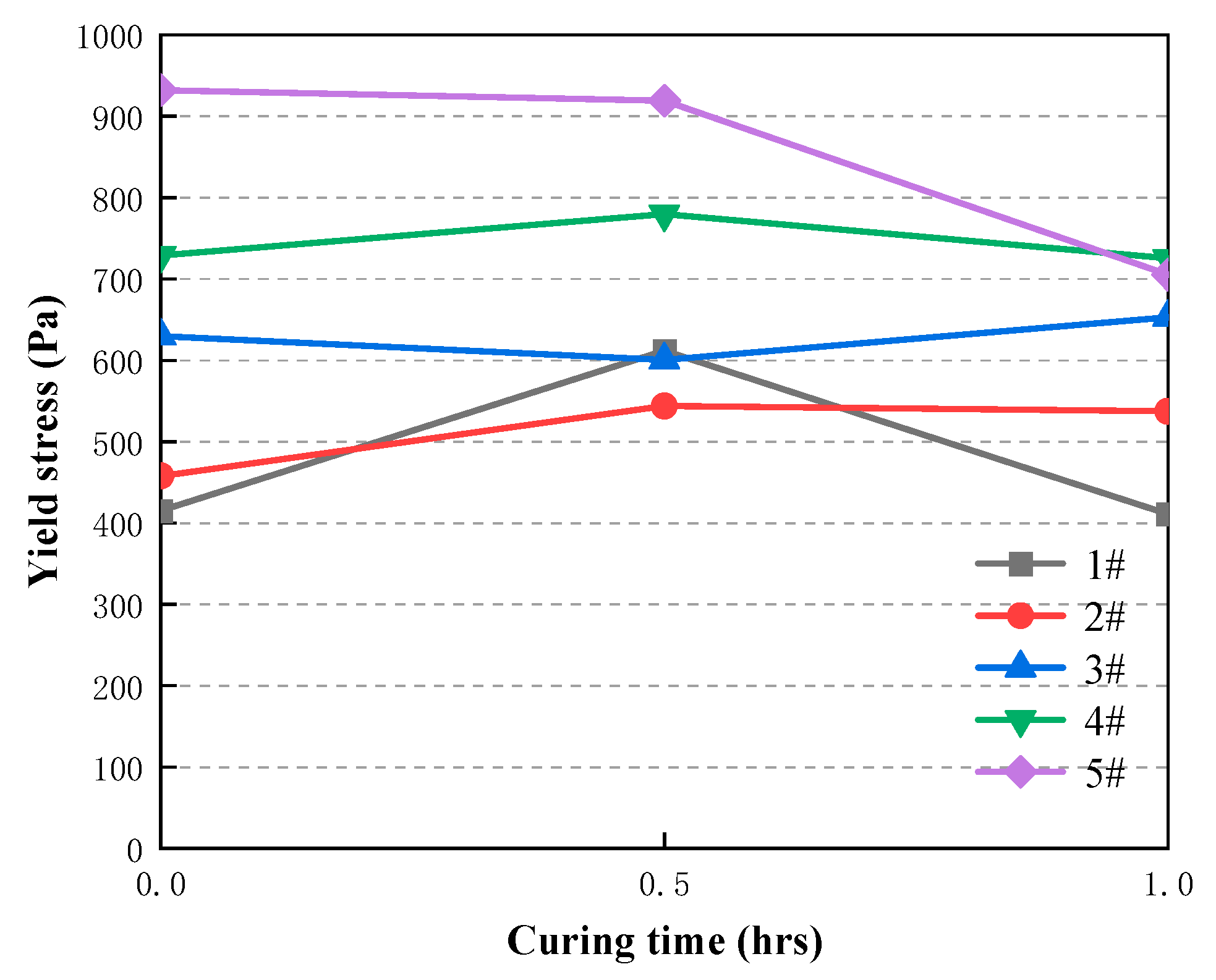
- Curing time (0h-0.5h) results in a higher yield stress of the CAFB. It is because a longer curing time is associated with greater degree of cement hydration products. Curing time (0.5h-1h) results in a lower yield stress of the CAFB. Is is because more hydration products is associated with an decrease in the aeolian sand inter particle frictional resistance of the CAFB.
- Addition of plasticizer to the CAFB significantly reduces the yield stress and viscosity of CAFB. An addition of 0.05% of the admixture results in over 65% reduction in yield stress at the time of preparation as well as after 1 h. A similar reduction was observed in the improvement of viscosity. The marginal reduction upon increasing the admixture to 0.1% is much less, indicating that an optimum percentage is around 0.05.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nasir, O.; Fall, M. Coupling Binder Hydration, Temperature and Compressive Strength Development of Underground Cemented Paste Backfill at Early Ages. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2010, 25, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, K. Effect of Coarse Aggregate Characteristics on Concrete Rheology. Construction and Building Materials 2011, 25, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, J.; Klein, B.; Zhou, N.; deWit, B. Experimental Characterization of the Influence of Solid Components on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Cemented Paste Backfill. International Journal of Mineral Processing 2017, 168, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbin, I.M.; Rahimi R, S.; Allahyari, H.; Fallah, F. Feasibility Study of Waste Poly Ethylene Terephthalate (PET) Particles as Aggregate Replacement for Acid Erosion of Sustainable Structural Normal and Lightweight Concrete. Journal of Cleaner Production 2016, 126, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Ma, H.; Ouyang, S.; Germain, D.; Hou, T. Influential Factors in Transportation and Mechanical Properties of Aeolian Sand-Based Cemented Filling Material. Minerals 2019, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minerals | Free Full-Text | Influential Factors in Transportation and Mechanical Properties of Aeolian Sand-Based Cemented Filling Material. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/9/2/116 (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Mining Developments and Social Impacts on Communities: Bowen Basin Case Studies: Rural Society: Vol 19, No 3. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.5172/rsj.19.3.211 (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, C.; Fourie, A.; Xiao, C. Recycling Phosphogypsum and Construction Demolition Waste for Cemented Paste Backfill and Its Environmental Impact. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 186, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Effect of Superplasticisers on the Workability and Compressive Strength of Concrete Made with Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates - ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S095006181100599X (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Saleh, S.; Mahmood, A.H.; Hamed, E.; Zhao, X.-L. The Mechanical, Transport and Chloride Binding Characteristics of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete Utilising Seawater, Sea Sand and SCMs. Construction and Building Materials 2023, 372, 130815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, T.; Ercikdi, B.; Deveci, H. Utilisation of Construction and Demolition Waste as Cemented Paste Backfill Material for Underground Mine Openings. Journal of Environmental Management 2018, 222, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercikdi, B.; Külekci, G.; Yılmaz, T. Utilization of Granulated Marble Wastes and Waste Bricks as Mineral Admixture in Cemented Paste Backfill of Sulphide-Rich Tailings. Construction and Building Materials 2015, 93, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercikdi, B.; Cihangir, F.; Kesimal, A.; Deveci, H.; Alp, İ. Utilization of Industrial Waste Products as Pozzolanic Material in Cemented Paste Backfill of High Sulphide Mill Tailings. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2009, 168, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahmaran, M.; Christianto, H.A.; Yaman, İ.Ö. The Effect of Chemical Admixtures and Mineral Additives on the Properties of Self-Compacting Mortars. Cement and Concrete Composites 2006, 28, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Wu, A.; Hu, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. The Effect of Solid Components on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Cemented Paste Backfill. Minerals Engineering 2012, 35, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Gao, F.; Li, S. Research and Application of Surface Paste Disposal for Clay-Sized Tailings in Tropical Rainy Climate. International Journal of Mineral Processing 2016, 157, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Grabinsky, M. Apparent Yield Stress Measurement in Cemented Paste Backfill. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment 2013, 27, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creber, K.J.; McGuinness, M.; Kermani, M.F.; Hassani, F.P. Investigation into Changes in Pastefill Properties during Pipeline Transport. International Journal of Mineral Processing 2017, 163, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizani, S.; Simms, P. Method-Dependent Variation of Yield Stress in a Thickened Gold Tailings Explained Using a Structure Based Viscosity Model. Minerals Engineering 2016, 98, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, S.; Deb, D.; Sreenivas, T. Variability in Rheology of Cemented Paste Backfill with Hydration Age, Binder and Superplasticizer Dosages. Advanced Powder Technology 2018, 29, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yield Stress and Thixotropy: On the Difficulty of Measuring Yield Stresses in Practice - Soft Matter (RSC Publishing). Available online: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2006/SM/b517840a (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Haiqiang, J.; Fall, M.; Cui, L. Yield Stress of Cemented Paste Backfill in Sub-Zero Environments: Experimental Results. Minerals Engineering 2016, 92, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, M.; Célestin, J.C.; Pokharel, M.; Touré, M. A Contribution to Understanding the Effects of Curing Temperature on the Mechanical Properties of Mine Cemented Tailings Backfill. Engineering Geology 2010, 114, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Fall, M. A Coupled Thermo–Hydro-Mechanical–Chemical Model for Underground Cemented Tailings Backfill. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2015, 50, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Deng, T.; Zhao, R. A Coupled THMC Modeling Application of Cemented Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill. Construction and Building Materials 2018, 158, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Huang, G.; Li, A.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, Y. A Study of Supermolecular Polarization of Comb-like Polycarboxylate Admixtures Synthesized with Polyoxyethylene Macromolecules. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2012, 174, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yilmaz, E.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H. Effect of Superplasticizer Type and Dosage on Fluidity and Strength Behavior of Cemented Tailings Backfill with Different Solid Contents. Construction and Building Materials 2018, 187, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; He, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y. Effects of Superplasticizers on Carbonation Resistance of Concrete. Construction and Building Materials 2016, 108, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, W.; Espagne, M.; Aı̈tcin, P.-C. Ettringite Formation: A Crucial Step in Cement Superplasticizer Compatibility. Cement and Concrete Research 2003, 33, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.K.; Noh, M.H.; Park, T.H. Rheological Properties of Cementitious Materials Containing Mineral Admixtures. Cement and Concrete Research 2005, 35, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, S.; Grice, T.G.; Boger, D.V. Analysis of the Slump Test for On-Site Yield Stress Measurement of Mineral Suspensions. International Journal of Mineral Processing 2003, 70, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Fall, M.; Cui, L. Freezing Behaviour of Cemented Paste Backfill Material in Column Experiments. Construction and Building Materials 2017, 147, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, T.; Chaouche, M. Parallel Superposition Rheology of Cement Pastes. Cement and Concrete Composites 2019, 104, 103393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Hernández, F.-J. Rheological Behavior of Fresh Cement Pastes. Fluids 2018, 3, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercikdi, B.; Cihangir, F.; Kesimal, A.; Deveci, H.; Alp, İ. Utilization of Water-Reducing Admixtures in Cemented Paste Backfill of Sulphide-Rich Mill Tailings. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2010, 179, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzuy, N.Q.; Boger, D.V. Direct Yield Stress Measurement with the Vane Method. Journal of Rheology 1985, 29, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lei, J.; Guo, L.; Du, X.; Li, J. The Application of Thermal Analysis, XRD and SEM to Study the Hydration Behavior of Tricalcium Silicate in the Presence of a Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer. Thermochimica Acta 2015, 613, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeta Potential Measurement | SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/protocol/10.1007/978-1-60327-198-1_6 (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Elakneswaran, Y.; Nawa, T.; Kurumisawa, K. Zeta Potential Study of Paste Blends with Slag. Cement and Concrete Composites 2009, 31, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, A.; Tanimura, M.; Shimoyama, Y. Rheological Properties of Highly Flowable Mortar Containing Limestone Filler-Effect of Powder Content and W/C Ratio. Cement and Concrete Research 2005, 35, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiqiang, J.; Fall, M.; Cui, L. Yield Stress of Cemented Paste Backfill in Sub-Zero Environments: Experimental Results. Minerals Engineering 2016, 92, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Kaufmann, J.; Winnefeld, F.; Plank, J. Impact of Particle Size on Interaction Forces between Ettringite and Dispersing Comb-Polymers in Various Electrolyte Solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2014, 419, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Glasser, F.P. Thermal Stability and Decomposition Mechanisms of Ettringite at <120°C. Cement and Concrete Research 2001, 31, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.H.; Chaouche, M.; Moranville, M. Influence of Organic Admixtures on the Rheological Behaviour of Cement Pastes. Cement and Concrete Research 2006, 36, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, N. Early-Age Strength of Aeolian Sand-Based Cemented Backfilling Materials: Experimental Results. Arab J Sci Eng 2018, 43, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Xu, F. Effect of Fly Ash Belite Cement on Hydration Performance of Portland Cement. Crystals 2021, 11, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, J.; Buchler, P.M.; Coelho, A.C.V.; Cartledge, F.K. Hydration of a Portland Cement Blended with Calcium Carbonate. Thermochimica Acta 2000, 346, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. Mechanical Properties and Meso-Structure Response of Cemented Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill with Cracks under Seepage- Stress Coupling. Construction and Building Materials 2020, 250, 118863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zhang, J.; Ouyang, S.; Deng, X.; Dong, C.; Du, E. Feasibility Study and Performance Optimization of Sand-Based Cemented Paste Backfill Materials. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 259, 120798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, A.; Zhou, N. Reutilisation of Coal Gangue and Fly Ash as Underground Backfill Materials for Surface Subsidence Control. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 254, 120113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, S.; Fall, M. Time- and Temperature-Dependent Rheological Properties of Cemented Paste Backfill That Contains Superplasticizer. Powder Technology 2020, 360, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. Transportability and Pressure Drop of Fresh Cemented Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill (CGFB) Slurry in Pipe Loop. Powder Technology 2015, 284, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chemical composition | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Na2O | CaO | K2O4 | Fe2O3 | other | Total |
| Mass percentage (%) | 9.78 | 68.94 | 2.34 | 6.65 | 2.13 | 2.24 | 7.92 | 100 |
| Chemical composition | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | Total |
| Mass percentage (%) | 22.23 | 62.06 | 0.65 | 2.95 | 3.11 | 0.99 | 8.01 | 100 |
| Chemical composition | Al2O3 | SiO2 | S | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | Total |
| Mass percentage(%) | 31.89 | 56.89 | 0.66 | 1.39 | 1.84 | 1.95 | 5.38 | 100 |
| Chemical composition | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Other | Total |
| Mass percentage(%) | 65.08 | 22.36 | 5.53 | 3.46 | 1.27 | 2.30 | 100 |
| Time/min | rheology index | 1# | 2# | 3# | 4# | 5# |
| 60 | μ(pa·s) | 0.052 | 0.038 | 0.115 | 0.017 | 0.0104 |
| τ0/pa | 410.891 | 537.44 | 652.84 | 725.24 | 705.04 | |
| n | 0.788 | 1.636 | 1.359 | 1.682 | 0.121 | |
| R2 | 0.954 | 0.972 | 0.852 | 0.831 | 0.409 | |
| 30 | μ(pa·s) | 1.12 | 0.385 | 0.989 | 1.781 | 0.384 |
| τ0/pa | 611.650 | 543.827 | 600.575 | 779.76 | 919.08 | |
| n | 3.048 | 1.452 | 1.024 | 0.997 | 1.085 | |
| R2 | 0.956 | 0.989 | 0.964 | 0.953 | 0.626 | |
| 3 | μ(pa·s) | 1.166 | 1.763 | 0.148 | 0.563 | 0.041 |
| τ0/pa | 415.16 | 457.91 | 629.84 | 728.86 | 931.98 | |
| n | 1.210 | 1.080 | 1.496 | 1.269 | 1.621 | |
| R2 | 0.982 | 0.978 | 0.981 | 0.961 | 0.802 |
| Correlation model | a | b | ||
| -5.971 | 0.138 | 0.753 | 0.423 | |
| -12.486 | 0.173 | 0.753 | 0.423 | |
| 4.945 | -0.026 | 0.753 | 0.423 | |
| 3.637 | -0.012 | 0.753 | 0.423 | |
| 2.890 | -0.004 | 0.750 | 0.417 | |
| 3169.028 | -52.021 | 0.981 | 0.951 | |
| 5632.278 | -65.278 | 0.981 | 0.951 | |
| -959.012 | 9.643 | 0.981 | 0.951 | |
| -464.177 | 4.659 | 0.981 | 0.951 | |
| -183.410 | 1.532 | 0.980 | 0.947 |
| Correlation model | a | b | ||
| 0.784 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.333 | |
| 0.647 | 0.004 | 0.020 | 0.333 | |
| 1.027 | -0.0005 | 0.021 | 0.333 | |
| 0.997 | -0.0002 | 0.021 | 0.333 | |
| 0.985 | -0.0001 | 0.023 | 0.333 | |
| 2344.996 | -33.924 | 0.868 | 0.672 | |
| 3951.053 | -42.566 | 0.868 | 0.671 | |
| -347.240 | 6.290 | 0.868 | 0.672 | |
| -24.474 | 3.038 | 0.868 | 0.672 | |
| 160.503 | 0.996 | 0.864 | 0.662 |
| Correlation model | a | b | ||
| -0.156 | 0.004 | 0.395 | 0.126 | |
| -0.353 | 0.005 | 0.395 | 0.126 | |
| 0.174 | -0.0007 | 0.395 | 0.126 | |
| 0.134 | -0.0004 | 0.395 | 0.126 | |
| 0.111 | -0.0001 | 0.392 | 0.128 | |
| 2115.179 | -30.948 | 0.934 | 0.831 | |
| 3581.505 | -38.847 | 0.935 | 0.831 | |
| -340.291 | 5.734 | 0.934 | 0.830 | |
| -46.059 | 2.770 | 0.934 | 0.830 | |
| 118.957 | 0.915 | 0.936 | 0.836 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





